Electrospun Zr-Doped CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Characterization
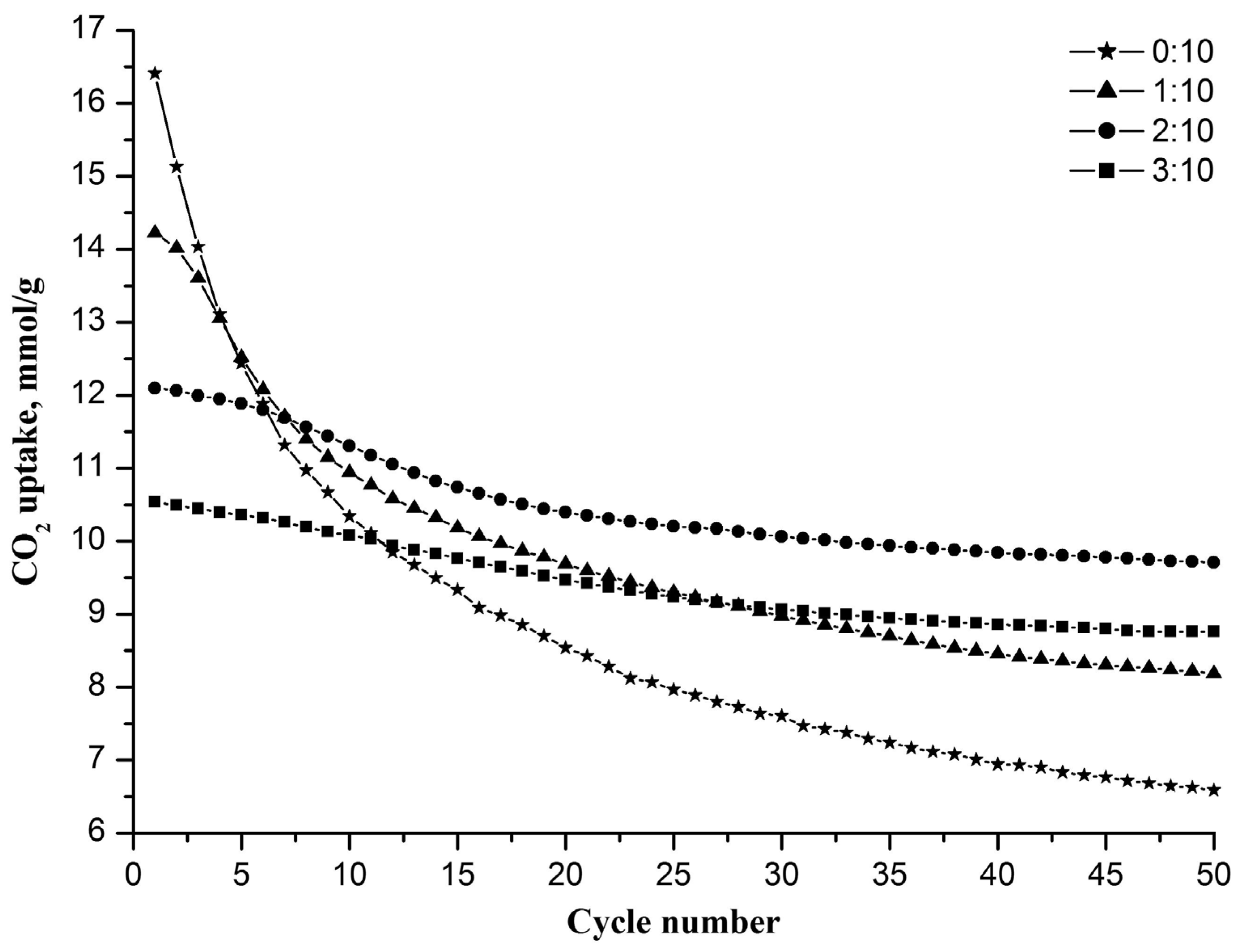
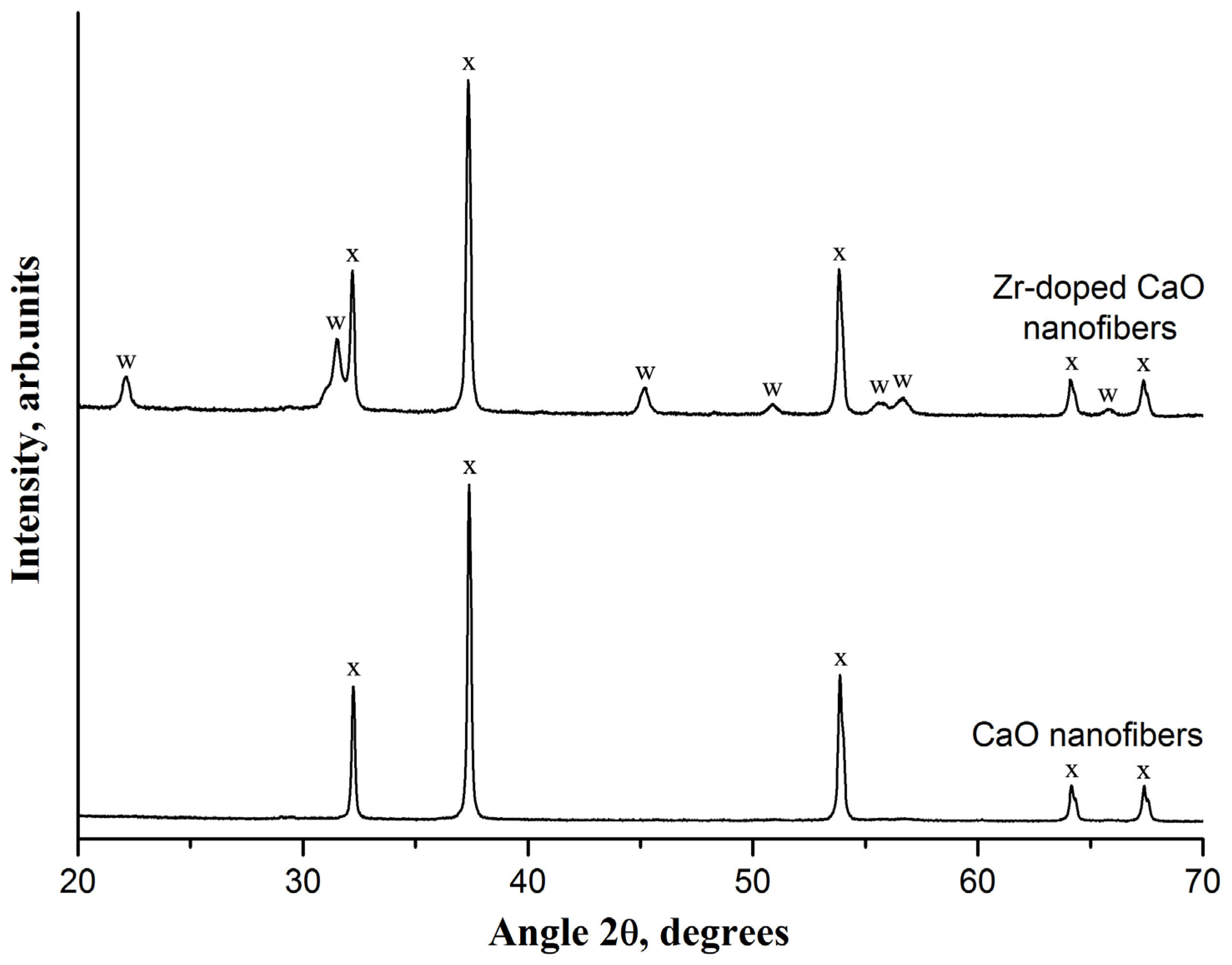
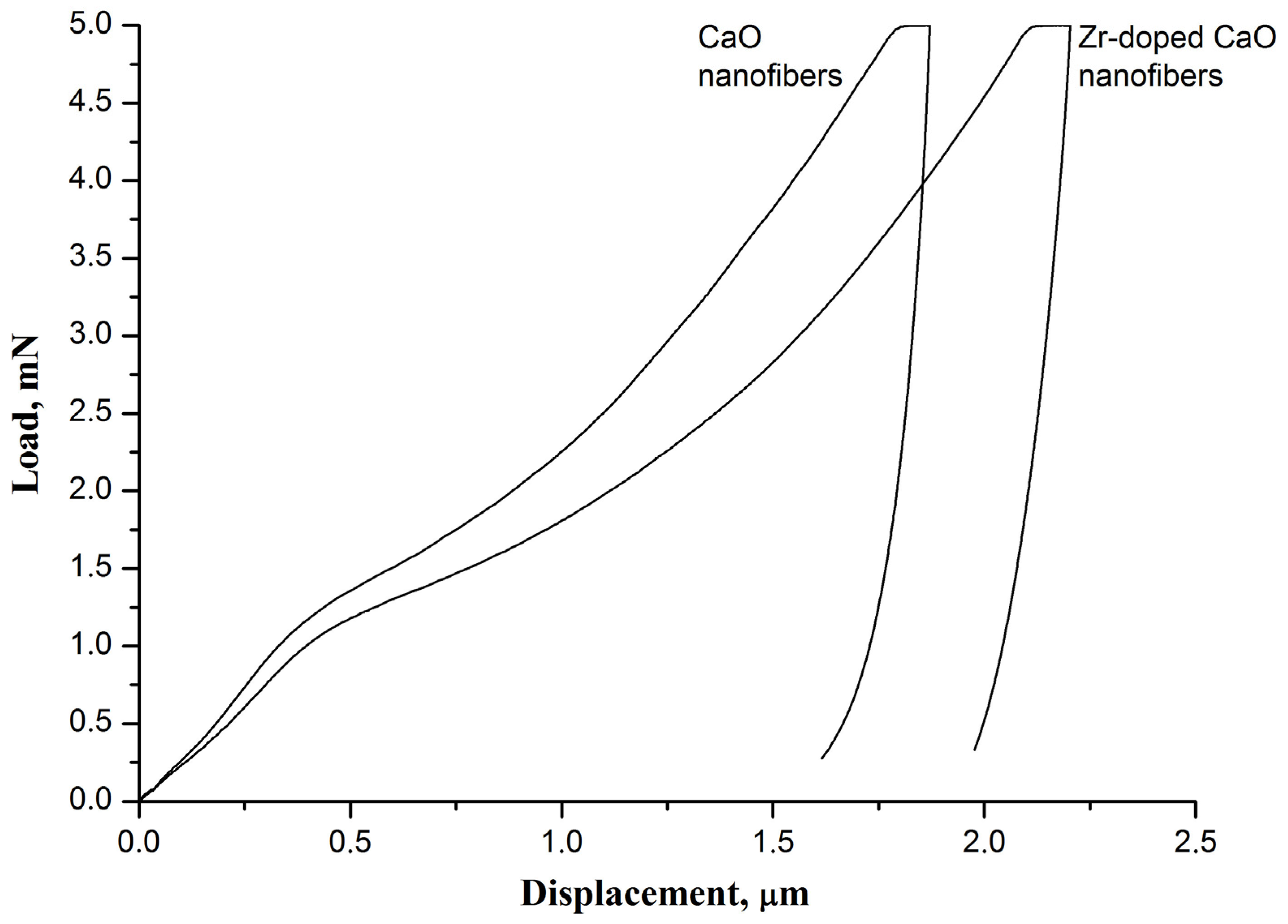
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gür, T.M. Carbon dioxide emissions, capture, storage and utilization: Review of materials, processes and technologies. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 89, 100965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, L.K.G.; Subramanyam, S.; Chengala, M.D.; Olivera, S.; Venkatesh, K. Progress in hydrotalcite like compounds and metal-based oxides for CO2 capture: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Leigh, W.; Feron, P.; Yu, H.; Tade, M. Systematic study of aqueous monoethanolamine (MEA)-based CO2 capture process: Techno-economic assessment of the MEA process and its improvements. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, C.; Shen, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Progress in the development and application of CaO-based adsorbents for CO2 capture—A review. Mater. Today Sustain. 2018, 1–2, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.Y.; Ngu, L.H.; Hashim, S.S. A review of CO2 adsorbents performance for different carbon capture technology processes conditions. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 1076–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yang, S.; Hu, L.; Cai, S.; Wu, L.; Kawi, S. Carbonaceous materials as adsorbents for CO2 capture: Synthesis and modification. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Sun, Z. Review on the development of sorbents for calcium looping. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7806–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaudeen, S.A.; Acharya, B.; Dutta, A. CaO-based CO2 sorbents: A review on screening, enhancement, cyclic stability, regeneration and kinetics modeling. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 23, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, H. Incorporation of CaO into inert supports for enhanced CO2 capture: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Wu, X.; Cheung, O.; Liu, W. Synthetic solid oxide sorbents for CO2 capture: State-of-the art and future perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, B.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Adwek, G.O.; Anthony, E.J.; Williams, P.T.; Wu, C. Fundamental studies of carbon capture using CaO-based materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 9977–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, D.; Abanades, J.C. Determination of the critical product layer thickness in the reaction of CaO with CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 5608–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Pérez, M.O. Research progress on the applications of electrospun nanofibers in catalysis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Montero-Jiménez, M.; Rojas-Quishpe, S.; León, C.D.A.; Heredia-Moya, J.; Rosero-Chanalata, A.; Orbea-Hinojosa, C.; Piñeiros, J.L. Nude and modified electrospun nanofibers, application to air purification. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for wastewater treatment applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.J.D.; Chung, M.; Waqas, M.; Koutsos, V.; Smith, S.; Radacsi, N. Sponge-like piezoelectric micro- and nanofiber structures for mechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Electrospun metal oxide nanofibers and their conductometric gas sensor application. Part 2: Gas sensors and their advantages and limitations. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.; Roy, K.; Chinnappan, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, W.; Ghosh, R. A review on electrospun nanofibers based advanced applications: From health care to energy devices. Polymers 2021, 13, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, P.; Szabó, E.; Domokos, A.; Hirsch, E.; Galata, D.; Farkas, B.; Démuth, B.; Andersen, S.; Vigh, T.; Verreck, G.; et al. Scale-up of electrospinning technology: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, G. One-step preparation of PVDF/GO electrospun nanofibrous membrane for high-efficient adsorption of Cr(VI). Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Yu, D.-G.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z. Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release of acyclovir. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 846, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakoglu, S.; Kołbuk, D.; Sajkiewicz, P. Multifluid electrospinning for multi-drug delivery systems: Pros and cons, challenges, and future directions. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, D.; Musale, S.; Panzade, P.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Sonwane, P.; Madibone, M.; Choundhe, P.; Giram, P.; Cavalu, S. Surface functionalization of nanofibers: The multifaceted approach for advanced biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, B.; Panda, P.K.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of functional ceramic nanofibers. Open Ceram. 2022, 11, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodaev, V.V.; Razlivalova, S.S.; Tyurin, A.I.; Vasyukov, V.M. The nanofibrous CaO sorbent for CO2 capture. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Otto, A.; Robinius, M.; Stolten, D. A Review of post-combustion CO2 capture technologies from coal-fired power plants. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Cripps, A.C. Nanoindentation, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 282. [Google Scholar]
- Koirala, R.; Gunugunuri, K.R.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Smirniotis, P.G. Effect of zirconia doping on the structure and stability of CaO-based sorbents for CO2 capture during extended operating cycles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 24804–24812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radfarnia, H.R.; Iliuta, M.C. Development of zirconium-stabilized calcium oxide absorbent for cyclic high-temperature CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10390–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Bilton, M.; Brown, A.P.; Cunliffe, A.M.; Dvininov, E.; Dupont, V.; Comyn, T.P.; Milne, S.J. Durability of CaO-CaZrO3 sorbents for high-temperature CO2 capture prepared by a wet chemical method. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, Z. Sol-gel-derived synthetic CaO-based CO2 sorbents incorporated with different inert materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 14065–14074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Khan, A.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Smirniotis, P.G. Flame-made durable doped-CaO nanosorbents for CO2 capture. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodaev, V.V.; Razlivalova, S.S. The Zr-doped CaO CO2 sorbent fabricated by wet high-energy milling. Energies 2020, 13, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, M.; Müller, C.R. Sol-gel-derived, CaO-based, ZrO2-stabilized CO2 sorbents. Fuel 2014, 127, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Pre-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture Materials; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Gazquez, G.C.; Chen, H.; Veldhuis, S.A.; Solmaz, A.; Mota, C.; Boukamp, B.A.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; ten Elshof, J.E.; Moroni, L. Flexible yttrium-stabilized zirconia nanofibers offer bioactive cues for osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5789–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodaev, V.V.; Tyurin, A.I.; Razlivalova, S.S.; Korenkov, V.V.; Golovin, Y.I. Effect of zirconia nanofibers structure evolution on the hardness and Young’s modulus of their mats. Polymers 2021, 13, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, C.; He, Z.; Wu, S. Studies on CO2 uptake by CaO/Ca3Al2O6 sorbent in calcium looping cycles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 120, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M. Incorporation of CaO into novel Nd2O3 inert solid support for high temperature CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Steady-State Value of CO2 Uptake Capacity, mmol/g | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Electrospinning | 9.7 | Present work |
| Flame spray pyrolysis | 11.0 | [28] |
| Surfactant template/ultrasound-assisted | 3.4 | [29] |
| Wet mixing | 6.8 | [30] |
| Sol–gel | 7.3 | [31] |
| Coprecipitation | 5.2 | [32] |
| Wet high-energy milling | 8.6 | [33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodaev, V.V.; Razlivalova, S.S.; Tyurin, A.I.; Vasyukov, V.M. Electrospun Zr-Doped CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040747
Rodaev VV, Razlivalova SS, Tyurin AI, Vasyukov VM. Electrospun Zr-Doped CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(4):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodaev, Vyacheslav V., Svetlana S. Razlivalova, Alexander I. Tyurin, and Vladimir M. Vasyukov. 2023. "Electrospun Zr-Doped CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture" Nanomaterials 13, no. 4: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040747
APA StyleRodaev, V. V., Razlivalova, S. S., Tyurin, A. I., & Vasyukov, V. M. (2023). Electrospun Zr-Doped CaO Sorbent for CO2 Capture. Nanomaterials, 13(4), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040747





