Recent Progress in Piezoelectric-Triboelectric Effects Coupled Nanogenerators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Working Principle of Piezoelectric/Triboelectric Nanogenerator
2.1. Piezoelectric Effect
2.2. Working Principle of PENG
2.3. Triboelectric Effect
2.4. Working Principle of TENG
3. Strategy for Enhancing the Performance
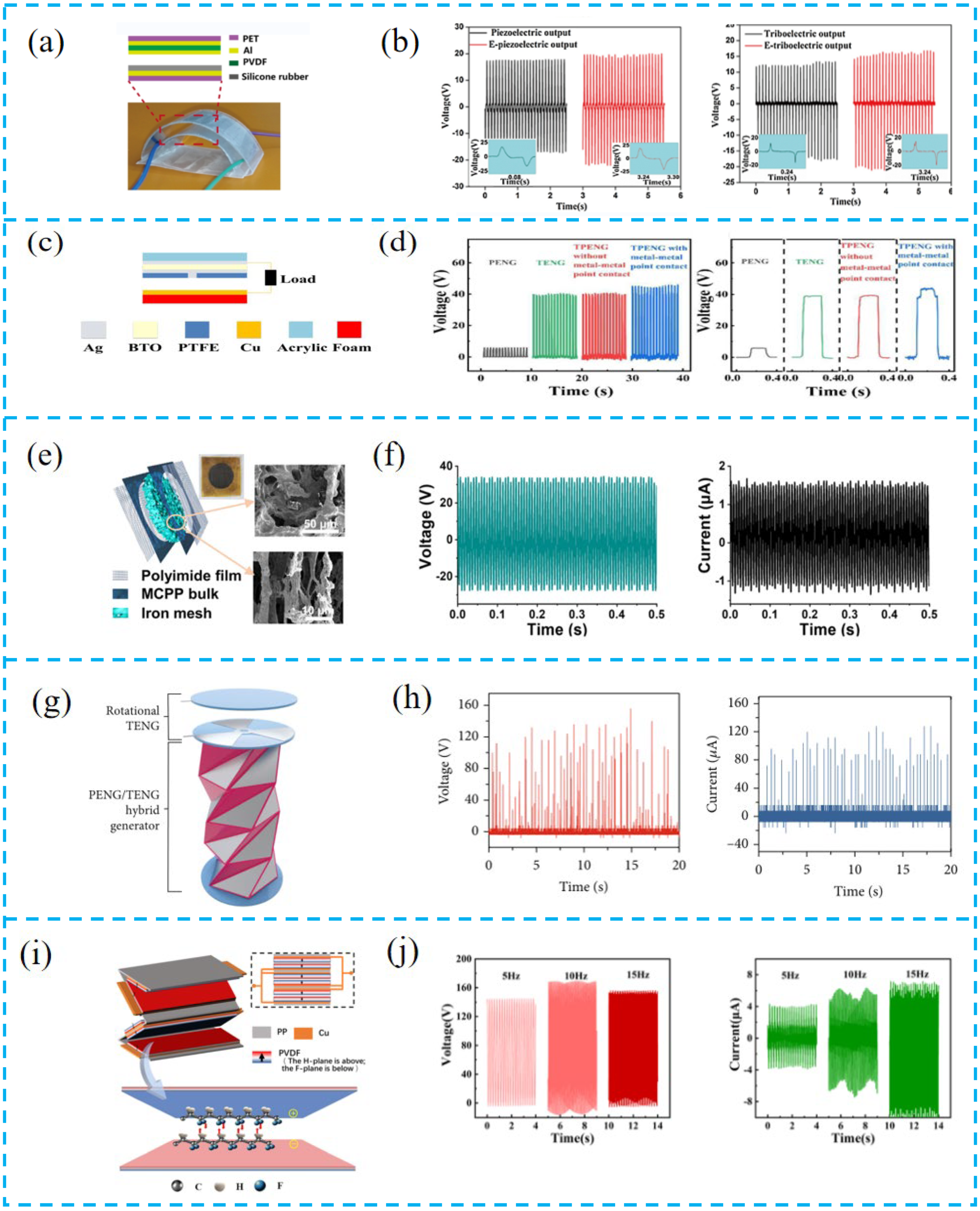
3.1. Structural Design of PTCNGs
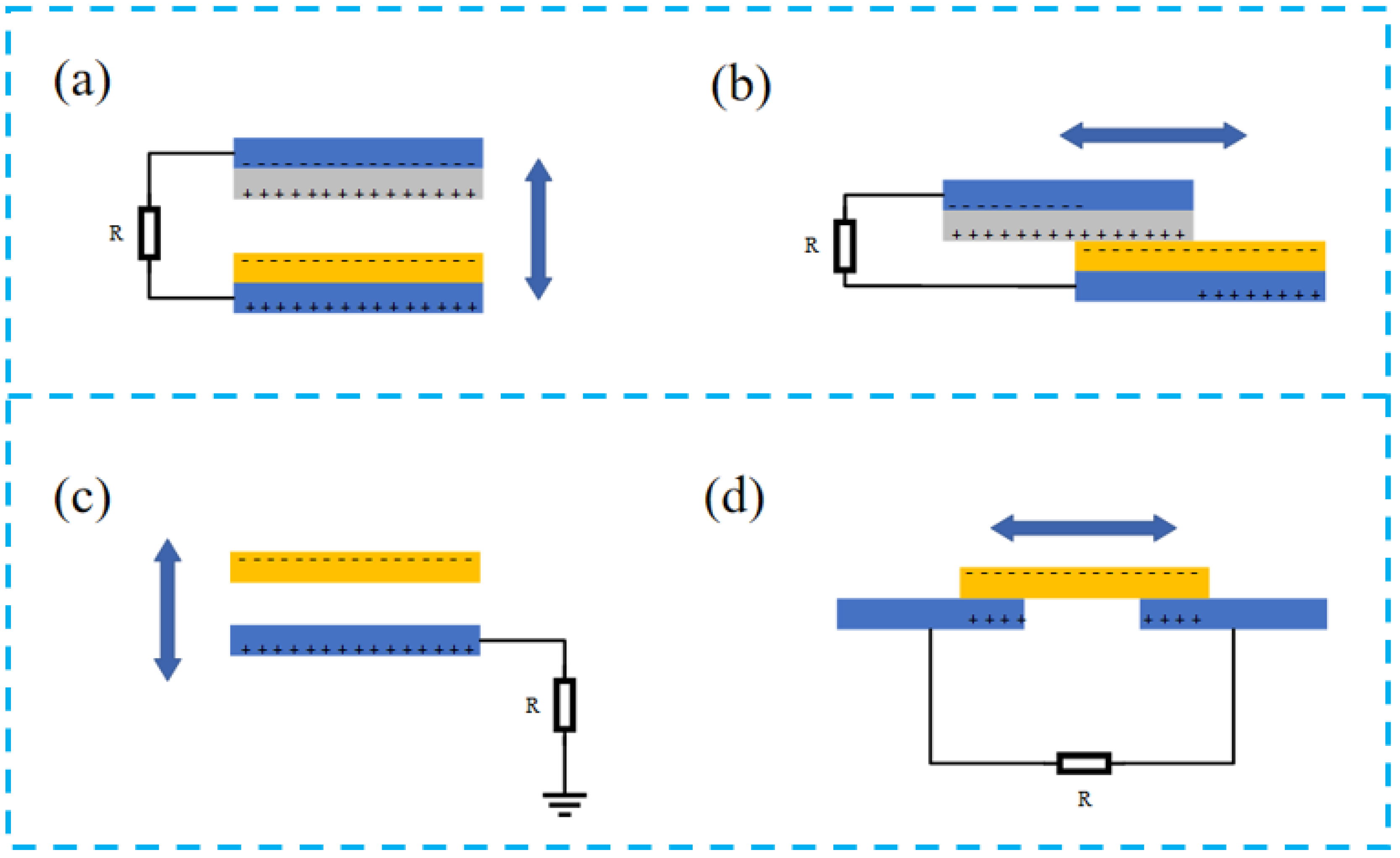
3.1.1. Electrode Design Strategy
3.1.2. Overall Structure Design of PTCNGs
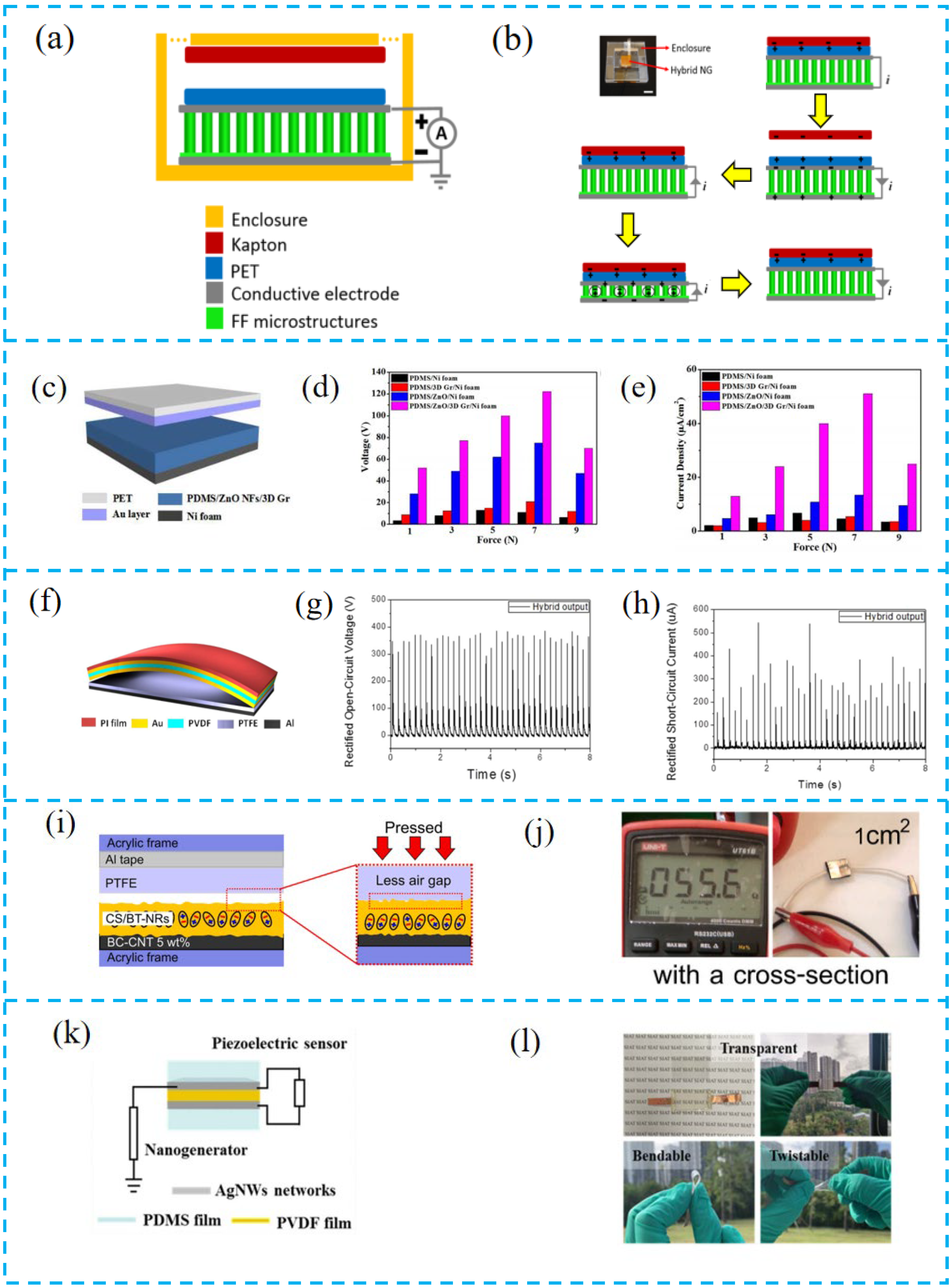
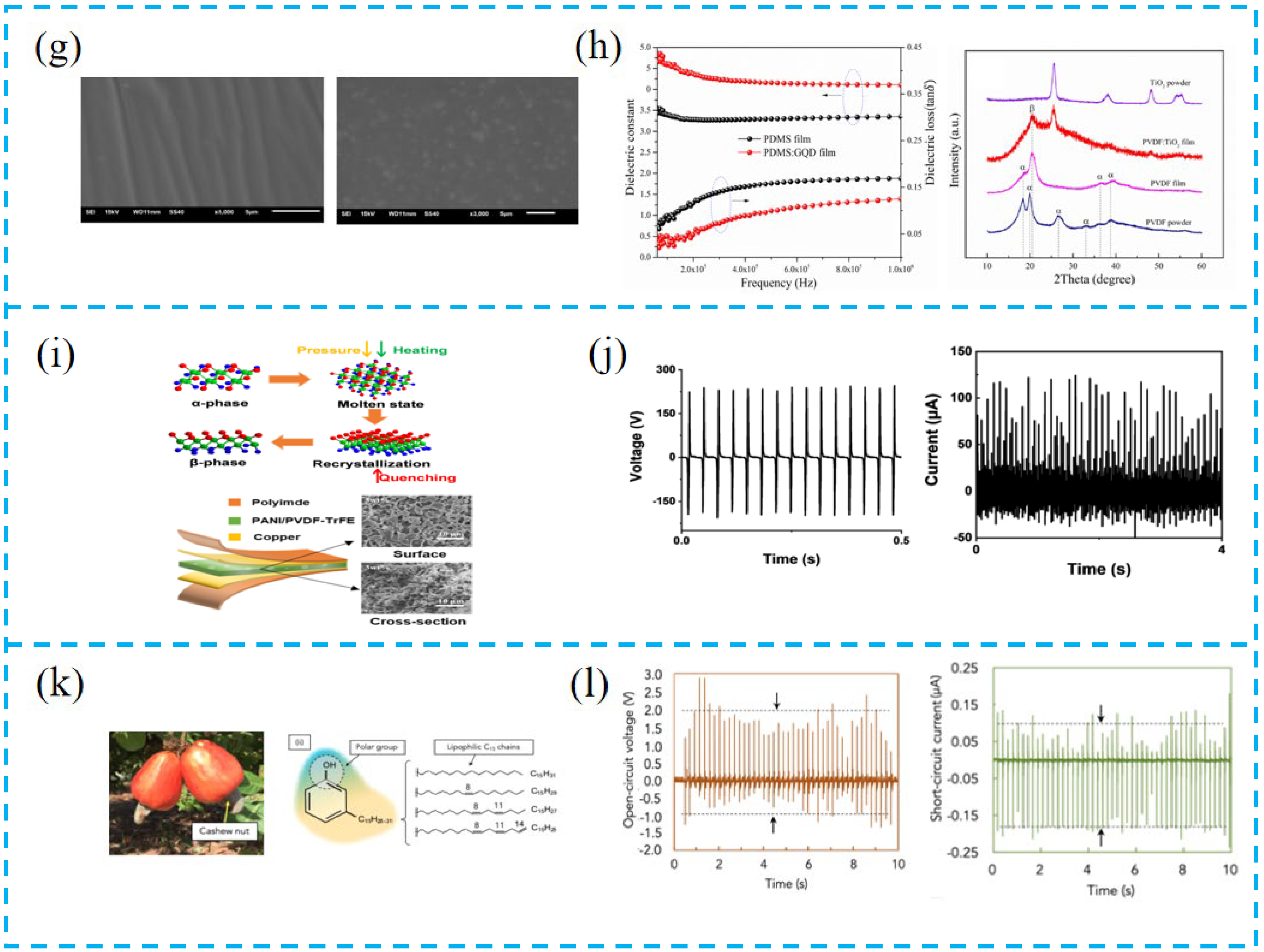
3.2. Material Selection
3.3. Surface Modification
4. Application of PTCNGs
4.1. Tactile Sensors Based on PTCNG
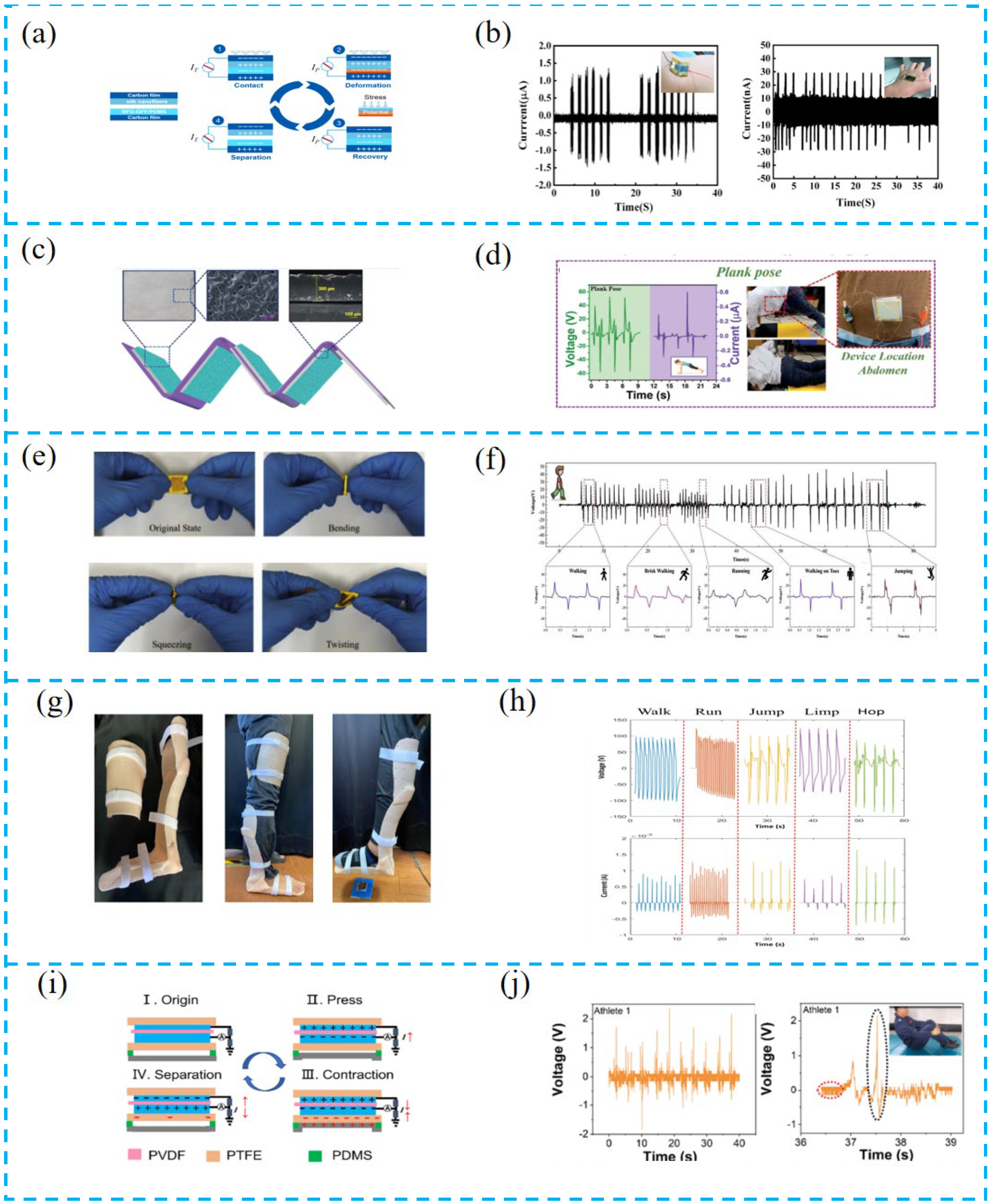
4.1.1. Tactile Sensor for Motion Monitoring
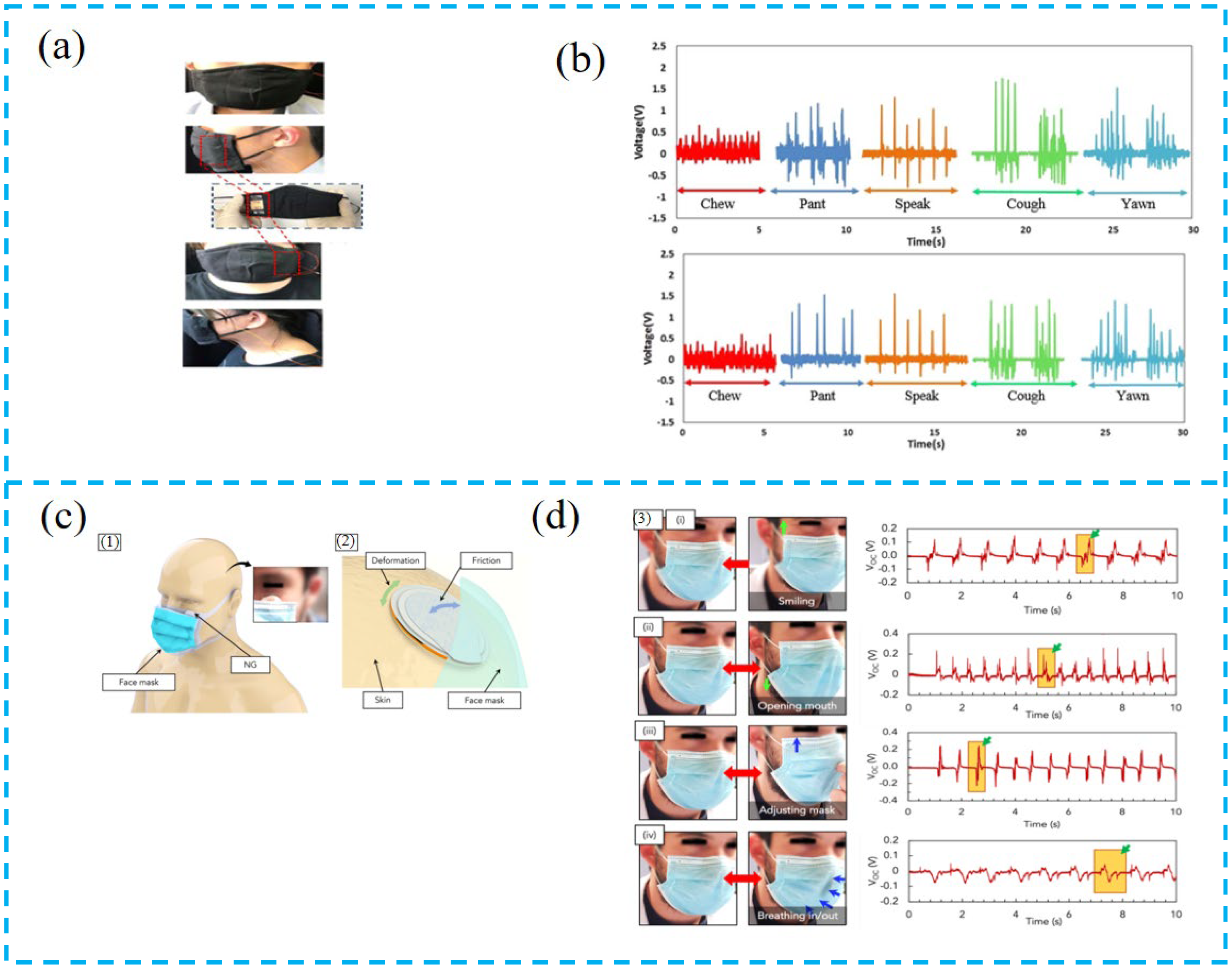
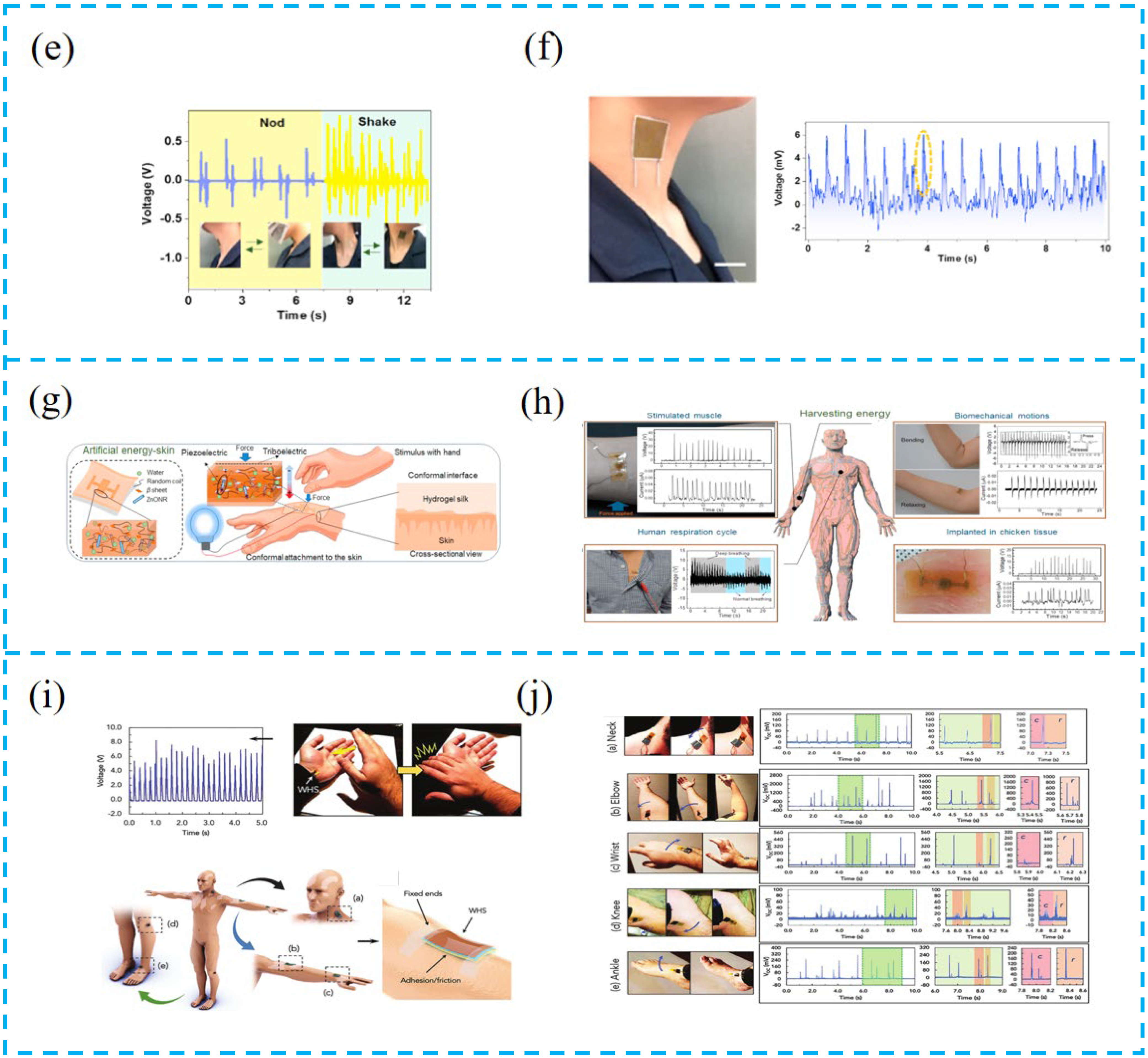
4.1.2. Tactile Sensor for Disease Monitoring
4.2. Energy-Harvesting System Based on PTCNG
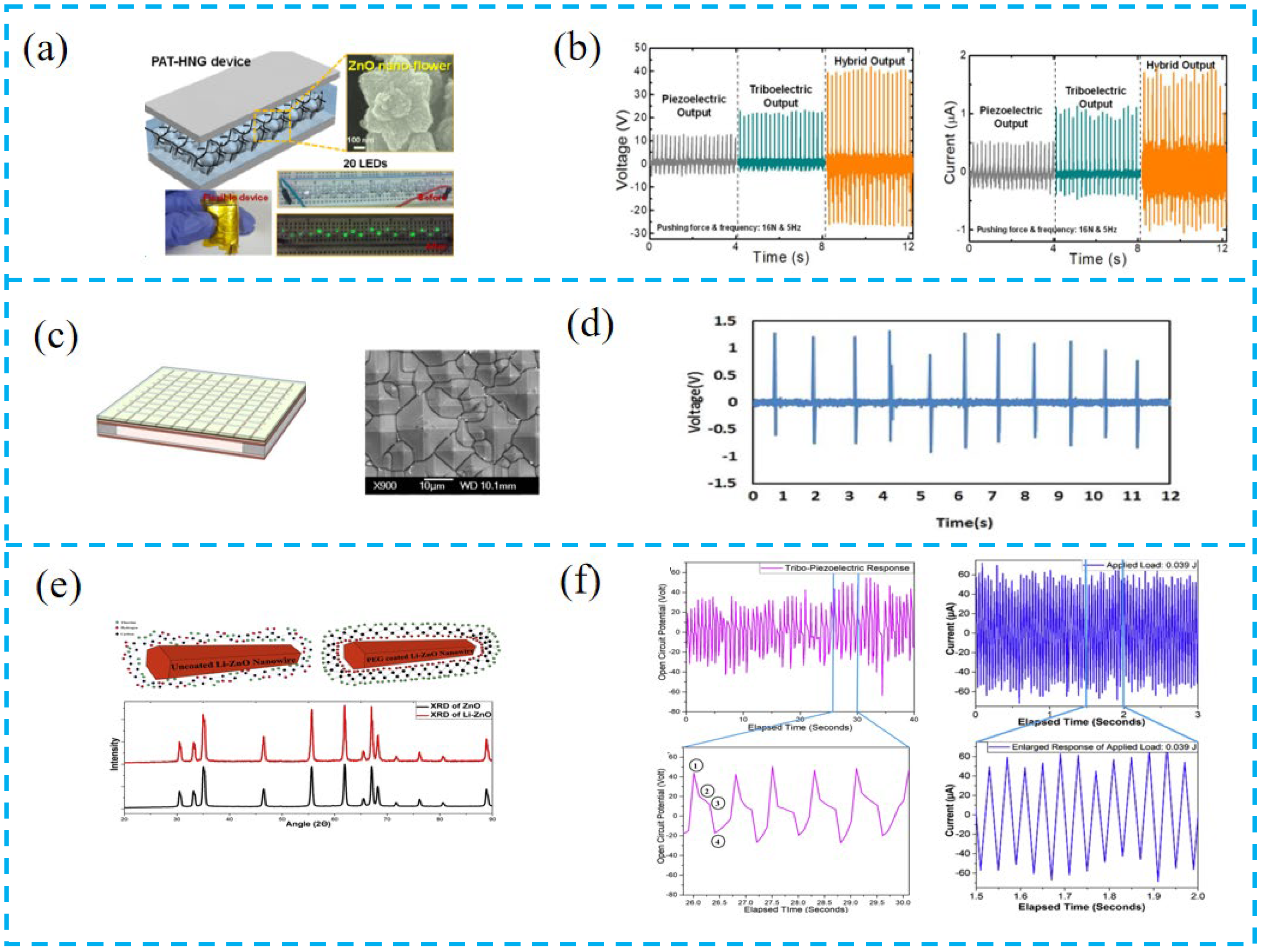
4.2.1. Clean Energy Harvesting
4.2.2. Self-Powered System Based on PTCNG
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Ni, Q.; Sun, Y.; Min, G.; Al-Rubaye, S. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Industrial Cyber-Physical IoT Systems in 5G Era. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 2618–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhong, Q.; Zhong, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, B.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Cloth-Based Power Shirt for Wearable Energy Harvesting and Clothes Ornamentation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14912–14916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Wang, G.N.; Schroeder, B.C.; Yan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, O.; Tran, H.; et al. Fully stretchable active-matrix organic light-emitting electrochemical cell array. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W. Skin-interfaced sensors in digital medicine: From materials to applications. Matter 2020, 2, 1414–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Zhong, Q.; Hu, Q.; Wu, N.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Hu, B.; Zhou, J. Stretchable Self-Powered Fiber-Based Strain Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.L. Fiber/Fabric-Based Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Flexible/Stretchable and Wearable Electronics and Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. From flexible electronics technology in the era of IoT and artificial intelligence toward future implanted body sensor networks. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.C.; Wu, C.; Pisignano, D.; Wang, Z.L.; Persano, L. Polymer nanogenerators: Opportunities and challenges for large-scale applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 135, 45674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, G.; Nashalian, A.; Chen, J. Advances in self-powered chemical sensing via a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2065–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharino, U.; Sinsanong, Y.; Pongampai, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Pakawanit, P.; Sriphan, S.; Vittayakorn, N.; Vittayakorn, W. Influence of pore morphologies on the mechanical and tribo-electrical performance of polydimethylsiloxane sponge fabricated via commercial seasoning templates. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 189, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriphan, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Khaisaat, S.; Sawanakarn, O.; Pharino, U.; Phunpruch, S.; Maluangnont, T.; Vittayakorn, N. Flexible capacitive sensor based on 2D-titanium dioxide nanosheets/bacterial cellulose composite film. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 155502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, L.; Shang, C.; Liang, S.; Guo, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Nanogenerator-based devices for biomedical applications. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wen, D. Wearable biochemical sensors for human health monitoring: Sensing materials and manufacturing technologies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3423–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Gao, W.; Javey, A. Flexible Electrochemical Bioelectronics: The Rise of In Situ Bioanalysis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bu, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.L. Tribotronics for Active Mechanosensation and Self-Powered Microsystems. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriphan, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Maluangnont, T.; Pakawanit, P.; Rojviriya, C.; Vittayakorn, N. Multifunctional Nanomaterials Modification of Cellulose Paper for Efficient Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Yang, R. Effect of humidity and pressure on the triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Wang, C.; Shao, R.; Sun, S. Advances and prospects of triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered system. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2021, 12, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric nanogenerators—A review of nanostructured piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.L. Nanowire Structured Hybrid Cell for Concurrently Scavenging Solar and Mechanical Energies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5866–5872. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Pan, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid cells for simultaneously harvesting multi-type energies for self-powered micro/nanosystems. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Compact Hybrid Cell Based on a Convoluted Nanowire Structure for Harvesting Solar and Mechanical Energy. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Dipole-moment-induced effect on contact electrification for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Research 2014, 7, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Human walking-driven wearable all-fiber triboelectric nanogenerator containing electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric nanofibers. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.; Kim, B.H.; Kwon, J.W. Paper-Based ZnO Nanogenerator Using Contact Electrification and Piezoelectric Effects. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2015, 24, 519–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, X.; Peng, X.; Zhang, H. Low-frequency wide-band hybrid energy harvester based on piezoelectric and triboelectric mechanism. Sci. Chin. Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, X.; Meng, B.; Liu, W. r-Shaped Hybrid Nanogenerator with Enhanced Piezoelectricity. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 7, 8554–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, L.; Tay, F.E.H.; Lee, C. Investigation of contact electrification based broadband energy harvesting mechanism using elastic PDMS microstructures. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2014, 24, 104002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y. 3D Fiber-Based Hybrid Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and as a Self-Powered Pressure Sensor. ACS Nano 2014, 7, 10674–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, B.; Zhang, H. Coupling of Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Effects: From Theoretical Analysis to Experimental Verification. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, H.; Zhao, T.; Yu, Y.; Dong, S. High-Temperature BiScO3-PbTiO3Piezoelectric Vibration Energy Harvester. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7186–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Ren, K. A Poly(l-Lactic Acid) Polymer-Based Thermally Stable Cantilever for Vibration Energy Harvesting Applications. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2017, 1, 1700068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tao, X.; Zeng, W.; Yang, B.; Shang, S. Quantifying Energy Harvested from Contact-Mode Hybrid Nanogenerators with Cascaded Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Units. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, S.; Ren, K.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid piezo/triboelectric nanogenerator for highly efficient and stable rotation energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, S.W. Hybrid Energy Harvesters: Toward Sustainable Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Mahmud, A.; Ban, D. Evolution From Single to Hybrid Nanogenerator: A Contemporary Review on Multimode Energy Harvesting for Self-Powered Electronics. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2019, 18, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, J.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.-W.; Lin, L. A comprehensive review on piezoelectric energy harvesting technology: Materials, mechanisms, and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistral, C.; Basrour, S.; Chaillout, J. Comparison of electroactive polymers for energy scavenging applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 075019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yao, K. Crystallization mechanism and piezoelectric properties of solution-derived ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, A.; Delfino, D.; Denegri, G.; Massucco, S. Management and Dynamic Performances of Combined Cycle Power Plants During Parallel and Islanding Operation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1998, 13, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Song, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Nanogenerator Driven by Ultrasonic Waves. Science 2007, 316, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Qin, Y.; Xu, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered nanowire devices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, A.; Johar, M.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Bagal, I.V.; Ha, J.-S.; Lee, J.K.; Ryu, S.-W. Effect of crystal orientation of GaN/V2O5 core-shell nanowires on piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepelin, N.A.; Glushenkov, A.M.; Lussini, V.C.; Fox, P.J.; Dicinoski, G.W.; Shapter, J.G.; Ellis, A.V. New developments in composites, copolymer technologies and processing techniques for flexible fluoropolymer piezoelectric generators for efficient energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1143–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Ounaies, Z.; Wise, K.E.; Harrison, J.S. In situ poling and imidization of amorphous piezoelectric polyimides. Polymer 2004, 45, 5417–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunyan, L.; Pei-Ming, W.; Soohyun, L.; Gorton, A.; Schulz, M.J.; Ahn, C.H. Flexible Dome and Bump Shape Piezoelectric Tactile Sensors Using PVDF-TrFE Copolymer. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2008, 17, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, N.; Koç, M. A comprehensive review on the state-of-the-art of piezoelectric energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoonsuk, T.; Sriphan, S.; Nawanil, C.; Chanlek, N.; Vittayakorn, W.; Vittayakorn, N. Tetragonal BaTiO3 nanowires: A template-free salt-flux-assisted synthesis and its piezoelectric response based on mechanical energy harvesting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 8277–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Kar, E.; Bose, N.; Mukherjee, S. NiO@SiO2/PVDF: A Flexible Polymer Nanocomposite for a High Performance Human Body Motion-Based Energy Harvester and Tactile e-Skin Mechanosensor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10505–10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriphan, S.; Nawanil, C.; Vittayakorn, N. Influence of dispersed phase morphology on electrical and fatigue properties of BaTiO3/PDMS nanogenerator. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-Y.; Choi, D.; Jin, M.-J.; Kim, I.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.-W. Mechanically Powered Transparent Flexible Charge-Generating Nanodevices with Piezoelectric ZnO Nanorods. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.G.; Oh, S.M.; Jung, W.S.; Moon, H.G.; Baek, S.H.; Nahm, S.; Yoon, S.J.; Kang, C.Y. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of vertically aligned single-crystalline NKN nano-rod arrays. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Mantini, G.; Di Carlo, A.; D’Amico, A.; Falconi, C.; Wang, Z.L. Piezoelectric potential in vertically aligned nanowires for high output nanogenerators. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yao, N.; Shi, Y. 1.6 V nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting using PZT nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2133–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Qin, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, Z.L. Power generation with laterally packaged piezoelectric fine wires. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Yang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible high-output nanogenerator based on lateral ZnO nanowire array. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3151–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Oh, J.; Ryu, C.; Yoo, W.J.; Kang, C.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; et al. Highly stretchable piezoelectric-pyroelectric hybrid nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; You, Q.; Sessler, G.M. Low-Cost, Large-Area, Stretchable Piezoelectric Films Based on Irradiation-Crosslinked Poly(propylene). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Lin Wang, Z. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacks, D.J.; Mohan Sankaran, R. Contact electrification of insulating materials. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 453001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.C.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Sensors and Systems Based on Nanogenerators. Sensors 2020, 20, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbritter, A.; Borda, L.; Zawadowski, A. Slow two-level systems in point contacts. Adv. Phys. 2004, 53, 939–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, Z. Fundamental theories and basic principles of triboelectric effect: A review. Friction 2018, 7, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kar-Narayan, S. Materials-Related Strategies for Highly Efficient Triboelectric Energy Generators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric-generator-driven pulse electrodeposition for micropatterning. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L. On the first principle theory of nanogenerators from Maxwell’s equations. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG)—Sparking an Energy and Sensor Revolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Guan, M.; He, Y. Vibration Energy Harvesting in Automobiles to Power Wireless Sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Beijing, China, 27–29 September 2012; pp. 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theory of freestanding triboelectric-layer-based nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ding, W.; Zi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ji, L.; Liu, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric microplasma powered by mechanical stimuli. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Wang, H.; Shi, Q.; Dhakar, L.; Wang, J.; Thakor, N.V.; Yen, S.-C.; Lee, C. Development of battery-free neural interface and modulated control of tibialis anterior muscle via common peroneal nerve based on triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Nano Energy 2017, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; He, T.; Lee, C. More than energy harvesting—Combining triboelectric nanogenerator and flexible electronics technology for enabling novel micro-/nano-systems. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, T.; Lee, C. Development of neural interfaces and energy harvesters towards self-powered implantable systems for healthcare monitoring and rehabilitation purposes. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wu, H.; Yao, G.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Zhong, W.; Chen, X.; Yin, Z.; et al. Giant Voltage Enhancement via Triboelectric Charge Supplement Channel for Self-Powered Electroadhesion. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10262–10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, M.; Shi, Q.; Wen, F.; Liu, L.; Dong, B.; Haroun, A.; Yang, Y.; Vachon, P.; Guo, X.; et al. Progress in TENG technology—A journey from energy harvesting to nanoenergy and nanosystem. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, M.V.; Graham, S.A.; Patnam, H.; Manchi, P.; Yu, J.S. Dopamine treated SnO2/PVDF composite films for hybrid mechanical energy harvester. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 221, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, A.; Medda, S.K.; Devi, P.S.; Sen, S. Nano-ZnO decorated ZnSnO3 as efficient fillers in PVDF matrixes: Toward simultaneous enhancement of energy storage density and efficiency and improved energy harvesting activity. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 20908–20921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Kelly, S.; Yang, R. Piezoelectric peptide-based nanogenerator enhanced by single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 074108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kang, D.J. Poly(dimethylsiloxane)/ZnO Nanoflakes/Three-Dimensional Graphene Heterostructures for High-Performance Flexible Energy Harvesters with Simultaneous Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32281–32288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.S.; Kang, M.G.; Moon, H.G.; Baek, S.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Wang, Z.L.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, C.Y. High output piezo/triboelectric hybrid generator. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongampai, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Pinpru, N.; Pulphol, P.; Vittayakorn, W.; Pakawanit, P.; Vittayakorn, N. Triboelectric-piezoelectric hybrid nanogenerator based on BaTiO3-Nanorods/Chitosan enhanced output performance with self-charge-pumping system. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 208, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liang, X.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Y.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.-P. Transparent and flexible hybrid nanogenerator with welded silver nanowire networks as the electrodes for mechanical energy harvesting and physiological signal monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 45040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hou, X.; Niu, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Guo, T.; Chou, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W. The d-arched piezoelectric-triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator as a self-powered vibration sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Lu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z. All-in-one hybrid tribo/piezoelectric nanogenerator with the point contact and its adjustable charge transfer by ferroelectric polarization. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 28277–28284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, G.; Cui, J.; Yu, S.; Zheng, L.; et al. Integrated piezo-tribo hybrid acoustic-driven nanogenerator based on porous MWCNTs/PVDF-TrFE aerogel bulk with embedded PDMS tympanum structure for broadband sound energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Song, M.; Chung, S.-H.; Choi, W.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.-H.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. Triangulated Cylinder Origami-Based Piezoelectric/Triboelectric Hybrid Generator to Harvest Coupled Axial and Rotational Motion. Research 2021, 2021, 7248579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tong, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cao, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Effective Mechanical Energy Harvesting from PVDF Multilayers by Head-to-Head Parallel Assembly. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 11133–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.H.; Khare, N. Flexible ZnO-PVDF/PTFE based piezo-tribo hybrid nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, M.; Chen, H.; Cheng, X.; Song, Y.; Su, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H. A wave-shaped hybrid piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerator based on P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, A.M.; Sadaf, M.U.K.; Tasnim, F.; Vasquez, H.; Lozano, K.; Uddin, M.J. KNN based piezo-triboelectric lead-free hybrid energy films. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, G.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Dual Effects in Mechanical-Energy Harvesting Using BaTiO3/Polydimethylsiloxane Composite Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34335–34341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, C.; Pan, X.; Cao, F.; Wang, H. Significantly enhanced energy harvesting based on Ba(Ti,Sn)O3 and P(VDF-CTFE) composite by piezoelectric and triboelectric hybrid. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toroń, B.; Mistewicz, K.; Jesionek, M.; Kozioł, M.; Zubko, M.; Stróż, D. A new hybrid piezo/triboelectric SbSeI nanogenerator. Energy 2022, 238, 122048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Hassan, G.; Shuja, A. Fabrication of self-healing hybrid nanogenerators based on polyurethane and ZnO for harvesting wind energy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 3982–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhou, X.; Lv, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Kongcharoen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, P.S. Stretchable, Breathable, and Stable Lead-Free Perovskite/Polymer Nanofiber Composite for Hybrid Triboelectric and Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Dudem, B.; Yu, J.S. High-Performance Flexible Piezoelectric-Assisted Triboelectric Hybrid Nanogenerator via Polydimethylsiloxane-Encapsulated Nanoflower-like ZnO Composite Films for Scavenging Energy from Daily Human Activities. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8525–8535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu Fang, L.; Tsai, C.Y.; Xu, M.H.; Wu, S.W.; Lo, W.C.; Lu, Y.H.; Fuh, Y.K. Hybrid nano-textured nanogenerator and self-powered sensor for on-skin triggered biomechanical motions. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 155502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.R.; Abdullah, A.M.; Hussain, I.; Lopez, J.; Cantu, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Mao, Y.; Danti, S.; Uddin, M.J. Lithium doped zinc oxide based flexible piezoelectric-triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, P.; Wu, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, G. A flexible piezoelectric-triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator in one structure with dual doping enhancement effects. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2021, 32, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H. PANI/PVDF-TrFE porous aerogel bulk piezoelectric and triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator based on in-situ doping and liquid nitrogen quenching. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariello, M.; Qualtieri, A.; Mele, G.; De Vittorio, M. Metal-Free Multilayer Hybrid PENG Based on Soft Electrospun/-Sprayed Membranes with Cardanol Additive for Harvesting Energy from Surgical Face Masks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 20606–20621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Shen, G. Flexible and transparent capacitive pressure sensor with patterned microstructured composite rubber dielectric for wearable touch keyboard application. Sci. Chin. Mater. 2018, 61, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, T. Silk-molded flexible, ultrasensitive, and highly stable electronic skin for monitoring human physiological signals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, D.; Zheng, Z.; Huangfu, G.; Guo, Y. Lead-free BiFeO3 film on glass fiber fabric: Wearable hybrid piezoelectric-triboelectric nanogenerator. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 3573–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.; Vivekananthan, V.; Hajra, S.; Abisegapriyan, K.S.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Kim, S.J. Synergetic enhancement of energy harvesting performance in triboelectric nanogenerator using ferroelectric polarization for self-powered IR signaling and body activity monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 22257–22268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hou, X.; Cui, M.; Zhang, S.; He, J.; Geng, W.; Mu, J.; Chou, X. Highly skin-conformal wearable tactile sensor based on piezoelectric-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Lo, H.H.; Wang, J.; Lee, T.H.; Fuh, Y.K. Self-Powered, Hybrid, Multifunctional Sensor for a Human Biomechanical Monitoring Device. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Jia, C.; Zhao, T.; Mao, Y. A Stretchable and Self-Healing Hybrid Nano-Generator for Human Motion Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2021, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Lou, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Energy autonomous hybrid electronic skin with multi-modal sensing capabilities. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogurla, N.; Roy, B.; Kim, S. Self-powered artificial skin made of engineered silk protein hydrogel. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariello, M.; Fachechi, L.; Guido, F.; De Vittorio, M. Conformal, Ultra-thin Skin-Contact-Actuated Hybrid Piezo/Triboelectric Wearable Sensor Based on AlN and Parylene-Encapsulated Elastomeric Blend. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, A.; Abdullah, A.; Bagal, I.V.; Ha, J.-S.; Lee, J.K.; Ryu, S.-W. Self-powered and flexible piezo-sensors based on conductivity-controlled GaN nanowire-arrays for mimicking rapid- and slow-adapting mechanoreceptors. Npj Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
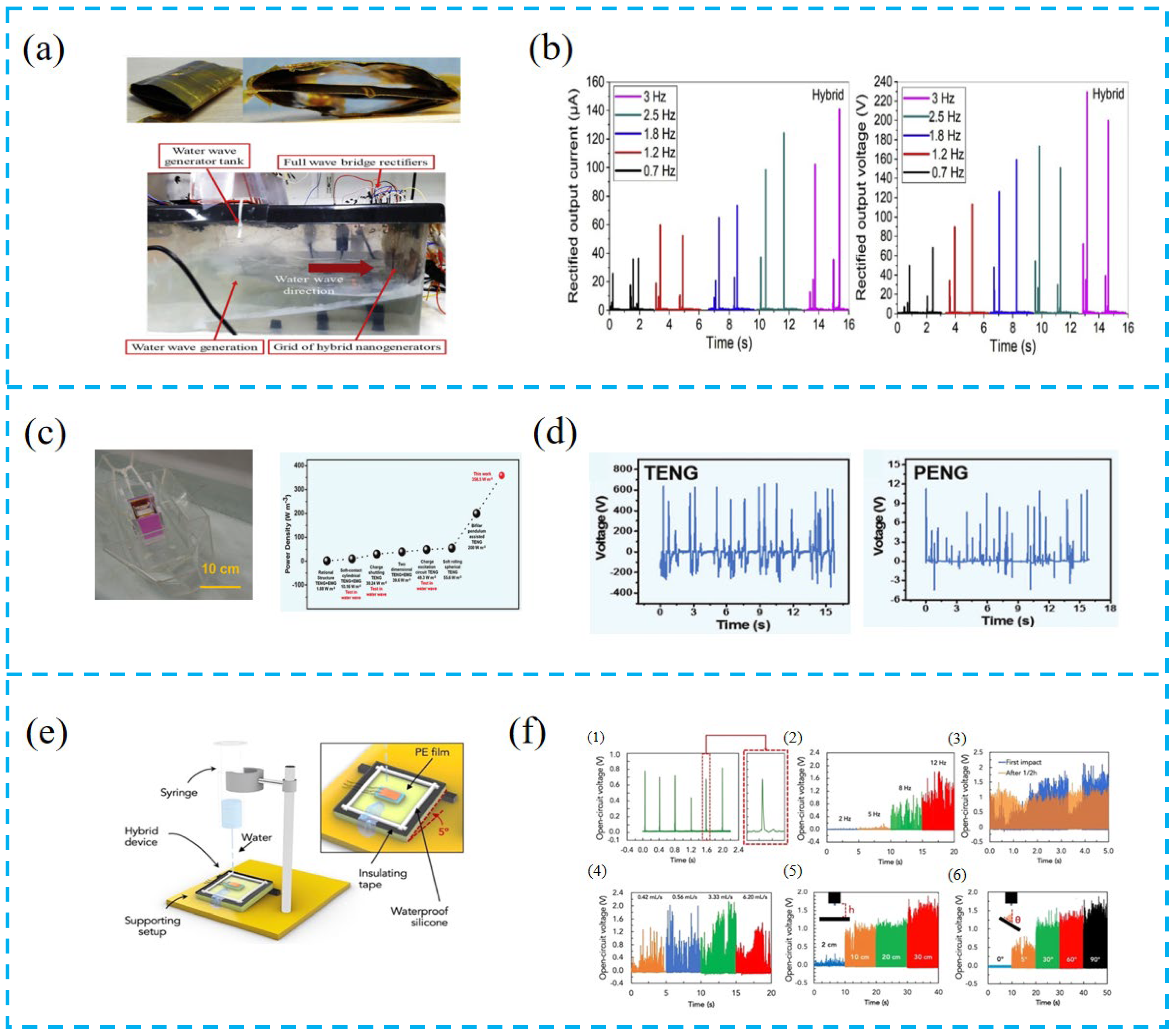
- Jurado, U.T.; Pu, S.H.; White, N.M. Grid of hybrid nanogenerators for improving ocean wave impact energy harvesting self-powered applications. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. High Space Efficiency Hybrid Nanogenerators for Effective Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariello, M.; Fachechi, L.; Guido, F.; De Vittorio, M. Multifunctional sub-100 µm thickness flexible piezo/triboelectric hybrid water energy harvester based on biocompatible AlN and soft parylene C-PDMS-Ecoflex™. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zou, H.-X.; Zhao, L.-C.; Li, M.; Wei, K.-X.; Huang, L.-P.; Zhang, W.-M. A synergetic hybrid mechanism of piezoelectric and triboelectric for galloping wind energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 117, 043902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gong, S.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Ren, K. A Wind-Driven Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) Electret and Polylactide Polymer-Based Hybrid Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Temperature Detection System. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 5, 2000192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
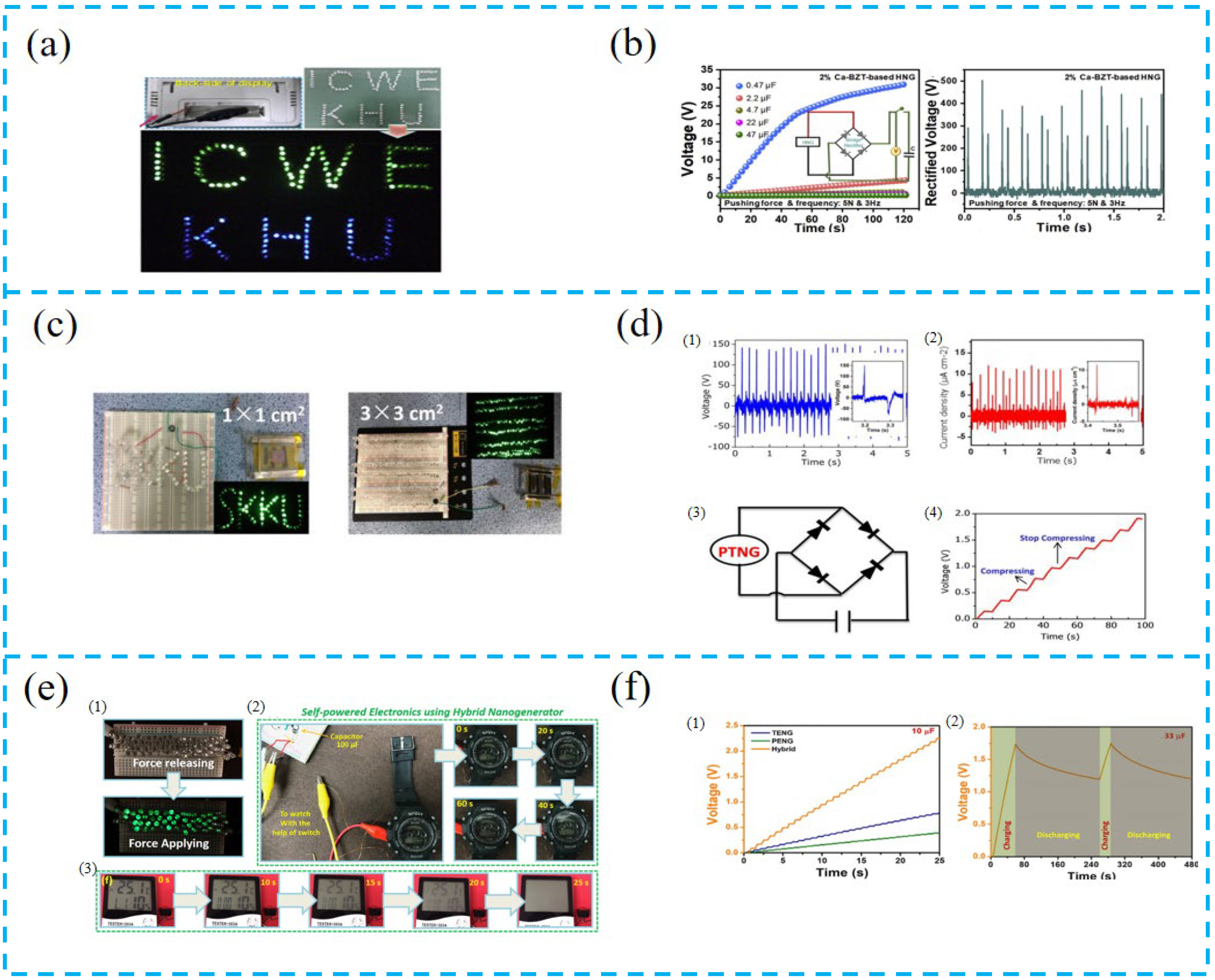
- Patnam, H.; Dudem, B.; Alluri, N.R.; Mule, A.R.; Graham, S.A.; Kim, S.-J.; Yu, J.S. Piezo/triboelectric hybrid nanogenerators based on Ca-doped barium zirconate titanate embedded composite polymers for wearable electronics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Qian, Y.; Lee, B.S.; Zhang, F.; Rasheed, A.; Jung, J.E.; Kang, D.J. Ultrahigh Output Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Hybrid Nanogenerators Based on ZnO Nanoflakes/Polydimethylsiloxane Composite Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44415–44420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivekananthan, V.; Maria Joseph Raj, N.P.; Alluri, N.R.; Purusothaman, Y.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Kim, S.-J. Substantial improvement on electrical energy harvesting by chemically modified/sandpaper-based surface modification in micro-scale for hybrid nanogenerators. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 514, 145904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Lee, C.; Luo, G.; Mao, Q.; Yang, P.; Lin, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Self-sustained autonomous wireless sensing based on a hybridized TENG and PEG vibration mechanism. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.-L.; Huang, P.; Qian, H.-Y.; Ba, Y.-Y.; Ren, Z.-Y.; Tu, C.; Gong, T.-X.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.-S. Hybrid nanogenerator-based self-powered double-authentication microsystem for smart identification. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Recent Progress in Piezoelectric-Triboelectric Effects Coupled Nanogenerators. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030385
Wang Y, Cao X, Wang N. Recent Progress in Piezoelectric-Triboelectric Effects Coupled Nanogenerators. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(3):385. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030385
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yifei, Xia Cao, and Ning Wang. 2023. "Recent Progress in Piezoelectric-Triboelectric Effects Coupled Nanogenerators" Nanomaterials 13, no. 3: 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030385
APA StyleWang, Y., Cao, X., & Wang, N. (2023). Recent Progress in Piezoelectric-Triboelectric Effects Coupled Nanogenerators. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030385






