The Use of Semiconductor Quantum Dots with Large, Built-In Spontaneous Polarizations for the Electric Potential Stimulation of Biological Structures on the Nanoscale
Abstract
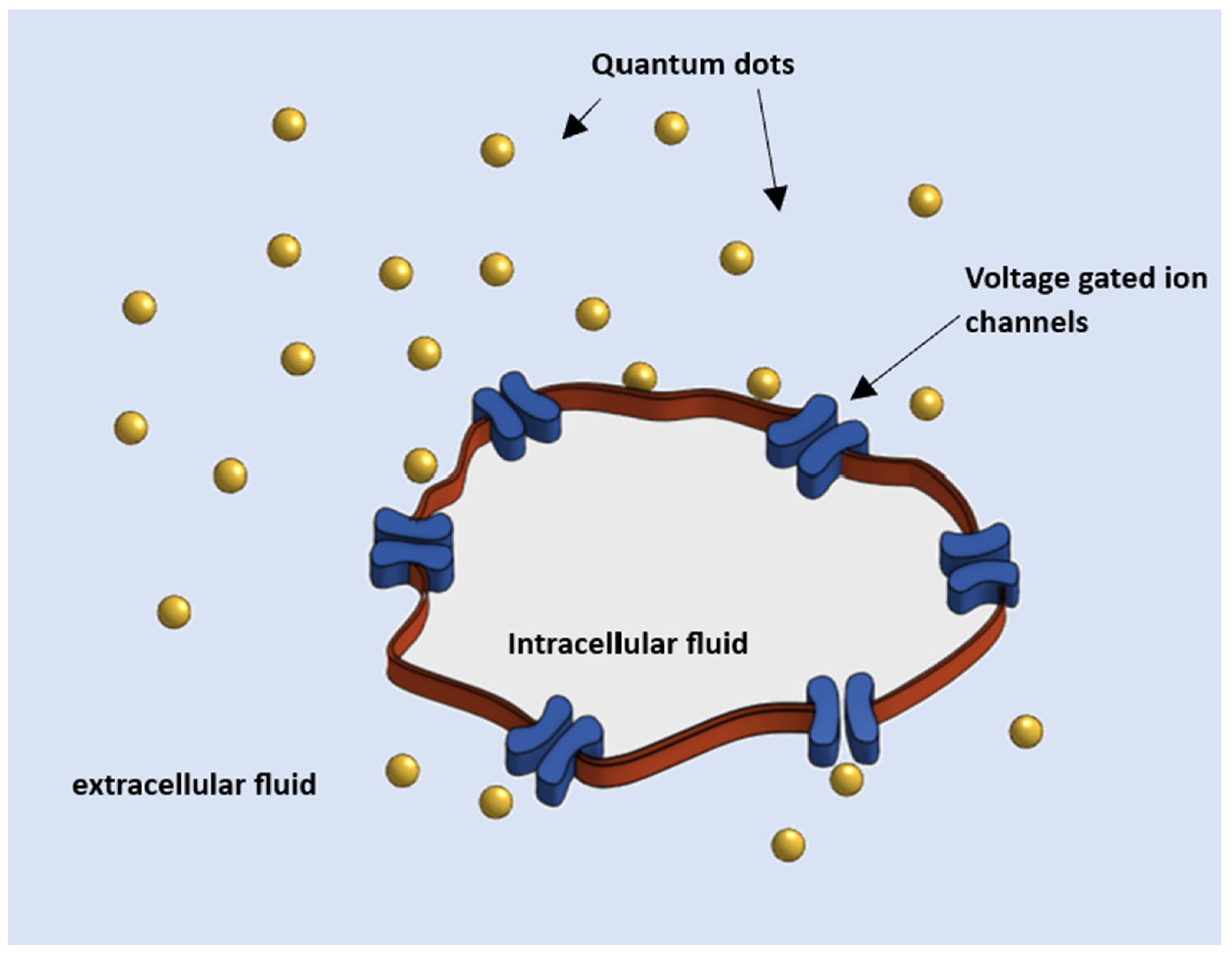
:1. Introduction
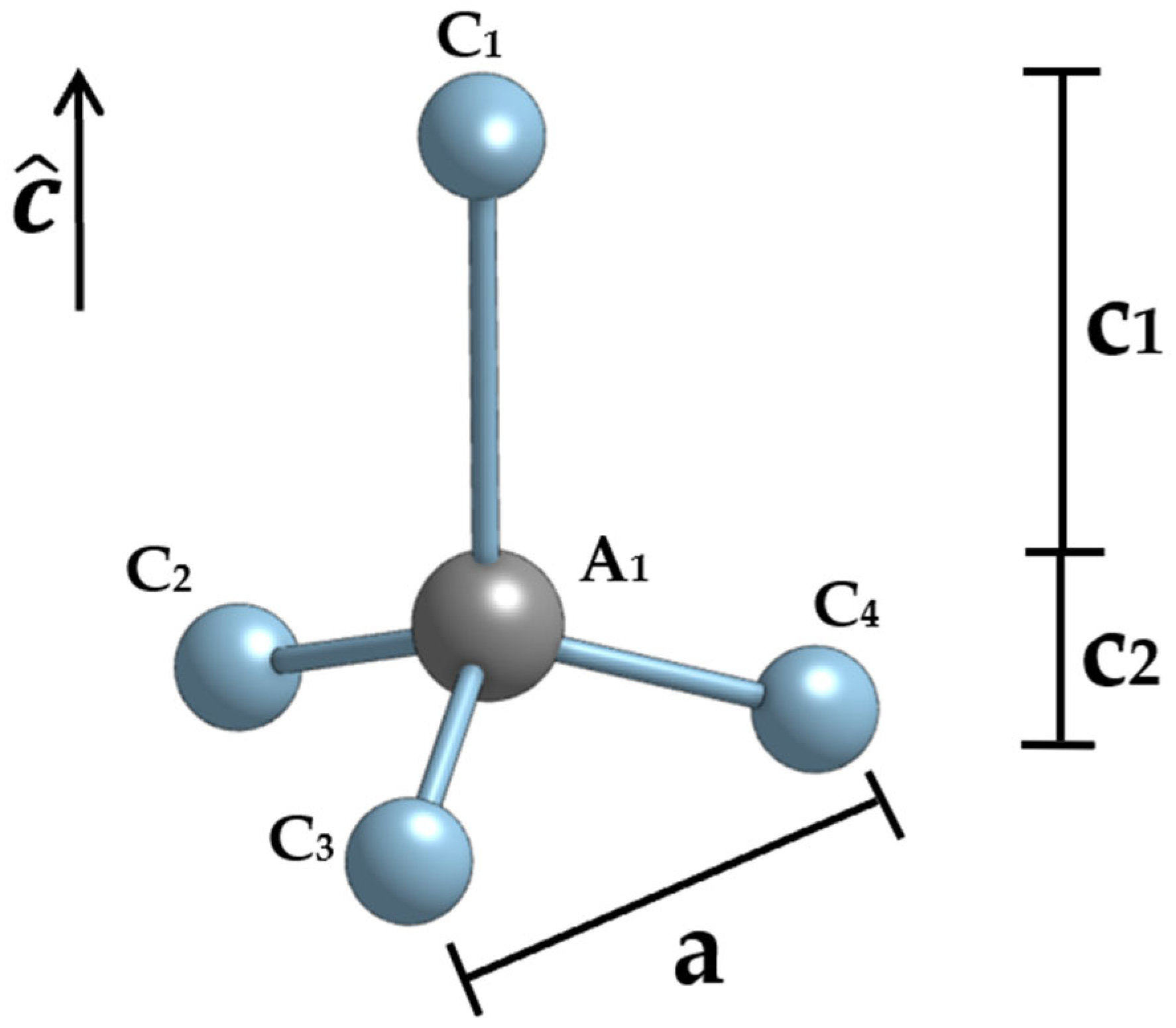
2. Materials and Method
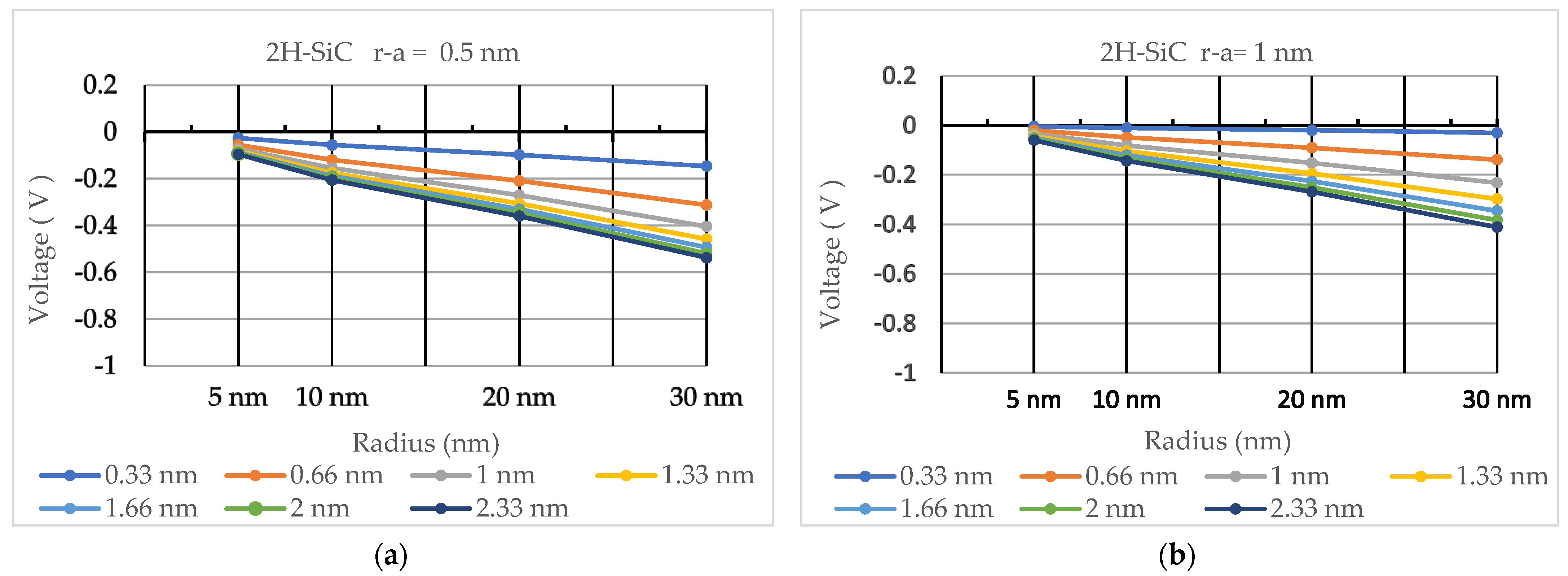
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kandel, E.; Koester, J.D.; Mack, S.H.; Siegelbaum, S. Principles of Neural Science, 6th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 1259642232/139781259642234. [Google Scholar]
- Brus, L.E. Electron–electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: The size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 4403–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, M.; Manoth, M.; Singh, V.; Gowd, G.S.; Choudhry, V.; Vadera, S.; Kumar, N. Synthesis of stable dispersion of ZnO quantum dots in aqueous medium showing visible emission from bluish green to yellow. J. Lumin. 2009, 129, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Y.L.; Tok, A.I.Y.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Zeng, X.T.; Zhang, X.H. Chemical Synthesis of ZnO Nanocrystals. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2007, 6, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mićić, O.I.; Ahrenkiel, S.P.; Bertram, D.; Nozik, A.J. Synthesis, structure, and optical properties of colloidal GaN quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, S. Fabrication of 4H–SiC nanoparticles using femtosecond pulsed laser ablation in deionized water. Opt. Mater. 2022, 132, 112817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, W.; Dutta, M.; Stroscio, M. Spontaneous Polarization Calculations in Wurtzite II-Oxides, III-Nitrides, and SiC Polytypes through Net Dipole Moments and the Effects of Nanoscale Layering. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troy, W.; Dutta, M.; Stroscio, M.A. Spontaneous Polarization in Nanoparticles. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2021, 42, 1838–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Yi, J.; Isheim, D.; Rotenberg, M.; Meng, L.; Shi, F.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Prominski, A.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Laser writing of nitrogen-doped silicon carbide for biological modulation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corson, D.R.; Lorrain, P. Introduction to Electromagnetic Fields and Waves, 2nd ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1962; pp. 93–94. ISBN 0-7167-0331-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lähnemann, J.; Brandt, O.; Jahn, U.; Pfüller, C.; Roder, C.; Dogan, P.; Grosse, F.; Belabbes, A.; Bechstedt, F.; Trampert, A.; et al. Direct experimental determination of the spontaneous polarization of GaN. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 081302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, A.D.; O’reilly, E.P. Theory of the electronic structure of GaN/AlN hexagonal quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 15851–15870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SFarid, S.; Choi, M.; Datta, D.; Stroscio, M.A.; Dutta, M. Spontaneous polarization induced electric field in zinc oxide nanowires and nanostars. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 163108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, F.; Fiorentini, V.; Vanderbilt, D. Spontaneous polarization and piezoelectric constants of III-V nitrides. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 56, R10024–R10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, S.Y.; Troshin, A.V. Estimates of the spontaneous polarization in silicon carbide. Phys. Solid State 2007, 49, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Meshik, X.; Mukherjee, S.; Farid, S.; Doan, S.; Covnot, L.; Dutta, M.; Stroscio, M.A. Electrostatic force analysis, optical measurements, and structural characterization of zinc oxide colloidal quantum dots synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 194304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Gao, T.; Yang, X.; Dai, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, A.; Lieber, C.M. Specific detection of biomolecules in physiological solutions using graphene transistor biosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14633–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerström, H.; Estrada, E.V.; Danielsson, J.; Oliveberg, M. Colloidal stability of the living cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10113–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesler, V.; Murmann, B.; Soh, H.T. Going beyond the Debye Length: Overcoming Charge Screening Limitations in Next-Generation Bioelectronic Sensors. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16194–16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, K.; Gao, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Bai, J. Current characteristic signals of aqueous solution transferring through microfluidic channel under non-continuous DC electric field. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 107139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshik, X.; Choi, M.; Baker, A.; Malchow, R.P.; Covnot, L.; Doan, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Farid, S.; Dutta, M.; Stroscio, M.A. Modulation of voltage-gated conductances of retinal horizontal cells by UV-excited TiO2 nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; You, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lim, Z.S.; Zou, X.; Chen, L.; Ramesh, R.; Wang, J. Non-volatile memory based on the ferroelectric photovoltaic effect. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistewicz, K. Recent Advances in Ferroelectric Nanosensors: Toward Sensitive Detection of Gas, Mechanothermal Signals, and Radiation. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 2651056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Katsouras, I.; Asadi, K.; Groen, W.A.; Blom, P.W.M.; de Leeuw, D.M. Retention of intermediate polarization states in ferroelectric materials enabling memories for multi-bit data storage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 232907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta, R. Macroscopic polarization in crystalline dielectrics: The geometric phase approach. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1994, 66, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King-Smith, R.D.; Vanderbilt, D. Theory of polarization of crystalline solids. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 1651–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerphagnon, J. Invariants of the Third-Rank Cartesian Tensor: Optical Nonlinear Susceptibilities. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 2, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, A.D.; Posternak, M.; Resta, R.; Baldereschi, A. Ab initiostudy of piezoelectricity and spontaneous polarization in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 10715–10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.-T.; Shi, H.-J.; Chen, S.-P.; Tang, Y.-Z.; Tan, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-F.; Sun, Z.; Wang, F.X.; Wan, M.-Y. Large Spontaneous Polarization Ferroelectric Property, Switchable Second-Harmonic Generation Responses, and Magnetism in an Fe-Based Compound. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 6189–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Gao, K.-G.; Yao, Z.-S.; Tao, J. High-Temperature Metal-Free Molecular Ferroelectrics with Large Spontaneous Polarization. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 8778–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, A. Pyroelectricity and Spontaneous Polarization in LiNbO3. J. Appl. Phys. 1966, 37, 3071–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaton, J.B.; Ederer, C.; Waghmare, U.V.; Spaldin, N.A.; Rabe, K.M. First-principles study of spontaneous polarization in multiferroic BiFeO3. Phys. Rev. 2005, B71, 014113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhmanson, S.M.; Calzolari, A.; Meunier, V.; Bernholc, J.; Nardelli, M.B. Spontaneous polarization and piezoelectricity in boron nitride nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 235406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
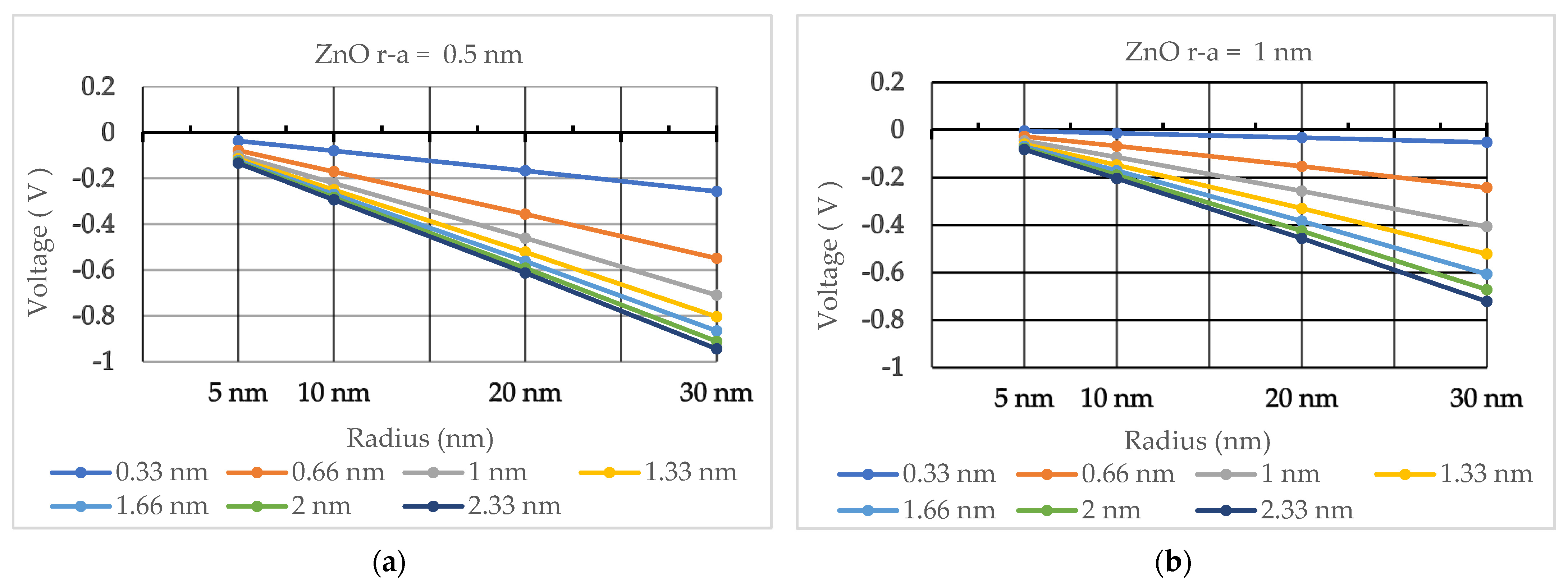
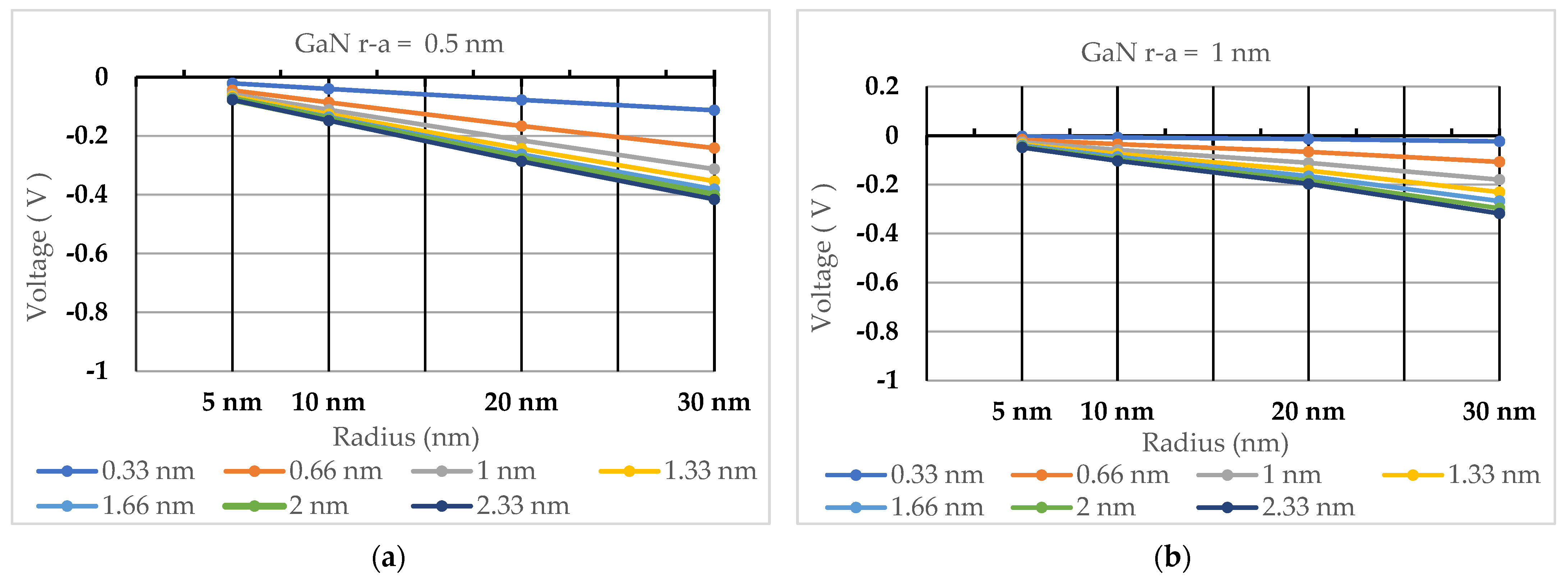
| Radius of Quantum Dot | ZnO P(high) C/m2 | ZnO P(low) C/m2 | GaN P(high) C/m2 | GaN P(low) C/m2 | 2H-SiC P(high) C/m2 | 2H-SiC P(low) C/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −0.039 | −0.080 | −0.004 | −0.065 | −0.012 | −0.073 |
| 10 nm | −0.044 | −0.069 | −0.011 | −0.046 | −0.020 | −0.059 |
| 20 nm | −0.047 | −0.062 | −0.016 | −0.031 | −0.024 | −0.040 |
| 30 nm | −0.049 | −0.060 | −0.019 | −0.029 | −0.028 | −0.034 |
| Debye Length | 0.33 nm | 0.66 nm | 1 nm | 1.33 nm | 1.66 nm | 2 nm | 2.33 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −0.03655 | −0.07796 | −0.10087 | −0.11419 | −0.12305 | −0.12952 | −0.13419 |
| 10 nm | −0.08012 | −0.17091 | −0.22112 | −0.25033 | −0.26975 | −0.28393 | −0.29416 |
| 20 nm | −0.16701 | −0.35624 | −0.46090 | −0.52178 | −0.56227 | −0.59181 | −0.61314 |
| 30 nm | −0.25730 | −0.54884 | −0.71009 | −0.80388 | −0.86626 | −0.91178 | −0.94463 |
| Debye Length | 0.33 nm | 0.66 nm | 1 nm | 1.33 nm | 1.66 nm | 2 nm | 2.33 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −6.2465 × 10−3 | −0.02842 | −0.04758 | −0.06097 | −0.07080 | −0.07844 | −0.08419 |
| 10 nm | −0.01526 | −0.06941 | −0.11619 | −0.14891 | −0.17292 | −0.19157 | −0.20563 |
| 20 nm | −0.03397 | −0.15458 | −0.25874 | −0.33160 | −0.38506 | −0.42659 | −0.45789 |
| 30 nm | −0.05363 | −0.24402 | −0.40846 | −0.52349 | −0.60789 | −0.67344 | −0.72286 |
| Debye Length | 0.33 nm | 0.66 nm | 1 nm | 1.33 nm | 1.66 nm | 2 nm | 2.33 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −0.02119 | −0.04521 | −0.05849 | −0.06621 | −0.07135 | −0.07510 | −0.07781 |
| 10 nm | −0.04042 | −0.08621 | −0.11154 | −0.12627 | −0.13607 | −0.14322 | −0.14838 |
| 20 nm | −0.07815 | −0.16669 | −0.21567 | −0.24415 | −0.26310 | −0.27692 | −0.286902 |
| 30 nm | −0.11331 | −0.24169 | −0.31270 | −0.35400 | −0.38147 | −0.40151 | −0.41598 |
| Debye Length | 0.33 nm | 0.66 nm | 1 nm | 1.33 nm | 1.66 nm | 2 nm | 2.33 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −3.62191 × 10−3 | −0.01648 | −0.02759 | −0.03535 | −0.04105 | −0.04548 | −0.04882 |
| 10 nm | −7.69523 × 10−3 | −0.03501 | −0.05861 | −0.07512 | −0.08723 | −0.09663 | −0.10372 |
| 20 nm | −0.01465 | −0.06665 | −0.11157 | −0.14299 | −0.16604 | −0.18394 | −0.19744 |
| 30 nm | −0.02362 | −0.10746 | −0.17987 | −0.23053 | −0.26769 | −0.29656 | −0.31832 |
| Debye Length | 0.33 nm | 0.66 nm | 1 nm | 1.33 nm | 1.66 nm | 2 nm | 2.33 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −0.02610 | −0.05569 | −0.07205 | −0.08157 | −0.08790 | −0.09251 | −0.09585 |
| 10 nm | −0.05602 | −0.11949 | −0.15459 | −0.17500 | −0.18859 | −0.19849 | −0.20565 |
| 20 nm | −0.09805 | −0.20917 | −0.27062 | −0.30637 | −0.33014 | −0.34748 | −0.36000 |
| 30 nm | −0.1463 | −0.3121 | −0.40390 | −0.45725 | −0.49273 | −0.51862 | −0.53731 |
| Debye Length | 0.33 nm | 0.66 nm | 1 nm | 1.33 nm | 1.66 nm | 2 nm | 2.33 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 nm | −4.46 × 10−3 | −0.02030 | −0.03398 | −0.04355 | −0.05057 | −0.056027 | −0.06013 |
| 10 nm | −0.01066 | −0.04852 | −0.08123 | −0.104107 | −0.12089 | −0.133927 | −0.143755 |
| 20 nm | −0.019946 | −0.09075 | −0.15192 | −0.194703 | −0.22609 | −0.250474 | −0.268854 |
| 30 nm | −0.030504 | −0.13880 | −0.23233 | −0.2977658 | −0.34577 | −0.383058 | −0.411168 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zia, N.; Stroscio, M.A.; Dutta, M. The Use of Semiconductor Quantum Dots with Large, Built-In Spontaneous Polarizations for the Electric Potential Stimulation of Biological Structures on the Nanoscale. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243143
Zia N, Stroscio MA, Dutta M. The Use of Semiconductor Quantum Dots with Large, Built-In Spontaneous Polarizations for the Electric Potential Stimulation of Biological Structures on the Nanoscale. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(24):3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243143
Chicago/Turabian StyleZia, Nida, Michael A. Stroscio, and Mitra Dutta. 2023. "The Use of Semiconductor Quantum Dots with Large, Built-In Spontaneous Polarizations for the Electric Potential Stimulation of Biological Structures on the Nanoscale" Nanomaterials 13, no. 24: 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243143
APA StyleZia, N., Stroscio, M. A., & Dutta, M. (2023). The Use of Semiconductor Quantum Dots with Large, Built-In Spontaneous Polarizations for the Electric Potential Stimulation of Biological Structures on the Nanoscale. Nanomaterials, 13(24), 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243143






