Critical Electrospinning Parameters for Synthesis Control of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
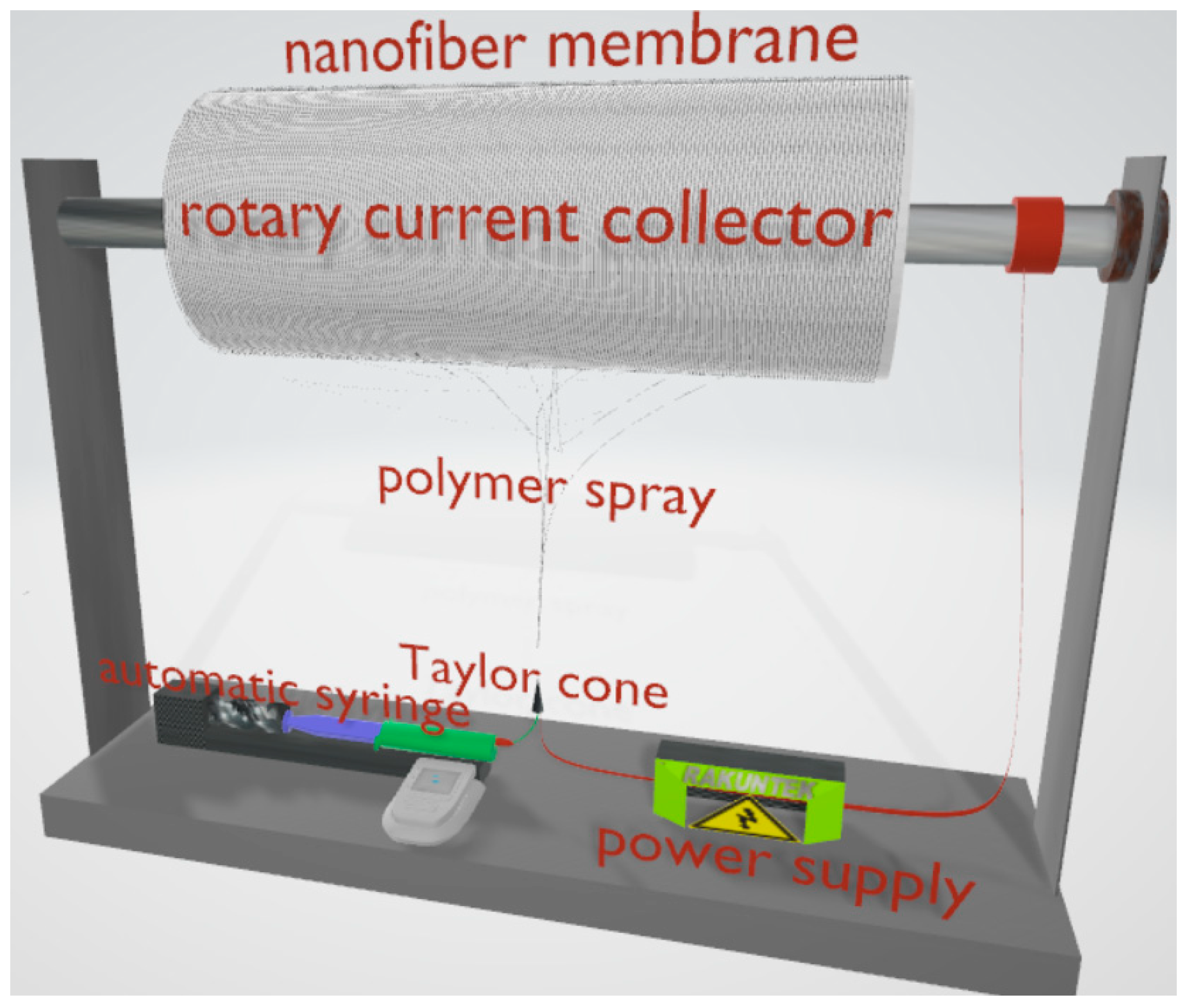
2.1. PAN Fiber Preparation
2.2. PAN Fibers Characterization
3. Results
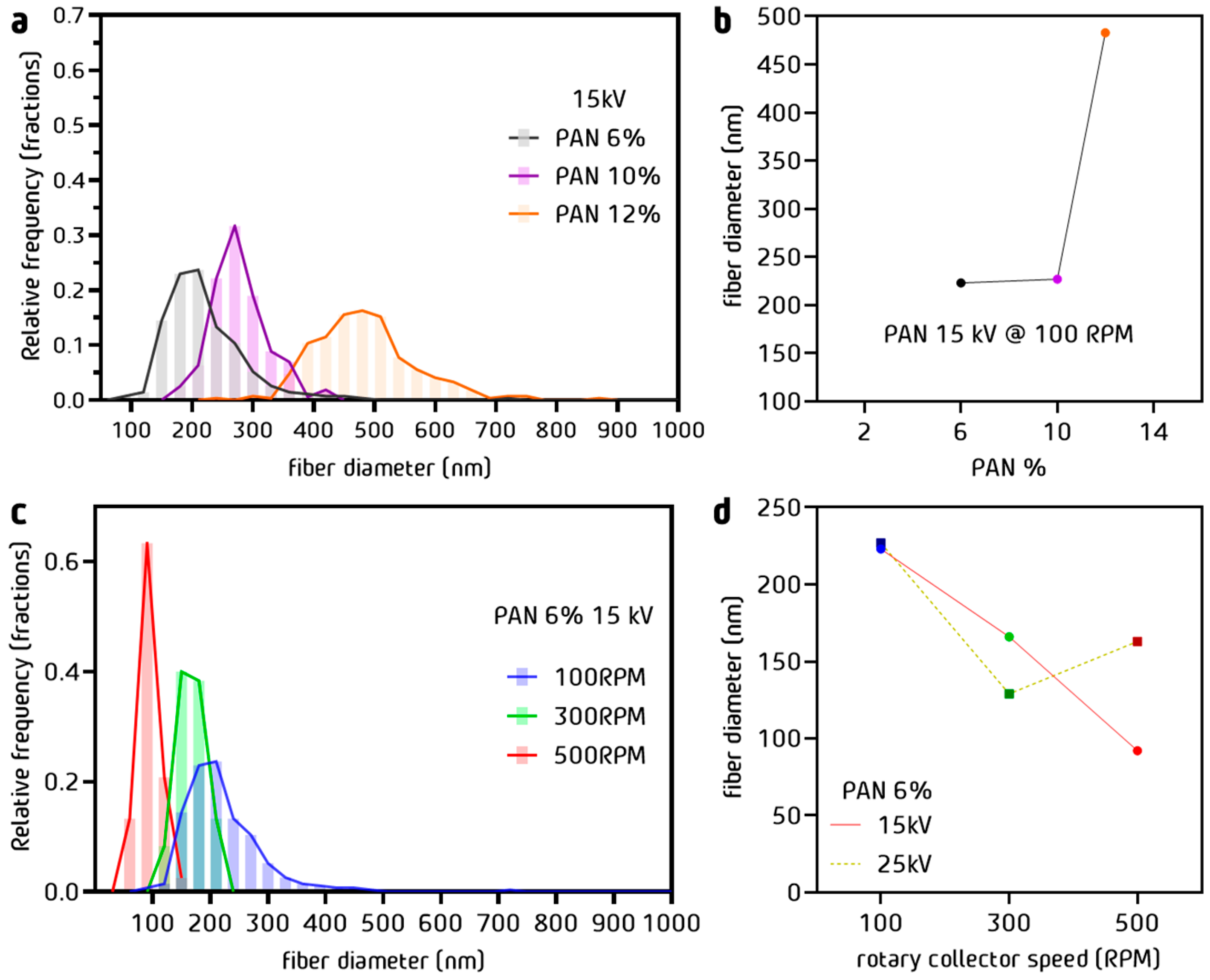
3.1. Dimensions of PAN Fibers
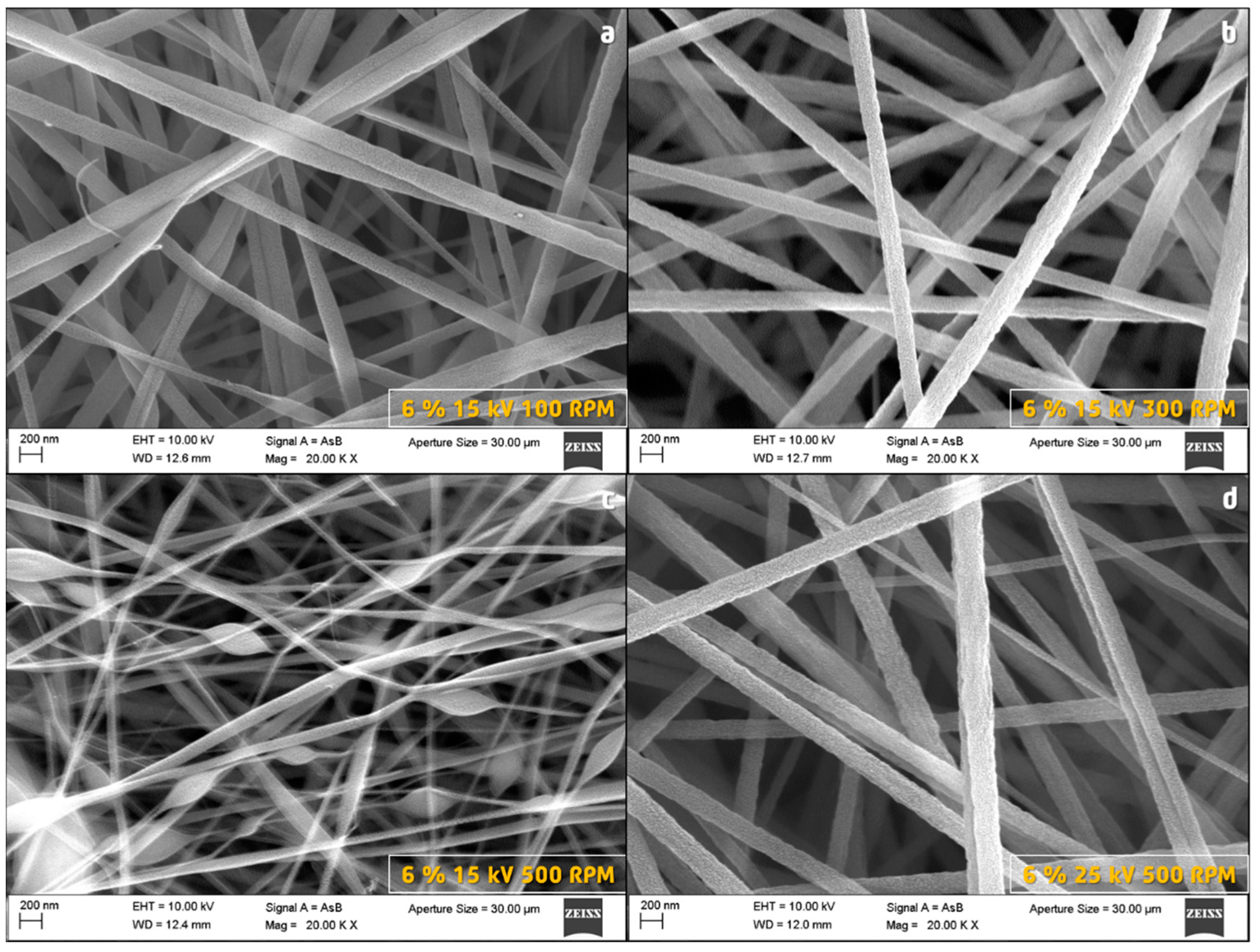
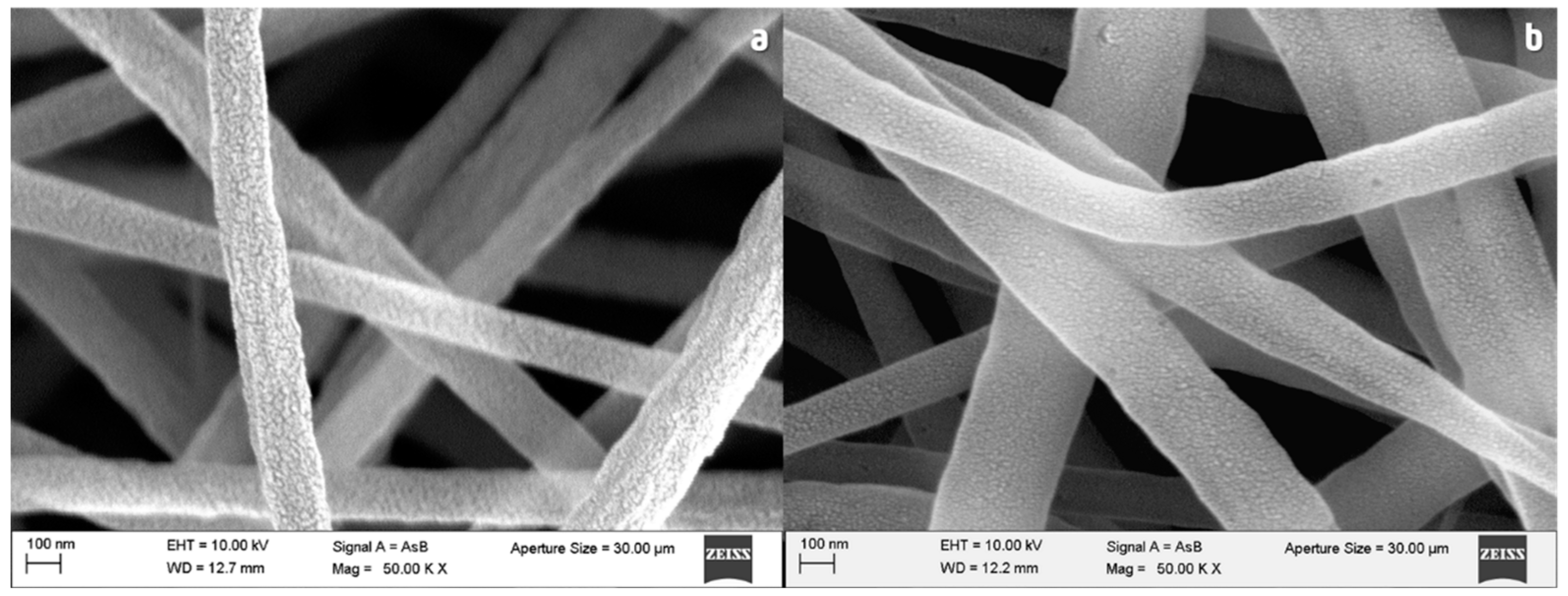
3.2. Morphology of PAN Fibers
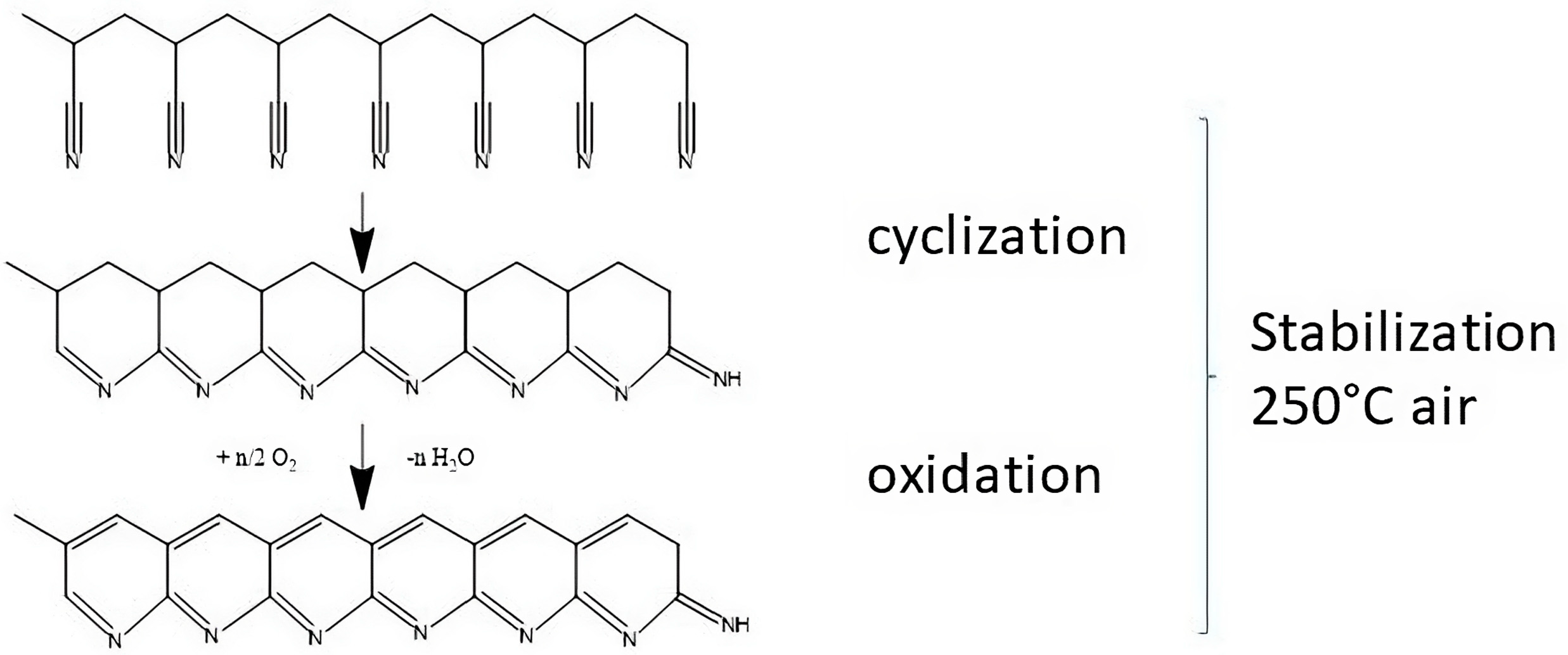
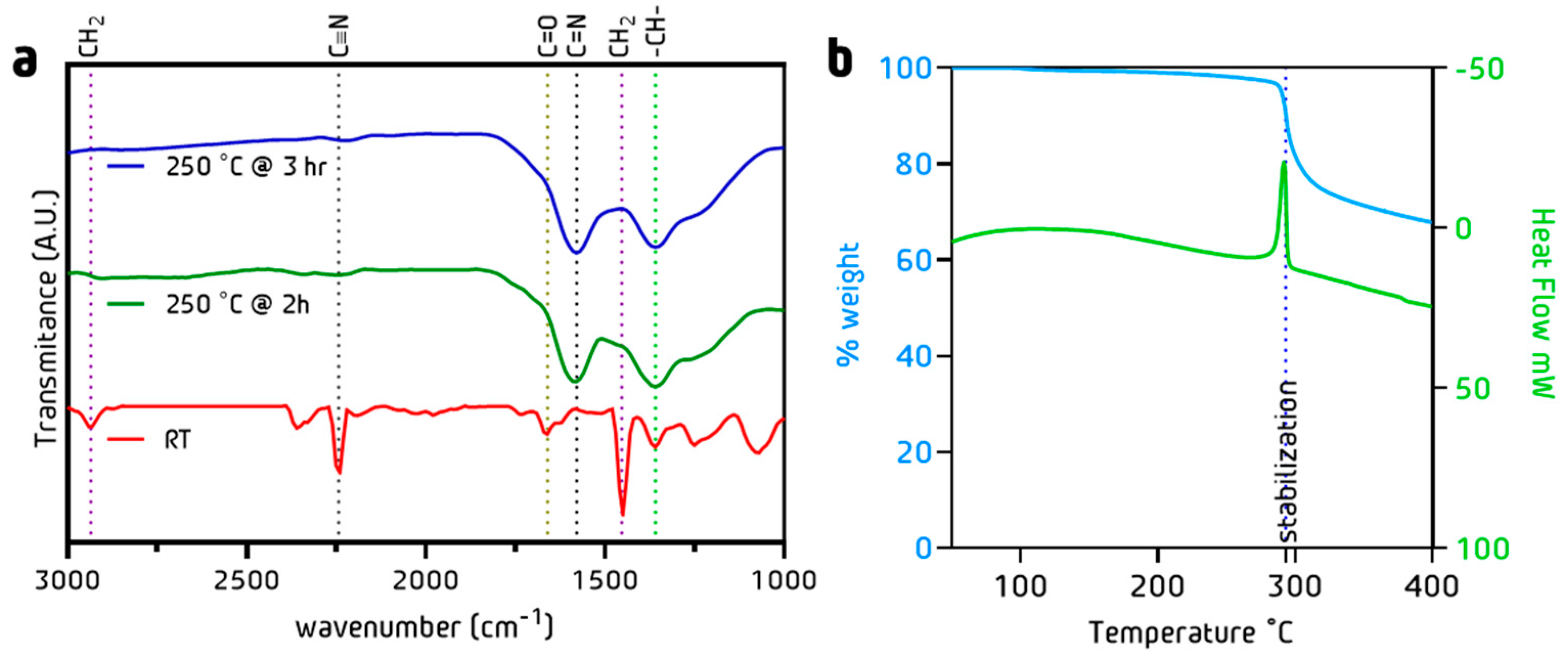
3.3. Stabilization Process: Chemical and Morphology Evolution
3.4. Wettability of PAN Fibers
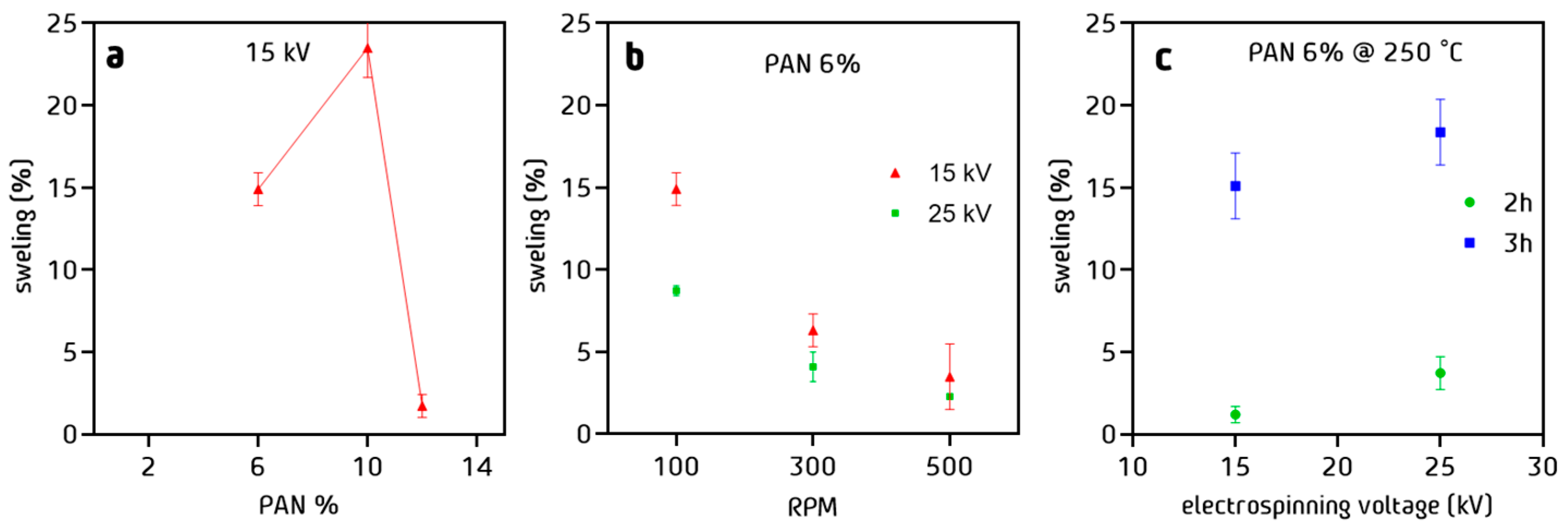
3.5. Water Uptake of PAN Cloth
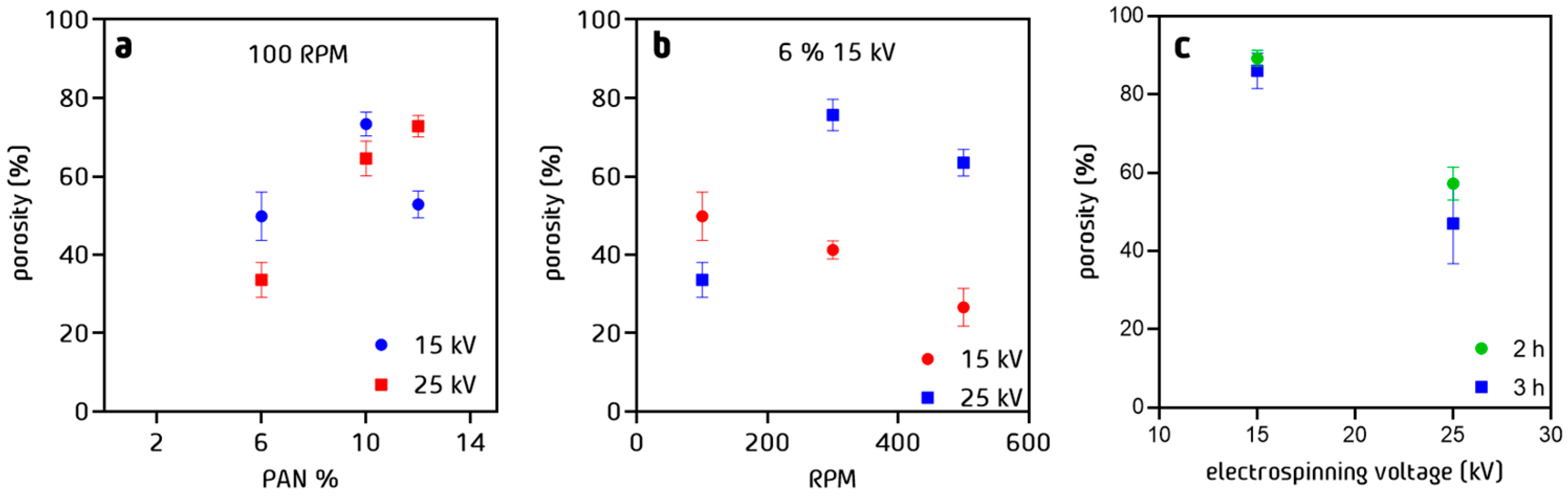
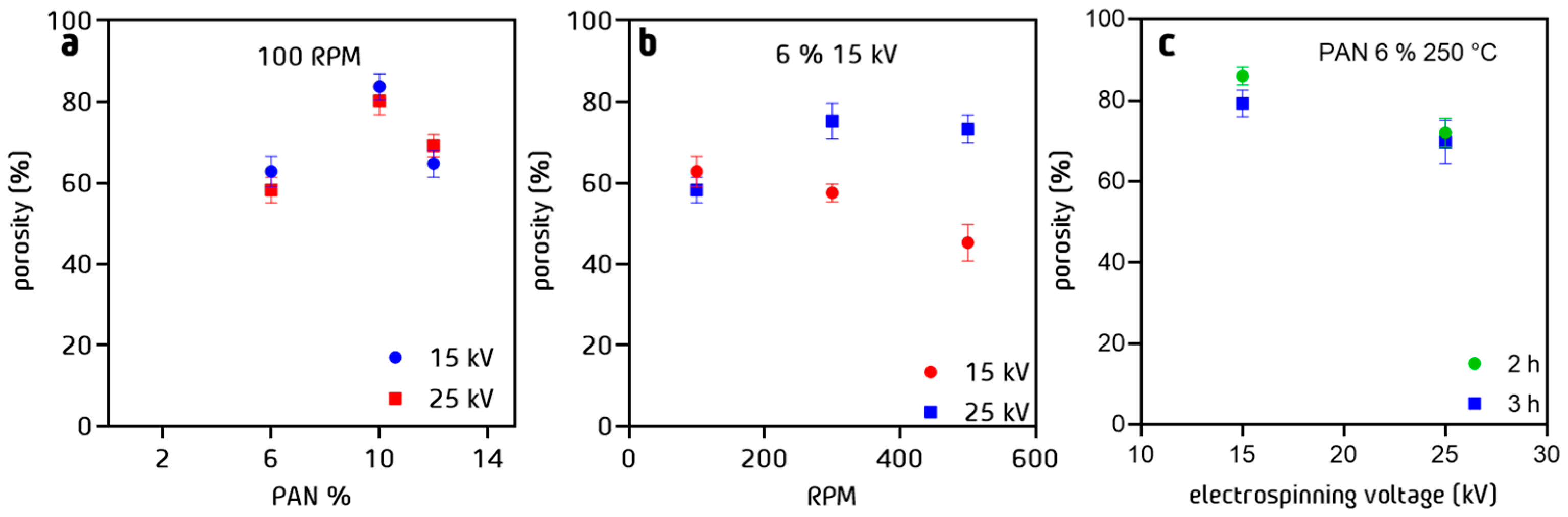
3.6. Porosity of PAN Cloth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacon, R. Growth, Structure, and Properties of Graphite Whiskers. J. Appl. Phys. 1960, 31, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Ichihashi, T. Single-Shell Carbon Nanotubes of 1-Nm Diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, K.P.; Geus, J.W. Carbon Nanofibers: Catalytic Synthesis and Applications. Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 2000, 42, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xie, N.; Zhong, J. Carbon Nanofibers and Their Composites: A Review of Synthesizing, Properties and Applications. Materials 2014, 7, 3919–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Amini, F.; Ehrmann, A. Recent Advances in Carbon Nanofibers and Their Applications—A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 138, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuge, R.; Tamura, N.; Manako, T.; Nakano, K.; Nakahara, K. High-Rate Charge/Discharge Properties of Li-Ion Battery Using Carbon-Coated Composites of Graphites, Vapor Grown Carbon Fibers, and Carbon Nanohorns. J. Power Sources 2014, 266, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Sundararaj, U. Review of the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanofiber/Polymer Composites. Compos. A Appl. Sci. 2011, 42, 2126–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Kim, A.A.; Lohani, P.C.; Yoo, D.J.; Kim, H.J. Assembling Zinc Cobalt Hydroxide/Ternary Sulfides Heterostructure and Iron Oxide Nanorods on Three-Dimensional Hollow Porous Carbon Nanofiber as High Energy Density Hybrid Supercapacitor. J. Energy Storage 2023, 60, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Kim, H.J. Confinement of Zn-Mg-Al-Layered Double Hydroxide and α-Fe2O3 Nanorods on Hollow Porous Carbon Nanofibers: A Free-Standing Electrode for Solid-State Symmetric Supercapacitors. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 429, 132345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Awasthi, G.P.; Kim, H.J. Novel Insight into the Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) Ions by MOF Derived Co-Al Layered Double Hydroxide @hematite Nanorods on 3D Porous Carbon Nanofiber Network. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 417, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolano, G.; Farina, F.; Cavaliere, S.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J. Towards Ultrathin Pt Films on Nanofibres by Surface-Limited Electrodeposition for Electrocatalytic Applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3974–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Basu, S.; Shetti, N.P.; Mondal, K.; Sharma, A.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Versatile Graphitized Carbon Nanofibers in Energy Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1334–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, M.E.; Ruda-Eberenz, T.A.; Chai, M.; Andrews, R.; Hatfield, R.L. Properties That Influence the Specific Surface Areas of Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2013, 57, 1148–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.; Li, P.; Chatterjee, B.; Zheng, T.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Luo, T.; Choi, S.; Hippalgaonkar, K.; De Boer, M.P.; et al. Crystalline Polymer Nanofibers with Ultra-High Strength and Thermal Conductivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Lee, J.S. Electrospinning-Based Carbon Nanofibers for Energy and Sensor Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, R.; Khan, M.I. Carbon Nanotubes: A Review on Properties, Synthesis Methods and Applications in Micro and Nanotechnology. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 4183–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugulothu, D.; Barhoum, A.; Nerella, R.; Ajmer, R.; Bechelany, M. Fabrication of Nanofibers: Electrospinning and Non-Electrospinning Techniques. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; ISBN 9783319536552. [Google Scholar]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre Diameter Fibres of Polymer, Produced by Electrospinning. J. Nanotechnol. 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulefera, I.; Trabelsi, M.; Mamun, A.; Sabantina, L. Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers from Biomass and Biomass Blends—Current Trends. Polymers 2021, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Aboagye, A.; Kelkar, A.; Lai, C.; Fong, H. A Review: Carbon Nanofibers from Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile and Their Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, R.; Haghighat Mamaghani, A.; Boluk, Y.; Hashisho, Z. Synthesis and Characterization of Electrospun PAN-Based Activated Carbon Nanofibers Reinforced with Cellulose Nanocrystals for Adsorption of VOCs. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 410, 128412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, S.K.; Yang, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Polyacrylonitrile-Based Nanofibers—A State-of-the-Art Review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Khan, T.; Basit, M.; Masood, R.; Raza, Z.A. Polyacrylonitrile-Based Electrospun Nanofibers—A Critical Review. Mater. Werkst. 2022, 53, 1575–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramuthu, L.; Venkatesan, M.; Liang, F.C.; Benas, J.S.; Cho, C.J.; Chen, C.W.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, R.H.; Kuo, C.C. Conjugated Copolymers through Electrospinning Synthetic Strategies and Their Versatile Applications in Sensing Environmental Toxicants, PH, Temperature, and Humidity. Polymers 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Hassan, T.; Jabri, T.; Riaz, S.; Khan, A.; Iqbal, K.M.; Khan, S.U.; Wasim, M.; Shah, M.R.; Khan, M.Q.; et al. Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Viroblock/ZnO/PAN Hybrid Antiviral Nanocomposite for Personal Protective Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, N.; Kizildag, N.; Onen, A.; Karacan, I.; Eren, O. Polyacrylonitrile-Polyaniline Composite Nanofiber Webs: Effects of Solvents, Redoping Process and Dispersion Technique. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 2223–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-S.; Lin, C.-H. The Effect of Molecular Weight on the Cross Section and Properties of Polyacrylonitrile Precursor and Resulting Carbon Fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 42, 3045–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Liu, S.; Hou, H. Synthesis of Polyacrylonitrile and Mechanical Properties of Its Electrospun Nanofibers. E-Polymers 2018, 18, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabadi, S.M.S.; Kheradmand, A.; Montazeri, V.; Ziaee, H. Effects of Process and Ambient Parameters on Diameter and Morphology of Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Polym. Sci. A 2015, 57, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. Concept of Minimum Electrospinning Voltage (MEV) in Electrospinning of PAN-DMF System: Effect of Distance. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celep, G.K.; Dincer, K. Optimization of Parameters for Electrospinning of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers by the Taguchi Method. Int. Polym. Process. 2017, 32, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirecci, A.; Özkoç, Ü.; İçoğlu, H.İ. Determination of Optimal Production Parameters for Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 116, 4961–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Bai, T.J.; Wang, Z.Z.; He, T.S. PAN-Derived Electrospun Nanofibers for Supercapacitor Applications: Ongoing Approaches and Challenges; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 56, ISBN 1085302105. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaghitalab, V.; Haghi, A.K. A Study on Electrospinning of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantopoulos, G.; Soulis, S.; Dragatogiannis, D.; Charitidis, C. Introduction of a Methodology to Enhance the Stabilization Process of Pan Fibers by Modeling and Advanced Characterization. Materials 2020, 13, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismar, E.; Sarac, A.S. Oxidation of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Webs as a Precursor for Carbon Nanofiber: Aligned and Non-Aligned Nanofibers. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, A.L.; Alexander, D.L.J.; Pierlot, A.P.; Denning, R.; Miao, M. Predicting the Cyclization Index and Density of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Tow from Processing Conditions. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 3241–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.K.; Lai, K.; Liu, W.; Yao, M.; Sun, R.J. Preparation of Carbon Nanofibres through Electrospinning and Thermal Treatment. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, J.; Zambrzycki, M.; Smolka, W.; Panek, A.; Gubernat, M.; Czaja, P.; Marzec, M.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A. Influence of Heat Treatment of Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers on Biological Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Karim, M.R.; Alharbi, H.F.; Alharthi, N.H. Novel Optimised Highly Aligned Electrospun PEI-PAN Nanofibre Mats with Excellent Wettability. Polymer 2019, 180, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafaña-López, L.; Reyes-Valadez, D.M.; González-Vargas, O.A.; Suárez-Toriello, V.A.; Jaime-Ferrer, J.S. Custom-Made Ion Exchange Membranes at Laboratory Scale for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes 2019, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, S.; Ehsani, M.; Zandi, M. Stimuli-Responsive Electrospun Nanofibers Based on PNVCL-PVAc Copolymer in Biomedical Applications. Prog. Biomater. 2021, 10, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langwald, S.V.; Ehrmann, A.; Sabantina, L. Measuring Physical Properties of Electrospun Nanofiber Mats for Different Biomedical Applications. Membranes 2023, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Structural Morphology and Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Karacan, I. Structural Characterization of Thermally Stabilized Poly(Acrylonitrile) Fibers by Means of X-ray Diffraction, FT-IR Spectroscopy, and TGA Analysis. Icontech Int. J. 2021, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szepcsik, B.; Pukánszky, B. The Mechanism of Thermal Stabilization of Polyacrylonitrile. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 671, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.G.; Minus, M.L.; Rasheed, A.; Kumar, S. Stabilization and Carbonization of Gel Spun Polyacrylonitrile/Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Composite Fibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 3781–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.Y.; Jo, A.Y.; Jung, G.Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Lee, S. Accelerating the Stabilization of Polyacrylonitrile Fibers by UV Irradiation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 73, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Liu, H.; Cao, W.; Xu, L. PAN Fiber Diameter Effect on the Structure of PAN-Based Carbon Fibers. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Process | 2 h | 3 h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydrogenation | 6.48 | 13.42 | |
| Cyclization | 62.96 | 81.94 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz Rocha, J.E.; Moreno Tovar, K.R.; Navarro Mendoza, R.; Gutiérrez Granados, S.; Cavaliere, S.; Giaume, D.; Barboux, P.; Jaime Ferrer, J.S. Critical Electrospinning Parameters for Synthesis Control of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192648
Ruiz Rocha JE, Moreno Tovar KR, Navarro Mendoza R, Gutiérrez Granados S, Cavaliere S, Giaume D, Barboux P, Jaime Ferrer JS. Critical Electrospinning Parameters for Synthesis Control of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(19):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192648
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz Rocha, Juan Emmanuel, Karla Rebeca Moreno Tovar, Ricardo Navarro Mendoza, Silvia Gutiérrez Granados, Sara Cavaliere, Domitille Giaume, Philippe Barboux, and Jesús Salvador Jaime Ferrer. 2023. "Critical Electrospinning Parameters for Synthesis Control of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers" Nanomaterials 13, no. 19: 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192648
APA StyleRuiz Rocha, J. E., Moreno Tovar, K. R., Navarro Mendoza, R., Gutiérrez Granados, S., Cavaliere, S., Giaume, D., Barboux, P., & Jaime Ferrer, J. S. (2023). Critical Electrospinning Parameters for Synthesis Control of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Nanomaterials, 13(19), 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192648







