Nano-Precision Processing of NiP Coating by Magnetorheological Finishing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Equipment
2.1. The Characteristics of NiP Coating
2.2. Processing Equipment and Polishing Fluid of MRF
3. Analysis of Removal Characteristics of MRF
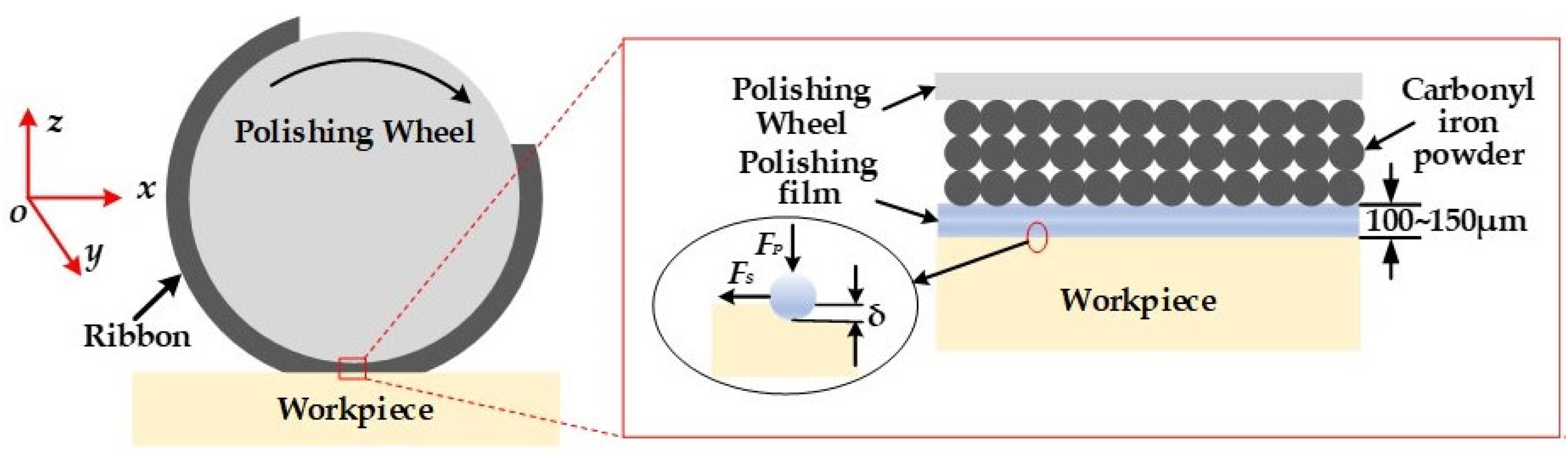
3.1. Material Removal Model of MRF
3.2. Evaluation of Removal Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Orthogonal Test of Process Parameters
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Weight Analysis and Level Optimization of Factors
5.2. Processing Results and Discussion of NiP Coating through MRF
5.3. Discussion on Surface Performance of NiP Coating
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Risse, S.; Gebhardt, A.; Damm, C.; Peschel, T.; Stöckl, W.; Feigl, T.; Kirschstein, S.; Eberhardt, R.; Kaiser, N.; Tünnermanna, A. Novel TMA telescope based on ultra precise metal mirrors. In Proceedings of the SPIE–Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2008: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter, Marseille, France, 23–28 June 2008; Volume 7010, pp. 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Paolo, C.; Vania, D.D.; Paola, Z.; Emanuele, P.; Gianluca, M.; Luca, T.; Daniele, B.; Emiliano, D.; Matteo, L.; Fausto, C.; et al. The primary mirror of the ARIEL mission: Study of thermal, figuring and finishing treatments and optical characterization of Al 6061 samples mirrors. In Proceedings of the SPIE–Astronomical Optics: Design, Manufacture, and Test of Space and Ground Systems II, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 August 2019; Volume 11116, pp. 404–416. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Xue, S. High-Efficiency Chemical-Mechanical Magnetorheological Finishing for Ultra-Smooth Single-Crystal Silicon. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K.; Yamamura, K. Highly efficient planarization of sliced 4H–SiC (0001) wafer by slurryless electrochemical mechanical polishing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 144, 103431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K.; Yamamura, K. Dominant factors and their action mechanisms on material removal rate in electrochemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC (0001) surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, W.P., Jr. Basic Properties of Metal Optics. Opt. Eng. 1977, 16, 164320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkopf, R.; Gebhardt, A.; Scheiding, S.; Rohde, M.; Stenzel, O.; Gliech, S.; Giggel, V.; Löscher, H.; Ullrich, G.; Rucks, P.; et al. Metal mirrors with excellent figure and roughness. In Proceedings of the SPIE–Optical Fabrication, Testing, and Metrology III, Glasgow, UK, 2–4 September 2008; Volume 7102, pp. 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Beier, M.; Hartung, J.; Peschel, T.; Damm, C.; Gebhardt, A.; Scheiding, S.; Stumpf, D.; Zeitner, U.D.; Risse, S.; Eberhardt, R.; et al. Development, fabrication, and testing of an anamorphic imaging snap-together freeform telescope. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3530–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, H.; Henrik, V.; Jan, K. Theoretical compensation of static deformations of freeform multimirror substrates. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 4020–4031. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Yu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Wang, D.; Yi, Z.; Wang, S. The Improvement of Surface Roughness for OAP Aluminum Mirrors—From Terahertz to Ultraviolet. In Proceedings of the SPIE—International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: IRMMW-THz Technologies and Their Applications, Beijing, China, 28–30 October 2017; Volume 10623, pp. 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Tromp, N.; Drost, M.; Pragt, J. Astron extreme light weighting. In Proceedings of the SPIE–The International Society for Optical Engineering, Glasgow, UK, 21–25 June 2004; Volume 5495, pp. 372–382. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, D.; Zhang, X. Ultra-precision fabrication of a nickel-phosphorus layer on the aluminum substrate by SPDT and MRF. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, F62–F67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinast, J.; Beier, M.; Gebhardt, A.; Risse, S.; Tünnermann, A. Polishability of thin electrolytic and electroless NiP layers. In Proceedings of the SPIE–Optifab, Rochester, NY, USA, 12–15 October 2015; Volume 9633, pp. 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Chang, S.; Pak, S.; Lee, K.J.; Jeong, B.; Lee, G.; Kim, G.H.; Shin, S.K.; Yoo, S.M. Fabrication of electroless nickel plated aluminum freeform mirror for an infrared off-axis telescope. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 10137–10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Zhou, T.; He, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Yan, J. Effects of relative tool sharpness on surface generation mechanism of precision turning of electroless nickel phosphorus coating. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Han, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, J.; Wang, J.; Ran, J. Generation mechanism and dual-dynamics simulation of surface patterns in single-point diamond turning of single-crystal copper. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 75, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, G.; Luo, T. Forced-based tool deviation induced form error identification in single-point diamond turning of optical spherical surfaces. Precis. Eng. 2021, 72, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yu, J.; Song, Z.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, Z.; Pei, S.; Liu, B.; Ye, J. Customized design and efficient fabrication of two freeform aluminum mirrors by single point diamond turning technique. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Kang, C.; Liang, F.; Yan, G.; Fang, F. Diffractive optical characteristics of nanometric surface topography generated by diamond turning. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 67, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zong, W. Diffraction effect and its elimination method for diamond-turned optics. Opt. Express. 2019, 27, 1326–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, H.; Lai, T.; Yang, Q.; Xiong, Y. A High Efficiency and Precision Smoothing Polishing Method for NiP Coating of Metal Mirror. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, Y.; Shimomura, T.; Fushiki, A.; Beaucamp, A.; Inasaki, I.; Kunieda, H.; Ogasaka, Y.; Yamashita, K. Ultra-precision polishing of electroless nickel molding dies for shorter wavelength applications. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 57, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrigan, K.G. Visible Quality Aluminum and Nickel Superpolish Polishing Technology Enabling New Missions. In Proceedings of the SPIE–Infrared Technology and Applications XXXVII, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–29 April 2011; Volume 8012, pp. 1087–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Xue, S. Prediction of surface roughness and the material removal rate in magnetorheological finishing. Opt. Express. 2022, 30, 46157–46169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhat, R.; Balasubramaniam, R.; Jain, V.K. Analysis of magnetorheological fluid behavior in chemo-mechanical magnetorheological finishing (CMMRF) process. Precis. Eng. 2017, 49, 122–135. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Ye, M.; Wang, C. Predicting the Material Removal Rate (MRR) in surface Magnetorheological Finishing (MRF) based on the synergistic effect of pressure and shear stress. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Wei, C.; Hu, C.; Situ, G.; Shao, Y.; Shao, J. Novel magic angle-step state and mechanism for restraining the path ripple of magnetorheological finishing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 161, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Yan, Q.; Pan, J.; Lu, J.; Fu, Y. Simulation and experimental research on magnetorheological finishing under dynamic pressure with a gap-varying. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 82, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manas, D.; Jain, V.; Ghoshdastidar, P. Fluid flow analysis of magnetorheological abrasive flow finishing (MRAFF) process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 415–426. [Google Scholar]
- William, K.; Sergei, G. Material removal in magnetorheological finishing of optics. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Aric, B.; Stephen, D.; William, I.; Roger, F. Experiments and observations regarding the mechanisms of glass removal in magnetorheological finishing. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, D.; Don, G.; Marc, T. Improvement of figure and finish of diamond turned surfaces with magneto-rheological finishing (MRF). In Proceedings of the SPIE–Window and Dome Technologies and Materials IX, Orlando, FL, USA, 28 March–1 April 2005; Volume 5786, pp. 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher, S.; Christopher, H.; Paul, D.; Bob, H. Improving surface figure and microroughness of IR materials and diamond turned surfaces with Magnetorheological Finishing (MRF). In Proceedings of the SPIE–Window and Dome Technologies and Materials X, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–13 April 2007; Volume 6545, pp. 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Tiana, M.; Jian, Z.; Hai, R. Preparation and properties of thick nickel-phosphorus amorphous plating on SiCp/Al composite by double zincate pretreatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 5009, 164806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, S.; Gordon, S.; Richard, S.; Rolf, R.; Lyndon, S.; Elmar, P.; Peter, S.; Andreas, G. Mathematical modelling of influence functions in computer-controlled polishing: Part II. Appl. Math. Model. 2008, 432, 2907–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M. Morphology characterization of polishing spot and process parameters optimization in magnetorheological finishing. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 80, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Mathematics model of magnetorheological finishing. In Proceedings of the SPIE–In Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technology 2000, Chengdu, China, 1–4 November 2000; Volume 4231, pp. 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; David, A. A chemical mechanical polishing model incorporating both the chemical and mechanical effects. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2001, 14, 112–133. [Google Scholar]
- Elson, J.M.; Rahn, J.P.; Bennett, J.M. Relationship of the total integrated scattering from multilayer-coated optics to angle of incidence, polarization, correlation length, and roughness cross-correlation properties. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 3207–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameters | Current (A) | Wheel Speed (rpm) | Pressed Depth (mm) | Flow Rate (mL/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical | 6.5~7.5 | 150~210 | 0.2~0.4 | 80~120 |
| Factor | A Current (A) | B Wheel Speed (rpm) | C Pressed Depth (mm) | D Flow Rate (mL/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.5 | 150 | 0.2 | 80 |
| 2 | 7 | 180 | 0.3 | 100 |
| 3 | 7.5 | 210 | 0.4 | 120 |
| No. | Current (A) | Wheel Speed (rpm) | Pressed Depth (mm) | Flow Rate (mL/s) | PRR (μm/min) | VRR (mm3/min) | Roughness Ra (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.5 | 150 | 0.2 | 80 | 2.163 | 0.00515 | 1.371 |
| 2 | 6.5 | 180 | 0.3 | 100 | 5.022 | 0.182 | 1.613 |
| 3 | 6.5 | 210 | 0.4 | 120 | 5.116 | 0.198 | 1.420 |
| 4 | 7 | 150 | 0.3 | 120 | 1.982 | 0.0628 | 1.022 |
| 5 | 7 | 180 | 0.4 | 80 | 4.158 | 0.0933 | 1.546 |
| 6 | 7 | 210 | 0.2 | 100 | 4.707 | 0.0816 | 1.372 |
| 7 | 7.5 | 150 | 0.4 | 100 | 4.772 | 0.135 | 1.039 |
| 8 | 7.5 | 180 | 0.2 | 120 | 2.630 | 0.0398 | 0.985 |
| 9 | 7.5 | 210 | 0.3 | 80 | 5.528 | 0.0754 | 1.159 |
| Object | Factors | Ranges | Order | Preferred Combination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRR | A | 0.484 | B > C > D > A | A1B3C2D2 |
| B | 2.811 | |||
| C | 1.01 | |||
| D | 0.927 | |||
| VRR | A | 0.04915 | C > D > B > A | A1B3C3D2 |
| B | 0.05068 | |||
| C | 0.09992 | |||
| D | 0.07492 | |||
| Roughness | A | 0.407 | A > B > D > C | A3B1C1D3 |
| B | 0.237 | |||
| C | 0.092 | |||
| D | 0.217 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Peng, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Luo, T.; Lai, T. Nano-Precision Processing of NiP Coating by Magnetorheological Finishing. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142118
Xu C, Peng X, Hu H, Liu J, Li H, Luo T, Lai T. Nano-Precision Processing of NiP Coating by Magnetorheological Finishing. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(14):2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142118
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chao, Xiaoqiang Peng, Hao Hu, Junfeng Liu, Huang Li, Tiancong Luo, and Tao Lai. 2023. "Nano-Precision Processing of NiP Coating by Magnetorheological Finishing" Nanomaterials 13, no. 14: 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142118
APA StyleXu, C., Peng, X., Hu, H., Liu, J., Li, H., Luo, T., & Lai, T. (2023). Nano-Precision Processing of NiP Coating by Magnetorheological Finishing. Nanomaterials, 13(14), 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13142118






