Abstract
Exploring bifunctional electrocatalysts to lower the activation energy barriers for sluggish electrochemical reactions for both the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) are of great importance in achieving lower energy consumption and higher conversion efficiency for future energy conversion and storage system. Despite the excellent performance of precious metal-based electrocatalysts for OER and ORR, their high cost and scarcity hamper their large-scale industrial application. As alternatives to precious metal-based electrocatalysts, the development of earth-abundant and efficient catalysts with excellent electrocatalytic performance in both the OER and the ORR is urgently required. Herein, we report a core–shell CoFeS2@CoS2 heterostructure entangled with carbon nanotubes as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for both the OER and the ORR. The CoFeS2@CoS2 nanocubes entangled with carbon nanotubes show superior electrochemical performance for both the OER and the ORR: a potential of 1.5 V (vs. RHE) at a current density of 10 mA cm−2 for the OER in alkaline medium and an onset potential of 0.976 V for the ORR. This work suggests a processing methodology for the development of the core–shell heterostructures with enhanced bifunctional performance for both the OER and the ORR.
1. Introduction
The accelerated depletion of fossil fuels and accompanying environmental pollution have driven the development of advanced technologies for highly efficient energy conversion and storage systems, including fuel cells, metal–air batteries, and water electrolysis systems [1,2,3,4]. Particularly, recent technological advances in bifunctional electrocatalysts boosting both the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) are of great importance, and have enabled the reduction of energy consumption and the enhancement of energy conversion efficiency for sustainable energy systems [5]. So far, precious-metal based electrocatalysts, including platinum, ruthenium oxide, and iridium oxide, for the OER and the ORR are employed as important components for industrial-level energy conversion and storage systems [6]. However, their scarcity on earth, poor durability, and high cost hamper the large-scale industrial application and thus, the exploration of nonprecious metal-based electrocatalysts with low cost, durability and high catalytic activity to both ORR and OER are significant [7]. Nonprecious transition metal chalcogenides consisting of transition metal atoms (i.e., Co, Ni, Fe) and chalcogen atoms (i.e., S, Se, Te) have attracted great attention due to their low cost, high electrical conductivity, and electrochemical durability for both the OER and the ORR [8,9,10]. Several design strategies for metal chalcogenides, including structure, phase, and defect engineering, have been suggested to increase the active site exposure and to reduce the energy barrier of catalytic reactions to enhance the performance of both the OER and the ORR [11]. Among them, the design of the core–shell structure is considered as one of the effective strategies, not only to increase the contact area at the interface of the heterostructure, but also to provide the synergetic electrochemical performance of the constituents. For example, J. Bai et al. reported that the core–shell Co9S8@MoS2 heterostructure shows outstanding OER and ORR performance for water splitting and Zn–air batteries, respectively [12]. To improve the electrocatalytic activity of the transition metal chalcogenides further for both the OER and the ORR, conductive supports, including graphene, reduced graphene oxide and graphene/carbon nanotubes, are considered to promote electron transfer during the OER and ORR [13,14,15,16,17,18]. It is reported that porous nitrogen-doped carbon as a conductive support for cobalt sulfide promotes high catalytic activity and durability for both the OER and the ORR [19]. In addition, M. Shen et al. reported that encapsulation of cobalt–iron double sulfides through carbon support using nitrogen-doped mesoporous graphitic carbon improves the electrocatalytic activity and durability for the ORR and the OER [20]. Therefore, there is value in developing the transition metal based core–shell heterostructures combined with conductive support for synergetic electrochemical performance for both the OER and the ORR.
Herein, we report a novel synthesis route to prepare core–shell CoFeS2@CoS2 nanocubes entangled with carbon nanotubes via a hydrothermal method, followed by post-annealing under a reducing atmosphere. CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs show outstanding OER activity, with an overpotential of 269 mV at a current density of 10 mA cm−2, a Tafel slope of 19.68 mV dec−1, and good durability in alkaline medium. In addition, CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs show excellent ORR performance with an onset potential of 0.976 V, close to that of Pt/C.
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Preparation of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs
The CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs samples were synthesized via a two-step process. In the first step, 1.05 mmol CoCl2·6H2O, 1.05 mmol FeCl2·6H2O, and carbon nanotubes (CNT) were dissolved in 30 mL deionized water. After Co, Fe, and CNTs powder were completely dissolved, 5 mg of thioacetamide (TAA) was added to this solution and magnetically stirred for 30 min. The obtained mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and the autoclave was tightly sealed and kept at 150 °C for 12 h to produce CoS2/CNTs. After cooling to 25 °C naturally, the product was collected by centrifugation, washed several times thoroughly with deionized water, and dried at 60 °C for 8 h. Subsequently, dried CoS2/CNTs powder was placed in a crucible and calcined in a tube furnace under Ar atmosphere at 350 °C for 1 h with a ramping rate of 5 °C min−1 to obtain CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs.
2.2. Material Characterization
The surface morphology and element composition were examined with a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, NNS-450, FEI). Transmission electron microscope (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) images were obtained using a TALOS F200X instrument. The corresponding element mapping images were obtained with image correctors. The crystal structural characterization of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs particles was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, X’Pert-Pro MPD, PANalytical, Malvern, UK) using Cu Kα radiation at 40 kV and 30 mA, in the range from 10° to 80° with a scan rate of 0.02° per second. The chemical valence state for chemical oxidation analysis was determined by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS, ESCALAB 250Xi, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Electrochemical Characterization
Electrochemical measurements were conducted on an electrochemical workstation (model Autolab PGSTAT; Metrohm) in 0.1 M and 1.0 M KOH and evaluated using a standard three-electrode electrochemical cell with a rotating disk electrode (RDE). For the preparation of the working electrode, a sample was dispersed in a Nafion® solution (10 μL, 5 wt%) of water and ethanol (volume ratio 3:1). Samples were tested in 0.1 M and 1 M KOH aqueous solution by using a glassy carbon (GC) electrode as the working electrode, with a diameter of 3 mm, which yielded an approximate catalyst loading of 0.253 mg cm−2. The working electrode was dried at room temperature prior to electrochemical measurements. Before testing the ORR, the electrolytes were generally saturated with O2, and the flow rate of oxygen was maintained during the whole test. The obtained potentials (vs. Ag/AgCl) were calibrated to the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) according to the Nernst equation (ERHE = EAg/AgCl + 0.0591pH + 0.197). The polarization curves were measured by linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) at a scan rate of 5 Mv s−1. Electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) were recorded under an AC voltage of 5 mV with frequencies in the range of 50 kHz to 0.1 Hz. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was performed in the range of 1.32 to 1.48 V (vs. RHE) with scan rates of 20 mV, 40 mV, 60 mV, 80 mV, 100 mV, and 120 mV. The electrical double layer specific capacitance (Cdl) of catalysts was determined from CV. Overall water splitting tests were performed in an electrode configuration with CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs.
3. Results and Discussion
The XRD patterns of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs are presented in Figure 1a. CoS2 forms after hydrothermal processing. Subsequent post annealing under reducing conditions transforms CoS2 to mixed CoFeS2 and CoS2 phases. Further, the diffracted peaks at 26° indicate the presence of CNTs in both samples. It is noted that similar X-ray diffraction patterns were observed from pure CoFeS2@CoS2, except for the diffracted peak at 26° indicating CNTs, as shown in Figure S1. Electron micrographs of CoS2/CNTs show that nanoparticles with irregular shapes are entangled with CNTs, as shown in Figure 1b,c. After post annealing under reducing conditions, the irregularly shaped CoS2 particles transform to CoFeS2@CoS2 nanocubes. CoFeS2@CoS2 without CNTs also has a similar microstructure, as shown in Figure S2. TEM images and the corresponding EDS maps indicate the CoS2 nanoparticles with a lattice spacing of 1.62 Å of (200) and 2.47 of (210), which become entangled with CNTs after hydrothermal processing, as presented in Figure 1d–f. After post annealing, the CoS2 nanoparticles transform to the core(CoFeS2)–shell(CoS2) nanocubes entangled with CNTs, confirmed by the outer CoS2 and inner CoFeS2 with a lattice spacing of 2.47 Å of (210) and 1.95 Å of (100), respectively (Figure 1g–i). The Selected area diffraction (SAED) pattern of CoFeS2@CoS2 is shown in Figure S3. It is clear that the diffraction rings with d-spacings of 0.247 and 0.162 nm correspond to (210) and (200) of CoS2, respectively. In addition, the diffraction rings with d-spacing of 0.195 nm correspond to (100) of CoFeS2. It is noted that morphology of the CNTs remain similar after synthesis.
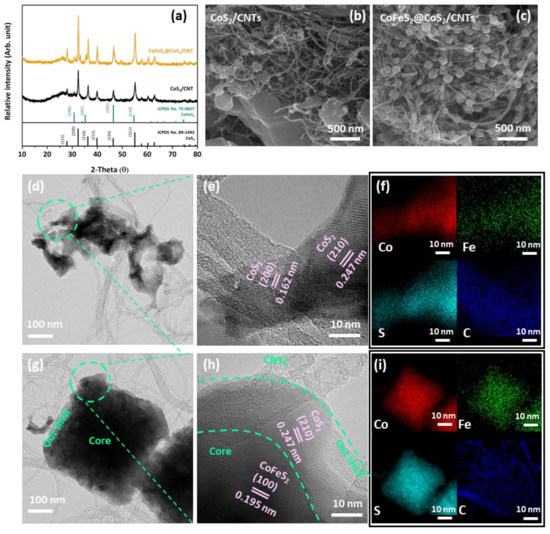
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs. FE-SEM image of (b) CoS2/CNT and (c) CoFeS2@CoS2/CNT. (d) TEM and (e) high-resolution TEM image of CoS2/CNTs with (f) elemental mapping images. (g) TEM and (h) high-resolution TEM images of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs with (i) HAADF-STEM image and elemental mapping images.
To better understand the effect of post annealing under reducing conditions on the chemical nature of constituent ions, XPS analysis was performed, and results are shown in Figure 2. There are three major peaks of the XPS spectra, Co 2p (Figure 2a), Fe 2p (Figure 2b), and S 2p (Figure 2c), which describe the chemical nature of CoS2 and CoFeS2@CoS2. As shown in Figure 2a,b, the Co 2p states of the CoS2 are observed at 781.3 eV and 783.1 eV (Co 2p3/2), 797.5 eV and 801.7 eV (Co 2p1/2), and 786.3 eV and 805.1 eV (satellite peaks), while Co 2p states of CoFeS2@CoS2 are 778.4 eV and 780.2 eV (Co 2p3/2), 793.6 eV and 796.7 eV (Co 2p1/2), and 782.7 eV and 803.1 eV (satellite peaks). In addition, the Fe 2p states of CoS2 are observed at 711.7 eV and 716.5 eV with satellite peaks at 724.1 eV, while the Fe 2p states of CoFeS2@CoS2 are at 712.1 eV and 716.8 eV with satellite peaks at 724.5 eV. The S 2p states of CoS2 are observed at 163.8 eV (S 2p3/2), while the S 2p states of CoFeS2 are observed at 162.7 eV (S 2p3/2) and 164.2 eV (S 2p1/2), as shown in Figure 2c. The XPS results indicate that both CoS2 and CoFeS2 contain the oxidation states of Co2+ and Co3+, Fe2+ and Fe3+, and S22−. It is noted that reducing conditions during post annealing of CoS2 stabilizes Fe2+ and thus, the peak shift of the Fe 2p state toward a lower binding energy (Figure 2b), which promotes the incorporation of the Fe2+ into the Co sites of CoS2. In addition, the peak shift of the Co 2p and S 2p states towards a lower binding energy indicates the modulated metal–sulfur bonding induced by Fe incorporation into the Co sites of CoS2, as shown in Figure 2a,c [21,22,23,24].
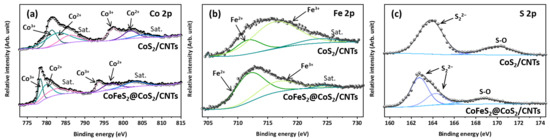
Figure 2.
(a) Co 2p, (b) Fe 2p, and (c) S 2p spectra of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs.
The LSV polarization curves of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs are shown Figure 3a. Compared to the overpotential of CoS2/CNTs and IrO2, CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs show superior OER activity, with an overpotential of 269 mV and 320 mV at 10 mA cm−2 and at 100 mA cm−2, respectively. A recent DFT calculation study suggests that the electronic states of Co are tuned by synergetic interaction between sulfur and the adjacent iron, which can lower the overpotential for OER process [25]. In addition, compared to pure CoFeS2@CoS2, CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs shows a lower overpotential, smaller Tafel plot, and resistance of charge transfer, in Figure S4a–c, respectively. This indicates that the catalytic activity of the CoFeS2@CoS2 with CNTs is superior to that of CoFeS2@CoS2, which can also explain the important role of the CNTs in boosting the catalytic activity of the CoFeS2@CoS2 [26,27,28,29].
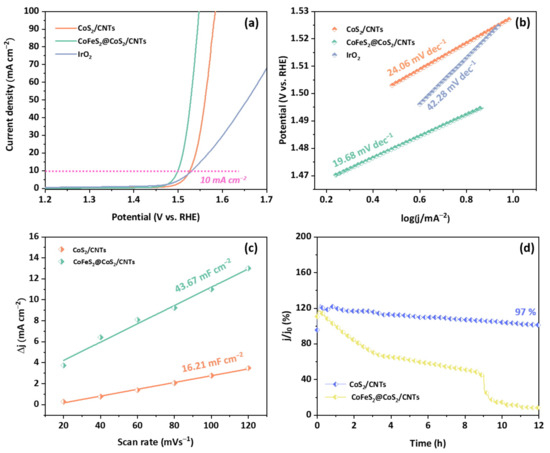
Figure 3.
Electrocatalytic activity of CoS2/CNTs, CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs, and IrO2 for the OER. (a) LSV polarization curves; (b) Tafel plots; (c) Cdl; (d) long-term stability test at j = 10 mA cm−2.
The Tafel slopes of the CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs samples were also investigated to understand the reaction kinetics (Figure 3b). The CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs exhibits a relatively lower Tafel slope of 19.68 mV dec−1, compared to that of CoS2/CNTs (24.06 mV) and IrO2 (42.28 mV dec−1), which indicates more the favorable OER kinetics of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs. The CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs show superior OER performance compared to the recently reported state-of-the-art OER electrocatalysts (Table S1). In addition, the higher Cdl of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs (43.67 mF cm−2) compared to that of CoS2/CNTs (16.21 mF cm−2) suggests that the improved OER activity of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs can be attributed to the large electrochemically active surface area (ECSA), as shown in Figure 3c and Figure S5. For practical application, the long-term stability is also important factor to evaluate the electrochemical performance of the OER electrocatalysts. The electrocatalytic stability of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs was evaluated using chronoamperometric measurements at an overpotential of 269 mV at 10 mA cm−2. After 12 h of the OER, the current density of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs was decreased by less than 3% of its initial value (Figure 3d). During the long-term OER stability test, Co 2p (Figure 4a), Fe 2p (Figure 4b), and S 2p (Figure 4c) peaks of the XPS spectra were changed. It is noted that the initial j/j0 value exceeding 100% can be attributed to the excellent OER activity of the electrochemically active byproducts formed during the OER process, which is also reported in previous literature [30]. Moreover, a slight change in the valence states of the Co and Fe in CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs was observed: both Co 2p and Fe 2p peaks are slightly shifted to higher binding energy due to the oxidation on the electrode surface, which suggests the tolerance of the optimized CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs against corrosion under long-term oxidizing conditions. This can be attributed to the synergistic interaction of CoFeS2@CoS2 with CNTs, which improves the stability of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs [31,32].
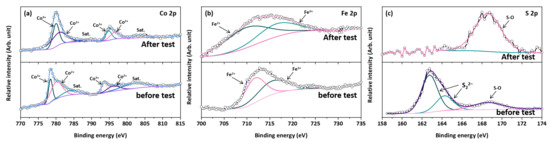
Figure 4.
(a) Co 2p, (b) Fe 2p, and (c) S 2p spectra of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs before/after long-term stability test.
Most importantly, the S 2p peak indicating metal–sulfur bonding at 163.7 and 163.8 eV disappeared, while a new S 2p peak indicating the sulfur–oxygen bonding at 168.5 eV appears, implying that the oxidation of sulfide occurs [33]. As shown in Figures S6 and S7, the oxidation of CoFeS2@CoS2 leads to the transformation to various chemical compounds, including FeOOH, CoO, and CoFe2O4. Notably, the formation of the FeOOH nanosheet and CoFe2O4 on the surface of CoFeS2@CoS2 can provide active sites to promote the OER process [34,35]. However, the formation of the less active CoO phase can lead to the gradual deterioration of CoFeS2@CoS2 during the OER process.
The electrocatalytic activity of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs for ORR is analyzed by obtaining the LSV curves as shown in Figure 5a. CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs exhibits ORR performance with an onset potential (Eonset) of 0.976 V and a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.871 V (vs. RHE), which is superior to that of CoS2/CNTs. CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs show a lower Tafel slope (24.43 mV dec−1) than CoS2/CNTs (78.31 mV dec−1) and Pt/C (25.73 mV dec−1), which indicates the superior catalytic activity of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs (Figure 5b). To further understand the kinetics of the ORR for CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs, Koutecký–Levich (K-L) plots were evaluated as shown in Figure 5c. The average number of the transferred electrons per oxygen molecule was calculated as 4.3 in the potential range between 0.35 and 0.5 V using the K-L equation, which indicates that CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs follows a four-electron pathway for the ORR. It is noted that the four-electron pathway for the ORR is preferred over the two-electron pathway for higher energy conversion efficiency as complete oxygen reduction occurs [29]. In addition, the polarization curve of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs exhibits negligible current loss after 2000 cycles at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1. (Figure 5d) After the ORR cycle test, the oxidation of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs was also observed, which transforms to various chemical compounds, including CoO and CoFe2O4, as shown in Figure S8. This observation is well-matched with the experimental results of previous studies, which reveals the transformation of transition metal-based sulfide into various oxides under ORR conditions [36,37,38]. Based on the electrochemical performance of CoS2/CNTs and CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs, the potential difference (ΔE = Ej=10 − E1/2) between Ej=10 for the OER and E1/2 for the ORR of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs has a smaller ΔE (0.67 V) than CoS2/CNTs (ΔE = 0.82 V) as shown in Figure 5e, which suggests the outstanding bifunctional (OER/ORR) catalytic activity of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs.
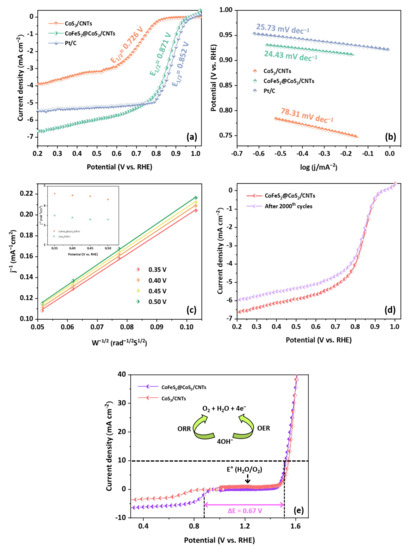
Figure 5.
Electrocatalytic activity of CoS2/CNTs, CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs, and Pt/C for the ORR: (a) LSV polarization curves; (b) Tafel plots; (c) K-L plot; (d) LSV polarization curves after 1st and 2000th cycles; (e) overall polarization curves of the catalysts within the ORR and OER potential.
4. Conclusions
A core–shell CoFeS2@CoS2 heterostructure entangled with carbon nanotubes is prepared by a facile hydrothermal synthesis, followed by post heat treatment under a reducing atmosphere. The CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs electrocatalyst shows highly efficient OER performance in alkaline solution, with an overpotential of 269 mV and yielding a current density of 10 mA cm−2 with a Tafel slope of 19.68 mV dec−1. In addition, the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs electrocatalyst has outstanding ORR performance, with an onset potential (Eonset) of 0.976 V and a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.871 V (vs. RHE). Given the overpotentials for OER (Ej=10) and ORR (E1/2), the potential difference (ΔE = Ej=10 − E1/2) is only 0.67 V, which shows the excellent catalytic activity of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs for the both OER and the ORR as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nano12060983/s1, Figure S1: XRD data of pure CoFeS2@CoS2, Figure S2: (a–c) Microstructure of pure CoFeS2@CoS2, Figure S3: (a) TEM image of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs with (b) SAED pattern, Figure S4: OER properties of the CoFeS2@CoS2 with/without CNTs (a) LSV curve, (b) Tafel plot, (c) Nyquist plot, Figure S5: CV measurements in a capacitive current region at scan rates 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, and 120 s−1 of (a) CoS2/CNTs and (b) CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs, Figure S6: Morphology and structure characterizations of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs after stability test for 12 h. (a–d) TEM image and HRTEM images and (e–h) element maps, Figure S7: X-ray diffraction patterns of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs after 12 h of OER, Figure S8: (a) TEM and (b–c) HRTEM images of the CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs after 2000 cycles of ORR, Table S1: Comparison of OER/ORR catalytic activity of CoFeS2@CoS2/CNTs with the recently reported Co, Fe-based catalysts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.; Data curation, S.Y.; Investigation, D.K.; Project administration, C.A.; Resources, K.R.P.; Validation, N.O.; Writing—original draft, J.J. and K.M.K.; Writing—review & editing, H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study has been conducted with the support of the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology as “Establishment of the Rapid Manufacturing Platform for Ceramic additive Manufacturing (KITECH EH-22-00126)”. This work was also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2020R1A2C1101466).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict interest.
References
- Zhao, J.; Qin, R.; Liu, R. Urea-bridging synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon tube supported single metallic atoms as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst for zinc-air battery. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 256, 117778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Fan, L.; Tao, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, G.; Guo, S. The Kirkendall effect for engineering oxygen vacancy of hollow Co3O4 nanoparticles toward high-performance portable zinc–air batteries. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13978–13982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Ge, Y.; Chu, H.; Smith, W.; Dong, P.; Ajayan, P.M.; Shen, J. Controlled synthesis of 3D porous structured cobalt-iron based nanosheets by electrodeposition as asymmetric electrodes for ultra-efficient water splitting. Appl. Catal. B. 2019, 244, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Nam, G.; Li, P.; Wang, S.; Jang, H.; Wei, T.; Cho, J. Cu97P3-x-yOxNy/NPC as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for rechargeable zinc-air battery. J. Power Sources 2019, 421, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X. Novel Nanomaterials for Biomedical, Environmental and Energy Applications, Micro and Nano Technologies, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 435–464. [Google Scholar]
- Bezerra, L.S.; Maia, G. Developing efficient catalysts for the OER and ORR using a combination of Co, Ni, and Pt oxides along with graphene nanoribbons and NiCo2O4. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17691–17705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Lin, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Shan, G.; Wang, J. A review of oxygen reduction mechanisms for metal-free carbon-based electrocatalysts. Npj Comput. Mater. 2019, 5, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Gago, A.; Timperman, L.; Alonso-Vante, N. Chalcogenide metal centers for oxygen reduction reaction: Activity and tolerance. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.R.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S.H. Solution-based synthesis and design of late transition metal chalcogenide materials for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Small 2012, 8, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.R.; Xu, Y.F.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S.H. Nanostructured metal chalcogenides: Synthesis, modification, and applications in energy conversion and storage devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2986–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Ju, J.; Han, X.; Deng, Y. Metal chalcogenides: An emerging material for electrocatalysis. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 050902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Meng, T.; Guo, D.; Wang, S.; Mao, B.; Cao, M. Co9S8@MoS2 core–shell heterostructures as trifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting and Zn–air batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1678–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, C.; Lei, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, T.; Lai, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D. Sea urchin-like Ni–Fe sulfide architectures as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12350–12357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Lou, X.W. Formation of Ni–Fe mixed diselenide nanocages as a superior oxygen evolution electrocatalyst. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Wen, Z. Oxygen-containing amorphous cobalt sulfide porous nanocubes as high-activity electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in an alkaline/neutral medium. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 4936–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J. NiCo2S4@graphene as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5002–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, P.; Prabu, M.; Sanetuntikul, J.; Shanmugam, S. Cobalt sulfide nanoparticles grown on nitrogen and sulfur codoped graphene oxide: An efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3625–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.C.; Hassan, F.M.; Seo, M.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Hoque, M.A.; Lee, D.U.; Chen, Z. Shape-controlled octahedral cobalt disulfide nanoparticles supported on nitrogen and sulfur-doped graphene/carbon nanotube composites for oxygen reduction in acidic electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 6340–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zheng, X.; Tian, J.; Jin, C.; Ke, K.; Yang, R. Cobalt sulfide embedded in porous nitrogen-doped carbon as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Ruan, C.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Covalent entrapment of cobalt–iron sulfides in N-doped mesoporous carbon: Extraordinary bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fu, S.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Facilely Tuning Porous NiCo2O4 Nanosheets with Metal Valence-State Alteration and Abundant Oxygen Vacancies as Robust Electrocatalysts Towards Water Splitting. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 4000–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Scaini, M.; Hochst, H.; Bancroft, G.M.; Schaufuss, A.G.; Szargan, R. Synchrotron XPS evidence for Fe2+-S and Fe3+-S surface species on pyrite fracture-surfaces, and their 3D electronic states. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Owusu, K.A.; Mai, L. Porous nickel–iron selenide nanosheets as highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19386–19392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Majeed, A.; Shen, X.; Qin, S. Hybrid cathode composed of pyrite-structure CoS2 hollow polyhedron and ketjen black@ ulfur materials propelling polysulfide conversion in lithium sulfur batteries. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 27122–27131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Dou, Y.; He, C.T.; Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Adekoya, D.; Zhang, S. Sulfur doping optimized intermediate energetics of FeCoOOH for enhanced oxygen evolution catalytic activity. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2021, 2, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lyu, F.; Bai, Y.; Gao, A.; Feng, J.; Cai, Z.; Yin, Y. Porous cobalt oxide nanoplates enriched with oxygen vacancies for oxygen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 2018, 43, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douka, A.I.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zaman, S.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Xia, B.Y. A zeolitic-imidazole frameworks-derived interconnected macroporous carbon matrix for efficient oxygen electrocatalysis in rechargeable zinc–air batteries. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.; Su, Y.Q.; Dong, C.L.; Qi, R.; Huang, L.; Qin, Y.; Yu Xia, B. Scalable Molten Salt Synthesis of Platinum Alloys Planted in Metal–Nitrogen–Graphene for Efficient Oxygen Reduction. Angew. Chem. 2020, 134, e202115835. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, S.; Huang, L.; Douka, A.I.; Yang, H.; You, B.; Xia, B.Y. Oxygen reduction electrocatalysts toward practical fuel cells: Progress and perspectives. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 17976–17996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Tang, C.; Li, B.Q.; Zhang, Q. A review of anion-regulated multi-anion transition metal compounds for oxygen evolution electrocatalysis. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Zhou, X.; Cong, B.; Hong, W.; Chen, G. Tailoring the d-Band Centers Endows (NixFe1–x)2P Nanosheets with Efficient Oxygen Evolution Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 9086–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zou, Z.; Huang, J.; Gao, F. NiFe2O4 nanoparticles/NiFe layered double-hydroxide nanosheet heterostructure array for efficient overall water splitting at large current densities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26283–26292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, H.; Ali, G.; Chung, K.Y.; Hong, Y.R.; Mhin, S. Parallelized reaction pathway and stronger internal band bending by partial oxidation of metal sulfide–graphene composites: Important factors of synergistic oxygen evolution reaction enhancement. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4091–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Cao, Q.; Yang, L.; Che, R. Morphology-optimized interconnected Ni3S2 nanosheets coupled with Ni(OH)2 nanoparticles for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 827, 154163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Hao, S.; Wu, Y.; Pei, K.; You, W.; Che, R. Interfacial charge redistribution in interconnected network of Ni2P–Co2P boosting electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution in both acidic and alkaline conditions. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 424, 130444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, F.; Hu, X. A nickel iron diselenide-derived efficient oxygen-evolution catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabayoje, O.; Shoola, A.; Wygant, B.R.; Mullins, C.B. The role of anions in metal chalcogenide oxygen evolution catalysis: Electrodeposited thin films of nickel sulfide as “pre-catalysts”. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, K.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. High-precision regulation synthesis of Fe-doped Co2P nanorod bundles as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution in all-pH range and seawater. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 55, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).