Abstract
Considering the risk associated with exposure to benzene and toluene in water resources, researchers have been motivated to conduct studies to remove them from aqueous solutions. Thus, by performing the present study, the potential of Fe3O4/zeolite imidazolate framework nanoparticles (Fe3O4@ZIF-8) was evaluated for the adsorption of benzene and toluene. Accordingly, the solution pH, Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dosage, mixing time, concentration of benzene and toluene, and temperature, were the parameters considered for conducting the batch experiments, for which their effect on adsorption efficiency was evaluated. Our conducted experiments introduced the neutral pH as the best pH range to obtain the maximum removal. Fitting the adsorption data into the various models revealed the aptness of the Langmuir isotherm equation in describing experimental information and highest adsorption capacity; for benzene it was 129.4, 134.2, 137.3, and 148.2 mg g−1, but for toluene it was 118.4, 125.2, 129.6, and 133.1 mg g−1, for temperature 20, 30, 40, and 50 °C, respectively. Using obtained optimal conditions, the adsorption efficiencies of benzene and toluene were obtained to be 98.4% and 93.1%, respectively. Kinetic studies showed acceptable coefficients for PSO kinetics and confirmed its suitability. Also, the recyclability results showed that for six consecutive periods of the adsorption-desorption process, the percentage of removal decreased by only 6% for benzene and toluene. Moreover, calculating thermodynamic parameter changes for benzene and toluene removal confirmed the favorability and spontaneity of the studied process and its endothermic nature. Considering the above findings, Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was found to be an operative adsorbent for removing pollutants.
1. Introduction
The increase in excessive consumption of different sources present in the environment, due to technological advances in the industry, has led to an increase in its destruction [1,2]. One of these sources is oil and its extraction, which, due to its toxic compounds, threatens human and animal health and ruins the environment. The rapid development of this industry, the increase in the speed of oil extraction, and the emergence of related industries have worsened the pollution situation [3,4]. One of the oil product hydrocarbons contains compounds such as benzene and toluene, which are mono-aromatic groups and contaminate groundwater resources [5]. These compounds have an extensive application in industries as solvents for organic compounds and equipment cleaning [6]. Some of the ways they infiltrate groundwater include leakage of petroleum products from storage tanks, pipes, and improper landfills. Benzene has been introduced as the priority pollutant and definitive carcinogen (Group A), and toluene has been a carcinogen in group E [5,7]. Benzene has been introduced to be a genotoxic carcinogen (such as lung cancer) and has been associated with adverse hematological effects (leukemia or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma) [8,9]. Moreover, neurological disorders, in addition to carcinogenic effects, have been reported for exposure to toluene [10]. Hence, it has been found that much attention should be given to the control and elimination of these compounds in groundwater, and efforts should be taken to introduce effective techniques to remove them.
To remove these types of pollutant, various techniques have been subjected to study [11,12,13,14,15]. According to the results of the studies that employed the above-mentioned techniques, adsorption is a method with high efficiency and high popularity [16]; low-cost operation, high uptake capacity, and absence of chemical sludge are the features which provided this popularity for the mentioned method [17,18]. Despite this, some drawbacks have been found for the application of the conventional adsorbent, i.e., activated carbon, which is indicative of the necessity for more research and attempts to introduce superior adsorbents [19]. Attempting to find low-cost adsorbents have led to employing available and low-cost substances such as agricultural plants, mineral wastes, etc. [20,21]. However, the adsorbents produced by these substances could not actually provide successful adsorbents because they did not have sufficient adsorption capacities and satisfactory removal efficiency [22,23].
Jiagwe et al. [24] reviewed some important granular activated carbon derived from biomass waste materials for water treatment. Production steps such as granulation with and without binders, as well as different carbonization and activation methods used to enhance strength and increase attrition resistance of the waste-based GAC, have been presented. The use of these GACs for water treatment has exhibited a great potential, sometimes performing better than commercial carbons, depending on the target contaminant. Also, Chen et al. [25] reviewed the conversion of crayfish-shell derivatives to functional materials and their environmental applications. Crayfish shells and their derivatives provide a cost-effective and sustainable platform for the functional utilization of biological materials. The primary components, such as chitin, protein, and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine, can be separated by modified chemical or biological methods. Furthermore, crayfish shells can be converted into functional carbon-based materials, which are extensively used as cheap and abundant adsorbents or mesoporous carbon supports in chemical reactions. However, based on the limited research on crayfish shells and their derived functional materials, more research attention is needed to solve the scientific and technical challenges of crayfish-shell utilization.
By continuation of the studies and research on this subject, nanomaterials such as carbon nanomaterials have been addressed to be associated with a high ability for removing the pollutant due to their excellent properties. For instance, Bina et al. (2012) used carbon nanotubes to remove benzene and toluene and reported favorable results [10]. Mohammadi et al. (2017) employed cupric oxide nanoparticles for removing benzene and toluene and found the removal efficiency of 98.7% for benzene and 92.5% for toluene, using their studied adsorbent [23]. Mahmud et al. (2018) studied the removal efficiencies of BTEX using iron nanoparticles and obtained satisfactory results for its application [26]. Despite the benefits, the toxicity and high production costs detected for these materials have led to restricting their application [27]. MOF is a type of nanomaterial which has recently found more applicability in different areas of science; this favorability of use is due to having exceptional features, e.g., large surface area, stability in water and high porosity [27,28]. ZIF-8 is a MOF with good stability in water. It is a microporous MOF with a framework structure, which has led to its being introduced as a suitable adsorbent for removing various types of pollutants [29,30]. Despite the advantages mentioned above, the problem associated with its separation (this problem rises due to the small size of ZIF-8 particles), which needs a long time and is difficult to achieve, limits its application [31,32]. Magnetic nanoparticles, i.e., Fe3O4, have a facile separability from solutions, which leads to increasing their popularity, since it leads to eliminating the processes such as centrifugation and filtration for removing these types of adsorbents from solutions. Its combination with ZIF-8 can lead to integrating the properties of these two nanoparticles so that the new composite is easily separated after adsorption [33]. Based on this, the Fe3O4/ZIF-8 has been studied as an adsorbent by many researchers. For example, Hue et al. (2018) used Fe3O4/ZIF-8 for the adsorption of As(III) from an aqueous solution. El-Desouky (2021) synthesized Fe3O4/ZIF-8 for the adsorption of anionic dyes [34]. Also, Qu et al. (2022) utilized this composite in another study as an adsorbent for removing phenol [35]. In all the studies, as mentioned earlier, Fe3O4/ZIF-8 was found to be an effective and excellent adsorbent with remarkable surface area, high reusability, and recyclability. Furthermore, Ma et al. [36] investigated the ZIF-67@wood obtained by in situ growth of ZIF-67 on wood, which is carbonized to prepare magnetic WC-Co composites. The hierarchical porous structure of wood can facilitate the rapid passage of dye solution, and promote full contact between magnetic core–shell Co/C nanoparticles and dyes. The adsorption capacities of CR and MB by Co/C-1000 are 1117.03 and 805.08 mg g−1, respectively.
Based on the above, since benzene and toluene are toxic and harmful compounds for different sectors of the life cycle, and there is no report for employment of Fe3O4/ZIF-8 in the adsorption process for removing the mentioned pollutant, the present study assessed the ability of Fe3O4/ZIF-8 in adsorption of benzene and toluene. Moreover, characteristics of the prepared adsorbent were identified using some common analyses. In addition, studies related to the effect of parameters (pH, Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dosage, mixing time, concentration of pollutant, and temperature), isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic of the adsorption process, which is imperative and necessary in the adsorption process, were also conducted. Finally, evaluating the reusability of the Fe3O4/ZIF-8 was another object of the present study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Benzene and toluene (analytical grade and purity of greater than 99%) were employed as target pollutants in this study; these chemicals were provided by Merck and were used with no further purification. Other chemicals required for conducting the present study were hexahydrate zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O, 98%), 2-methylimidazole (C4H6N2 99%), ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), sodium hydroxide (NaOH, ≥98%), methanol (CH3OH), ≥99%), hydrochloric acid (HCl, ≥36.5%), ammonium ferrous sulfate ((NH4)2(FeSO4)2·6H2O and ferric chloride, which was supplied by Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4
Synthesizing Fe3O4 nanoparticles was done based on a modified co-precipitation process using Fe3+ and Fe2+ [22]. First, a solution with a 1:2 molar ratio between Fe2+ and Fe3+ should be formed; this was done by liquefying ferrous ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2(FeSO4)2·6H2O, 1.97 g, 5 mmol) and ferric chloride (FeCl3·6H2O, 1.622 g, 10 mmol) in distilled water (100 mL). Instilling ammonia solution under a nitrogen blanket (NH3·H2O, 28 percent, 0.7 M) was done after 20 min. Mechanical stirring was applied for the formation of the precipitate, and heating was then carried out for 30 min at 80 °C. After centrifuging nanoparticles and cooling them to room temperature, they were washed three times with distilled water.
2.3. Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazole Framework-8 (ZIF-8)
Producing ZIF-8 in the present study was achieved according to results reported in a previous study [31]; based on this, Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O (2.97 g) was first poured into double distilled water (3 mL). Then, 2-methylimidazole (1.64 g) was added to the NH4OH solution (20.75 mL). Finally, two prepared solutions, i.e., Zn(NO3)2 and 2-methylimidazole, were mixed. The combination of mentioned solutions led to the immediate formation of milky suspension, which was agitated for 10 min at room temperature and led to its crystallization. After completion of the process, collecting the final product was done by centrifugation. It was then rinsed with deionized water (three to four times) until reaching a pH of around 7. Finally, the drying process at 60 °C was applied for the resultant product.
2.4. Synthesis of Fe3O4@ZIF-8
2 mmol, 0.595 g of Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O, and 0.05 g Fe3O4 were dissolved as (solution A) in 7.5 mL of methanol. Then, solution B was prepared by liquefying 2-methylimidazole (0.65 g, 8 mmol) in 7.5 mL of methanol. After preparing the above solutions, solution A was instilled into solution B under ultrasonic treatment. The resultant obtained from the reaction between those solutions was brown Fe3O4@ZIF-8 precipitate, which was collected by centrifugation process. It was then dried at 60 °C. The whole synthesis route is illustrated in Figure 1.
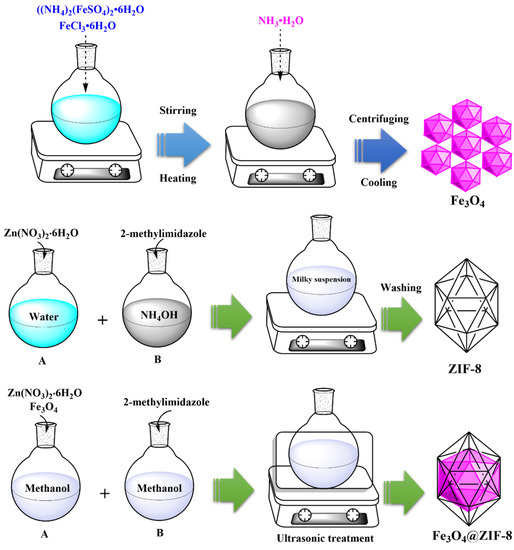
Figure 1.
Synthesis route of Fe3O4, ZIF-8 and Fe3O4@ZIF-8.
2.5. Adsorption Experimental Design
To conduct the adsorption experiments of the studied pollutants, a determined amount of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was poured into glass flasks, which were filled with 100 mL of the pollutants being investigated. After covering the glass flasks with Teflon caps, they were exposed to stirring in a thermostatic shake water bath, at 150 rpm for a certain amount of time. For regulating the pH of the studied solution, NaOH (0.1 M) and HCl (0.1 M) were employed. After completion of the process, an external magnet was utilized to separate Fe3O4@ZIF-8. Calculating the adsorption capacity (qe, mg g−1) and the removal percentage (%) was achieved using the below equations [37]:
Determining the initial and equilibrium concentrations of the studied pollutants in solutions was carried out utilizing Shimadzu visible spectrophotometer (DR5000); this test was conducted at wavelengths of 206 and 254 nm for toluene and benzene, respectively.
2.6. Devices Used in the Study
The following devices were used for adsorbent analysis: TEM model (LEO 912 AB) and SEM model (Mira 3-XMU), Fourier transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (Thermo Nicollet AVATAR5700), surface-area analyzer (ASAP2020, USA), vibrating sample magnetometer (Micromeritics Instrument Corp., Norcross, GA, USA), and X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku D/Max 2500, Tokyo, Japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations
According to Figure 2a (the SEM image of the Fe3O4@ZIF-8 composite), an uneven surface was observed for the Fe3O4@ZIF-8 composite. Moreover, according to TEM images (Figure 2b), a distribution of magnetic nanoparticles on the crystal surfaces of ZIF-8 was approved.
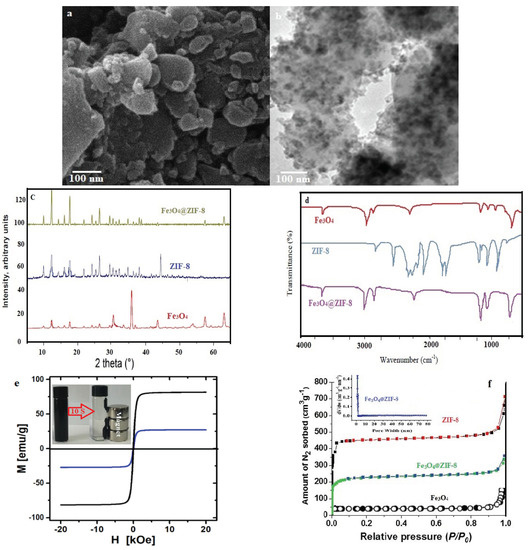
Figure 2.
SEM patterns (a) TEM patterns, (b) XRD patterns, (c) FTIR spectra, (d) Magnetization curves, (e) Adsorption-desorption isotherms and (f) BJH pore size distribution of Fe3O4@ZIF-8.
Diffraction of X-ray (XRD) was another test employed in this study to additionally validate the loading of Fe3O4 on ZIF-8 (Figure 2c). There were similarities between the XRD of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 and ZIF-8; this indicates the constancy of the ZIF-8 crystals’ sodality structure, even after synthesizing the Fe3O4 particles. Except for three peaks observed at 2θ = 33.4, 35.7, and 43.6° corresponding to the (220), (311), and (400) magnetite crystal facets (JCPDS No. 19-0629), which implied the high purity of the final Fe3O4@ZIF-8 particles, there were no other peaks [31].
FT-IR (in the range of 400.0 to 4000.0 cm−1) was another test used in the present study; this test evaluates the functional groups of the studied adsorbent. In Figure 2d, FT-IR spectra for ZIF-8, Fe3O4, and Fe3O4@ZIF-8 were provided. The peak was observed at 2922 cm−1 is an indicative of C-H group and OH stretching in carboxylic group (usually overlaps C-H). However, no carbonyl group was observed in the range 1710–1740 cm−1. In the distributed deep peak, the Fe-O bond absorption is featured at 614 cm−1. FT-IR spectrum of ZIF-8 represented the peaks of 2500–3500 cm−1 (the vibrations of the ZIF-8 pairs), 1384 cm−1 ((C-N) vibration), and peaks of 1667 cm−1 and 1580 cm−1 (the bending and stretching N-H vibration in the imidazole). However, the bands at 1350–1500 cm−1 were correspondent with the complete stretching ring. In addition, the peak of 421 cm−1 is raised by the Zn-N stretch mode [27]. Considering the results, it is clear that except for the peak at 614 cm−1, which is in correspondence with the Fe–O bonds, there is a closeness between the FT-IR spectrum of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 and ZIF-8. In conclusion, the successful production of composites is inferred by the above results.
According to the magnetic hysteresis loops measured for Fe3O4 and Fe3O4@ZIF-8 (shown in Figure 2e), there is a superparamagnetic characteristic for the composite with insignificant remanent magnetization at zero external magnetic field. Fe3O4 exhibited a saturation magnetization of 81.7 emu g−1, which diminished to 26.9 emu g−1 after loading ZIF-8; this diminution is described based on the addition of ZIF-8, which is a non-magnetic substance. The robust magnetic response facilitates the quick separation (<10 s) of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 particles from an aqueous solution using a magnet. Moreover, through mild agitation in the absence of a magnetic field, it is possible to redisperse the composite particles after adsorptive removal.
Figure 2f represents the results of nitrogen sorption isotherms, which were achieved for ZIF-8, Fe3O4, and Fe3O4@ZIF-8 at 77 K. As anticipated, a type I isotherm characteristic of microporous solids was detected for pure ZIF-8 (23). Considering the results of the BET model, a specific surface area of 1394 m2 g−1 was obtained for ZIF-8. Furthermore, for Fe3O4, the average pore diameter, pore volume, and specific surface area, were observed to be 5.41 nm, 0.077 cm3 g−1, and 21.2 m2 g−1, respectively. Nevertheless, the values of the above parameters for Fe3O4@ZIF-8 were detected to be 3.17 nm, 0.612 cm3 g−1, and 942 m2 g−1, respectively. After loading ZIF-8 on the surface of Fe3O4, results were representative of an enhancement in the pore volume and specific surface area of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 and a decline in pore size, which leads to enhancing active sites on Fe3O4@ZIF-8 and developing the adsorption of target pollutants from water. In addition, 67.5 wt.% shares of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 composite were related to the ZIF-8.
3.2. Influence of Parameters
One of the critical factors introduced by different studies for applying adsorbents in the adsorption process, is solution pH. The proton transfer may happen on the surface of adsorbents under different pH values, which results in adsorption in reaction pathways [37]. Determination of the optimum solution pH was done based on changing its values from 3 to 11 using an initial concentration of 100 mg∙L−1 and a Fe3O4@ZIF-8 concentration of 0.75 g L−1, and selecting the pH with the best adsorption efficiency. According to the results of this part, represented in Figure 2a, the removal efficiencies at pH of 3 and 7 were about 75.7% and 98.4% for benzene and 64.3% and 93.1% for toluene, respectively, which suggests the increasing trend for adsorption efficiency until pH of 7. However, a continuous increase in pH was observed to be associated with a diminution of adsorption efficiency. Based on the above observations, a pH of 7 was the optimum pH value for benzene and toluene adsorption and was considered optimal for the next experiments.
Adsorption decreases at high pH, which could be attributed to the competition between benzene and toluene and hydroxide (OH−) ions for same active sites available on the surface of Fe3O4@ZIF-8. Additionally, the lower adsorption of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 at extremely acidic (3–5) and basic (9–11) conditions is attributed to the surface polarity and hydrogen bonding between adsorbent and adsorbate [23]. Moreover, the surface groups (–COOH) are of paramount importance for binding of hydrophobic contaminants and the solution pH affected the surface charges through protonation and deprotonation of the organic compounds. At neutral conditions, strong electrostatic interactions occur due to the interactions of oxygen-bearing functional groups (with a negative charge) on Fe3O4@ZIF-8 and π electrons of ring structures (with a positive charge), which develops the adsorption efficiency; based on this, the electrostatic interaction has a role in the adsorption process [37].
The adsorbent dose has been found to be an important factor since it is able to represent the potential of the adsorbent, i.e., Fe3O4@ZIF-8, for a known initial benzene and toluene concentration. Therefore, the studies to determine the changes in benzene and toluene adsorption, by changing the Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dosage, were conducted using 0.1 to 1 g L−1 of the adsorbent at a pH of 7, and initial benzene and toluene concentration of 100 mg L−1 for 75 min. According to the results of this part (Figure 3b), there is an association between benzene and toluene removal efficiency and the studied factor, i.e., Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dosage; based on this, an increase in the adsorbent dosage from 0.1 to 0.75 g led to an improving removal efficiency from 44.7% to 98.4% for benzene and from 39.8% to 93.1% for toluene. In addition, a rapid enhancement was detected in benzene and toluene removal capacity by increasing the Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dose from 0.1 to 0.75 g. To explain the obtained result, it should be mentioned that although the number of available sites develops by increasing the adsorbent dosage, they remain unsaturated in the adsorption process [38]. Moreover, dosages above 0.75 g L−1 exhibited a slight effect on the adsorption capacity of Fe3O4@ZIF-8; according to this, 0.75 g L−1 was considered as the optimum dosage.
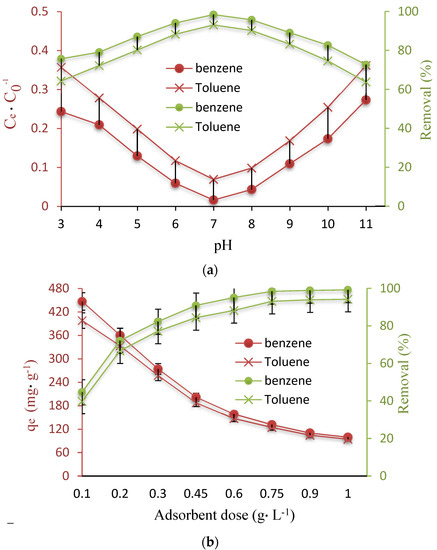
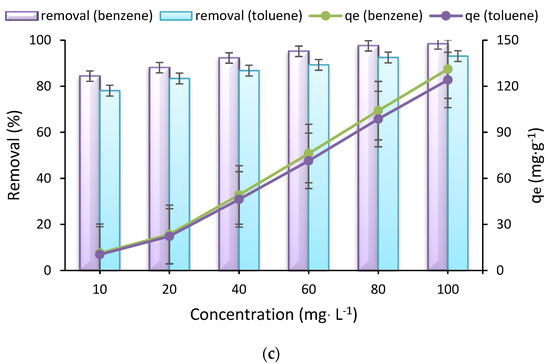
Figure 3.
(a) Effect of pH on benzene and toluene removal, (b) Effect of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 dose, (c) Effect of concentration on capacity adsorption and removal.
The results related to the effect of initial benzene and toluene concentration, represented in Figure 2c, depict that there is a link between rising the initial pollutant concentration and the removal efficiency and adsorption capacity. For instance, removal efficiencies for initial benzene concentrations of 10 mg L−1 and 100 mg L−1 (contact time 75 min, pH = 7, dose 0.75 g L−1, and temperature 30 °C) were more than 84.4% (with an adsorption capacity of 11.25 mg g−1) and 98.4% (with an adsorption capacity of 131.2 mg g−1), respectively. This trend was also perceived for toluene. Above mentioned observations confirm the dependence of the removal efficiency of studied pollutants by Fe3O4@ZIF-8 on their concentrations. Enhancing the driving force related to the concentration gradient has been reported as the reason for developing adsorption capacity, due to increasing the initial benzene and toluene concentration at a fixed dose of adsorbent [39,40]. Based on this, initial concentrations of the pollutant molecules are considered as effective factors to enhance driving force, which can participate in overcoming the mass transfer resistance of all molecules between the aqueous and solid phases.
3.3. Investigation of Contact Time and Kinetic Studies
Equilibration time in adsorption studies is one of the most important parameters, which should be determined. The high adsorption rate in the early stages of adsorption can be due to the high driving force and fast transfer of toluene and benzene molecules, and the adsorbent surface. After 75 min for benzene and 90 min for toluene, the amount of absorption decreases to some extent (Figure 4a). The reason for this can be the separation of some toluene and benzene from the adsorbent during the desorption stage, and the reduction of available active sites. This state is caused by the lower dissolution rate of toluene (530 mg L−1), compared to benzene (1970 mg L−1), the higher molecular weight of toluene (92 g mol−1) than benzene (78 g mol−1), and the higher boiling point of toluene (110.7), compared to the boiling point of benzene (80.1) [3].
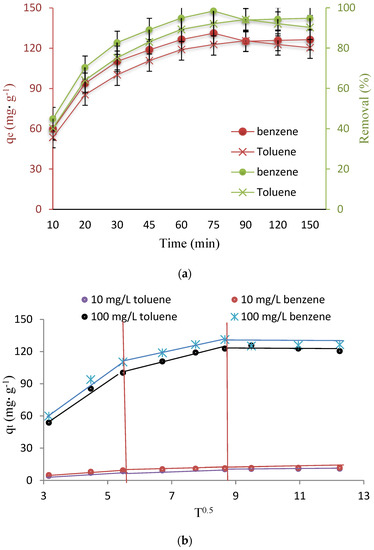
Figure 4.
(a) Effect of contact time on capacity adsorption and (b) IPD plots.
Also, the evaluation of the kinetic parameters of the process was carried out through the PFO and PSO, IPD, and Elovich kinetic equations [39,40,41]. The equations related to the isotherms were shown in Table 1. Examining the parameter values of PFO and PSO equations of toluene and benzene adsorption process by Fe3O4@ZIF-8, in Table 1, showed that, based on the correlation coefficient values, the data obtained from the adsorption test are more consistent with the PSO model compared to the PFO. Also, the results showed that the correlation coefficient of PSO is very high and the value of qe cal is close to the value of qe exp. Therefore, the adsorption process follows the PSO model, which indicates the chemical interaction between the adsorbent and the adsorbate.

Table 1.
Kinetic parameters for the adsorption of benzene and toluene on Fe3O4@ZIF-8.
Determining the mechanism and the controlling or limiting step of the ion exchange process is usually done through the IPD model. The rate constants of the adsorption of toluene and benzene ions by studied Fe3O4@ZIF-8, according to the mentioned model, were shown in Figure 4b, which represents three stages in the process of toluene and benzene ions adsorption by Fe3O4@ZIF-8: it includes the first stage, i.e., the transfer of toluene and benzene ions from the solution to the liquid film around the adsorbent; the second step, i.e., the mentioned ions reach the adsorbent surface from the film; and the third step, i.e., their penetration from the surface to the internal sites of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 [42,43]. By comparing the trend of the slope of each stage, it can be seen that the first stage, i.e., the arrival of toluene and benzene ions to the film around the adsorbent, is carried out with the highest rate for which this phenomenon is possible, mostly by stirring the solution.
3.4. Isotherm Studies
In this research, the mechanism and behavior of toluene and benzene ions’ adsorption on Fe3O4@ZIF-8 were studied by examining the equilibrium and kinetics of the process. To determine and check the isotherm model governing the process, after analyzing the concentration of toluene and benzene in the samples, the equilibrium data were fitted on the linear form of D-R-, Temkin, Freundlich, and Langmuir models, and after deriving the equation of the fitting line, the constants related to each was calculated and determined [44,45,46]. The equations and parameters calculated related to the isotherms were shown in Table 2. According to this table, almost all the models examined have a good fit on the laboratory data, so that the correlation coefficient is above 0.9 in all cases. Also, the R2 value for the Langmuir models was calculated to be higher than 0.99, which indicates the fit on the data and the use of their constants to describe the process.

Table 2.
Isotherm parameters for adsorption of benzene and toluene at various temperatures.
The extracted data of the Langmuir model show that the maximum adsorption capacity for benzene was 129.4, 134.2, 137.3, and 148.2 mg g−1, and for toluene was 118.4, 125.2, 129.6, and 133.1 mg g−1, for temperature 20, 30, 40, and 50 °C, respectively. On the other hand, the proper fit of the data on the Freundlich model indicates that the process is not limited to a specific surface of the adsorbent, and that the surface for studied benzene and toluene has heterogeneity with different adsorption energies. Researchers have always tried to link the constant parameters in the model (1/n and KF) with the adsorption mechanism. In general, in the Freundlich model, 1/n and KF are constants that describe all the factors affecting the adsorption capacity and the desirability of the adsorption process on the adsorbent, respectively. When the value of n is in the range of 1 to 10, the adsorption process is classified in the desired class [47,48]. The higher value of n (the lower value of 1/n) represents the more significant inhomogeneity of the absorbent surface for the pollutant. According to the data in the above table, the numerical value of 1/n for the investigated adsorbent for benzene and toluene is lower than one, which indicates that the process is favorable and adsorption of benzene and toluene ions from the solution is easy [49]. The comparison of the adsorption capacity obtained from this study with similar studies was shown in Table 3, and as can be seen, it has a good adsorption capacity compared to the adsorbent used in this study.

Table 3.
Comparison of adsorption capacity of different adsorbents.
The DR model is another isotherm equation that the laboratory data obtained followed this model with a high correlation coefficient. This model is generally used to describe the adsorption mechanism [50,51]. This model’s constant value of E may be used to determine whether the process is physical or chemical. This value represents the average amount of energy required to remove the molecules of the adsorbed species from the surface of the adsorbent. When the value of E is less than 8 kJ mol−1, the process is a physical process, and when it is in the range of 8 to 16 kJ/mol, it is a chemical process [52,53,54]. As can be seen in the data table of the used models, this value for benzene and toluene adsorption is higher than 8 kJ mol−1, which indicates the dominant role of chemical adsorption in the adsorption process of benzene and toluene on Fe3O4@ZIF-8 adsorbent.
3.5. Effect of Temperature and Thermodynamics Study
The results of the effect of temperature are shown in Figure 5a, and as it is quite clear, with the increase in temperature from 20 to 50 °C, the removal percentage and adsorption capacity for both benzene and toluene increases, which shows that it is endothermic adsorption of benzene and toluene [55,56].
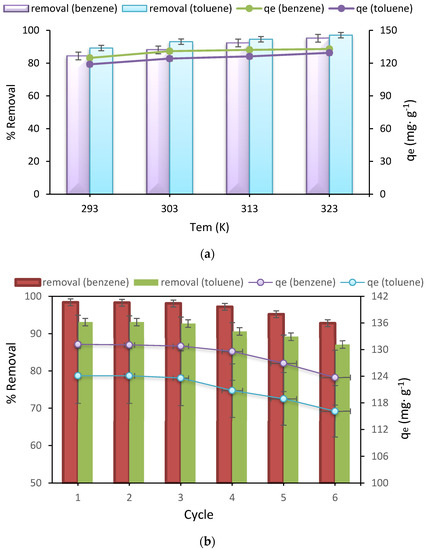
Figure 5.
(a) Effect of temperature, (b) Reusability study of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 on benzene and toluene uptake.
Thermodynamic studies were conducted based on related parameters, i.e., ΔG0, ΔH0, and ΔS0 at different temperatures. The adsorption process is represented by the following [57,58,59].
ΔG0 = −RT ln Kc
Considering the slopes and intercepts obtained from plotting a graph of ln Kc vs. 1. T−1, estimating ΔH0 and ΔS0 is performed. According to the results, the adsorption has endothermic nature considering the positive values obtained for ΔH° value (ΔH° = 35.07 kJ mol−1 for benzene and ΔH0 = 79.21 kJ mol−1 for toluene) [60,61,62,63]. However, the positive values of ΔS0 (ΔS0 = 0.139 kJ mol−1K−1 for benzene and ΔS0 = 0.295 kJ mol−1K−1 for toluene) are representative of the increasing entropy of the system during the adsorption process [64,65]. It shows that our studied process is a somewhat temperature-dependent process. Moreover, at the studied temperature (at 293, 303, 313, and 323 K), ΔG0 values for benzene adsorption were −5.82, −7.25, −8.19, and −10.17 kJ mol−1, while the values for toluene adsorption were −7.23, −10.78, −12.95, and −16.35 kJ mol−1, respectively. The negative values for ΔG° were indicative of the spontaneous nature of the evaluated adsorption, and increasing temperature enhances the adsorption capability of benzene and toluene [66,67,68].
3.6. Adsorbent Recyclability
In this study, adsorption-desorption tests were performed in six different stages to recover the adsorbent under study. Thus, after adsorption, the Fe3O4@ZIF-8 was separated using a magnet, and the separated adsorbent was washed with distilled water and methanol in a ratio of one to one. Then, it was placed in the ultrasonic device for 30 min, and the magnetic separation was again performed using a magnet. After desorption, the adsorption phase began. In this section, the optimal parameters obtained in the results section were used. The results were shown in Figure 5b, and as can be seen, after six successive adsorption-desorption runs, the removal percentage for benzene changed from 98.4 to 92.8%, and the adsorption capacity of 123.7 mg g−1 in the initial adsorption reached 116.1 mg g−1. Also, the removal percentage of toluene in six consecutive steps attained from 93.1 to 87.1%, and the adsorption capacity in the first step was 124.1 mg g−1, and for the sixth run, it was 116.1 mg g−1. Therefore, for the removal of toluene in six steps, a 6% reduction in removal was observed, and for benzene in six steps, a 5.6% reduction in removal was observed, which is a very acceptable value. This decrease in removal can be due to the loss of the adsorbent during washing and the decrease in the amount of adsorbent, and the lack of complete desorption of the adsorbent in the desorption stage, which reduces the active sites of the adsorbent and subsequently removal efficiency [69,70].
4. Conclusions
This study was to evaluate the efficiency of a magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@ZIF-8) for adsorbing two pollutants, i.e., benzene and toluene; mentioned nanocomposite was prepared using Fe3O4 and ZIF-8, according to the co-precipitation method. According to the results, a high surface area (942 m2 g−1) was detected for Fe3O4@ZIF-8 composites. Isotherm studies were indicative of the suitability of the Langmuir model for expressing the adsorption isotherm; based on this, monolayer adsorption is detected for the uptake of benzene and toluene on Fe3O4@ZIF-8. The comparison of R2 values (0.99 for both pollutants) revealed the suitability of PSO for fitting the data obtained from studies related to adsorption kinetics. Considering the thermodynamic studies, the adsorption process is a spontaneous and endothermic. Considering the results of this research, due to the acceptable efficiency of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 in the adsorption of benzene and toluene, and its easy separation after the process, it has been found to be a nanocomposite for practical application.
Author Contributions
D.B.: conceptualization, investigation data, and collecting, figure analysis, writing-original draft. G.Z.K.: draft writing, correcting, and reading. T.J.A.-M.: writing, reading, figure analysis, correcting, and resourcing. G.M.: writing—revising and figure analysis. S.S.: Data analysis, revising, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is funded by Zahedan University of Medical Sciences, Zahedan, Iran.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the student research committee of Zahedan University of medical sciences for their financial support (code project; 10769). We would like to appreciate all the fellows of our research group.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| C0 = concentrations of benzene and toluene in mg L−1 at the start |
| Ce = concentrations of benzene and toluene in mg L−1 at equilibrium |
| V = benzene and toluene volume at mL |
| m = Fe3O4@ZIF-8 masses in mg |
| KL = (L mg−1) is the Langmuir adsorption constant |
| KF = Freundlich constant (L g−1) |
| n = heterogeneity factor (If the value of n < 1, the adsorption is a chemical process; if n > 1, then it is a physical process). |
| qe = adsorption capacity at equilibrium |
| qm = maximum adsorption capacity |
| RL = dimensionless separation factor |
| The values of RL show whether the biosorption process is irreversible (RL = 0), linear (RL = 1), favorable (0 < RL < 1) or undesirable (RL > 1) |
| ΔG° = Gibbs free energy (kJ mol−1) |
| ΔS° = entropy (kJ mol−1 K−1) |
| ΔH° = enthalpy (kJ mol−1) |
| K1 = equilibrium rate constant for pseudo-first order kinetics (PFO) (1.min−1) |
| K2 = equilibrium rate constant for pseudo-second order kinetics (PSO) (g mg−1 minmg) |
| Kb =Intra-Particle Diffusion (IPD) rate constant (mg g−1 min−1/2) |
| C= thickness of the boundary layer |
| D-R isotherm constant (mol2 kJ−2) |
| Polanyi potential |
| E = The adsorption energy (kJ.mol−1) |
| KT = constant of equilibrium binding (L.mg−1) |
| B = Temkin constant associated with the heat of adsorption (J/mol) |
| D-R = Dubinin-Radushkevich |
| XRD = X-ray Powder Diffraction |
| FTIR= Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer |
| SEM = Scanning electron microscope |
| TEM = Transmission Electron Microscope |
| VSM = Vibrating Sample Magnetometer |
| BET = Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| MOF = Metal-organic framework |
References
- Lakshman, M. Fe3O4@SiO2-Pip-SA nanocomposite: A novel and highly efficient reusable acidic catalyst for synthesis of rhodanine derivatives. J. Syn. Chem. 2022, 1, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Mehdinejad, M.H.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Mahdavi, Y.; Pourzamani, H.; Hajizadeh, Y. Degradation of diclofenac by heterogeneous electro-Fenton process using magnetic single-walled carbon nanotubes as a catalyst. J. Water. Process. Eng. 2019, 31, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhurebor, K.E.; Athar, H.; Adetunji, C.O.; Aigbe, U.O.; Onyancha, R.B.; Abifarin, O. Environmental implications of petroleum spillages in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ji, H. Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soils with microbial and microbial combined methods: Advances, mechanisms, and challenges. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranchie, F.A.; Angnunavuri, P.N.; Attiogbe, F.; Nerquaye-Tetteh, E.N. Occupational exposure of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene (BTEX) to pump attendants in Ghana: Implications for policy guidance. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2019, 5, 1603418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeshwaran, P.; Megharaj, M.; Chadalavada, S.; Bowman, M.; Naidu, R. Petroleum hydrocarbons (PH) in groundwater aquifers: An overview of environmental fate, toxicity, microbial degradation and risk-based remediation approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 10, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, N.; Setyadhi, L.; Wibowo, D.; Setiawan, J.; Ismadji, S. Adsorption of benzene and toluene from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon and its acid and heat treated forms: Influence of surface chemistry on adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, D.; Guyton, K.Z.; Grosse, Y.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L. Carcinogenicity of benzene. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1574–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warden, H.; Richardson, H.; Richardson, L.; Siemiatycki, J.; Ho, V. Associations between occupational exposure to benzene, toluene and xylene and risk of lung cancer in Montréal. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, B.; Amin, M.M.; Rashidi, A.; Pourzamani, H. Benzene and toluene removal by carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2012, 14, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, P.; Kelleher, B.; Allen, C. Assessment of anaerobic biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons: The impact of molecular biology approaches. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, M.M.; Vianna, M.T.G.; Marques, M. Graphene and graphene nanocomposites for the removal of aromatic organic compounds from the water: Systematic review. Mater. Res. Exp. 2018, 5, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindrova, E.; Chocova, M.; Demnerova, K.; Brenner, V. Bacterial aerobic degradation of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene. Folia Microbiol. 2002, 47, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Mat, H.; Yunus, M.A.C. (Eds.) Batch Adsorptive Removal of BTEX From Aqueous Solution: A Review. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Separation Technology 2020 (ICoST 2020), Senai, Kualalumpur, Malaysia, 15–16 August 2020; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, C.P.; Vidal, C.B.; Barros, A.L.; Costa, L.S.; Vasconcellos, L.C.; Dias, F.S. Adsorption of BTX (benzene, toluene, o-xylene, and p-xylene) from aqueous solutions by modified periodic mesoporous organosilica. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C. Removal of emerging contaminants from the environment by adsorption. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Rashed, M.N. Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater. Org. Pollut. Monit. Risk. Treat. 2013, 7, 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Largitte, L.; Pasquier, R. A review of the kinetics adsorption models and their application to the adsorption of lead by an activated carbon. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-G.; Yu, L.-Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.-H.; Jiang, X.-Y. Graphene nanosheets as novel adsorbents in adsorption, preconcentration and removal of gases, organic compounds and metal ions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ihsanullah, I.; Younas, M.; Shah, M.U.H. Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 278, 119510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzynska, K. Removal of cadmium from wastewaters with low-cost adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y. MIL series of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as novel adsorbents for heavy metals in water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, L.; Bazrafshan, E.; Noroozifar, M.; Ansari-Moghaddam, A.; Barahuie, F. Adsorptive removal of benzene and toluene from aqueous environments by cupric oxide nanoparticles: Kinetics and isotherm studies. J. Chem. 2017, 69, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and Application of Granular Activated Carbon from Biomass Waste Materials for Water Treatment: A Review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, H. A review on conversion of crayfish-shell derivatives to functional materials and their environmental applications. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.S.; Mostafa, M.K.; Abdel-Gawad, S.A. Artificial intelligence for the removal of benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene and xylene (BTEX) from aqueous solutions using iron nanoparticles. Water Supply 2018, 18, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimbaluk, G.V.; Ramsdorf, W.A.; Perussolo, M.C.; Santos, H.K.F.; De Assis, H.C.D.S.; Schnitzler, M.C. Evaluation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes toxicity in two fish species. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ramesh, M.; Deepa, C. Metal-organic frameworks and their composites. In Metal-Organic Frameworks for Chemical Reactions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–18. ISBN 9780128220993. [Google Scholar]
- Gurusamy, L.; Anandan, S.; Wu, J. Nanomaterials derived from metal-organic frameworks for energy storage supercapacitor application. Met.-Org. Framew. Chem. React. 2020, 11, 441–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.; Liu, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X. Adsorptive removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 465, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.R.; Do, X.H.; Cho, K.Y.; Jeong, K.; Baek, K.Y. Amine-functionalized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals for adsorption of radioactive iodine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 9852–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajializadeh, A.; Ansari, M.; Foroughi, M.; Jahani, S.; Kazemipour, M. Zeolite Imidazolate Framework Nanocrystals Electrodeposited on Stainless Steel Fiber for Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Su, S.; Rao, J.; Li, S.; Lei, T.; Bai, H. Magnetic metal-organic framework (Fe3O4@ ZIF-8) core-shell composite for the efficient removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks (Fe3O4@ ZIF-8) composites for U (VI) and Eu (III) elimination: Simultaneously achieve favorable stability and functionality. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desouky, M.; El-Bindary, A. Magnetic metal-organic framework (Fe3O4@ZIF-8) nanocomposites for adsorption of anionic dyes from wastewater. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2021, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Magnetic Fe3O4/ZIF-8 composite as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for phenol adsorption from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 294, 121169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, S.; Tian, Z.; Duan, G.; Pan, H.; Yue, Y.; Li, S.; Jian, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; et al. MOFs meet wood: Reusable magnetic hydrophilic composites toward efficient water treatment with super-high dye adsorption capacity at high dye concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Taheri, Z.; Shim, M.J.; Lee, S.M.; Jeon, C. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics and equilibrium of ibuprofen from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from Lemna minor. Desal Water Treat. 2021, 215, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Al Rawi, O. Capacity and Modeling of Acid Blue 113 Dye Adsorption onto Chitosan Magnetized by Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Şahin, S.A. Acid Orange 7 adsorption onto quaternized pistachio shell powder from aqueous solutions. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.J.R.; Corso, C.R. Decolorization and removal of toxicity of textile azo dyes using fungal biomass pelletized. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, R.; Shirkhanloo, H.; Rashidi, A.M. Dynamic and static removal of benzene from air based on task-specific ionic liquid coated on MWCNTs by sorbent tube-headspace solid-phase extraction procedure. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.K.S.; Lim, L.Z.; Lim, M.J.W.; Ong, L.L.; Khezri, B.; Pumera, M.; Webster, R.D. Evaluation of the sorbent properties of single and multiwalled carbon nanotubes for volatile organic compounds through thermal desorption gaschromatography/mass spectrometry. Chem. Plus Chem. 2015, 80, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, C.; Xiao, J.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, L. Benzene/toluene/water vapor adsorption and selectivity of novel C-PDA adsorbents with high uptakes of benzene and toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konicki, W.; Aleksandrzak, M.; Moszyn, D.; Mijowska, E. Adsorption of anionic azo-dyes from aqueous solution onto graphene oxide: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 496, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balarak, D.; Zafariyan, M.; Igwegbe, C.A. Adsorption of Acid Blue 92 Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Xin, X.; Liu, X.; Raman, M.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W.; Doble, M. Transport of anionic azo dyes from aqueous solution to Gemini surfactant-modified wheat bran: Synchrotron infrared, molecular interaction and adsorption studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, P.Z.; Asilian, H.; Jonidi Jafari, A. Adsorption of xylene from air by natural Iranian zeolite. Health Scope 2014, 3, 17528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Mostafapour, F.K. Adsorption of acid red 66 dye from aqueous solution by heat-treated rice husk. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2018, 22, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Teimoori, S.; Hassani, A.H.; Panahi, M.; Mansouri, N. Review: Methods for removal and adsorption of volatile organic compounds from environmental matrixes. Anal. Methods Environ. Chem J. 2020, 3, 34–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Yang, F.H.; Yang, R.T. new sorbents for desulfurization by π-complexation: Thiophene/benzene adsorption. Ind Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 41, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, L.; Torabian, A.; Kazemian, H.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Azimi, A.; Nazmara, S.; Mohammadi, M. Adsorption of BTEX on surfactant modified granulated natural zeolite nano particles, parameters optimizing by applying taguchi experimental design method. Clean Soil Air Water. 2011, 39, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Repo, E.; He, F.; Zhang, X. Dual functional sites strategies toward enhanced heavy metal remediation: Interlayer expanded Mg-Al layered double hydroxide by intercalation with L-cysteine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saner, A.; Carvalho, P.N.; Catalano, J.; Anastasakis, K. Renewable adsorbents from the solid residue of sewage sludge hydrothermal liquefaction for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, S.; Xiang, H.; Gao, T. Selectively capacitive recovery of rare earth elements from aqueous solution onto Lewis base sites of pyrrolic-N doped activated carbon electrodes. Carbon 2022, 197, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Zinchenko, A. Conversion of waste bottle PET to magnetic microparticles adsorbent for dye-simulated wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Saloot, M.K. Synthesis of activated carbon from Lemna minor plant and magnetized with iron (III) oxide magnetic nanoparticles and its application in removal of Ciprofloxacin. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyanati-Tilaki, R.A.; Yousefi, Z.; Yazdani-Cherati, J. The ability of azollaand lemna minor biomass for adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions. J. Mazand. Univ. Med. Sci. 2013, 23, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mahvi, A.H.; Khatibi, A.D. Effective adsorption of ciprofloxacin antibiotic using powdered activated carbon magnetized by iron(III) oxide magnetic nanoparticles. J. Porous. Mater. 2021, 28, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Hameed, H.M. A coated of Ca/Fe layered hydroxide onto a synthesized adsorbent from (banana peels) for removal of cadmium from simulated wastewater. Caspian. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 19, 825–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, R.; Biswas, C.; Ahmed, J.; Naime, J.; Ara, M. A Study on the Adsorption of Cadmium(II) from Aqueous Solution onto Activated Carbon Originated from Bombax ceiba Fruit Shell. J. Chem. Health. Risks 2020, 10, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarnejad, R.; Azizi, A.; Asadi, S.; Mohammadi, M. Green Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles using Centaurea cyanus Plant Extract: A Cationic Dye Adsorption Application. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Lin, H.; Xu, R.; Zhu, H.; Xu, X. Lanthanum carbonate grafted ZSM-5 for superior phosphate uptake: Investigation of the growth and adsorption mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, X.; Bao, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H. Zheng, C. Construction of a novel lanthanum carbonate-grafted ZSM-5 zeolite for effective highly selective phosphate removal from wastewater. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 324, 111289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaei, S.; Noorisepehr, M.; Pourzamani, H.; Salari, M.; Moradnia, M.; Darvishmotevalli, M. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for degradation of Reactive Black 5: Batch and column study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials and chemical modifications for enhanced key wood properties: A review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Flotation in water and wastewater treatment. Processes 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikkaliotis, D.G.; Christoforidis, A.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Adsorption of copper ions onto chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) beads functionalized with poly(ethylene glycol). Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Nanaki, S.G.; Koltsakidou, A.; Papageorgiou, M.; Kechagia, M.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Effectively designed molecularly imprinted polymers for selective isolation of the antidiabetic drug metformin and its transformation product guanylurea from aqueous media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 866, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).