Synthesis of Aluminum Phosphate-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes: Effects on Morphological, Mechanical, and Rheological Properties of PEO/PBAT Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
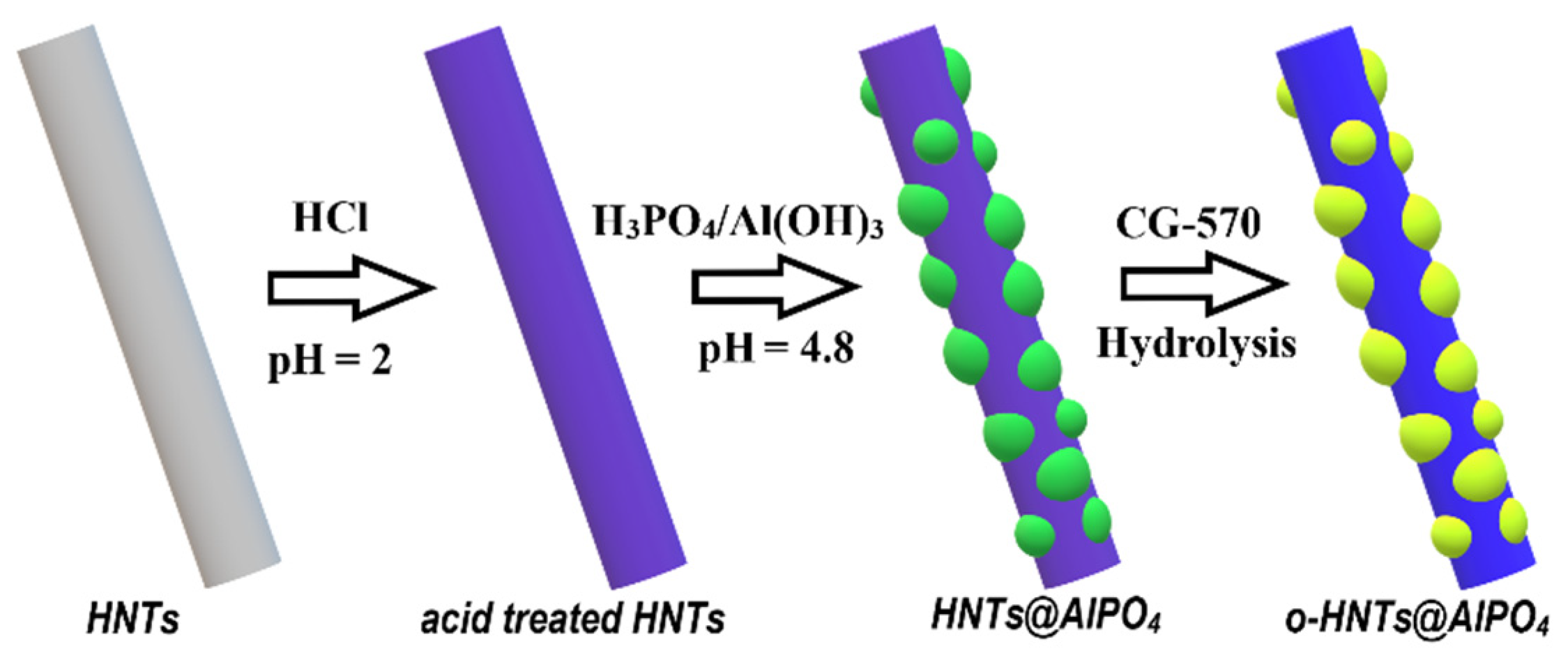
2.2. Fabrication and Modification of HNTs@AlPO4
2.3. Preparation of PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO4 Films
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
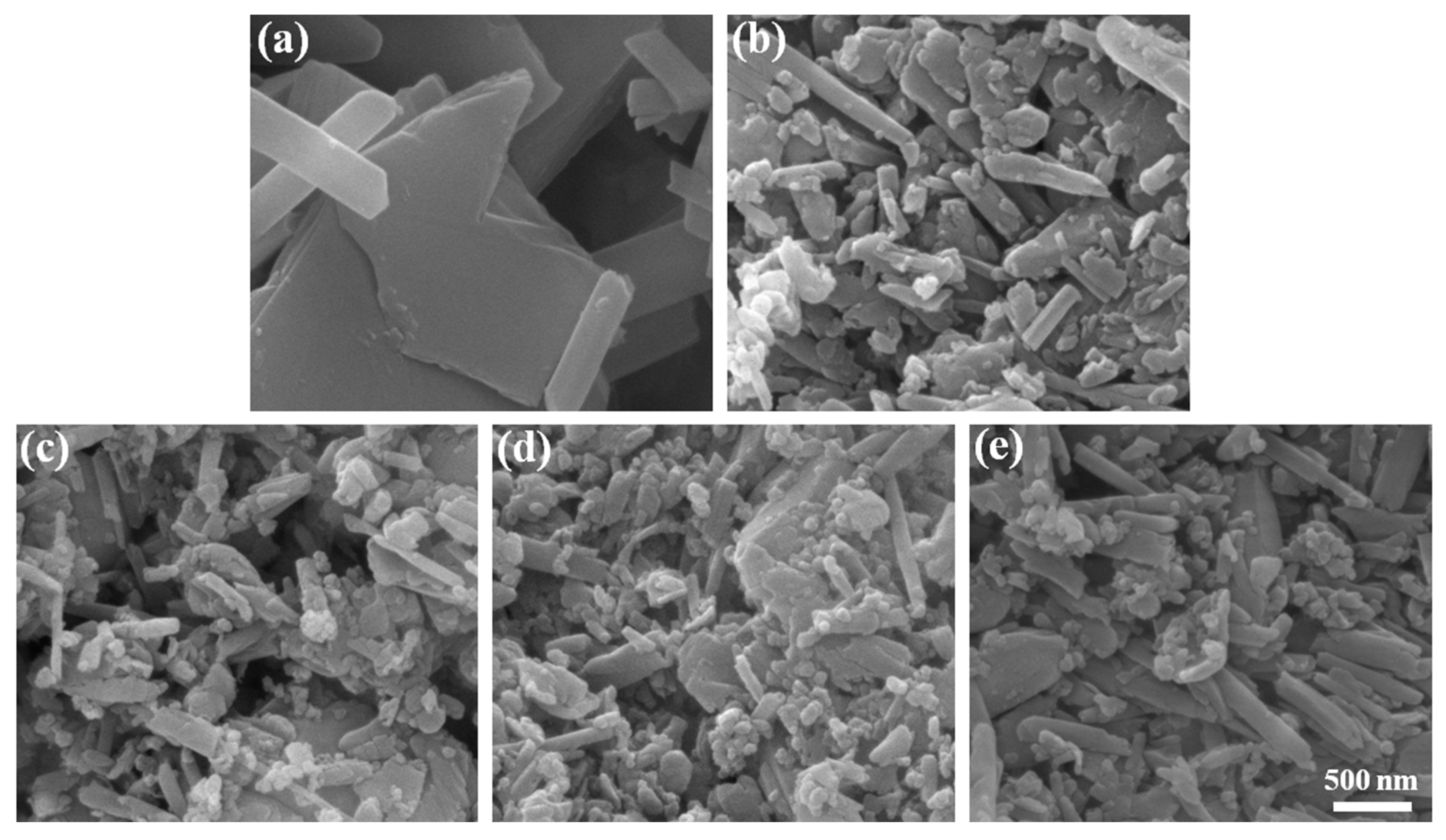
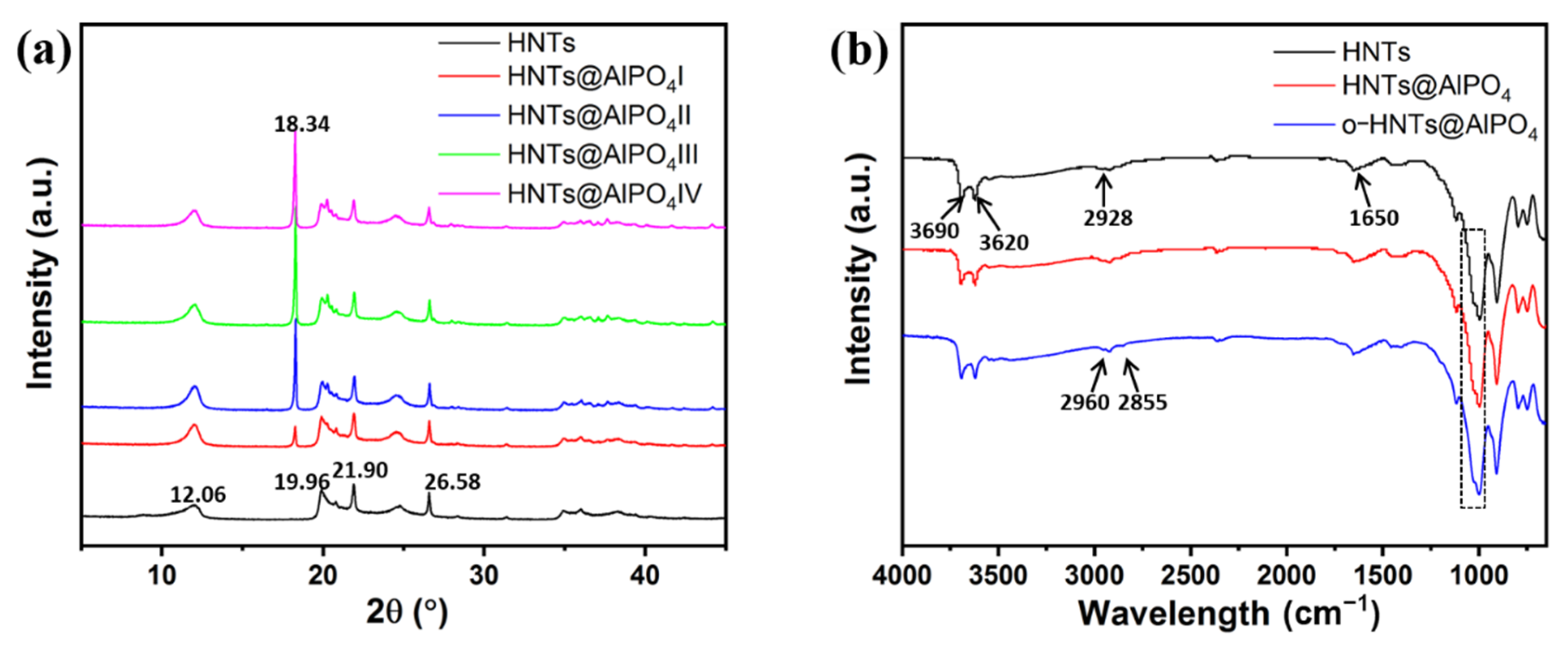
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization of HNTs@AlPO4
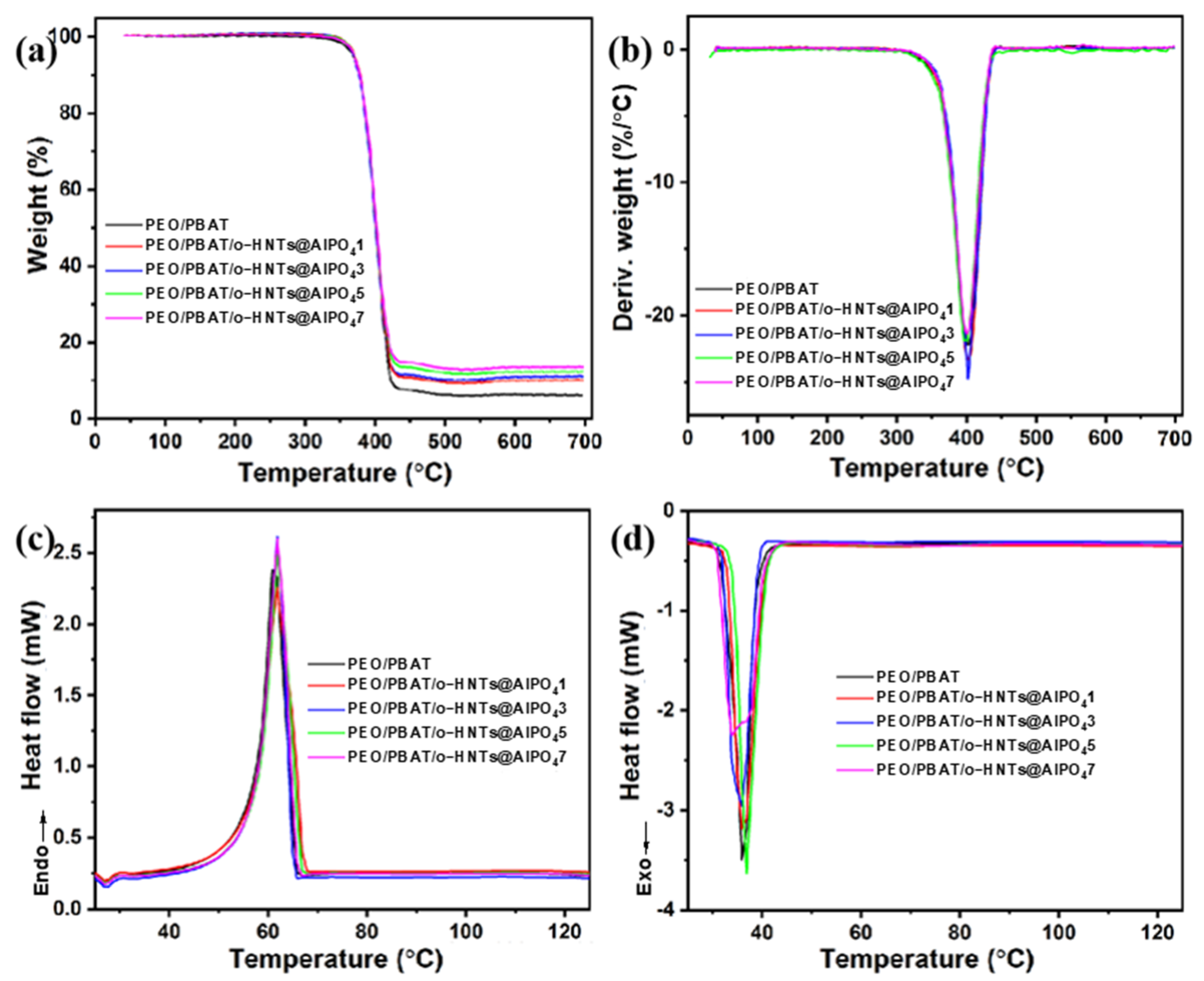
3.2. Thermal Properties of PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO4 Films
3.3. Mechanical Properties of PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO4 Films
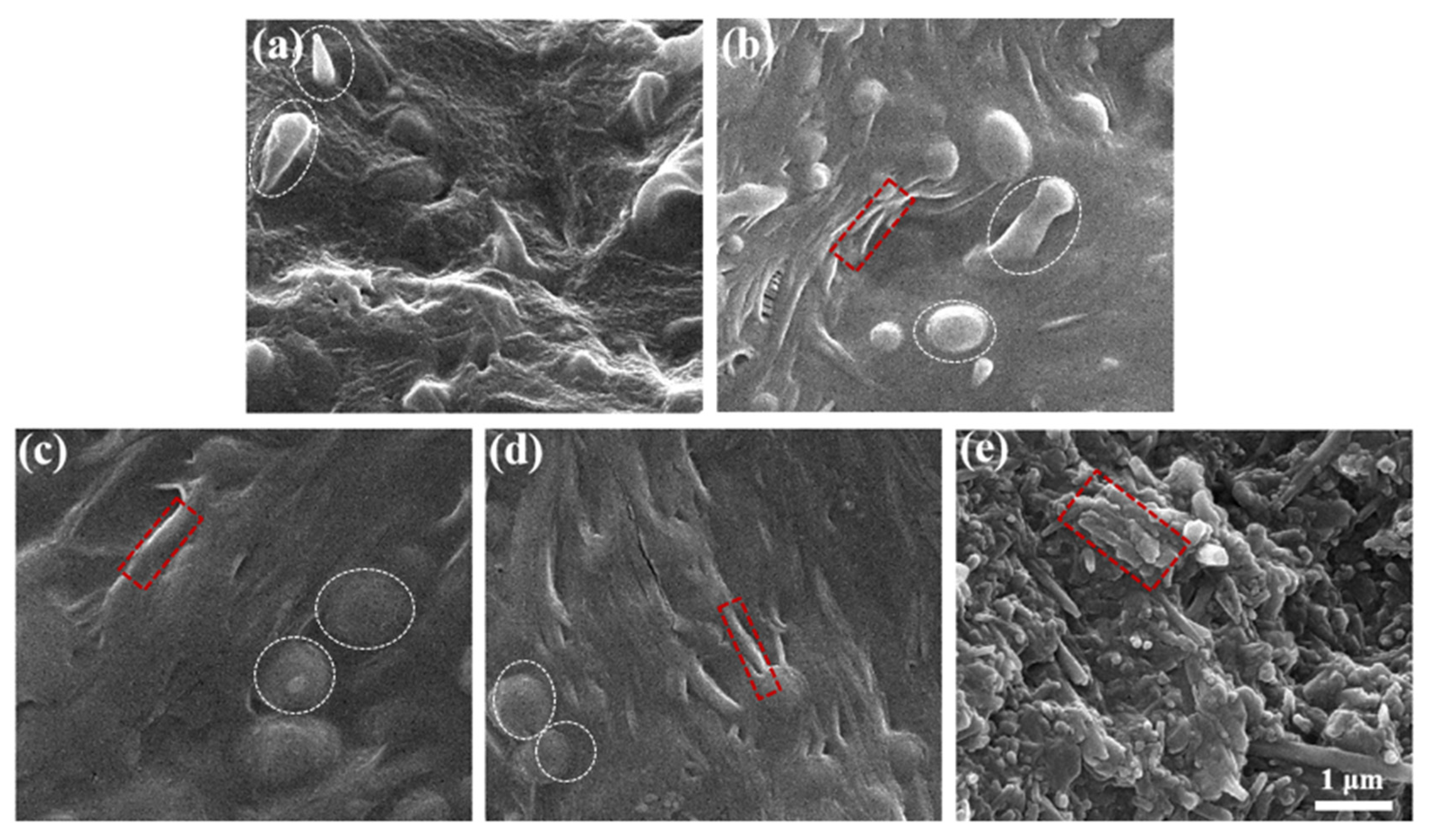
3.4. Cryofractured Surfaces of PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO4 Films
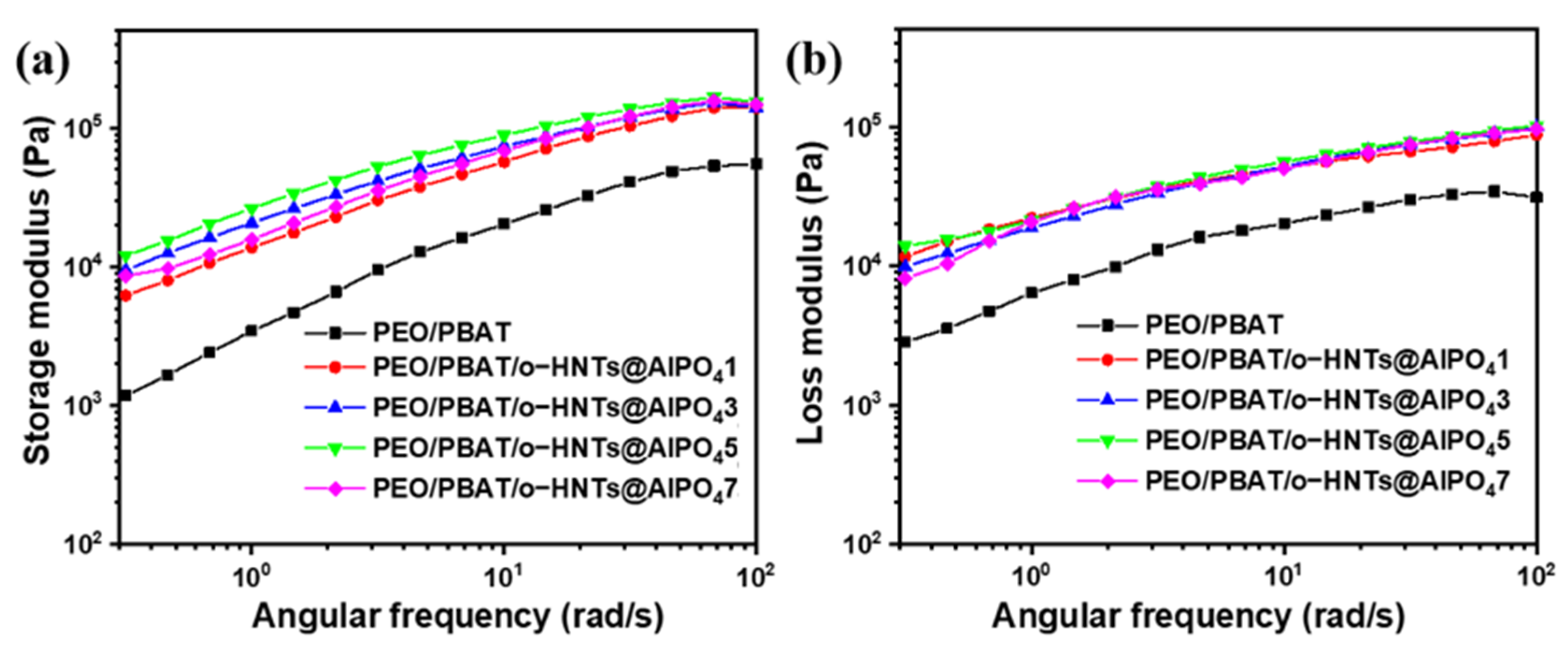
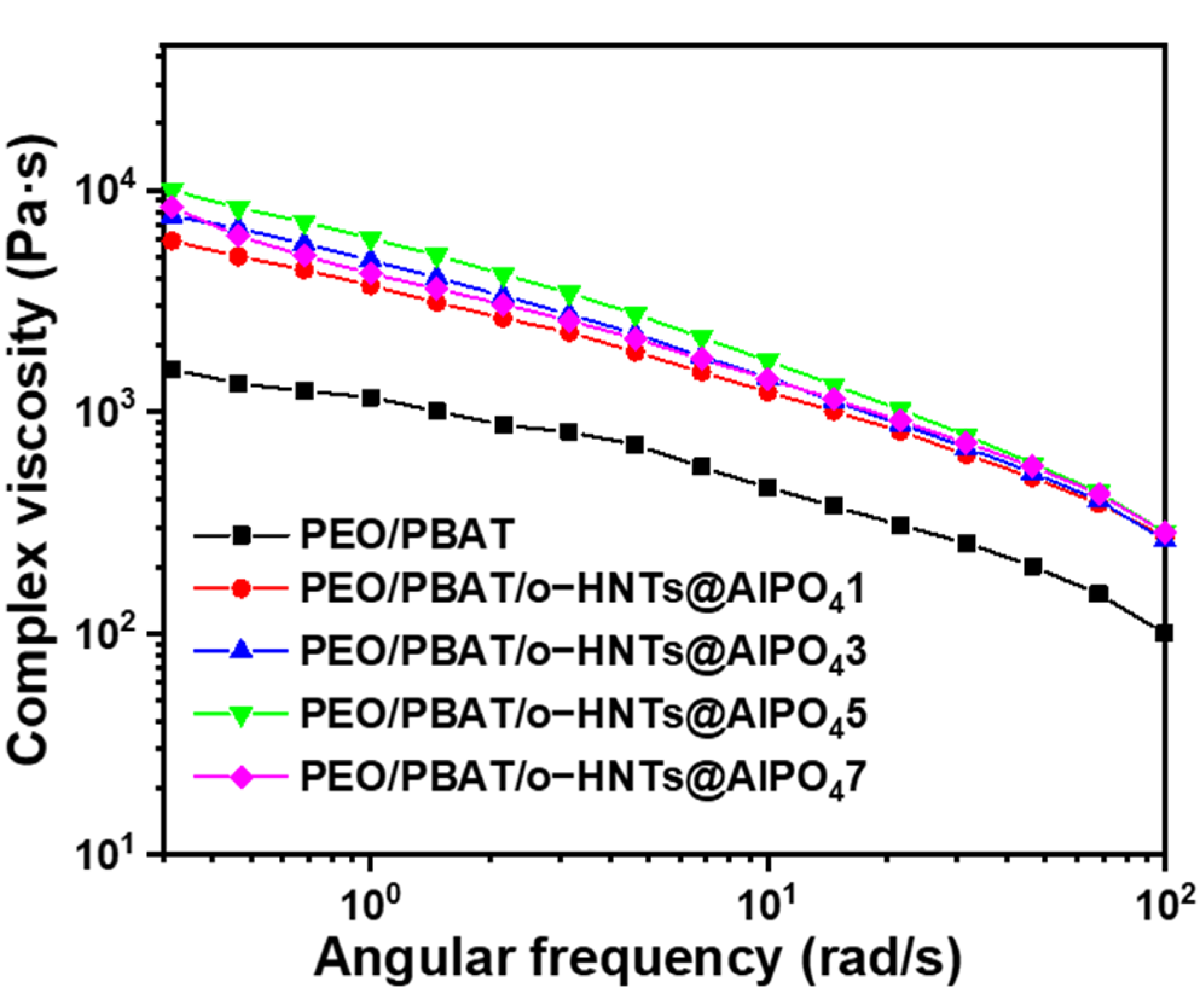
3.5. Rheological Properties of PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO4 Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umoren, S.A.; Solomon, M.M. Protective polymeric films for industrial substrates: A critical review on past and recent applications with conducting polymers and polymer composites/nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 104, 380–450. [Google Scholar]
- Mangaraj, S.; Yadav, A.; Bal, L.M.; Dash, S.K.; Mahanti, N.K. Application of biodegradable polymers in food packaging industry: A comprehensive review. J. Pack. Technol. Res. 2019, 3, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Sapkota, J.; Qin, J.; Siraleartmukul, K.; Siriwongrungson, V. Polymeric materials and films in dentistry: An overview. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 14, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolinsky, J.B.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Local drug delivery strategies for cancer treatment: Gels, nanoparticles, polymeric films, rods, and wafers. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamróz, E.; Kulawik, P.; Kopel, P. The effect of nanofillers on the functional properties of biopolymer-based films: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tayyar, N.A.; Youssef, A.M.; Al-Hindi, R. Antimicrobial food packaging based on sustainable bio-based materials for reducing foodborne Pathogens: A review. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125915. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.D.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Z.W.; Kühnert, I.; Wang, Y. Selective localization of carbon nanotubes and its effect on the structure and properties of polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 123, 101471. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Okada, K.; Sodenaga, M.; Hikima, Y.; Ohshima, M.; Sekiguchi, T.; Yano, H. Effect of surface modification on the dispersion, rheological behavior, crystallization kinetics, and foaming ability of polypropylene/cellulose nanofiber nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Yang, L.; Sun, S.; Zheng, Q. Effect of agglomeration on the selective distribution of nanoparticles in binary polymer blends. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, J. The influence of additives on the stability behavior of electrolyte, discharges and PEO films characteristics. J. Alloy. Comp. 2010, 493, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulami, Q.A.; Rajeh, A. Synthesis of the SWCNTs/TiO2 nanostructure and its effect study on the thermal, optical, and conductivity properties of the CMC/PEO blend. Results Phys. 2021, 28, 104675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, S.; Li, J.; Michael Davidson, P.; Kit, K. Physical, mechanical, and antibacterial properties of chitosan/PEO blend films. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soraya, W.; Autchara, P.; Napassorn, P.; Thananchai, P.; Wanvimol, P. Strengthened silk-fibroin/poly(ethylene oxide) nonwoven nanofibers: A dual green process using pure water for electrospinning and electron beam-assisted cross-linking. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2653–2672. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, A.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Poly(ethylene oxide)-promoted dispersion of graphene nanoplatelets and its effect on the properties of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) based nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2019, 253, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qi, C.; Li, Y.; Tao, H. The degradation investigation of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blend: Thermal stability, mechanical properties and PALS analysis. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 180, 109239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Feng, L.; Bian, X.; Li, G.; Chen, X. Evaluation of PLA content in PLA/PBAT blends using TGA. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dil, E.J.; Carreau, P.J.; Favis, B.D. Morphology, miscibility and continuity development in poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Polymer 2015, 68, 202–212. [Google Scholar]
- Dil, E.J.; Virgilio, N.; Favis, B.D. The effect of the interfacial assembly of nano-silica in poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends on morphology, rheology and mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 85, 6352–6646. [Google Scholar]
- Urquijoa, J.; Aranburua, N.; Dagréoub, S.; Guerrica-Echevarríaa, G.; Eguiazábal, J.I. CNT-induced morphology and its effect on properties in PLA/PBAT-based nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 93, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguet, A.; Cassagnau, P.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M. Structuration, selective dispersion and compatibilizing effect of (nano) fillers in polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1526–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Carreau, P.J.; Taguet, A. Morphological and rheological properties of PLA, PBAT, and PLA/PBAT blend nanocomposites containing CNCs. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Wu, Y.; Tang, W.; Song, S.; Yao, J.; Wen, Z.; Lu, L.; Savilov, S.V.; Hu, N.; Molenda, J. Preparation of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte via in situ synthesis of SiO2 nanoparticles in PEO. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yang, J.; Zhao, H.; He, H.; Hu, M.; Xie, S. Preparation methods of polypropylene/nano-silica/styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene composite and its effect on electrical properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; He, B.; Guo, W.; Hua, L.; Yang, Q. Effects of nano-CaCO3 content on the crystallization, mechanical properties, and cell structure of PP nanocomposites in microcellular injection molding. Polymers 2018, 10, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Okada, K.; Hikima, Y.; Ohshima, M.; Sekiguchi, T.; Yano, H. Effect of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) surface treatment on cellular structures and mechanical properties of polypropylene/CNF nanocomposite foams via core-back foam injection molding. Polymers 2019, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.T.; Zhou, C.H.; Kabwe, F.B.; Wu, Q.Q.; Li, C.S.; Zhang, J.R. Exfoliation of montmorillonite and related properties of clay/polymer nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 169, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavliňáková, V.; Fohlerová, Z.; Pavliňák, D.; Khunová, V.; Vojtová, L. Effect of halloysite nanotube structure on physical, chemical, structural and biological properties of elastic polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofibers for wound healing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Bai, L.; Trifkovic, M.; Cheng, X.; Macosko, C.W. Controlling the morphology of immiscible cocontinuous polymer blends via silica nanoparticles jammed at the interface. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3911–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Tang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Yan, X. Preparation and characterization of PEO-PMMA polymer composite electrolytes doped with nano-Al2O3. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essabir, H.; Raji, M.; Essassi, E.M.; Rodrigue, D.; Bouhfid, R. Morphological, thermal, mechanical, electrical and magnetic properties of ABS/PA6/SBR blends with Fe3O4 nano-particles. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17120–17130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, T.; Xie, S.; Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Tian, Q.; Tu, C.; Yan, W. Influence of organo-sepiolite on the morphological, mechanical, and rheological properties of PP/ABS blends. Polymers 2019, 11, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Xie, J.; Li, T.; Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Tian, Q.; Tu, C.; Yan, W. Surface modification of sepiolite: Effects on thermomechanical properties of PP/PA6 blends. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xie, P.; Yang, Z.; Luo, G.; Huang, W.; Tian, Q.; Tu, C.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Yan, W. Flame-retardant behaviors of aluminum phosphates coated sepiolite in epoxy resin. J. Fire Sci. 2021, 39, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.; Ni, L.; Huo, P.; Lu, Z.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Yan, Y. Preparation high photocatalytic activity of CdS/halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) nanocomposites with hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Jiang, G.H.; Ding, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.K.; Wang, X.H.; Chen, W.X. Photocatalytic activity of heterostructures based on TiO2 and halloysite nanotubes. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4154–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.F.; Qian, D.Y.; Wu, D.L.; Ma, X.F. Magnetic halloysite nanotubes/iron oxide composites for the adsorptionof dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Wu, J. Halloysite nanotubes (HNTs)@ZIF-67 composites—a new type of heterogeneous catalyst for the Knoevenagel condensation reaction. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 17621–17628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, B.; Kakkarakkal Kottiyath, V.; Kapur, G.S.; Kant, S.; Choudhary, V. Morphological studies and thermo-mechanical behavior of polypropylene/sepiolite nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, E285–E294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Fang, J.; Zheng, M.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, C. Morphology evolution and rheological behaviors of PP/SR thermoplastic vulcanizate. Polymers 2019, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Brosse, N.; Pizzi, A.; Hoppe, S.; Xi, X.; Zhou, X. Polypropylene blend with polyphenols through dynamic vulcanization: Mechanical, rheological, crystalline, thermal, and UV protective property. Polymers 2019, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sundararaj, U. Thermal, rheological, and mechanical behaviors of LLDPE/PEMA/clay nanocomposites: Effect of interaction between polymer, compatibilizer, and nanofiller. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanavaz, R.; Razavi Aghjeh, M.K.; Babaluo, A.A. Rheology, morphology, and thermal behavior of HDPE/clay nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2010, 31, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Designation | HNTs (g) | Al(OH)3 (g) | H3PO4 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HNTs@AlPO4I | 10 | 0.58 | 4.33 |
| HNTs@AlPO4II | 10 | 1.17 | 8.67 |
| HNTs@AlPO4III | 10 | 1.75 | 13.00 |
| HNTs@AlPO4IV | 10 | 2.33 | 17.33 |
| Sample Designation | PEO (g) | PBAT (g) | HNTs@AlPO4 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEO/PBAT | 2.8 | 1.2 | 0 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO41 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 0.04 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO43 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 0.12 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO45 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 0.20 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO47 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 0.28 |
| Sample Designation | T0 (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Carbon Residue (wt.%) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO/PBAT | 307.59 | 401.40 | 6.18 | 61.29 | 36.24 | 86.62 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO41 | 309.09 | 401.67 | 9.45 | 61.72 | 36.45 | 88.74 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO43 | 310.59 | 401.78 | 10.18 | 61.89 | 36.52 | 86.20 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO45 | 309.83 | 401.86 | 11.80 | 61.98 | 36.98 | 88.44 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO47 | 308.42 | 401.37 | 13.07 | 61.97 | 34.32 | 89.07 |
| Sample Designation | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEO/PBAT | 3.59 ± 0.08 | 202.72 ± 6.81 | 49.23 ± 3.85 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO41 | 3.82 ± 0.12 | 238.82 ± 7.35 | 54.32 ± 3.61 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO43 | 4.52 ± 0.09 | 241.03 ± 8.18 | 66.20 ± 4.23 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO45 | 3.68 ± 0.15 | 252.51 ± 7.64 | 71.32 ± 4.57 |
| PEO/PBAT/o-HNTs@AlPO47 | 2.52 ± 0.21 | 187.57 ± 8.56 | 47.22 ± 4.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Jin, X.; He, X.; Huang, W.; Tian, Q.; Fu, Q.; Yan, W. Synthesis of Aluminum Phosphate-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes: Effects on Morphological, Mechanical, and Rheological Properties of PEO/PBAT Blends. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12172896
Wang K, Jin X, He X, Huang W, Tian Q, Fu Q, Yan W. Synthesis of Aluminum Phosphate-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes: Effects on Morphological, Mechanical, and Rheological Properties of PEO/PBAT Blends. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(17):2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12172896
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kui, Xuefei Jin, Xiuhong He, Weijiang Huang, Qin Tian, Qiuping Fu, and Wei Yan. 2022. "Synthesis of Aluminum Phosphate-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes: Effects on Morphological, Mechanical, and Rheological Properties of PEO/PBAT Blends" Nanomaterials 12, no. 17: 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12172896
APA StyleWang, K., Jin, X., He, X., Huang, W., Tian, Q., Fu, Q., & Yan, W. (2022). Synthesis of Aluminum Phosphate-Coated Halloysite Nanotubes: Effects on Morphological, Mechanical, and Rheological Properties of PEO/PBAT Blends. Nanomaterials, 12(17), 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12172896







