Formation of Nano-Fibrous Patterns on Aluminum Substrates via Photolithographic Fabrication of Electrospun Photosensitive Polyimide Fibrous Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
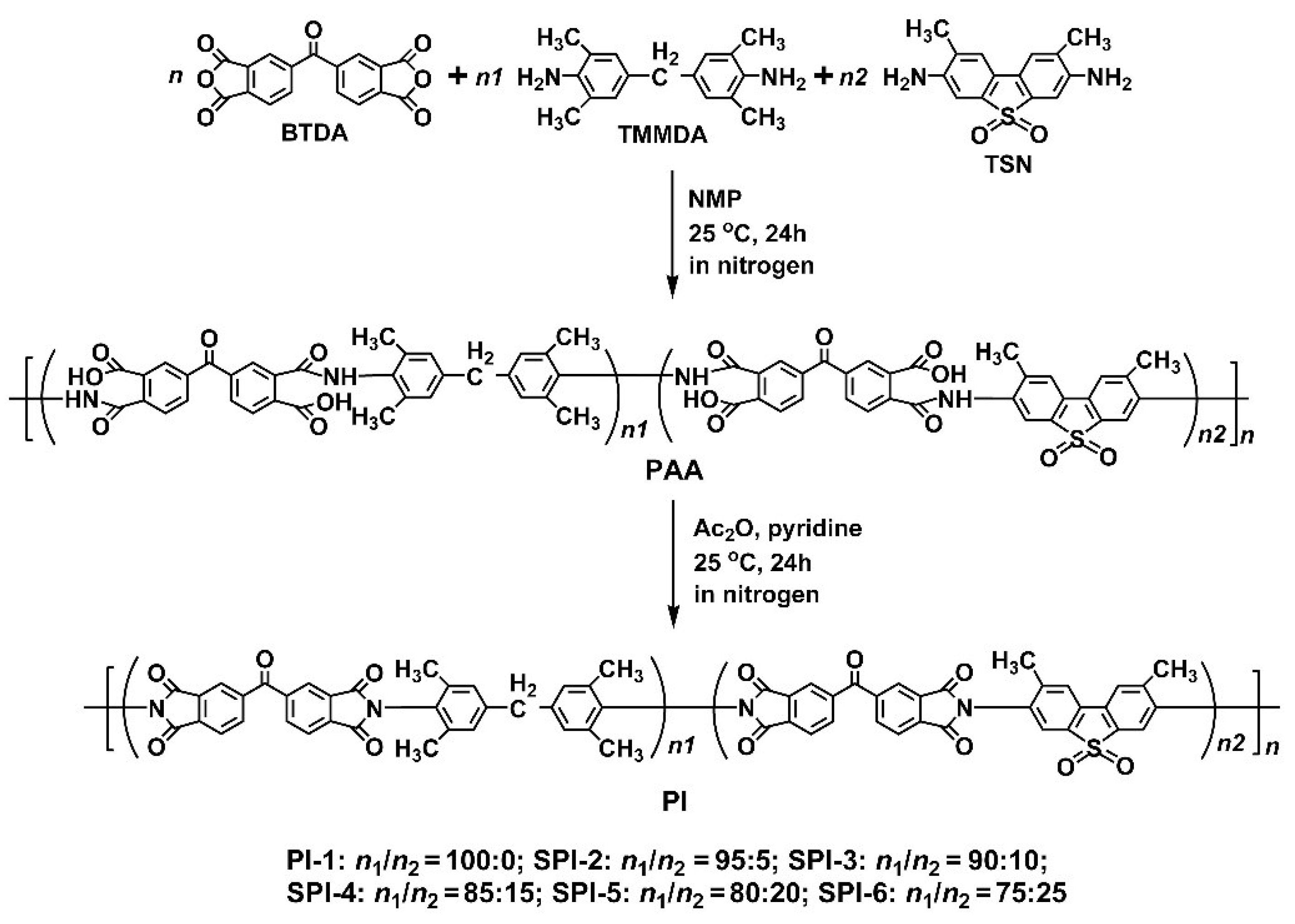
2.3. Synthesis of Photosensitive PI Resins
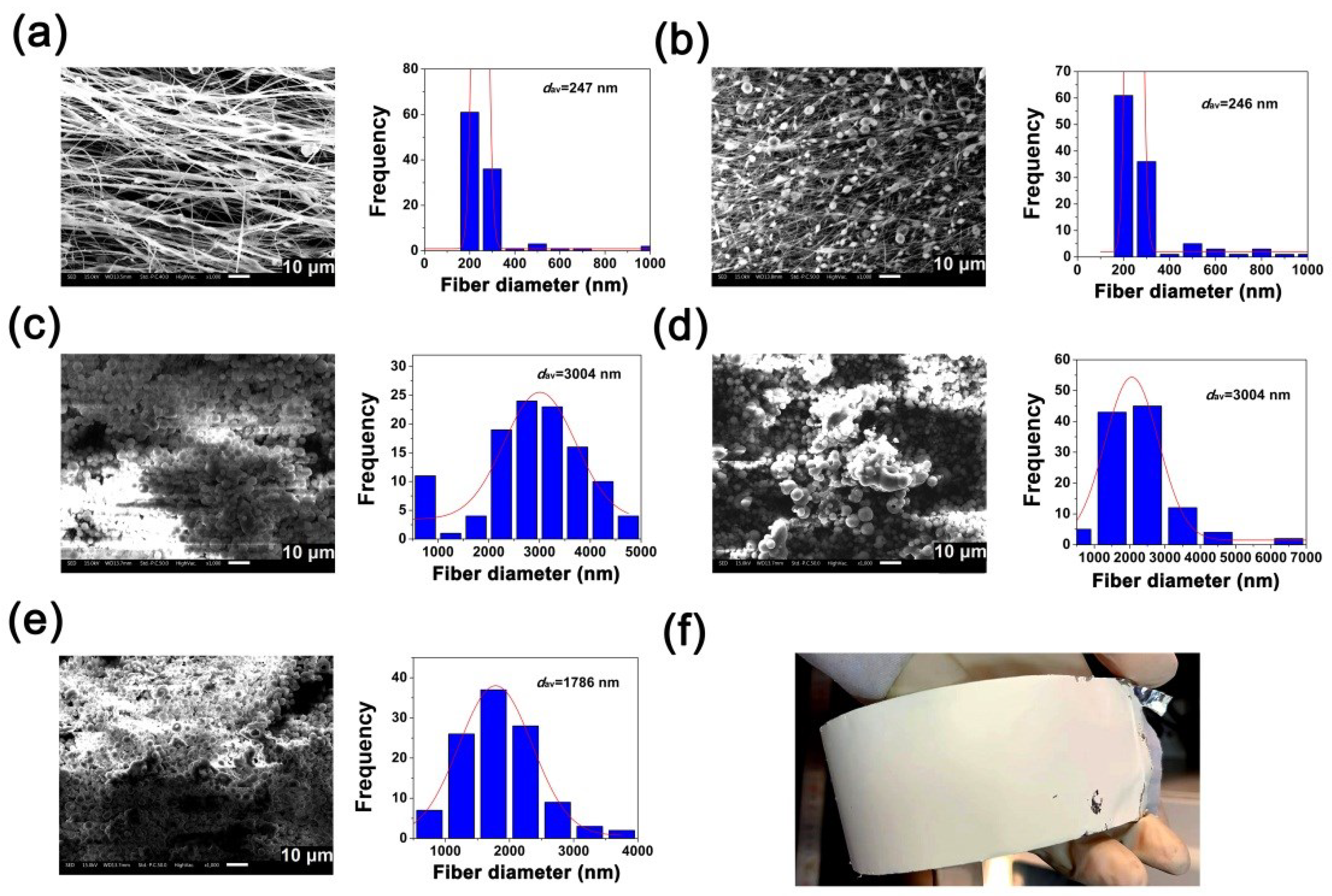
2.4. Fabrication of PI NFMs via Electrospinning
3. Results and Discussion
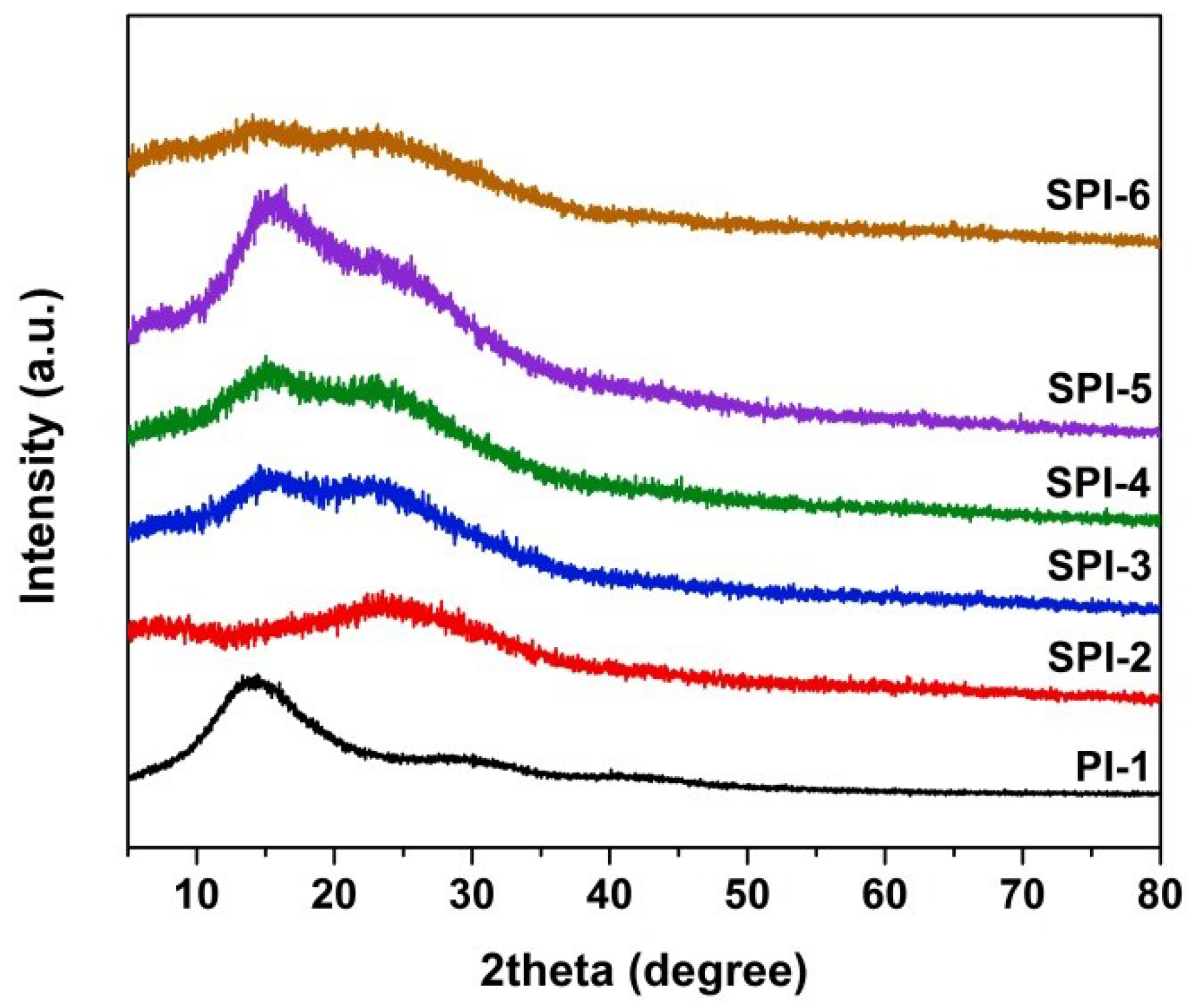
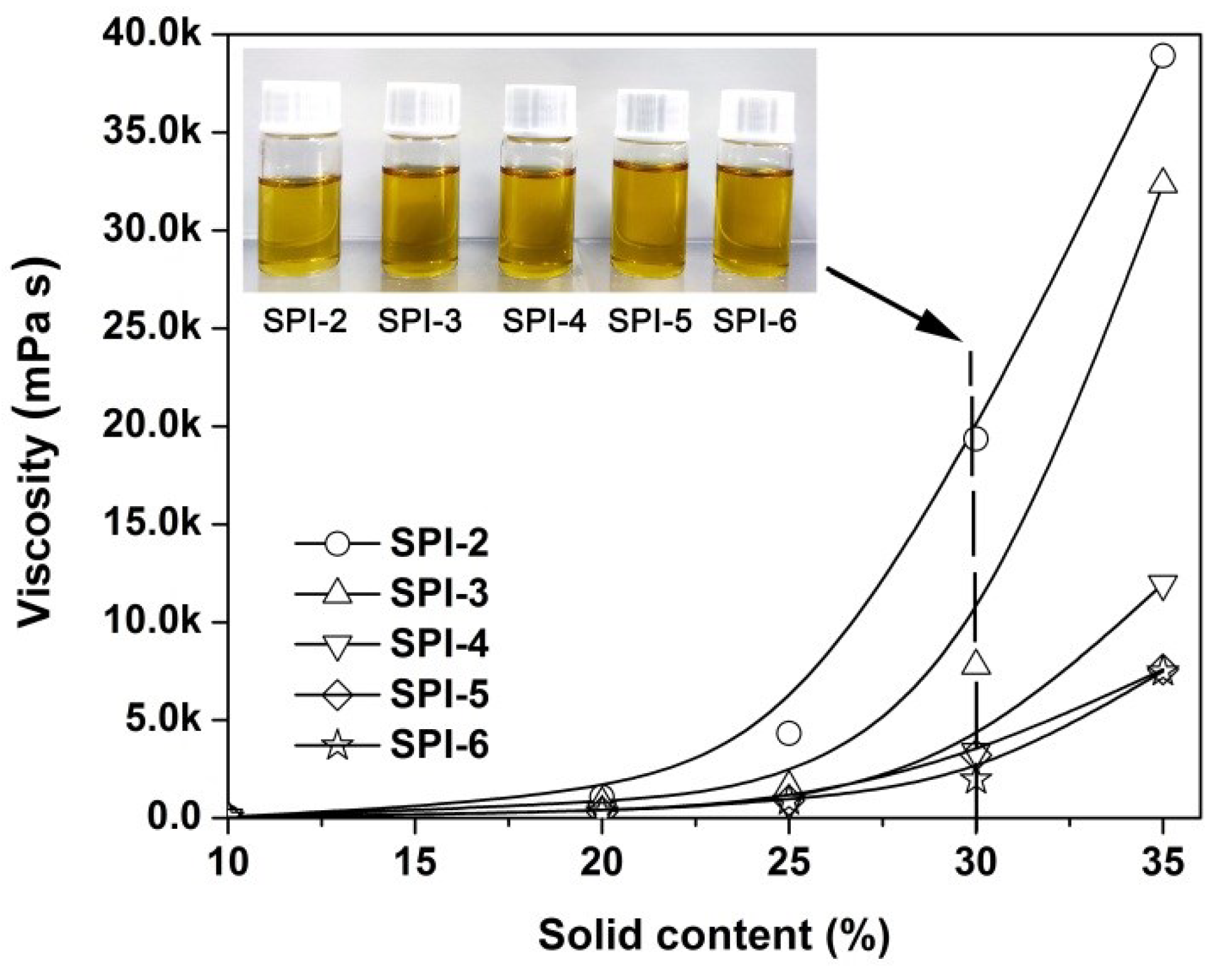
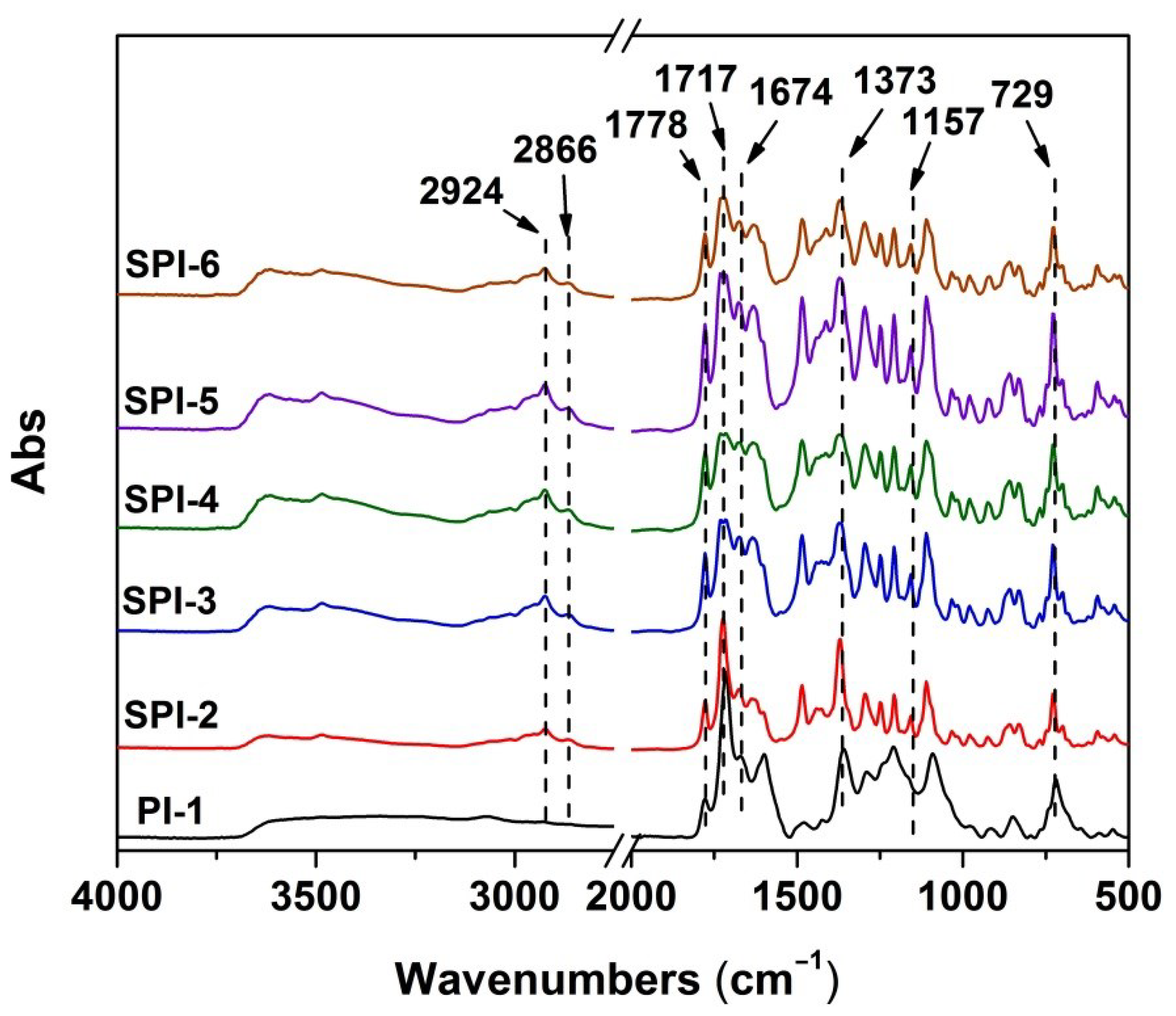
3.1. PI Resin Synthesis and Electrospun PI NFMs Preparation
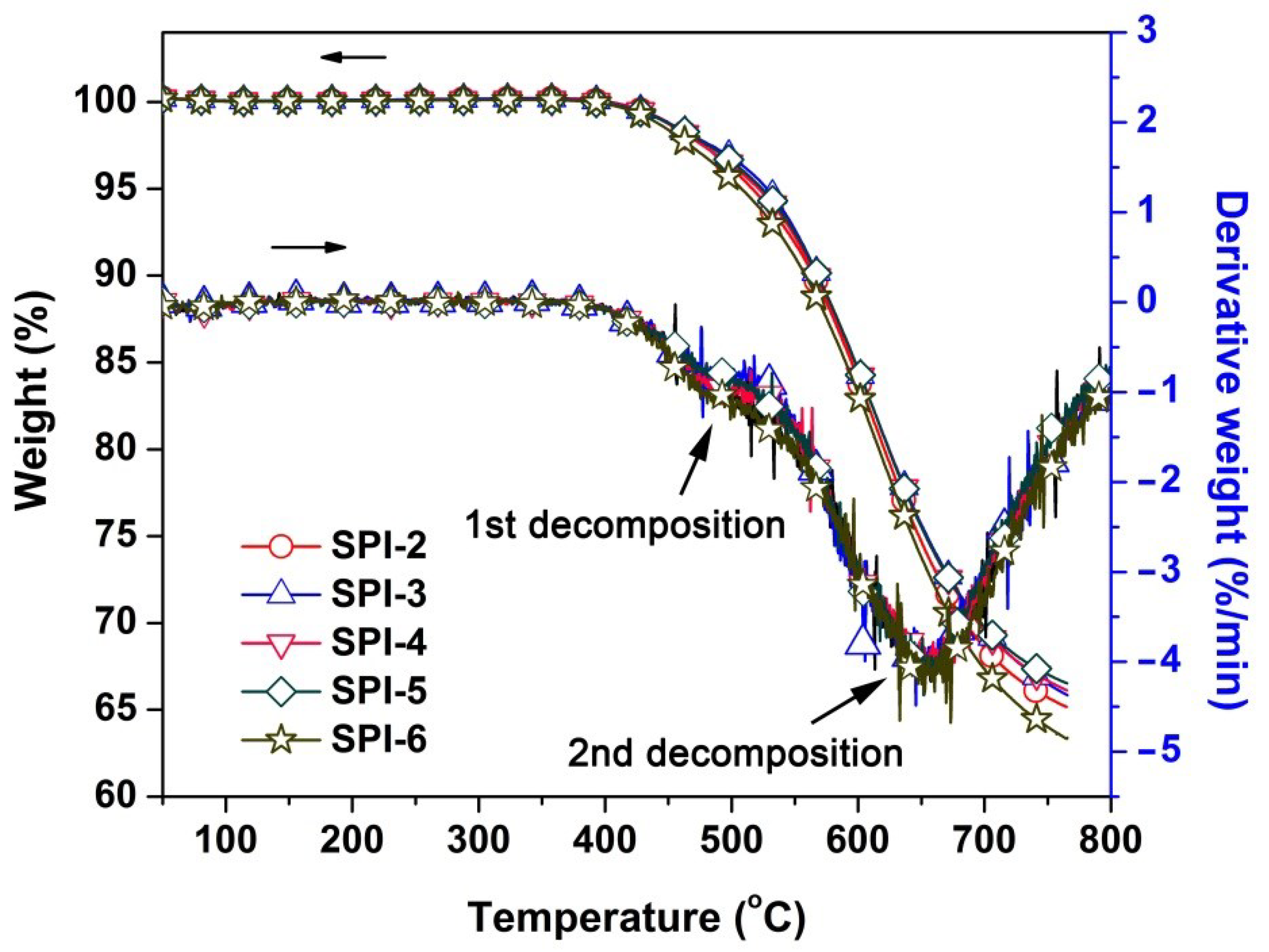
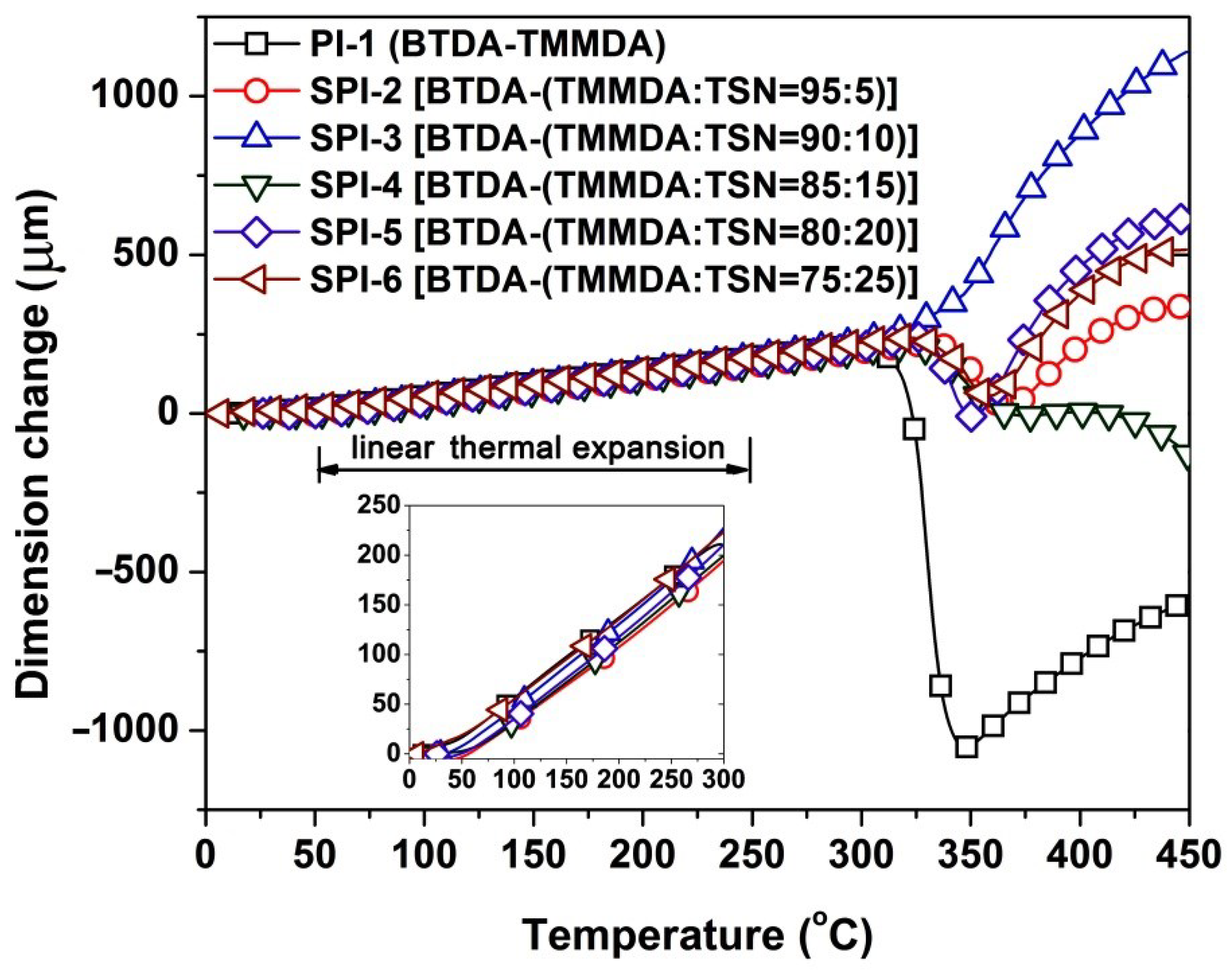
3.2. Thermal Properties
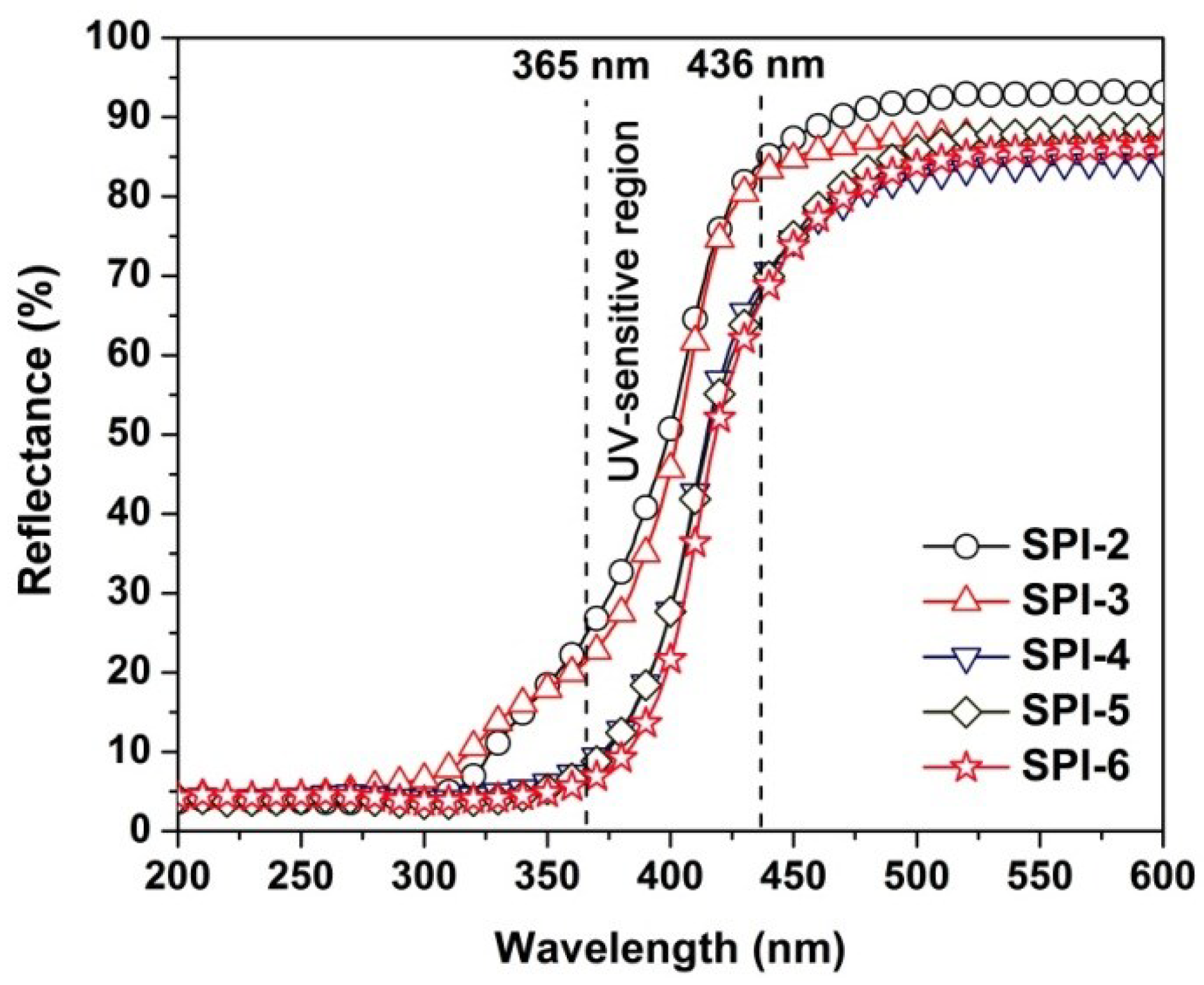
3.3. Optical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, J.; Miyauchi, M.; Simmons, T.J.; Dordick, J.S.; Linhardt, R.J. Electrospinning of nanomaterials and applications in electronic components and devices. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 5507–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, K.Q. Electrospun nanofibers for optical applications. In Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; Ding, B., Wang, X., Yu, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 603–617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, S.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun functional nanofiber membrane for antibiotic removal in water: Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suja, P.S.; Reshmi, C.R.; Sagitha, P.; Sujith, A. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes for water purification. Polym. Rev. 2017, 57, 467–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.H.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: Fabrication, modification and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 77, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mishra, P.; Verma, K.; Mondal, A.; Chaudhary, R.G.; Abolhasani, M.M.; Loganathan, S. Electrospinning production of nanofibrous membranes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 767–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Liu, L.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun flexible nanofibrous membranes for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20075–20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, Y. Progress of improving mechanical strength of electrospun nanofibrous membranes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Tanioka, A. Functionality in electrospun nanofibrous membranes based on Fiber’s size, surface area, and molecular orientation. Membranes 2011, 1, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for wastewater treatment applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Venkateswaran, S.; Hsiao, B.S. Ultra-fine electrospun nanofibrous membranes for multicomponent wastewater treatment: Fitration and adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagitha, P.; Reshmi, C.R.; Sundaran, S.P.; Sujith, A. Recent advances in post-modification strategies of polymeric electrospun membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 105, 227–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green electrospun nanofbers and their application in air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Kai, D.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun photosensitive nanofibers: Potential for photocurrent therapy in skin regeneration. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2013, 12, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tian, S.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, D. Highly sensitive photoresponsive polyamide 6 nanofibrous membrane containing embedded spiropyran. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 18775–18794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, M.; Ahmed, F.; Ali, S.; Mehdi, M.; Ullah, S.; Duy-Nam, P.; Khatri, Z.; Kim, I.S. Photosensitive nanofibers for data recording and erasing. J. Textile Inst. 2021, 112, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Guo, C.Y.; Huangfu, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhi, X.X.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, X.M. Highly solvent-stable polyimide ultrafine fibrous membranes fabricated by a novel ultraviolet-assisted electrospinning technique via organo-soluble intrinsically negative phtosensitive varnishes. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2021, 15, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, J.G.; Yang, Y.; Guo, C.Y.; Huangfu, M.G.; Zhang, Y. Solvent-resistant ultrafine nonwoven fibrous membranes by ultraviolet-assisted electrospinning of organo-soluble photosensitive polyimide resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Jia, Y.J.; An, Y.C.; Zhi, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.G.; Li, J.S. Photo-patternable, high-speed electrospun ultrafine fibers fabricated by intrinsically negative photosensitive polyimide. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 18458–18464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Guo, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.M.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, X.M. An ultraviolet-assisted electrospinning procedure of polyimide ultrafine fibrous membranes fabricated by ester-type negative photosensitive polyimide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 17647–17658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Guo, C.Y.; Huangfu, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L.M.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, X.M. Enhancement of solvent resistance of polyimide electrospun mat via the UV-assisted electrospinning and photosensitive varnish. Polymers 2019, 11, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Xie, J.; Sameen, D.E.; Ahmed, S.; Dai, J.; Qin, W.; Li, S.; Liu, Y. Electrospun antibacterial poly(vinyl alcohol)/Ag nanoparticles membrane grafted with 3,3′,4,4′-benzoophenone tetracarboxylic acid for efficient air filtration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 533, 147516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Vergaelen, M.; Schoolaert, E.; Hoogenboom, R.; Clerck, K.D. Effect of crosslinking stage on photocrosslinking of benzophenone functionalized poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) nanofibers obtained by aqueous electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goponenko, A.V.; Hou, H.Q.; Dzenis, Y.A. Avoiding fusion of electrospun 3,3′,4,4′- biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride-4,4′-oxydianiline copolymer nanofibers during conversion to polyimide. Polymer 2011, 52, 3776–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.L.; Wang, D.Y.; Du, H.P.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, X.M. Reduced coefficients of linear thermal expansion of colorless and transparent semi-alicyclic polyimide films via incorporation of rigid-rod amide moiety: Preparation and properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.A.; Sastri, V.R.; Tesoro, G.; Reiser, A.; Eachus, R. On the cross-linking mechanism of benzophenone-containing polyimides. Macromolecules 1985, 21, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, O.; Smolka, P.; Falcigno, P.A. Novel auto-photosensitive polyimides with tailored properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1992, 32, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, L.; Wu, L.; Jiang, G.; Liu, J. Preimidized auto-photosensitive polyimides containing methyl-substituted benzanilide units with increased high-temperature dimensional stability for advanced optical applications: Preparation and properties. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.G.; Ge, Z.Y.; Li, Z.X.; He, M.H.; Liu, J.G.; Pang, Z.Z.; Fan, L.; Yang, S.Y. Synthesis and characterization of new inherent photoimageable polyimides based on fluorinated tetramethyl-substituted diphenylmethanediamines. Polymer 2002, 43, 6057–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.P.; Chen, R.S.; Chiang, H.C. Organosoluble and light-colored fluorinated polyimides based on 1,2-bis(4-amino-2-trifluoromethylphenoxy)benzene and aromatic dianhydrides. Polym. J. 2003, 35, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


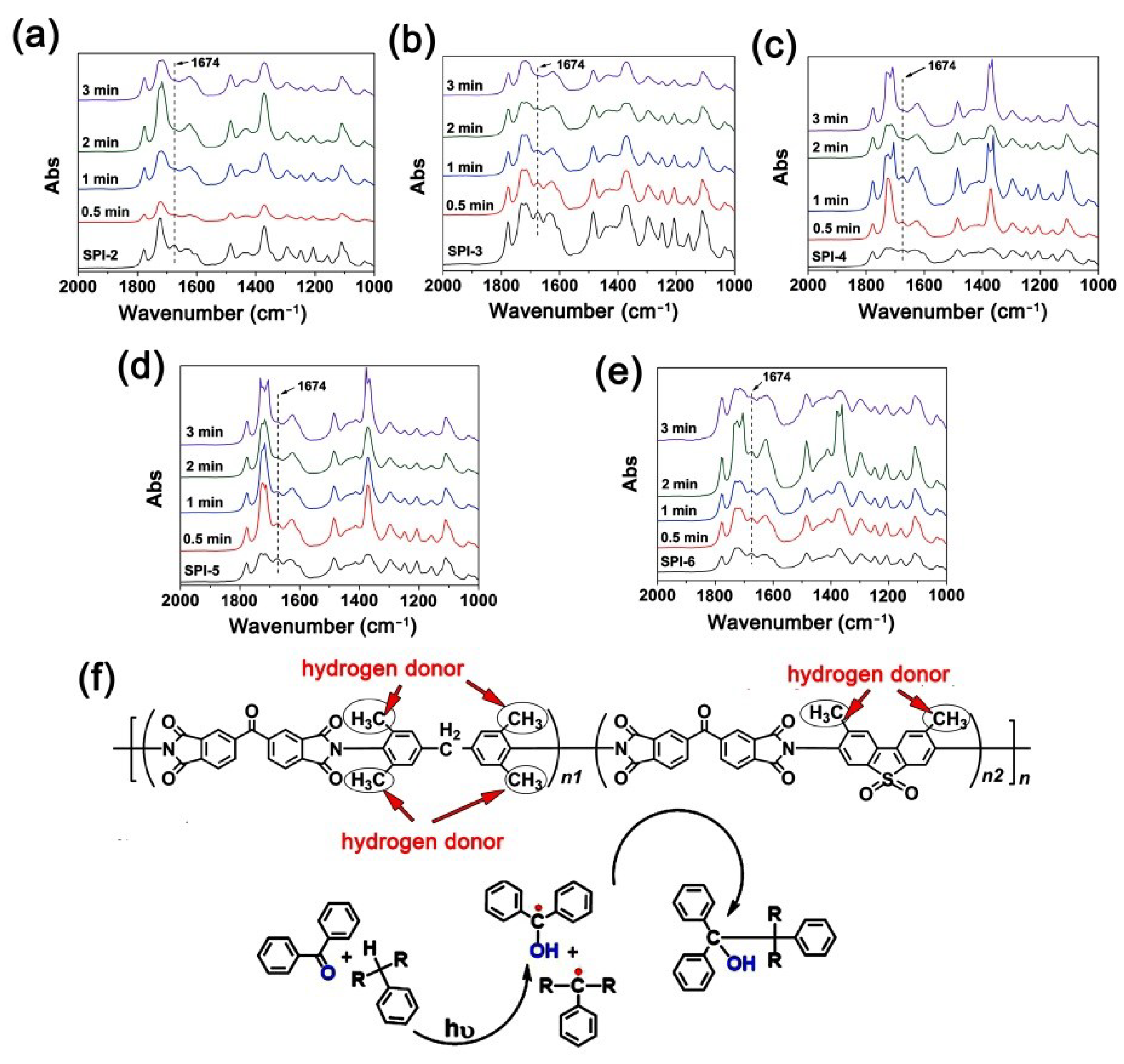

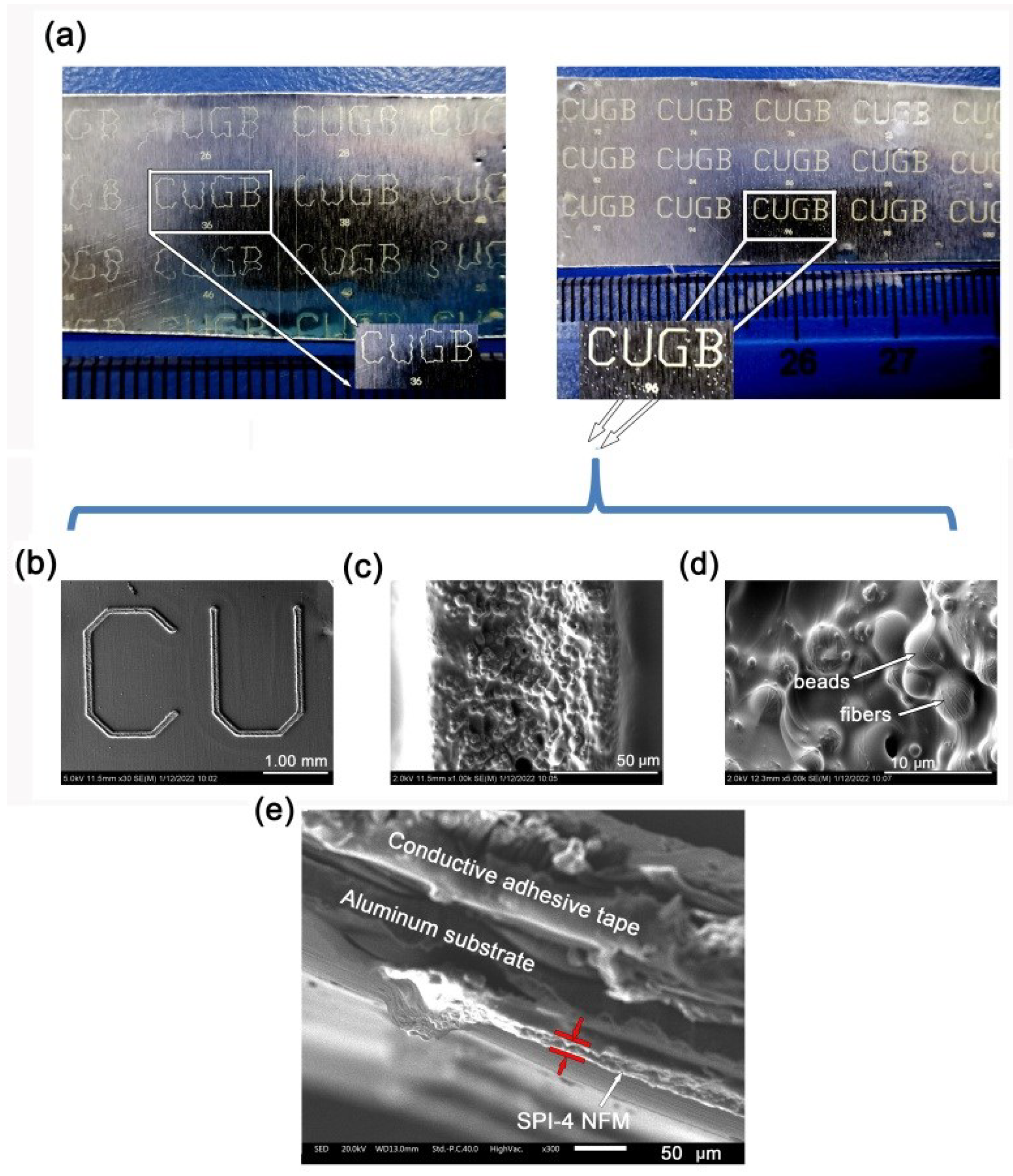
| PI | BTDA (g, mol) | TMMDA (g, mol) | TSN (g, mol) | NMP (g) | Ac2O (g, mol) | Pyridine (g, mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI-1 | 16.1115, 0.05 | 12.7185, 0.05 | 0 | 69.2 | 25.5, 0.25 | 15.8, 0.20 |
| SPI-2 | 16.1115, 0.05 | 12.0826, 0.0475 | 0.6859, 0.0025 | 86.6 | 25.5, 0.25 | 15.8, 0.20 |
| SPI-3 | 16.1115, 0.05 | 11.4467, 0.0450 | 1.3717, 0.0050 | 86.8 | 25.5, 0.25 | 15.8, 0.20 |
| SPI-4 | 16.1115, 0.05 | 10.8107, 0.0425 | 2.0576, 0.0075 | 86.9 | 25.5, 0.25 | 15.8, 0.20 |
| SPI-5 | 16.1115, 0.05 | 10.1748, 0.0400 | 2.7434, 0.0100 | 87.1 | 25.5, 0.25 | 15.8, 0.20 |
| SPI-6 | 16.1115, 0.05 | 9.5389, 0.0375 | 3.4293. 0.0125 | 87.2 | 25.5, 0.25 | 15.8, 0.20 |
| (η)inh 1 (dL g−1) | Molecular Weight 2 | Solubility 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn (×104 g mol−1) | Mw (×104 g mol−1) | PDI | NMP | DMAc | GBL | CPA | THF | ||
| PI-1 | 1.00 | 5.06 | 8.98 | 1.77 | ++ | ++ | − | ++ | ++ |
| SPI-2 | 0.78 | 4.70 | 8.83 | 1.88 | ++ | ++ | − | ++ | ++ |
| SPI-3 | 0.62 | 3.80 | 6.97 | 1.83 | ++ | ++ | − | ++ | ++ |
| SPI-4 | 0.56 | 3.43 | 6.03 | 1.76 | ++ | ++ | − | ++ | + |
| SPI-5 | 0.50 | 3.16 | 5.46 | 1.73 | ++ | ++ | − | ++ | + |
| SPI-6 | 0.47 | 2.87 | 5.13 | 1.79 | ++ | ++ | − | ++ | + |
| Tg 1 (°C) | T5% 2 (°C) | T10% 2 (°C) | Rw750 3 (%) | CTE 4 (×10−6/K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI-1 | 347.6 | 530.2 | 568.5 | 72.3 | 56.5 |
| SPI-2 | 366.7 | 516.4 | 564.6 | 65.7 | 55.7 |
| SPI-3 | 337.6 | 527.8 | 568.4 | 66.5 | 54.0 |
| SPI-4 | 366.2 | 521.6 | 566.3 | 66.7 | 53.3 |
| SPI-5 | 351.1 | 524.0 | 568.1 | 67.0 | 51.0 |
| SPI-6 | 359.6 | 507.6 | 558.3 | 64.0 | 50.9 |
| R365 1 (%) | R436 1 (%) | L* 2 | a* 2 | b* 2 | WI 3 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI-1 | 34.2 | 85.3 | 91.98 | −1.31 | 6.34 | 89.69 |
| SPI-2 | 24.4 | 84.0 | 93.23 | −1.65 | 5.25 | 91.28 |
| SPI-3 | 21.1 | 82.5 | 93.17 | −1.65 | 6.26 | 90.59 |
| SPI-4 | 8.2 | 68.7 | 89.36 | −2.87 | 9.73 | 85.30 |
| SPI-5 | 7.6 | 69.8 | 90.72 | −3.37 | 11.72 | 84.68 |
| SPI-6 | 6.1 | 66.4 | 89.72 | −3.42 | 11.82 | 83.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.-s.; Ren, X.; Du, X.-z.; Wang, Z.-z.; He, Z.-b.; Yuan, S.-q.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, X.-x.; Liu, J.-g. Formation of Nano-Fibrous Patterns on Aluminum Substrates via Photolithographic Fabrication of Electrospun Photosensitive Polyimide Fibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162745
Gao Y-s, Ren X, Du X-z, Wang Z-z, He Z-b, Yuan S-q, Pan Z, Zhang Y, Zhi X-x, Liu J-g. Formation of Nano-Fibrous Patterns on Aluminum Substrates via Photolithographic Fabrication of Electrospun Photosensitive Polyimide Fibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162745
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yan-shuang, Xi Ren, Xuan-zhe Du, Zhen-zhong Wang, Zhi-bin He, Shun-qi Yuan, Zhen Pan, Yan Zhang, Xin-xin Zhi, and Jin-gang Liu. 2022. "Formation of Nano-Fibrous Patterns on Aluminum Substrates via Photolithographic Fabrication of Electrospun Photosensitive Polyimide Fibrous Membranes" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162745
APA StyleGao, Y.-s., Ren, X., Du, X.-z., Wang, Z.-z., He, Z.-b., Yuan, S.-q., Pan, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhi, X.-x., & Liu, J.-g. (2022). Formation of Nano-Fibrous Patterns on Aluminum Substrates via Photolithographic Fabrication of Electrospun Photosensitive Polyimide Fibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162745







