Removal of Methylene Blue by Crosslinked Egg White Protein/Graphene Oxide Bionanocomposite Aerogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of GO
2.3. Preparation of PGO Aerogels
2.4. Characterization of the Aerogels
2.5. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
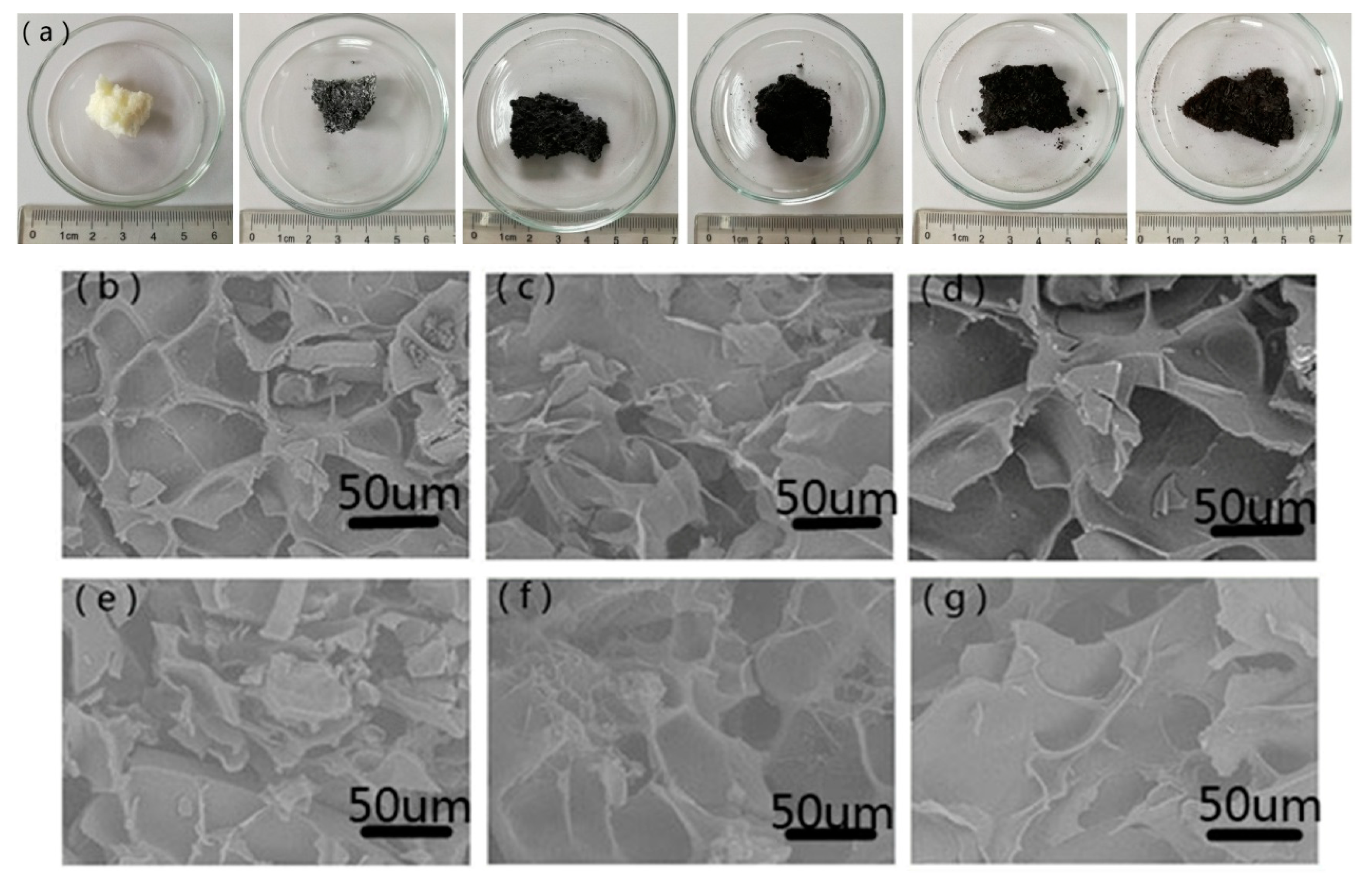
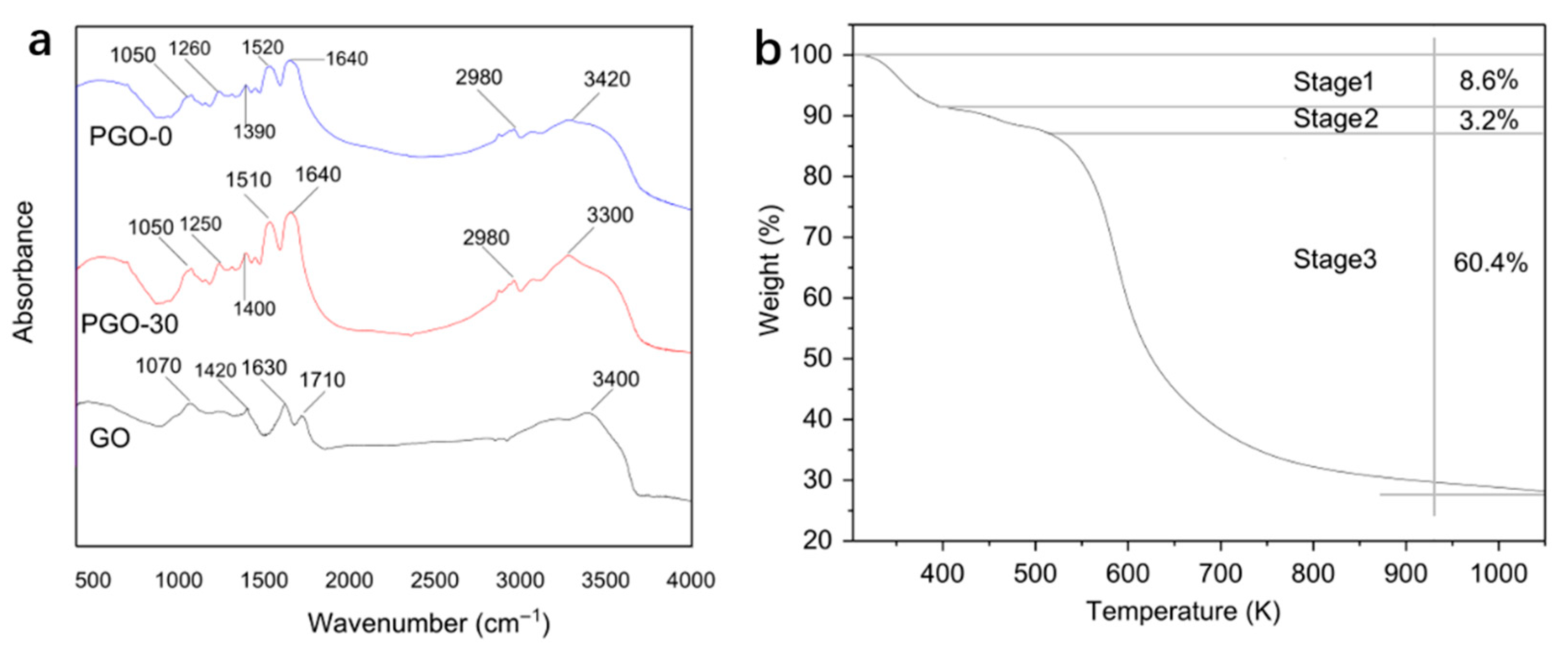
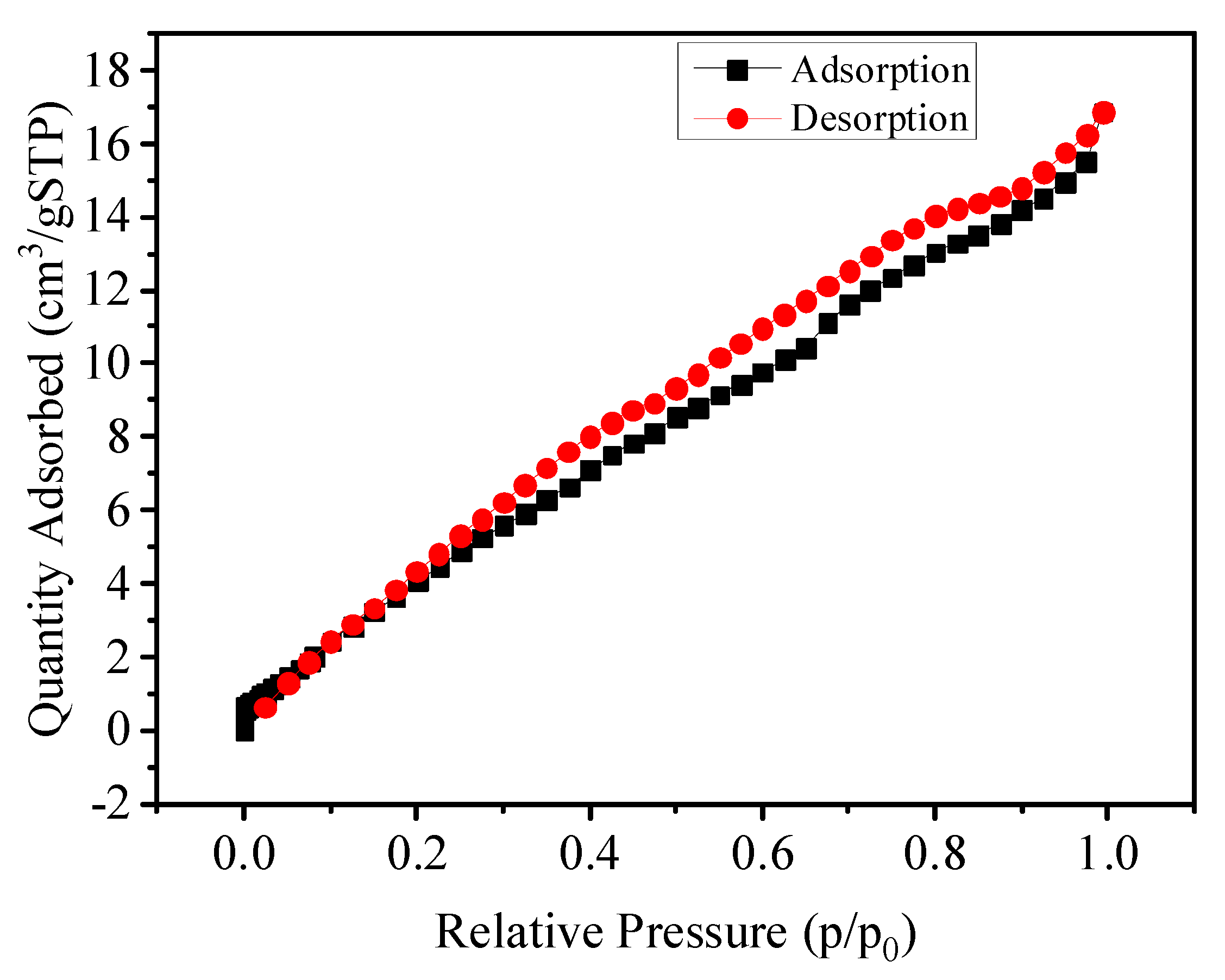
3.1. Characterization of the Samples
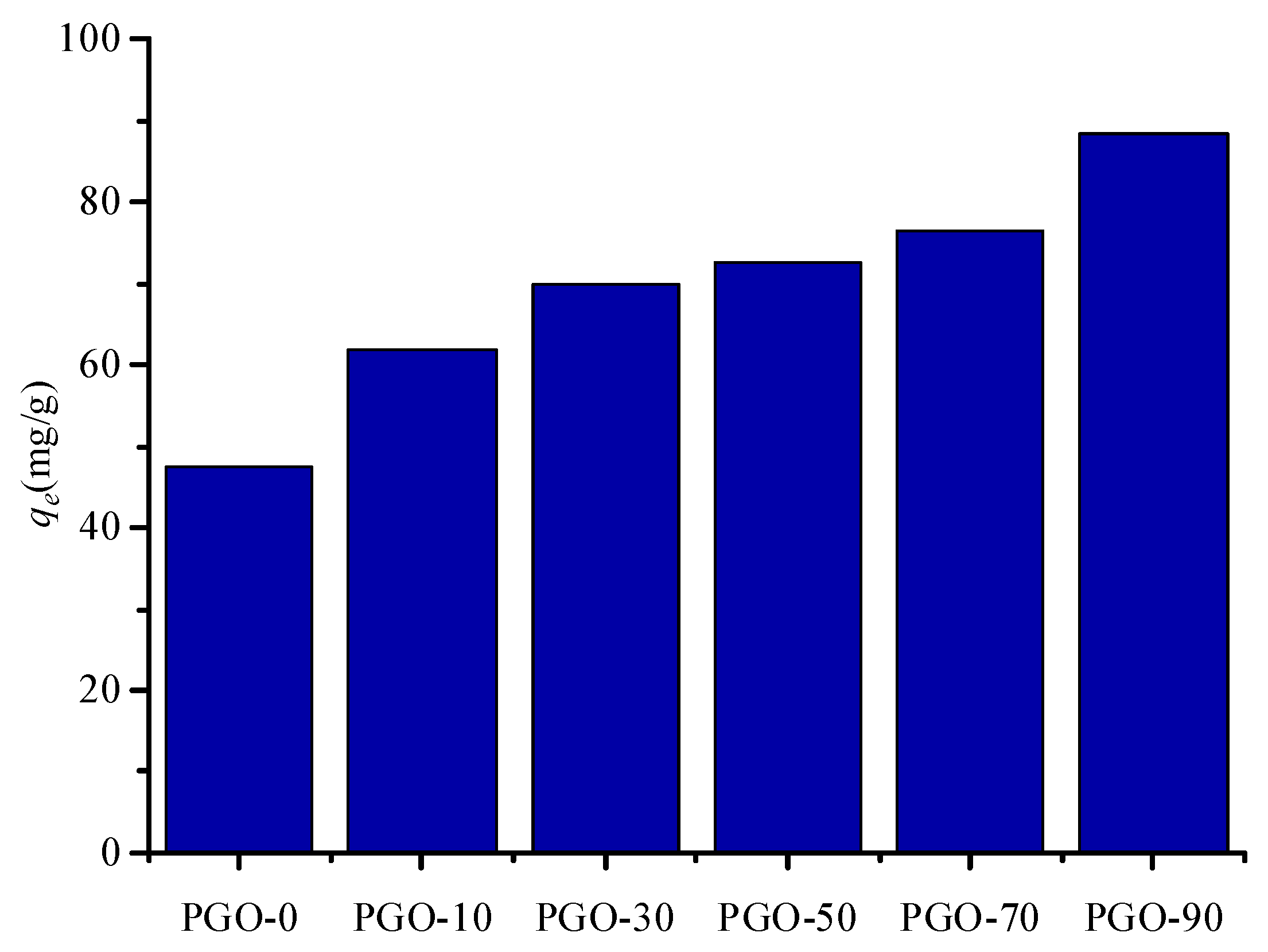
3.2. Adsorption of MB
3.2.1. Effect of Initial pH
3.2.2. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.2.3. Effect of Temperature
3.2.4. Effect of Contact Time
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
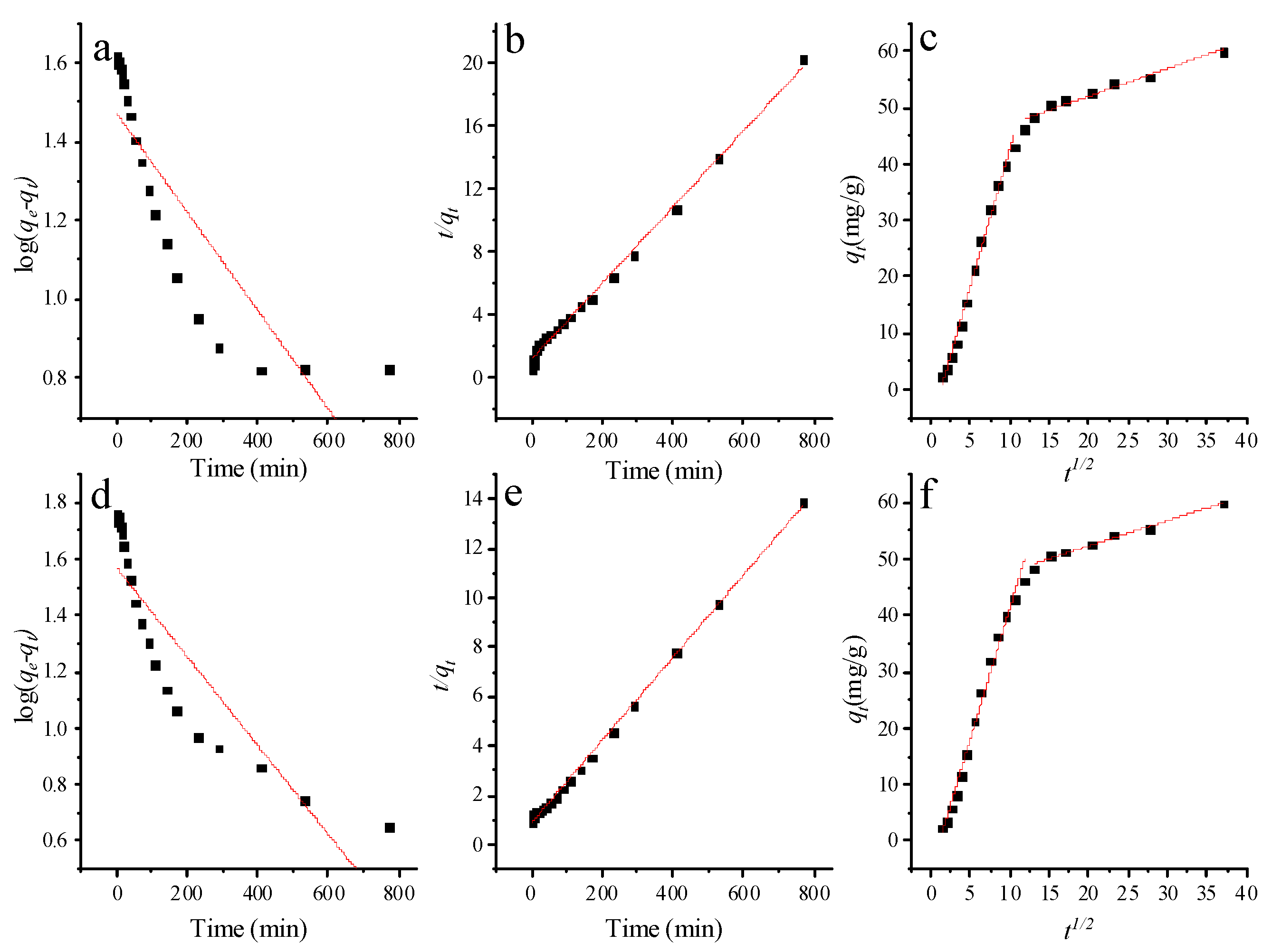
3.4. Kinetic Studies
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamic
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, M.H.; Sun, G. Antimicrobial cationic dyes: Part 2—Thermal and hydrolytic stability. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 63, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methneni, N.; Morales-González, J.A.; Jaziri, A.; Ben Mansour, H.; Fernandez-Serrano, M. Persistent organic and inorganic pollutants in the effluents from the textile dyeing industries: Ecotoxicology appraisal via a battery of biotests. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscusi, G.; Lamberti, E.; Gorrasi, G. Hemp fibers modified with graphite oxide as green and efficient solution for water remediation: Application to methylene blue. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Sun, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K.; et al. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Padhi, D.K.; Parida, K. Visible light driven LaFeO3 nano sphere/RGO composite-photocatalysts for efficient water decomposition reaction. Catal. Today 2020, 353, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cseri, L.; Topuz, F.; Abdulhamid, M.A.; Alammar, A.; Budd, P.M.; Szekely, G. Electrospun Adsorptive Nanofibrous Membranes from Ion Exchange Polymers to Snare Textile Dyes from Wastewater. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paździor, K.; Bilińska, L.; Ledakowicz, S. A review of the existing and emerging technologies in the combination of AOPs and biological processes in industrial textile wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Mei, Y.; Pan, B. Treatment of reverse-osmosis concentrate of printing and dyeing wastewater by electro-oxidation process with controlled oxidation-reduction potential (ORP). Chemosphere 2018, 201, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McYotto, F.; Wei, Q.; Macharia, D.K.; Huang, M.; Shen, C.; Chow, C.W. Effect of dye structure on color removal efficiency by coagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Cui, M.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y. Barium alginate as a skeleton coating graphene oxide and bentonite-derived composites: Excellent adsorbent based on predictive design for the enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Du, Q.; Sui, K.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Xia, Y. Filtration and adsorption properties of porous calcium alginate membrane for methylene blue removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, T.; Naushad, M.; Eldesoky, G.E.; Al-Saeedi, S.I.; Nafady, A.; Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, A. Effective and fast adsorptive removal of toxic cationic dye (MB) from aqueous medium using amino-functionalized magnetic multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 282, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber-Samandari, S.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Joneidi-Yekta, H.; Mohseni, M. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gelatin-based magnetic nanocomposite beads comprising carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeel, B.; Bussy, C.; Merino, S.; Vázquez, E.; Flahaut, E.; Mouchet, F.; Evariste, L.; Gauthier, L.; Koivisto, A.J.; Vogel, U.; et al. Safety Assessment of Graphene-Based Materials: Focus on Human Health and the Environment. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10582–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.-Q.; Cao, J.-P.; Dang, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Wei, X.-Y. Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Porous Carbon with High Oxygen Content Derived from Organic Waste Liquid with Superior Electric Double Layer Performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4037–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shi, M.; Lu, W.; Zhu, D.; Li, L.; Gan, L. Core-shell reduced graphene oxide/MnOx@carbon hollow nanospheres for high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, T.; Peng, Q. Graphene-based nanomaterials and their potentials in advanced drug delivery and cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaj, S.; Hubbard, W.; Reina, A.; Kong, J.; Branton, D.; Golovchenko, J.A. Graphene as a subnanometre trans-electrode membrane. Nature 2010, 467, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Gao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L. Metal/graphene oxide batteries. Carbon 2017, 125, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, C.; Wang, D.-W. Graphene oxide: An emerging electromaterial for energy storage and conversion. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 55, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, K.; Cao, A.; Wei, J.; Li, C.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, D. Graphene-On-Silicon Schottky Junction Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2743–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Dai, L. Graphene-based Schottky junction solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24224–24229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Sun, J.; Du, Q.; Yang, X.; Ji, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Xia, Y. Removal of methylene blue from water by cellulose/graphene oxide fibres. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xia, L. Highly effective removal of basic fuchsin from aqueous solutions by anionic polyacrylamide/graphene oxide aerogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 453, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yedinak, E.; Lou, J.; Ci, L. High performance agar/graphene oxide composite aerogel for methylene blue removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Elella, M.H.; Goda, E.S.; Gab-Allah, M.A.; Hong, S.E.; Pandit, B.; Lee, S.; Gamal, H.; Rehman, A.U.; Yoon, K.R. Xanthan gum-derived materials for applications in environment and eco-friendly materials: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xia, L. Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions by Polyvinyl Alcohol/Graphene Oxide Composites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saheed, I.O.; Da Oh, W.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Lu, Y. Highly Hydrophobic, Compressible, and Magnetic Polystyrene/Fe3O4/Graphene Aerogel Composite for Oil-Water Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5460–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidy, R.J.; Lam, V.; Fimognari, N.; Mamo, J.C.; Hackett, M.J. FTIR studies of the similarities between pathology induced protein aggregation in vivo and chemically induced protein aggregation ex vivo. Vib. Spectrosc. 2017, 91, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Zhang, M.; Lin, X.; Tuo, Y.; Murad, M.S.; Mu, G.; Jiang, S. Development and characterization of acid-induced whey protein concentrate and egg white protein composite gel. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.; Kim, S.-J. The Chemical and structural analysis of graphene oxide with different degrees of oxidation. Carbon 2013, 53, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, Y.; Sirousazar, M.; Kheiri, F. Crosslinked swellable clay/egg white bionanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Zheng, M.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. Gellan gum/graphene oxide aerogels for methylene blue purification. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doudrick, K.; Nosaka, T.; Herckes, P.; Westerhoff, P. Quantification of graphene and graphene oxide in complex organic matrices. Environ. Sci. Nano 2015, 2, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alver, E.; Metin, A.U.; Brouers, F. Methylene blue adsorption on magnetic alginate/rice husk bio-composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Elgarhy, G.S.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Omer, A.M. Carboxymethyl cellulose/carboxylated graphene oxide composite microbeads for efficient adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Fang, Q.; Chen, B. Environmental Applications of Three-Dimensional Graphene-Based Macrostructures: Adsorption, Transformation, and Detection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Du, Q.; Li, M.; Sun, Y.; Cui, M.; Li, L. Study on the Adsorption Performance of Casein/Graphene Oxide Aerogel for Methylene Blue. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29243–29253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Du, Q. Methylene blue adsorption by activated carbon, nickel alginate/activated carbon aerogel, and nickel alginate/graphene oxide aerogel: A comparison study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12443–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Du, Q.; Wang, D.; Sui, K.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Xia, Y. Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies for Removal of Methylene Blue Using beta-Cyclodextrin/Activated Carbon Aerogels. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3362–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, M.; Hameed, B.H. Modified mesoporous clay adsorbent for adsorption isotherm and kinetics of methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions using nanoscale zero valent iron-reduced graphite oxide modified composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, H.J.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Arumugam, T.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Vasudevan, D. An efficient removal of crystal violet dye from waste water by adsorption onto TLAC/Chitosan composite: A novel low cost adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Reghioua, A.; Yaseen, Z.M. Zwitterion composite chitosan-epichlorohydrin/zeolite for adsorption of methylene blue and reactive red 120 dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhang, B.-G.; Dai, Y.-R. A critical review on the electrospun nanofibrous membranes for the adsorption of heavy metals in water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.-H.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: Fabrication, modification and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 77, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liao, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhao, D.; Huo, J.; An, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.; Sun, B.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and methylene blue adsorption of multiple-responsive hydrogels loaded with Huangshui polysaccharides, polyvinyl alcohol, and sodium carboxyl methyl cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, M.; Tahmasebpoor, M.; Foroutan, R. Enhanced adsorption capacity of low-cost magnetic clinoptilolite powders/beads for the effective removal of methylene blue: Adsorption and desorption studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, D.; Diro, A.; Melak, F.; Girma Asere, T. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using Biowaste Materials: Barley Bran and Enset Midrib Leaf. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 4849758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, C.; Ma, J.; Ma, X.; Han, R. Adsorption of Copper Ions and Methylene Blue in a Single and Binary System on Wheat Straw. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 3229–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

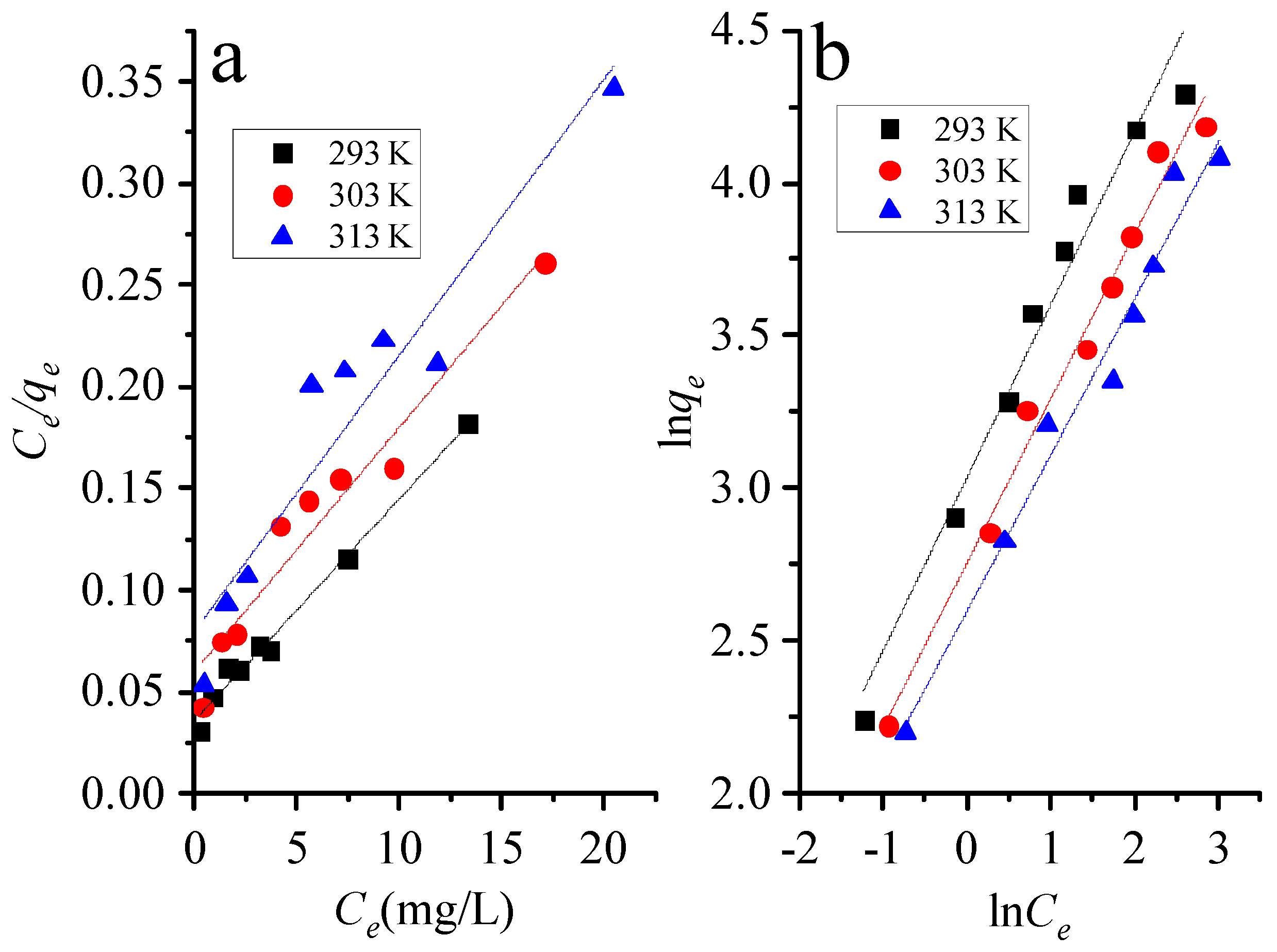
| Temp (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg/g) | kL (L/mg) | R2 | RL | kF (L/mg) | 1/n | R2 | |
| 293 | 91.7 | 3.26 | 0.987 | 0.0579 | 20.8 | 0.57 | 0.962 |
| 303 | 83.3 | 4.98 | 0.940 | 0.0386 | 15.7 | 0.54 | 0.982 |
| 313 | 73.8 | 5.87 | 0.900 | 0.0330 | 13.4 | 0.51 | 0.972 |
| C0 (mg/L) | 20 | 50 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | k1 (min−1) | 2.88 × 10−3 | 3.62 × 10−3 |
| qe (mg/g) | 29.6 | 37.1 | |
| R2 | 0.733 | 0.784 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | k2 (g/mg∙min) | 4.79 × 10−4 | 3.20 × 10−4 |
| qe (mg/g) | 41.6 | 59.8 | |
| R2 | 0.995 | 0.998 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion model | kid1 | 4.87 | 4.64 |
| C1 | −6.02 | −5.05 | |
| R12 | 0.991 | 0.986 | |
| kid2 | 0.493 | 0.449 | |
| C2 | 42.1 | 43.3 | |
| R22 | 0.944 | 0.976 |
| T/K | ΔG (kJ/mol) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔS (J/mol∙K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | −4.13 | −24.6 | −69.9 |
| 303 | −3.43 | ||
| 313 | −2.73 |
| Adsorbent Material | Removal Capacity (mg·g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogels loaded with Huangshui polysaccharides, polyvinyl alcohol, and sodium carboxyl methyl cellulose | 71.07 | [48] |
| Clinoptilolite/Fe3O4(Clin/Fe3O4) nanocomposite powders | 45.662 | [49] |
| Alginate/Clinoptilolite/Fe3O4 (Alg/Clin/Fe3O4) nanocomposite beads | 12.484 | [49] |
| Barley Bran | 63.2 | [50] |
| Enset Midrib Leaf | 35.5 | [50] |
| Wheat Straw | 60.66 | [51] |
| Egg White Protein/Graphene Oxide Bionanocomposite Aerogels | 91.7 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Du, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Chen, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, S.; Jing, Z. Removal of Methylene Blue by Crosslinked Egg White Protein/Graphene Oxide Bionanocomposite Aerogels. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152659
Jin Y, Du Q, Li Y, Zhang Y, Chen B, Wang M, Chen K, Sun Y, Zhao S, Jing Z. Removal of Methylene Blue by Crosslinked Egg White Protein/Graphene Oxide Bionanocomposite Aerogels. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152659
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yonghui, Qiuju Du, Yanhui Li, Yang Zhang, Bing Chen, Mingzhen Wang, Kewei Chen, Yaohui Sun, Shiyong Zhao, and Zhenyu Jing. 2022. "Removal of Methylene Blue by Crosslinked Egg White Protein/Graphene Oxide Bionanocomposite Aerogels" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152659
APA StyleJin, Y., Du, Q., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Chen, B., Wang, M., Chen, K., Sun, Y., Zhao, S., & Jing, Z. (2022). Removal of Methylene Blue by Crosslinked Egg White Protein/Graphene Oxide Bionanocomposite Aerogels. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2659. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152659





