Lightweight and Compression-Resistant Carbon-Based Sandwich Honeycomb Absorber with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
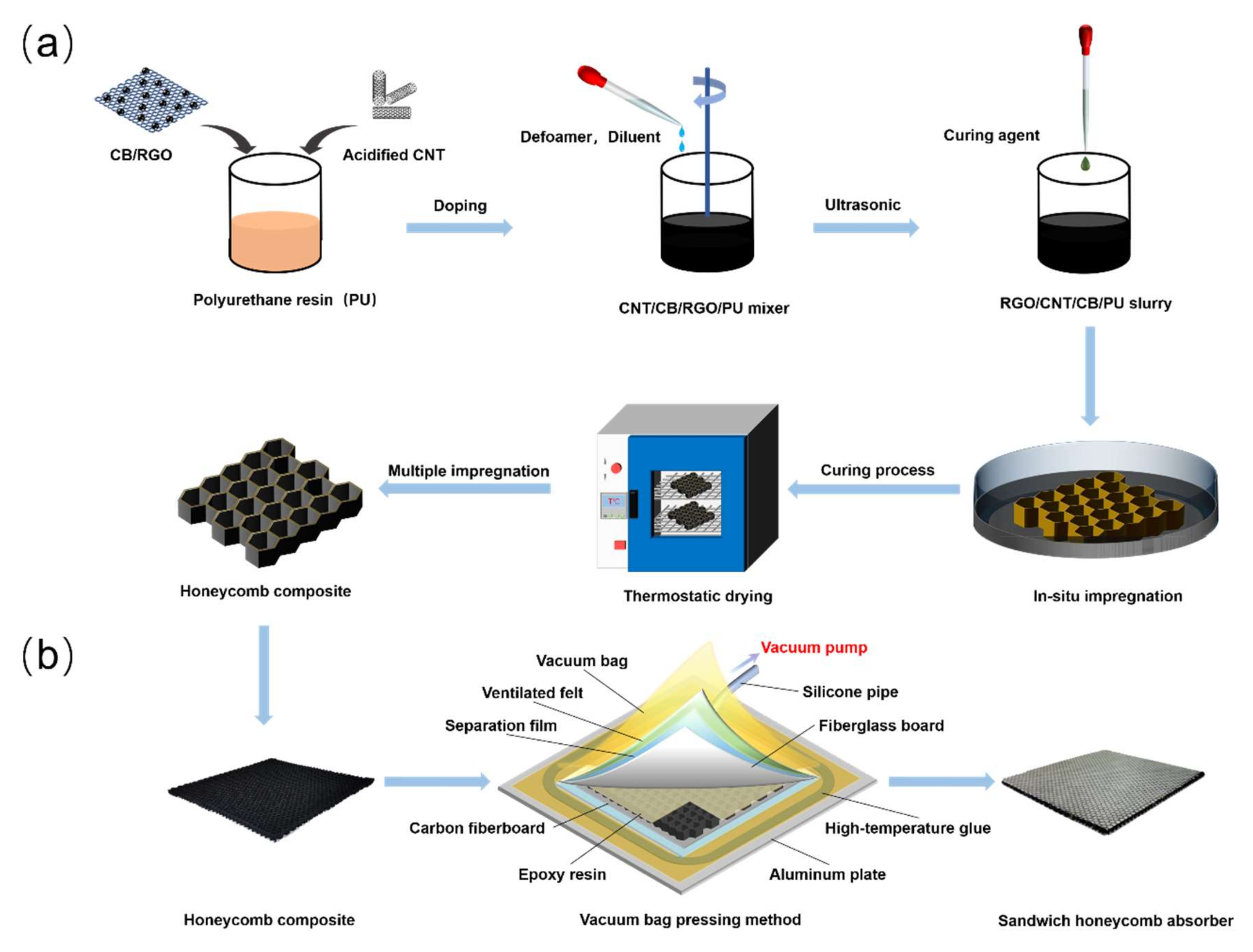
2.2. Preparation of CNT/CB/RGO/PU HC Composites
2.3. Preparation of CNT/CB/RGO/PU SHC Absorbers
2.4. Analytical and Testing Instruments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Analyses
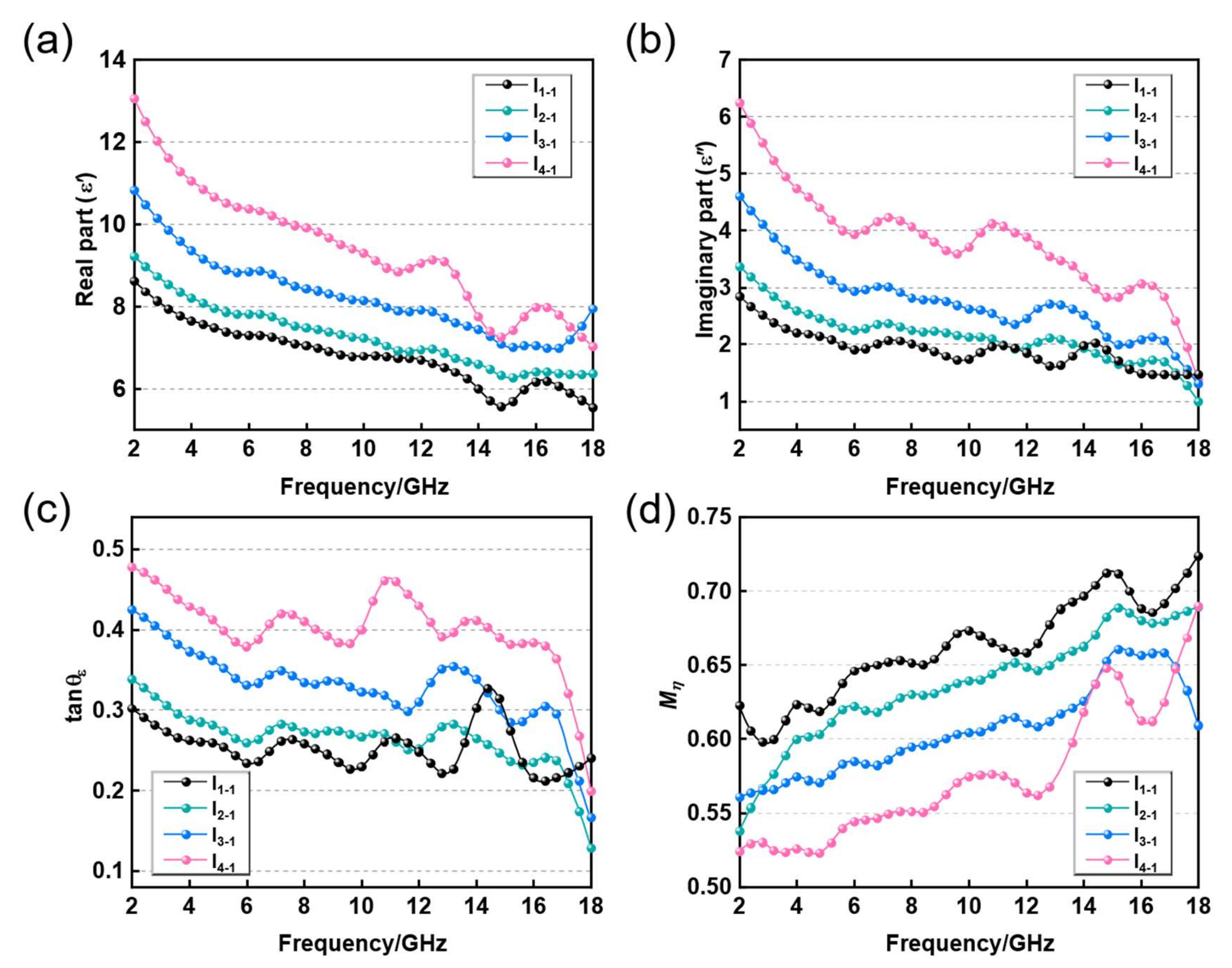
3.2. Dielectric Performance Analysis of CNT/CB/RGO/PU Composite
3.3. Absorption Properties of CNT/CB/RGO/PU HC Core Composite
3.3.1. Analysis of Absorption Performance of Single-Layer HC Composite
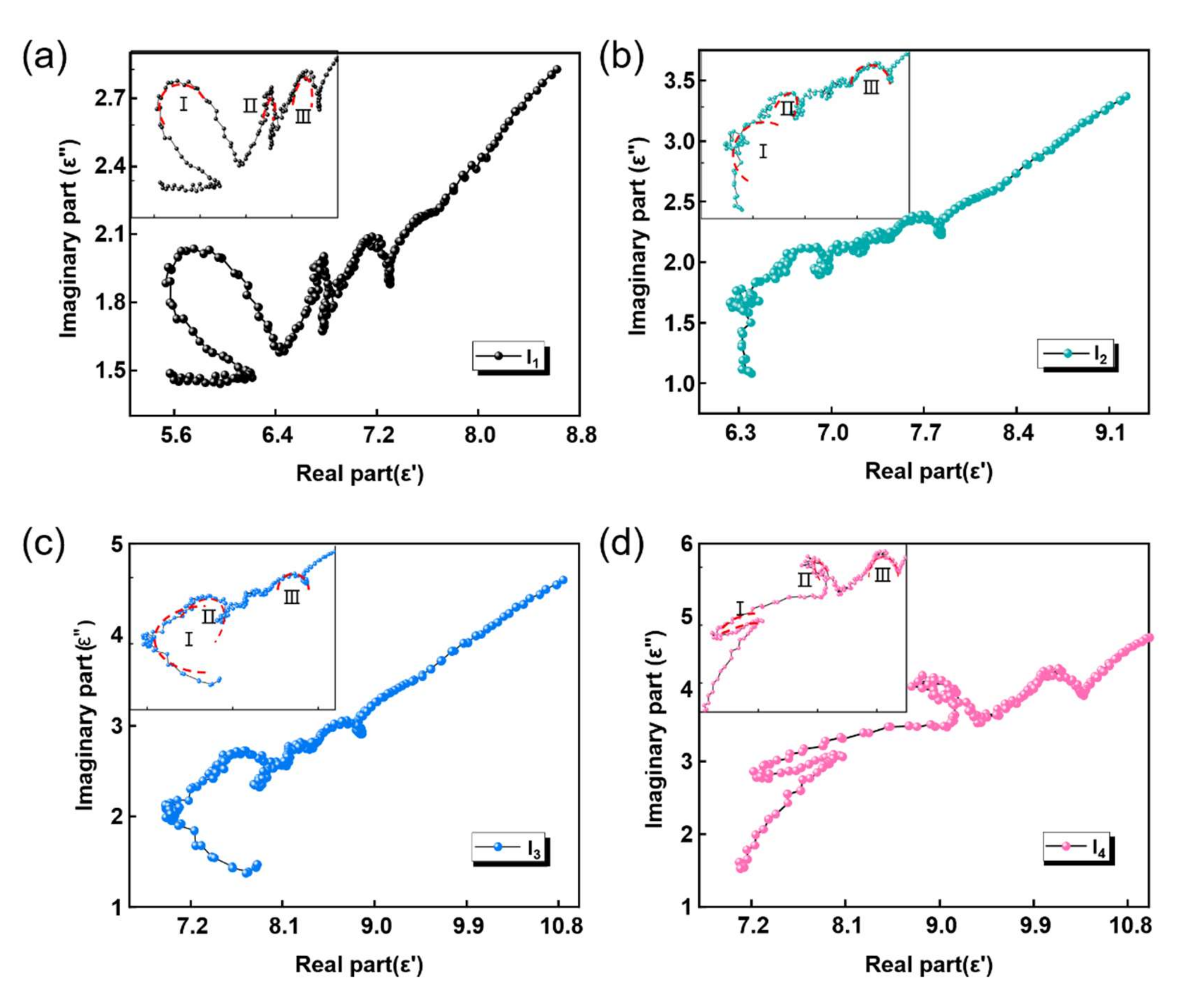
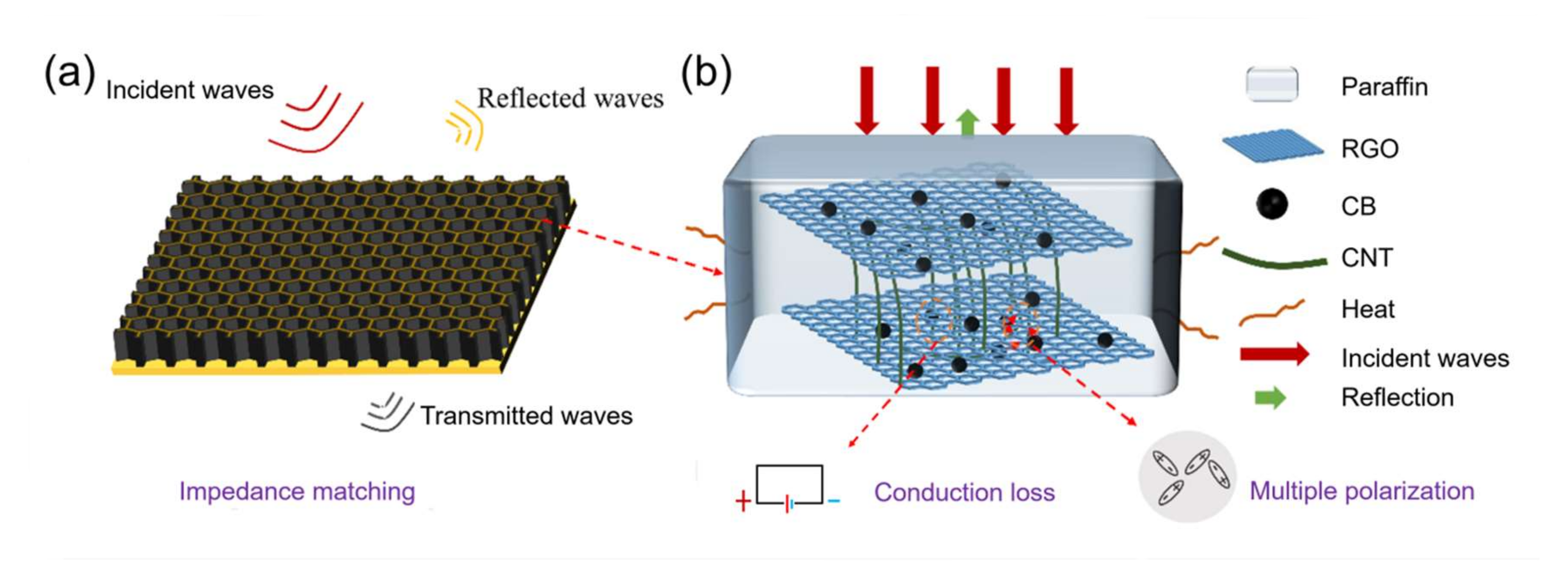
3.3.2. Analysis of Loss Mechanism of Single-Layer HC Composite
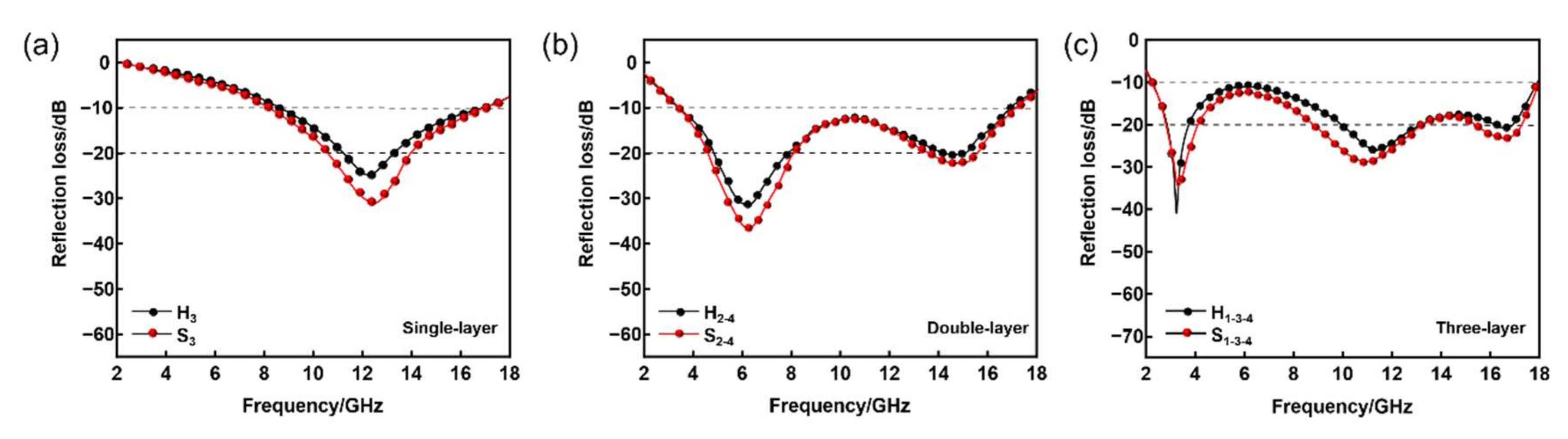
3.3.3. Analysis of Absorbing Performance of Multi-Layer HC Composite
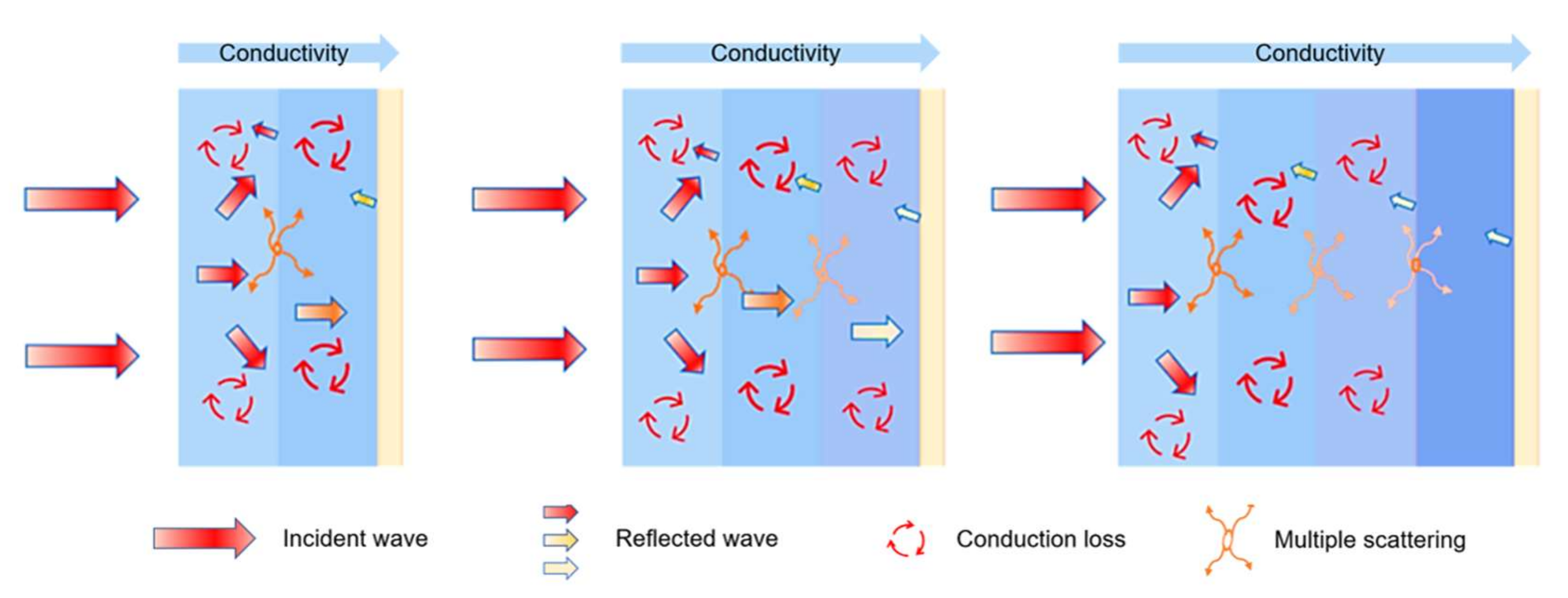
3.3.4. Analysis of Loss Mechanism of Multi-Layer HC Composite
3.4. Analysis of Absorption Performance of Sandwich Honeycomb Absorber
3.5. Mechanical Properties of SHC Absorber
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zeng, X.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of the filler size on the electrical percolation threshold of carbon black-carbon nanotube-polymer composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Song, Y.; Hou, Z.; Liu, Z. Microwave Absorption and Mechanical Properties of CNTs/PU Composites with Honeycomb Structure. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.-L.; Guan, X.-T.; Fan, L.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-B.; Cao, W.-Q.; Wang, C.-Y.; Cao, M.-S. Strong and thermostable polymeric graphene/silica textile for lightweight practical microwave absorption composites. Carbon 2016, 100, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, L.; Xie, J.; Liang, D.; Lu, H.; Deng, L. A Study on the Effective Permittivity of Carbon/PI Honeycomb Composites for Radar Absorbing Design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 3679–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, C.; Cheng, M.; Li, Z.; Bandaru, S.; Chen, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Multiscale design of carbon-based, high-efficiency and wide-frequency microwave-absorption composites. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 20467–20475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.H.K.; Portes, R.; Junior, M.D.A.; Florez-Vergara, D.; Gama, A.; Silva, V.; Quirino, S.; Baldan, M.R. X Band electromagnetic property influence of multi-walled carbon nanotube in hybrid MnZn ferrite and carbonyl iron composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yan, Z.; Yue, K.; Li, A.; Qian, L. Multi-scale structural nitrogen-doped rGO@CNTs composites with ultra-low loading towards microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 538, 147943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bi, S.; Wang, X.; Hou, G.-L.; Su, X.-J.; Liu, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Li, H. Excellent microwave absorption of carbon black/reduced graphene oxide composite with low loading. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 13990–14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Duan, Y.; Dai, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. The electromagnetic response of composition-regulated honeycomb structural materials used for broadband microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 88, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, E.; Akiba, E. Electromagnetic absorbing materials using nonwoven fabrics coated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2014, 78, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chen, Z.; Ai, S.; Hou, B.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, H.; Cui, S. Porous SiC/melamine-derived carbon foam frameworks with excellent electromagnetic wave absorbing capacity. J. Adv. Ceram. 2019, 8, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Kou, H.; Xu, H.; Guo, J. Gradient multi-layer structural design of CNTs/SiO2 composites for improving microwave absorbing properties. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3013–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Fan, H. Oblique incidence performance of radar absorbing honeycombs. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 99, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Gong, R.; Cao, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of metal magnetic micropowder-coated honeycomb sandwich structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Gong, R. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of foam-based honeycomb sandwich structures. Eur. Lett. 2009, 85, 58003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Bai, H.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, Z. Lightweight Composite Microwave Absorbing Materials Based on Graphene Aerogels with Honeycomb Structure. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL)—Rapid Res. Lett. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Q.; Ju, W.; Che, W.; Liao, S.; Jiang, H.; Tang, M.; Long, J.; et al. Paper-based composites as a dual-functional material for ultralight broadband radar absorbing honeycombs. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birman, V.; Kardomateas, G.A. Review of current trends in research and applications of sandwich structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 142, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bi, S.; Su, Z.-A.; Hou, G.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.-Y. Surface modification and microwave absorption properties of lightweight CNT absorbent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 21048–21058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhang, T.; Lin, H.; Jia, D.; Zhong, B.; Wen, G.; et al. A theoretical strategy of pure carbon materials for lightweight and excellent absorption performance. Carbon 2021, 174, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Huang, W.; Luo, J. Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-J.; Zhang, J.-Y.; He, P.; Hou, Z.-L. Size-modulated electromagnetic properties and highly efficient microwave absorption of magnetic iron oxide ceramic opened-hollow microspheres. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 23043–23049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-L.; Hou, Z.-L.; Bi, S.; Fang, H.-M. Modeling for multi-resonant behavior of broadband metamaterial absorber with geometrical substrate. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 127802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Yang, R.; Lu, D.; Yang, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Tang, Z.; Gui, X. Lightweight, three-dimensional carbon Nanotube@TiO2 sponge with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 2018, 144, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-L.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Hou, Z.-L.; Bi, S.; Zhao, Q.-L. Multifunctional broadband microwave absorption of flexible graphene composites. Carbon 2019, 141, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huyan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Tubular carbon nanofibers: Synthesis, characterization and applications in microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 152, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Du, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhao, H.; Han, X. MOFs-derived multi-chamber carbon microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2019, 157, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Xiang, Z.; Xiong, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, L.; Lu, W. Sandwich-Like Fe&TiO2@C Nanocomposites Derived from MXene/Fe-MOFs Hybrids for Electromagnetic Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Han, C.; Cao, W.-Q.; Cao, M.-S.; Yang, H.-J.; Yuan, J. A Nano-Micro Engineering Nanofiber for Electromagnetic Absorber, Green Shielding and Sensor. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.P.; Ji, G.; Xu, Z.J. Biomass-Derived Porous Carbon-Based Nanostructures for Microwave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, J.; Yang, H.; Fang, X.; Yuan, J. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4586–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Jiao, T.; Gu, J.; Tang, Y.; Kong, J. Graphene Shield by SiBCN Ceramic: A Promising High-Temperature Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Material with Oxidation Resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39307–39318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cao, M.-S.; Luo, Q.; Shi, H.-L.; Wang, W.-Z.; Yuan, J. Electromagnetic Property and Tunable Microwave Absorption of 3D Nets from Nickel Chains at Elevated Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22615–22622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msc, A.; Yzc, A.; Peng, H.A.; Jcs, A.; Wqc, B.; Jie, Y.B. 2D MXenes: Electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1265–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Che, R.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Dahyan, D.A.; Zhao, D. Broadening microwave absorption via a multi-domain structure. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 046104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; You, W.; Che, R. Hollow Engineering to Co@N-Doped Carbon Nanocages via Synergistic Protecting-Etching Strategy for Ultrahigh Microwave Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pei, K.; Xing, L.; Yu, X.; You, W.; Che, R. Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance from Magnetic Coupling of Magnetic Nanoparticles Suspended within Hierarchically Tubular Composite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Shi, W.; Ong, S.J.H.; Lu, X.; Wang, P.L.; Ji, G.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, L.; Xu, Z.J. Defect Engineering in Two Common Types of Dielectric Materials for Electromagnetic Absorption Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhu, X.; Lei, H.; Fang, D.; Zhang, Z. Optimal Design of Broadband Radar Absorbing Sandwich Structure with Circuit Analog Absorber Core. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2015, 7, 1550020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, C.-G. Characteristics of an electromagnetic wave absorbing composite structure with a conducting polymer electromagnetic bandgap (EBG) in the X-band. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2485–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Meng, G.; Zhang, L.; Gao, T.; Sun, S.; Pang, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of ordered CdTe nanowire arrays. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 76, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, B.A.; Munk, P.; Pryor, J. On Designing Jaumann and Circuit Analog Absorbers (CA Absorbers) for Oblique Angle of Incidence. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jung, H.-T. A new triple-layered composite for high-performance broadband microwave absorption. Compos. Struct. 2015, 122, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Shen, X.; Song, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y. Double-layer microwave absorber based on nanocrystalline Zn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4/α-Fe microfibers. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, T. Switchable quarter-wave plate with graphene based metamaterial for broadband terahertz wave manipulation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 27230–27239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Seow, J.Z.Y.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Z.J.; Ji, G. A Flexible and Lightweight Biomass-Reinforced Microwave Absorber. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Sheng, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Ji, G. Environmentally Friendly and Multifunctional Shaddock Peel-Based Carbon Aerogel for Thermal-Insulation and Microwave Absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Gu, W.; Sheng, J.; Lv, X.; Mao, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Tian, Z.; Ji, G. From intrinsic dielectric loss to geometry patterns: Dual-principles strategy for ultrabroad band microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample Code | Thickness | Stack Number (from Top to Bottom) |
|---|---|---|
| #1-2 | 10 mm | 1, 2 |
| #1-3 | 10 mm | 1, 3 |
| #1-4 | 10 mm | 1, 4 |
| #2-3 | 10 mm | 2, 3 |
| #2-4 | 10 mm | 2, 4 |
| #3-4 | 10 mm | 3, 4 |
| #1-2-3 | 15 mm | 1, 2, 3 |
| #1-2-4 | 15 mm | 1, 2, 4 |
| #1-3-4 | 15 mm | 1, 3, 4 |
| #2-3-4 | 15 mm | 2, 3, 4 |
| #1-2-3-4 | 20 mm | 1, 2, 3, 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, S.; Song, Y.; Hou, G.; Li, H.; Yang, N.; Liu, Z. Lightweight and Compression-Resistant Carbon-Based Sandwich Honeycomb Absorber with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152622
Bi S, Song Y, Hou G, Li H, Yang N, Liu Z. Lightweight and Compression-Resistant Carbon-Based Sandwich Honeycomb Absorber with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152622
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Song, Yongzhi Song, Genliang Hou, Hao Li, Nengjun Yang, and Zhaohui Liu. 2022. "Lightweight and Compression-Resistant Carbon-Based Sandwich Honeycomb Absorber with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152622
APA StyleBi, S., Song, Y., Hou, G., Li, H., Yang, N., & Liu, Z. (2022). Lightweight and Compression-Resistant Carbon-Based Sandwich Honeycomb Absorber with Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152622







