Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spent Coffee Ground Extracts: Process Modelling and Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. SCGs
2.3. Production of SCG Extracts
2.4. Synthesis of AgNPs
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Production of SCG Extracts
3.2. Spectrophotometric Characterization of AgNPs
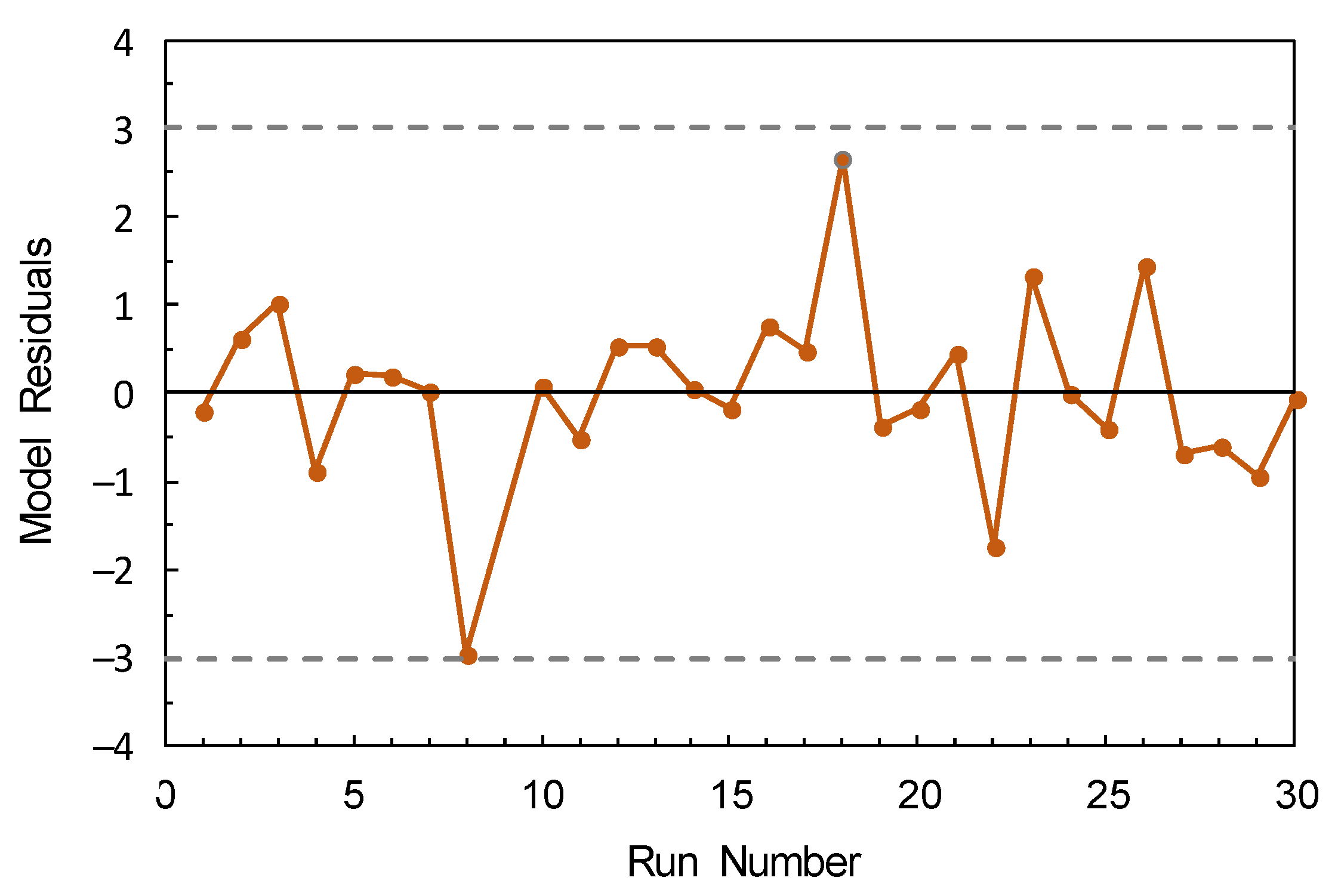
3.3. Model Fitting
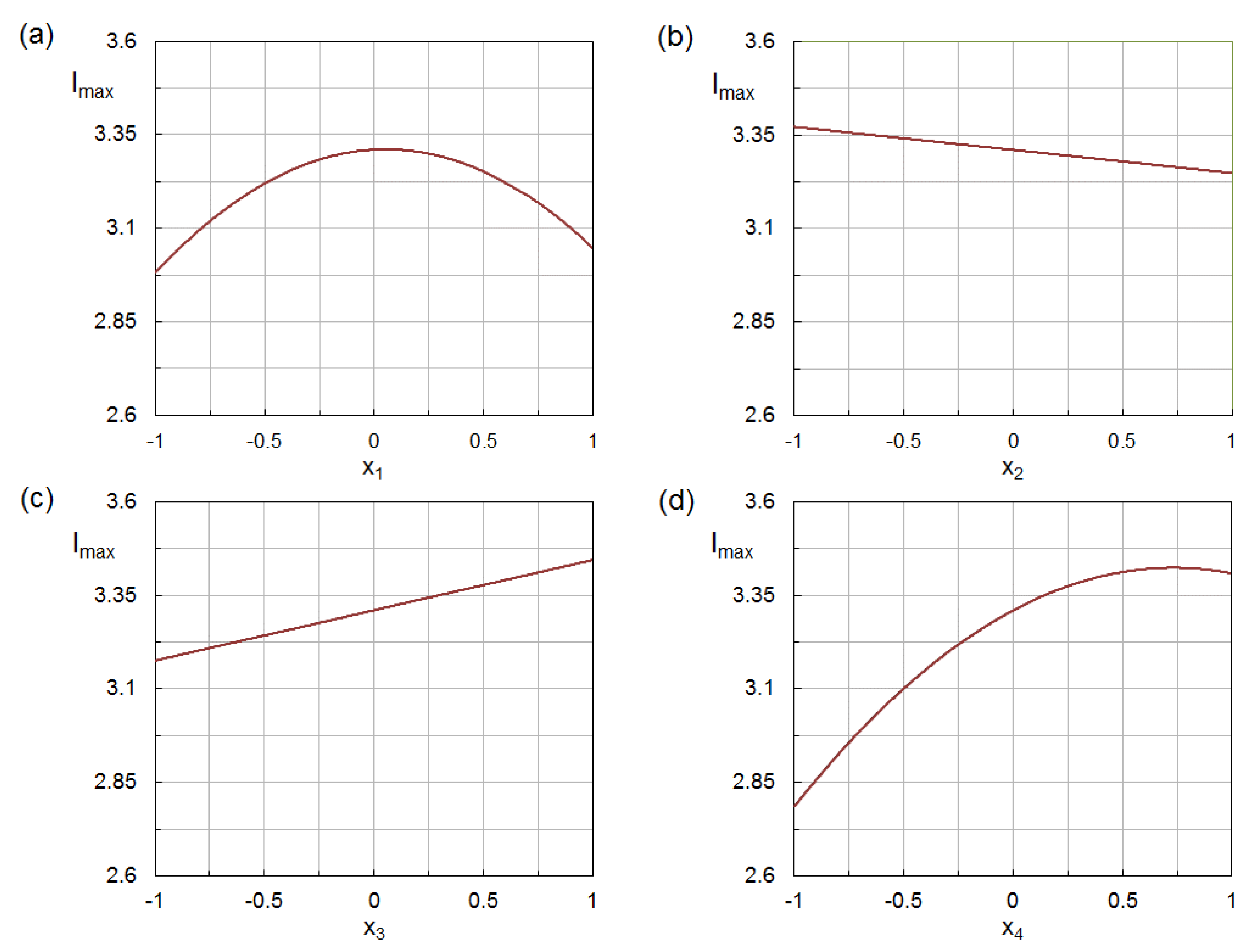
3.4. Analysis of Influencing Factors
- (a)
- Two of the four investigated factors, namely, the ethanol concentration in the aqueous solvent (C) and the pH of the reaction medium, affected the production of AgNPs through both a linear and a quadratic term;
- (b)
- Concerning the linear terms, the silver-to-phenolic ratio (R) gave a negative contribution on the response variable, while the contributions of the remaining factors were positive and increased in in the order: C < T < pH;
- (c)
- There were two positive interactions: between the silver-to-phenolic ratio (R) and the temperature (T), and between the silver-to-phenolic ratio (R) and the pH, indicating that the R factor had a more pronounced effect on the production of AgNPs at higher temperature and pH.
3.5. Process Optimization
3.6. Characterization of AgNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zahoor, M.; Nazir, N.; Iftikhar, M.; Naz, S.; Zekker, I.; Burlakovs, J.; Uddin, F.; Kamran, A.W.; Kallistova, A.; Pimenov, N.; et al. A review on silver nanoparticles: Classification, various methods of synthesis, and their potential roles in biomedical applications and water treatment. Water 2021, 13, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Umar, K.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Silver nanoparticles: Various methods of synthesis, size affecting factors and their potential applications—A review. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Mahmoudi-Gom Yek, S.; Motahharifar, N.; Ghafori Gorab, M. Recent developments in the plant-mediated green synthesis of Ag-based nanoparticles for environmental and catalytic applications. Chem. Rec. 2019, 19, 2436–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumail, H.; Khalid, S.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, H.; Amin, S.; Ullah, B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through plants. Endocr. Metab. Immun. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, B.A.; Baek, K.-H. Valorization of agro-industrial biowaste to green nanomaterials for wastewater treatment: Approaching green chemistry and circular economy principles. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 311, 114806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H. Silver nanoparticle biosynthesis by using phenolic acids in rice husk extract as reducing agents and dispersants. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuorro, A.; Iannone, A.; Natali, S.; Lavecchia, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using bilberry and red currant waste extracts. Processes 2019, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tade, R.S.; Nangare, S.N.; Patil, P.O. Agro-industrial waste-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial activity. Nano Biomed. Eng. 2020, 12, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Omran, B.A.; Aboelazayem, O.; Nassar, H.N.; El-Salamony, R.A.; El-Gendy, N.S. Biovalorization of mandarin waste peels into silver nanoparticles and activated carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.V.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Taliansky, M.E.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Kalinina, N.O. “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 2014, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauwel, P.; Küünal, S.; Ferdov, S.; Rauwel, E. A review on the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their morphologies studied via TEM. Adv. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 682749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Restrepo, C.V.; Villa, C.C. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles, influence of capping agents, and dependence on size and shape: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, A.A.; Kalay, S.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Culha, M. Quantitative structure–activity relationship between antioxidant capacity of phenolic compounds and the plasmonic properties of silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2018, 189, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhin, A.; Batasheva, S.; Kruychkova, M.; Cherednichenko, Y.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Biogenic silver nanoparticles: Synthesis and application as antibacterial and antifungal agents. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salayová, A.; Bedlovičová, Z.; Daneu, N.; Baláž, M.; Lukáčová Bujňáková, Z.; Balážová, Ľ.; Tkáčiková, Ľ. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using various medicinal plant extracts: Morphology and antibacterial efficacy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Mojab, F.; Vahidi, H.; Marashi, B.; Talank, N.; Hosseini, O.; Saravanan, M. Green synthesis, characterization, antibacterial and biofilm inhibitory activity of silver nanoparticles compared to commercial silver nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 129, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Vega, R.; Loarca-Pina, G.; Vergara-Castaneda, H.A.; Oomahb, B.D. Spent coffee grounds: A review on current research and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, M.; Ramadan, K.M.; Awad, O.I.; Ibrahim, T.K.; Inayat, A.; Ma, X. Environmental impacts of biodiesel production from waste spent coffee grounds and its implementation in a compression ignition engine. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.; Madhava Naidu, M. Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaya, J.; Prates Pereira, A.; Mills-Lamptey, B.; Benjamin, J.; Chuck, C.J. Conceptualization of a spent coffee grounds biorefinery: A review of existing valorisation approaches. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 118, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNutt, J.; He, Q.S. Spent coffee grounds: A review on current utilization. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocco, D.; Lavecchia, R.; Natali, S.; Zuorro, A. Production of metal nanoparticles by agro-industrial wastes: A green opportunity for nanotechnology. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 47, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, H.-W.; Kuo, C.-J.; Kao, L.-H.; Lin, G.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y. Polysaccharidic spent coffee grounds for silver nanoparticle immobilization as a green and highly efficient biocide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzella, L.; Cerruti, P.; Aprea, P.; Paolillo, R.; Pellegrino, G.; Moccia, F.; Condorelli, G.G.; Vollaro, A.; Ambrogi, V.; Catania, M.R.; et al. Silver nanoparticles on hydrolyzed spent coffee grounds (HSCG) for green antibacterial devices. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R. Polyphenols and energy recovery from spent coffee grounds. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2011, 25, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Zuorro, A.; Iannone, A.; Lavecchia, R. Water-organic solvent extraction of phenolic antioxidants from brewers’ spent grain. Processes 2019, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 9th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zuorro, A. Optimization of polyphenol recovery from espresso coffee residues using factorial design and response surface methodology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 152, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamov, T.R.; Evstaf’Ev, I.V.; Olenin, A.Y.; Lisichkin, G.V. The formation of mono- and bimetallic silver-containing seed nanoparticles. Colloid J. 2014, 76, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumberland, S.; Lead, J. Particle size distributions of silver nanoparticles at environmentally relevant conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 9099–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diegoli, S.; Manciulea, A.L.; Begum, S.; Jones, I.P.; Lead, J.R.; Preece, J.A. Interaction between manufactured gold nanoparticles and naturally occurring organic macromolecules. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brzezicha, J.; Błażejewicz, D.; Brzezińska, J.; Grembecka, M. Green coffee VS dietary supplements: A comparative analysis of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 155, 112377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Sentkowska, A.; Pyrzyńska, K.; De Peña, M.P. Chlorogenic acids, caffeine content and antioxidant properties of green coffee extracts: Influence of green coffee bean preparation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 242, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Getaneh, E.; Fanta, S.W.; Satheesh, N. Effect of broken coffee beans particle size, roasting temperature, and roasting time on quality of coffee beverage. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 8871577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.E.; Hernández, S.S.; Tolosa, A.R.; Burillo, S.P.; Olalla Herrera, M. Evaluation of differences in the antioxidant capacity and phenolic compounds of green and roasted coffee and their relationship with sensory properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 128, 109457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.S.P.; Nunes, F.M.; Domingues, M.R.; Coimbra, M.A. Coffee melanoidins: Structures, mechanisms of formation and potential health impacts. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalcik, A.; Obruca, S.; Marova, I. Valorization of spent coffee grounds: A review. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 110, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuorro, A.; Maffei, G.; Lavecchia, R. Effect of solvent type and extraction conditions on the recovery of phenolic compounds from artichoke waste. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 39, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Yoosaf, K.; Ipe, B.I.; Suresh, C.H.; Thomas, K.G. In situ synthesis of metal nanoparticles and selective naked-eye detection of lead ions from aqueous media. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12839–12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguerre, M.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. The physico-chemical basis of phenolic antioxidant activity. Lipid Technol. 2014, 26, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Kwon, S.G.; Hyeon, T. Nonclassical nucleation and growth of inorganic nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.M.; Akbari, A. Metal nanoparticles synthesis through natural phenolic acids. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegboyega, N.F.; Sharma, V.K.; Siskova, K.; Zbořil, R.; Sohn, M.; Schultz, B.J.; Banerjee, S. Interactions of aqueous Ag+ with fulvic acids: Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle formation and investigation of stability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashwani, Z.-U.-R.; Khan, T.; Khan, M.A.; Nadhman, A. Synthesis in plants and plant extracts of silver nanoparticles with potent antimicrobial properties: Current status and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9923–9934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuorro, A.; Iannone, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Natali, S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using kiwifruit juice. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 81, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar]








| Factor | Factor Level | Unit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −α | −1 | 0 | +1 | +α | ||
| Solvent composition (C) | 10 | 30 | 50 | 70 | 90 | % v/v |
| Silver-to-phenolic ratio (R) | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | mol/mol |
| Temperature (T) | 10 | 25 | 40 | 55 | 70 | °C |
| pH | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | − |
| SO | RO | Factor Level | y | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | |||
| 1 | 22 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 2.380 |
| 2 | 26 | +1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 2.733 |
| 3 | 3 | −1 | +1 | −1 | −1 | 2.201 |
| 4 | 29 | +1 | +1 | −1 | −1 | 2.087 |
| 5 | 7 | −1 | −1 | +1 | −1 | 2.653 |
| 6 | 24 | +1 | −1 | +1 | −1 | 2.714 |
| 7 | 18 | −1 | +1 | +1 | −1 | 2.775 |
| 8 | 8 | +1 | +1 | +1 | −1 | 2.329 |
| 9 | 14 | −1 | −1 | −1 | +1 | 3.015 |
| 10 | 20 | +1 | −1 | −1 | +1 | 3.058 |
| 11 | 4 | −1 | +1 | −1 | +1 | 2.798 |
| 12 | 21 | +1 | +1 | −1 | +1 | 2.986 |
| 13 | 30 | −1 | −1 | +1 | +1 | 3.118 |
| 14 | 1 | +1 | −1 | +1 | +1 | 3.170 |
| 15 | 25 | −1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | 3.268 |
| 16 | 13 | +1 | +1 | +1 | +1 | 3.418 |
| 17 | 11 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.012 |
| 18 | 16 | +2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.257 |
| 19 | 12 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 3.484 |
| 29 | 17 | 0 | +2 | 0 | 0 | 3.230 |
| 21 | 15 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 3.025 |
| 22 | 19 | 0 | 0 | +2 | 0 | 3.545 |
| 23 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 1.846 |
| 24 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +2 | 3.099 |
| 25 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.430 |
| 26 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.366 |
| 27 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.332 |
| 28 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.256 |
| 29 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.247 |
| 30 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.235 |
| Coefficient | Term | Value | SE | Low CI | High CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a0 | intercept | 3.310 | 0.031 | 3.24 | 3.37 |
| a1 | C | 0.032 | 0.022 | −0.013 | 0.078 |
| a2 | R | −0.062 | 0.022 | −0.11 | −0.016 |
| a3 | T | 0.134 | 0.022 | 0.089 | 0.18 |
| a4 | pH | 0.311 | 0.022 | 0.27 | 0.36 |
| a11 | C × C | −0.297 | 0.020 | −0.34 | −0.25 |
| a44 | pH × pH | −0.212 | 0.020 | −0.25 | −0.17 |
| a23 | R × T | 0.078 | 0.027 | 0.022 | 0.13 |
| a24 | R × pH | 0.075 | 0.027 | 0.019 | 0.13 |
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 8 | 6.497 | 0.812 | 69.67 | <0.0001 |
| Residual error | 21 | 0.245 | 0.012 | ||
| Lack-of-fit | 16 | 0.214 | 0.013 | 2.19 | 0.1972 |
| Pure error | 5 | 0.031 | 0.006 | ||
| Total | 29 | 6.742 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuorro, A.; Iannone, A.; Miglietta, S.; Lavecchia, R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spent Coffee Ground Extracts: Process Modelling and Optimization. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152597
Zuorro A, Iannone A, Miglietta S, Lavecchia R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spent Coffee Ground Extracts: Process Modelling and Optimization. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152597
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuorro, Antonio, Annalaura Iannone, Selenia Miglietta, and Roberto Lavecchia. 2022. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spent Coffee Ground Extracts: Process Modelling and Optimization" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152597
APA StyleZuorro, A., Iannone, A., Miglietta, S., & Lavecchia, R. (2022). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spent Coffee Ground Extracts: Process Modelling and Optimization. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152597








