Lanthanide (Eu, Tb, La)-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Whey as an Eco-Friendly Chelating Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of ZnO Doped with Eu, Tb, and La
2.3. TEM-EDS Analysis
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.6. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
2.7. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
2.8. Raman Scattering Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization by TEM and DLS
3.2. STEM-EDS Analysis
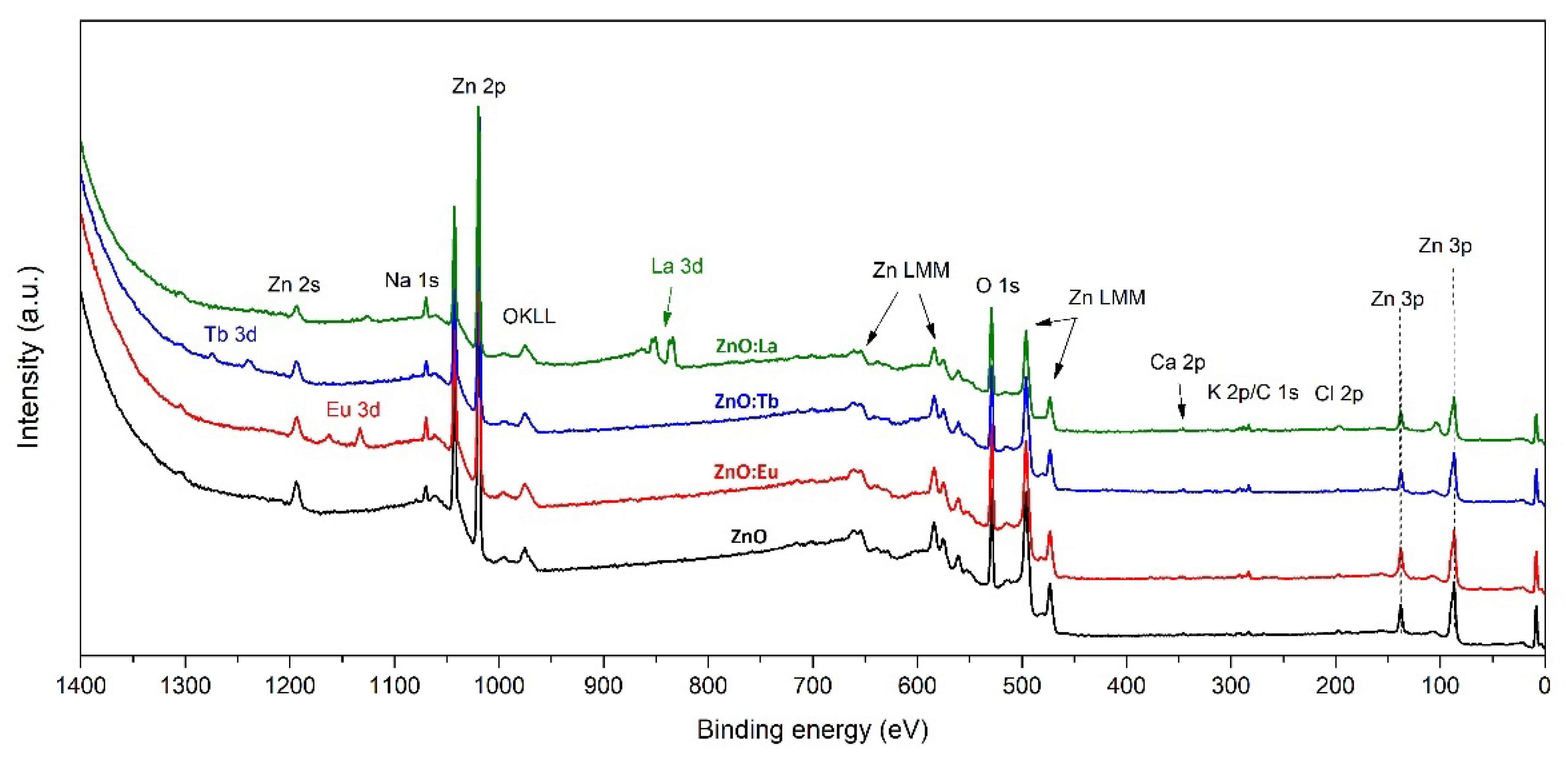
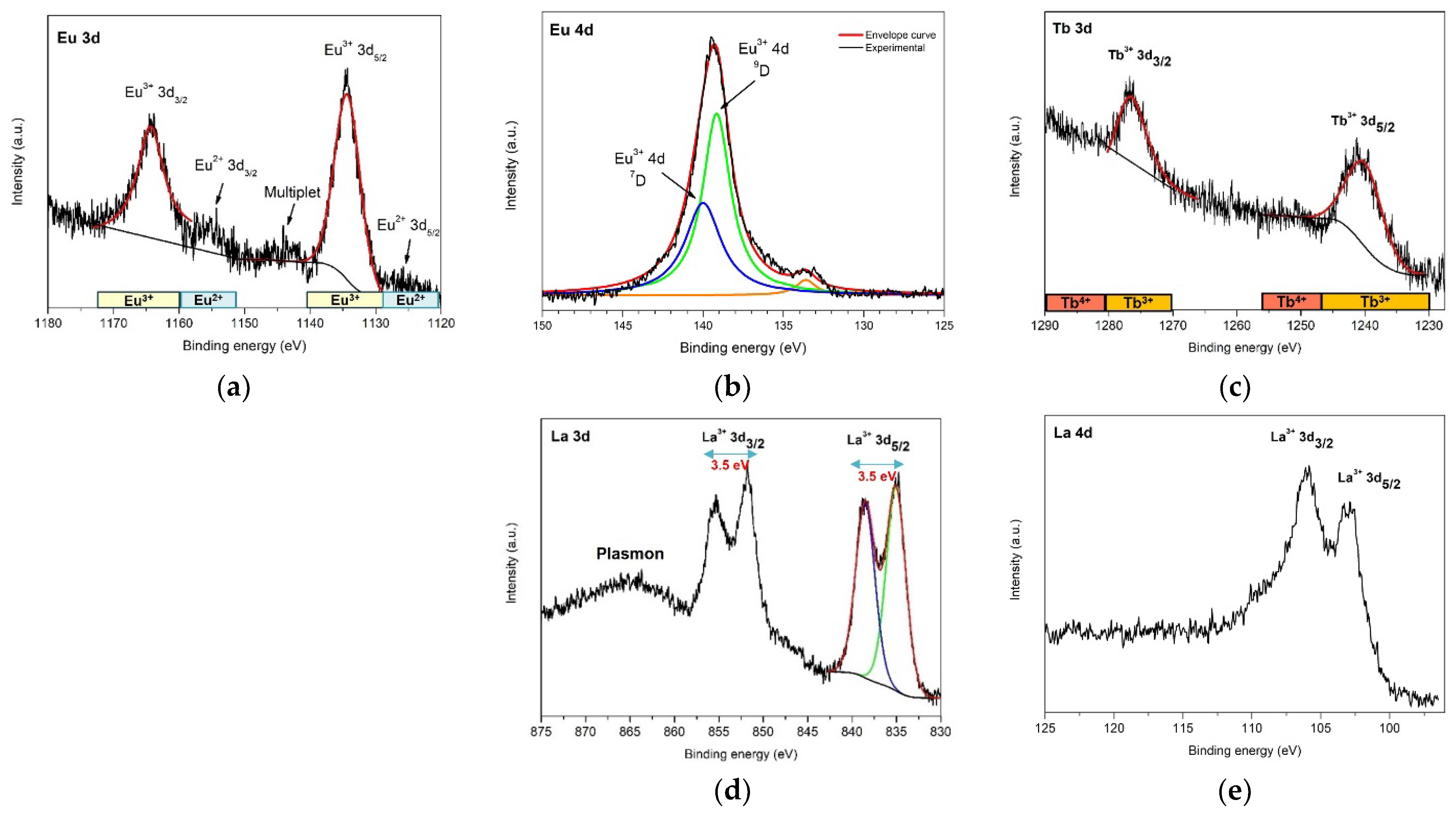
3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
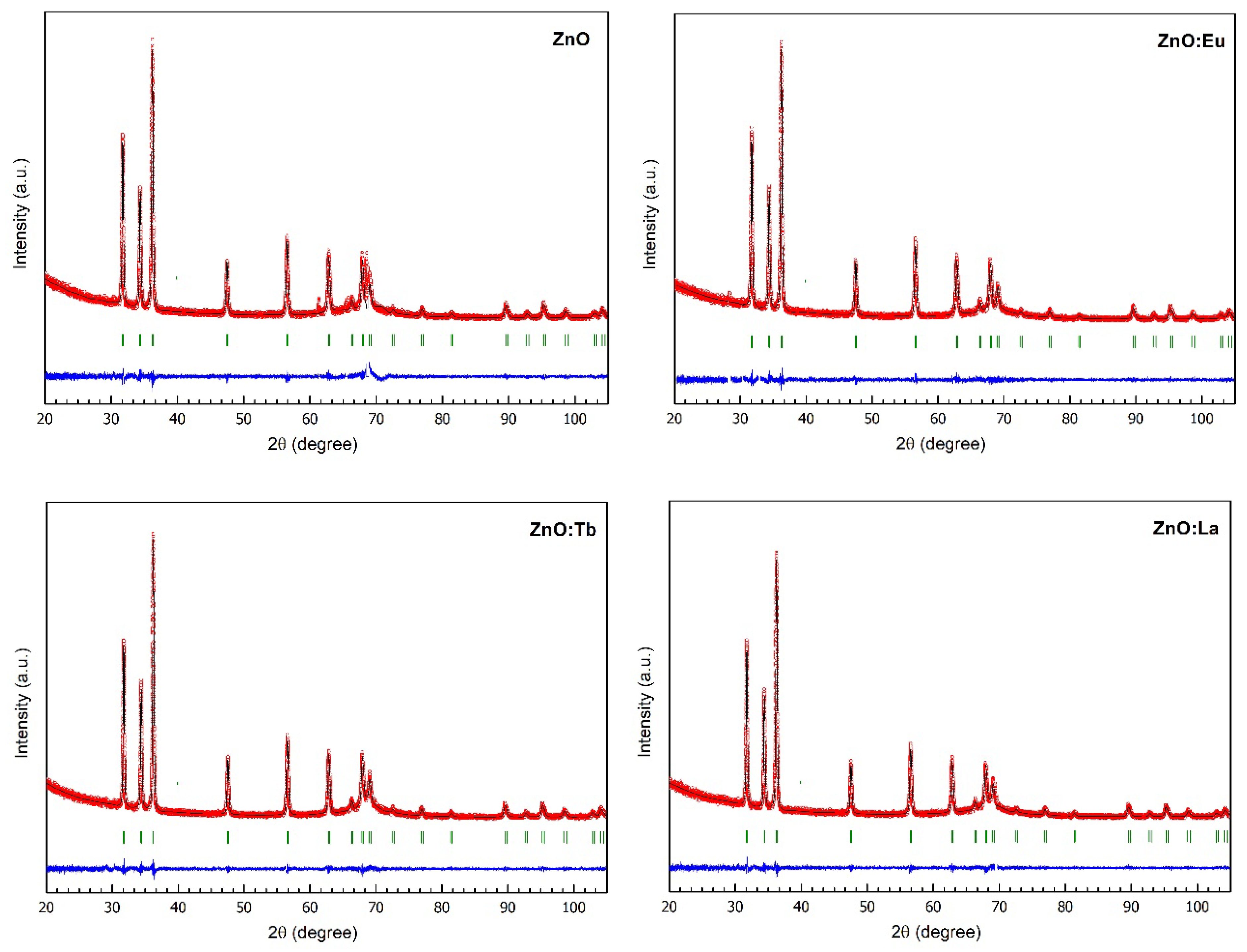
3.4. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
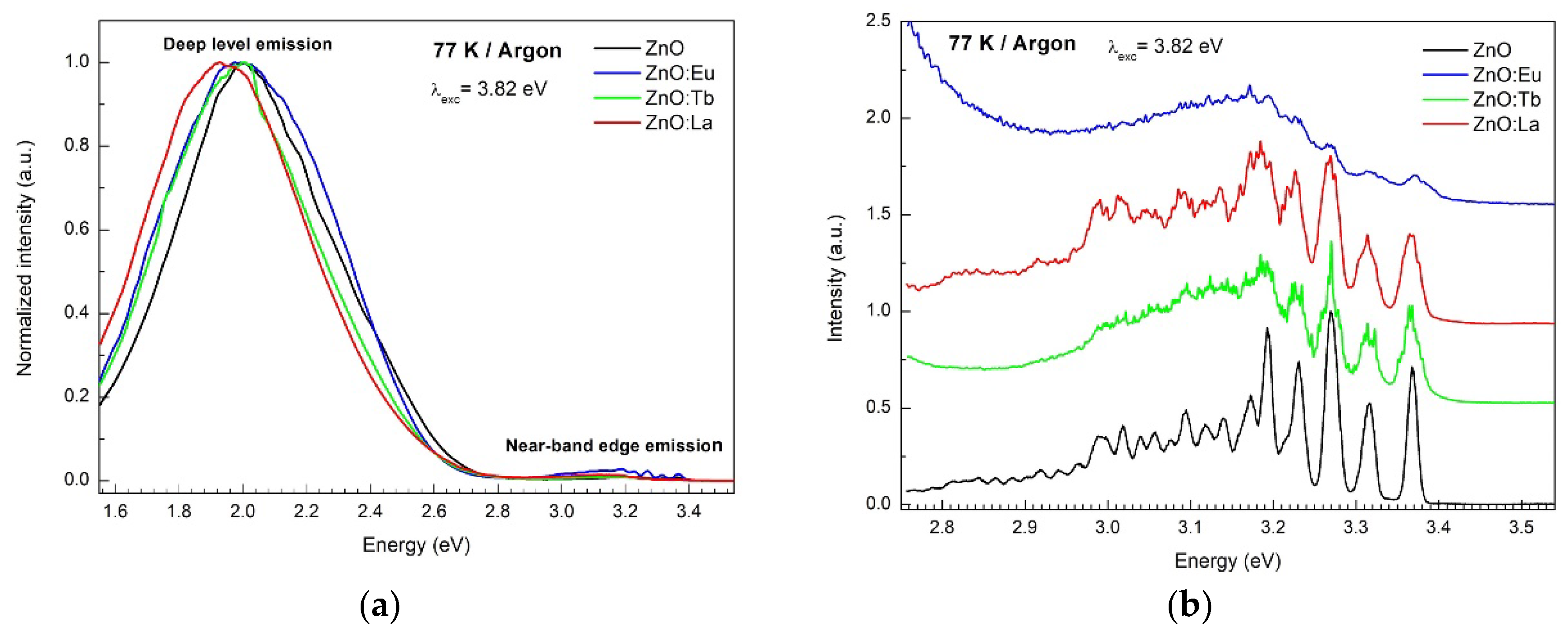
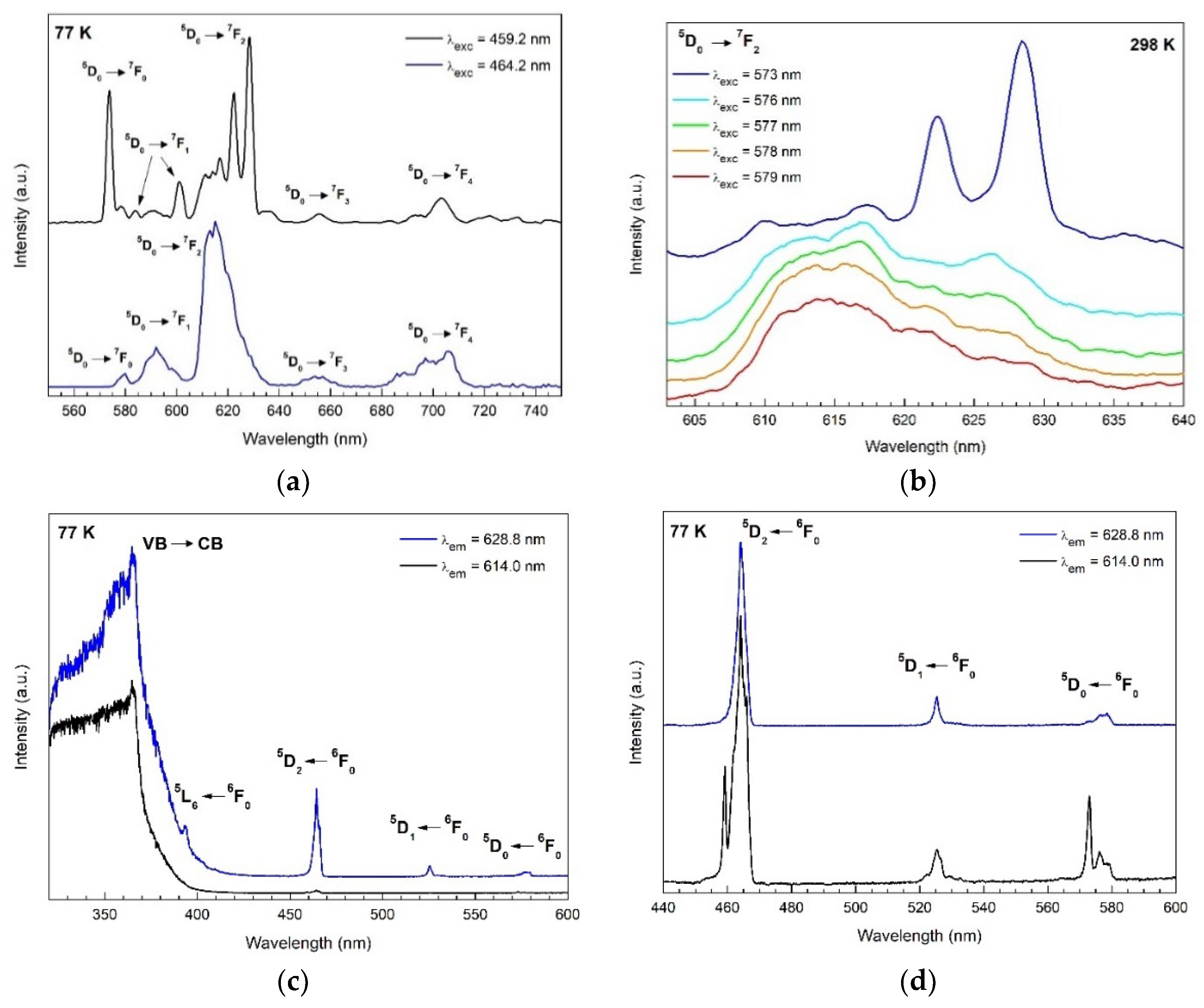
3.5. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
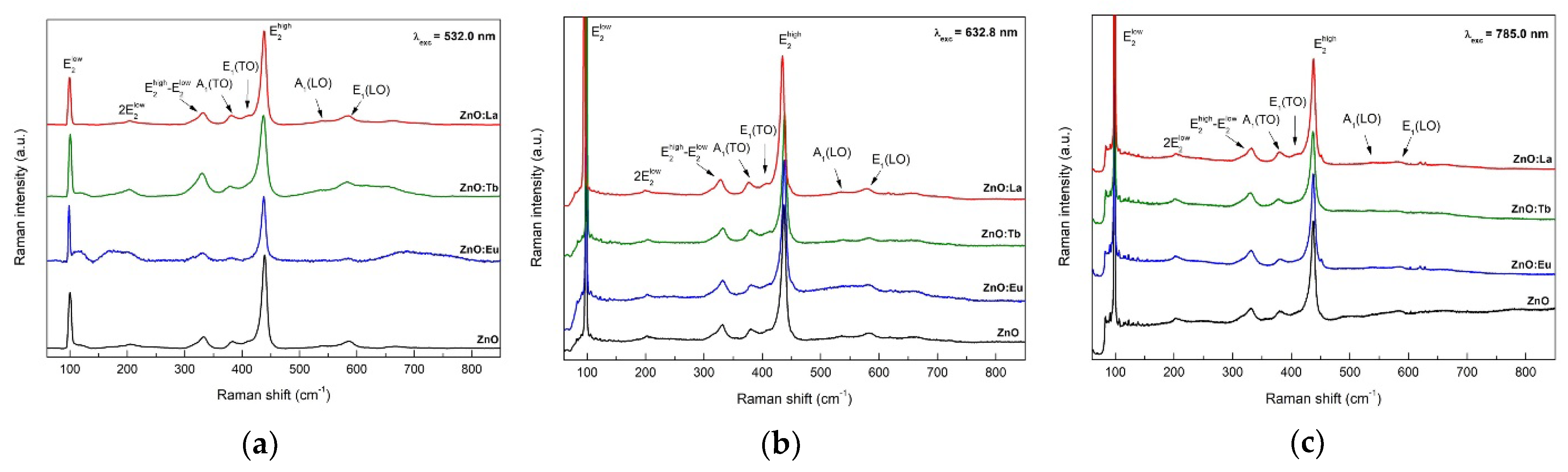
3.6. Raman Scattering Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottardo, S.; Mech, A.; Drbohlavová, J.; Małyska, A.; Bøwadt, S.; Riego-Sintes, J.; Rauscher, H. Towards safe and sustainable innovation in nanotechnology: State-of-play for smart nanomaterials. Nanoimpact 2021, 21, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.E.; Valsami-Jones, E. Safe by design for nanomaterials—Late lessons from early warnings for sustainable innovation. Nanoethics 2021, 15, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remzova, M.; Zouzelka, R.; Brzicova, T.; Vrbova, K.; Pinkas, D.; Rőssner, P.; Topinka, J.; Rathousky, J. Toxicity of TiO2, ZnO, and SiO2 nanoparticles in human lung cells: Safe-by-design development of construction materials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OECD. Nanotechnology for Green Innovation; OECD Science, Technology and Industry Policy Papers No. 5; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Hong, W.; Yang, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, H. Nano zinc oxide induced fetal mice growth restriction, based on oxide stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manivannan, N.; Sycheva, A.; Kristály, F.; Muránszky, G.; Baumli, P. Structural differences and adsorption behaviour of alkaline metals doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Sharma, D.K. A review on rare earth (Ce and Er)-doped zinc oxide nanostructures. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 34, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Shohag, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Islam, M.R.; Nafady, M.H.; Akter, A.; Mitra, S.; Roy, A.; Emran, T.B.; Cavalu, S. Exploring the journey of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) toward biomedical applications. Materials 2022, 15, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, T.; Meydan, I.; Seckin, H.; Bekmezci, M.; Sen, F. Green synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol-gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mani, G.; Kyobum, K.; Sengottuvelan, B. Water soluble self-aggregates induced green emission of biocompatible citric acid-PEG hyper branched polymer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shnain, Z.Y.; Toma, M.A.; Abdulhussein, B.A.; Saleh, N.J.; Ibrahim, M.; Manuel, N.; Mahmood, A. The effect of solvent-modification on the physicochemical properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method. Bull. Chem. React. 2022, 17, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, B.L.; Kolesnichenko, V.L.; O’Connor, C.J. Recent advances in the liquid-phase syntheses of inorganic nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3893–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebzadeh, H.; Rohani, A.; Sistani, A.; Hassanpour, A.; Gardy, J. Modelling and optimisation of the sol-gel conditions for synthesis of semi-hexagonal titania-based nano-catalyst for esterification reaction. Catalysts 2022, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, V.A.; Xavier, M.J.S.; Rodrigues, E.S.; de Oliveira, C.A.; Farias, P.M.A.; Stingl, A.; Ferreira, N.S.; Silva, M.S. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using whey as an effective chelating agent. Mater. Lett. 2020, 259, 126853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wong, S.-S.; Pham, S.Q.; Tan, J.J. Effects of globular protein type and concentration on the physical properties and flow behaviors of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by micellar casein-globular protein mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Azeredo, H.M.C.; Rosa, M.F.; De Sá, M.; Souza Filho, M.; Waldron, K.W. The use of biomass for packaging films and coatings. In Advances in Biorefineries; Waldron, K., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 819–874. ISBN 9780857095213. [Google Scholar]
- Cliff, G.; Lorimer, G.W. The quantitative analysis of thin specimens. J. Microsc. 1975, 103, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinard, P.T.; Protheroe, A.; Holland, J.; Burgess, S.; Statham, P.J. Development and validation of standardless and standards-based X-ray microanalysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 891, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.I.; Newbury, D.E.; Michael, J.R.; Ritchie, N.W.M.; Scott, J.H.J.; Joy, D.C. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-ray Microanalysis, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 44–47. ISBN 978-1-4939-6674-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.A. Statistical Methods for Research Workers, 5th ed.; Crew, F.A.E., Cutler, D.W., Eds.; Oliver and Boyd: Edinburgh, UK, 1946; pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Nunney, T.; White, R. Characterizing materials for energy generation using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Micros. Today 2011, 19, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, C.D. Auger lines in X-ray photoelectron spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1972, 44, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Sc, Ti, V, Cu and Zn. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, F.C.; Bundaleski, N.; Teodoro, O.M.N.D.; Correia, M.R.; Rebouta, L.; Mendes, A.; Tavares, C.J. XPS analysis of ZnO:Ga films deposited by magnetron sputtering: Substrate bias effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1993, 192, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, R.W.G. The Structure of Crystals; Supplement for 1930–1934 to the 2nd ed.; Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1935; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P.; Cox, D.E.; Hastings, J.B. Rietveld refinement of Debye–Scherrer synchrotron X-ray data from Al2O3. J. Appl. Cryst. 1987, 20, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finger, L.W.; Cox, D.E.; Jephcoat, A.P. A correction for powder diffraction peak asymmetry due to axial divergence. J. Appl. Cryst. 1994, 27, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollase, W.A. Correction of intensities for preferred orientation in powder diffractometry: Application of the March model. J. Appl. Cryst. 1986, 19, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.M.; Liu, D.P.; Xia, Y.Y.; Chen, J.S. Polyether-grafted ZnO nanoparticles with tunable and stable photoluminescence at room temperature. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3062–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Karmakar, D.; Basu, S.; Jha, S.N.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Gadkari, S.C.; Gupta, S.K. Effect of size and aspect ratio on structural parameters and evidence of shape transition in zinc oxide nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 2014, 75, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinhold, R.; Allen, M. Polarity-dependent photoemission of in situ cleaved zinc oxide single crystals. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.-J.; Oh, S.-J. Surface valence transition in trivalent Eu insulating compounds observed by photoelectron spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, R15613–R15616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaros, A.; Toloman, D.; Nasui, M.; Mos, R.B.; Petrisor, T.; Vasile, B.S.; Surdu, V.A.; Perhaita, I.; Biris, A.; Pana, O. A valence states approach for luminescence enhancement by low dopant concentration in Eu-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 6075–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Sun, L.-D.; Yan, C.-H. Efficient energy transfer in monodisperse Eu-doped ZnO nanocrystals synthesized from metal acetylacetonates in high-boiling solvents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 12234–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.-Y.; Sugano, M.; Sun, X.-Y.; Su, W.-H. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study on Ba1−xEuxTiO3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 242, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, S.P.; Edelstain, N.; McFeely, F.R.; Ley, L.; Shirley, D.A. X-ray photoemission spectra of the 4d levels in rare-earth metals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 29, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, W.-D.; Laubschat, C.; Nowik, I.; Kaindl, G. Shake-up excitations and core-hole screening in Eu systems. Phys. Rev. B 1981, 24, 5422–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, A.F.; Thornton, G. A study of final state structure in the X-PE spectra of the rare-earth oxides, Part III: Ionisation of a 4d electron. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1976, 13, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, C.; Rai, R.; Sathe, A.; Schaefer, A.; Weaver, J.F. Oxidation of a Tb2O3(111) thin film on Pt(111) by gas-phase oxygen atoms. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 20916–20926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.M.; Fan, H.T.; Pan, S.S.; Ye, C.; Li, G.H. Influence of annealing on the structural and optical properties of ZnO:Tb thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 053507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalia, B.D.; Lang, W.C.; Norris, P.R.; Watson, L.M.; Fabian, D.J.; Price, W.C. X-ray photoelectron core-level studies of the heavy rare-earth metals and their oxides. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1977, 354, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunding, M.F.; Hadidi, K.; Diplas, S.; Løvvik, O.M.; Norby, T.E.; Gunnæs, A.E. XPS characterisation of in situ treated lanthanum oxide and hydroxide using tailored charge referencing and peak fitting procedures. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2011, 184, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.H.; Zhou, X.; Pang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Vovk, E.I.; Cong, L.; van Bavel, A.P.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Understanding of binding energy calibration in XPS of lanthanum oxide by in situ treatment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 22351–22358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, A.; Ogasawara, H. Theory of core-level spectroscopy of rare-earth oxides. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1992, 60, 257–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y. Effects of phase transformation on photoluminescence behavior of ZnO:Eu prepared in different solvents. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.M.; Jappor, H.R.; Al-Marzoki, K.; Al-Hydary, I.A.; Edrees, S.J.; Shukur, M.M. Unraveling the effect of Gd doping on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductor nanorods. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33207–33221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemban, T.H.; Sequeira, M.C.; Zhang, Z.; Venkatesh, S.; Alves, E.; Lorenz, K.; Roqan, I.S. Identifying the influence of the intrinsic defects in Gd-doped ZnO thin-films. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 065301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, M.; Thakur, P.; Gautam, S.; Chae, K.H.; Tanemura, M.; Hihara, T.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Soga, T.; Kim, S.S.; Asokan, K.; et al. Investigations on the structural, optical and electronic properties of Nd doped ZnO thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 105410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Casero, R.; Gutiérrez-Llorente, A.; Pons-Y-Moll, O.; Seiler, W.; Defourneau, R.M.; Defourneau, D.; Millon, E.; Perrière, J.; Goldner, P.; Viana, B. Er-doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed-laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 054905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bail, A. Whole powder pattern decomposition methods and applications: A retrospection. Powder Diffr. 2005, 20, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, B.K.; Alves, H.; Hofmann, D.M.; Kriegseis, W.; Forster, D.; Bertram, F.; Christen, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Straßburg, M.; Dworzak, M.; et al. Bound exciton and donor-acceptor pair recombinations in ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi B 2004, 241, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Averseng, F.; Haque, F.; Borghetti, P.; Krafft, J.-M.; Baptiste, B.; Costentin, G.; Stankic, S. Defect-related multicolour emissions in ZnO smoke: From violet, over green to yellow. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5102–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Averseng, F.; Krafft, J.-M.; Borghetti, P.; Costentin, G.; Stankic, S. Controlled formation of native defects in ultrapure ZnO for the assignment of green emissions to oxygen vacancies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 12696–12704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Interpretation of europium(III) spectra. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 295, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bünzli, J.C.G.; Eliseeva, S.V. Basics of lanthanide photophysics. In Lanthanide Luminescence: Photophysical, Analytical and Biological Aspects; Hänninen, P., Härmä, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-642-21022-8. [Google Scholar]
- Badalawa, W.; Matsui, H.; Osone, T.; Hasuike, N.; Harima, H.; Tabata, H. Correlation between structural and luminescent properties of Eu3+-doped ZnO epitaxial layers. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 053502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Tu, D. Lanthanide-Doped Luminescent Nanomaterials, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-40363-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.Y.; Liu, G.K. The standard and anomalous crystal-field spectra of Eu3+. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Pushpal, G. Lanthanide-doped luminescent nanophosphors via ionic liquids. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 715531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaev, Y.E.; Tronc, P. Ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic ordering in the wurtzite-type diluted magnetic semiconductors. Phys. Solid State 2012, 54, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, P.H. Point Group Symmetry Application: Methods and Tables; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; ISBN 978-1-4613-3143-8. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, T.C.; Hauenstein, R.J. Fundamental properties of ZnO. In Zinc Oxide Materials for Electronic and Optoelectronic Device Applications; Litton, C.W., Reynolds, D.C., Collins, T.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-470-51971-4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, W.; Li, R.; Liu, G.; Antonio, M.R.; Chen, X. Optical spectroscopy of Eu3+ doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Song, H.; Lu, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Kong, X. Luminescent properties of LaPO4:Eu nanoparticles and nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16697–16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, H.; Ebisawa, K.; Okuno, T. Intense green luminescence from Eu2+-doped ZnO microstructures. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, L839–L841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Som, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, V.; Ntwaeaborwa, O.M.; Coetsee, E.; Swart, H.C. Tunable and white emission from ZnO:Tb3+ nanophosphors for solid state lighting applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, A.; Davesnne, C.; Labbé, C.; Cardin, J.; Marie, P.; Frilay, C.; Boudin, S.; Portier, X. Annealing effects on the photoluminescence of terbium doped zinc oxide films. Thin Solid Films 2014, 553, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G.; Jorio, A. Group Theory: Application to the Physics of Condensed Matter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-32897-1. [Google Scholar]
- Arguello, C.A.; Rosseau, D.L.; Porto, S.P.S. First-order Raman effect in wurtzite-type crystals. Phys. Rev. 1969, 181, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuscó, R.; Alarcón-Lladó, E.; Ibáñez, J.; Artús, L.; Jiménez, J.; Wang, B.; Callahan, M.J. Temperature dependence of Raman scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 165202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, J.M.; Cardona, M. Resonant Raman scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 16, 3753–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


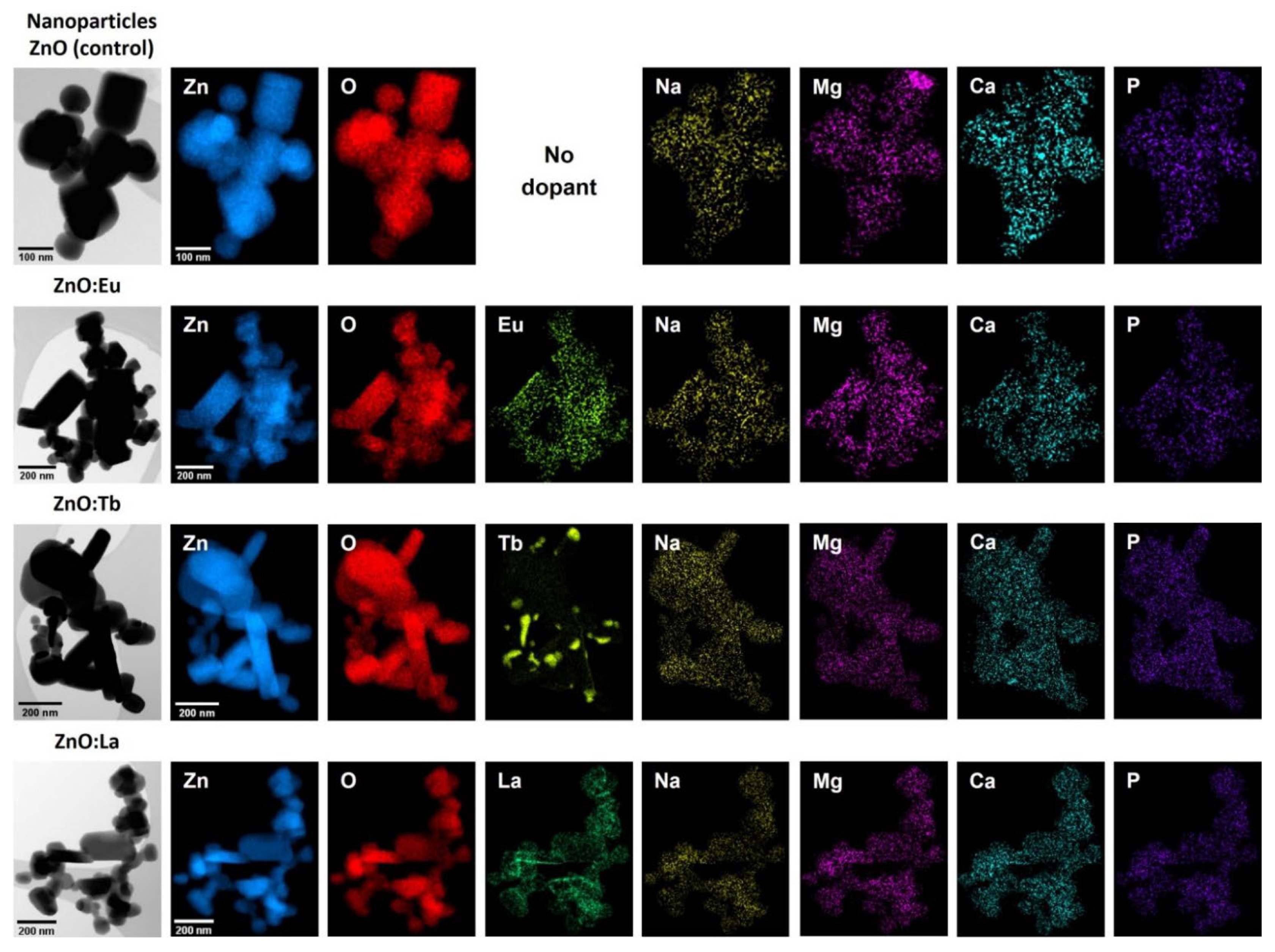


| Sample | ZnO | ZnO:Eu | ZnO:Tb | ZnO:La |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morphologies | Rod, hexagonal, and spherical shape | |||
| Particle size distribution (PSD) | ||||
| Geometric mean size (nm) | 179.34 ± 1.51 | 134.32 ± 1.52 | 111.63 ± 1.86 | 110.52 ± 1.66 |
| Aspect ratio (AR) | 1.25 ± 0.24 | 1.29 ± 0.26 | 1.36 ± 0.34 | 1.37 ± 0.36 |
| AR change | 0% | 3.2% | 8.8% | 9.6% |
| Span (dispersion) | 1.09 | 1.16 | 2.02 | 1.59 |
| Number of Modes Mode center (nm) | 1 mode 170 | 1 mode 110 | 1 mode 70 | 1 mode 90 |
| Decreased size | 0% | −26% | −38% | −38% |
| Elemental Composition (at%) | Atomic Ratio | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Zn 2p3/2 | O 1s | Ln (Eu/Tb/La) | Na 1s | Ca 2p3/2 | K 2p3/2 | Cl 2p3/2 | Zn/O | Zn(Na,Ln)/O | Ln/Zn |
| ZnO | 45.04 | 48.13 | - | 3.84 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 1.46 | 0.94 | 1.02 | - |
| ZnO:Eu | 38.74 | 50.10 | 1.81 | 5.48 | 0.61 | 1.36 | 1.84 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.05 |
| ZnO:Tb | 40.49 | 49.29 | 1.51 | 4.67 | 1.06 | 1.68 | 1.29 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.04 |
| ZnO:La | 31.65 | 52.92 | 4.63 | 5.77 | 0.76 | 1.69 | 2.58 | 0.60 | 0.79 | 0.15 |
| ZnO | ZnO:Eu | ZnO:Tb | ZnO:La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space Group | P63mc | P63mc | P63mc | P63mc |
| Cell parameters | ||||
| a (Å) | 3.24976 (2) | 3.25003 (2) | 3.25023 (2) | 3.25019 (2) |
| c (Å) | 5.20536 (3) | 5.20544 (3) | 5.20483 (3) | 5.20487 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 47.608 (0) | 47.617 (0) | 47.620 (0) | 47.616 (0) |
| Density (g/cm3) | 5.796 | 5.925 | 6.195 | 6.020 |
| Conventional Rietveld Reliability Factors (%) | ||||
| Rp | 6.30 | 5.80 | 5.79 | 5.75 |
| Rwp | 8.69 | 7.87 | 7.88 | 7.87 |
| Rexp | 7.33 | 7.31 | 7.13 | 7.31 |
| RBragg | 2.58 | 2.53 | 2.48 | 2.51 |
| RF | 2.22 | 2.60 | 2.30 | 2.48 |
| Χ2 | 1.40 | 1.16 | 1.22 | 1.16 |
| Structure | ||||
| O atomic coordinate in z-axis | 0.38710 (30) | 0.38746 (28) | 0.38294 (25) | 0.38130 (24) |
| Zn occupancy | 0.929 (3) | 0.918 (2) | 0.909 (2) | 0.904 (2) |
| O occupancy | 0.998 (9) | 1.000 (3) | 1.007 (2) | 1.000 (2) |
| Na occupancy | 0.021 (7) | 0.021 (7) | 0.035 (7) | 0.028 (6) |
| Ln occupancy (Eu, Tb, La) | - | 0.015 (1) | 0.028 (1) | 0.016 (1) |
| Zn Biso (Å2) | 0.355 (8) | 0.739 (9) | 0.819 (8) | 1.085 (8) |
| O Biso (Å2) | 0.945 (38) | 1.184 (41) | 0.964 (35) | 1.474 (37) |
| Na Biso (Å2) | 0.897 (8) | 0.991 (9) | 0.809 (8) | 1.075 (8) |
| Ln Biso (Å2) (Eu, Tb, La) | - | 0.994 (9) | 0.799 (8) | 0.985 (8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picasso, C.; Salinas, Y.; Brüggemann, O.; Scharber, M.C.; Sariciftci, N.S.; Cardozo, O.D.F.; Rodrigues, E.S.; Silva, M.S.; Stingl, A.; Farias, P.M.A. Lanthanide (Eu, Tb, La)-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Whey as an Eco-Friendly Chelating Agent. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132265
Picasso C, Salinas Y, Brüggemann O, Scharber MC, Sariciftci NS, Cardozo ODF, Rodrigues ES, Silva MS, Stingl A, Farias PMA. Lanthanide (Eu, Tb, La)-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Whey as an Eco-Friendly Chelating Agent. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(13):2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132265
Chicago/Turabian StylePicasso, Carolina, Yolanda Salinas, Oliver Brüggemann, Markus Clark Scharber, Niyazi Serdar Sariciftci, Olavo D. F. Cardozo, Eriverton S. Rodrigues, Marcelo S. Silva, Andreas Stingl, and Patricia M. A. Farias. 2022. "Lanthanide (Eu, Tb, La)-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Whey as an Eco-Friendly Chelating Agent" Nanomaterials 12, no. 13: 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132265
APA StylePicasso, C., Salinas, Y., Brüggemann, O., Scharber, M. C., Sariciftci, N. S., Cardozo, O. D. F., Rodrigues, E. S., Silva, M. S., Stingl, A., & Farias, P. M. A. (2022). Lanthanide (Eu, Tb, La)-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Whey as an Eco-Friendly Chelating Agent. Nanomaterials, 12(13), 2265. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12132265










