Engineering Gold Nanostructures for Cancer Treatment: Spherical Nanoparticles, Nanorods, and Atomically Precise Nanoclusters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
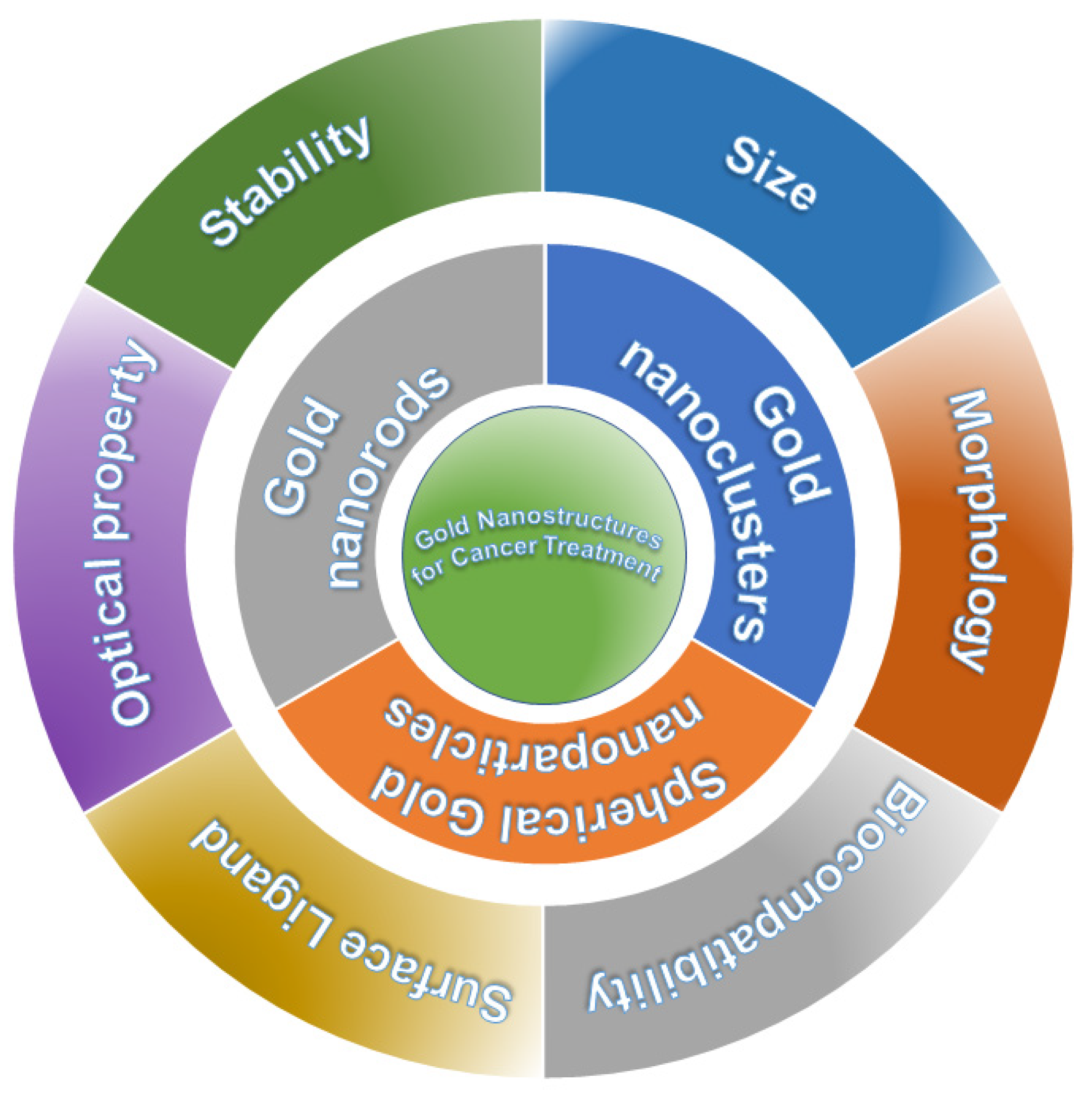
2. Gold Nanostructures for Cancer Treatment
2.1. Spherical Gold Nanoparticles
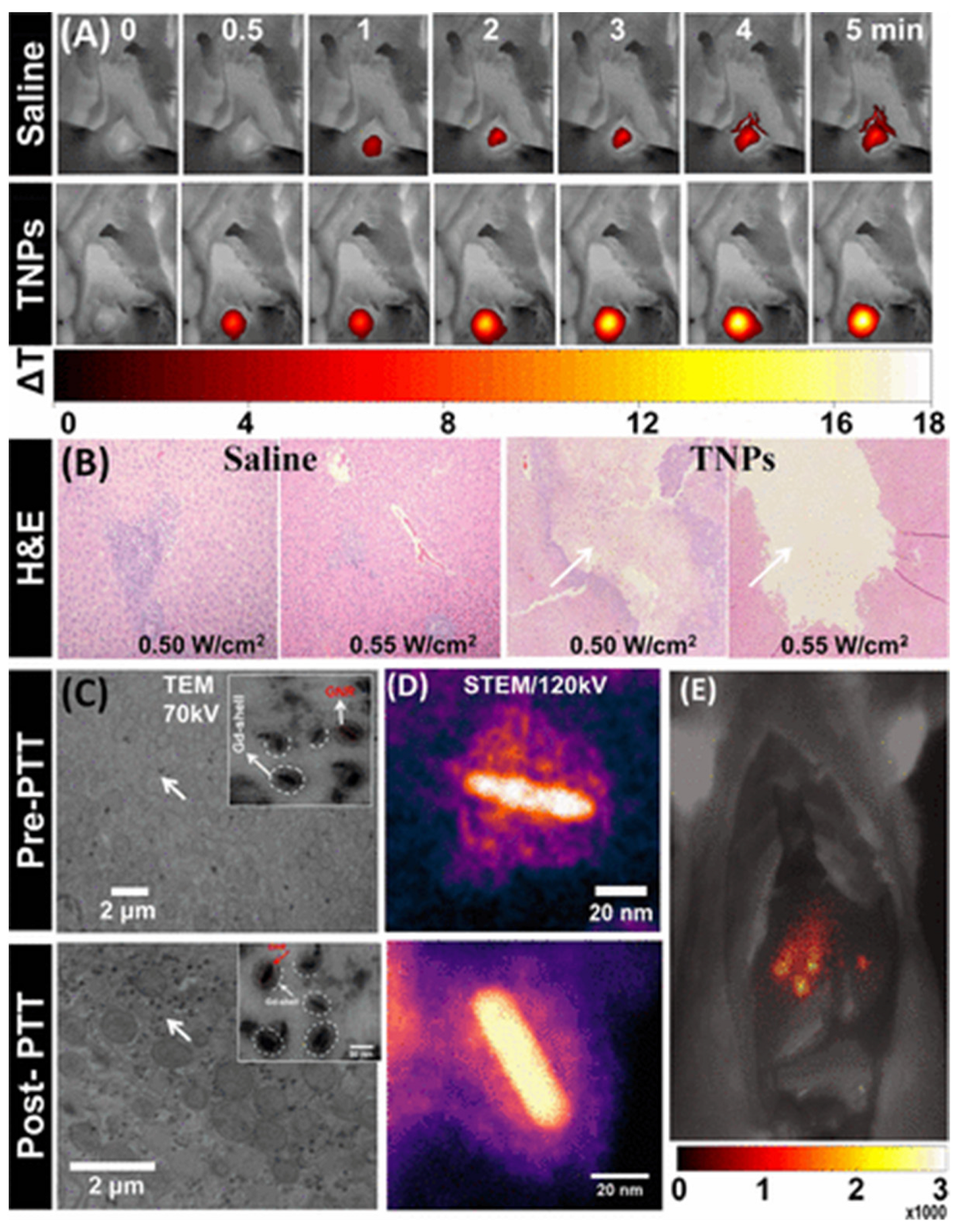
2.2. Gold Nanorods
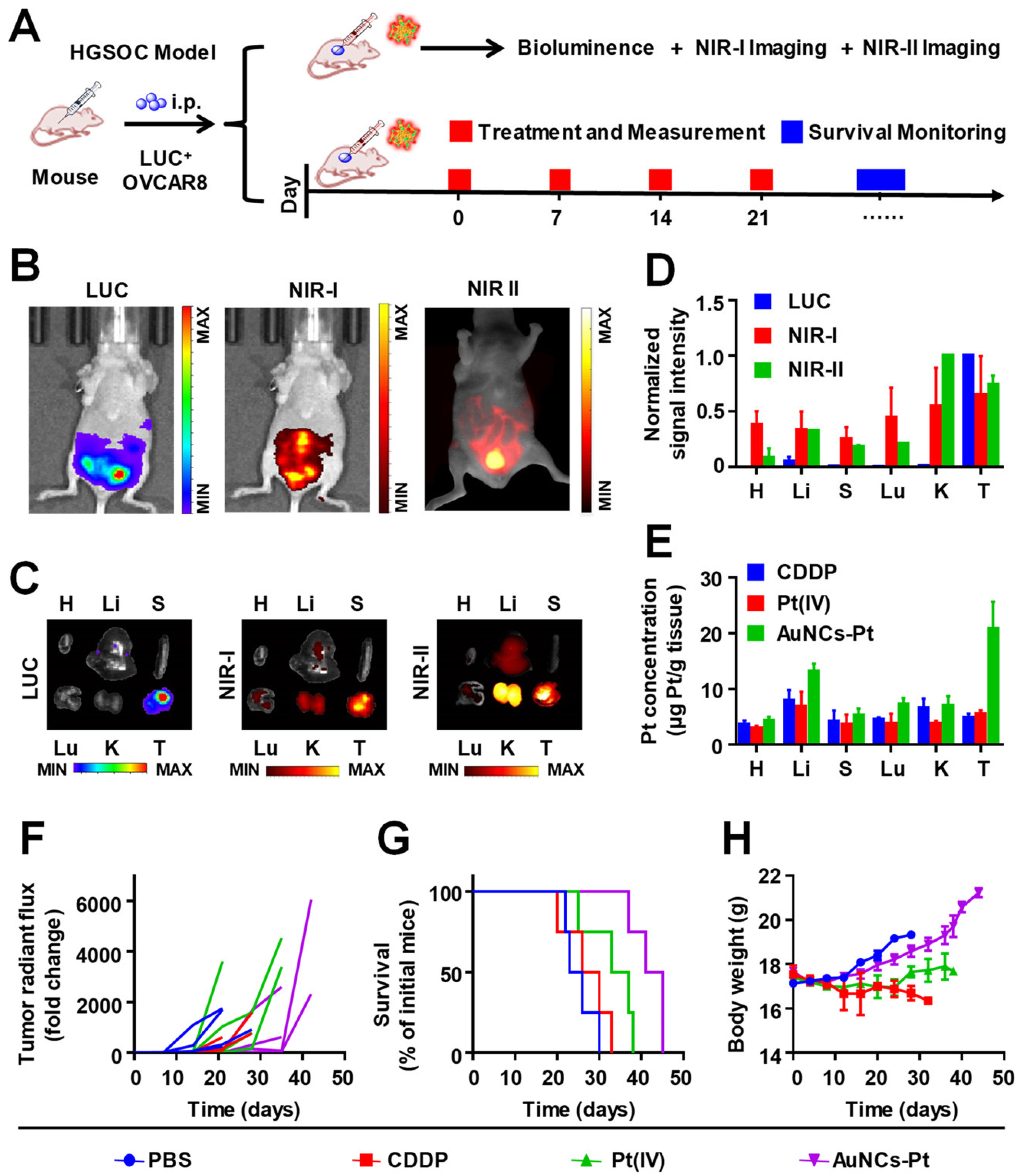
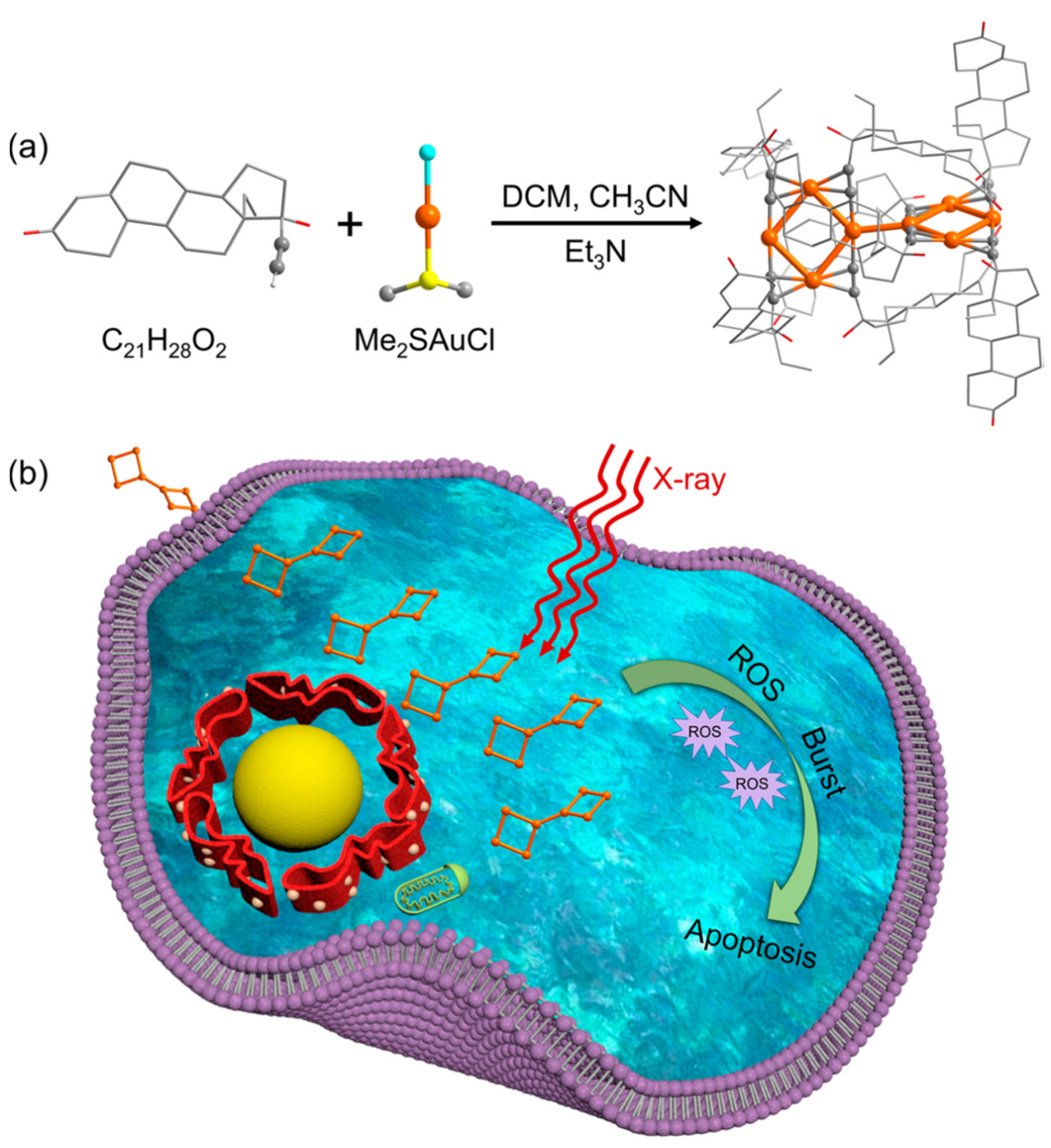
2.3. Atomically Precise Gold Nanoclusters
3. Challenges and Perspectives
- The targeting specificity issue. Even though the gold nanostructures can be designed to bind to specific cancer cells, there is still an urgent need for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics at the early stage with a high level of targeting specificity [103]. Currently, the widely employed cancer treatment strategies such as photoimaging and photothermal therapy still have the limitations such as non-specific binding and the unnecessary activation of the normal host immune response.
- The modulation of the gold nanostructures to meet the complex biological environment can be challenging. Upon the surface modification of the gold structures, the pharmacokinetic parameters of the gold nanostructures and the cellular response will be correspondingly changed, while in vivo, the fundamental comprehensive understanding of the interactions between the gold nanostructures and the biological moieties is still lacking [104].
- Some gold nanostructures (e.g., the gold nanocluster case mentioned in this review) can be used for both NIR-I and NIR-II imaging; however, when choosing both regions, the excitation wavelength range is quite limited, and the imaging effectiveness and efficiency still have room to improve. Determining how to modify the composition, morphology, and structure of these gold nanomaterials to work better for both NIR-I and NIR-II regions is still extremely challenging.
- For photothermal treatment based on gold nanostructures, the efficacy is highly dependent on the penetration depth of the NIR lasers, and the heating intensity can decrease with the increase in the laser penetration depth. This means that the laser intensity and the plasmonic effects of the gold nanostructures could be critical and deserve special attention in future studies.
- Even if gold nanostructures have been successfully documented for in vitro, in vivo, pre-clinical, and clinical studies, considering the cytotoxicity, the internalization of gold nanostructure with tissues, the complex biological environment, the long-term stability of the gold nanostructure’s integrity, and the high costs of preparing specifically designed nanogold agents, the way to realizing gold nanostructures for practical applications of cancer treatment is still long.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riley, R.S.; Day, E.S. Gold nanoparticle-mediated photothermal therapy: Applications and opportunities for multimodal cancer treatment. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ryu, N.-E.; Lim, D.-J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beik, J.; Khateri, M.; Khosravi, Z.; Kamrava, S.K.; Kooranifar, S.; Ghaznavi, H.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A. Gold nanoparticles in combinatorial cancer therapy strategies. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 387, 299–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Black, K.C.L.; Luehmann, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X.; Wan, D.; Liu, S.-Y.; Li, M.; Kim, P.; et al. Comparison Study of Gold Nanohexapods, Nanorods, and Nanocages for Photothermal Cancer Treatment. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wu, F.-G.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Jia, H.-R.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Liu, P.; Gu, N.; Chen, Z. Shape-Dependent Radiosensitization Effect of Gold Nanostructures in Cancer Radiotherapy: Comparison of Gold Nanoparticles, Nanospikes, and Nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13037–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadeer, N.S.; Murphy, C.J. Recent Progress in Cancer Thermal Therapy Using Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 4691–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, I.; Pradeep, T. Atomically Precise Clusters of Noble Metals: Emerging Link between Atoms and Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8208–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.W. Nanoelectrochemistry: Metal Nanoparticles, Nanoelectrodes, and Nanopores. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2688–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-R.; Goswami, N.; Yang, H.-H.; Xie, J. Functionalization of metal nanoclusters for biomedical applications. Analyst 2016, 141, 3126–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Hong, G.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Chang, J.; Gong, M.; He, H.; Yang, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, L.; et al. Atomic-Precision Gold Clusters for NIR-II Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, Z.R.; Marín, M.J.; Russell, D.A.; Searcey, M. Active targeting of gold nanoparticles as cancer therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8774–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavifard, S.; Jalili, S.; Rahmati, F.; Vasseghian, Y.; Ali, G.A.M.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Application of Dendrimer/Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy: A Review. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4231–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Yan, H.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.-J.; Zhang, J. Ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4944–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Sarwar, R.; Iqbal, A.; Bashir, U.; Farooq, U.; Halim, S.A.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Recent advances in combinatorial cancer therapy via multifunctionalized gold nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignani, S.; Shi, X.; Ceña, V.; Rodrigues, J.; Tomas, H.; Majoral, J.-P. Engineered non-invasive functionalized dendrimer/dendron-entrapped/complexed gold nanoparticles as a novel class of theranostic (radio)pharmaceuticals in cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, K.M.; Mendoza, S.; López-Romero, J.M.; Gasca-Tirado, J.R.; Manzano-Ramírez, A. Gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, application in colon cancer therapy and new approaches—review. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2021, 14, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, S.; Laraib, U.; Er, S.; Rahdar, A.; Hassanisaadi, M.; Zafar, M.N.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Bilal, M. Application of Green Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromma, K.; Chithrani, D.B. Advances in Gold Nanoparticle-Based Combined Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acunto, M.; Cioni, P.; Gabellieri, E.; Presciuttini, G. Exploiting gold nanoparticles for diagnosis and cancer treatments. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 192001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyadi, K.; Rahdar, A.; Esmaili, N.; Sayyadi, J. Application of gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and therapy: A mini-review. Adv. Nanochem. 2019, 1, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Alimardani, V.; Roudbali, P.L.; Ghasemi, Y.; Kaviani, E. Gold nanoparticles application in liver cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 25, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminabad, N.S.; Farshbaf, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Recent Advances of Gold Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications: State of the Art. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 77, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zutta Villate, J.M.; Hahn, M.B. Radioactive gold nanoparticles for cancer treatment. Eur. Phys. J. D 2019, 73, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.; Fontinha, D.; Martins, C.; Pires, D.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. Gold Nanoparticles for Vectorization of Nucleic Acids for Cancer Therapeutics. Molecules 2020, 25, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xue, Y.; Liu, M. Recent progress in the applications of gold-based nanoparticles towards tumor-targeted imaging and therapy. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7635–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendoeira, A.; García, L.R.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. Light Irradiation of Gold Nanoparticles Toward Advanced Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Therap. 2020, 3, 1900153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Ashby, C.R.; Zeng, L.; Fan, Y.-F.; Chen, Z.-S. Gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, physiochemical properties and therapeutic applications in cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Malviya, R. Understanding and advancement in gold nanoparticle targeted photothermal therapy of cancer. BBA-Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Xin, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. Gold Nanoparticle Mediated Phototherapy for Cancer. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 5497136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emami, F.; Banstola, A.; Vatanara, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.O.; Jeong, J.-H.; Yook, S. Doxorubicin and Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles for Colorectal Cancer Photochemotherapy. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1184–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, N.; Mao, C.; Yang, M. Protein-Induced Gold Nanoparticle Assembly for Improving the Photothermal Effect in Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11136–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lei, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Gold nanoparticles modified hollow carbon system for dual-responsive release and chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of tumor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Crawford, B.M.; Vo-Dinh, T. Gold nanoparticles-mediated photothermal therapy and immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, T.; Qin, X.; Qiao, Q.; Shang, L.; Song, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z. Intracellularly Generated Immunological Gold Nanoparticles for Combinatorial Photothermal Therapy and Immunotherapy against Tumor. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6635–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sun, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, X.; Xie, M.; You, Z. Ultra-small gold nanoparticles self-assembled by gadolinium ions for enhanced photothermal/photodynamic liver cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, M.A.; Köper, I. Biomedical applications of polyelectrolyte coated spherical gold nanoparticles. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Q.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, S. Gold nanoparticle-mediated delivery of paclitaxel and nucleic acids for cancer therapy (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4475–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; Zareyi, H.; Sheervalilou, R.; Laurent, S.; Ghaznavi, H.; Samadian, H. Gold nanoparticle-mediated bubbles in cancer nanotechnology. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.U.; Novosad, V.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Wali, H.; Ali, A.; Fateh, A.A.; Neogi, P.B.; Neogi, A.; Wang, Z. Gold Nanoparticles-enabled Efficient Dual Delivery of Anticancer Therapeutics to HeLa Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; He, D.; Tu, J.; Wang, R.; Zu, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Shi, D.; Webster, T.J.; Shen, Y. The comparative effect of wrapping solid gold nanoparticles and hollow gold nanoparticles with doxorubicin-loaded thermosensitive liposomes for cancer thermo-chemotherapy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8628–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X. Benzeneselenol-modified gold nanoclusters for cancer therapy. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6664–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, N.; O’Connell, F.; Prina-Mello, A.; O’Sullivan, J.; Marcone, S. Gold nanoparticles and obese adipose tissue microenvironment in cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2022, 525, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safwat, M.A.; Soliman, G.M.; Sayed, D.; Attia, M.A. Fluorouracil-Loaded Gold Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Skin Cancer: Development, in Vitro Characterization, and in Vivo Evaluation in a Mouse Skin Cancer Xenograft Model. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Q.; Dong, N.; Yang, X.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Development of gold nanorods for cancer treatment. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 220, 111458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, C. Mesoporous Silica-Coated Gold Nanorods as a Light-Mediated Multifunctional Theranostic Platform for Cancer Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Singh, B.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, M.-H.; Kim, K. Combinational Chemotherapy and Photothermal Therapy Using a Gold Nanorod Platform for Cancer Treatment. Part. Part. Syst. Character. 2020, 37, 2000099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.U.; Lin, J.; Younas, M.R.; Liu, X.; Shen, L. Synthesis of gold nanorods and their performance in the field of cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, P.M.; Rompicharla, S.V.K.; Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. An overview of synthetic strategies and current applications of gold nanorods in cancer treatment. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 432001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlapisi, N.; Motaung, T.E.; Linganiso, L.Z.; Oluwafemi, O.S.; Songca, S.P. Encapsulation of Gold Nanorods with Porphyrins for the Potential Treatment of Cancer and Bacterial Diseases: A Critical Review. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2019, 2019, 7147128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sagheer, L.A.M.; Alshahrie, A.; Mahmoud, W.E. Facile approach for developing gold nanorods with various aspect ratios for an efficient photothermal treatment of cancer. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 618, 126394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzer, O.; Ankri, R.; Motiei, M.; Popovtzer, R. Theranostic Approach for Cancer Treatment: Multifunctional Gold Nanorods for Optical Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 646713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Dube, A. Effect of the polyelectrolyte coating on the photothermal efficiency of gold nanorods and the photothermal induced cancer cell damage. IET Nanobiotechnology 2017, 11, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Qian, J.; He, S. Biologically Inspired Polydopamine Capped Gold Nanorods for Drug Delivery and Light-Mediated Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24368–24384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z. Targeted cancer imaging and photothermal therapy via monosaccharide-imprinted gold nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6716–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.R.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Wu, Y.; Han, T.; Peng, X.; Mackey, M.A.; Wang, D.; Shin, H.J.; Chen, Z.G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Efficacy, long-term toxicity, and mechanistic studies of gold nanorods photothermal therapy of cancer in xenograft mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parchur, A.K.; Sharma, G.; Jagtap, J.M.; Gogineni, V.R.; LaViolette, P.S.; Flister, M.J.; White, S.B.; Joshi, A. Vascular Interventional Radiology-Guided Photothermal Therapy of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis with Theranostic Gold Nanorods. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6597–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Jeong, C.B.; Choi, J.S.; Chang, K.S.; Yoon, M. Gold nanorods-conjugated TiO2 nanoclusters for the synergistic combination of phototherapeutic treatments of cancer cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Peng, Q.; Yang, L.; Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L. High-Performance Dual Combination Therapy for Cancer Treatment with Hybrid Membrane-Camouflaged Mesoporous Silica Gold Nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57732–57745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud Nouf, N.; Sabbah, D.A.; Abu-Dahab, R.; Abuarqoub, D.; Abdallah, M.; Ameerah; Khalil, E.A. Cholesterol-coated gold nanorods as an efficient nano-carrier for chemotherapeutic delivery and potential treatment of breast cancer: In vitro studies using the MCF-7 cell line. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12718–12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, B.E.; White, M.K.; Nima Alsudani, Z.A.; Watanabe, F.; Biris, A.S.; Ali, N. Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanorods in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacardo, D.B.; Neupane, B.; Rikard, S.M.; Lu, Y.; Mo, R.; Mishra, S.R.; Tracy, J.B.; Wang, G.; Ligler, F.S.; Gu, Z. A dual wavelength-activatable gold nanorod complex for synergistic cancer treatment. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12096–12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Guo, S.; Chen, R.; Zhou, D. pH and near-infrared light dual-stimuli responsive drug delivery using DNA-conjugated gold nanorods for effective treatment of multidrug resistant cancer cells. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Feng, B.; Cui, Z.; Lin, B.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; et al. Treatment of metastatic breast cancer by combination of chemotherapy and photothermal ablation using doxorubicin-loaded DNA wrapped gold nanorods. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8374–8384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Qian, J.; Hou, G.; Wang, Y.; Ji, L.; Suo, A. NIR/pH dual-responsive polysaccharide-encapsulated gold nanorods for enhanced chemo-photothermal therapy of breast cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H.; Peng, S.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Hu, Q.-H.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Q.-H. Gold nanorods conjugated with biocompatible zwitterionic polypeptide for combined chemo-photothermal therapy of cervical cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 207, 112014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ji, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhu, W. Dual-responsive nanohybrid based on degradable silica-coated gold nanorods for triple-combination therapy for breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2021, 128, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Burns, R.; Tichnell, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Oxygen Reduction Reaction and Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Catalyzed by Pd–Ru Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Porous Carbon Nanosheets. Catalysts 2018, 8, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Sheng, H.; Astruc, D.; Zhu, M. Atomically Precise Noble Metal Nanoclusters as Efficient Catalysts: A Bridge between Structure and Properties. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 526–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Li, L. Near-Infrared-Light-Assisted in Situ Reduction of Antimicrobial Peptide-Protected Gold Nanoclusters for Stepwise Killing of Bacteria and Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11063–11071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Gold nanoclusters for theranostic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, K.; Shanavas, A. The Role of Gold Nanoclusters as Emerging Theranostic Agents for Cancer Management. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2021, 9, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Looij, S.M.; Hebels, E.R.; Viola, M.; Hembury, M.; Oliveira, S.; Vermonden, T. Gold Nanoclusters: Imaging, Therapy, and Theranostic Roles in Biomedical Applications. Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. Glucose decorated gold nanoclusters: A membrane potential independent fluorescence probe for rapid identification of cancer cells expressing Glut receptors. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 155, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, B. Novel iodinated gold nanoclusters for precise diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2219–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yan, H.; Stogniy, M.Y.; Sivaev, I.B.; Bregadze, V.I.; Wang, X. Carborane Derivative Conjugated with Gold Nanoclusters for Targeted Cancer Cell Imaging. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, L. Gold nanocluster grafted conjugated polymer nanoparticles for cancer cell imaging and photothermal killing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 597, 124764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-P.; Wu, T.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-C.; Chen, Y.-X.; Chen, G.-S.; Lin, S.-Y. Self-Supplying O2 through the Catalase-Like Activity of Gold Nanoclusters for Photodynamic Therapy against Hypoxic Cancer Cells. Small 2017, 13, 1700278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Park, S.; Lim, K.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, E.S.; Oh, K.T.; Choi, H.-G.; Youn, Y.S. Facile fabrication of highly photothermal-effective albumin-assisted gold nanoclusters for treating breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Ma, N.; Xia, L.-Y.; Cheng, X.; Jia, H.-R.; Liu, P.; Gu, N.; Chen, Z.; et al. Glutathione-Depleting Gold Nanoclusters for Enhanced Cancer Radiotherapy through Synergistic External and Internal Regulations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10601–10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Shen, W.; Zhou, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhong, J.; Liu, T.; Yang, K. Radionuclide labeled gold nanoclusters boost effective anti-tumor immunity for augmented radio-immunotherapy of cancer. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, B.; Guo, R.; Miao, Y.; Li, B. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-mediated ultrasmall gold nanoclusters and hNIS gene synergize radiotherapy for breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2866–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Du, X.; Jia, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Liu, T.-C.; Li, Y.-Q. A transformable gold nanocluster aggregate-based synergistic strategy for potentiated radiation/gene cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2314–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Wang, X.; Walker, E.; Springer, S.; Ramamurthy, G.; Burda, C.; Basilion, J.P. Targeted Chemoradiotherapy of Prostate Cancer Using Gold Nanoclusters with Protease Activatable Monomethyl Auristatin E. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 14916–14927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, T.; Li, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, R. Toward the Tailoring Chemistry of Metal Nanoclusters for Enhancing Functionalities. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhu, M. Tailoring the photoluminescence of atomically precise nanoclusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2422–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, X. Engineering luminescent metal nanoclusters for sensing applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 451, 214268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Chen, T.; Yuan, X.; Xie, J. Toward Total Synthesis of Thiolate-Protected Metal Nanoclusters. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Jin, R. Programmable Metal Nanoclusters with Atomic Precision. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Qian, S.; Yang, G.; Du, F.; Yuan, X. The beauty of binary phases: A facile strategy for synthesis, processing, functionalization, and application of ultrasmall metal nanoclusters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 438, 213900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Chen, J.; Luo, Z.; Wu, D.; Shen, X.; Song, S.-S.; Sun, Y.-M.; Liu, P.-X.; Zhao, J.; Huo, S.; et al. Enhanced Tumor Accumulation of Sub-2 nm Gold Nanoclusters for Cancer Radiation Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Song, S.; Sun, Y.; Fan, S.; Fan, F.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Ultrasmall Au10−12(SG)10−12 Nanomolecules for High Tumor Specificity and Cancer Radiotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4565–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, B.; Jiang, X.; Das, A.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, M.; Jin, R.; Zheng, J. Glomerular barrier behaves as an atomically precise bandpass filter in a sub-nanometre regime. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Du, B.; Huang, Y.; Yu, M.; Zheng, J. Cancer Photothermal Therapy with ICG-Conjugated Gold Nanoclusters. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Zhai, S.; Hu, W.; Chi, S.; Song, D.; Liu, Z. Gold nanoclusters as a GSH activated mitochondrial targeting photosensitizer for efficient treatment of malignant tumors. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21384–21389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.; Ma, W.; Yu, M.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Illuminating Platinum Transportation while Maximizing Therapeutic Efficacy by Gold Nanoclusters via Simultaneous Near-Infrared-I/II Imaging and Glutathione Scavenging. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13536–13547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Han, X.; Liu, Z. Nanoparticle-Enhanced Radiotherapy to Trigger Robust Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.; Gao, P.; Zhou, W.; Mei, C.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.-F.; Chu, P.K.; Chen, T. Sequentially Triggered Delivery System of Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots with Surface Charge-Switching Ability for Precise Tumor Radiosensitization. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12401–12415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, J.; Liang, C.; Chao, Y.; Jin, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z. Self-Supplied Tumor Oxygenation through Separated Liposomal Delivery of H2O2 and Catalase for Enhanced Radio-Immunotherapy of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6360–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.-T.; Yang, G.; Mo, S.-J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Li, B.-J.; Ma, W.; Guo, Y.-X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.-Q.; et al. Atomically Precise Gold–Levonorgestrel Nanocluster as a Radiosensitizer for Enhanced Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8320–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-M.; Jia, T.-T.; Li, B.; Ma, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zang, S.-Q. Tuning the properties of atomically precise gold nanoclusters for biolabeling and drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8766–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.; Garg, A.; Ravikumar, V.; Mijakovic, I. Gold Nanoparticles in Diagnostics and Therapeutics for Human Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-S.; Liu, S.-J.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Chu, X.-D.; Lin, Z.-B.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, S.-H.; Guo, Y.-G.; Ding, H.; Pan, Y.-L.; et al. The Application of and Strategy for Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 687399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Gold Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, W.; Ma, G.; Shen, Q.; Tang, Z. Engineering Gold Nanostructures for Cancer Treatment: Spherical Nanoparticles, Nanorods, and Atomically Precise Nanoclusters. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12101738
He W, Ma G, Shen Q, Tang Z. Engineering Gold Nanostructures for Cancer Treatment: Spherical Nanoparticles, Nanorods, and Atomically Precise Nanoclusters. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(10):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12101738
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Wei, Guanyu Ma, Quanli Shen, and Zhenghua Tang. 2022. "Engineering Gold Nanostructures for Cancer Treatment: Spherical Nanoparticles, Nanorods, and Atomically Precise Nanoclusters" Nanomaterials 12, no. 10: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12101738
APA StyleHe, W., Ma, G., Shen, Q., & Tang, Z. (2022). Engineering Gold Nanostructures for Cancer Treatment: Spherical Nanoparticles, Nanorods, and Atomically Precise Nanoclusters. Nanomaterials, 12(10), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12101738






