Synthesis of In Situ Photoinduced Halloysite-Polypyrrole@Silver Nanocomposite for the Potential Application in Humidity Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
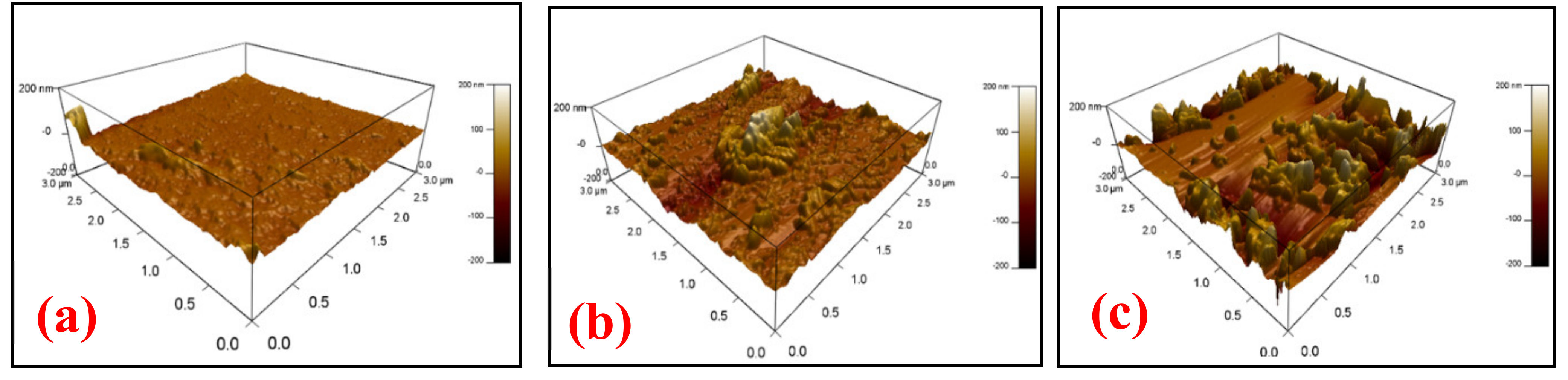
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bibi, F.; Guillaume, C.; Vena, A.; Gontard, N.; Sorli, B.J.S.; Physical, A.A. Wheat gluten, a bio-polymer layer to monitor relative humidity in food packaging: Electric and dielectric characterization. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.-G.; Shiu, W.-L.; Tsai, M.-S. Flexible humidity sensor based on Au nanoparticles/graphene oxide/thiolated silica sol–gel film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorache, F.; Petrila, I.; Slatineanu, T.; Dumitrescu, A.M.; Iordan, A.R.; Dobromir, M.; Palamaru, M.N. Humidity sensor characteristics and electrical properties of Ni–Zn–Dy ferrite material prepared using different chelating-fuel agents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holze, R.; Stejskal, J. Recent trends and progress in research into structure and properties of polyaniline and polypyrrole—Topical Issue. Chem. Pap. 2013, 67, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, R.; Darabont, A.; Nan, A.; Aldea, N.; Macovei, D.; Bica, D.; Vekas, L.; Pana, O.; Soran, M.; Koos, A.; et al. New polypyrrole-multiwall carbon nanotubes hybrid materials. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2006, 8, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Navarro-Cuñado, A.M.; Arnáiz-Lozano, V.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole based electrochemical sensor for selective determination of 4-ethylphenol. Talanta 2020, 207, 120351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Lin, X.; Dai, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Humidity sensors based on MCM-41/polypyrrole hybrid film via in-situ polymerization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, C. Recent advances in self-actuation and self-sensing materials: State of the art and future perspectives. Talanta 2020, 212, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, R. Conductive Photopolymers: In Situ Synthesis of Metal nanoparticles. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Dai, B. AuCl3 on polypyrrole-modified carbon nanotubes as acetylene hydrochlorination catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 142, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, K.; Singh, A.; Aswal, D.K.; Losno, R.; Benna-Zayani, M.; Chehimi, M.M. Novel, ternary clay/polypyrrole/silver hybrid materials through in situ photopolymerization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivic, N.; Kuroishi, P.K.; Dumur, F.; Gigmes, D.; Dove, A.P.; Sardon, H. Recent advances and challenges in the design of organic photoacid and photobase generators for polymerizations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10410–10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jlassi, K.; Chandran, S.; Mičušik, M.; Benna-Zayani, M.; Yagci, Y.; Thomas, S.; Chehimi, M.M. Poly (glycidyl methacrylate)-grafted clay nanofiller for highly transparent and mechanically robust epoxy composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Jia, D. Newly emerging applications of halloysite nanotubes: A review. Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Fauzi, M.A.; Bakar, A.A. Morphological, thermal and tensile properties of halloysite nanotubes filled ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, F.; Armata, N.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G. Adsorption studies of molecules on the halloysite surfaces: A computational and experimental investigation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2951–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Hydrophobically modified halloysite nanotubes as reverse micelles for water-in-oil emulsion. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7472–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Sanzillo, V. Modified halloysite nanotubes: Nanoarchitectures for enhancing the capture of oils from vapor and liquid phases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Cabet, E.; Lilienbaum, A.; Hamadi, S.; Abderrabba, M.; Chehimi, M.M. Polypyrrole/Ag/mesoporous silica nanocomposite particles: Design by photopolymerization in aqueous medium and antibacterial activity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N.K.; Tiwari, K.; Roy, A.; Mishra, A.; Govindan, A. Ag-Loaded WO3 Ceramic Nanomaterials: Characterization and Moisture Sensing Studies. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2013, 10, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Touati, F.; Shakoor, R. Improvement of humidity sensing properties of PVDF-TiO2 nanocomposite films using acetone etching. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, K.; Benna-Zayani, M.; Chehimi, M.M.; Yagci, Y. Efficient photoinduced In situ preparation of clay/poly (glycidyl methacrylate) nanocomposites using hydrogen-donor silane. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2015, 53, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousli, F.; Snoussi, Y.; Khalil, A.M.; Jlassi, K.; Mekki, A.; Chehimi, M.M. Surface Modification of Polymeric Substrates with Photo-and Sonochemically Designed Macromolecular Grafts. Surf. Modif. Polym. Methods Appl. 2019, 273–315. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, S.; Liu, W.; Yao, C.; Li, X.; Kong, Y.; Liu, X.; Mao, H.; Li, Y. Preparation of polyaniline–polypyrrole binary composite nanotube using halloysite as hard-template and its characterization. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and characterization of coaxial halloysite/polypyrrole tubular nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6857–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C. Characteristics of vibration modes of polypyrrole on surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 571, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, L. Polypyrrole nanofiber arrays synthesized by a biphasic electrochemical strategy. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2276–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Hwang, B.-J. Identification of oxidized polypyrrole on Raman spectrum. Synth. Met. 2000, 113, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballav, N.; Choi, H.J.; Mishra, S.B.; Maity, A. Polypyrrole-coated halloysite nanotube clay nanocomposite: Synthesis, characterization and Cr (VI) adsorption behaviour. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 102, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; Chaudhuri, I.; Khanra, K.; Bhattacharyya, N. Biological application of green silver nanoparticle synthesized from leaf extract of Rauvolfia serpentina Benth. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2016, 6, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, K.; Sliem, M.H.; Eid, K.; Krupa, I.; Chehimi, M.M.; Abdullah, A.M. Novel Enzyme-Free Multifunctional Bentonite/Polypyrrole/Silver Nanocomposite Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide Detection over a Wide pH Range. Sensors 2019, 19, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravčáková, M.; Omastová, M.; Olejníková, K.; Pukánszky, B.; Chehimi, M.M. The preparation and properties of sodium and organomodified-montmorillonite/polypyrrole composites: A comparative study. Synth. Met. 2007, 157, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Shi, P.; Yan, W.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.; Kim, S.H. Thickness and Structure of Adsorbed Water Layer and Effects on Adhesion and Friction at Nanoasperity Contact. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, L.; Mandal, A.R.; Mandal, S. Humidity-sensing properties of conducting polypyrrole-silver nanocomposites. J.Exp Nanosci. 2008, 3, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Sadaoka, Y.; Matsuguchi, M. Humidity sensors based on polymer thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 35, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Yun, S.; Kim, J. Flexible humidity and temperature sensor based on cellulose–polypyrrole nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 165, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.-G.; Wang, C.-P. Flexible humidity sensor based on TiO2 nanoparticles-polypyrrole-poly-[3-(methacrylamino) propyl] trimethyl ammonium chloride composite materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, R.; Nematdoust, S. A resistive-type humidity sensor based on polypyrrole and ZnO nanoparticles: Hybrid polymers vis-a-vis nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 112129–112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | O | Al | Si | C | Ag | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNT | 43.4 | 16.6 | 14.5 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| HNT-DMA | 46.6 | 9.5 | 7.5 | 34 | 0 | 1.7 |
| HNT-DMA-PPy@Ag | 45 | 10.6 | 8.7 | 33 | 0.6 | 2.7 |
| Materials | Si | Al | O | C | N | N(NO3) | Ag | Na | K | Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNT | 16.5 | 7.9 | 62.3 | 2.10 | - | - | - | 2.80 | 0.11 | 0.50 |
| HNT-NH2* | 24.4 | 12.0 | 59.2 | 9.8 | 1.50 | - | - | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.92 |
| HNT-NH2-PPy@Ag | 14.7 | 6.7 | 36.2 | 38.0 | 5.28 | 0.13 | 2.10 | traces | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Sample Type | 0.25 w/W% HNT-DMA-PPy@Ag film | 0.5 w/W% HNT-DMA-PPy@Ag film | 1 w/W% HNT-DMA-PPy@Ag film |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle image |  | 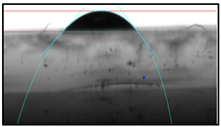 |  |
| Contact angle | 68.2° | 46.6° | 37° |
| Material | Experimental details | Sensing Range | Response/Recovery time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose–PPy nanocomposite | Chemical oxidative polymerization. Time = 30 min at RT CuCl2/Py: 10 mL/5 vol% Regenerated cellulose films emerged infiltrate of PPy | 30–90%RH | ∼418 s | [36] |
| TiO2 NPs/PPy/PMAPTAC) | Photopolymerization Time = 20 min under UV light at RT AgNO3/Pyrrole/TiO2 NP PMAPTAC/AIBN PET substrate | 11–90%RH | 30–45 s | [37] |
| PPy-ZnO nanocomposite | Chemical oxidative polymerization. Time = 60 min at 70 °C PPy-ZnO NP PPy/ZnO: 50 mg/11.8 mg | 11–75%RH | 180–60 s | [38] |
| HNT-DMA-PPy@Ag | In situ photopolymerization Time = 20 min at RT HNT/AgNO3/Py = 1 g/0.1 M/0.5 M | 10–90%RH | 30–35 s | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jlassi, K.; Mallick, S.; Mutahir, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Touati, F. Synthesis of In Situ Photoinduced Halloysite-Polypyrrole@Silver Nanocomposite for the Potential Application in Humidity Sensors. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071426
Jlassi K, Mallick S, Mutahir H, Ahmad Z, Touati F. Synthesis of In Situ Photoinduced Halloysite-Polypyrrole@Silver Nanocomposite for the Potential Application in Humidity Sensors. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(7):1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071426
Chicago/Turabian StyleJlassi, Khouloud, Shoaib Mallick, Hafsa Mutahir, Zubair Ahmad, and Farid Touati. 2020. "Synthesis of In Situ Photoinduced Halloysite-Polypyrrole@Silver Nanocomposite for the Potential Application in Humidity Sensors" Nanomaterials 10, no. 7: 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071426
APA StyleJlassi, K., Mallick, S., Mutahir, H., Ahmad, Z., & Touati, F. (2020). Synthesis of In Situ Photoinduced Halloysite-Polypyrrole@Silver Nanocomposite for the Potential Application in Humidity Sensors. Nanomaterials, 10(7), 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10071426






