Ab-Initio Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Boron- and Nitrogen-Doped Penta-Graphene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Models and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Geometrical Structure and Stability
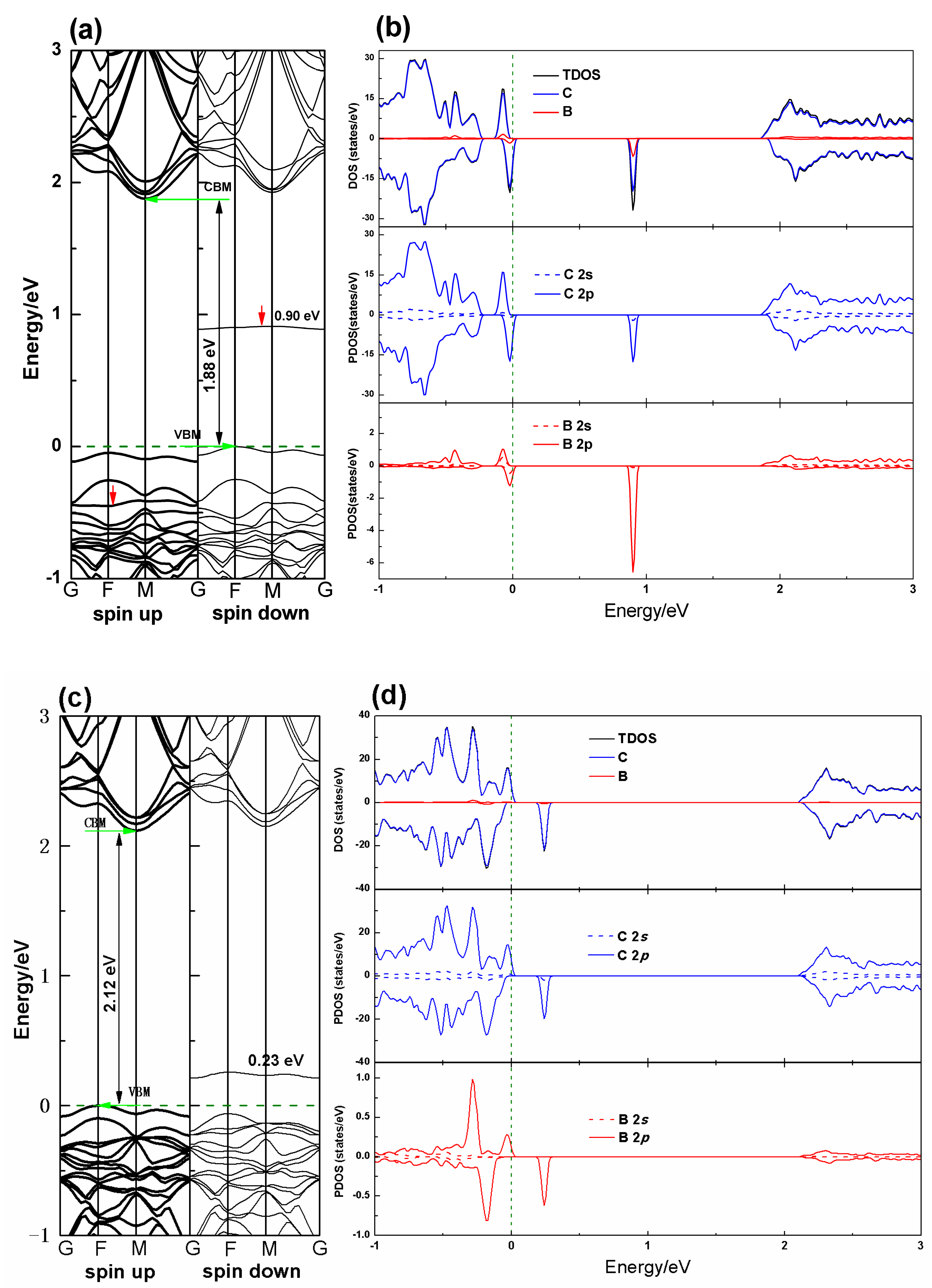
3.2. Electronic Properties
3.3. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electronic field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pykal, M.; Jurečka, P.; Karlický, F.; Otyepka, M. Modelling of graphene functionalization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 6351–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.G.; Mandelli, D.; Urbakh, M.; Hod, O. Nanoserpents: Graphene nanoribbon motion on two-dimensional hexagonal materials. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6009–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Sonvane, Y.; Hussain, T.; Ahuja, R. Achieving ultrahigh carrier mobilities and opening the band gap in two-dimensional Si2BN. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 21716–21723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.P.; Jiao, J.T.; Hou, Y.S.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.P.; Wang, T.X.; Fu, Z.M.; Xu, G.L.; Wu, R.Q. How does the electric current propagate through fully-hydrogenated borophene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 21552–21556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Dai, Z.X.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.G.; Li, D.S.; Sun, C.H. Two-dimensional boron sheets as metal-free catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 19051–19055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix, A.J.; Zhou, X.F.; Kiraly, B.; Wood, J.D.; Alducin, D.; Myers, B.D.; Liu, X.L.; Fisher, B.L.; Santiago, U.; Guest, J.R.; et al. Synthesis of borophenes: Anisotropic, two-dimensional boron polymorphs. Science 2015, 350, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, S.S.; Ma, Y.D.; Du, A.J.; Liao, T.; Gu, Y.T.; Kou, L.Z. Distorted Janus transition metal dichalcogenides: Stable two-dimensional materials with sizable band gap and ultrahigh carrier mobility. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 19153–19160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Li, H.D.; Wang, J.T. Prediction of a new two-dimensional metallic carbon allotrope. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 2024–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, S.D. Two-dimensional carbon allotropes from graphene to graphyne. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3677–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.S.; Kawazoe, Y.; Jena, P. Penta-graphene: A new carbon allotrope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2372–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, F.Q.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q. Tuning the electronic and mechanical properties of penta-graphene via hydrogenation and fluorination. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 14191–14197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Varshney, V.; Lee, J.; Zhang, T.; Wohlwend, J.L.; Roy, A.K.; Luo, T. Hydrogenation of penta-graphene leads to unexpected large improvement in thermal conductivity. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, R.; Wu, S.Y.; Chen, H.T. Nitrogen-doped penta-graphene as a superior catalytic activity for CO oxidation. Carbon 2018, 132, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Su, W.S.; Chen, H.T. A new carbo n allotrope: Penta-graphene as a metal-free catalyst for CO oxidation. Carbon 2017, 114, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.W.; Zhan, H.F.; Zhu, Y.B.; Wu, H.G.; Gu, Y. Mechanical properties of penta-graphene nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9642–9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Cao, X.R.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, R.J.; Zheng, Y.X.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, C.Z.; Ho, K.M.; Fan, Y.J.; et al. Novel penta-graphene nanotubes: Strain-induced structural and semiconductor-metal transitions. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 19310–19317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, T.; Beltrán, J.I.; Schliemann, J. Tight-binding approach to penta-graphene. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einollahzadeh, H.; Fazeli, S.M.; Dariani, R.S. Studying the electronic and phononic structure of penta-graphane. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Maiyalagan, T.; Wang, X. Review on recent progress in nitrogen-doped graphene: Synthesis, characterization, and its potential applications. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoli, S.; Favaro, M. Doping graphene with boron: A review of synthesis methods, physicochemical characterization, and emerging applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 5002–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Jindal, V.K. Designing band gap of graphene by B and N dopant atoms. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdiyorov, G.R.; Dixit, G.; Madjet, M.E. Band gap engineering in penta-graphene by substitutional doping: First-principles calculations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 475001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, N.; Wu, S.Y.; Chen, H.T. Boron- and nitrogen-doped penta-graphene as a promising material for hydrogen storage: A computational study. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2002, 14, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.J.; Segall, M.D.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Probert, M.I.J.; Refson, K.; Payne, M.C. First principles methods using CASTEP. Z. Krist. 2005, 220, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, V.; Winkler, B.; White, J.A.; Packard, C.J.; Payne, M.C.; Akhmatskaya, E.V.; Nobes, R.H. Electronic structure, properties, and phase stability of inorganic crystals: A pseudopotential plane-wave study. Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2000, 77, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.C.; Teter, M.P.; Allen, D.C.; Arias, T.A.; Joannopoulos, J.D. Iterative minimization techniques for ab initio total-energy calculations: Molecular dynamics and conjugate gradients. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 1045–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, C.J.; Mauri, F. All-electron magnetic response with pseudopotentials: NMR chemical shifts. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbanshi, B.; Sarkar, S.; Mandal, B.; Sarkar, P. Energetic and electronic structure of penta-graphene nanoribbons. Carbon 2016, 100, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
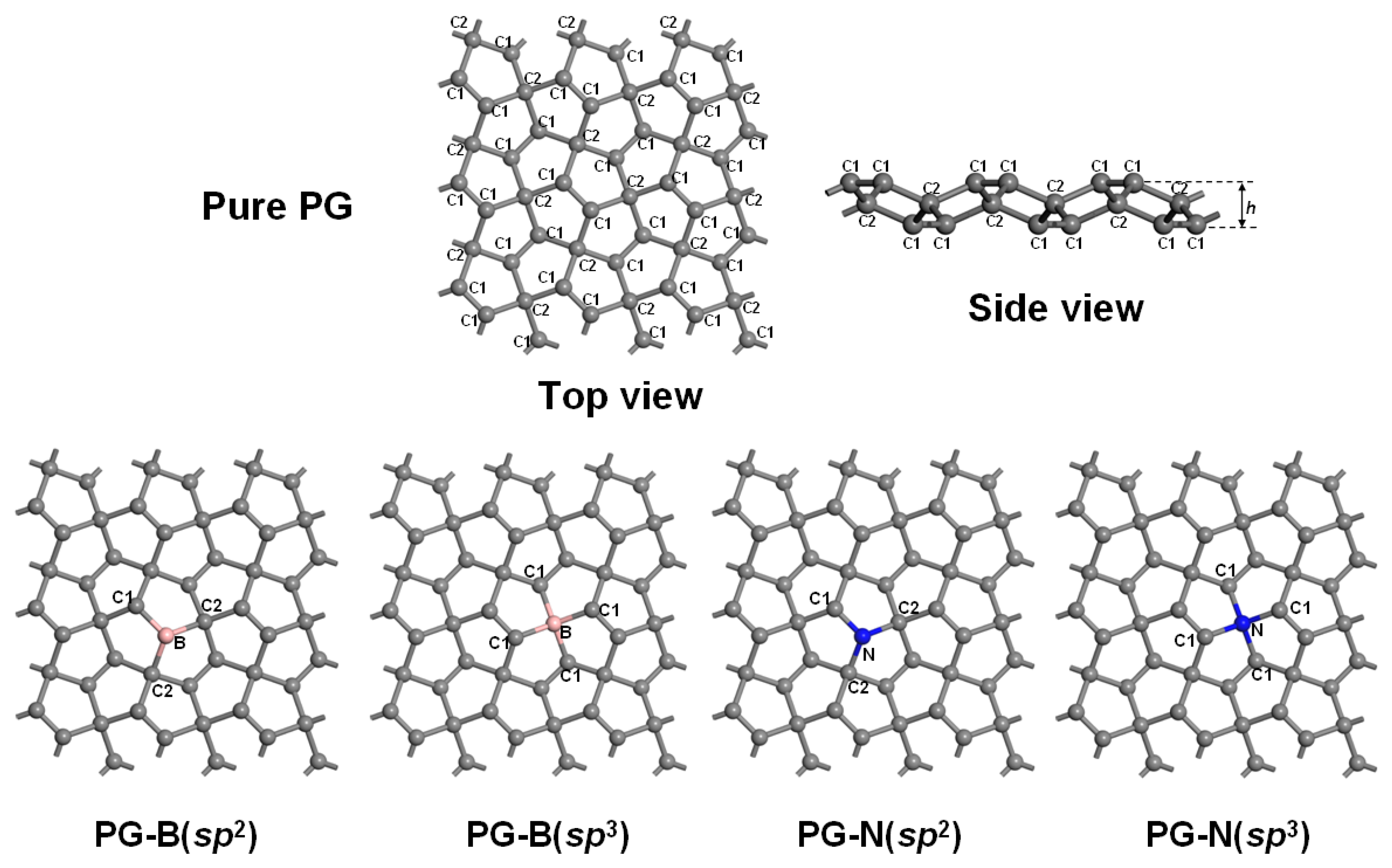




| System | a (Å) | b (Å) | h (Å) | d (Å) | Eg (eV) | Ef (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure PG | 10.904 | 10.904 | 1.203 | C1–C1 = 1.337 C1–C2 = 1.547 | 2.22 | - |
| PG–B (sp2) | 10.920 | 10.920 | 1.394 | B–C1 = 1.502 B–C2 = 1.613 | 1.88 | 1.39 |
| PG–B (sp3) | 10.948 | 10.948 | 1.304 | B–C1 = 1.594 | 2.12 | 1.75 |
| PG–N (sp2) | 10.873 | 10.873 | 1.286 | N–C1 = 1.384 N–C2 = 1.542 | 2.10 | −1.02 |
| PG–N (sp3) | 10.873 | 10.871 | 1.310 | N–C1 = 1.546 | 1.97 | 1.14 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Cao, Y.; Dai, X.; Ding, X.-Y.; Chen, L.; Li, B.-S.; Wang, D.-Q. Ab-Initio Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Boron- and Nitrogen-Doped Penta-Graphene. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040816
Zhang C, Cao Y, Dai X, Ding X-Y, Chen L, Li B-S, Wang D-Q. Ab-Initio Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Boron- and Nitrogen-Doped Penta-Graphene. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(4):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040816
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chao, Yu Cao, Xing Dai, Xian-Yong Ding, Leilei Chen, Bing-Sheng Li, and Dong-Qi Wang. 2020. "Ab-Initio Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Boron- and Nitrogen-Doped Penta-Graphene" Nanomaterials 10, no. 4: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040816
APA StyleZhang, C., Cao, Y., Dai, X., Ding, X.-Y., Chen, L., Li, B.-S., & Wang, D.-Q. (2020). Ab-Initio Study of the Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Boron- and Nitrogen-Doped Penta-Graphene. Nanomaterials, 10(4), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040816





