Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Carbon–Ti Composites
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Photocatalytic Tests
3. Results and Discussion
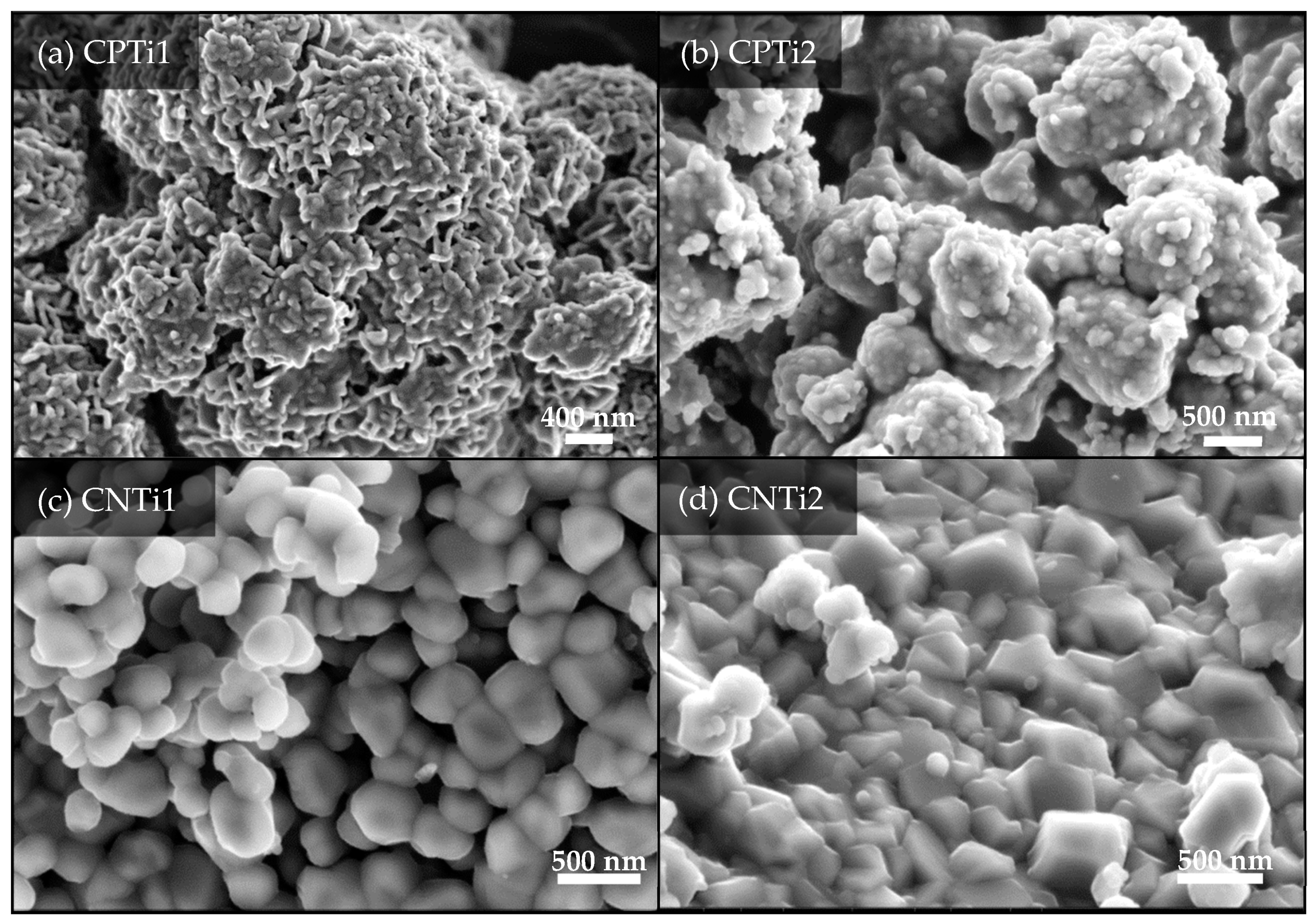
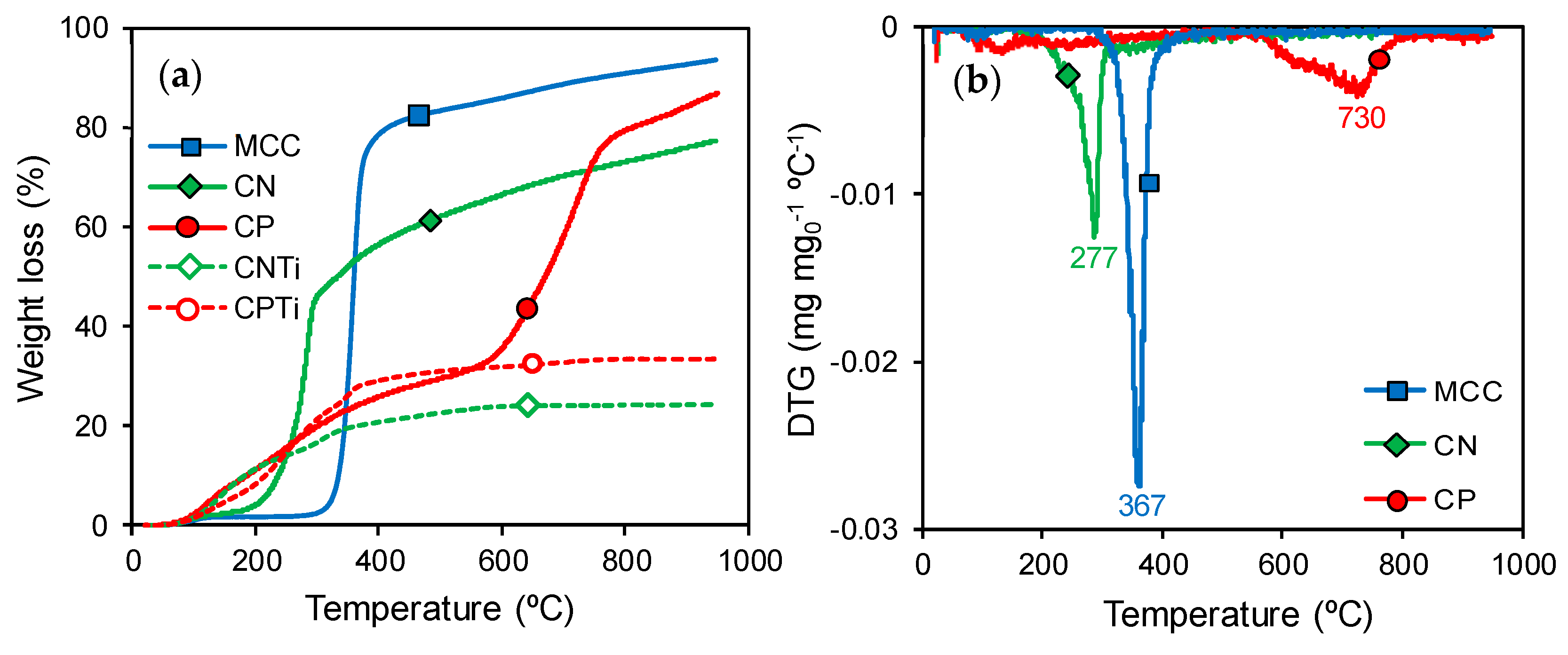
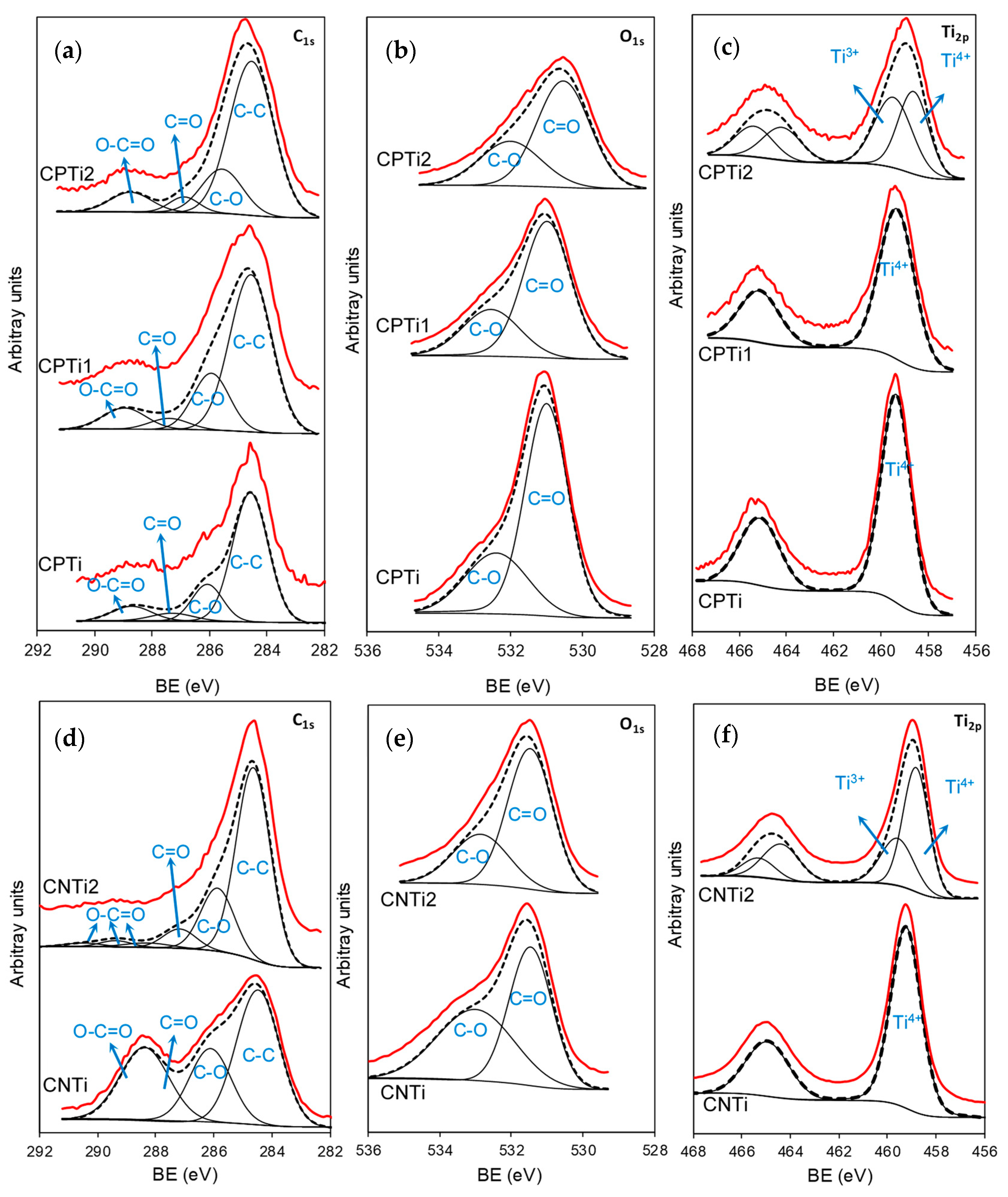
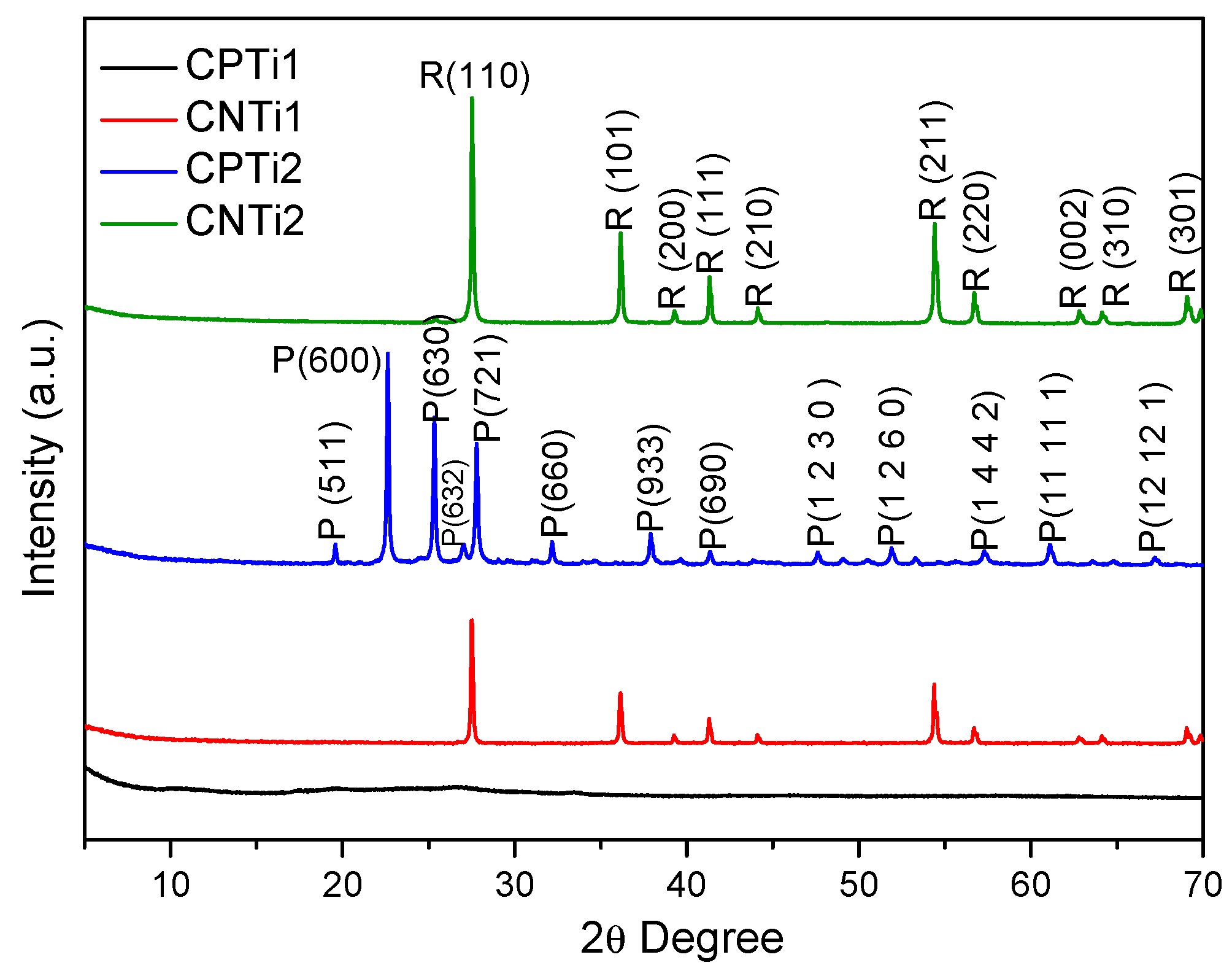
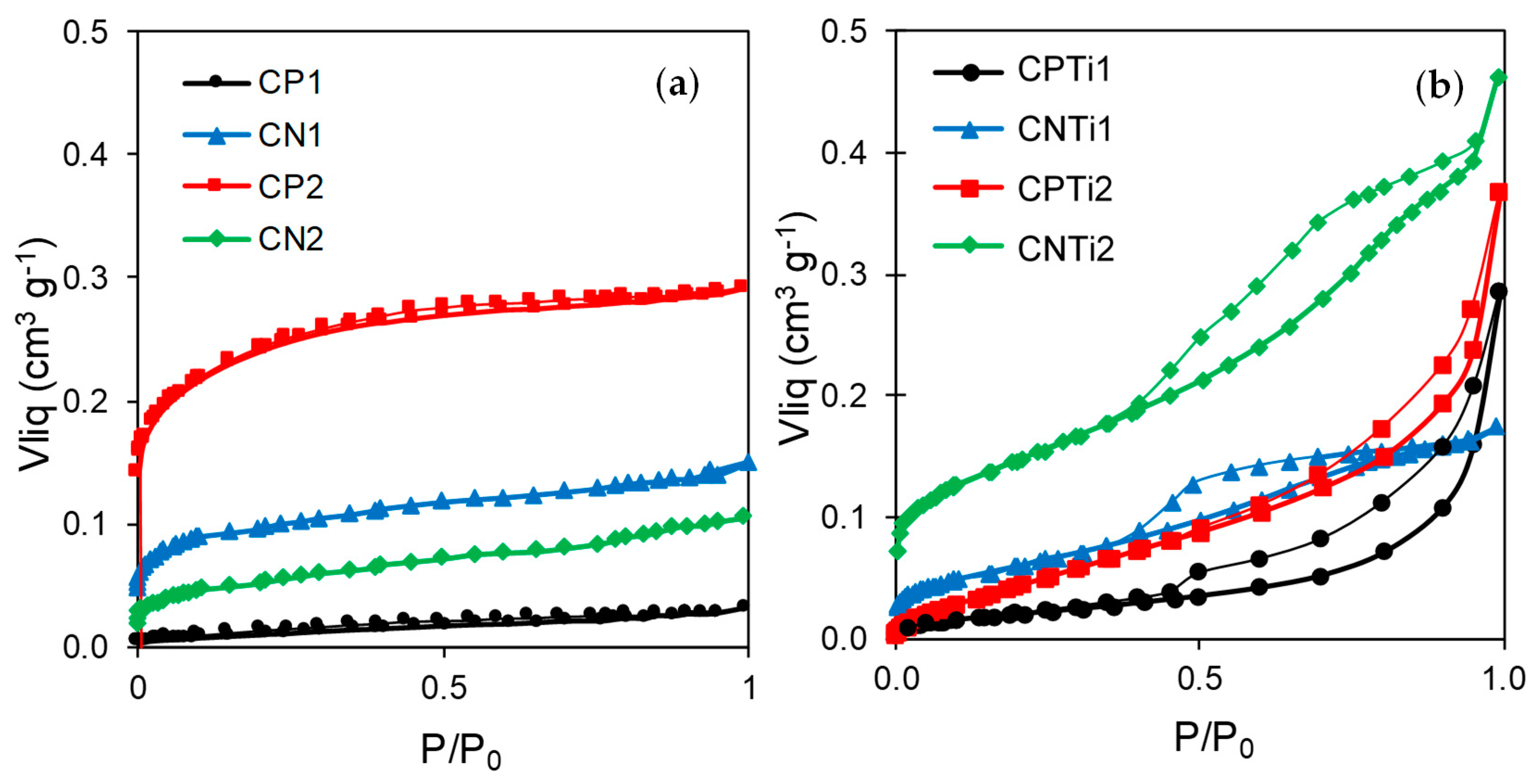
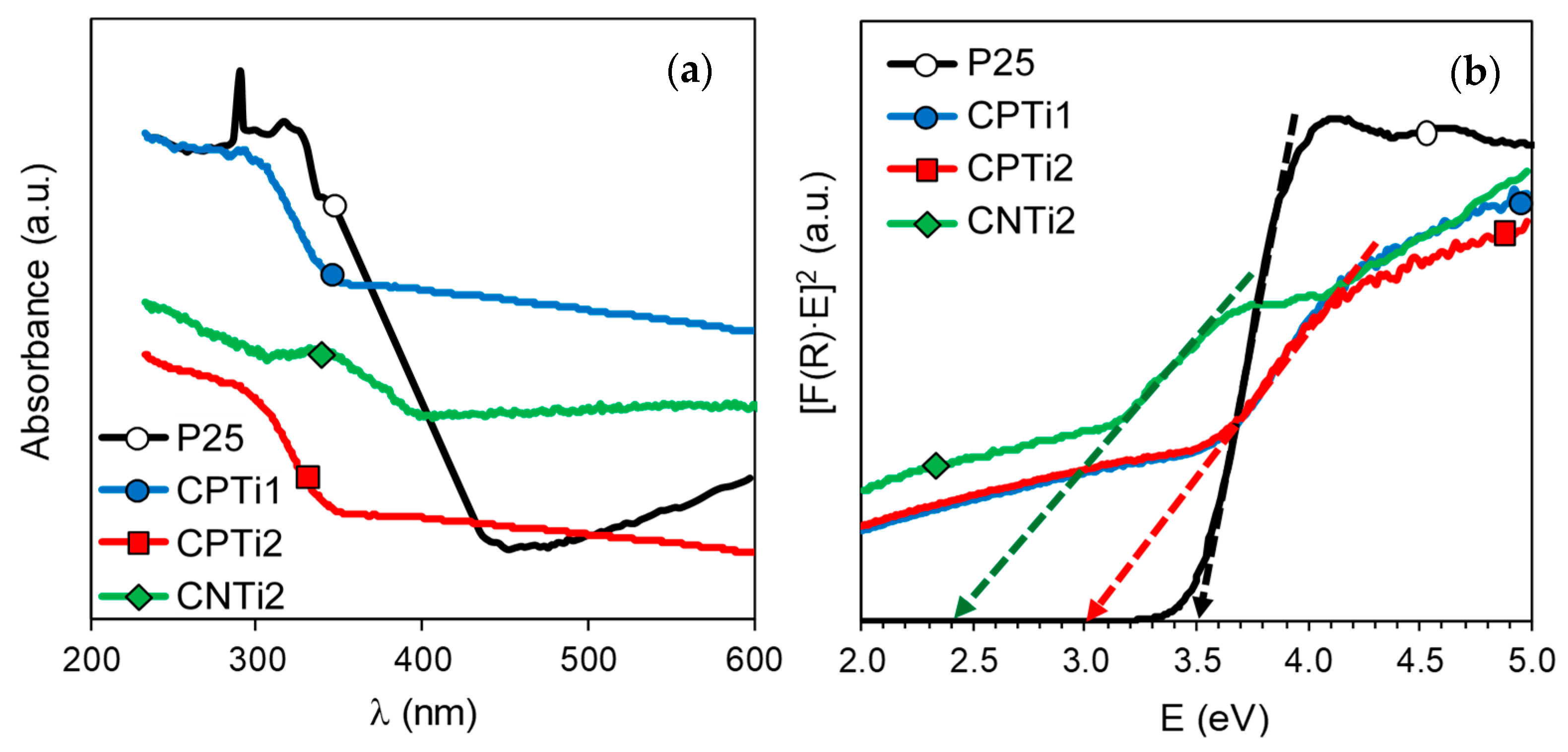
3.1. Materials Characterization
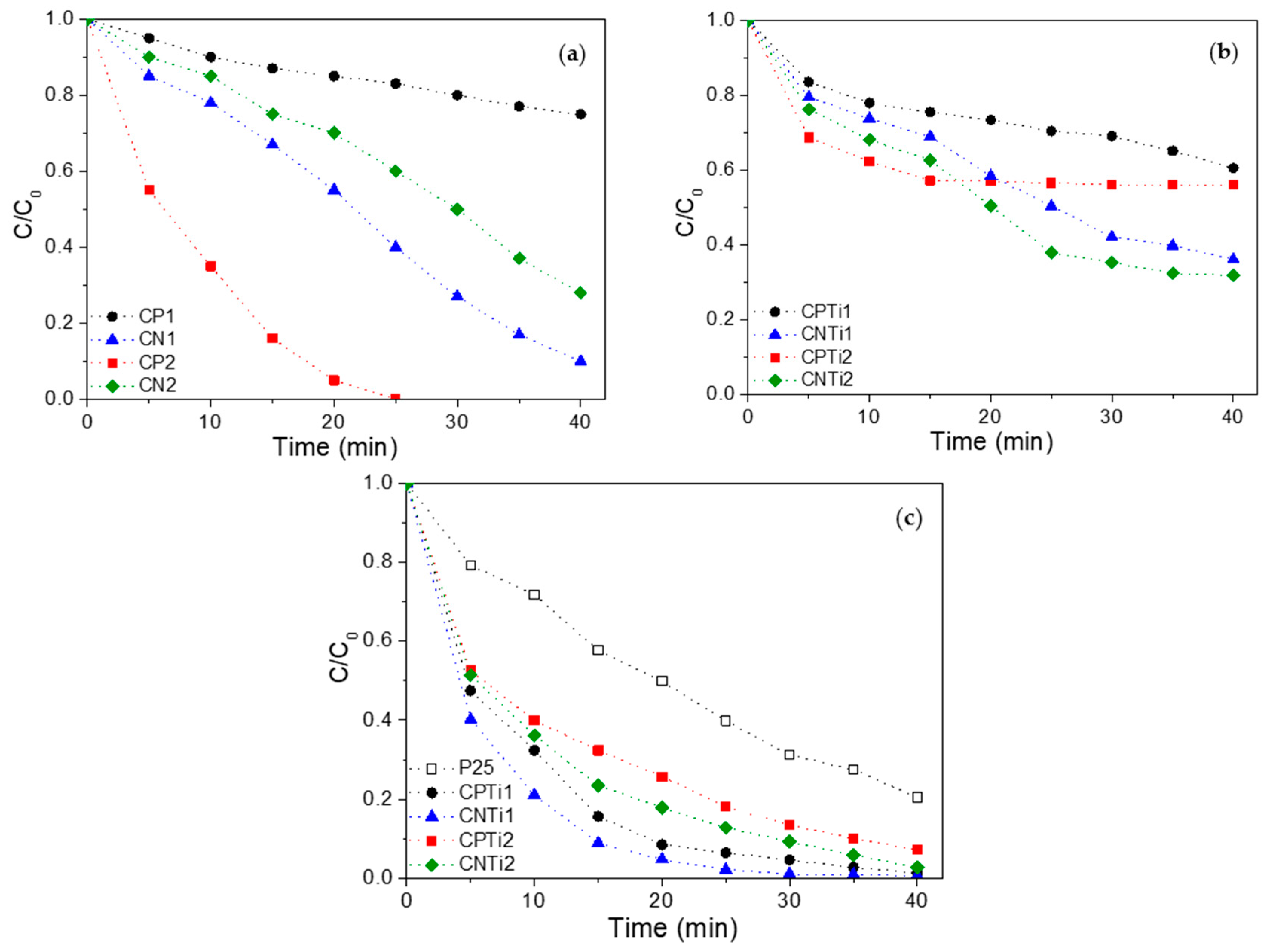
3.2. Removal of Orange G (OG) Azo Dye
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, M.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wei, Z.-S.; Hu, J.-Q.; Pan, S.-D.; Xiao, R.-Y.; Dong, C.-Y.; Jin, M.-C. Rapid decolorization of dye Orange G by microwave enhanced Fenton-like reaction with delafossite-type CuFeO2. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Huai, J.; Gong, W.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, J. Magnetic carbon nanotubes synthesis by Fenton’s reagent method and their potential application for removal of azo dye from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 378, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, R.K.; Zain, M.F.M.; Jamil, M. An environment-friendly solution for indoor air purification by using renewable photocatalysts in concrete: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 62, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailón-García, E.; Elmouwahidi, A.; Álvarez, M.A.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. New carbon xerogel-TiO2 composites with high performance as visible-light photocatalysts for dye mineralization. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 201, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.T.; Pillai, S.C.; Seery, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.G.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Byrne, J.A.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Likodimos, V.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Falaras, P.; Silva, A.M.T. Advanced nanostructured photocatalysts based on reduced graphene oxide-TiO2 composites for degradation of diphenhydramine pharmaceutical and methyl orange dye. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2012, 123–124, 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pei, X.; Chen, X. Effects of indium doping on properties of xIn-0.1%Gd-TiO2 photocatalyst synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 104, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliev, V.; Tomova, D.; Bilyarska, L. Promoting the oxidative removal rate of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on gold-doped WO3/TiO2/reduced graphene oxide photocatalysts under UV light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2018, 351, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Ting, J.-M. Novel nitrogen-doped anatase TiO2 mesoporous bead photocatalysts for enhanced visible light response. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9992–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindha, A.; Sivakumar, T. Visible active N, S co-doped TiO2/graphene photocatalysts for the degradation of hazardous dyes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2017, 340, 46–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seri-Levy, A.; Samuel, J.; Farin, D.; Avnir, D. Photoprocesses on Fractal Surfaces. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Anpo, M., Matsuura, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 47, pp. 353–374. [Google Scholar]
- Leary, R.; Westwood, A. Carbonaceous nanomaterials for the enhancement of TiO2 photocatalysis. Carbon 2011, 49, 741–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Torres, S.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Design of graphene-based TiO2 photocatalysts-a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 3676–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Puma, G.; Bono, A.; Krishnaiah, D.; Collin, J.G. Preparation of titanium dioxide photocatalyst loaded onto activated carbon support using chemical vapor deposition: A review paper. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.G.; Faria, J.L. Photocatalytic oxidation of benzene derivatives in aqueous suspensions: Synergic effect induced by the introduction of carbon nanotubes in a TiO2 matrix. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 101, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Torres, S.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Graphene oxide-P25 photocatalysts for degradation of diphenhydramine pharmaceutical and methyl orange dye. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 275, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, A.Z.M. Biopolymers for superhydrophobic photocatalytic coatings. In Biopolymers and Biotech Admixtures for Eco-Efficient Construction Materials; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Ivanov, V., Karak, N., Jonkers, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 421–447. [Google Scholar]
- Ananpattarachai, J.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Enhancement of chromium removal efficiency on adsorption and photocatalytic reduction using a bio-catalyst, titania-impregnated chitosan/xylan hybrid film. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016, 130, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Mutalib, M.A.; Hir, Z.A.M.; Zain, M.F.M.; Mohamad, A.B.; Minggu, L.J.; Awang, N.A.; Salleh, W.N.W. An overview on cellulose-based material in tailoring bio-hybrid nanostructured photocatalysts for water treatment and renewable energy applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1232–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortelli, S.; Blosi, M.; Albonetti, S.; Vaccari, A.; Dondi, M.; Costa, A.L. TiO2 based nano-photocatalysis immobilized on cellulose substrates. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2014, 276, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallouli, N.; Elghniji, K.; Trabelsi, H.; Ksibi, M. Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol on TiO2 nanoparticles and TiO2/cellulosic fiber under UV and sunlight irradiation. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3640–S3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, A.W.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Przepiórski, J.; Kordala, R.; Pernak, J. Cellulose-TiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced UV–Vis light absorption. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Naikoo, G.A.; Sheikh, M.U.D.; Bano, M.; Khan, F. Effective photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye using alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite hydrogel under direct sunlight irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2016, 327, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garusinghe, U.M.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Batchelor, W.; Garnier, G. Water Resistant Cellulose—Titanium Dioxide Composites for Photocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, H.; Bailón-García, E.; Morales-Torres, S.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Physicochemical properties of new cellulose-TiO2 composites for the removal of water pollutants: Developing specific interactions and performances by cellulose functionalization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5032–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S.; Jamshidi, M. Sol–gel synthesis of carbon-doped TiO2 nanoparticles based on microcrystalline cellulose for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Environ. Technol. 2019, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckli, F. Porosity in Carbons. Characterization and Applications; Arnold: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, R.C.; Donnet, J.B.; Stoeckli, F. Active Carbon; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, H.; Bailón-García, E.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Morales-Torres, S. Synthesis of TixOy nanocrystals in mild synthesis conditions for the degradation of pollutants under solar light. Appl. Catal. B. 2019, 241, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.I.G.; Bica, C.I.D.; Nachtigall, S.M.B.; Rehman, N.; Rosa, S.M.L. Kinetical thermal degradation study of maize straw and soybean hull celluloses by simultaneous DSC–TGA and MDSC techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 565, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanlı, A.G.; Windle, A.H. Carbon fibres from cellulosic precursors: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4236–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prauchner, M.J.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F. Chemical versus physical activation of coconut shell: A comparative study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 152, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmouwahidi, A.; Bailón-García, E.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Carrasco-Marín, F. Activated carbons from KOH and H3PO4-activation of olive residues and its application as supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 229, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Rockstraw, D.A. Physical and chemical properties of carbons synthesized from xylan, cellulose, and Kraft lignin by H3PO4 activation. Carbon 2006, 44, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivo-Vilches, J.F.; Bailón-García, E.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Tailoring the surface chemistry and porosity of activated carbons: Evidence of reorganization and mobility of oxygenated surface groups. Carbon 2014, 68, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Role of oxygen functionalities on the synthesis of photocatalytically active graphene–TiO2 composites. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2014, 158–159, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Wan Salleh, W.N.; Jaafar, J.; Rosmi, M.S.; Hir, Z.A.M.; Abd Mutalib, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Tanemura, M. Carbon as amorphous shell and interstitial dopant in mesoporous rutile TiO2: Bio-template assisted sol-gel synthesis and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, J.M.; Bedia, J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. HEMP-derived activated carbon fibers by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Fuel 2009, 88, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Bian, L.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Pan, X. A novel biotemplated synthesis of TiO2/wood charcoal composites for synergistic removal of bisphenol A by adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; Maldonado-Hodar, F.J. Synthesis and surface characteristics of silica- and alumina-carbon composite xerogels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 4818–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Surface Characteristics of Titania/Carbon Composite Aerogels. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2295–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, N.; Anita; Rajput, P.; Bhattacharya, D.; Jha, S.N.; Biring, S.; Sen, S. Anatase to rutile phase transition promoted by vanadium substitution in TiO2: A structural, vibrational and optoelectronic study. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 14128–14134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liang, R.; Hu, A.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Y.N. Generation of oxygen vacancies in visible light activated one-dimensional iodine TiO2 photocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36959–36966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, A.; Ida, K.; Bhaskar, T.; Uddin, M.A.; Takashima, S.; Hirai, T.; Sakata, Y. Preparation of novel TiP2O7 carbon composite using ion-exchanged resin (C467) and evaluation for photocatalytic decomposition of 2-propanol. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2004, 260, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H. Polyhierarchically structured TiP2O7/C microparticles with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 10681–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoux, S.; Masquelier, C. Lithium insertion into titanium phosphates, silicates, and sulfates. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 5057–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Souza, D.R.; de Mesquita, J.P.; Lago, R.M.; Caminhas, L.D.; Pereira, F.V. Cellulose nanocrystals: A versatile precursor for the preparation of different carbon structures and luminescent carbon dots. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 93, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Gómez, R. Band-gap energy estimation from diffuse reflectance measurements on sol–gel and commercial TiO2: A comparative study. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Hao, M.; Shi, J.; Cao, Z.; He, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Novel visible light response Ag3PO4/TiP2O7 composite photocatalyst with low Ag consumption. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailón-García, E.; Elmouwahidi, A.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Development of Carbon-ZrO2 composites with high performance as visible-light photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 217, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, M.; Harsha, N.; Suhailath, K.; Mohamed, A.P.; Shukla, S. Hydrogen phosphate anions modified hydrogen titanate nanotubes for methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution: Validating novel method of predicting adsorption capacity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylidi, M.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X.E. Pathways of solar light-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Appl. Catal., B 2003, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachheb, H.; Puzenat, E.; Houas, A.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.-M. Photocatalytic degradation of various types of dyes (Alizarin S, Crocein Orange G, Methyl Red, Congo Red, Methylene Blue) in water by UV-irradiated titania. Appl. Catal., B 2002, 39, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, R.; Sun, S.; Qiao, L. Photocatalytic degradation and kinetics of Orange G using nano-sized Sn(IV)/TiO2/AC photocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2006, 260, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.R.; Pons, M.N.; Zahraa, O. Photocatalytic degradation of three azo dyes using immobilized TiO2 nanoparticles on glass plates activated by UV light irradiation: Influence of dye molecular structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadale, T.; Kulkarni, M.; Pravarthana, D.; Ramadan, W.; Thakur, P. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes using Au:TiO2, γ-Fe2O3:TiO2 functional nanosystems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, K.; Ette, P.M.; Madras, G.; Ramesha, K. Visible light assisted photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes on TiO2–CNT nanocomposites. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-N.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Wang, M.-Q.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Bao, S.-J. Interface engineered construction of porous g-C3N4/TiO2 heterostructure for enhanced photocatalysis of organic pollutants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshuman, A.; Saremi-Yarahmadi, S.; Vaidhyanathan, B. Enhanced catalytic performance of reduced graphene oxide–TiO2 hybrids for efficient water treatment using microwave irradiation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7709–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

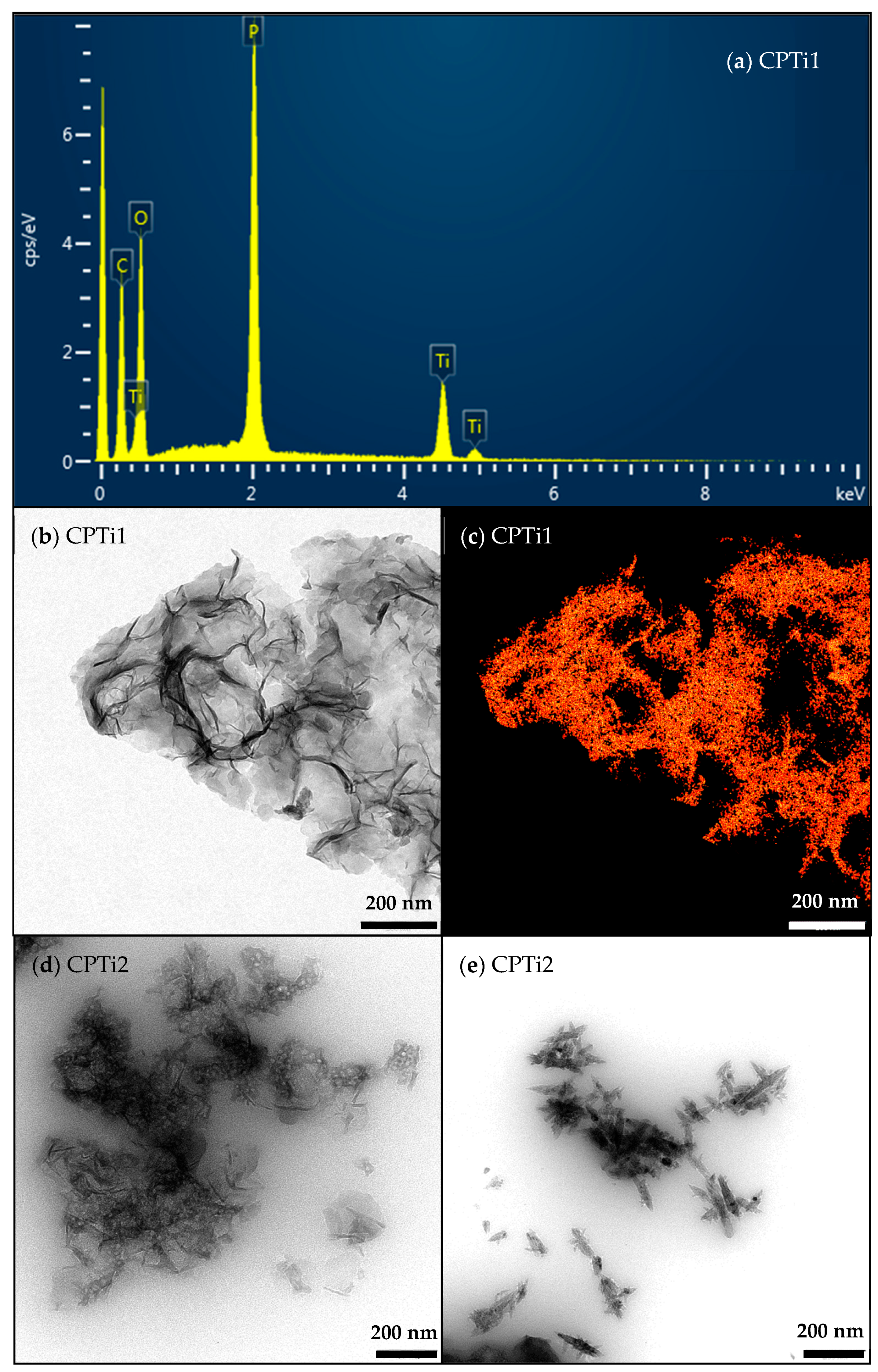
| Sample | pHPZC (±0.2) | Atomic Content (±0.1 wt. %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | P | Ti | ||
| CPTi | n.d. | 8.5 | 47.3 | - | 26.8 | 17.4 |
| CPTi1 | 2.7 | 22.0 | 42.7 | - | 21.9 | 13.4 |
| CPTi2 | 2.8 | 27.3 | 36.4 | - | 22.8 | 13.5 |
| CNTi | n.d. | 18.7 | 36.2 | 1.2 | - | 43.9 |
| CNTi2 | 6.5 | 16.4 | 35.4 | - | - | 48.2 |
| Sample | SBET (±5 m2·g−1) | Smicro (±5 m2·g−1) | L0 (±0.1 nm) | W0 (±0.01 cm3·g−1) | Vmeso (±0.01 cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP1 | 17 | 20 | 2.2 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| CP2 | 552 | 624 | 1.5 | 0.22 | 0.07 |
| CN1 | 226 | 253 | 1.5 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| CN2 | 115 | 122 | 1.7 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| CPTi1 | 28 | 35 | 1.4 | 0.01 | 0.27 |
| CPTi2 | 30 | 48 | 1.8 | 0.02 | 0.35 |
| CNTi1 | 124 | 141 | 1.6 | 0.05 | 0.13 |
| CNTi2 | 319 | 360 | 1.5 | 0.13 | 0.34 |
| Material | OG Concentration | Irradiation Source | Removal (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 (Degussa P25) | 84.2 μM, 2.5 g/L catalyst | UV high-pressure mercury lamp | 100%, 120 min | [56] |
| Sn(IV)/TiO2/AC | 110.5 μM, 12.5 g/L catalyst | UV high-pressure mercury light | 99.1%, 60 min | [57] |
| TiO2 (99% anatase) on glass plates | 66.3 μM | UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) | 100%, 130 min | [58] |
| Au–TiO2 | 25 μM | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 100%, 60 min | [59] |
| 10%CNT–TiO2 | 110.5 μM, 1 g/L catalyst | Metal halide lamp + cut-off filter (λ > 400 nm) | 100%, 120 min | [60] |
| CX–TiO2 | 55.3 μM, 1 g/L catalyst | Vis TeptoLux 2.0 lamp | 90%, 400 min | [4] |
| g-C3N4–TiO2 | 200 μM, 0.5 g/L | Simulated solar light (Xe Lamp) | 82%, 10 min | [61] |
| rGO–TiO2 | 10 μM | Microwave irradiation | 88%, 20 min | [62] |
| CNTi1 | 22 μM, 1.0 g/L | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 99%, 40 min | This work |
| CPTi1 | 22 μM, 1.0 g/L | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 100%, 40 min | This work |
| TiO2 (Degussa P25) | 22 μM, 1.0 g/L | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 79%, 40 min | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamad, H.; Bailón-García, E.; Morales-Torres, S.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729
Hamad H, Bailón-García E, Morales-Torres S, Carrasco-Marín F, Pérez-Cadenas AF, Maldonado-Hódar FJ. Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(4):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamad, Hesham, Esther Bailón-García, Sergio Morales-Torres, Francisco Carrasco-Marín, Agustín F. Pérez-Cadenas, and Francisco J. Maldonado-Hódar. 2020. "Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties" Nanomaterials 10, no. 4: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729
APA StyleHamad, H., Bailón-García, E., Morales-Torres, S., Carrasco-Marín, F., Pérez-Cadenas, A. F., & Maldonado-Hódar, F. J. (2020). Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials, 10(4), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729