An Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanocomposite as a Potential New Biological Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Antimicrobial Properties of Nanocomposites—Spot Test
2.4. Anticancer Studies
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. Cytotoxicity Studies
2.4.3. Time-Dependent Measurement of the ROS Level
2.4.4. Cell Cycle Assay
2.4.5. Annexin V Binding Assay
2.4.6. Immunoblotting
2.4.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Structural Analysis—XRD and Raman Studies
3.2. Microscopic Observations vs the Chemical Composition
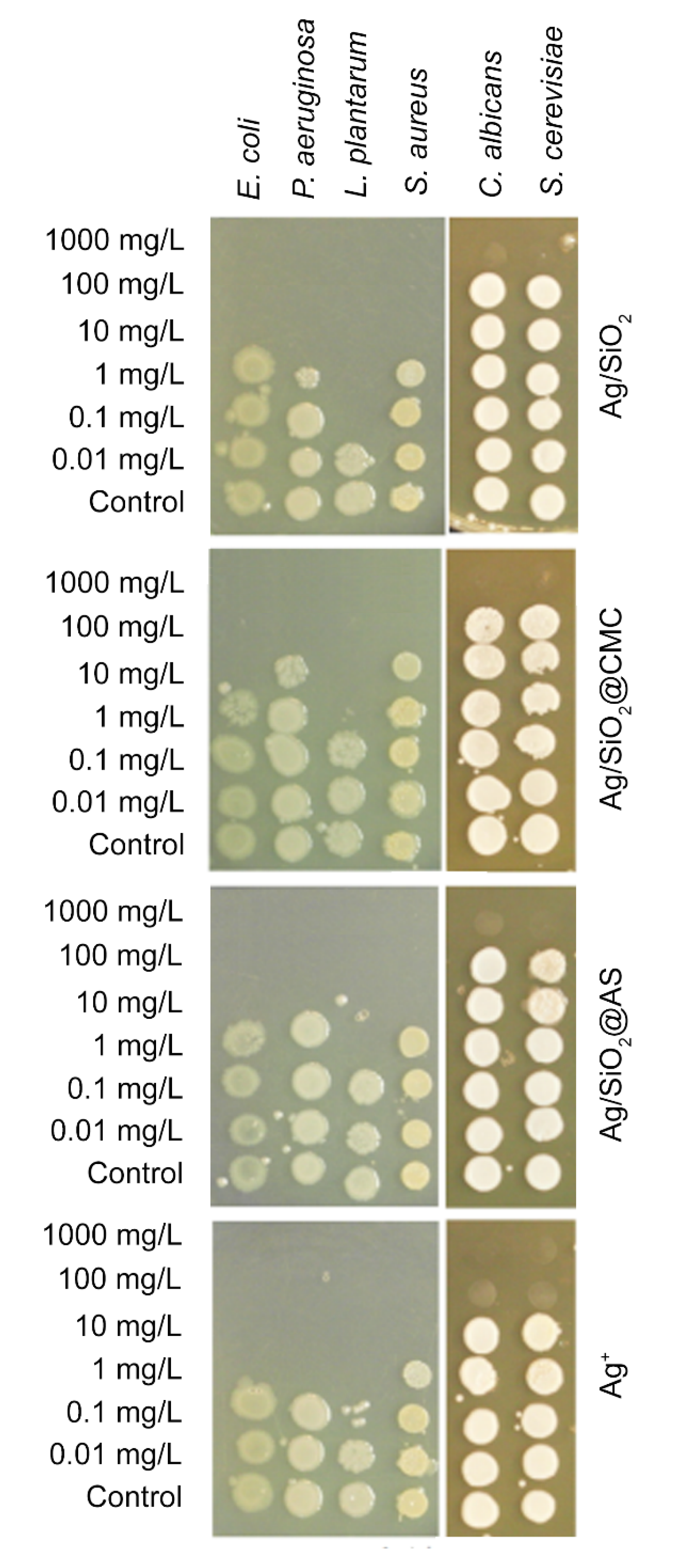
3.3. Antimicrobial Properties
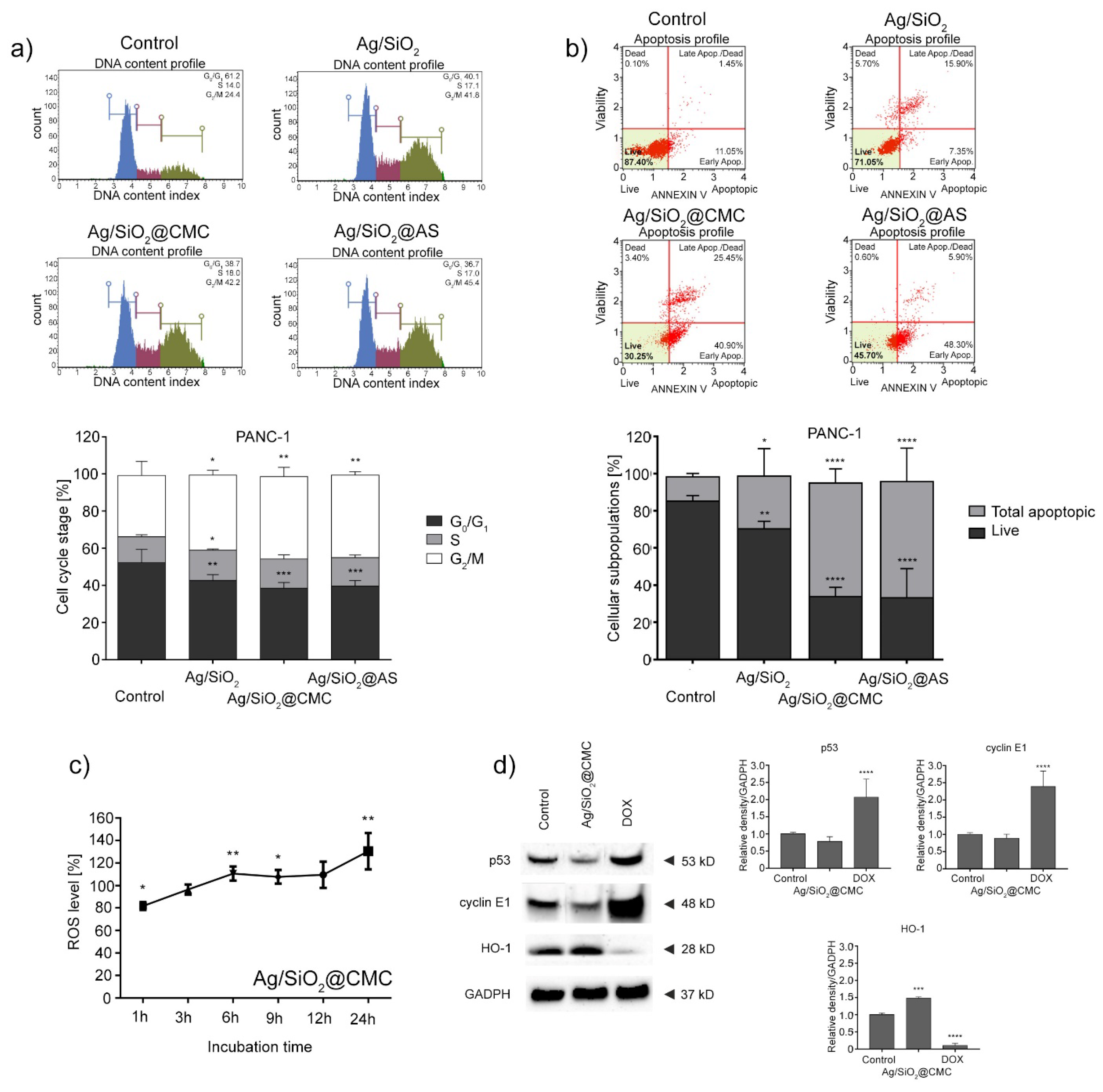
3.4. Anticancer Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamil, B.; Javed, R.; Qazi, A.S.; Syed, M.A. Nanomaterials: Toxicity, Risk Managment and Public Perception. In Nanomaterials: Ecotoxicity, Safety and Public Perception; Rai, M., Biswas, J.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 283–304. ISBN 978-3-030-05144-0. [Google Scholar]
- Buffat, P.; Borel, J.-P. Size effect on the melting temperature of gold particles. Phys. Rev. A 1976, 13, 2287–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolessi, F.; Andreoni, W.; Tosatti, E. Melting of small gold particles: Mechanism and size effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Bhadauria, A.S.; Kumar, P.; Bera, H.; Saha, S. 2—Bioactive and drug-delivery potentials of polysaccharides and their derivatives. In Polysaccharide Carriers for Drug Delivery; Maiti, S., Jana, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Swaston, Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 19–48. ISBN 978-0-08-102553-6. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, H.; Karthikeyan, C. 1—Natural polysaccharides: Structural features and properties. In Polysaccharide Carriers for Drug Delivery; Maiti, S., Jana, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Swaston, Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-0-08-102553-6. [Google Scholar]
- Orive, G.; Ponce, S.; Hernández, R.M.; Gascón, A.R.; Igartua, M.; Pedraz, J.L. Biocompatibility of microcapsules for cell immobilization elaborated with different type of alginates. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3825–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotelli, P.V.; Da, D.S.; Sola-Penna, M.; Rossi, A.M.; Farina, M.; Andrade, L.R.; Takeuchi, A.Y.; Rocha-Leão, M.H. Microcapsules of alginate/chitosan containing magnetic nanoparticles for controlled release of insulin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.; Vacanti, J.P. Tissue engineering. Science 1993, 260, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konarska, Z.; Gieruszczak-Białek, D.; Pieścik-Lech, M.; Skórka, A.; Szajewska, H. Alginiany w leczeniu refluksu żołądkowo-przełykowego u dzieci: Przegląd systematyczny badań z randomizacją. Pediatr. Pol. 2015, 90, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalekshmy, G.P.; Lekshmi Devi, L.; Joseph, J.; Rekha, M.R. 2—An overview on the potential biomedical applications of polysaccharides. In Functional Polysaccharides for Biomedical Applications; Maiti, S., Jana, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Swaston, Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 33–94. ISBN 978-0-08-102555-0. [Google Scholar]
- Anita, B.B.; Thatheyus, A.J.; Ramya, D. Biodegradation of Carboxymethyl Cellulose using Aspergillus flavus. Sci. Int. 2013, 1, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollabaugh, C.B.; Burt, L.H.; Walsh, A.P. Carboxymethylcellulose. Uses and Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1945, 37, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Polysaccharide-Based Metallic Nanoparticles: A Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttacavoli, M.; Albanese, N.N.; Cara, G.D.; Alduina, R.; Faleri, C.; Gallo, M.; Pizzolanti, G.; Gallo, G.; Feo, S.; Baldi, F.; et al. Anticancer activity of biogenerated silver nanoparticles: An integrated proteomic investigation. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9685–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Cheng, F.-Y.; Chiu, H.-W.; Tsai, J.-C.; Fang, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-W.; Wang, Y.-J. Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, apoptosis and the autophagic effects of silver nanoparticles in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4706–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Low, K.M.G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Jain, J.; Rajwade, J.M.; Paknikar, K.M. Cellular responses induced by silver nanoparticles: In vitro studies. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 179, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chairuangkitti, P.; Lawanprasert, S.; Roytrakul, S.; Aueviriyavit, S.; Phummiratch, D.; Kulthong, K.; Chanvorachote, P.; Maniratanachote, R. Silver nanoparticles induce toxicity in A549 cells via ROS-dependent and ROS-independent pathways. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.; Sethu, S.; Lim, H.K.; Balaji, G.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Hande, M.P. Differential regulation of intracellular factors mediating cell cycle, DNA repair and inflammation following exposure to silver nanoparticles in human cells. Genome Integr. 2012, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, E.-K.; Kwak, M.-K. Silver nanoparticles-mediated G2/M cycle arrest of renal epithelial cells is associated with NRF2-GSH signaling. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 211, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, H.C.; Wang, T.; Liao, C.Y.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.F.; Yan, B.; Jiang, G.B. Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: Effect of particle size. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.W.; Gurunathan, S.; Jeong, J.-K.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kwon, D.-N.; Park, J.-K.; Kim, J.-H. Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethling-Graff, R.; Rumpker, R.; Richter, M.; Verano-Braga, T.; Kjeldsen, F.; Brewer, J.; Hoyland, J.; Rubahn, H.-G.; Erdmann, H. Exposure to silver nanoparticles induces size- and dose-dependent oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Jin, P.; Wei, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Inhibition of autophagy enhances the anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles. Autophagy 2014, 10, 2006–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathy, V.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Nurmi, J.T.; Baer, D.R.; Amonette, J.E.; Chun, C.L.; Penn, R.L.; Reardon, E.J. Aging of Iron Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solution: Effects on Structure and Reactivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Engineering nanosilver as an antibacterial, biosensor and bioimaging material. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2011, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, C.-N.; Ho, C.-M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.-Y.; Yu, W.-Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.-H.; Chiu, J.-F.; Che, C.-M. Silver nanoparticles: Partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible Particle-Specific Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benn, T.M.; Westerhoff, P. Nanoparticle Silver Released into Water from Commercially Available Sock Fabrics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4133–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, E.; Piccapietra, F.; Wagner, B.; Marconi, F.; Kaegi, R.; Odzak, N.; Sigg, L.; Behra, R. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, G.A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Liu, Z.-G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique Cellular Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles: Size-Dependent Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, P.C.; Nam, J.D.; Jung, H.-C.; Oh, Y.S.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, Y. kwan Sintering and consolidation of silver nanoparticles printed on polyimide substrate films. Macromol. Res. 2009, 17, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.W.; Liu, M.; Ge, W.; Fu, Z.P.; Reinhardt, K.; Knize, R.J.; Lu, Y. Morphology and optical absorption change of Ag/SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles under thermal annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 083903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourali, P.; Baserisalehi, M.; Afsharnezhad, S.; Behravan, J.; Ganjali, R.; Bahador, N.; Arabzadeh, S. The effect of temperature on antibacterial activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Biometals 2013, 26, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Toxicology of nanoparticles: A historical perspective. Nanotoxicology 2007, 1, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Azimirad, R.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Low temperature self-agglomeration of metallic Ag nanoparticles on silica sol–gel thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 195305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Rajarathinam, K. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles and its immobilization on alginate coated sutures for the prevention of surgical wound infections and the in vitro release studies. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2012, 2, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Gaur, A.; Kumar, S.; Park, J.-W. Development of silver nanoparticles-loaded CMC hydrogel using bamboo as a raw material for special medical applications. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, P.; Thangapandiyan, S.; Immanuel, G. CMC stabilized nano silver synthesis, characterization and its antibacterial and synergistic effect with broad spectrum antibiotics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 158, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengert, E.; Saveleva, M.; Abalymov, A.; Atkin, V.; Wuytens, P.C.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Vasiliev, A.L.; Gorin, D.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Skirtach, A.G.; et al. Silver Alginate Hydrogel Micro- and Nanocontainers for Theranostics: Synthesis, Encapsulation, Remote Release and Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21949–21958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peszke, J.; Dulski, M.; Nowak, A.; Balin, K.; Zubko, M.; Sułowicz, S.; Nowak, B.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Talik, E.; Wojtyniak, M.; et al. Unique properties of silver and copper silica-based nanocomposites as antimicrobial agents. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28092–28104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Recent progress on silica coating of nanoparticles and related nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. Weinh. 2010, 22, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulski, M.; Peszke, J.; Włodarczyk, J.; Sułowicz, S.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Dudek, K.; Podwórny, J.; Malarz, K.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A.; Zubko, M.; et al. Physicochemical and structural features of heat treated silver-silica nanocomposite and their impact on biological properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, L.; Laskowska, M.; Fijalkowski, K.; Piech, H.; Jelonkiewicz, J.; Jaskulak, M.; Gnatowski, A.; Dulski, M. New Class of Antimicrobial Agents: SBA-15 Silica Containing Anchored Copper Ions. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.; Podwórny, J.; Dulski, M.; Nowak, A.; Peszke, J. X-ray investigations into silica/silver nanocomposite. Powder Diffr. 2017, 32, S82–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitl, O.; Dutra Zanotto, E.; Hench, L.L. Highly bioactive P2O5–Na2O–CaO–SiO2 glass-ceramics. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2001, 292, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Szade, J.; Talik, E.; Ratuszna, A.; Ostafin, M.; Peszke, J. Structural, spectroscopic and biological investigation of copper oxides nanoparticles with various capping agents. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 145, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangishetty, M.K.; Scott, R.W.J.; Kelly, T.L. Thermal degradation mechanism of triangular Ag@SiO2 nanoparticles. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 9827–9834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Szade, J.; Talik, E.; Zubko, M.; Wasilkowski, D.; Dulski, M.; Balin, K.; Mrozik, A.; Peszke, J. Physicochemical and antibacterial characterization of ionocity Ag/Cu powder nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2016, 117, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.; He, T.; Li, X.-M. Ammonia-free preparation of Ag@SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppi, S.; Kasemets, K.; Ivask, A.; Künnis-Beres, K.; Sihtmäe, M.; Kurvet, I.; Aruoja, V.; Kahru, A. A novel method for comparison of biocidal properties of nanomaterials to bacteria, yeasts and algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña, S.M.; Quintana, P.; Aguilar, D.H.; Toledo, J.A.; Ángeles-Chávez, C.; Cortés, M.A.; León, L.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; López, T.; Sánchez, R.M.T. Antibacterial activity of montmorillonites modified with silver. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2008, 281, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P. A Raman spectroscopic study of glasses in the system CaO-MgO-SiO2. Am. Mineral. 1984, 69, 645–659. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Chen, M.; Rasch, R.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, B. Structure Studies of Silicate Glasses by Raman Spectroscopy. In Advances in Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts, Washigton, DC, USA, 22–25 May 2016; Reddy, R.G., Chaubal, P., Pistorius, P.C., Pal, U., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2001; ISBN 978-0-471-85298-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alessi, A.; Agnello, S.; Buscarino, G.; Gelardi, F.M. Structural properties of core and surface of silica nanoparticles investigated by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, G.; Agnello, S.; Buscarino, G.; Gelardi, F.M. Thermally Induced Structural Modification of Silica Nanoparticles Investigated by Raman and Infrared Absorption Spectroscopies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 13991–13997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissberger, A.E.; Galeener, F.L. Raman studies of vitreous SiO2 versus fictive temperature. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 28, 3266–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, L.; Coupry, C.; Eremin, K.; Hall, C. The use of Raman spectrometry to predict the stability of historic glasses. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2006, 37, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidgwick, N.V. The Chemical Elements and Their Compounds; Oxford Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1950; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Matson, D.W.; Sharma, S.K.; Philpotts, J.A. The structure of high-silica alkali-silicate glasses. A Raman spectroscopic investigation. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1983, 58, 323–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K. Raman investigation of ring configurations in vitreous silica. Nature 1981, 292, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viard, J.; Beche, E.; Perarnau, D.; Berjoan, R.; Durand, J. XPS and FTIR study of silicon oxynitride thin films. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 17, 2025–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.; Aisawa, S.; Hirahara, H.; Kudo, T.; Mori, K. Self-reduction and size controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles on carbon nanospheres by grafting triazine-based molecular layer for conductivity improvement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, S.V.; Galindo, R.E.; Benito, N.; Palacio, C.; Cavaleiro, A.; Carvalho, S. Ag+ release inhibition from ZrCN–Ag coatings by surface agglomeration mechanism: Structural characterization. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 325303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Wang, C.; Mao, W.; Zhang, S.; Lu, R. Highly enhanced plasmonic photocatalytic activity of Ag/AgCl/TiO2 by CuO co-catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.J.; Zeng, L.L.; Tao, X.M.; Chen, W. Holey reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for high performance room temperature gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17415–17420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędziora, A.; Speruda, M.; Krzyżewska, E.; Rybka, J.; Łukowiak, A.; Bugla-Płoskońska, G. Similarities and Differences between Silver Ions and Silver in Nanoforms as Antibacterial Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.M. The bacterial RecA protein: Structure, function and regulation. In Molecular Genetics of Recombination; Aguilera, A., Rothstein, R., Eds.; Topics in Current Genetics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 53–94. ISBN 978-3-540-71021-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-R.; Xie, X.-B.; Shi, Q.-S.; Duan, S.-S.; Ouyang, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-B. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Biometals 2011, 24, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Nunez, N.V.; Ixtepan, T.L.d.C.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. Bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomoni, R.; Léo, P.; Montemor, A.F.; Rinaldi, B.G.; Rodrigues, M. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2017, 10, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangelova, N.; Aleksandrov, L.; Angelova, T.; Georgieva, N.; Müller, R. Preparation and characterization of SiO2/CMC/Ag hybrids with antibacterial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.-L.; Hsieh, Y.-K.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, I.-C.; Huang, Y.-J. Trojan-horse mechanism in the cellular uptake of silver nanoparticles verified by direct intra- and extracellular silver speciation analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3813–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sonshine, D.A.; Shervani, S.; Hurt, R.H. Controlled release of biologically active silver from nanosilver surfaces. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; de Jesus, M.B.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.M.; Hess, K.L.; Gearhart, J.M.; Geiss, K.T.; Schlager, J.J. In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.J.; Hosseinian, F.; Willmore, W.G. A Current Overview of the Biological and Cellular Effects of Nanosilver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.-J.; Choi, J. p38 MAPK Activation, DNA Damage, Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis as Mechanisms of Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Jurkat T Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8337–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butz, J.; Wickstrom, E.; Edwards, J. Characterization of mutations and loss of heterozygosity of p53 and K-ras2 in pancreatic cancer cell lines by immobilized polymerase chain reaction. BMC Biotechnol. 2003, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, B.; Girard, L.; Hollestelle, A.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Soussi, T. Analysis of TP53 Mutation Status in Human Cancer Cell Lines: A Reassessment. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitolli, C.; Wang, Y.; Mancini, M.; Shi, Y.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. Do Mutations Turn p53 into an Oncogene? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.F.; Grainger, D.W. In vitro assessments of nanomaterial toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, P.; Sun, Z. Toxic Effect of Silica Nanoparticles on Endothelial Cells through DNA Damage Response via Chk1-Dependent G2/M Checkpoint. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mytych, J.; Zebrowski, J.; Lewinska, A.; Wnuk, M. Prolonged Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on p53/p21 Pathway-Mediated Proliferation, DNA Damage Response and Methylation Parameters in HT22 Hippocampal Neuronal Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinska, E.; Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak, A.; Wojcik, M.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Silver nanoparticles of different sizes induce a mixed type of programmed cell death in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 4675–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-López, L.Z.; Espinoza-Gómez, H.; Somanathan, R. Silver nanoparticles: Electron transfer, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress, beneficial and toxicological effects. Mini review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Saha, S.K.; Yang, G.-M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.-G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Biological Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulmeester, E.; Jochemsen, A.G. p53: A guide to apoptosis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

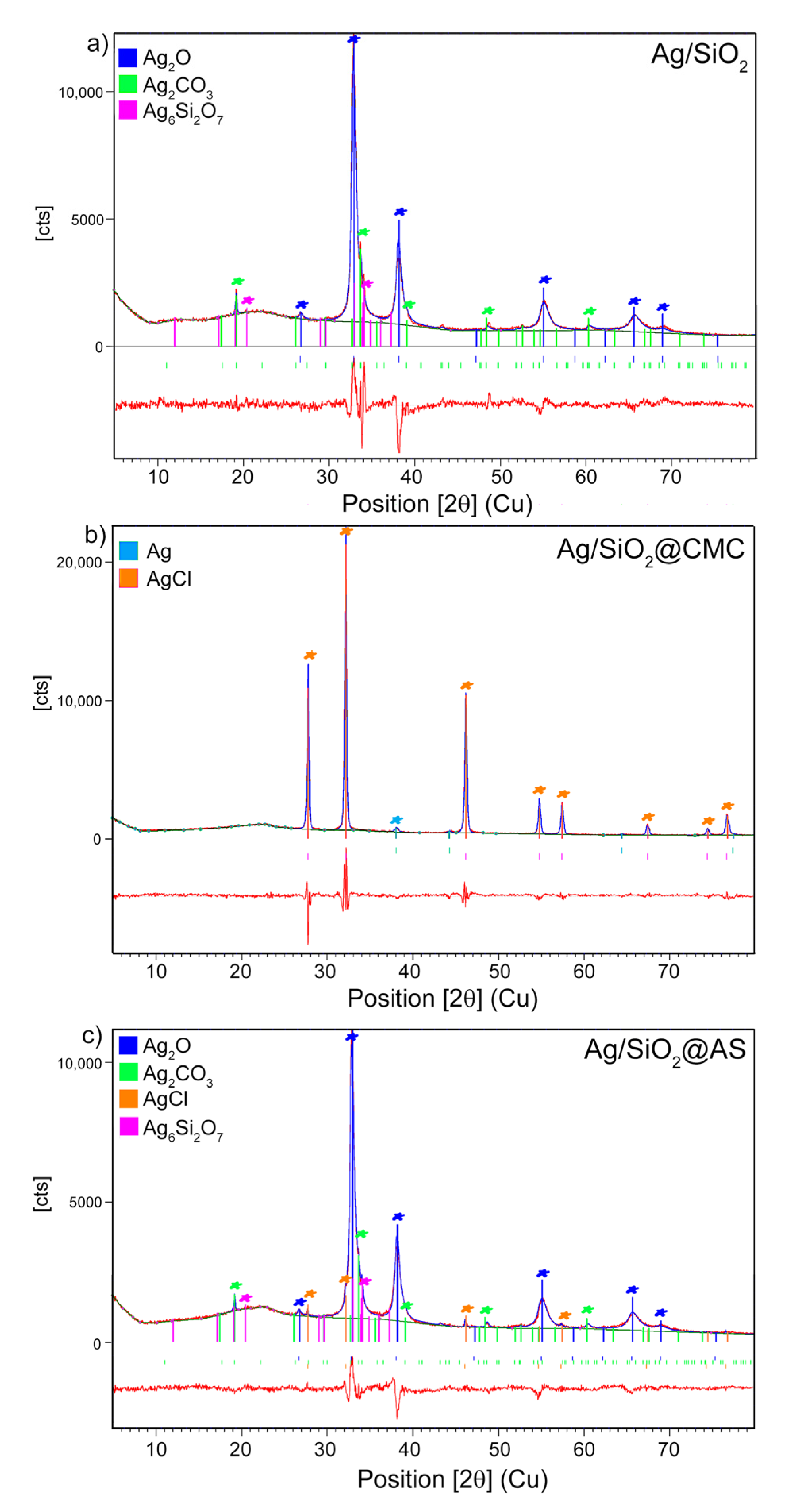
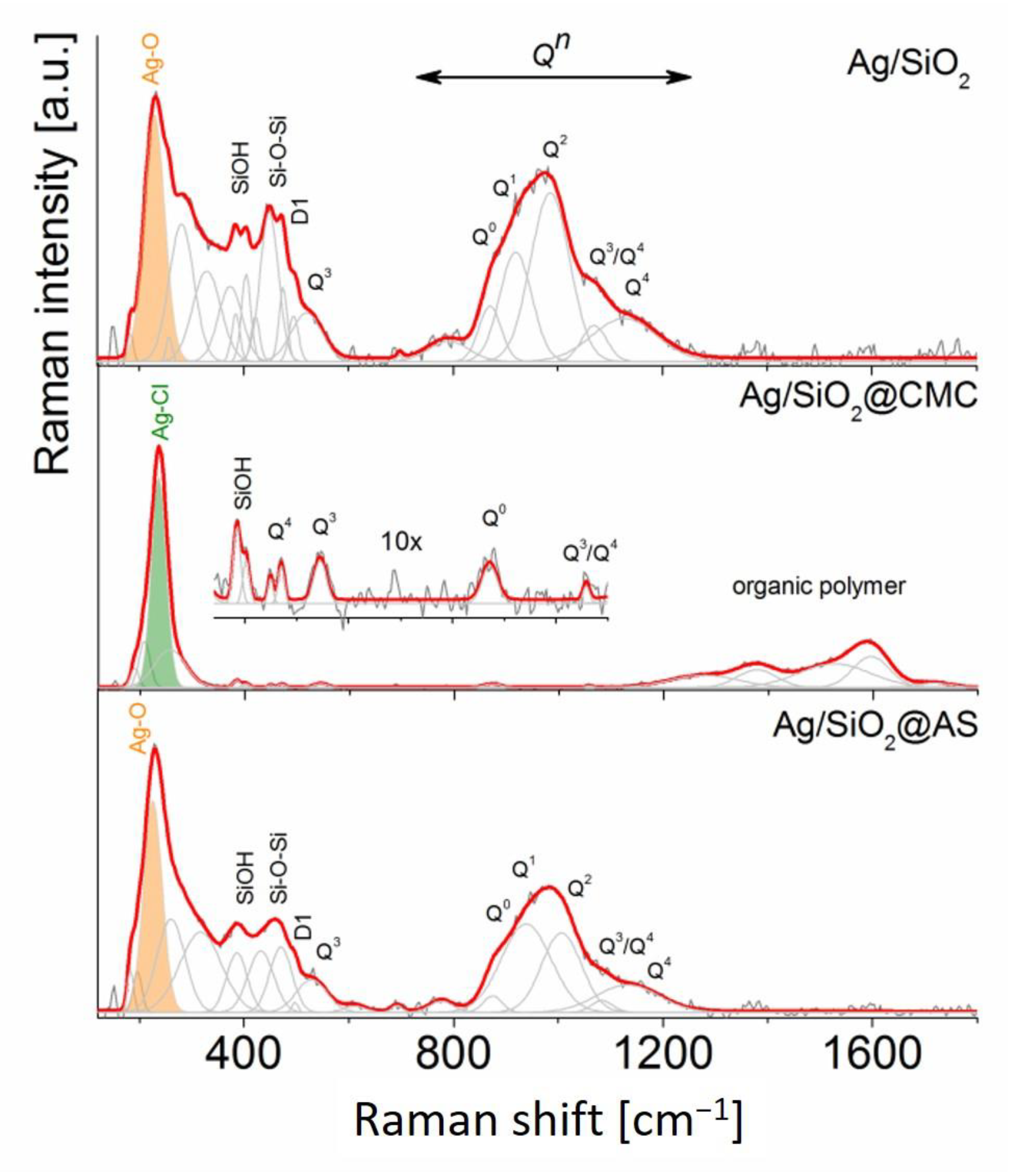
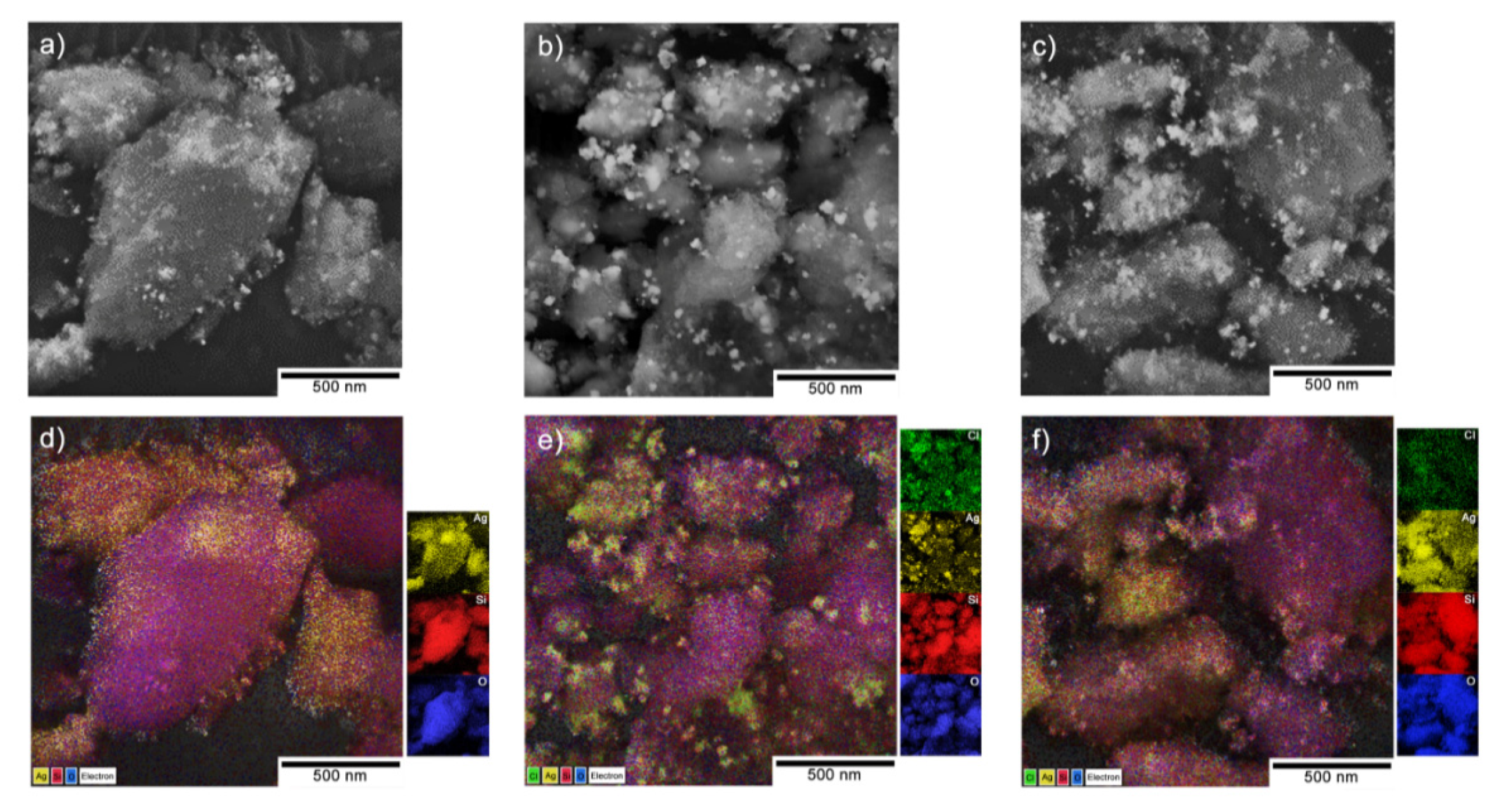
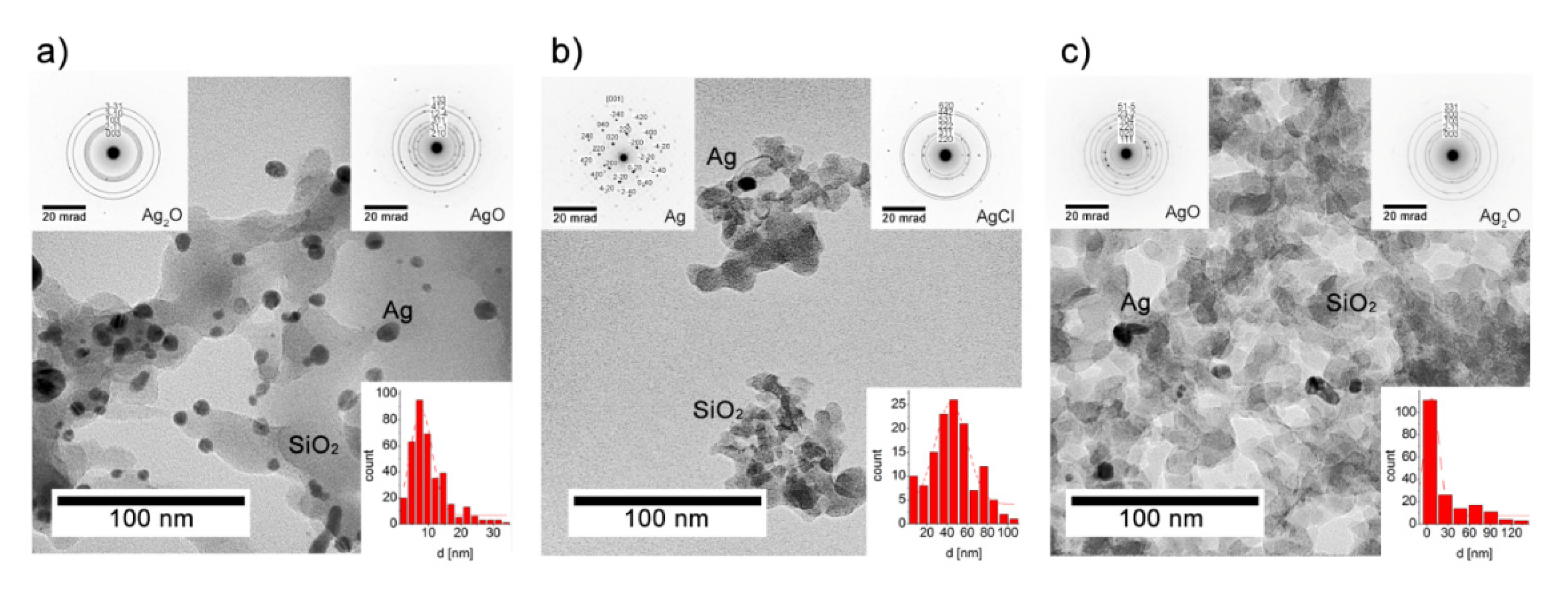
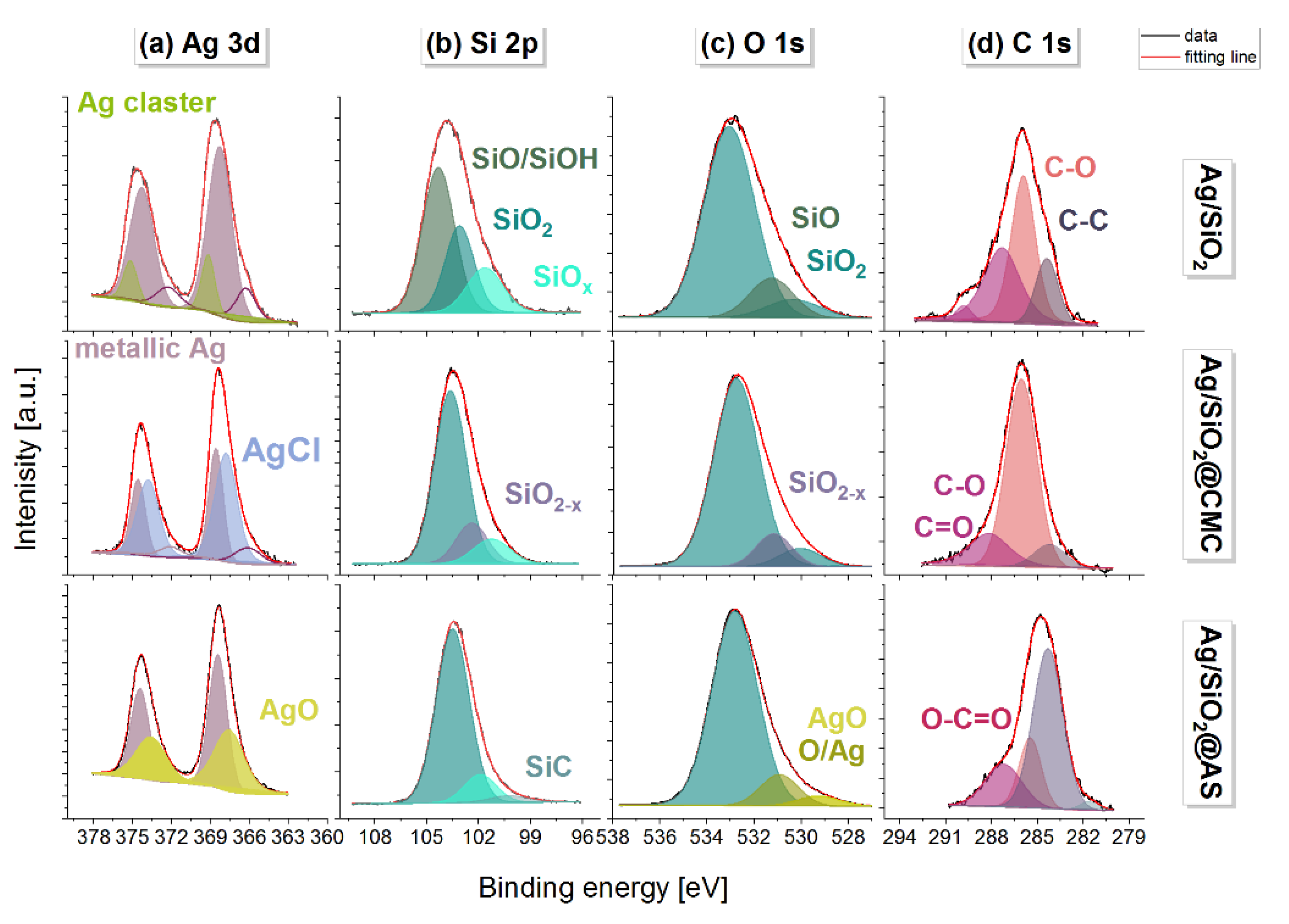
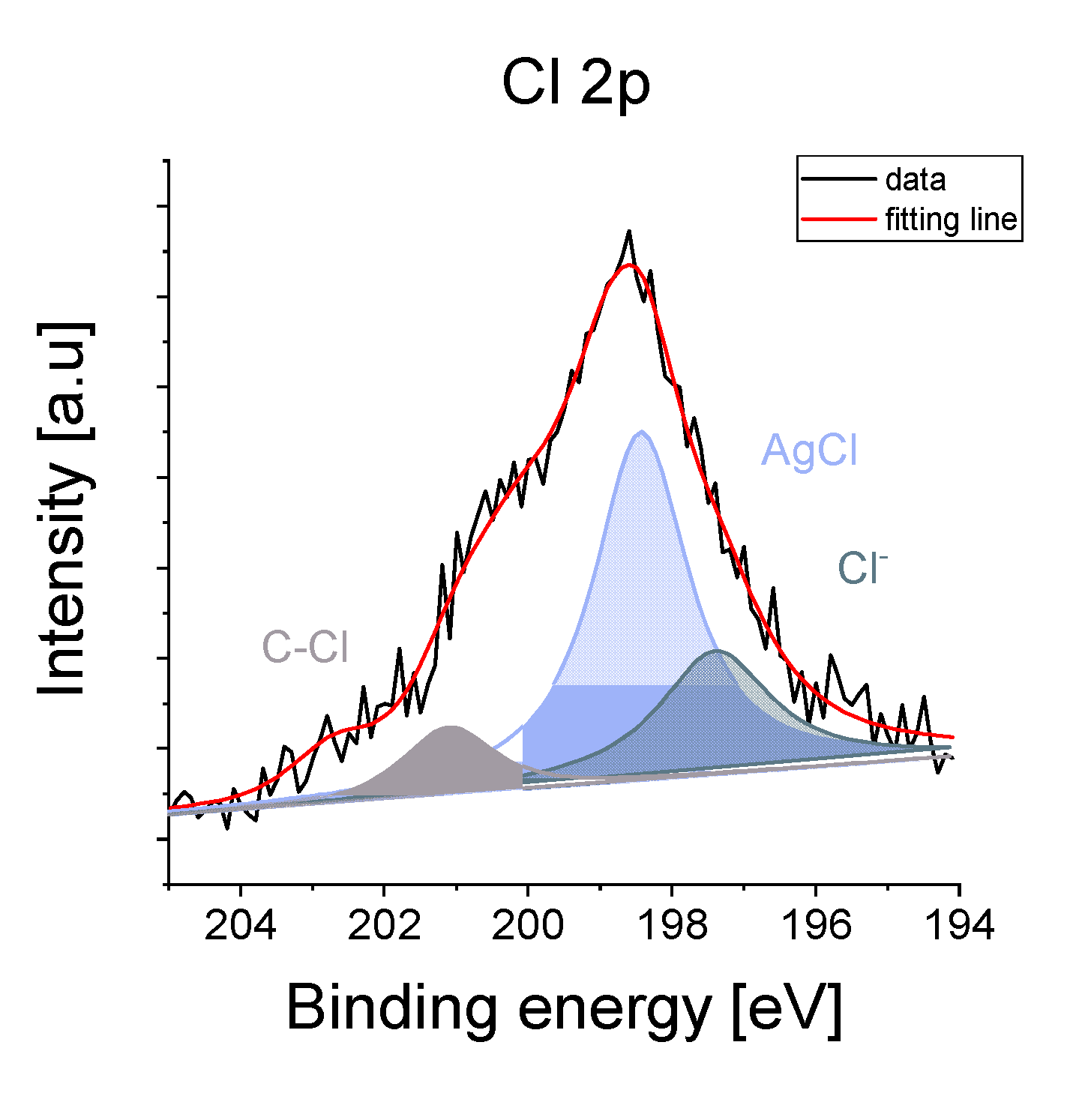
| Phase (Space Group) | Ag (Fm-3 m) | AgCl (Fm-3 m) | Ag2O (Pn-3 m) | β-Ag2CO3 (P31c) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lattice parameters | a0 [Å] | a0 [Å] | a0 [Å] | a0 [Å] | c0 [Å] |
| Ag/SiO2 | - | - | 4.710(9) | 9.208(4) | 6.490(7) |
| Ag/SiO2@CMC | 4.085(5) | 5.550(6) | - | - | - |
| Ag/SiO2@AS | - | 5.554(9) | 4.714(4) | 9.202(2) | 6.485(2) |
| Ag2O (AgSiO2) | AgCl (AgSiO2@CMC) | Ag2O (AgSiO2@AS) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | Crystallite Size [Å] | Direction | Crystallite Size [Å] | Direction | Crystallite Size [Å] |
| <111> | 172 | <111> | 901 | <111> | 168 |
| <200> | 135 | <200> | 747 | <200> | 132 |
| <220> | 82 | <220> | 674 | <220> | 81 |
| Element | Ag/SiO2 | Ag/SiO2@CMC | Ag/SiO2@AS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgO | Ag2O | Ag | AgCl | AgO | Ag2O | |
| a0 [Å] | 5.8517 | 3.072 | 4.0855 | 5.5463 | 5.8517 | 3.072 |
| b0 [Å] | 3.4674 | 3.072 | 4.0855 | 5.5463 | 3.4674 | 3.072 |
| c0 [Å] | 5.4838 | 4.941 | 4.0855 | 5.5463 | 5.4838 | 4.941 |
| system | monoclinic | trigonal | cubic | cubic | monoclinic | trigonal |
| space group | P21/c | P-3m1 | Fm-3m | Fm-3m | P21/c | P-3m1 |
| El. | EDS | XPS | EDS | XPS | EDS | XPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/SiO2 [at.%] | Ag/SiO2@CMC [at.%] | Ag/SiO2@AS [at.%] | ||||
| O | 63.3 (3.0) | 59.1 | 69.6 (1.6) | 59.4 | 71.1 (0.7) | 58.1 |
| Si | 24.1 (1.8) | 28.8 | 20.1 (0.5) | 30.7 | 20.9 (0.9) | 28.9 |
| Cl | - | - | 3.4 (0.9) | 0.9 | 0.2 (0.1) | - |
| Ag | 12.6 (2.2) | 1.6 | 6.8 (1.1) | 0.6 | 7.9 (1.3) | 1.8 |
| C | - | 10.5 | - | 8.4 | - | 11.2 |
| Nanocomposites | Gram-Negative Bacteria | Gram-Positive Bacteria | Yeast | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | P. aeruginosa | L. plantarum | S. aureus | C. albicans | S. cerevisiae | |
| AgSiO2 | 10 | 10 | 0.1 | 10 | 1000 | 1000 |
| AgSiO2@CMC | 10 | 100 | 1 | 100 | 1000 | 1000 |
| AgSiO2@AS | 10 | 10 | 1 | 10 | 1000 | 1000 |
| AgNO3 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 | 10 | 100 | 100 |
| Nanocomposite | IC50 Values [mg/L] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT116 | MCF-7 | U-251 | PANC-1 | |
| Ag/SiO2 | 24.0 ± 9.3 | 13.7 ± 1.6 | 34.2 ± 8.5 | 21.0 ± 2 |
| Ag/SiO2@CMC | 24.2 ± 2.4 | 16.1 ± 4.7 | 38.7 ± 4.3 | 12.6 ± 6.0 |
| Ag/SiO2@AS | 24.0 ± 6.3 | 11.1 ± 2.0 | 30.1 ± 5.2 | 19.7 ± 7.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulski, M.; Malarz, K.; Kuczak, M.; Dudek, K.; Matus, K.; Sułowicz, S.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A.; Nowak, A. An Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanocomposite as a Potential New Biological Agent. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122551
Dulski M, Malarz K, Kuczak M, Dudek K, Matus K, Sułowicz S, Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz A, Nowak A. An Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanocomposite as a Potential New Biological Agent. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122551
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulski, Mateusz, Katarzyna Malarz, Michał Kuczak, Karolina Dudek, Krzysztof Matus, Sławomir Sułowicz, Anna Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, and Anna Nowak. 2020. "An Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanocomposite as a Potential New Biological Agent" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122551
APA StyleDulski, M., Malarz, K., Kuczak, M., Dudek, K., Matus, K., Sułowicz, S., Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A., & Nowak, A. (2020). An Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Nanocomposite as a Potential New Biological Agent. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122551










