RF Thermal Plasma Synthesis of Ultrafine ZrB2-ZrC Composite Powders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
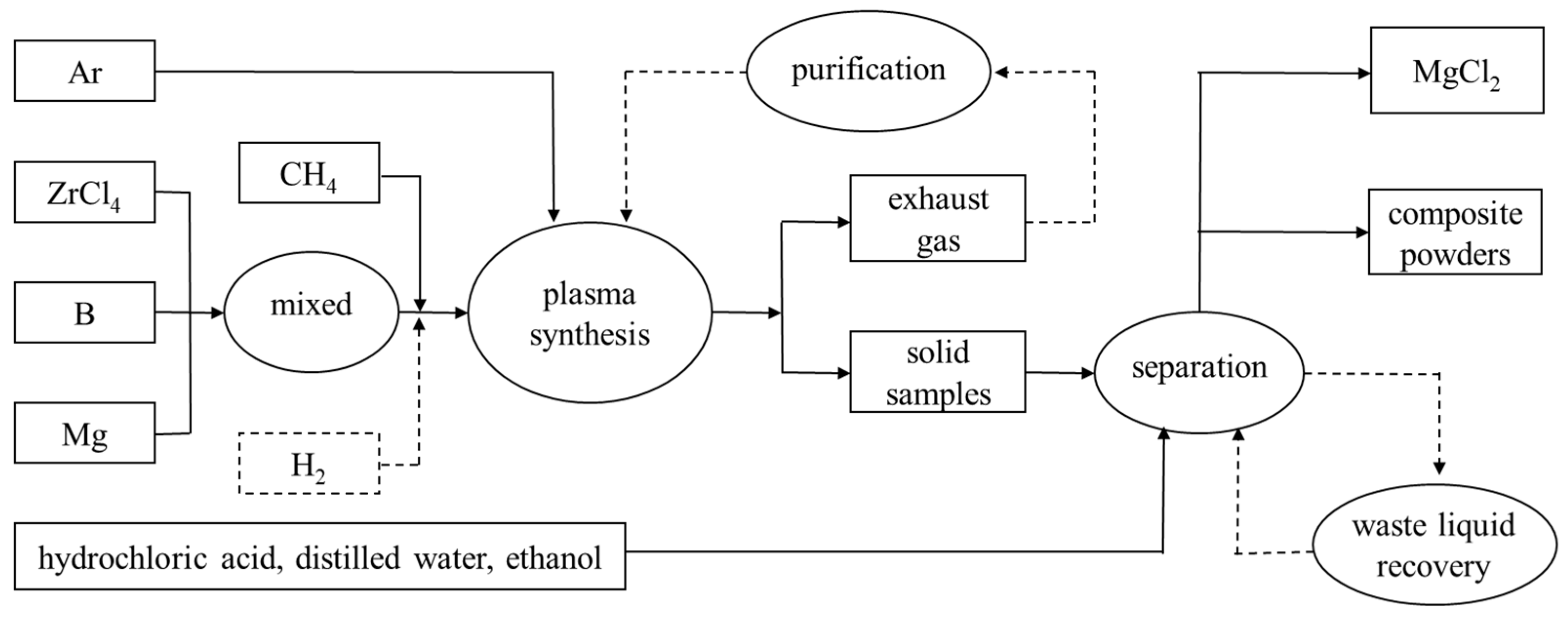
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
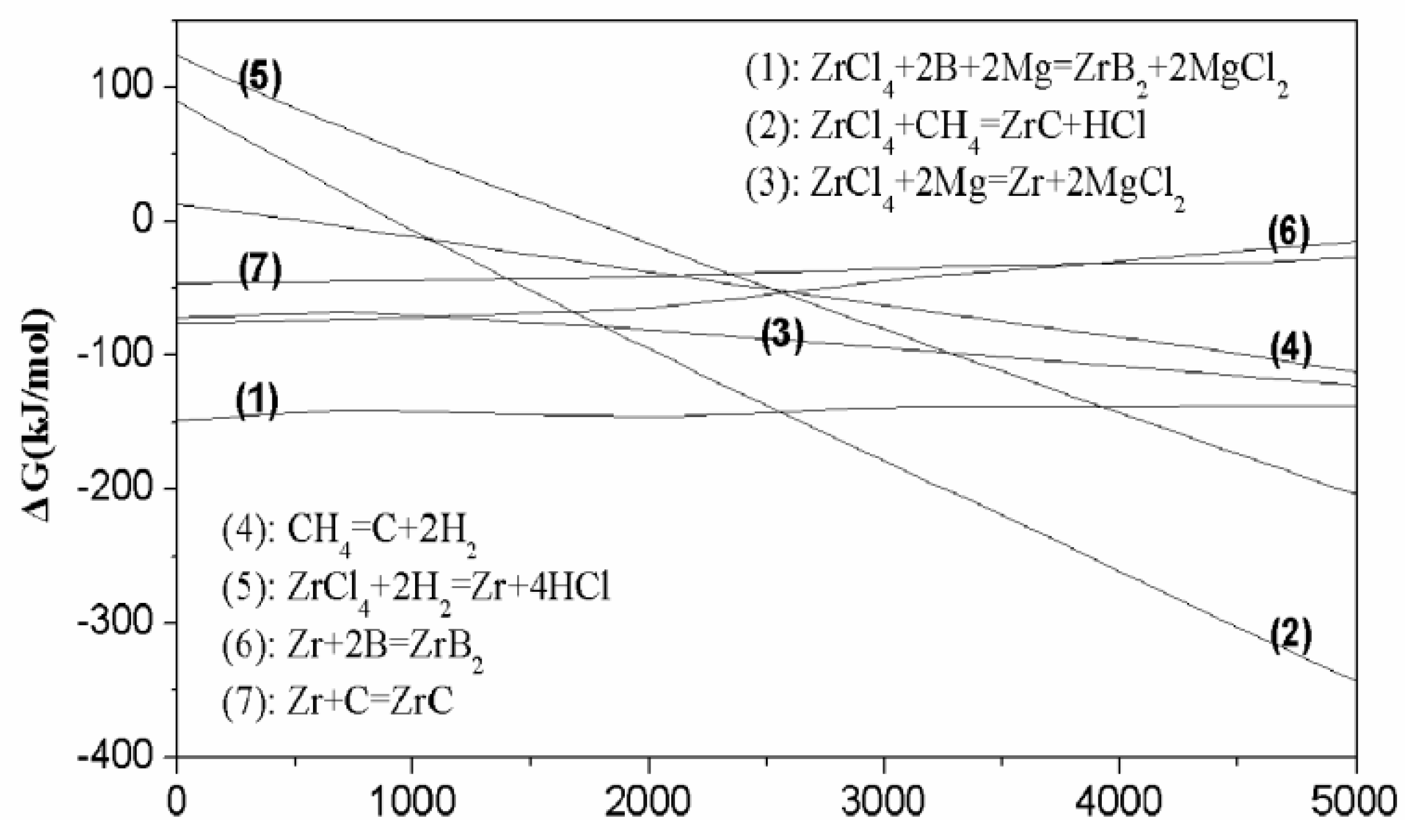
3.1. Thermodynamic Calculation
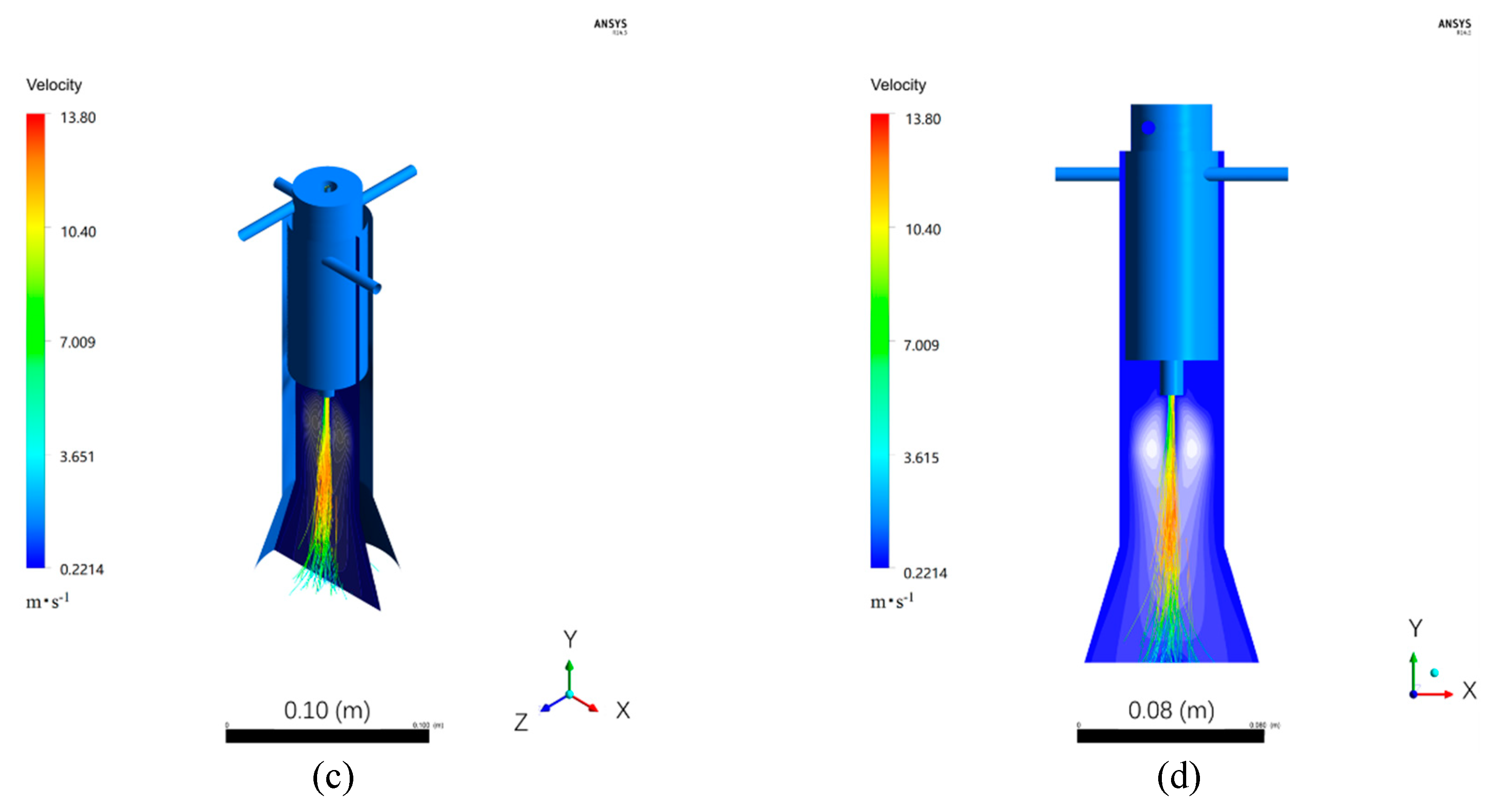
3.2. Numerical Simulation
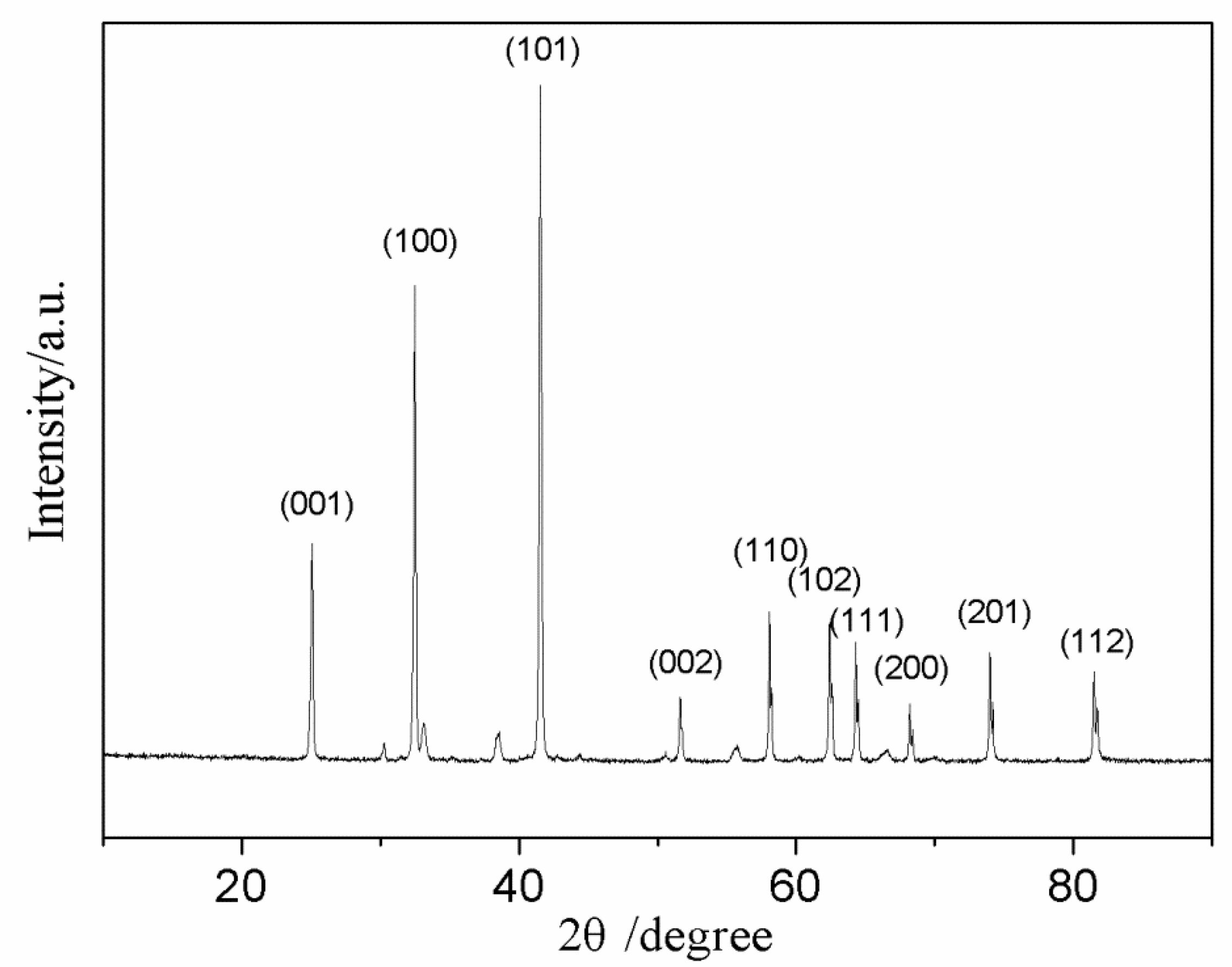
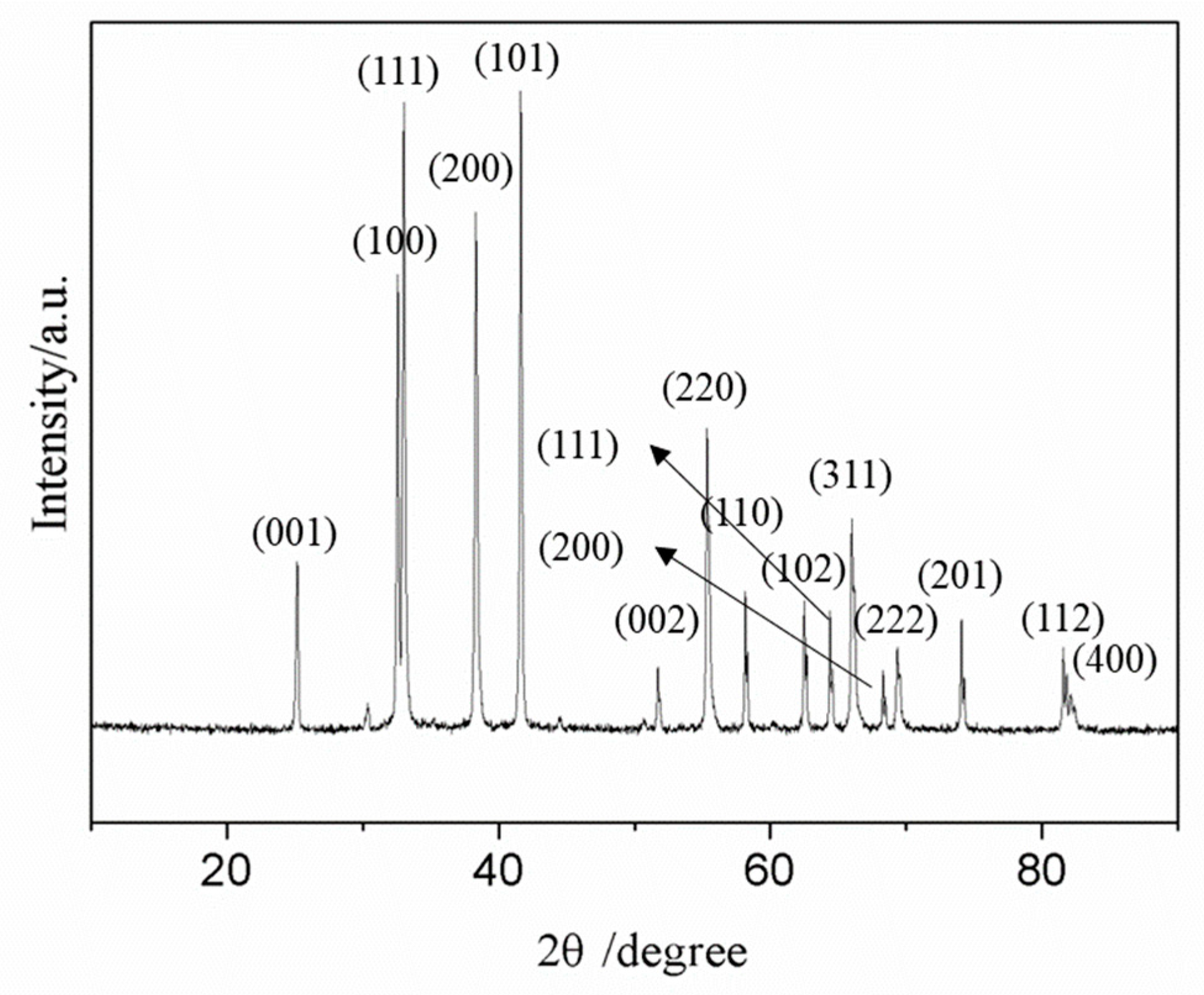
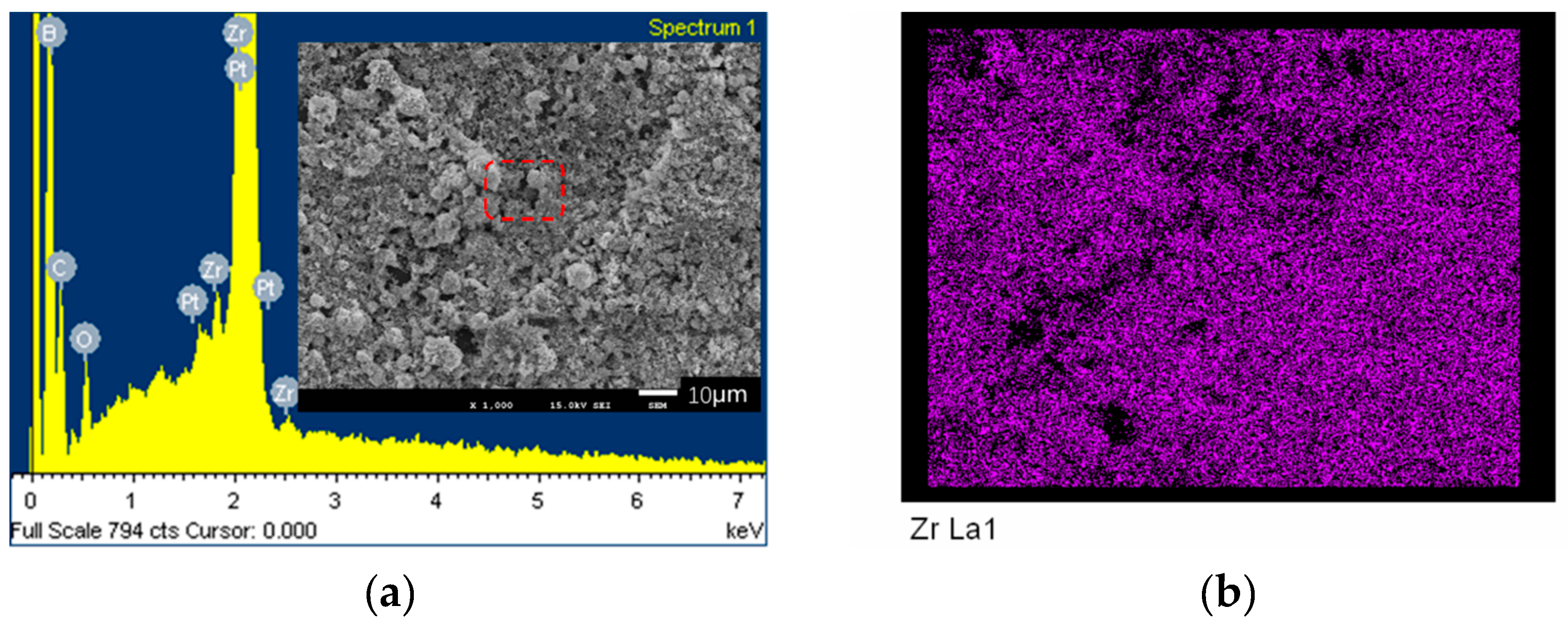
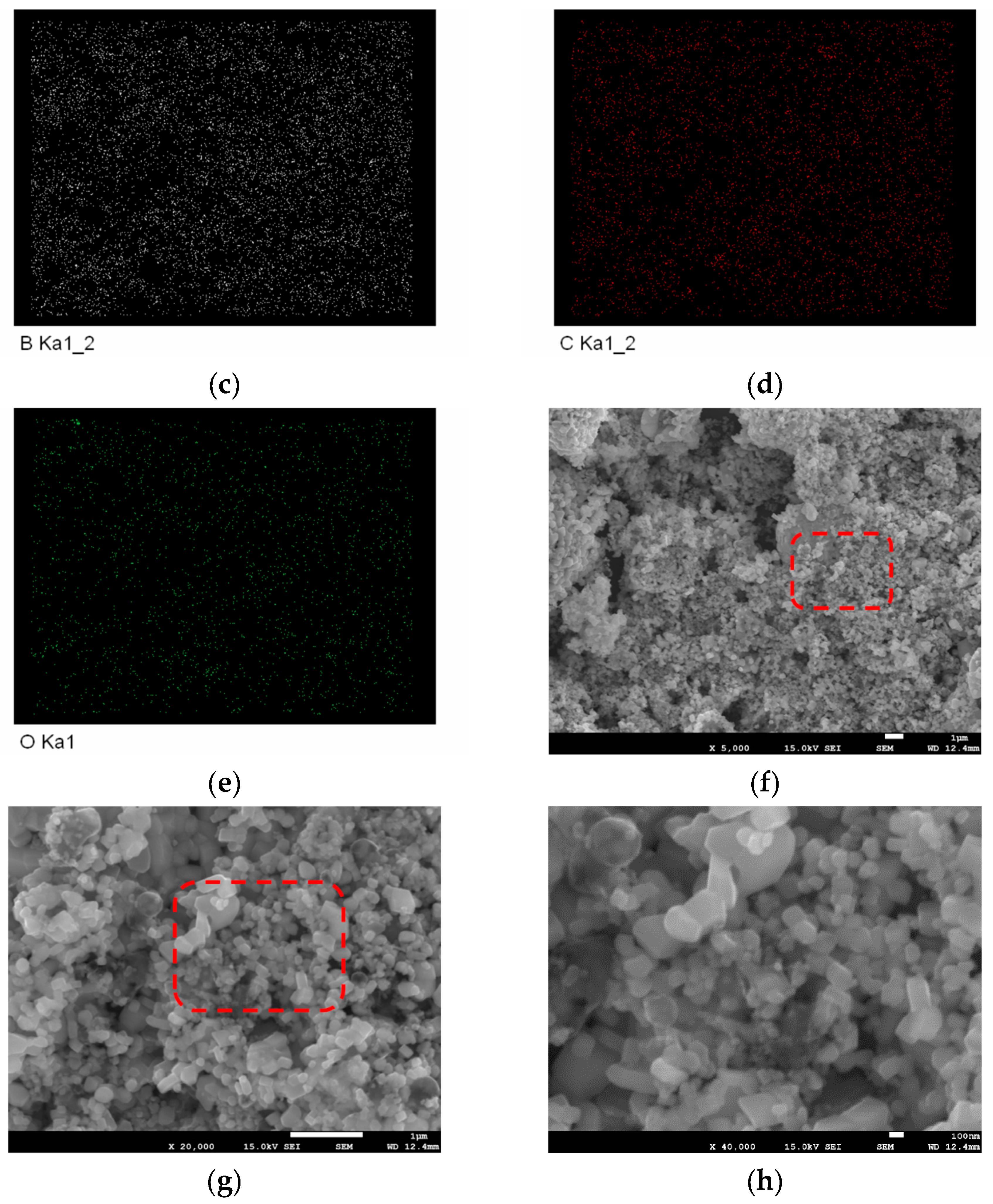
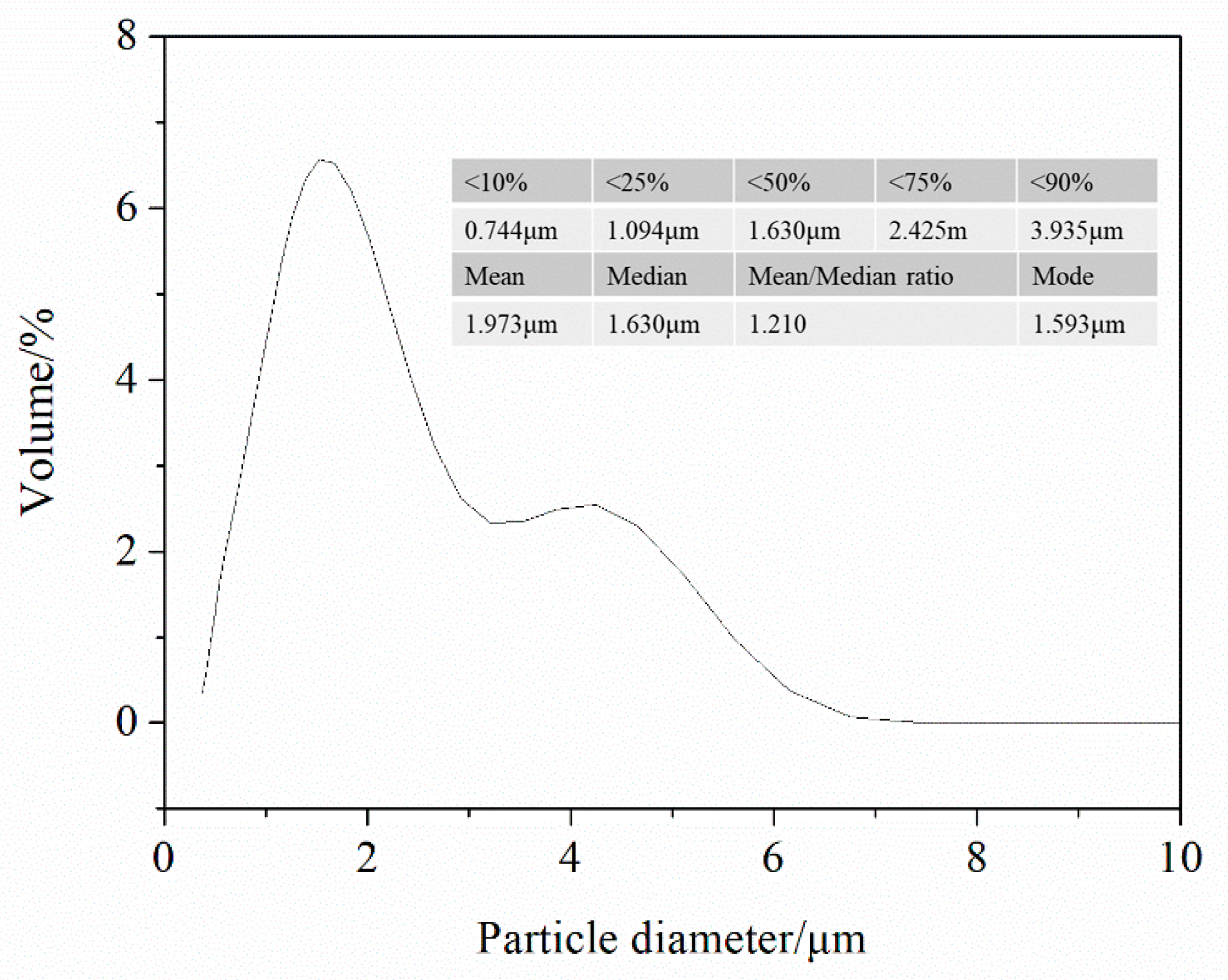
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- ZrB2 was preferentially generated rather than ZrC, and free C instead of B would exist in the resulting products when C and B exceed the stoichiometric ratio.
- (2)
- Solid raw materials could disperse well in the gaseous reactants, which leads to the uniform distribution of elements in ZrB2-ZrC composite powders.
- (3)
- Free carbon particles can be removed during post-treatment, and ZrB2-ZrC composite powders with a particle size of about 100 nm could be obtained.
- (4)
- The surface area of ZrB2-ZrC composite powders was 32.15 m2/g and the apparent density was 0.57 g/cm3.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassan, R.; Balani, K. Oxidation kinetics of ZrB2-and HfB2-powders and their SiC reinforced composites. Corros. Sci. 2020, 177, 109024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafa, N.P.; Kakroudi, M.G.; Asl, M.S. Advantages and disadvantages of graphite addition on the characteristics of hot-pressed ZrB2–SiC composites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 8561–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.; Seeber, A.; Wang, K.; Cheng, Y. Modification of ZrB2 powders by a sol–gel ZrC precursor-A new approach for ultra high temperature ceramic composites. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ke, C.; Zhang, J. Synthesis of ZrB2 powders by molten-salt participating silicothermic reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 834, 155062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, S.; Valefi, Z.; Ehsani, N. Ablation behavior of SiC/ZrB2 ultra-high temperature ceramic coatings by solid shielding shrouded plasma spray for high-temperature applications (temperature above 2000 °C). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ni, S.; Jin, H.; He, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Yuan, F. ZrB2 powders with low oxygen content: Synthesis and characterization. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2017, 15, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaa, J.J.; Wang, S.H.; Dai, J.X.; Zu, Y.F.; Li, W.Q.; Sha, R.Y. Improved microstructure and high temperature mechanical properties of C/C–SiC composites by introduction of ZrC nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, Z.; Huang, Q.; Tong, K.; Xie, X.; Zeng, C. Effect of ZrC particle distribution on the ablation resistance of C/C-SiC-ZrC composites fabricated using precursor infiltration pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 16062–16067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Li, J. ZrB2-SiC-ZrC coating on ZrC ceramics deposited by plasma spraying. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, A.; Balak, Z. Fracture toughness and hardness investigation in ZrB2–SiC–ZrC composite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 241, 122284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Hou, X. Preparation of ZrB2-ZrC-SiC-ZrO2 nanopowders with in-situ grown homogeneously dispersed SiC nanowires. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, Q.; Tan, B. Effect of in-situ grown SiC nanowires on the mechanical properties of HfC-ZrB2-SiC modified C/C composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 866e874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, M.S.; Nayebi, B.; Parvizi, S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Parvin, N.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Mohammadi, M. Toughening of ZrB2-based composites with in-situ synthesized ZrC from ZrO2 and graphite precursors. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.S.; Hilmas, G.E.; Fahrenholtz, W.G. Plasma arcwelding of ZrB2–20 vol% ZrC ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 3549–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, B.; Zou, H.; Zhao, G. In situ synthesis of ZrB2–ZrCx ceramic tool materials toughened by elongated ZrB2 grains. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Rangaraj, L. Properties of Cf/SiC-ZrB2-TaxCy composite produced by reactive hot pressing and polymer impregnation pyrolysis (RHP/PIP). J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z. Mechanical properties of the low-temperature reactive melt infiltrated ZrB2–ZrC based composites. Mater. Lett. 2012, 78, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zeng, F.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, F. Densification behavior and mechanical properties of spark plasma reaction sintered ZrB2–ZrC-B4C ceramics from B4C-Zr system. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 12122–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrell, C.; Beratan, H.; Bradt, R.; Stubican, V. Directional Solidification of (Ti, Zr) Carbide-(Ti, Zr) Diboride Eutectics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 67, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T. MA-SHS and SPS of ZrB2–ZrC composites. Solid State Ionics 2004, 172, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanra, A.; Godkhindi, M.; Pathak, L. Sintering behaviour of ultra-fine titanium diboride powder prepared by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çamurlu, H.E.; Maglia, F. Preparation of nano-size ZrB2 powder by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Duan, H.; Li, J.; Feng, Z. Morphology evolution of ZrB2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yang, R.; Xie, L.; Qu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Inorganic Nanostructures: Plasma-Assisted Approaches in Inorganic Nanostructure Fabrication (Adv. Mater. 13/2010). Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1451–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Bai, L.; Jin, H.; Jia, Z.; Hou, G.; Yuan, F. Simulation and experimental observation of silicon particles’ vaporization in RF thermal plasma reactor for preparing Si nano-powder. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.-K.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, T.H.; Shin, M.-S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Cho, G. Purification and Nitrogen Doping of Nanothin Exfoliated Graphite Through RF Thermal Plasma Treatment. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.H.; Kim, D.U.; Nam, J.S.; Hong, S.H.; Sohn, S.B.; Song, S.M. Radio Frequency Thermal Plasma Treatment for Size Reduction and Spheroidization of Glass Powders Used in Ceramic Electronic Devices. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Ishigaki, T. Spheroidization of Titanium Carbide Powders by Induction Thermal Plasma Processing. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 84, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Cheng, B.; Ding, F.; Yao, M.; Mingshui, Y.; Yuan, F. Synthesis of Uniform α-Si3N4 Nanospheres by RF Induction Thermal Plasma and Their Application in High Thermal Conductive Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2873–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Couillard, M.; Shin, H.; Plunkett, M.; Ruth, D.; Kingston, C.T.; Simard, B. Role of Hydrogen in High-Yield Growth of Boron Nitride Nanotubes at Atmospheric Pressure by Induction Thermal Plasma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kim, J.H.; Jasinski, J.B.; Clark, E.L.; Sunkara, M.K. Alkali-Assisted, Atmospheric Plasma Production of Titania Nanowire Powders and Arrays. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westover, A.S.; Kercher, A.K.; Kornbluth, M.; Naguib, M.; Palmer, M.J.; Cullen, D.A.; Dudney, N.J. Plasma Synthesis of Spherical Crystalline and Amorphous Electrolyte Nanopowders for Solid-State Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 11570–11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Jin, H.; Lu, C.; Yuan, F.; Huang, S.; Li, J. RF thermal plasma-assisted metallothermic synthesis of ultrafine ZrB2 powders. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, H.; Jin, H.; Yuan, F.; Huang, S.; Li, J. Radio-Frequency Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Synthesis of Ultrafine ZrC Powders. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2012, 10, E274–E281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knacke, O.; Kubaschewski, O.; Hesselmann, K. Thermochemical Properties of Inorganic Substances, 2nd ed; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; He, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Yao, H.; Li, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, F.-L. Modeling and Selection of RF Thermal Plasma Hot-Wall Torch for Large-Scale Production of Nanopowders. Materials 2019, 12, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Numbers | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power supply | 30 kW |
| 2 | Plasma gas (Ar) | 2.0 m3/h |
| 3 | Sheath gas (Ar) | 5.0 m3/h |
| 4 | Carrier gas (Ar/CH4) | 0.2 m3/h |
| 5 | Feed rate (CH4) | 0–0.6 L/min |
| 6 | Feed rate (H2) | 0–0.3 L/min |
| 7 | Feed rate (solid) | 4.0–16.0 g/min |
| CH4/ZrCl4 | Carbon Content | Oxygen Content |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 6.06% |
| 0.05 | 0.25% | 3.91% |
| 0.10 | 0.32% | 3.45% |
| C/B/Zr | Carbon Content | Oxygen Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1:2:2 | 5.29% | 3.5% |
| 0.3:2:1 | 0.32% | 3.45% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, L.; Yuan, F.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Jin, H.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. RF Thermal Plasma Synthesis of Ultrafine ZrB2-ZrC Composite Powders. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122497
Bai L, Yuan F, Fang Z, Wang Q, Ouyang Y, Jin H, He J, Liu W, Wang Y. RF Thermal Plasma Synthesis of Ultrafine ZrB2-ZrC Composite Powders. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122497
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Liuyang, Fangli Yuan, Zheng Fang, Qi Wang, Yuge Ouyang, Huacheng Jin, Jiaping He, Wenfu Liu, and Yinling Wang. 2020. "RF Thermal Plasma Synthesis of Ultrafine ZrB2-ZrC Composite Powders" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122497
APA StyleBai, L., Yuan, F., Fang, Z., Wang, Q., Ouyang, Y., Jin, H., He, J., Liu, W., & Wang, Y. (2020). RF Thermal Plasma Synthesis of Ultrafine ZrB2-ZrC Composite Powders. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122497







