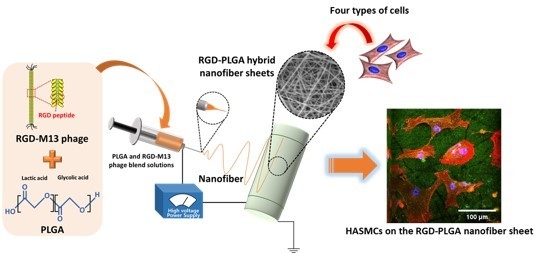
Biomimetic Hybrid Nanofiber Sheets Composed of RGD Peptide-Decorated PLGA as Cell-Adhesive Substrates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterizations of RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
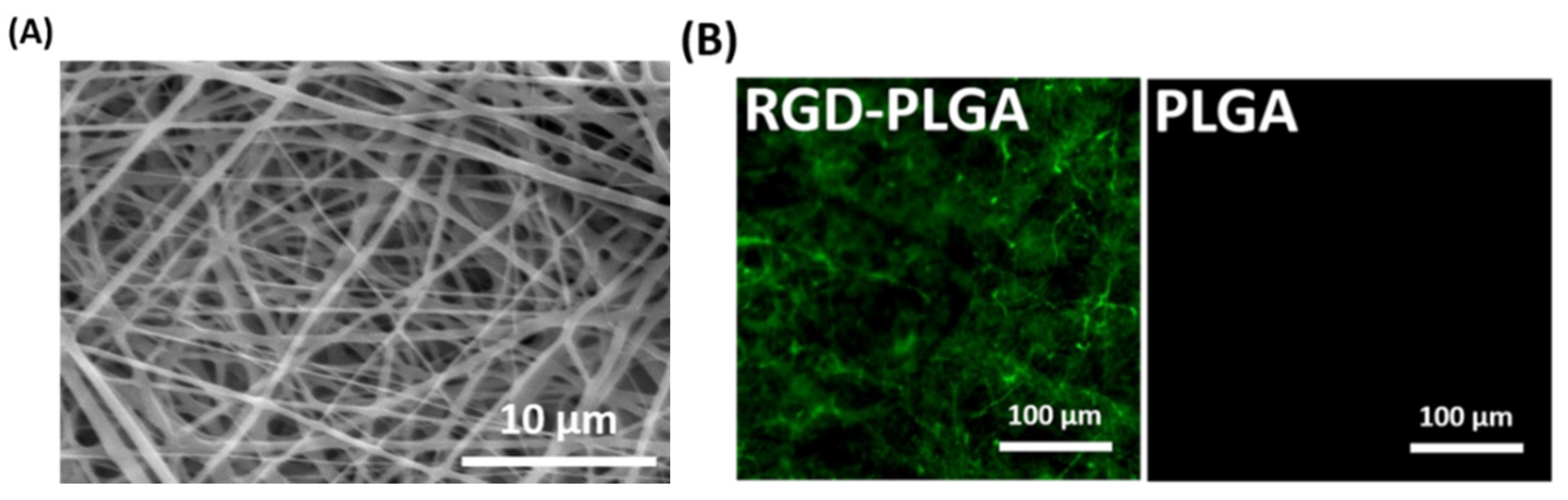
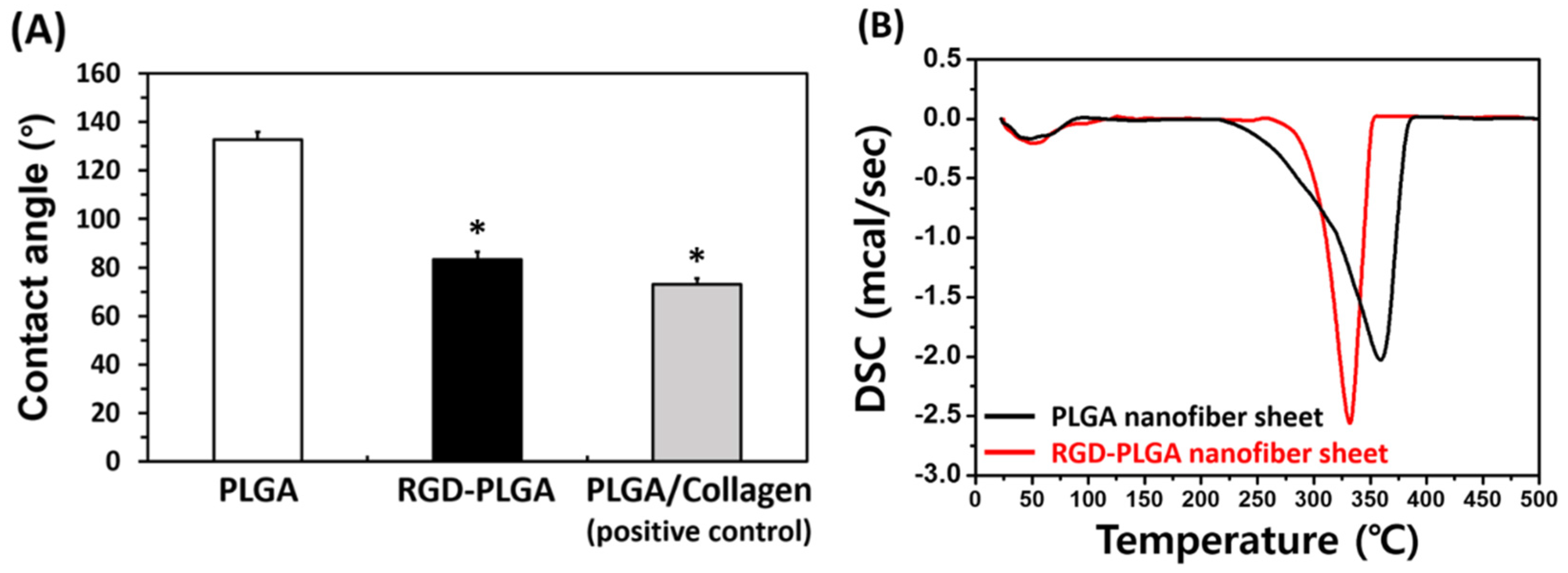
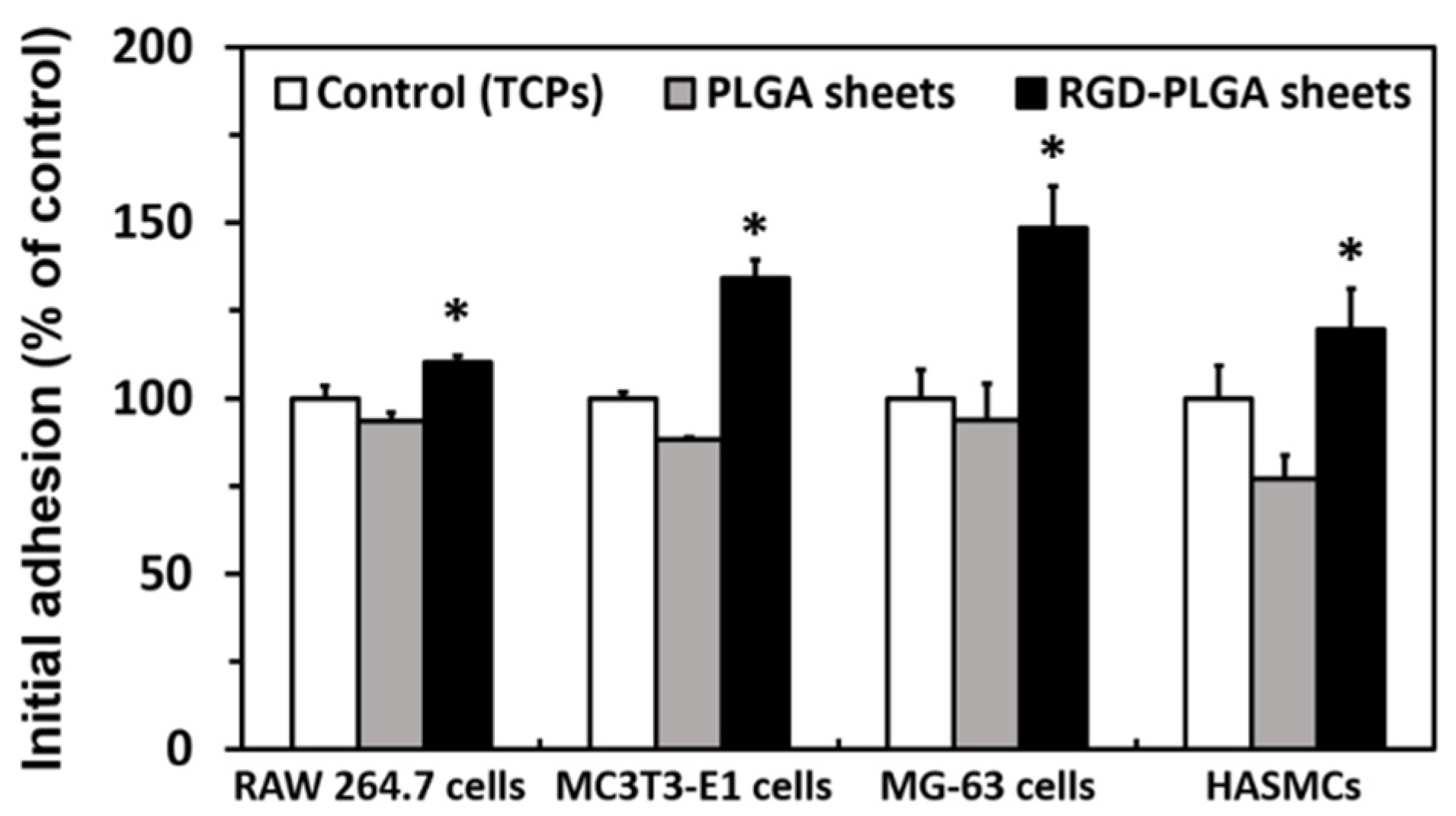
2.2. The Initial Cell Adhesion on RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
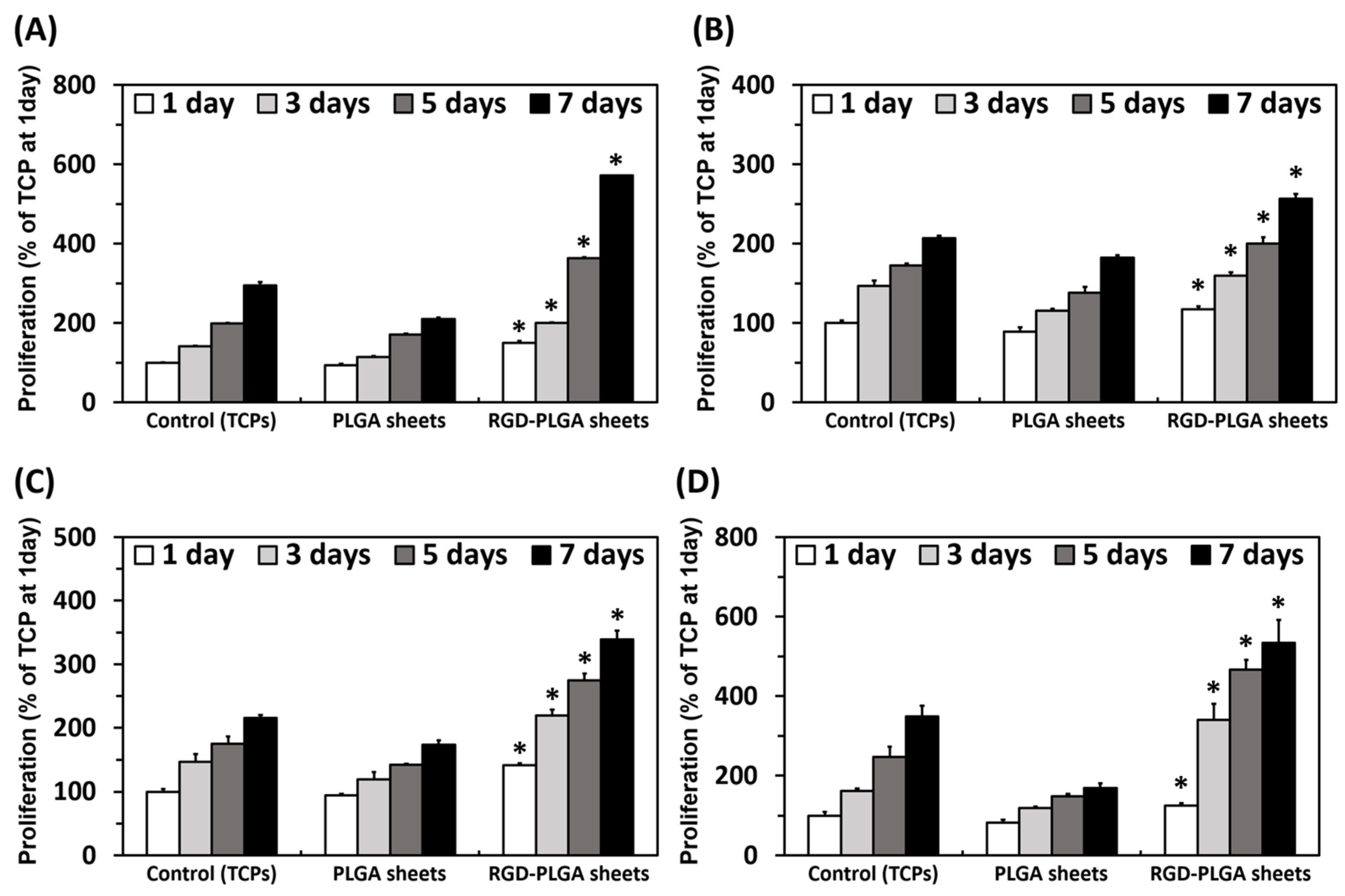
2.3. The Cell Proliferation on RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
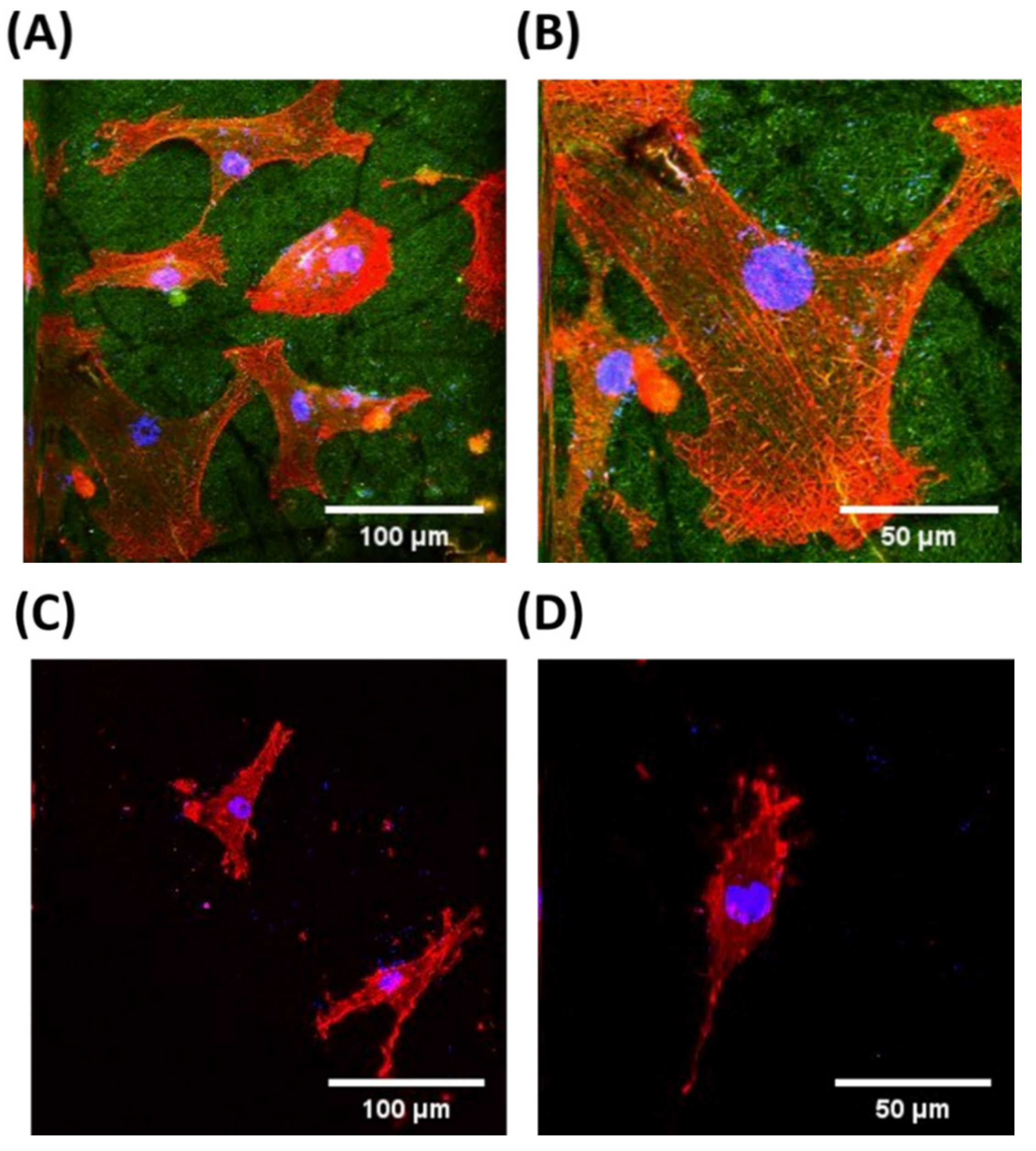
2.4. The Morphological Observation of HASMCs on RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
3. Experimental Section
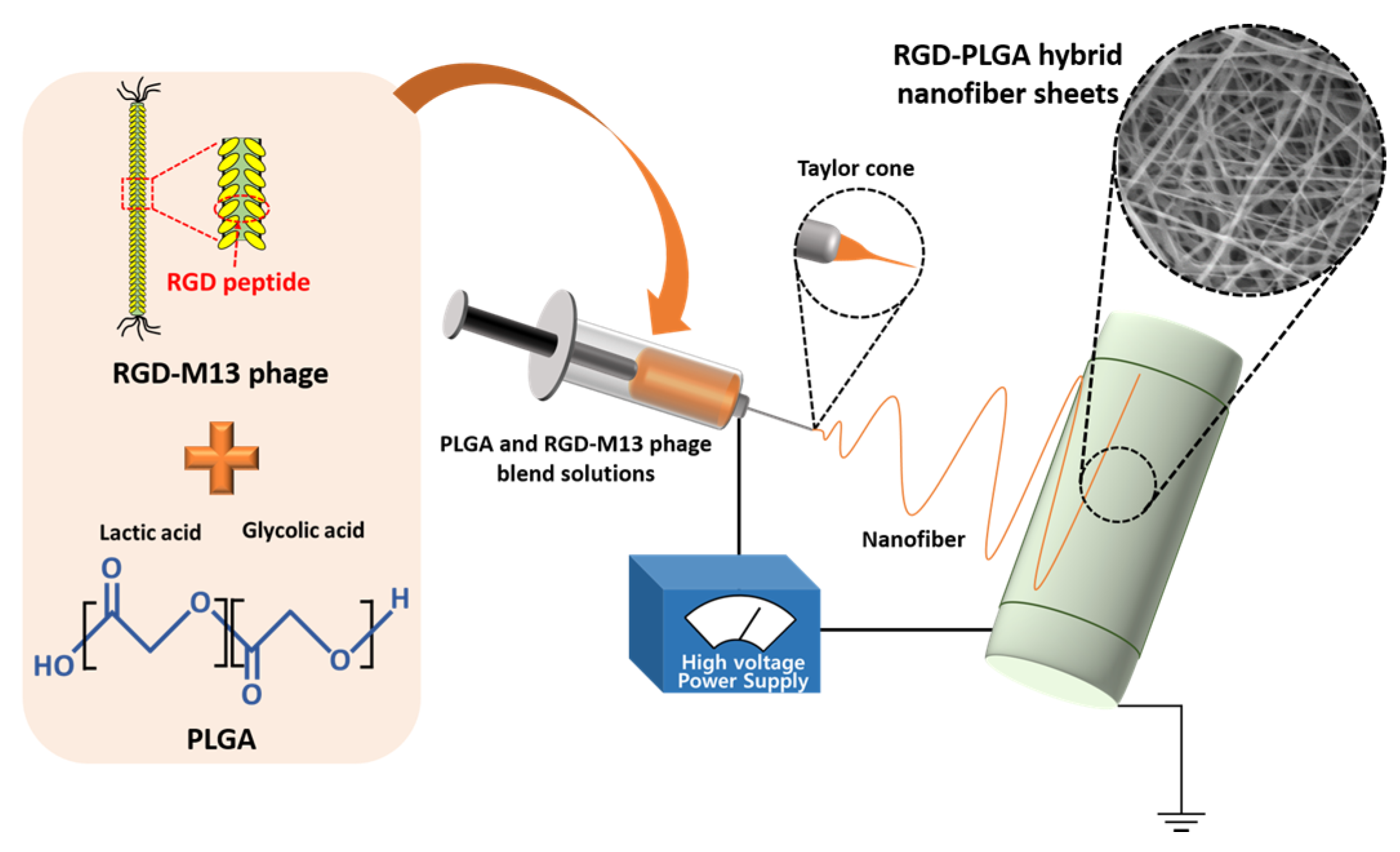
3.1. Fabrication of RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
3.2. Characterizations of RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
3.3. The Initial Cell Adhesion and Cell Proliferation Assays
3.4. Immunofluorescence Imaging of HASMCs on the RGD-PLGA Nanofiber Sheets
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murugan, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Design strategies of tissue engineering scaffolds with controlled fiber orientation. Tissue Eng. 2007, 8, 1845–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniash, E.; Hartgerink, J.D.; Storrie, H.; Stendahl, J.C.; Stupp, D.I. Self-assembling peptide amphiphile nanofiber matrices for cell entrapment. Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Jin, Q.; Giannobile, W.V.; Ma, P.X. The enhancement of osteogenesis by nano-fibrous scaffolds incorporating rhBMP-7 nanospheres. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Webster, T.J. Nanotechnology and nanomaterials: Promises for improved tissue regeneration. Nano Today 2009, 4, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.M.; Chen, V.J.; Jung, H.-M.; Kim, T.-I.; Shin, H.-I.; Baek, J.-H.; Ryoo, H.-M.; Ma, P.X. Comparative evaluation of nanofibrous scaffolding for bone regeneration in critical-size calvarial defects. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, N.; Johnson, J.K.; Bradley, P.A.; Parikh, K.S.; Lannutti, J.J.; Winter, J.O. Cell attachment to hydrogel-electrospun fiber mat composite materials. J. Funct. Biomater. 2012, 3, 497–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Memic, A.; Annabi, N.; Hossain, M.; Paul, A.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Dehghani, F.; Khademhosseini, A. Electrospun scaffolds for tissue engineering of vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, L.; Jin, O.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, J.; Hyon, S.-H.; Han, D.-W. Hyaluronic acid/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) core/shell fiber meshes loaded with epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate as skin tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2014, 14, 8458–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, L.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Hyun, J.K.; Jung, T.-G.; Hong, S.W.; Han, D.-W. Stimulated myoblast differentiation on graphene oxide-impregnated PLGA-collagen hybrid fibre matrices. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 21:1–21:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Hussain, M.; Mao, J.J. Continuing differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and induced chondrogenic and osteogenic lineages in electrospun PLGA nanofiber scaffold. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koker, S.; de Geest, B.G.; Cuvelier, C.; Ferdinande, L.; Deckers, W.; Hennink, W.E.; de Smedt, S.; Mertens, N. In vivo cellular uptake, degradation, and biocompatibility of polyelectrolyte microcapsules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3754–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmin, F.; Puoci, F.; Parisi, O.I.; Franzé, S.; Musazzi, U.M.; Cilurzo, F. Caffeic acid-PLGA conjugate to design protein drug delivery systems stable to irradiation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, L.J.; Suzuki, S.; Harkin, D.G.; Chirila, T.V. Incorporation of exogenous RGD peptide and inter-species blending as strategies for enhancing human corneal limbal epithelial cell growth on bombyx mori silk fibroin membranes. J. Funct. Biomater. 2013, 4, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.-B.; Chen, Y.-R.; Liu, H.-L. RGD-conjugated crosslinked chitosan scaffolds for culture and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 2013, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.M.; Jo, S.-Y.; Park, J.-S.; Gwon, H.-J.; Jeong, S.I.; Lim, Y.-M. Synergistic effect of dual-functionalized fibrous scaffold with BCP and RGD containing peptide for improved osteogenic differentiation. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-W.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-based fabrication of micro- and nanofibers using electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Mao, C. Virus activated artificial ECM induces the osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells without osteogenic supplements. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1242:1–1242:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zueger, C.; Chung, W.-J.; Yoo, S.Y.; Wang, E.; Meyer, J.; Ramesh, R.; Lee, S.-W. Virus-based piezoelectric energy generation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merzlyak, A.; Indrakanti, S.; Lee, S.-W. Genetically engineered nanofiber-like viruses for tissue regenerating materials. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Cao, B.; George, A.; Mao, C. Self-assembly and mineralization of genetically modifiable biological nanofibers driven by β-structure formation. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandra, N.; Abbineni, G.; Qu, X.; Huai, Y.; Wang, L.; Mao, C. Bacteriophage bionanowire as a carrier for both cancer-targeting peptides and photosensitizers and its use in selective cancer cell killing by photodynamic therapy. Small 2013, 9, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandra, N.; Wang, D.-D.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, C. Virus-mimetic cytoplasm-cleavable magnetic/silica nanoclusters for enhanced gene delivery to mesenchymal stem cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2013, 125, 11488–11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cao, B.; Zhen, Z.; Laxmi, A.A.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Mao, C. Controlled growth and differentiation of MSCs on grooved films assembled from monodisperse biological nanofibers with genetically tunable surface chemistries. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4744–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tomsia, A.P.; Mao, C. Phage nanofibers induce vascularized osteogenesis in 3D printed bone scaffolds. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4961–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Tomsia, A.; Mao, C. Untangling the effects of peptide sequences and nanotopographies in a biomimetic niche for directed differentiation of iPSCs by assemblies of genetically engineered viral nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6850–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, O.J.; Jung, C.Y.; Sohn, I.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, B.; Jhon, M.S.; Lee, N.-E. Nanocomposite nanofibers of poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) and graphene oxide nanosheets. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2011, 42, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.U.; Jahng, K.Y. An improved hydrophilicity via electrospinning for enhanced cell attachment and proliferation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2006, 78, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mondrinos, M.J.; Chen, X.; Gandhi, M.R.; Ko, F.K.; Lelkes, P.I. Co-electrospun poly(lactide-co-glycolide), gelatin, and elastin blends for tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 79, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, M.V.; Thomas, V.; Dean, D.R.; Nyairo, E. Fabrication and characterization of aligned nanofibrous PLGA/collagen blends as bone tissue scaffolds. Polymer 2009, 50, 3778–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pfeffer, R.; Dave, R.; Enick, R. Polymer encapsulation of fine particles by a supercritical antisolvent process. AIChE. J. 2009, 51, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, J.A.; Katare, Y.K.; Mitragotri, S. Particle shape: A new design parameter for micro- and nanoscale drug delivery carriers. J. Control. Release. 2007, 121, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersel, U.; Dahmen, C.; Kessler, H. RGD modified polymers: biomaterials for stimulated cell adhesion and beyond. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4385–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, S.L. Advantages of RGD peptides for directing cell association with biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4205–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.-J.; Merzlyak, A.; Yoo, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W. Genetically engineered liquid-crystalline viral films for directing neural cell growth. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9885–9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.-W.; Chung, W.-J.; Heo, K.; Jin, H.-E.; Lee, B.Y.; Wang, E.; Zueger, C.; Wong, W.; Meyer, J.; Kim, C.; et al. Biomimetic virus-based colourimetric sensors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3043:1–3043:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewska, A.; Yiu, G.; Yuste, R. A custom-made two-photon microscope and deconvolution system. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Phy. 2000, 441, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovhannisyan, V.; Hu, P.-S.; Chen, S.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Dong, C.-Y. Elucidation of the mechanisms of optical clearing in collagen tissue with multiphoton imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 046004:1–046004:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, Y.C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, J.-W.; Han, D.-W. Biomimetic Hybrid Nanofiber Sheets Composed of RGD Peptide-Decorated PLGA as Cell-Adhesive Substrates. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 367-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6020367
Shin YC, Lee JH, Kim MJ, Park JH, Kim SE, Kim JS, Oh J-W, Han D-W. Biomimetic Hybrid Nanofiber Sheets Composed of RGD Peptide-Decorated PLGA as Cell-Adhesive Substrates. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2015; 6(2):367-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6020367
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Yong Cheol, Jong Ho Lee, Min Jeong Kim, Ji Hoon Park, Sung Eun Kim, Jin Su Kim, Jin-Woo Oh, and Dong-Wook Han. 2015. "Biomimetic Hybrid Nanofiber Sheets Composed of RGD Peptide-Decorated PLGA as Cell-Adhesive Substrates" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 6, no. 2: 367-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6020367
APA StyleShin, Y. C., Lee, J. H., Kim, M. J., Park, J. H., Kim, S. E., Kim, J. S., Oh, J.-W., & Han, D.-W. (2015). Biomimetic Hybrid Nanofiber Sheets Composed of RGD Peptide-Decorated PLGA as Cell-Adhesive Substrates. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 6(2), 367-378. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb6020367