Do Non-Decision Times Mediate the Association between Age and Intelligence across Different Content and Process Domains?
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Material
2.3.1. Intelligence Assessment
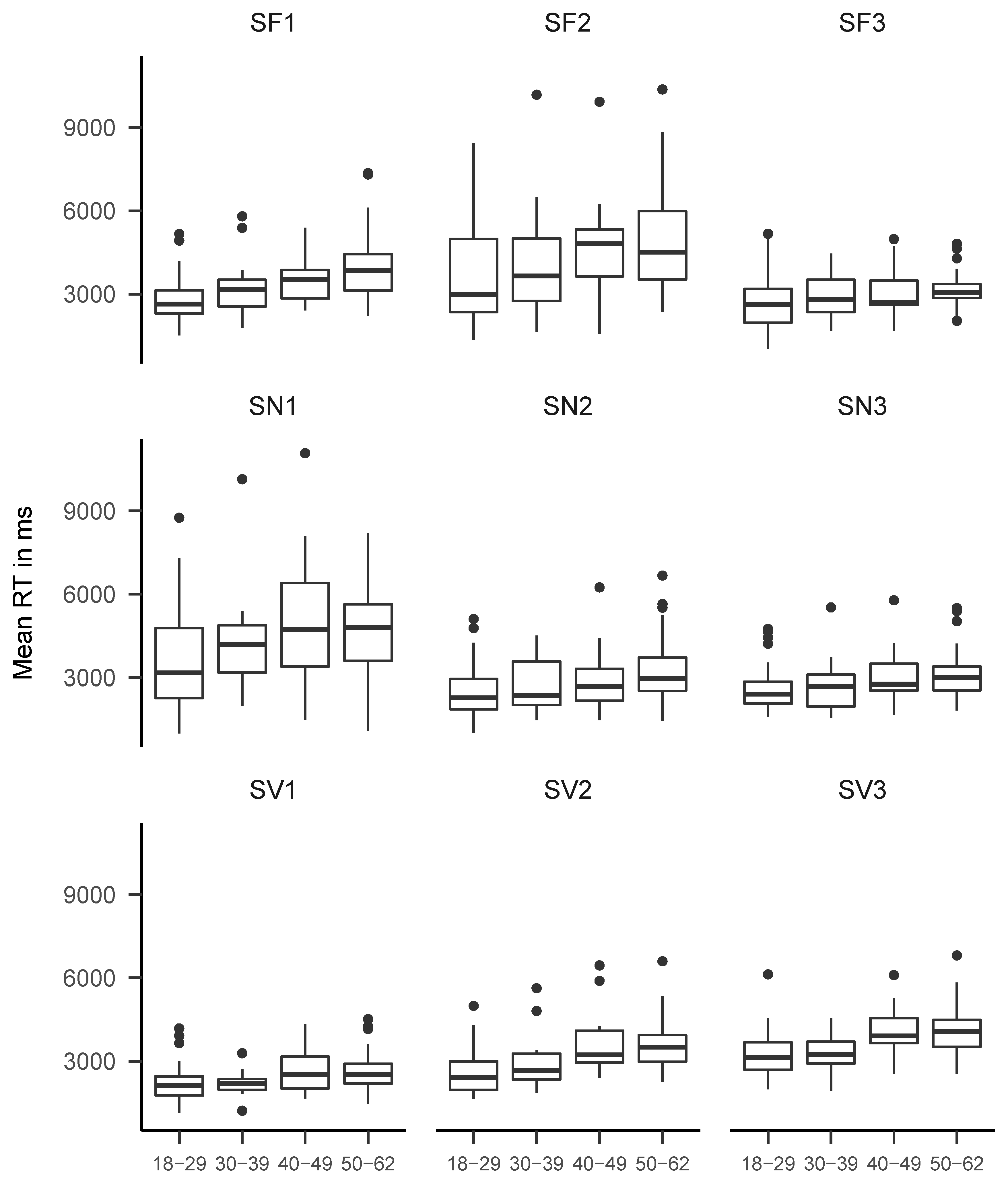
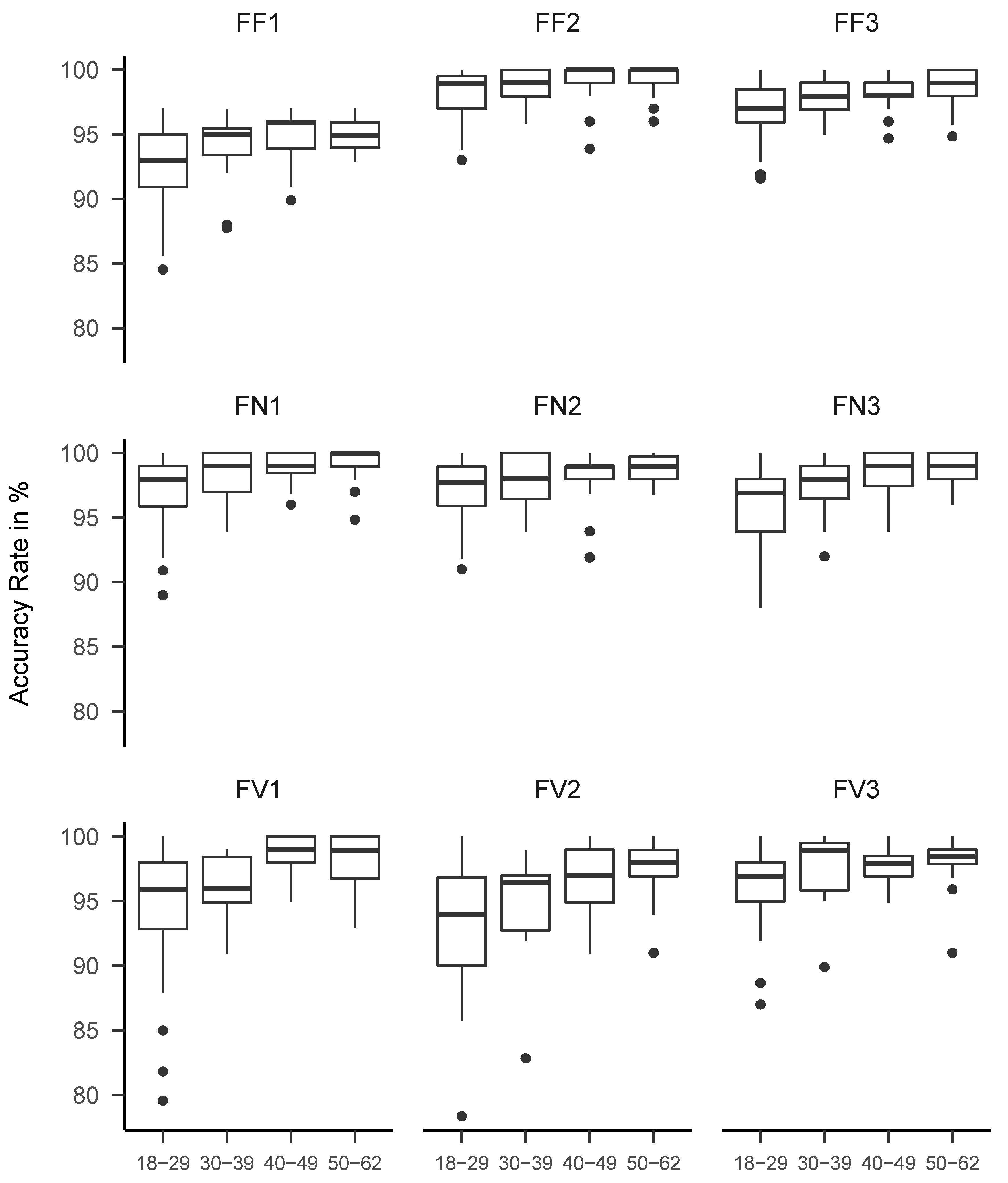
2.3.2. RT Tasks
2.4. Data Preparation
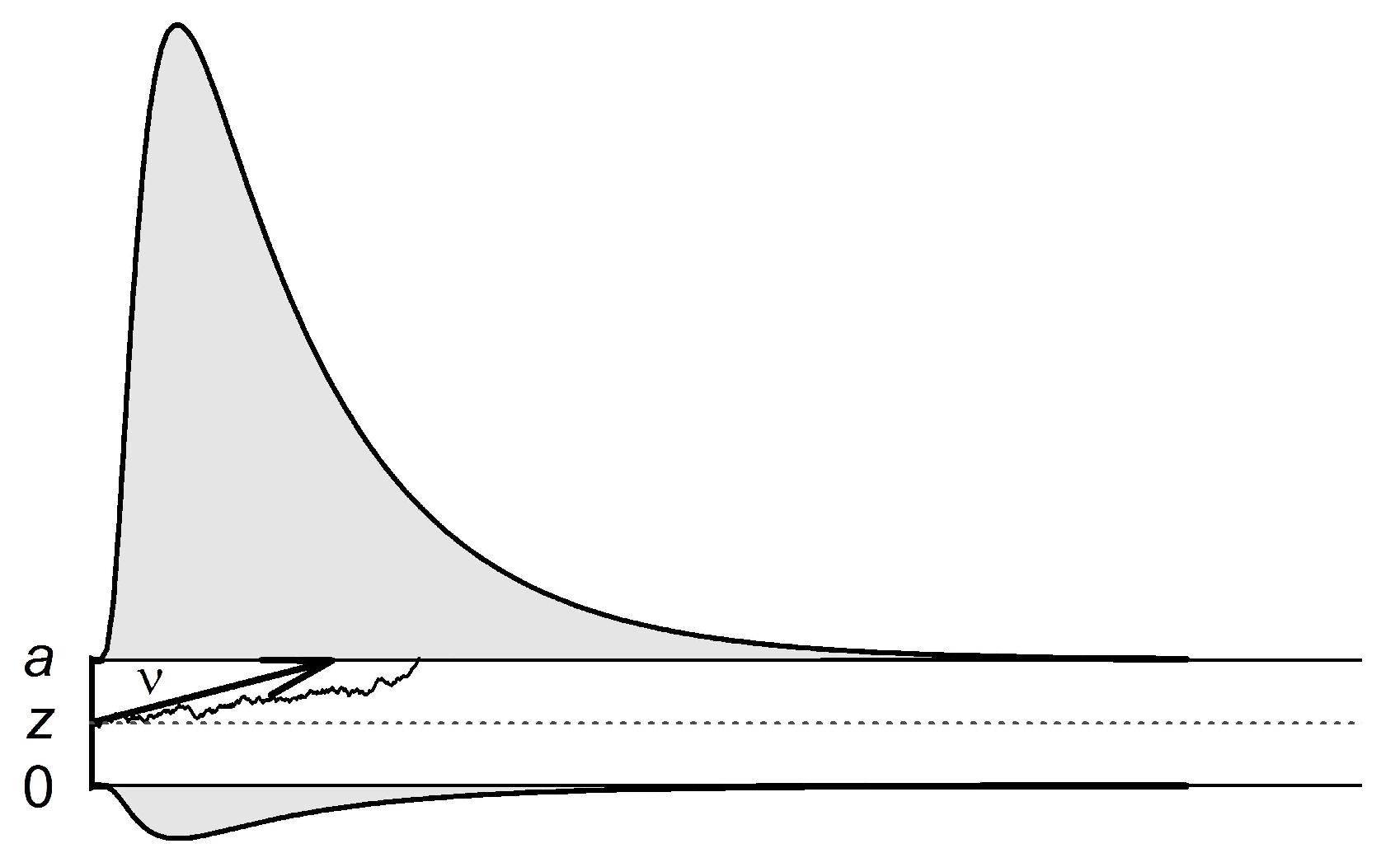
2.5. Parameter Estimation
2.6. Data Analysis
Mediation Models
3. Results
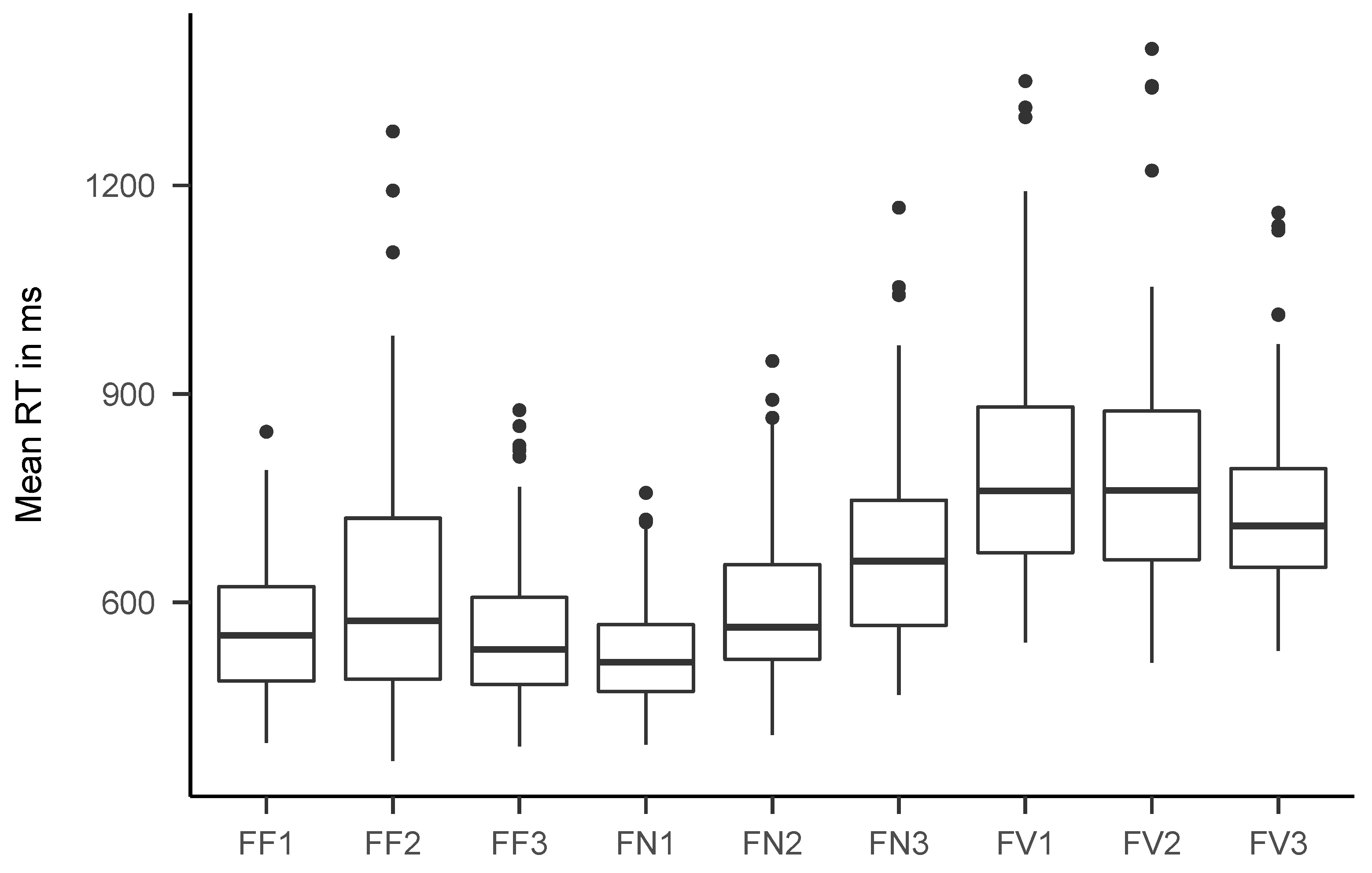
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Simple Correlations
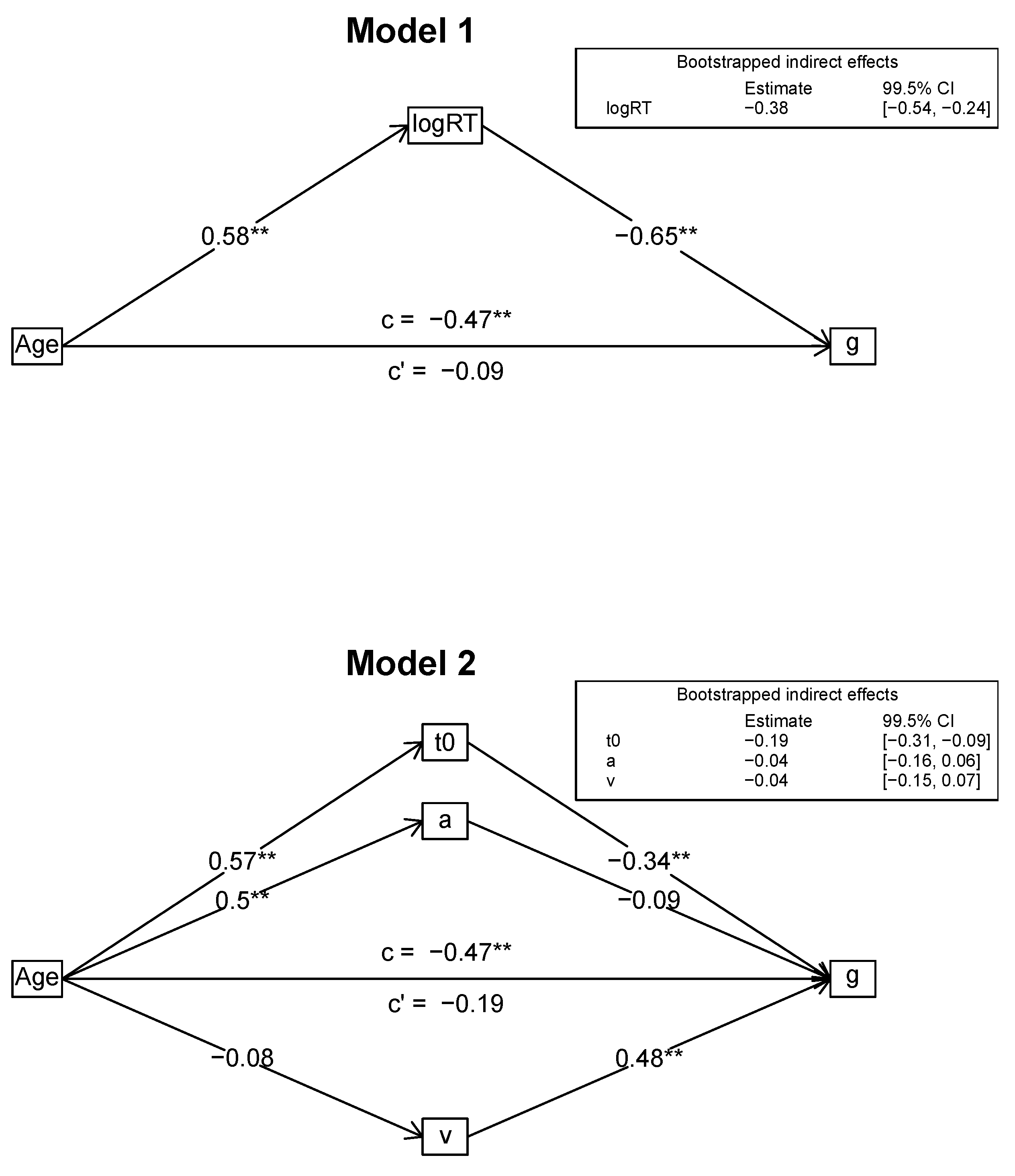
3.2. Mediation Analyses
3.2.1. Mediation Models with g as Outcome (Models 1 and 2)
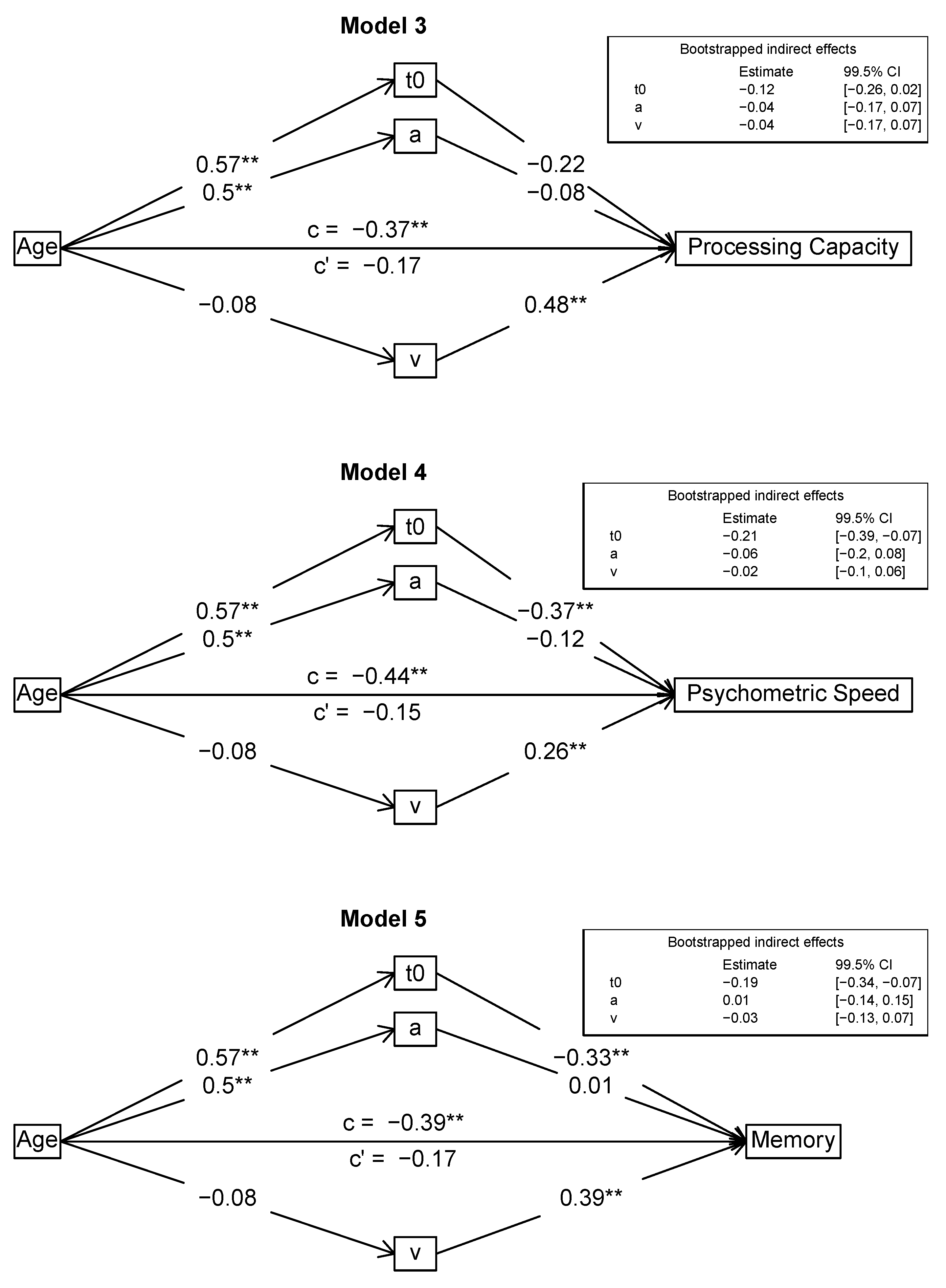
3.2.2. Mediation Models with Process Domains as Outcomes (Models 3–5)
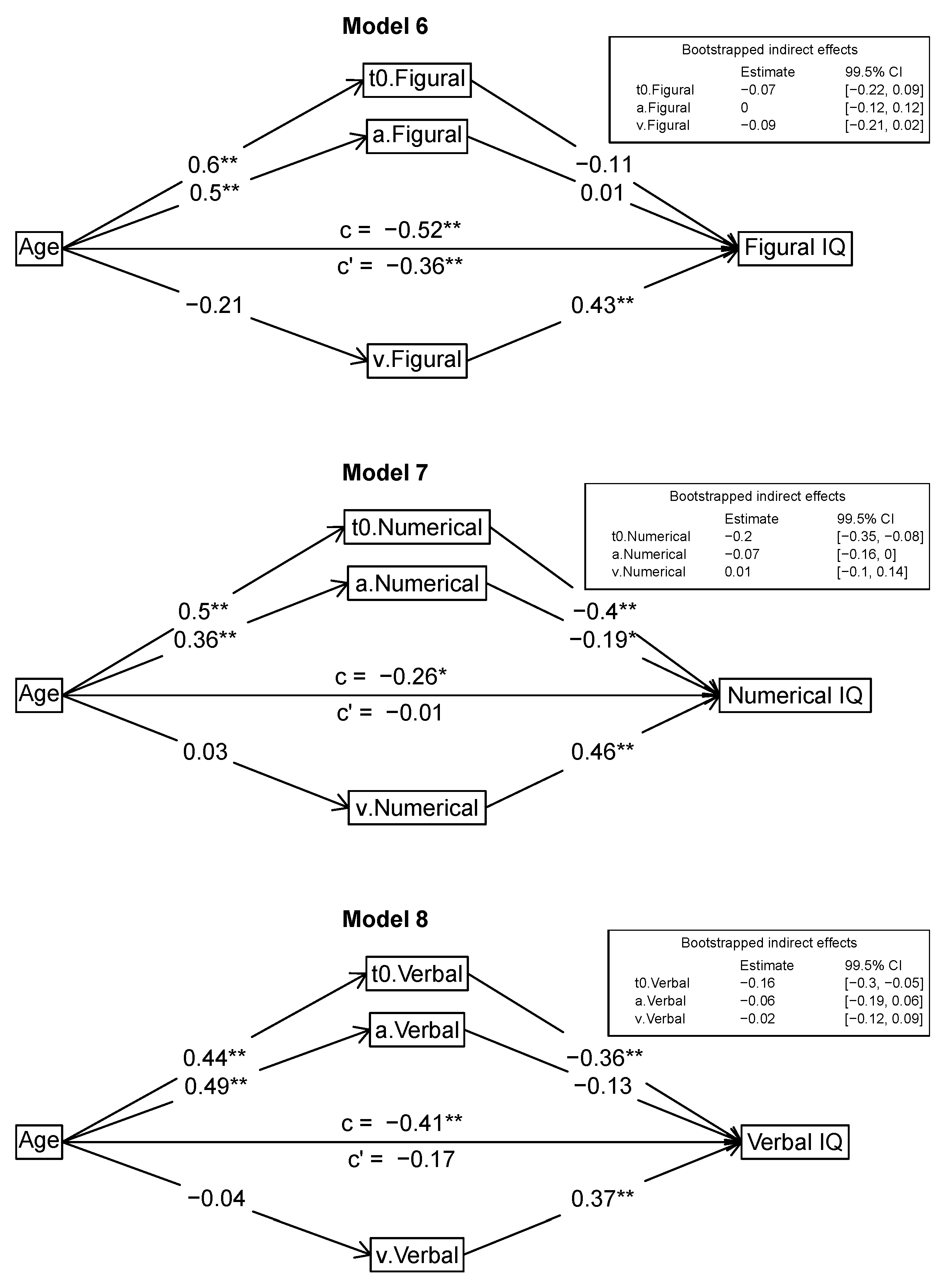
3.2.3. Mediation Models with Content Domain Scores as Outcomes (Models 6–8)
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Arnold, Nina R., Arndt Bröder, and Ute J. Bayen. 2015. Empirical validation of the diffusion model for recognition memory and a comparison of parameter-estimation methods. Psychological Research 79: 882–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, Frederik, and Marius Barth. 2018. Papaja: Create APA Manuscripts with R Markdown. R Package Version 0.1.0.9842. San Francisco: GitHub. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, B. Hunter, and Andrew J. Aschenbrenner. 2018. The importance of age-related differences in prospective memory: Evidence from diffusion model analyses. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 25: 1114–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattell, Raymond B. 1963. Theory of fluid and crystallized intelligence: A critical experiment. Journal of Educational Psychology 54: 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, Helen, Andrew J. Mackinnon, Ailsa Korten, and Anthony F. Jorm. 2001. The “common cause hypothesis” of cognitive aging: Evidence for not only a common factor but also specific associations of age with vision and grip strength in a cross-sectional analysis. Psychology and Aging 16: 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dully, Jessica, David P. McGovern, and Redmond G. O’Connell. 2018. The impact of natural aging on computational and neural indices of perceptual decision-making: A review. Behavioural Brain Research 355: 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, Deborah, Chandra A. Reynolds, John J. McArdle, and Nancy L. Pedersen. 2007. Age changes in processing speed as a leading indicator of cognitive aging. Psychology and Aging 22: 558–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartshorne, Joshua K., and Laura T. Germine. 2015. When does cognitive functioning peak? The asynchronous rise and fall of different cognitive abilities across the lifespan. Psychology Science 26: 433–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, John L., and Raymond B. Cattell. 1967. Age differences in fluid and crystallized intelligence. Acta Psychologica 26: 107–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczyk, Markus, Patrik Mittelstädt, and Carolin Wienrich’s. 2018. Parallel dual-task processing and task-shielding in older and younger adults: Behavioral and diffusion model results. Experimental Aging Research 44: 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, Arthur R. 2006. Clocking the Mind: Mental Chronometry and Individual Differences. Amsterdam: Elsevier. [Google Scholar]
- Jäger, Adolf O. 1982. Mehrmodale Klassifikation von Intelligenzleistungen [Multimodal classification of intelligent performance]. Diagnostica 28: 195–225. [Google Scholar]
- Jäger, Adolf Otto, Heinz-Martin Süß, and André Beauducel. 1997. Berliner Intelligenzstruktur-Test: BIS-Test. Göttingen: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Lerche, Veronika, Ursula Christmann, and Andreas Voss. 2018. Impact of Context Information on Metaphor Elaboration: A Diffusion Model Study. Experimental Psychology 65: 370–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerche, Veronika, Mischa von Krause, Andreas Voss, Gidon T. Frischkorn, Anna-Lena Schubert, and Dirk Hagemann. 2020. Diffusion modeling and intelligence: Drift rates show both domain-general and domain-specific relations with intelligence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, Veronika, and Andreas Voss. 2016. Model Complexity in Diffusion Modeling: Benefits of Making the Model More Parsimonious. Frontiers in Psychology 7: 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerche, Veronika, and Andreas Voss. 2019. Experimental validation of the diffusion model based on a slow response time paradigm. Psychological Research 83: 1194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerche, Veronika, Andreas Voss, and Markus Nagler. 2017. How many trials are required for parameter estimation in diffusion modeling? A comparison of different optimization criteria. Behavior Research 49: 513–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenberger, Ulman, Timo von Oertzen, Paolo Ghisletta, and Christopher Hertzog. 2011. Cross-sectional age variance extraction: What’s change got to do with it? Psychology and Aging 26: 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, David J., Matthew C. Costello, Nancy A. Dennis, Simon W. Davis, Anne M. Shepler, Julia Spaniol, Barbara Bucur, and Roberto Cabeza. 2010. Adult Age Differences in Functional Connectivity during Executive Control. Neuroimage 52: 643–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, David P., Aoife Hayes, Simon P. Kelly, and Redmond G. O’Connell. 2018. Reconciling age-related changes in behavioural and neural indices of human perceptual decision-making. Nature Human Behaviour 2: 955–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKoon, Gail, and Roger Ratcliff. 2012. Aging and IQ effects on associative recognition and priming in item recognition. Journal of Memory and Language 66: 416–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKoon, Gail, and Roger Ratcliff. 2013. Aging and predicting inferences: A diffusion model analysis. Journal of Memory and Language 68: 240–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oschwald, Jessica, Sabrina Guye, Franziskus Liem, Philippe Rast, Sherry Willis, Christina Röcke, Lutz Jäncke, Mike Martin, and Susan Mérillat. 2019. Brain structure and cognitive ability in healthy aging: A review on longitudinal correlated change. Reviews in the Neurosciences 31: 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. 2020. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff, Roger. 1978. A theory of memory retrieval. Psychological Review 85: 59–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, Roger. 2008. Modeling aging effects on two-choice tasks: Response signal and response time data. Psychology and Aging 23: 900–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliff, Roger, Pablo Gomez, and Gail McKoon. 2004. A Diffusion Model Account of the Lexical Decision Task. Psychological Review 111: 159–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, Roger, and Gail McKoon. 2008. The diffusion decision model: Theory and data for two-choice decision tasks. Neural Computation 20: 873–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, Roger, Anjali Thapar, and Gail McKoon. 2001. The effects of aging on reaction time in a signal detection task. Psychol Aging 16: 323–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, Roger, Anjali Thapar, and Gail McKoon. 2006. Aging and individual differences in rapid two-choice decisions. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 13: 626–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, Roger, Anjali Thapar, and Gail McKoon. 2010. Individual differences, aging, and IQ in two-choice tasks. Cognitive Psychology 60: 127–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter-Lorenz, Patricia A., and Denise C. Park. 2014. How does it stac up? revisiting the scaffolding theory of aging and cognition. Neuropsychology Review 24: 355–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, William. 2018. psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research. R Package Version 1.8.12. Evanston: Northwestern University. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseel, Yves. 2012. lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. Journal of Statistical Software 48: 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, Timothy A. 1996. The Processing-Speed Theory of Adult Age Differences in Cognition. Psychological Review 103: 403–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salthouse, Timothy A. 2004. What and When of Cognitive Aging. Current Directions in Psychological Science 13: 140–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, Timothy A. 2010. Selective review of cognitive aging. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 16: 754–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaie, K. Warner. 2005. What can we learn from longitudinal studies of adult development? Research in Human Development 2: 133–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, Anna-Lena, and Gidon T. Frischkorn. 2020. Neurocognitive Psychometrics of Intelligence: How Measurement Advancements Unveiled the Role of Mental Speed in Intelligence Differences. Current Directions in Psychological Science. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, Anna-Lena, Dirk Hagemann, and Gidon T. Frischkorn. 2017. Is general intelligence little more than the speed of higher-order processing? Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 146: 1498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, Anna-Lena, Dirk Hagemann, Christoph Löffler, and Gidon T. Frischkorn. 2020. Disentangling the Effects of Processing Speed on the Association between Age Differences and Fluid Intelligence. Journal of Intelligence 8: 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, Leah D., and Philip A. Vernon. 2008. Intelligence and speed of information-processing: A review of 50 years of research. Personality and Individual Differences 44: 535–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwinski, Martin J., and Charles B. Hall. 1998. Constraints on general slowing: A meta-analysis using hierarchical linear models with random coefficients. Psychology and Aging 13: 164–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaniol, Julia, David J. Madden, and Andreas Voss. 2006. A diffusion model analysis of adult age differences in episodic and semantic long-term memory retrieval. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 32: 101–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaniol, Julia, Andreas Voss, Holly J. Bowen, and Cheryl L. Grady. 2011. Motivational incentives modulate age differences in visual perception. Psychology and Aging 26: 932–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spieler, Daniel H. 2001. Modelling age-related changes in information processing. The European Journal of Cognitive Psychology 13: 217–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, Anjali, Roger Ratcliff, and Gail McKoon. 2003. A Diffusion Model Analysis of the Effects of Aging on Letter Discrimination. Psychol Aging 18: 415–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theisen, Maximilian, Veronika Lerche, Mischa von Krause, and Andreas Voss. 2020. Age differences in diffusion model parameters: A meta-analysis. Psychological Research. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker-Drob, Elliot M. 2011. Global and domain-specific changes in cognition throughout adulthood. Developmental Psychology 47: 331–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukey, John Wilder. 1977. Exploratory Data Analysis. Reading: Addison-Wesley Pub. Co. [Google Scholar]
- Verhaeghen, Paul, and Timothy A. Salthouse. 1997. Meta-analyses of age–cognition relations in adulthood: Estimates of linear and nonlinear age effects and structural models. Psychological Bulletin 122: 231–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voskuilen, Chelsea, Roger Ratcliff, and Gail McKoon. 2018. Aging and confidence judgments in item recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 44: 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, Andreas, Markus Nagler, and Veronika Lerche. 2013. Diffusion models in experimental psychology: A practical introduction. Experimental Psychology 60: 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, Andreas, Klaus Rothermund, and Jochen Voss. 2004. Interpreting the parameters of the diffusion model: An empirical validation. Memory & Cognition 32: 1206–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, Andreas, and Jochen Voss. 2007. Fast-dm: A free program for efficient diffusion model analysis. Behavior Research Methods 39: 767–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, Andreas, and Jochen Voss. 2008. A fast numerical algorithm for the estimation of diffusion model parameters. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 52: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, Andreas, Jochen Voss, and Veronika Lerche. 2015. Assessing cognitive processes with diffusion model analyses: A tutorial based on fast-dm-30. Frontiers in Psychology 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, Hadley, Mara Averick, Jennifer Bryan, Winston Chang, Lucy D’Agostino McGowan, Romain François, Garrett Grolemund, Alex Hayes, Lionel Henry, Jim Hester, and et al. 2019. Welcome to the tidyverse. Journal of Open Source Software 4: 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, Hadley, and Dana Seidel. 2019. scales: Scale Functions for Visualization. R Package Version 1.1.0. San Francisco: GitHub. [Google Scholar]
- Zimprich, Daniel, and Mike Martin. 2002. Can longitudinal changes in processing speed explain longitudinal age changes in fluid intelligence? Psychology and Aging 17: 690–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Fast | Slow | |
|---|---|---|
| FF1: dot-rectangle task (1.9) | SF1: maze task (2.1) | |
| Figural | FF2: simple area task (2.4) | SF2: complex area task (1.6) |
| FF3: polygon task (1.3) | SF3: pie task (2.7) | |
| FN1: number discrimination task (2.2) | SN1: mean value computation task (1.8) | |
| Numeric | FN2: odd-even task (1.5) | SN2: equation task (2.5) |
| FN3: simple inequation task (2.8) | SN3: complex inequation task (1.2) | |
| FV1: word category task (2.6) | SV1: grammar task (1.4) | |
| Verbal | FV2: lexical decision task (1.1) | SV2: statement task (2.3) |
| FV3: animacy task (1.7) | SV3: semantic category task (2.9) |
| Task | MRT | SDRT | MAcc. | SDAcc. | Mv | SDv | Ma | SDa | Mt0 | SDt0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF1 | 560 | 96 | 93.65 | 2.88 | 3.16 | 0.73 | 0.91 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.07 |
| FF2 | 620 | 176 | 98.68 | 1.60 | 3.26 | 1.02 | 1.53 | 0.53 | 0.36 | 0.07 |
| FF3 | 551 | 96 | 97.71 | 1.90 | 4.27 | 0.96 | 1.16 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 0.06 |
| FN1 | 527 | 78 | 98.03 | 2.26 | 4.97 | 1.82 | 1.47 | 1.31 | 0.39 | 0.07 |
| FN2 | 590 | 107 | 97.68 | 2.03 | 3.95 | 0.97 | 1.20 | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.06 |
| FN3 | 670 | 135 | 97.17 | 2.74 | 3.97 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 1.03 | 0.50 | 0.10 |
| FV1 | 792 | 164 | 96.22 | 3.76 | 2.81 | 0.88 | 1.52 | 0.73 | 0.51 | 0.08 |
| FV2 | 781 | 162 | 95.11 | 3.97 | 2.68 | 0.78 | 1.33 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.07 |
| FV3 | 737 | 124 | 97.18 | 2.41 | 3.21 | 0.89 | 1.35 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.07 |
| SF1 | 3234 | 1091 | 95.53 | 2.91 | 0.94 | 0.20 | 3.75 | 1.44 | 1.29 | 0.49 |
| SF2 | 4189 | 2009 | 86.69 | 6.50 | 0.58 | 0.17 | 3.71 | 1.37 | 1.48 | 0.92 |
| SF3 | 2856 | 906 | 80.47 | 9.10 | 0.50 | 0.18 | 3.06 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.40 |
| SN1 | 4168 | 1904 | 90.76 | 8.11 | 0.70 | 0.22 | 4.00 | 1.53 | 1.63 | 1.21 |
| SN2 | 2761 | 1098 | 91.16 | 5.48 | 0.80 | 0.25 | 3.25 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.31 |
| SN3 | 2805 | 885 | 93.51 | 3.71 | 1.08 | 0.33 | 2.85 | 0.92 | 1.50 | 0.42 |
| SV1 | 2380 | 709 | 96.36 | 2.39 | 1.17 | 0.20 | 3.08 | 0.84 | 1.09 | 0.35 |
| SV2 | 3030 | 1002 | 95.11 | 2.61 | 1.03 | 0.29 | 3.19 | 0.87 | 1.45 | 0.42 |
| SV3 | 3600 | 895 | 94.24 | 4.77 | 0.90 | 0.23 | 3.69 | 1.23 | 1.64 | 0.41 |
| Task | Mean RT | Mean log. RT | Accuracy Rate | Drift Rate | Boundary Sep. | Non-Decision Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF1 | 0.64 ** | 0.66 ** | 0.41 ** | −0.16 | 0.43 ** | 0.62 ** |
| FF2 | 0.54 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.27 * | −0.29 * | 0.37 ** | 0.50 ** |
| FF3 | 0.56 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.01 | 0.38 ** | 0.49 ** |
| FN1 | 0.61 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.37 ** |
| FN2 | 0.32 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.35 ** |
| FN3 | 0.59 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.50 ** | 0.09 | 0.34 ** | 0.40 ** |
| FV1 | 0.28 * | 0.32 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.25 | 0.36 ** | 0.25 |
| FV2 | 0.37 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.48 ** | 0.02 | 0.49 ** | 0.17 |
| FV3 | 0.46 ** | 0.48 ** | 0.34 ** | −0.07 | 0.21 | 0.44 ** |
| SF1 | 0.50 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.28 * | −0.31 ** | 0.33 ** | 0.25 * |
| SF2 | 0.25 | 0.32 ** | 0.23 | −0.08 | 0.22 | 0.28 * |
| SF3 | 0.24 | 0.31 ** | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.19 |
| SN1 | 0.26 | 0.27 * | 0.17 | −0.05 | 0.22 | 0.13 |
| SN2 | 0.25 * | 0.28 * | 0.29 * | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.29 * |
| SN3 | 0.25 * | 0.30 ** | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.42 ** |
| SV1 | 0.31 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.35 ** | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.31 ** |
| SV2 | 0.48 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.19 | −0.34 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.32 ** |
| SV3 | 0.45 ** | 0.47 ** | 0.24 | −0.09 | 0.32 ** | 0.30 ** |
| Task | Mean RT | Mean log. RT | Accuracy Rate | Drift Rate | Boundary Sep. | Non-Decision Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF1 | −0.46 ** | −0.46 ** | −0.33 ** | 0.13 | −0.34 ** | −0.44 ** |
| FF2 | −0.46 ** | −0.44 ** | −0.19 | 0.32 ** | −0.35 ** | −0.25 |
| FF3 | −0.62 ** | −0.63 ** | −0.21 | 0.25 | −0.29 * | −0.45 ** |
| FN1 | −0.57 ** | −0.57 ** | −0.13 | 0.18 | −0.07 | −0.36 ** |
| FN2 | −0.60 ** | −0.64 ** | −0.28 * | 0.33 ** | −0.33 ** | −0.48 ** |
| FN3 | −0.67 ** | −0.69 ** | −0.27 * | 0.15 | −0.27 * | −0.48 ** |
| FV1 | −0.48 ** | −0.50 ** | −0.12 | 0.21 | −0.28 * | −0.29 * |
| FV2 | −0.49 ** | −0.50 ** | −0.12 | 0.22 | −0.38 ** | −0.34 ** |
| FV3 | −0.51 ** | −0.53 ** | −0.08 | 0.32 ** | −0.18 | −0.41 ** |
| SF1 | −0.54 ** | −0.54 ** | −0.04 | 0.46 ** | −0.38 ** | −0.21 |
| SF2 | −0.35 ** | −0.40 ** | 0.03 | 0.37 ** | −0.28 * | −0.21 |
| SF3 | −0.22 | −0.24 | 0.25 | 0.34 ** | −0.07 | −0.23 |
| SN1 | −0.26 * | −0.23 | 0.24 | 0.41 ** | 0.00 | −0.25 |
| SN2 | −0.66 ** | −0.71 ** | 0.10 | 0.60 ** | −0.55 ** | −0.44 ** |
| SN3 | −0.67 ** | −0.72 ** | −0.06 | 0.44 ** | −0.52 ** | −0.49 ** |
| SV1 | −0.54 ** | −0.55 ** | −0.20 | 0.29 * | −0.34 ** | −0.51 ** |
| SV2 | −0.56 ** | −0.57 ** | −0.02 | 0.42 ** | −0.45 ** | −0.42 ** |
| SV3 | −0.62 ** | −0.64 ** | 0.01 | 0.42 ** | −0.41 ** | −0.25 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Age | ||||||||
| 2—g | −0.47 ** | |||||||
| 3—Processing Cap. | −0.37 ** | 0.91 ** | ||||||
| 4—Psy. Speed | −0.44 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.55 ** | |||||
| 5—Memory | −0.39 ** | 0.75 ** | 0.55 ** | 0.48 ** | ||||
| 6—mean log RT | 0.58 ** | −0.70 ** | −0.59 ** | −0.63 ** | −0.55 ** | |||
| 7—t0 | 0.57 ** | −0.60 ** | −0.46 ** | −0.57 ** | −0.51 ** | 0.78 ** | ||
| 8—a | 0.50 ** | −0.51 ** | −0.44 ** | −0.47 ** | −0.38 ** | 0.89 ** | 0.50 ** | |
| 9—v | −0.08 | 0.60 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.47 ** | −0.52 ** | −0.23 | −0.34 ** |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Age | ||||||||||||
| 2—Verbal IQ | −0.41 ** | |||||||||||
| 3—Figural IQ | −0.52 ** | 0.53 ** | ||||||||||
| 4—Numerical IQ | −0.26 * | 0.56 ** | 0.53 ** | |||||||||
| 5—t0 Verbal | 0.44 ** | −0.59 ** | −0.31 ** | −0.43 ** | ||||||||
| 6—t0 Figural | 0.60 ** | −0.40 ** | −0.40 ** | −0.33 ** | 0.70 ** | |||||||
| 7—t0 Numerical | 0.50 ** | −0.54 ** | −0.41 ** | −0.59 ** | 0.66 ** | 0.72 ** | ||||||
| 8—v Verbal | −0.04 | 0.53 ** | 0.24 | 0.37 ** | −0.28 * | −0.08 | −0.25 * | |||||
| 9—v Figural | −0.21 | 0.38 ** | 0.52 ** | 0.38 ** | −0.07 | −0.16 | −0.27 * | 0.49 ** | ||||
| 10—v Numerical | 0.03 | 0.39 ** | 0.27 * | 0.60 ** | −0.10 | 0.01 | −0.29 * | 0.50 ** | 0.53 ** | |||
| 11—a Verbal | 0.49 ** | −0.52 ** | −0.38 ** | −0.35 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.48 ** | −0.41** | −0.33 ** | −0.15 | ||
| 12—a Figural | 0.50 ** | −0.47 ** | −0.38 ** | −0.25 | 0.35 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.39 ** | −0.24 | −0.39 ** | −0.13 | 0.78 ** | |
| 13—a Numerical | 0.36 ** | −0.47 ** | −0.36 ** | −0.35 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.29 * | −0.25 | −0.34 ** | −0.09 | 0.73 ** | 0.73 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Krause, M.; Lerche, V.; Schubert, A.-L.; Voss, A. Do Non-Decision Times Mediate the Association between Age and Intelligence across Different Content and Process Domains? J. Intell. 2020, 8, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence8030033
von Krause M, Lerche V, Schubert A-L, Voss A. Do Non-Decision Times Mediate the Association between Age and Intelligence across Different Content and Process Domains? Journal of Intelligence. 2020; 8(3):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence8030033
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Krause, Mischa, Veronika Lerche, Anna-Lena Schubert, and Andreas Voss. 2020. "Do Non-Decision Times Mediate the Association between Age and Intelligence across Different Content and Process Domains?" Journal of Intelligence 8, no. 3: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence8030033
APA Stylevon Krause, M., Lerche, V., Schubert, A.-L., & Voss, A. (2020). Do Non-Decision Times Mediate the Association between Age and Intelligence across Different Content and Process Domains? Journal of Intelligence, 8(3), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence8030033





