Do Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Have Deep Learning Ability? An Exploratory Research in Inclusive Play
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Deep Learning Ability During Play Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
2.1. Deep Learning and Inclusive Play
2.2. Play Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
2.3. Influences on Learning in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
2.4. Research Questions
- Do children with ASD demonstrate deep learning ability during play?
- Are there significant differences in deep learning abilities among children with ASD across gender and age? And are there significant differences in the deep learning abilities of children with ASD in different types of play?
- What factors influence children’s deep learning ability?
3. Methods
3.1. Ethics
3.2. Participants
3.3. Instrument of Observation
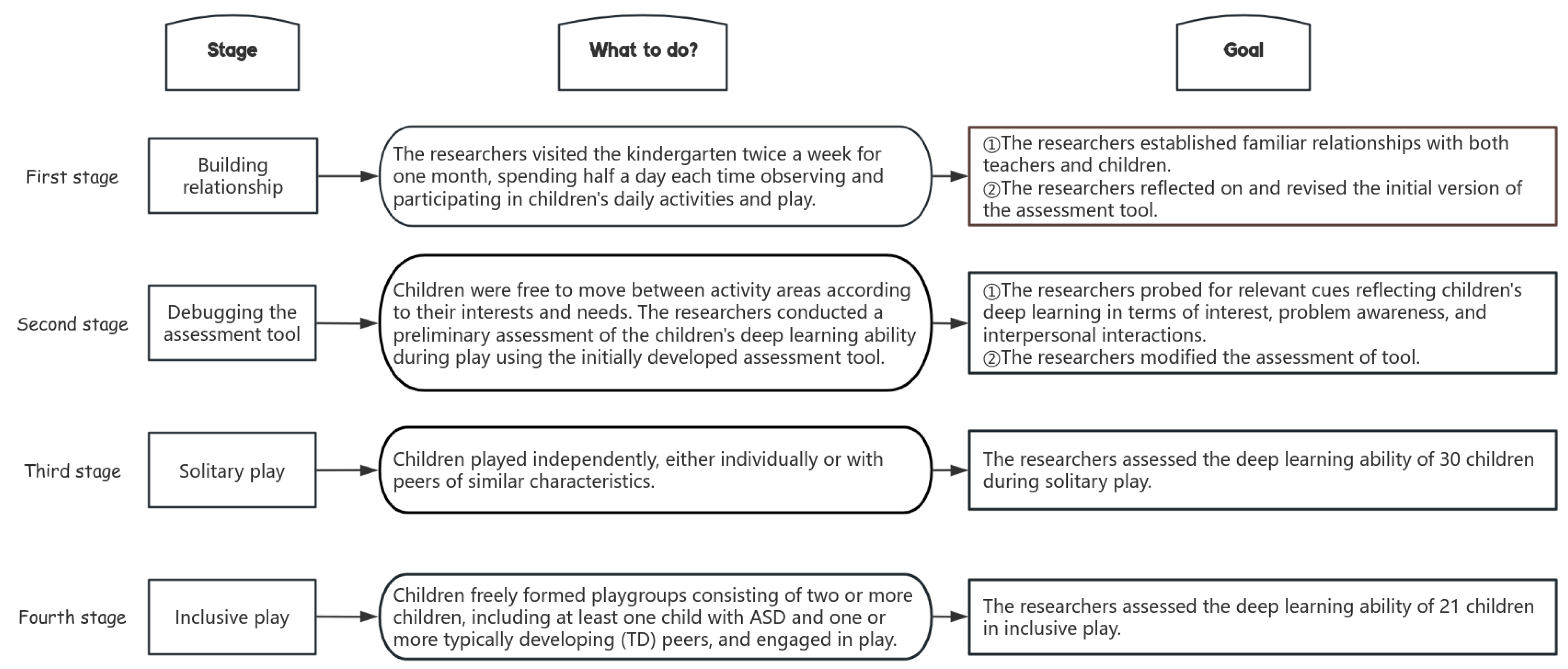
3.4. Research Procedure
3.5. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Do Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders Demonstrate Deep Learning Ability?
4.2. Are There Differences Among Different Ages in the Deep Learning Abilities of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders?
4.3. Are There Differences Between Different Genders in the Deep Learning Abilities of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders?
4.4. Are There Differences Between Solitary Play and Inclusive Play in the Deep Learning Abilities of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders?
4.5. Which Demographic Variables Influence Deep Learning Abilities During Play in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders?
4.5.1. Monthly per Capita Household Income
4.5.2. Primary Playmates
4.5.3. Siblings
4.5.4. Parental Occupation
5. Discussion
5.1. Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders Demonstrated Deep Learning Ability
5.2. Contrary to Common Recognition of Inclusive Play, Our Study Found a Paradoxical Result: Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders Demonstrated Stronger Deep Learning Abilities in Solitary Play than in Inclusive Play
5.3. Monthly per Capita Household Income, Father’s Occupation, Siblings, and Primary Playmates of Children Have a Significant Influence on the Deep Learning Ability in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
5.4. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Children with ASD | Children with autism spectrum disorders |
| Children with TD | Children with typical development |
| IP | Inclusive play |
| SP | Solitary play |
| SEL | Social emotional development |
| SES | Socioeconomic status |
References
- Abdelwahab, Mahmoud M., Khamis A. Al-Karawi, and H. E. Semary. 2024. Integrating gene selection and deep learning for enhanced Autisms’ disease prediction: A comparative study using microarray data. AIMS Mathematics 9: 17827–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Yingtong, and Xiaoxi Wang. 2022. Psychology and Education of Children with Special Needs. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. 2014. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Beijing: Beijing University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, Angelika, Dennis W. Moore, Rebecca Godfrey, and Claire M. Fletcher-Flinn. 2004. Social skills assessment of children with autism in free-play situations. Autism: The International Journal of Research & Practice 8: 369–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, Terry. 2003. Getting the mix right again: An updated and theoretical rationale for interaction. International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning 4: 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Haruhiko, Ikuko Yoshimura, and Shinichiro Wakabayashi. 1980. Effects of age on adaptive behavior levels and academic skill levels in autistic and mentally retarded children. Journal of Autism & Developmental Disorders 10: 173–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahiraey, Mohammad Hossein. 2010. Quality of collaborative and individual learning in virtual learning environments. Paper presented at the 2nd International Conference on E-Learning and E-Teaching (ICELET 2010), Tehran, Iran, December 1–2; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Cohen, Simon, Alan M. Leslie, and Uta Frith. 1985. Does the autistic child have a “theory of mind”? Cognition 21: 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruner, Jerome Seymour, Alison Jolly, and Kathy Sylva. 1976. Play: Its Role in Development and Evolution. New York: Penguin. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, Edward G., and Jane I. Carlson. 1993. Reduction of severe behavior problems in the community using a multicomponent treatment approach. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 26: 157–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, Theresa. 2005. Inclusive Play: Practical Strategies for Working with Children Aged 3 to 8. London: SAGE Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Jing, Tzu-Jung Lin, Laura Justice, and Brook Sawyer. 2017. The Social Networks of Children With and Without Disabilities in Early Childhood Special Education Classrooms. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 49: 2779–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Keyin, Senchao Chai, and Zhiyu Gong. 2024. Study on the Correlation between Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitution and Clinical Manifestations in Autistic Children Clinical Manifestations in Autistic Children. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China 22: 81–84. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzoD5T-GnhMTC9_CtwGgZN4Py4Y26iH9QcMLggIrYhFz1TIlqqDDywQbA7BreZwF5fCNAkjc76qncpQ836p4yGKXQdo__EN5DP4Bu4o40_KR37QeQpBBu8F0uv7mOEgml8J_ZUgYNgVv7vdCkD3X2FCe39qyWlvmt5Zfyim5ce4s7g==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Chen, Shunsen. 2010. The Principles and Operation of the Sandplay Therapy on Children with Autism, Chinese. Journal of Special Education, 42–47. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzry6WFKOV-8oEl_6UvaA32x6_JyFVIIG7qR9aBgi4ABHBDSWrRJgcyh7s2T7Ee5LKZVHono_19Rz2dUwNzxk0GNyWrolxOelDb_JeBuGSmqvCv1dhbdAAnJes7ZvMTZdFzFQJKb0mBCzQUzSTkKRdyMfoG-ivTajjxQfEl8QVPyzg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Chen, Xiaofang. 2019. Alienation and Reengage of LearningFrom the Perspective of Constructivism and Sociocultural Theory. Theory and Practice of Education 39: 55–59. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzqY2u9affYCxabCe4Yp-hrHLGO8Zf-Ki1m-4lb-YydvMzW-SinW9onYADppqEAf7LWqMkT-at4aEDKRQKEd7atueryoTHyxw51blmNCeFFxfcedlgKAoEvtCOgXADjru92f85jpnj3Y5c34WPvCJYFWpUjmF5fMXtgd_D2nxAn5AQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Cheng, Zi Juan, Chun Xiao Ma, Runke Huang, and Ying Bai. 2024. Preschool Children’s Deeper-Learning in Mature Play. Early Childhood Education Journal 53: 1391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Michelene T. H., and Ruth Wylie. 2014. The ICAP Framework: Linking Cognitive Engagement to Active Learning Outcomes. Educational Psychologist 49: 219–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti-Ramsden, Gina, and Kevin Durkin. 2012. Language Development and Assessment in the Preschool Period. Neuropsychology Review 22: 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, Blythe A., Clayton W. Schupp, David Simon, Niles Ryan, and Sally Mendoza. 2010. Elevated cortisol during play is associated with age and social engagement in children with autism. Molecular Autism 1: 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Min, and Juncai Xu. 2023. Detection of ASD Children through Deep-Learning Application of fMRI. Children 10: 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, Gemma, Caterina D’ardia, Donatella Valente, Ilaria Del Vecchio, Anna Fabrizi, and Paola Bernabei. 2003. Vineland adaptive behavior profiles in children with autism and moderate to severe developmental delay. Autism 7: 269–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernelius, Courtney L., and Keith M. Christensen. 2017. Systematic Review of Evidence-Based Practices for Inclusive Playground Design. Children, Youth and Environments 27: 78–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, Veronica P., Susan Hedges, Kara Hume, Diane M. Browder, Julie L. Thompson, Kathy Fallin, Farah El Zein, Colleen Klein Reutebuch, and Sharon Vaughn. 2014. Addressing the Academic Needs of Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder in Secondary Education. Remedial and Special Education 35: 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangi, Alejandro F., Julia A. Schnabel, Christos Davatzikos, Carlos Alberola-López, and Gabor Fichtinger, eds. 2018. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2018. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland AG. [Google Scholar]
- Fredricks, Jennifer A., Phyllis C. Blumenfeld, and Alison H. Paris. 2004. School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research 74: 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, Dominique, Valérie Courchesne, Catherine Cimon-Paquet, Claudine Jacques, and Isabelle Soulières. 2023. Visual abilities and exploration behaviors as predictors of intelligence in autistic children from preschool to school age. Autism 27: 2446–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandland, Guy. 2014. Developmentally Appropriate Play: Guiding Young Children to a Higher Level. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Publisher. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Qun. 2018. Development and Learning of Children with Special Needs. Beijing: Science Press. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Hua. 2016. The deep learning and its significance. Curriculum, Teaching Material and Method 36: 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happé, Francesca, and Uta Frith. 2006. The weak coherence account: Detail-focused cognitive style in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 36: 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzroni, Orit, Hila Agada, and Mark Leikin. 2019. Creativity in Autism: An Examination of General and Mathematical Creative Thinking Among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Children with Typical Development. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 49: 3833–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Xianli. 2022. Design and Guidance of Play Activities for Children with Special Needs. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Xiaofeng. 2023. A Single-case Study of Application of Peer Intervention Combined with Sports Games to Improve Social Skills of Children with Autism. Master’s thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Lirong. 2022. Deep Learning—Promoting Quality Teaching and Learning of Integrated Practical Activities in Primary Schools. Fuzhou: Fujian Education Press. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Weihe. 2008. Conquering Autism with Contemporary Science—An Intervention Education Approach from Clinical and Experimental Perspectives. Shanghai: East China Normal University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, Bob. 1998. Playwork in extremis: One of many applications of playwork’s values, methods, and worth. In International World of Play Conference. San Antonio: University of the Incarnate Word. [Google Scholar]
- Imbiriba, Tales, Ahmet Demirkaya, Ashutosh Singh, Deniz Erdogmus, and Matthew S. Goodwin. 2023. Wearable Biosensing to Predict Imminent Aggressive Behavior in Psychiatric Inpatient Youths with Autism. JAMA Network Open 6: 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, Therese, and Simon Baron-Cohen. 1997. Are people with autism and Asperger syndrome faster than normal on the embedded figures test? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 38: 527–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirer, Anat, and Nira Mashal. 2014. Verbal creativity in autism: Comprehension and generation of metaphoric language in high-functioning autism spectrum disorder and typical development. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 8: 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirer, Anat, Esther Adi-Japha, and Nira Mashal. 2020. Verbal and Figural Creativity in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder and Typical Development. Frontiers in Psychology 11: 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koegel, Robert L., Lynn Kern Koegel, and Alan Surratt. 1992. Language Intervention and Disruptive Behavior in Preschool-Children with Autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 22: 141–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Meng-Chuan, Michael V. Lombardo, Bonnie Auyeung, Bhismadev Chakrabarti, and Simon Baron-Cohen. 2015. Sex/Gender Differences and Autism: Setting the Scene for Future Research. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 54: 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Jianghua. 2004. Development and Learning of the Exceptional Child, 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, Vicky, and Jill Boucher. 1988. Spontaneous, Instructed and Elicited Play in Relatively Able Autistic-Children. British Journal of Developmental Psychology 6: 325–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Fanglu, and Zhucheng Liu. 2022. Inclusive play: “Legal” and “Educational” demonstrations of disabled children’s right to play. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 21–27. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzoWyeOH0O1d8gBZBTscfjQGopWdpPMz4WD70oQT4jBfM_jeWMFbfIrz5YqJeF-kog7VbbpnD9XZ0BT6ni73nsuuk6InmkKtsoCZYljzGrRkOF1gAVmhkJ3AygCuB3I0K1ZGn6ovZ3qlyiEUQ08eYTnVR2ouoNKHi4MEuRYnilUUJg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Lu, Sufang, Xia Cao, and Hongyun Gu. 2019. Innovations and Practices in Play Patterns for Promoting Deep Learning in Preschool Children. Journal of Shanghai Educational Research 7: 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Xueyi. 2002. Study on Social Class in Contemporary China. Beijing: Social Sciences Literature Publishing House. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Yingmei. 2011. An Overview of Foreign Researches into the Play-based Intervention of Autistic Childre. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 66–71. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzpYoz5-kTDnkjhqK7kv1YtZyfXg6k7MxzJorlJ7Lmv8fOpv5sW6ZrvUSk_Nmbz2cYrtUB_znwSv5wUr-t4MEjCPQKgBBok7Ba_iEAesrH2qL9YYOK9C-OOghH2KyA9ipx2Q8YWxjNKZj7XsvEy4680trpRjOGZAgUMKE8mbUqhbpA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Martin, Jacqueline L., and Hildy S. Ross. 2005. Sibling aggression: Sex differences and parents’ reactions. International Journal of Behavioral Development 29: 129–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogay, Hidir Selcuk, and Hojjat Adeli. 2024. Multiple Classification of Brain MRI Autism Spectrum Disorder by Age and Gender Using Deep Learning. Journal of Medical Systems 48: 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parten, Mildred B. 1932. Social participation among pre-school children. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology 27: 243–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, Pat, and Gill Poland. 1998. Play services for disabled children: Mothers’ satisfaction. Children & Society 12: 283–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Martín, Sergio, María Teresa García-Ordás, Martín Bayón-Gutiérrez, Natalia Prieto-Fernández, and José Alberto Benítez-Andrades. 2024. Enhancing ASD detection accuracy: A combined approach of machine learning and deep learning models with natural language processing. Health Information Science and Systems 12: 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, Whitby, Peggy J., and G. Richmond Mancil. 2009. Academic Achievement Profiles of Children with High Functioning Autism and Asperger Syndrome: A Review of the Literature. Education and Training in Developmental Disabilities 44: 551–60. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Lijuan, Linzhi Zhang, and Jianjun Ou. 2023. Potential categories of children with autism and their relationship to language abilities. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 37–44. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzqTxlryUBYTCNJrFuVcqvO59QJjNTVYJdcX0Q2yOsH7UGSe8Fyf6yM4ohSP1aTO-mjd7L7RM_ilU-KX8Iqo4AAduvRdKfAQg-VBznBE1qftm_SVjRlGYm9fMqg163QYcR_UIn9MIUbQulT5TIzBkBkL4N9C5ecHVXnoF4aL2XHNsQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Shi, Zhongying. 2001. Knowledge Transformation and Educational Reform. Beijing: Education Science Publishing House. [Google Scholar]
- Shipova, D. I., A. A. Kotov, and T. N. Kotov. 2025. Activity in choosing examples improves categorical prototype learning in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Clinical Psychology and Special Education 14: 114–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, Marian, and Rhonda Sena. 1993. Pretend Play in High Risk and Developmentally Delayed Children. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. [Google Scholar]
- Sobel, Kiley. 2018. Designing Technology for Inclusive Play. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Washington, Washington, DC, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Xueyun. 2014. How to Understand Autism Spectrum Disorders and Early Intervention. Beijing: Peking University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann-Bourque, Kathy S., Nancy C. Brady, and Kandace K. Fleming. 2011. Symbolic Play of Preschoolers with Severe Communication Impairments with Autism and Other Developmental Delays: More Similarities than Differences. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 42: 863–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilton, James R., and Donald R. Ottinger. 1964. Comparisons of the Toy Play of and Behavior of Autistic, Retarded, and Normal Children. Thousand Oaks: Psychological Reports. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Jie, and Minxuan Zhang. 2015. The Basic Experiences of the Successful Countries and Regions in PISA 2012. Comparative Education Review 37: 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xiaoying, and Siyuan Liu. 2020. The Basic Characteristics and Logical Structure of Children’s Deep Learning. Studies in Early Childhood Education 1: 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Y. 2021. An Exploratory Study on the Theory and Practice of Deep Learning in Early Childhood—Theory. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Xing, Na Lv, Linqin Ji, Liang Chen, and Wenxing Zhang. 2015. Children’s prosocial behavior and their psychosocial adjustment. Psychological Development and Education 31: 402–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Wen, Shufeng Wang, Qingqing Xie, and Liqun Gao. 2024. A play-based intervention model of verbal and non-verbal social communication skills in children with autism. Journal of Audiology and Speech Pathology 32: 75–79. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzqvo3pZE32WworJ-BjDO32JBl9WBmX-b2l-kbCHhcZhrqn44tIEd673R07rlQaywz_yxHi5slpEYUwmx-QKxu7kJO_3Rt4CveeyH8UhkO2_f8WvUuZJ7DL9RNDcnAvLJeOS7tt9GCADxA4dNiHSnESwF1utnPcz2CcV5Lr1QFupHA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Wolfberg, Pamela, Mila DeWitt, Gregory S. Young, and Thanh Nguyen. 2014. Integrated Play Groups: Promoting Symbolic Play and Social Engagement with Typical Peers in Children with ASD Across Settings. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 45: 830–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Yongjun. 2019. On the renewed understanding of deep learning. Curriculum, Teaching Material and Method 39: 51–58+36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Xiao, Na Yang, Leqiong Qian, and Shijie Zhou. 2014. Pretend Playing Training Improves Theory of Mind in Children with Autism. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology 22: 742–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Shuping, Wenwei Li, and Jian Wang. 2022. Review of domestic andforeign research on rehabilitation pathway of autistic children. China Journal of Health Psychology 30: 1902–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yantzi, Nicole M., Nancy Lynn Young, and Patricia McKeever. 2010. The suitability of school playgrounds for physically disabled children. Children’s Geographies 8: 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Jiajia, Yan Li, Mingyue Liu, Jing Wang, and Qidong Liu. 2024. Research on the activated mechanism of college students’ deep learning under the perspective of classroom orchestration with multilayered interaction: A thematic analysis case study based on college students’ reflection. Modern Distance Education, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Meiju, Fei Xiao, and Meng Deng. 2015. Empirical Research on Characteristics of Adaptive Behavior Development of Children with Autism. Education Research Monthly, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Nianli. 2002. Review and Research: The Cognitive Development of Autistic Children. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 60–64. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzpngXOysoBGjSljZXog1CX_2T3KXy0HLYUEimzld87M3AbUM3Is1HDb3xx3iscTFvJa1-JFtzkSMlpF9RR_s6zi_BwW0oHXUhz9kjALs_JADsefSvGsCX05CQ2ocnd-i3M21JrIgeZ6sshcdRRhgn0QgaxPTnTEzEhD-JE-P4VbCw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Zhou, Nianli, and Junming Fang. 2004. Experiment Research for Exploring Features of Pretending Play in Preschool Children with Autism. Chinese Journal of Special Education, 69–73. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=krTYG2tdvzqO0cE1OFpVQ8r6LOhV9UnIOYwhdctBlwl2hpt5kq79bqmgu8FqOHL3FNQGhTLw8CvcstHoi-K8MEzxod4ZbKs9o7WQ8m4Ng5IbFfpmCOqWH4gGflGAvbbppFa2Rd8VRcsYHn7P4vy-Kq7MgNc2yio1CtYub-vb9uHcOdNwiyJnLg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Zhu, Rui, and Nianli Zhou. 2014. How to Intervene in Play for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Beijing: Peking University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Xiangru, and Hua Zhang. 2013. Influences of Family Socioeconomic Status on the Development of Children. Journal of Henan University (Social Science) 53: 119–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukerman, Gil, Gili Yahav, and Ester Ben-Itzchak. 2019. Diametrically opposed associations between academic achievement and social anxiety among university students with and without autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research 12: 1376–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Kindergarten | Number | Name | Gender | Type of Children | Age | Verbal Language or Not | Participant in Which Play |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kindergarten A | 1 | TM1 | Male | Children with ASD | 7 | Verbal language | IP and SP |
| 2 | TM2 | Male | Children with ASD | 5 | Verbal language | IP | |
| 3 | TM3 | Male | Children with ASD | 5 | Verbal language | IP and SP | |
| 4 | TM5 | Male | Children with ASD | 6 | Not | SP | |
| 5 | TF1 | Female | Children with ASD | 6 | Verbal language | SP | |
| 6 | DF1 | Female | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| 7 | DF2 | Female | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| 8 | DM1 | Male | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| 9 | DM3 | Male | Children with TD | 5 | Verbal language | SP | |
| 10 | DM4 | Male | Children with TD | 5 | Verbal language | SP | |
| 11 | DF6 | Female | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | SP | |
| 12 | DF7 | Female | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | SP | |
| 13 | DF8 | Female | Children with TD | 5 | Verbal language | SP | |
| Kindergarten B | 14 | TM7 | Male | Children with ASD | 5 | Not | SP |
| 15 | TM8 | Male | Children with ASD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| 16 | DF4 | Female | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| Kindergarten C | 17 | TM9 | Male | Children with ASD | 6 | Verbal language | IP and SP |
| 18 | DM2 | Male | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| 19 | DM7 | Male | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | IP | |
| Kindergarten D | 20 | DM5 | Male | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | SP |
| 21 | DM6 | Male | Children with TD | 6 | Verbal language | SP |
| Norm | Name | Cronbach’s Alpha | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 1 Emotional experience | ||||
| Level 2 | 1.1 Interest | 1.2 Initiative | 1.3 Positive emotion experience | 1.4 Willpower | 0.914 |
| Level 1 | 2 Problem awareness | ||||
| Level 2 | 2.1 Attention | 2.2 Identify differences | 2.3 In-depth exploration of problems | 2.4 Problem representation | 0.883 |
| Level 1 | 3 Transfer and Application | ||||
| Level 2 | 3.1 Transfer | 3.2 Application | 3.3 Material selection | 3.4 Hands-on operation | 0.885 |
| Level 1 | 4 Problem solving | ||||
| Level 2 | 4.1 Speed of analyzing and responding to problems | 4.2 Strategies for implementing problem-solving | 4.3 Problem-solving methods | 4.4 Solve problem | 0.859 |
| Level 1 | 5 Interpersonal interaction | ||||
| Level 2 | 5.1 Awareness of interpersonal interaction | 5.2 Ability of interpersonal interaction | 5.3 Maintaining Interpersonal interaction | 0.886 | |
| Level 1 | 6 Cognitive quality | ||||
| Level 2 | 6.1 Account | 6.2 Causal relationship | 6.3 Reflection | 6.4 Creativity | 0.861 |
| Score | 115 | ||||
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 8.949 | 38.907 | 38.907 | 8.949 | 38.907 | 38.907 | 3.374 | 14.671 | 14.671 |
| 2.700 | 11.737 | 50.644 | 2.700 | 11.737 | 50.644 | 3.141 | 13.658 | 28.329 | |
| 3 | 2.392 | 10.400 | 61.044 | 2.392 | 10.400 | 61.044 | 3.099 | 13.472 | 41.801 |
| 4 | 1.536 | 6.678 | 67.722 | 1.536 | 6.678 | 67.722 | 2.928 | 12.729 | 54.530 |
| 5 | 1.354 | 5.886 | 73.608 | 1.354 | 5.886 | 73.608 | 2.741 | 11.919 | 66.449 |
| 6 | 1.077 | 4.684 | 78.292 | 1.077 | 4.684 | 78.292 | 2.724 | 11.843 | 78.292 |
| 7 | 0.670 | 2.913 | 81.205 | ||||||
| 8 | 0.559 | 2.429 | 83.634 | ||||||
| 9 | 0.517 | 2.249 | 85.883 | ||||||
| 10 | 0.454 | 1.976 | 87.859 | ||||||
| 11 | 0.402 | 1.747 | 89.606 | ||||||
| 12 | 0.358 | 1.558 | 91.164 | ||||||
| 13 | 0.326 | 1.419 | 92.583 | ||||||
| 14 | 0.319 | 1.388 | 93.971 | ||||||
| 15 | 0.286 | 1.245 | 95.216 | ||||||
| 16 | 0.226 | 0.983 | 96.199 | ||||||
| 17 | 0.185 | 0.804 | 97.002 | ||||||
| 18 | 0.161 | 0.700 | 97.702 | ||||||
| 19 | 0.158 | 0.685 | 98.387 | ||||||
| 20 | 0.134 | 0.583 | 98.970 | ||||||
| 21 | 0.107 | 0.464 | 99.434 | ||||||
| 22 | 0.082 | 0.357 | 99.790 | ||||||
| 23 | 0.048 | 0.210 | 100.000 | ||||||
| Item | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 | Factor 6 | Communality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 Interest | 0.858 | 0.155 | 0.132 | 0.057 | 0.058 | 0.247 | 0.845 |
| 1.2 Initiative | 0.789 | 0.134 | 0.154 | 0.215 | 0.132 | 0.246 | 0.788 |
| 1.3 Positive emotion experience | 0.862 | 0.095 | 0.098 | 0.198 | 0.042 | 0.156 | 0.826 |
| 1.4 Willpower | 0.883 | 0.001 | 0.040 | 0.008 | 0.031 | 0.130 | 0.799 |
| 2.1 Attention | 0.091 | 0.843 | 0.178 | 0.203 | −0.064 | 0.016 | 0.796 |
| 2.2 Identify differences | 0.062 | 0.801 | 0.204 | 0.237 | 0.081 | 0.168 | 0.779 |
| 2.3 In-depth exploration of problems | 0.170 | 0.739 | 0.144 | 0.251 | 0.039 | 0.180 | 0.693 |
| 2.4 Problem representation | 0.058 | 0.799 | 0.081 | 0.240 | 0.253 | 0.099 | 0.780 |
| 3.1 Transfer | −0.033 | 0.287 | 0.179 | 0.826 | 0.195 | 0.125 | 0.851 |
| 3.2 Application | 0.324 | 0.248 | 0.031 | 0.748 | 0.266 | 0.104 | 0.808 |
| 3.3 Material selection | 0.210 | 0.211 | 0.134 | 0.772 | 0.138 | 0.081 | 0.729 |
| 3.4 Hands-on operation | 0.068 | 0.336 | 0.296 | 0.749 | −0.051 | 0.085 | 0.776 |
| 4.1 Speed of analyzing and responding to problems | 0.213 | 0.008 | 0.100 | 0.203 | 0.282 | 0.789 | 0.799 |
| 4.2 Strategies for implementing problem-solving | 0.190 | 0.276 | 0.362 | 0.056 | 0.348 | 0.666 | 0.812 |
| 4.3 Problem-solving methods | 0.219 | 0.227 | 0.054 | 0.025 | −0.001 | 0.826 | 0.785 |
| 4.4 Solve problem | 0.271 | 0.055 | 0.260 | 0.113 | 0.052 | 0.718 | 0.675 |
| 5.1 Awareness of interpersonal interaction | 0.031 | 0.060 | 0.064 | 0.140 | 0.895 | 0.067 | 0.833 |
| 5.2 Ability of interpersonal interaction | 0.103 | 0.056 | 0.384 | 0.142 | 0.794 | 0.118 | 0.825 |
| 5.3 Maintaining Interpersonal interaction | 0.085 | 0.098 | 0.261 | 0.133 | 0.815 | 0.242 | 0.825 |
| 6.1 Account | −0.008 | 0.139 | 0.786 | 0.089 | 0.217 | 0.271 | 0.765 |
| 6.2 Causal relationship | 0.202 | 0.177 | 0.728 | 0.070 | 0.368 | 0.063 | 0.747 |
| 6.3 Reflection | 0.114 | 0.151 | 0.805 | 0.160 | 0.047 | 0.122 | 0.726 |
| 6.4 Creativity | 0.142 | 0.173 | 0.762 | 0.262 | 0.172 | 0.126 | 0.744 |
| Children with ASD | Children with TD | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusive play (n = 10) | 11 (2 + 9) | 10 (1 + 9) | 21 |
| Solitary play (n = 30) | 23 | 7 | 30 |
| Total | 34 | 17 | 51 |
| Dimensions | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional experience | 17.74 | 3.306 | 9 | 20 |
| Problem awareness | 15.12 | 2.422 | 8 | 19 |
| Transfer and application | 16.06 | 3.781 | 7 | 20 |
| Problem solving | 14.06 | 4.104 | 4 | 20 |
| Interpersonal interaction | 9.29 | 3.958 | 3 | 15 |
| Cognitive quality | 12.35 | 4.220 | 4 | 19 |
| Deep learning ability | 84.62 | 17.741 | 44 | 109 |
| Dimensions | Inclusive Play (n = 11) | Solitary Play (n = 23) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | |
| Emotional experience | 17.00 | 3.098 | 11 | 20 | 18.09 | 3.410 | 9 | 20 |
| Problem awareness | 14.36 | 2.248 | 11 | 18 | 15.48 | 2.466 | 8 | 19 |
| Transfer and application | 14.82 | 2.822 | 11 | 20 | 16.65 | 4.086 | 7 | 20 |
| Problem solving | 12.55 | 3.616 | 4 | 18 | 14.78 | 4.199 | 4 | 20 |
| Interpersonal interaction | 8.09 | 2.625 | 5 | 12 | 9.87 | 4.393 | 3 | 15 |
| Cognitive quality | 9.55 | 3.142 | 5 | 15 | 13.70 | 4.050 | 4 | 19 |
| Deep learning ability | 76.36 | 12.355 | 57 | 97 | 88.57 | 18.771 | 44 | 109 |
| Dependent Variable | B | SE | β | t | Sig. | VIF | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep learning ability | −35.774 | 8.869 | −0.581 | −4.033 | 0.000 *** | 1.000 | 0.337 | 0.316 | 16.269 |
| Emotional experience | −5.925 | 1.739 | −0.516 | −3.408 | 0.002 ** | 1.000 | 0.266 | 0.243 | 11.612 |
| Problem awareness | −4.151 | 1.293 | −0.493 | −3.209 | 0.003 ** | 1.000 | 0.243 | 0.220 | 10.299 |
| Transfer and application | −6.645 | 2.003 | −0.506 | −3.318 | 0.002 ** | 1.000 | 0.256 | 0.233 | 11.009 |
| Problem solving | −8.473 | 2.027 | −0.594 | −4.181 | 0.000 *** | 1.000 | 0.353 | 0.333 | 17.480 |
| Interpersonal interaction | −5.075 | 2.259 | −0.369 | −2.247 | 0.032 * | 1.000 | 0.136 | 0.109 | 5.048 |
| Cognitive quality | −5.505 | 2.402 | −0.376 | −2.292 | 0.029 * | 1.000 | 0.141 | 0.114 | 5.255 |
| Emotional Experience | Problem Awareness | Transfer and Application | Problem Solving | Interpersonal Interaction | Cognitive Quality | Deep Learning Ability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mann–Whitney U | 89.000 | 81.500 | 82.000 | 70.500 | 86.000 | 50.500 | 69.000 |
| Wilcoxon W | 155.000 | 147.500 | 148.000 | 136.500 | 152.000 | 116.500 | 135.000 |
| Z | −1.467 | −1.684 | −1.690 | −2.076 | −1.500 | −2.809 | −2.118 |
| Asymp. sig. (2-tailed) | 0.142 | 0.092 | 0.091 | 0.038 * | 0.134 | 0.005 ** | 0.034 * |
| Dimensions | Types of Play | Number of Cases | Rank Means | Ranks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional experience | SP | 23 | 19.13 | 440.00 |
| IP | 11 | 14.09 | 155.00 | |
| Problem awareness | SP | 23 | 19.46 | 447.50 |
| IP | 11 | 13.41 | 147.50 | |
| Transfer and application | SP | 23 | 19.43 | 447.00 |
| IP | 11 | 13.45 | 148.00 | |
| Problem solving | SP | 23 | 19.93 | 458.50 |
| IP | 11 | 12.41 | 136.50 | |
| Interpersonal interaction | SP | 23 | 19.26 | 443.00 |
| IP | 11 | 13.82 | 152.00 | |
| Cognitive quality | SP | 23 | 20.80 | 478.50 |
| IP | 11 | 10.59 | 116.50 | |
| Deep learning ability | SP | 23 | 20.00 | 460.00 |
| IP | 11 | 12.27 | 135.00 |
| Dependent Variable | B | SE | β | t | Sig. | VIF | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive quality | −4.150 | 1.389 | −0.467 | −2.987 | 0.005 ** | 1.000 | 0.218 | 0.194 | 8.924 |
| Dependent Variable | Model | B | SE | β | t | Sig. | VIF | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer and application | CNY 2000–5000 | −4.526 | 3.581 | −0.205 | −1.264 | 0.216 | 1.022 | 0.200 | 0.148 | 3.870 |
| CNY 5000–10,000 | −3.241 | 1.229 | −0.428 | −2.636 | 0.013 * | 1.022 | ||||
| CNY 10,000 and above | 0 |
| Dependent Variable | Model | B | SE | β | t | Sig. | VIF | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep learning ability | Parents | −42.607 | 6.244 | −0.785 | −6.824 | 0.000 *** | 1.134 | 0.661 | 0.615 | 14.157 |
| Grandparents | −21.857 | 8.325 | −0.294 | −2.625 | 0.014 * | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −21.857 | 4.333 | −0.598 | −5.045 | 0.000 *** | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers | −12.357 | 8.325 | −0.166 | −1.484 | 0.149 | 1.076 | ||||
| Emotional experience | Parents | −5.500 | 1.555 | −0.544 | −3.536 | 0.001 ** | 1.134 | 0.395 | 0.311 | 4.729 |
| Grandparents | 0.500 | 2.074 | 0.036 | 0.241 | 0.811 | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −3.250 | 1.079 | −0.477 | −3.011 | 0.005 ** | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers | −1.537 × 10−15 | 2.074 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 1.076 | ||||
| Problem awareness | Parents | −4.071 | 1.242 | −0.550 | −3.279 | 0.003 ** | 1.134 | 0.281 | 0.182 | 2.837 |
| Grandparents | −0.571 | 1.656 | −0.056 | −0.345 | 0.732 | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −1.238 | 0.862 | −0.248 | −1.437 | 0.161 | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers | −0.071 | 1.656 | −0.007 | −0.043 | 0.966 | 1.076 | ||||
| Transfer and application | Parents | −8.893 | 1.180 | −0.769 | −7.536 | 0.000 *** | 1.134 | 0.734 | 0.697 | 19.982 |
| Grandparents | −5.643 | 1.573 | −0.356 | −3.586 | 0.001 ** | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −5.476 | 0.819 | −0.702 | −6.688 | 0.000 *** | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers5 | −4.643 | 1.573 | −0.293 | −2.951 | 0.006 ** | 1.076 | ||||
| Problem solving | Parents | −8.929 | 1.739 | −0.711 | −5.134 | 0.000 *** | 1.134 | 0.509 | 0.441 | 7.521 |
| Grandparents | −4.429 | 2.319 | −0.258 | −1.910 | 0.066 | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −4.012 | 1.207 | −0.474 | −3.325 | 0.002 ** | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers | −2.429 | 2.319 | −0.141 | −1.047 | 0.304 | 1.076 | ||||
| Interpersonal interaction | Parents | −6.679 | 1.956 | −0.552 | −3.415 | 0.002 ** | 1.134 | 0.333 | 0.241 | 3.613 |
| Grandparents | −4.429 | 2.608 | −0.267 | −1.698 | 0.100 | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −3.012 | 1.357 | −0.369 | −2.219 | 0.034 * | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers | −0.429 | 2.608 | −0.026 | −0.164 | 0.871 | 1.076 | ||||
| Cognitive quality | Parents | −8.536 | 1.699 | −0.661 | −5.023 | 0.000 *** | 1.134 | 0.557 | 0.496 | 9.107 |
| Grandparents | −7.286 | 2.266 | −0.412 | −3.216 | 0.003 ** | 1.076 | ||||
| Siblings | −4.869 | 1.179 | −0.560 | −4.129 | 0.000 *** | 1.202 | ||||
| Teachers | −4.786 | 2.266 | −0.271 | −2.112 | 0.043 * | 1.076 | ||||
| Peers | 0 |
| Dependent Variable | Model | B | SE | β | t | Sig. | VIF | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep learning ability | Level 1 | 5.111 | 12.394 | 0.049 | 0.412 | 0.683 | 1.025 | 0.580 | 0.538 | 13.790 |
| Level 2 | 14.111 | 8.992 | 0.190 | 1.569 | 0.127 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 28.111 | 4.391 | 0.782 | 6.402 | 0.000 *** | 1.064 | ||||
| Emotional experience | Level 1 | 3.833 | 3.061 | 0.199 | 1.252 | 0.220 | 1.025 | 0.262 | 0.188 | 3.545 |
| Level 2 | 3.333 | 2.220 | 0.241 | 1.501 | 0.144 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 3.295 | 1.084 | 0.492 | 3.039 | 0.005 ** | 1.064 | ||||
| Problem awareness | Level 1 | −1.278 | 2.346 | −0.090 | −0.545 | 0.590 | 1.025 | 0.192 | 0.111 | 2.376 |
| Level 2 | 1.722 | 1.702 | 0.170 | 1.012 | 0.320 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 2.030 | 0.831 | 0.413 | 2.443 | 0.021 * | 1.064 | ||||
| Transfer and application | Level 1 | 2.611 | 2.276 | 0.118 | 1.147 | 0.260 | 1.025 | 0.688 | 0.657 | 22.057 |
| Level 2 | 1.611 | 1.651 | 0.102 | 0.976 | 0.337 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 6.534 | 0.806 | 0.852 | 8.104 | 0.000 *** | 1.064 | ||||
| Problem solving | Level 1 | 3.222 | 3.472 | 0.135 | 0.928 | 0.361 | 1.025 | 0.384 | 0.322 | 6.229 |
| Level 2 | 2.722 | 2.519 | 0.158 | 1.081 | 0.288 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 5.299 | 1.230 | 0.637 | 4.309 | 0.000 *** | 1.064 | ||||
| Interpersonal interaction | Level 1 | −4.444 | 3.299 | −0.193 | −1.347 | 0.188 | 1.025 | 0.402 | 0.342 | 6.713 |
| Level 2 | 3.556 | 2.394 | 0.215 | 1.485 | 0.148 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 4.632 | 1.169 | 0.577 | 3.963 | 0.000 *** | 1.064 | ||||
| Cognitive quality | Level 1 | 1.167 | 3.140 | 0.047 | 0.372 | 0.713 | 1.025 | 0.523 | 0.476 | 10.977 |
| Level 2 | 1.167 | 2.278 | 0.066 | 0.512 | 0.612 | 1.046 | ||||
| Level 5 | 6.321 | 1.112 | 0.739 | 5.682 | 0.000 *** | 1.064 | ||||
| Level 3 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Su, X. Do Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Have Deep Learning Ability? An Exploratory Research in Inclusive Play. J. Intell. 2025, 13, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13110135
Zhu Y, Su X. Do Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Have Deep Learning Ability? An Exploratory Research in Inclusive Play. Journal of Intelligence. 2025; 13(11):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13110135
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yanrong, and Xueyun Su. 2025. "Do Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Have Deep Learning Ability? An Exploratory Research in Inclusive Play" Journal of Intelligence 13, no. 11: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13110135
APA StyleZhu, Y., & Su, X. (2025). Do Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Have Deep Learning Ability? An Exploratory Research in Inclusive Play. Journal of Intelligence, 13(11), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13110135






