The Reassuring Absence of Acute Stress Effects on IQ Test Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stress Induction and Assessment
2.3. Assessment of Test Anxiety
2.4. Assessment of Fluid Intelligence
2.5. Experimental Procedure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Increase in Physiological and Subjective Stress Markers After Stress Induction
3.2. Stress and Test Anxiety Do Not Affect IQ-Test Performance
3.3. Exploratory Analysis: IQ Subscales
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ackerman, Phillip L., and Eric D. Heggestad. 1997. Intelligence, Personality, and Interests: Evidence for Overlapping Traits. Psychological Bulletin 121: 219–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, Phillip L., Margaret E. Beier, and Mary O. Boyle. 2005. Working Memory and Intelligence: The Same or Different Constructs? Psychological Bulletin 131: 30–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, Osman, Anne Bierbrauer, Nikolai Axmacher, and Oliver T. Wolf. 2023. Acute Stress Impairs Visual Path Integration. Neurobiology of Stress 26: 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, Alfredo. 2000. Correlation Between Intelligence Test Scores and Executive Function Measures. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 15: 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, Winfred, and David V. Day. 1994. Development of a Short Form for the Raven Advanced Progressive Matrices Test. Educational and Psychological Measurement 54: 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcraft, Marc H., and Elizabeth P. Kirk. 2001. The Relationships Among Working Memory, Math Anxiety, and Performance. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 130: 224–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsegyan, Areg, Scott M. Mackenzie, Brian D. Kurose, James L. McGaugh, and Benno Roozendaal. 2010. Glucocorticoids in the Prefrontal Cortex Enhance Memory Consolidation and Impair Working Memory by a Common Neural Mechanism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 16655–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, Douglas, Martin Mächler, Ben Bolker, and Steve Walker. 2015. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. Journal of Statistical Software 67: 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedek, Mathias, Emanuel Jauk, Markus Sommer, Martin Arendasy, and Aljoscha C. Neubauer. 2014. Intelligence, Creativity, and Cognitive Control: The Common and Differential Involvement of Executive Functions in Intelligence and Creativity. Intelligence 46: 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, Christopher R., Corinne L. Reid, Allison M. Fox, and Mike Anderson. 2012. A Unitary Executive Function Predicts Intelligence in Children. Intelligence 40: 458–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürkner, Paul-Christian. 2017. Brms: An R Package for Bayesian Multilevel Models Using Stan. Journal of Statistical Software 80: 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürkner, Paul-Christian. 2018. Advanced Bayesian Multilevel Modeling with the R Package Brms. The R Journal 10: 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürkner, Paul-Christian. 2021. Bayesian Item Response Modeling in R with Brms and Stan. Journal of Statistical Software 100: 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, Kaileigh A., Caitlin Peters, Hunter C. Willis, Dana Phan, Astin Cornwall, and Darrell A. Worthy. 2020. Acute Stress Enhances Tolerance of Uncertainty During Decision-Making. Cognition 205: 104448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassady, Jerrell C., and Ronald E. Johnson. 2002. Cognitive Test Anxiety and Academic Performance. Contemporary Educational Psychology 27: 270–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catron, David W., and Claudia C. Thompson. 1979. Test-Retest Gains in WAIS Scores After Four Retest Intervals. Journal of Clinical Psychology 35: 352–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattell, Raymond B. 1941. An Objective Test of Character-Temperament: I. The Journal of General Psychology 25: 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattell, Raymond B. 1943. The Measurement of Adult Intelligence. Psychological Bulletin 40: 153–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapell, Mark S., Z. Benjamin Blanding, Michael E. Silverstein, Masami Takahashi, Brian Newman, Aaron Gubi, and Nicole McCann. 2005. Test Anxiety and Academic Performance in Undergraduate and Graduate Students. Journal of Educational Psychology 97: 268–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, Cameron M., Linette Lawlor-Savage, and Vina M. Goghari. 2017. Comparing Brain Activations Associated with Working Memory and Fluid Intelligence. Intelligence 63: 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clow, Angela, Lisa Thorn, Phil Evans, and Frank Hucklebridge. 2004. The Awakening Cortisol Response: Methodological Issues and Significance. Stress 7: 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, Brian K., Dominque Delalot, and Tonia L. Werner. 2015. Hall V. Florida: Capital Punishment, IQ, and Persons with Intellectual Disabilities. The Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law 43: 230–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cristofori, Irene, Shira Cohen-Zimerman, and Jordan Grafman. 2019. Executive Functions. Handbook of Clinical Neurology 163: 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deary, Ian J. 2014. The Stability of Intelligence from Childhood to Old Age. Current Directions in Psychological Science 23: 239–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakshan, Nazanin, and Michael W. Eysenck. 2009. Anxiety, Processing Efficiency, and Cognitive Performance: New Developments from Attentional Control Theory. European Psychologist 14: 168–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, Adele. 2013. Executive Functions. Annual Review of Psychology 64: 135–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Xiaoju, Siwang Wei, Guiqing Wang, and Jiannong Shi. 2010. The Relationship Between Executive Functions and Intelligence on 11- to 12-Year-Old Children. Psychological Test and Assessment Modeling 52: 419–31. [Google Scholar]
- Enders, Craig K., and Davood Tofighi. 2007. Centering Predictor Variables in Cross-Sectional Multilevel Models: A New Look at an Old Issue. Psychol Methods 12: 121–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, Laura E., Frank D. Mann, Daniel A. Briley, Jessica A. Church, K. Paige Harden, and Elliot M. Tucker-Drob. 2016. Strong Genetic Overlap Between Executive Functions and Intelligence. Journal of Experimental Psychology General 145: 1141–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, Michael W., and Nazanin Derakshan. 2011. New Perspectives in Attentional Control Theory. Personality and Individual Differences 50: 955–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, Michael W., Nazanin Derakshan, Rita Santos, and Manuel G. Calvo. 2007. Anxiety and Cognitive Performance: Attentional Control Theory. Emotion 7: 336–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, Michael W., Susanna Payne, and Nazanin Derakshan. 2005. Trait Anxiety, Visuospatial Processing, and Working Memory. Cognition & Emotion 19: 1214–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, Rosa Angela, Giulia Picciotto, and Tindara Caprì. 2022. The Effects of Psychosocial and Cognitive Stress on Executive Functions and Automatic Processes in Healthy Subjects: A Pilot Study. Current Psychology 41: 7555–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, Franz, Edgar Erdfelder, Axel Buchner, and Albert-Georg Lang. 2009. Statistical Power Analyses Using G*Power 3.1: Tests for Correlation and Regression Analyses. Behavior Research Methods 41: 1149–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, Naomi P., Akira Miyake, Robin P. Corley, Susan E. Young, John C. DeFries, and John K. Hewitt. 2006. Not All Executive Functions Are Related to Intelligence. Psychological Science 17: 172–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geißler, Christoph F., Maximilian A. Friehs, Christian Frings, and Gregor Domes. 2023. Time-Dependent Effects of Acute Stress on Working Memory Performance: A Systematic Review and Hypothesis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 148: 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ger, Ebru, and Claudia M. Roebers. 2023. The Relationship Between Executive Functions, Working Memory, and Intelligence in Kindergarten Children. Journal of Intelligence 11: 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, Grace E., Caroline R. Mahoney, Tad T. Brunyé, Holly A. Taylor, and Robin B. Kanarek. 2014. Stress Effects on Mood, HPA Axis, and Autonomic Response: Comparison of Three Psychosocial Stress Paradigms. PLOS ONE 9: e113618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, Elizabeth V., Dongju Seo, and Rajita Sinha. 2019. Sex Differences in Neural Stress Responses and Correlation with Subjective Stress and Stress Regulation. Neurobiology of Stress 11: 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, David S., and Bruce S. McEwen. 2002. Allostasis, Homeostats, and the Nature of Stress. Stress 5: 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, Steven G., Ronald A. Kleinknecht, and Anthony E. Gallo. 1970. Neuropsychological Changes Associated with Carotid Endarterectomy. Cortex 6: 308–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavson, Daniel E., Chandra A. Reynolds, Robin P. Corley, Sally J. Wadsworth, John K. Hewitt, and Naomi P. Friedman. 2022. Genetic Associations Between Executive Functions and Intelligence: A Combined Twin and Adoption Study. Journal of Experimental Psychology General 151: 1745–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodapp, Volker. 1991. Das Prüfungsängstlichkeitsinventar TAI-G: Eine Erweiterte Und Modifizierte Version Mit Vier Komponenten. [The Test Anxiety Inventory TAI-G: An Expanded and Modified Version with Four Components.]. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie 5: 121–30. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, John L., and Raymond B. Cattell. 1967. Age Differences in Fluid and Crystallized Intelligence. Acta Psychologica 26: 107–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, Arthur R., and Li-Jen Weng. 1994. What Is a Good G? Intelligence 18: 231–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentsch, Valerie L., Lisa Pötzl, Oliver T. Wolf, and Christian J. Merz. 2022. Hormonal Contraceptive Usage Influences Stress Hormone Effects on Cognition and Emotion. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 67: 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joëls, Marian, and Tallie Z. Baram. 2009. The Neuro-Symphony of Stress. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 10: 459–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joëls, Marian, Henk Karst, and R. Angela Sarabdjitsingh. 2018. The Stressed Brain of Humans and Rodents. Acta Physiologica 223: e13066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Alan S. 2021. The Precipitous Decline in Reasoning and Other Key Abilities with Age and Its Implications for Federal Judges. Journal of Intelligence 9: 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, Clemens, Brigitte M. Kudielka, Jens Gaab, Nicole C. Schommer, and Dirk H. Hellhammer. 1999. Impact of Gender, Menstrual Cycle Phase, and Oral Contraceptives on the Activity of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Psychosomatic Medicine 61: 154–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, Clemens, Karl-Martin Pirke, and Dirk H. Hellhammer. 1993. The ‘Trier Social Stress Test’—a Tool for Investigating Psychobiological Stress Responses in Laboratory Setting. Neuropsychobiology 28: 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, Alexandra, Per B. Brockhoff, and Rune H. B. Christensen. 2017. LmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. Journal of Statistical Software 82: 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, Katja, Valerie L. Jentsch, and Oliver T. Wolf. 2023. Rapid Effects of Acute Stress on Cognitive Emotion Regulation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 151: 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, Lars, Peter Hartmann, and Helmuth Nyborg. 2008. The Stability of General Intelligence from Early Adulthood to Middle-Age. Intelligence 36: 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassiter, Kerry S., and T. Darin Matthews. 1999. Test-Retest Reliability of the General Ability Measure for Adults. Perceptual and Motor Skills 88: 531–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, Russel V. 2022. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least Square Means. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Lichtenberger, Elizabeth O., and Alan S. Kaufman. 2009. Essentials of WAIS-IV Assessment. Essentials of psychological assessment series; Hoboken: Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Liepmann, Detlev, André Beauducel, Burkhard Brocke, and Rudolf Amthauer, eds. 2007. Intelligenz-Struktur-Test 2000 R: 2., Erweiterte Und Überarbeitete Auflage. Göttingen: Hogrefe Verlag GmbH & Co. KG. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Yisi, Yan Wu, and Qiwei Yang. 2024. The Impact of Stress on the Risk Decision-Making Process. Psychophysiology 61: e14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarazzo, Joseph D. 1990. Psychological Assessment Versus Psychological Testing. Validation from Binet to the School, Clinic, and Courtroom. The American Psychologist 45: 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarazzo, Ruth G., Joseph D. Matarazzo, Anthony E. Gallo, and Arthur N. Wiens. 1979. IQ and Neuropsychological Changes Following Carotid Endarterectomy. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology 1: 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiran, Nachshon, and Nitzan Shahar. 2018. Working Memory Involvement in Reaction Time and Its Contribution to Fluid Intelligence: An Examination of Individual Differences in Reaction-Time Distributions. Intelligence 69: 176–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melby-Lervåg, Monica, and Charles Hulme. 2013. Is Working Memory Training Effective? A Meta-Analytic Review. Developmental Psychology 49: 270–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, Christian J., and Oliver T. Wolf. 2017. Sex Differences in Stress Effects on Emotional Learning. Journal of Neuroscience Research 95: 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Akira, Naomi P. Friedman, Michael J. Emerson, Alexander H. Witzki, Amy Howerter, and Tor D. Wager. 2000. The Unity and Diversity of Executive Functions and Their Contributions to Complex “Frontal Lobe” Tasks: A Latent Variable Analysis. Cognitive Psychology 41: 49–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, Tim P. 2016. Anxiety and Working Memory Capacity: A Meta-Analysis and Narrative Review. Psychological Bulletin 142: 831–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutafi, Joanna, Adrian Furnham, and Ioannis Tsaousis. 2006. Is the Relationship Between Intelligence and Trait Neuroticism Mediated by Test Anxiety? Personality and Individual Differences 40: 587–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowbray, Tony. 2012. Working Memory, Test Anxiety and Effective Interventions: A Review. The Australian Educational and Developmental Psychologist 29: 141–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Youyan, Shun Lau, and Albert K. Liau. 2011. Role of Academic Self-Efficacy in Moderating the Relation Between Task Importance and Test Anxiety. Learning and Individual Differences 21: 736–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolašević, Željka, Snežana Smederevac, Vojislava Bugarski Ignjatović, Jasmina Kodžopeljić, Ilija Milovanović, Mechthild Prinz, and Zoran Budimlija. 2020. Executive Functions and Intelligence- Are There Genetic Difference? Intelligence 82: 101480. Available online: https://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/intell/v82y2020ics0160289620300581.html (accessed on 10 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Peña, María Isabel, Macarena Suárez-Pellicioni, and Roser Bono. 2016. Gender Differences in Test Anxiety and Their Impact on Higher Education Students’ Academic Achievement. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences 228: 154–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, Matthew, Jim Stevenson, Julie A. Hadwin, and Roger Norgate. 2014. When Does Anxiety Help or Hinder Cognitive Test Performance? The Role of Working Memory Capacity. British Journal of Psychology 105: 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, Jerry C., Beth W. Granberg, W. Kirt Nichols, John G. Jones, and John E. Hewett. 1983. Mental Status Outcomes Following Carotid Endarterectomy: A Six-Month Analysis. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology 5: 345–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Pardo, José Angel, Kenia Martínez, Francisco J. Román, and Roberto Colom. 2016. Structural Efficiency Within a Parieto-Frontal Network and Cognitive Differences. Intelligence 54: 105–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötzl, Lisa, Oliver T. Wolf, and Christian J. Merz. 2023. Rapid and Delayed Stress Effects on Recognition of Female and Male Faces. Psychoneuroendocrinology 150: 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, Rizwan, and Nasir Mahmood. 2010. The Relationship Between Test Anxiety and Academic Achievement. Bulletin of Education and Research 32: 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, John C. 1938. Progressive Matrices: A Perceptual Test of Intelligence. London: H. K. Lewis. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, John C., John H. Court, and John Raven. 1985. A Manual for Raven’s Progressive Matrices and Vocabulary Scales. London: H. K. Lewis. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. 2021. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Redick, Thomas S., Zach Shipstead, Elizabeth A. Wiemers, Monica Melby-Lervåg, and Charles Hulme. 2015. What’s Working in Working Memory Training? An Educational Perspective. Educational Psychology Review 27: 617–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, Joachim M., and E. Ronald de Kloet. 1985. Two Receptor Systems for Corticosterone in Rat Brain: Microdistribution and Differential Occupation. Endocrinology 117: 2505–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, Stefania, Luciano Mecacci, and Maria Pia Viggiano. 2009. Anxiety, Cognitive Self-Evaluation and Performance: ERP Correlates. Journal of Anxiety Disorders 23: 1132–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, María, Alice Parr, Russell Thompson, Alexandra Woolgar, Teresa Torralva, Nagui Antoun, Facundo Manes, and John Duncan. 2010. Executive Function and Fluid Intelligence After Frontal Lobe Lesions. Brain 133: 234–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, Georgina, and Stafford Lightman. 2019. The Human Stress Response. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 15: 525–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, Timothy A. 2014. Relations Between Running Memory and Fluid Intelligence. Intelligence 43: 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandi, Carmen. 2013. Stress and Cognition. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Cognitive Science 4: 245–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savostyanov, Alexander N., Arthur C. Tsai, Michelle Liou, Evgeny A. Levin, Juin-Der Lee, Alexey V. Yurganov, and Gennady G. Knyazev. 2009. EEG-Correlates of Trait Anxiety in the Stop-Signal Paradigm. Neuroscience letters 449: 112–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, Frieder L., Stephan E. Vogel, Jennifer Diedrich, and Roland H. Grabner. 2018. Math Anxiety, Intelligence, and Performance in Mathematics: Insights from the German Adaptation of the Abbreviated Math Anxiety Scale (AMAS-G). Learning and Individual Differences 61: 109–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, Frank L., and John Hunter. 2004. General Mental Ability in the World of Work: Occupational Attainment and Job Performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 86: 162–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, Lars, Leila Haddad, and Hartmut Schächinger. 2008. HPA Axis Activation by a Socially Evaluated Cold-Pressor Test. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33: 890–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, Grant S., Matthew A. Sazma, and Andrew P. Yonelinas. 2016. The Effects of Acute Stress on Core Executive Functions: A Meta-Analysis and Comparison with Cortisol. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 68: 651–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, Grant S., Matthew A. Sazma, Andrew M. McCullough, and Andrew P. Yonelinas. 2017. The Effects of Acute Stress on Episodic Memory: A Meta-Analysis and Integrative Review. Psychological Bulletin 143: 636–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipstead, Zach, Thomas S. Redick, and Randall W. Engle. 2012. Is Working Memory Training Effective? Psychological Bulletin 138: 628–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolker, Harry R., Brent E. Depue, Andrew E. Reineberg, Joshua M. Orr, and Michael T. Banich. 2015. Individual Differences in Regional Prefrontal Gray Matter Morphometry and Fractional Anisotropy Are Associated with Different Constructs of Executive Function. Brain Structure and Function 220: 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Talarico, Juliana Nery de, Paulo Caramelli, Ricardo Nitrini, and Eliane Corrêa Chaves. 2007. The Influence of Schooling on Working Memory Performance in Elderly Individuals Without Cognitive Decline. Dementia & Neuropsychologia 1: 276–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. 1904. ‘General Intelligence,’ Objectively Determined and Measured. The American Journal of Psychology 15: 201–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starcke, Katrin, and Matthias Brand. 2016. Effects of Stress on Decisions Under Uncertainty: A Meta-Analysis. Psychological Bulletin 142: 909–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, Robert J. 1985. Human Intelligence: The Model Is the Message. Washington, DC: American Association for the Advancement of Science, December 6, Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.230.4730.1111 (accessed on 22 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, Robert J. 2018. Theories of Intelligence. In APA Handbook of Giftedness and Talent. APA Handbooks in Psychology®. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, pp. 145–61. [Google Scholar]
- Strenze, Tarmo. 2007. Intelligence and Socioeconomic Success: A Meta-Analytic Review of Longitudinal Research. Intelligence 35: 401–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourva, Anna, and George Spanoudis. 2020. Speed of Processing, Control of Processing, Working Memory and Crystallized and Fluid Intelligence: Evidence for a Developmental Cascade. Intelligence 83: 101503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aken, Loes, Roy P. C. Kessels, Ellen Wingbermühle, William M. van der Veld, and Jos I. M. Egger. 2016. Fluid Intelligence and Executive Functioning More Alike Than Different? Acta Neuropsychiatrica 28: 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maas, Han, Kees-Jan Kan, and Denny Borsboom. 2014. Intelligence Is What the Intelligence Test Measures. Seriously. Journal of Intelligence 2: 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, Elke, Reinhard Beyer, Judith Horn, Manja Foth, Boris Bornemann, Jan Ries, Juerg Kramer, Elke Warmuth, Hauke R. Heekeren, and Isabell Wartenburger. 2010. Resource Allocation and Fluid Intelligence: Insights from Pupillometry. Psychophysiology 47: 158–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, Alois, Jelena Jaunzeme, and Steffen Jaksztat. 2008. Eine Kurzform Des Prüfungsängstlichkeitsinventars TAI-G. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie 22: 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, David. 2008. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale–Fourth Edition: Technical and Interpretive Manual. San Antonio: Pearson Assessment. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm, Oliver, and Klaus Oberauer. 2006. Why Are Reasoning Ability and Working Memory Capacity Related to Mental Speed? An Investigation of Stimulus-Response Compatibility in Choice Reaction Time Tasks. European Journal of Cognitive Psychology 18: 18–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Oliver T., Piray Atsak, Dominique J. F. de Quervain, Benno Roozendaal, and Katja Wingenfeld. 2016. Stress and Memory: A Selective Review on Recent Developments in the Understanding of Stress Hormone Effects on Memory and Their Clinical Relevance. Journal of Neuroendocrinology 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisman, Chen, and Yoav Ganzach. 2022. The Claim That Personality Is More Important Than Intelligence in Predicting Important Life Outcomes Has Been Greatly Exaggerated. Intelligence 92: 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlomuzica, Armin, Miriam Lange, Sarah Reher, Alla Machulska, and Mike Rinck. 2022. The Effects of Psychological Stress on Approach Tendencies for Smoking-Related Cues in Smokers. European Journal of Neuroscience 55: 2581–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 collection of saliva sample;
collection of saliva sample;  assessment of blood pressure, middle arterial pressure, and heart rate.
assessment of blood pressure, middle arterial pressure, and heart rate.
 collection of saliva sample;
collection of saliva sample;  assessment of blood pressure, middle arterial pressure, and heart rate.
assessment of blood pressure, middle arterial pressure, and heart rate.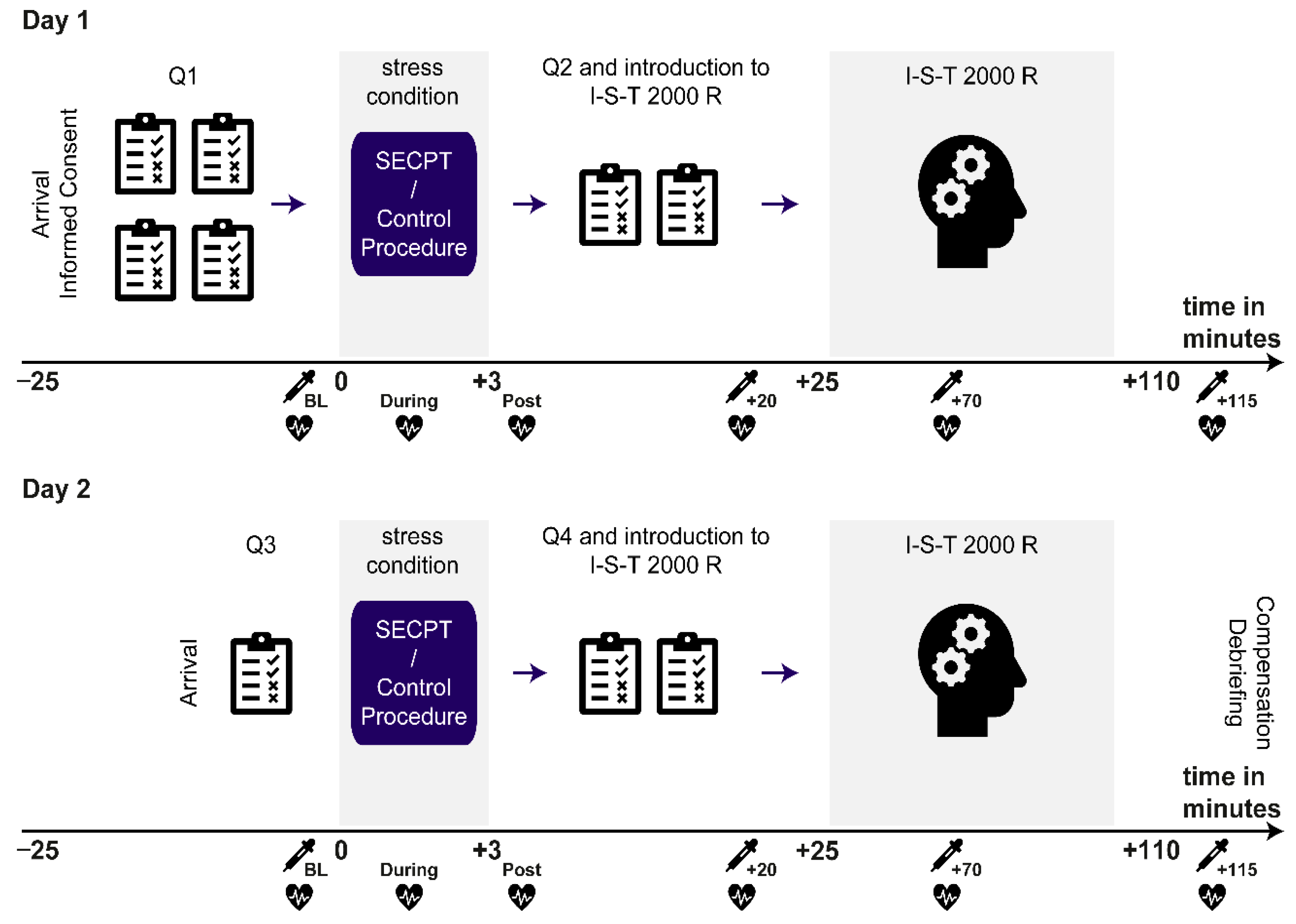



| dz | f | Power (1 − β) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.063 | 0.235 |
| 0.3 | 0.095 | 0.457 |
| 0.4 | 0.123 | 0.694 |
| 0.5 | 0.158 | 0.869 |
| 0.6 | 0.190 | 0.959 |
| 0.7 | 0.221 | 0.991 |
| 0.8 | 0.253 | 0.999 |
| Control Condition | Stress Condition | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| difficulty | 1.25 ± 4.04 | 65.00 ± 25.12 | <.001 |
| unpleasantness | 3.00 ± 13.44 | 49.75 ± 31.74 | <.001 |
| stressfulness | 1.50 ± 4.27 | 44.75 ± 29.53 | <.001 |
| painfulness | 0.75 ± 3.50 | 71.75 ± 23.95 | <.001 |
| Control Condition | Stress Condition | Cohen’s d | |
|---|---|---|---|
| total IQ | 113.20 ± 14.02 | 114.48 ± 14.66 | 0.09 |
| numerical IQ | 113.91 ± 15.13 | 115.04 ± 16.56 | 0.07 |
| verbal IQ | 109.56 ± 11.87 | 110.76 ± 11.27 | 0.10 |
| figural IQ | 106.26 ± 16.16 | 106.64 ± 14.53 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akan, O.; Yildirim, M.; Wolf, O.T. The Reassuring Absence of Acute Stress Effects on IQ Test Performance. J. Intell. 2025, 13, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13100131
Akan O, Yildirim M, Wolf OT. The Reassuring Absence of Acute Stress Effects on IQ Test Performance. Journal of Intelligence. 2025; 13(10):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13100131
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkan, Osman, Mustafa Yildirim, and Oliver T. Wolf. 2025. "The Reassuring Absence of Acute Stress Effects on IQ Test Performance" Journal of Intelligence 13, no. 10: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13100131
APA StyleAkan, O., Yildirim, M., & Wolf, O. T. (2025). The Reassuring Absence of Acute Stress Effects on IQ Test Performance. Journal of Intelligence, 13(10), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13100131





