Targeted Drug Delivery of Magnetic Nano-Particle in the Specific Lung Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methods
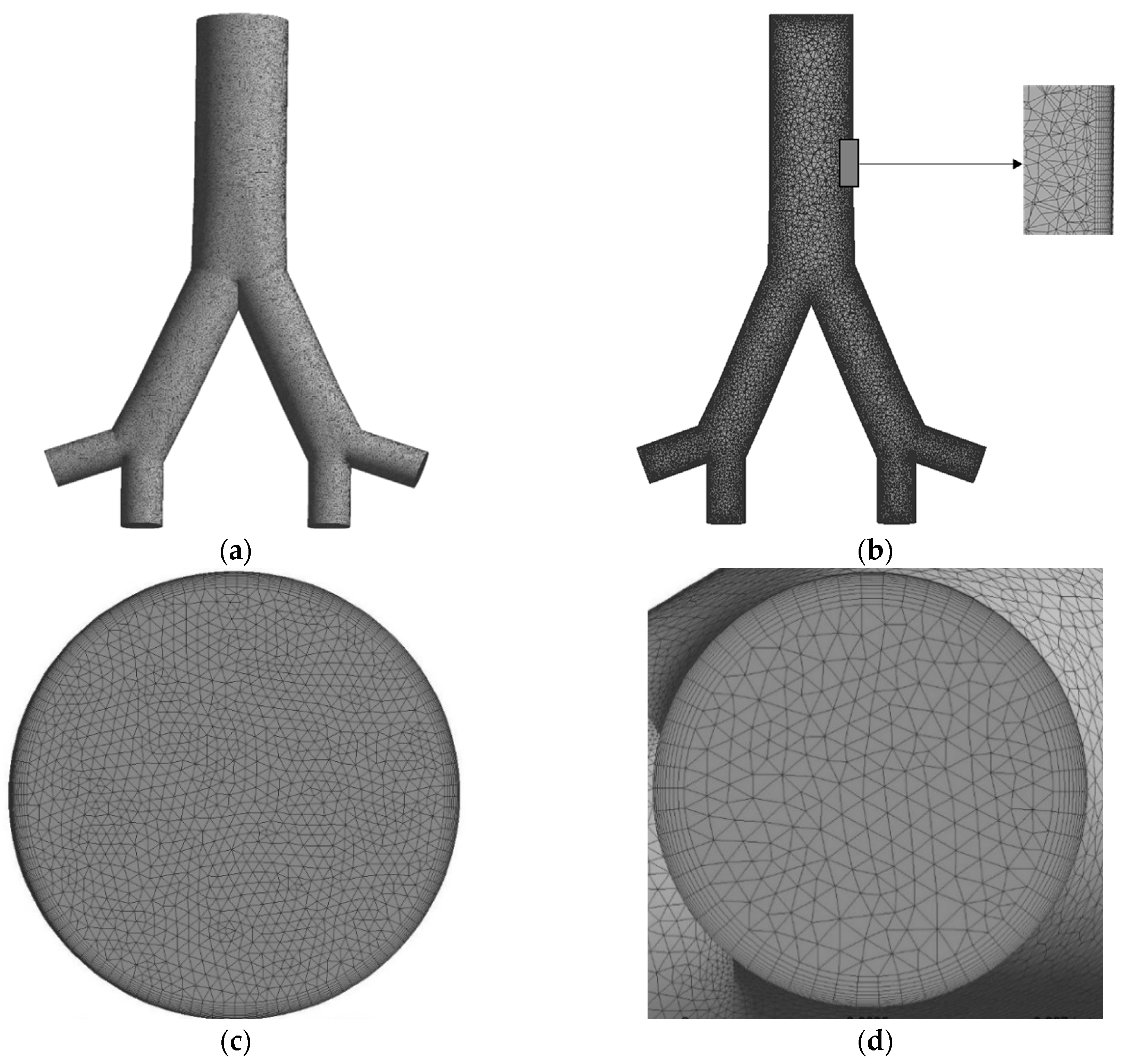
3. Computational Domain and Mesh Generation
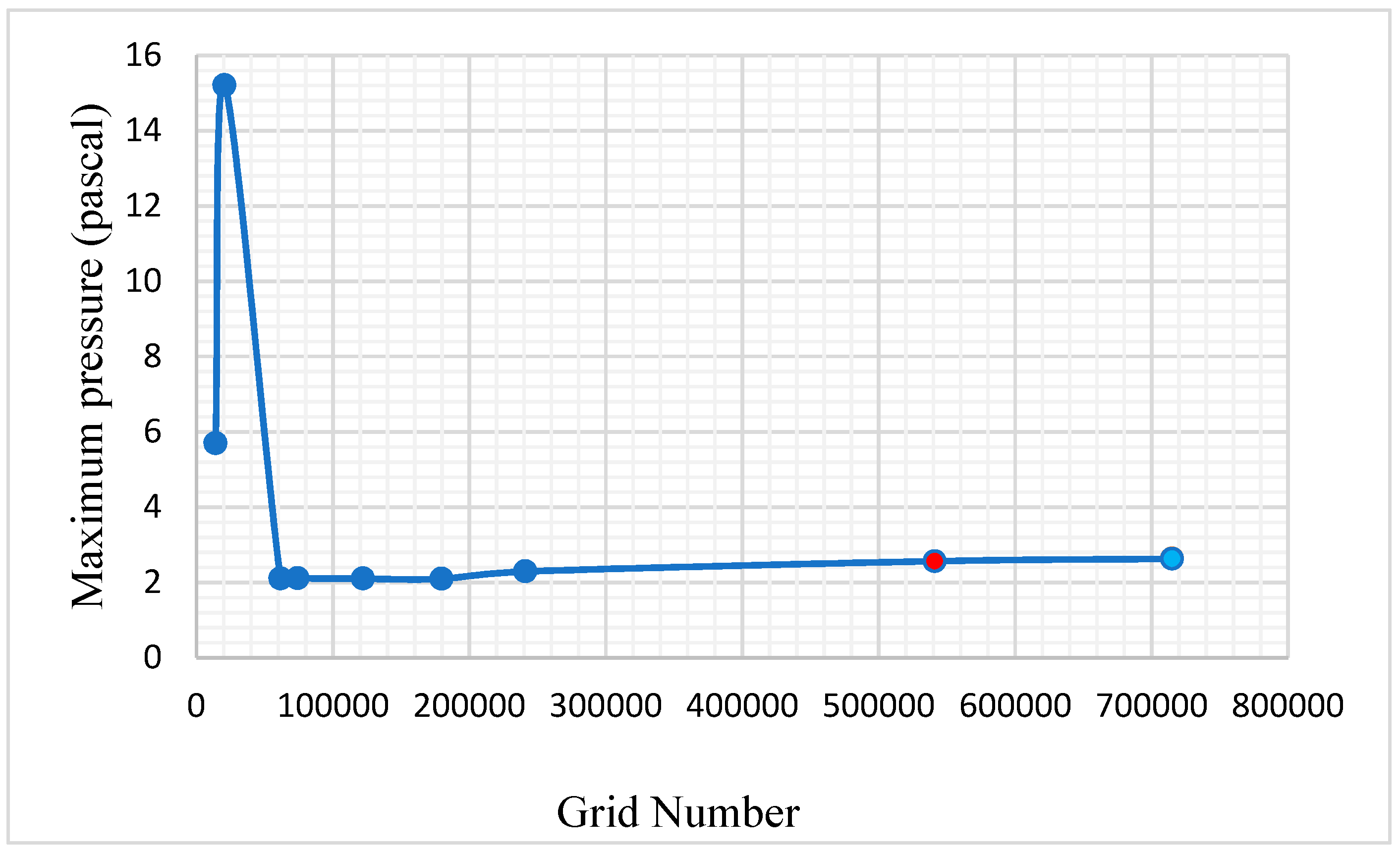
4. Grid Independence Test
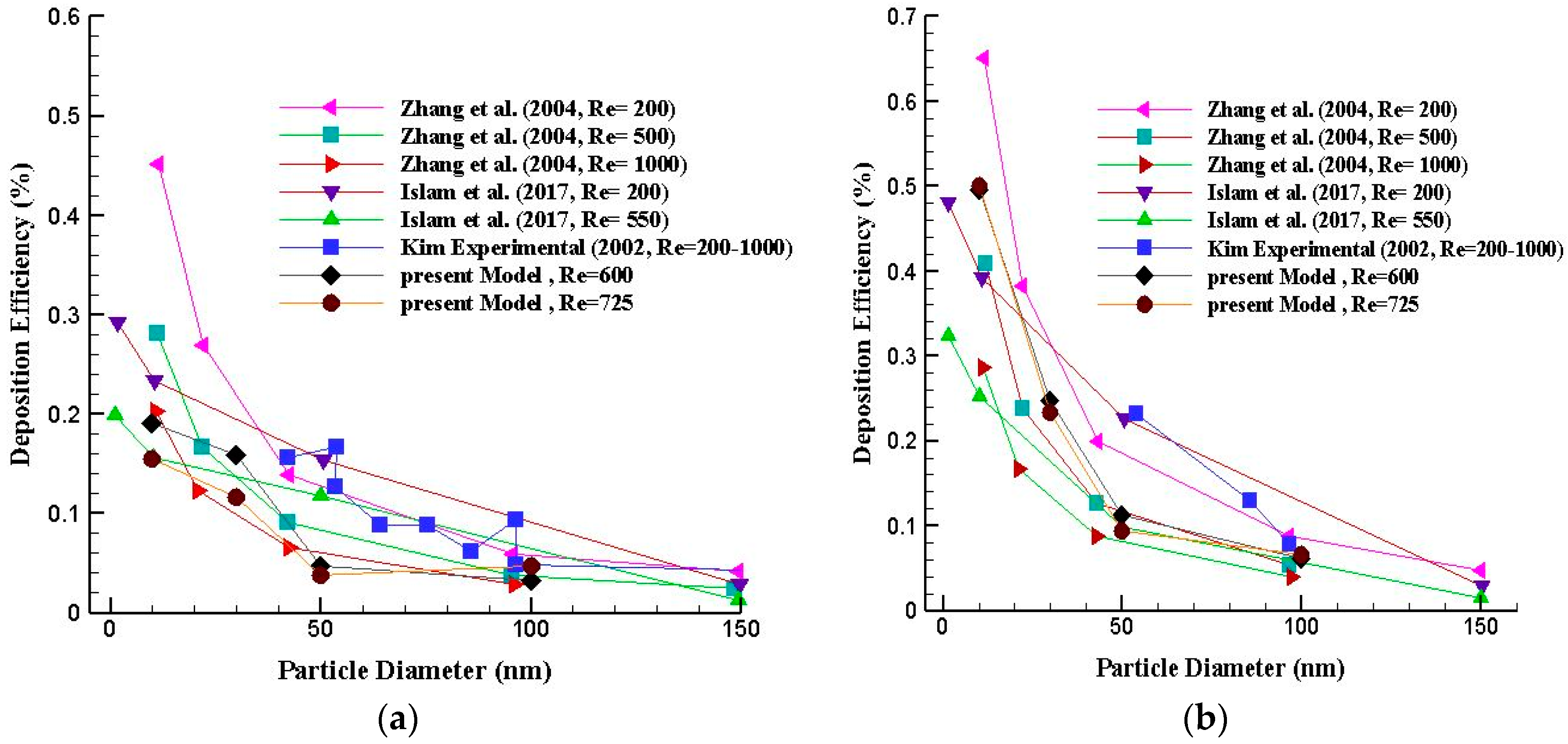
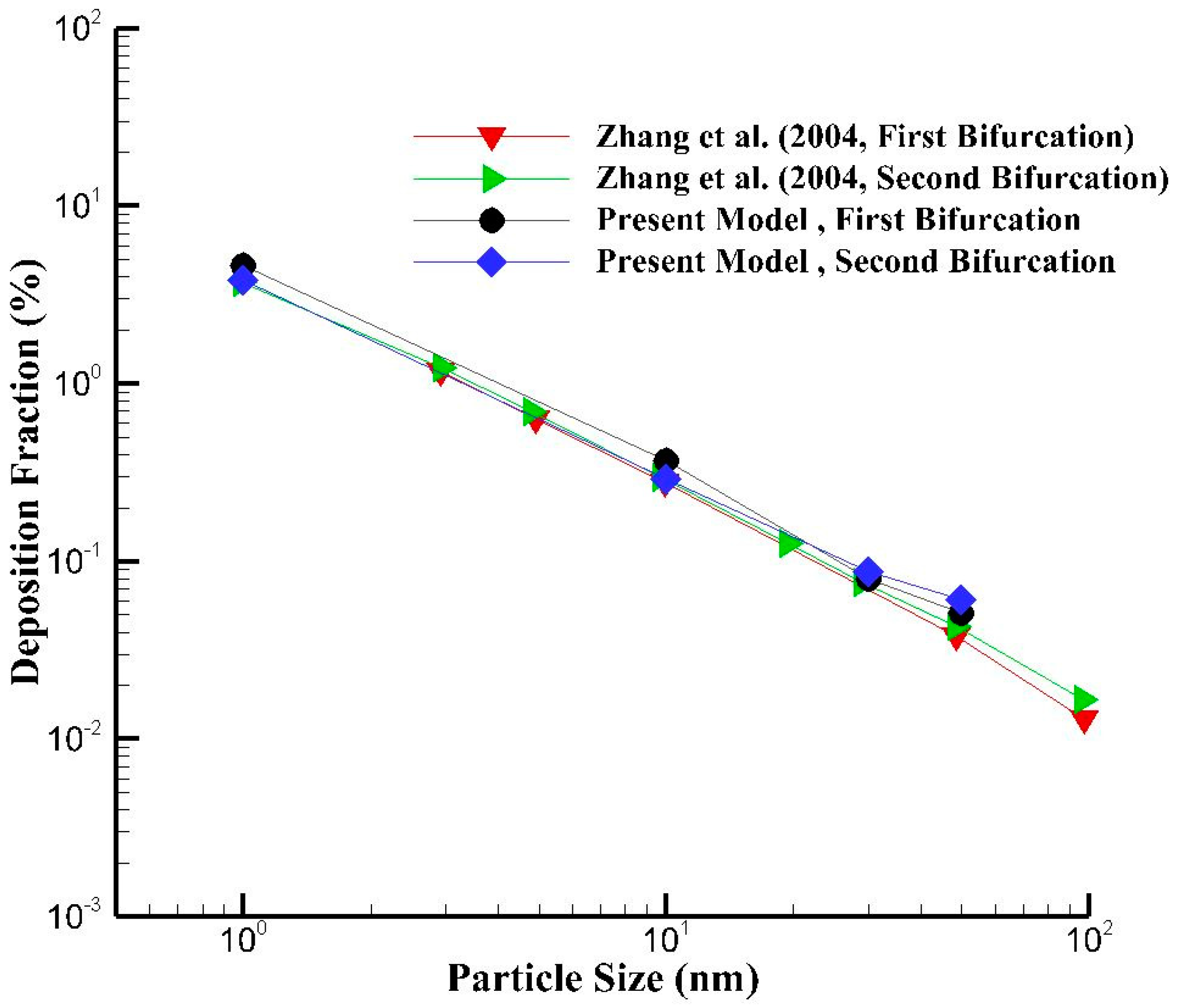
5. Model Validation
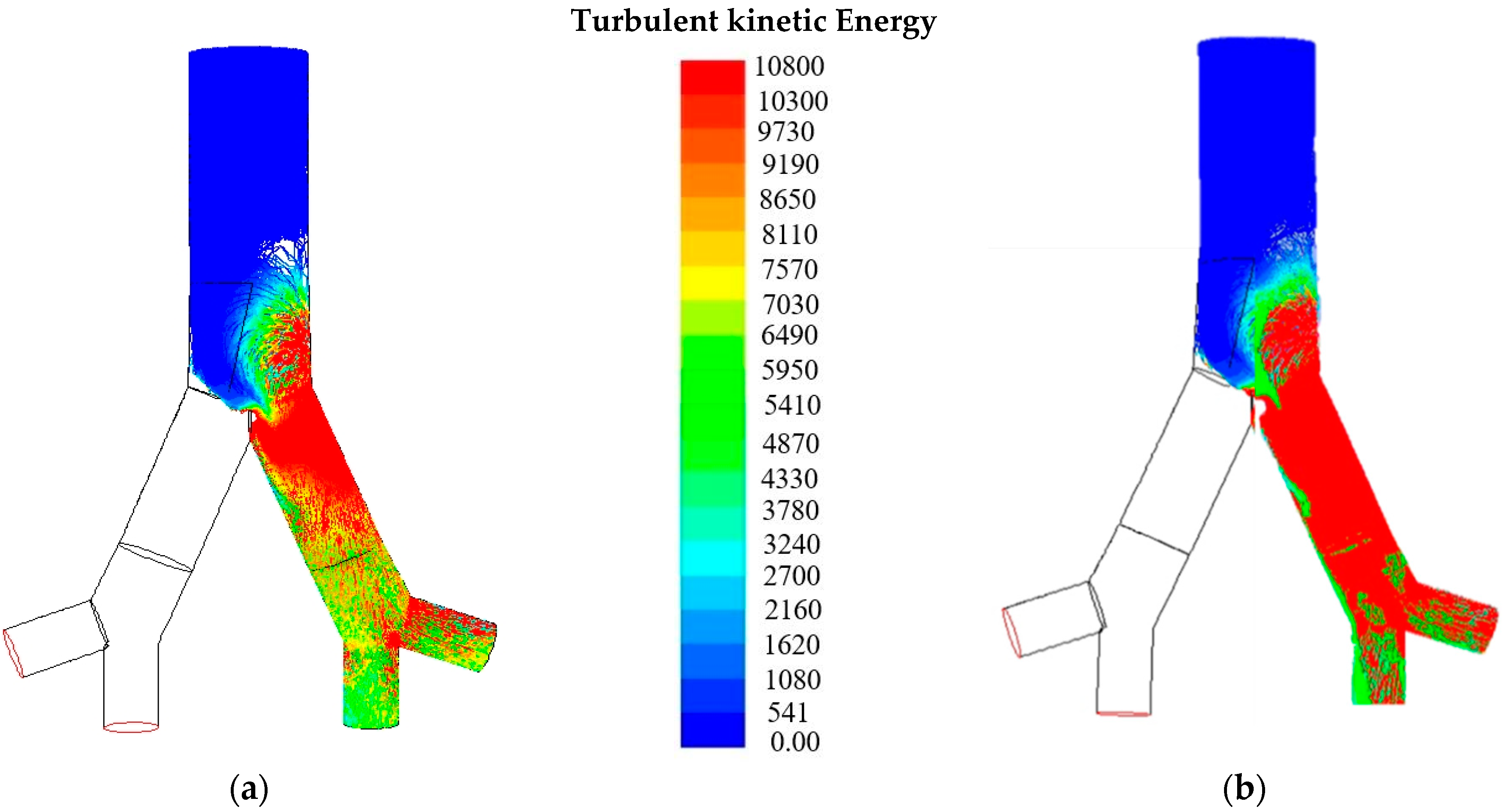
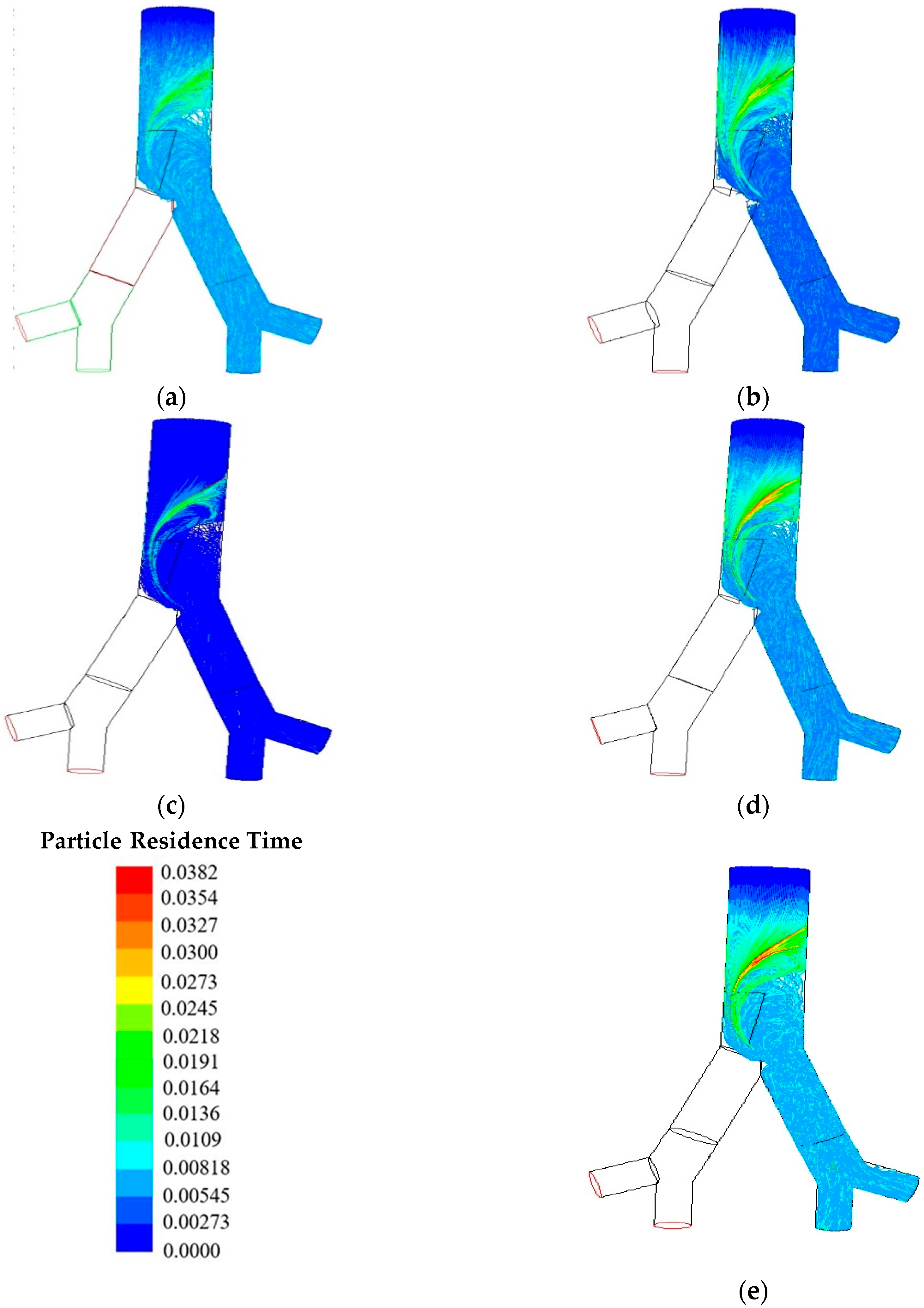
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
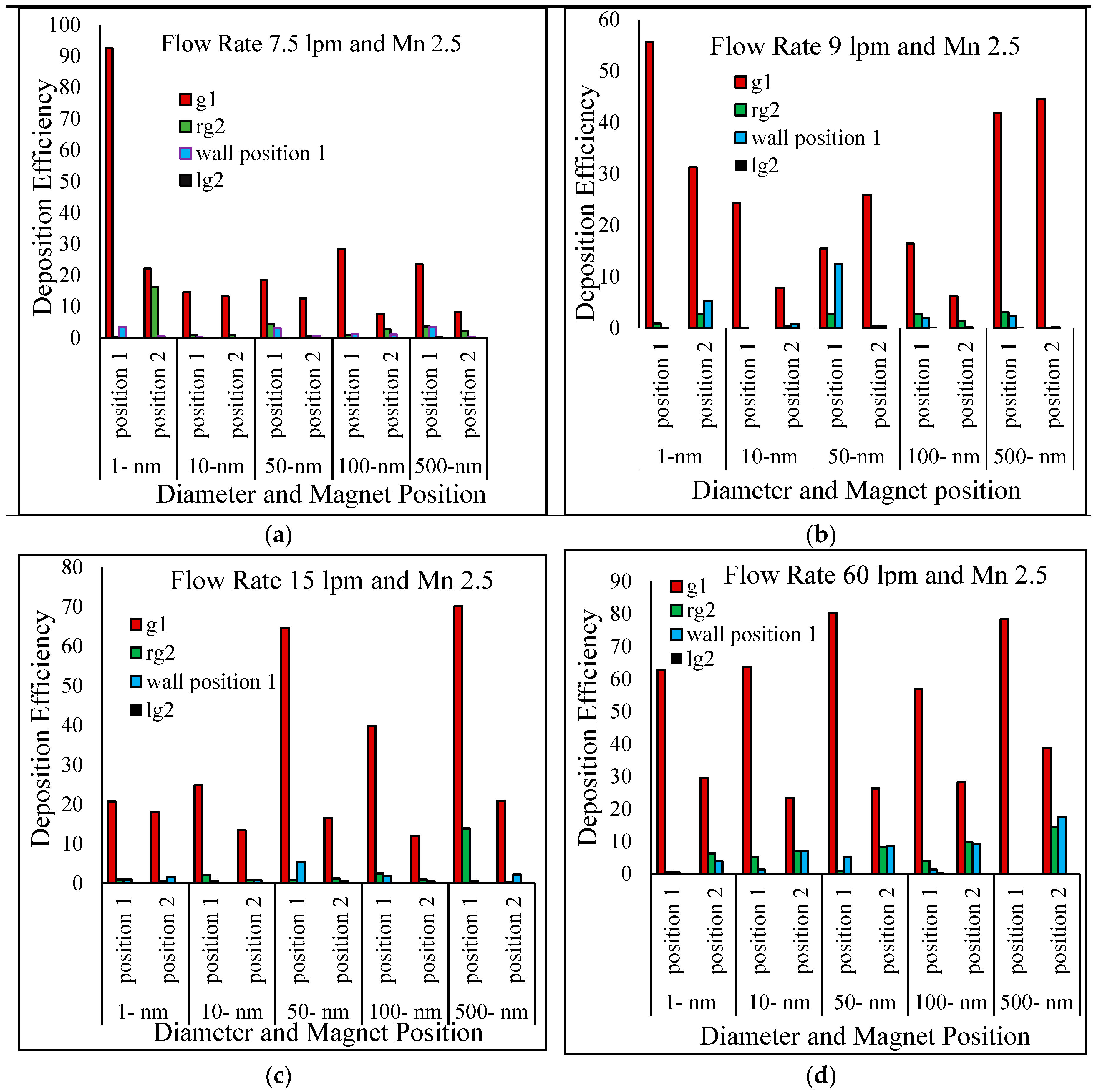
- Particle deposition efficiency on the targeted region were investigated as a function of four different breathing conditions, i.e., 7.5 lpm, 9 lpm, 15 lpm and 60 lpm. The present two-generation lung model shows that the maximum number of particles deposited in the targeted Position 1 for 7.5 lpm flow rates and in Position 2 for fast breathing condition (60 lpm).
- Particle diameter distribution effects in the targeted two different position were investigated for 1-nm, 50-nm, 100-nm and 500-nm particles. Most of the particle deposited on the targeted position and right lung (targeted region). The maximum number of depositions in the targeted Position 1 is for 1-nm and 7.5 lpm flow, for 50-nm and 100-nm it is happening for 60 lpm and for 500-nm it is 15 lpm flow rate. On contrary, for targeted Position 2, the deposition concentration is higher in Position 2 for 500-nm and 60lpm flow rates.
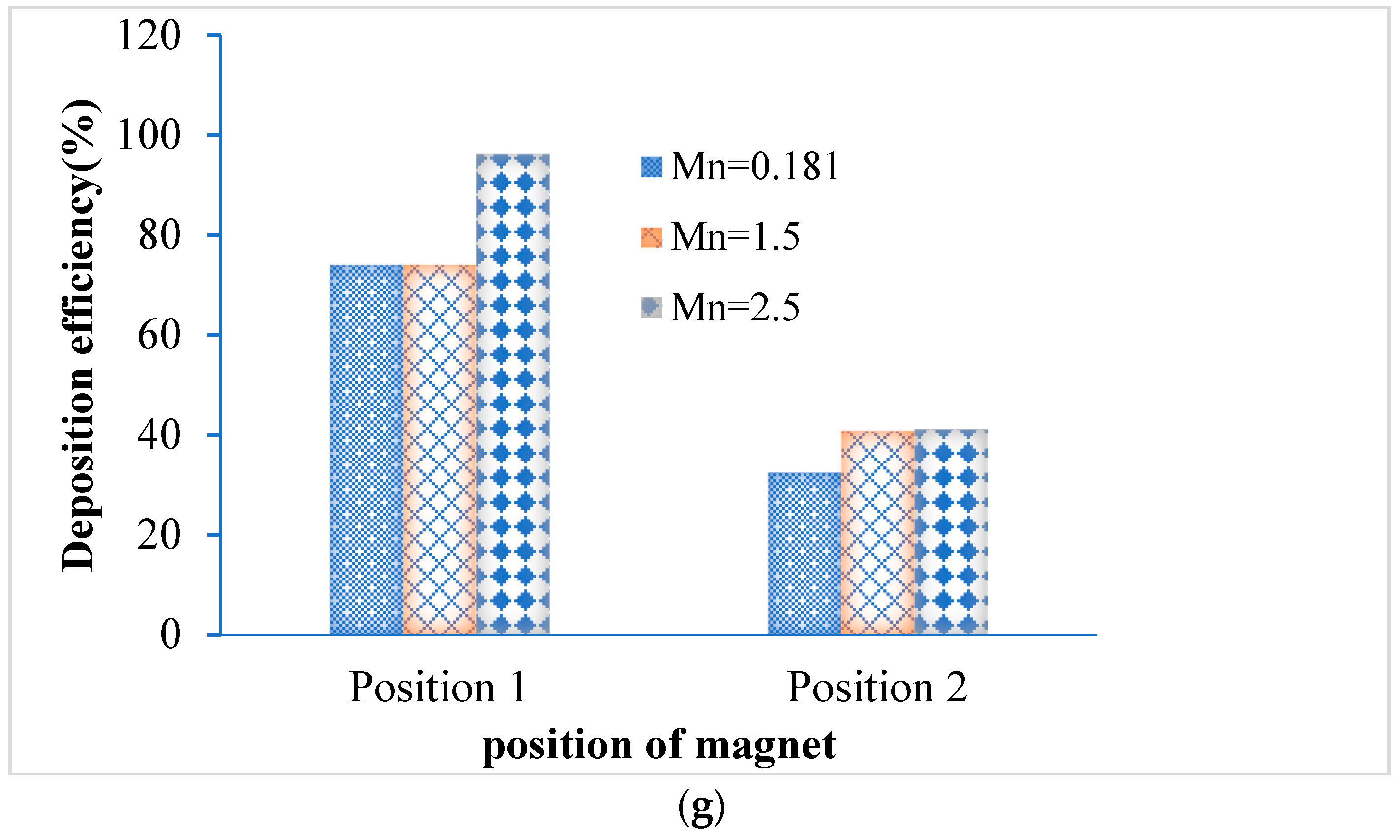
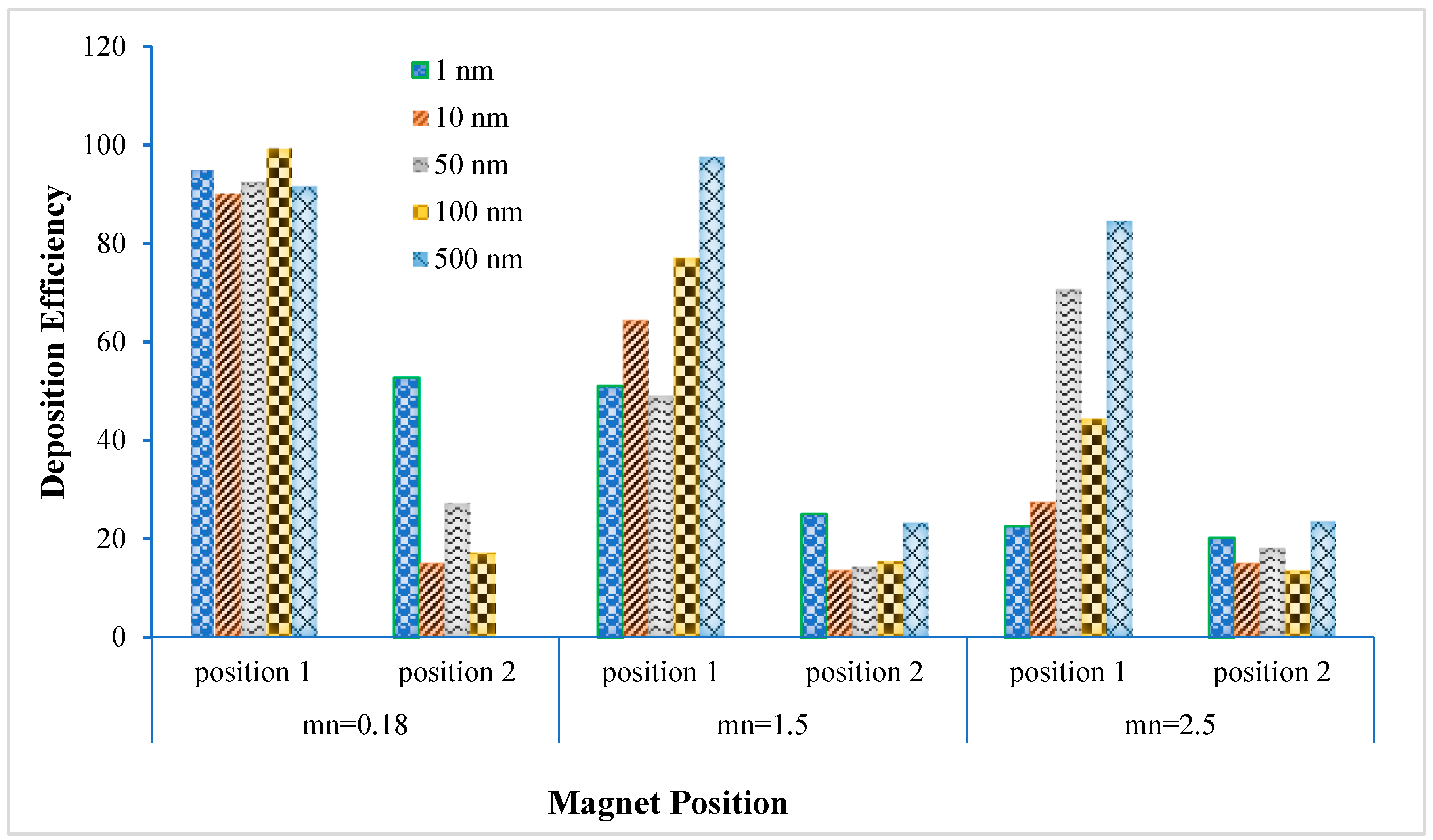
- The deposition scenario was investigated in the targeted position for three different magnetic number, i.e., 0.181, 1.5 and 2.5. The result shows that the overall deposition concentration is higher in both magnetic field position for small magnetic number 0.181 and flow rate is 15 lpm. On contrary, maximum number of the deposited particle in the targeted position are deposited for magnetic number 2.5 and 7.5 lpm flow rates.
- The nano-particle deposition was investigated for two different magnetic source position, i.e., Position 1 (wall position 1) and Position 2. Most of the particle deposited on the wall Position 1, Generation 1(g1), and rg2 (targeted region). Targeted magnetic particles attracted to the specific region of the lung, which allows direct treatment of those specific cells. This system reduces damage to healthy cells in the body.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lintermann, A.; Schröder, W. Simulation of aerosol particle deposition in the upper human tracheobronchial tract. Eur. J. Mech. B 2017, 63, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, P.; Aitken, R.; Hannan, W. Measurements of the total and regional deposition of inhaled particles in the human respiratory tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 1982, 13, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Qi, S.; Yue, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, B.; Sun, W.; Qian, W.; Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Wu, J. Structural and functional alterations of the tracheobronchial tree after left upper pulmonary lobectomy for lung cancer. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthavong, K.; Mouritz, A.P.; Dong, J.; Tu, J.Y. Inhalation and deposition of carbon and glass composite fibre in the respiratory airway. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 65, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Paul, G.; Ong, H.X.; Young, P.M.; Gu, Y.T.; Saha, S.C. A Review of Respiratory Anatomical Development, Air Flow Characterization and Particle Deposition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Islam, M.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Molla, M. Aerosol particle transport and deposition in a CT-scan based mouth-throat model. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2121, 040011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Gemci, T.; Yang, I.A.; Sauret, E.; Gu, Y.T. Polydisperse Microparticle Transport and Deposition to the Terminal Bronchioles in a Heterogeneous Vasculature Tree. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Gemci, T.; Yang, I.A.; Sauret, E.; Ristovski, Z.; Gu, Y.T. Euler-Lagrange Prediction of Diesel-Exhaust Polydisperse Particle Transport and Deposition in Lung: Anatomy and Turbulence Effects. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Sauret, E.; Gemci, T.; Gu, Y. Pulmonary aerosol transport and deposition analysis in upper 17 generations of the human respiratory tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 108, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Sauret, E.; Gu, Y. Numerical investigation of diesel exhaust particle transport and deposition in up to 17 generations of the lung airway. In Proceedings of the 20th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Perth, Australia, 5–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Sauret, E.; Gu, Y.; Ristovski, Z. Numerical investigation of aerosol particle transport and deposition in realistic lung airway. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Methods, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–17 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Sauret, E.; Ong, H.; Young, P.; Gu, Y. Euler–Lagrange approach to investigate respiratory anatomical shape effects on aerosol particle transport and deposition. Toxicol. Res. Appl. 2019, 3, 2397847319894675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C.; Sauret, E.; Gemci, T.; Yang, I.A.; Gu, Y.T. Ultrafine particle transport and deposition in a large scale 17-generation lung model. J. Biomech. 2017, 64, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Kleinstreuer, C. Airflow structures and nano-particle deposition in a human upper airway model. J. Comput. Phys. 2004, 198, 178–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, B.; Price, O.T. Deposition of Ultrafine (NANO) Particles inthe Human Lung. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 19, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinstreuer, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Modeling airflow and particle transport/deposition in pulmonary airways. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2008, 163, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dames, P.; Gleich, B.; Flemmer, A.; Hajek, K.; Seidl, N.; Wiekhorst, F.; Eberbeck, D.; Bittmann, I.; Bergemann, C.; Weyh, T.; et al. Targeted delivery of magnetic aerosol droplets to the lung. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmov, A.; Minko, T. Nanotechnology approaches for inhalation treatment of lung diseases. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 500–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.D.; Brown, J.S.; Zeman, K.L.; Hu, S.-C.; Scheuch, G.; Sommerer, K. Targeting delivery of aerosols to different lung regions. J. Aerosol Med. 2002, 15, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ally, J.; Martin, B.; Behrad Khamesee, M.; Roa, W.; Amirfazli, A. Magnetic targeting of aerosol particles for cancer therapy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Patel, B.B.; Tiwari, S. Colloidal nanocarriers: A review on formulation technology, types and applications toward targeted drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbe, A.S.; Alexiou, C.; Bergemann, C. Clinical Applications of Magnetic Drug Targeting. J. Surg. Res. 2001, 95, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, R.; Gaur, A. A Model for Magnetic Nanoparticles Transport in a Channel for Targeted Drug Delivery. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 10, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, W.H.; Azarmi, S.; Al-Hallak, M.H.D.K.; Finlay, W.H.; Magliocco, A.M.; Löbenberg, R. Inhalable nanoparticles, a non-invasive approach to treat lung cancer in a mouse model. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmehran, O.; Gorji, T.B.; Gorji-Bandpy, M. Magnetic drug targeting through a realistic model of human tracheobronchial airways using computational fluid and particle dynamics. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2016, 15, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boghi, A.; Russo, F.; Gori, F. Numerical simulation of magnetic nano drug targeting in a patient-specific coeliac trunk. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 437, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafcik, A.; Babinec, P.; Frollo, I. Computational analysis of magnetic field induced deposition of magnetic particles in lung alveolus in comparison to deposition produced with viscous drag and gravitational force. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Boghi, A.; Gori, F. Numerical simulation of magnetic nano drug targeting in patient-specific lower respiratory tract. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 451, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, F.; Boghi, A. A three dimensional exact equation for the turbulent dissipation rate of Generalised Newtonian Fluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, F.; Boghi, A. Two new differential equations of turbulent dissipation rate and apparent viscosity for non-newtonian fluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmehran, O.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Gorji-Bandpy, M.; Gorji, T.B. Simulation of magnetic drug targeting through tracheobronchial airways in the presence of an external non-uniform magnetic field using Lagrangian magnetic particle tracking. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 393, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, A.J.; Schuh, A.; Amine-Eddine, G.; McConnell, K.; Loew, W.; Fleck, R.J.; Amin, R.S. Assessing the relationship between movement and airflow in the upper airway using computational fluid dynamics with motion determined from magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 66, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longest, P.W.; Xi, J. Computational investigation of particle inertia effects on submicron aerosol deposition in the respiratory tract. J. Aerosol Sci. 2007, 38, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C. Ultrafine Particle Deposition in a Double Bifurcation Tube with Human G3–G5 Airway Geometry; Internal Report; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
| Flow Rates | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 7.5 lpm | 9 lpm | 15 lpm | 60 lpm | ||
| Particle Diameter | 1-nm | 1-, 50-, 100- and 500-nm | 1-, 50-, 100- and 500-nm | 1-, 50-, 100- and 500-nm | 1- and 100-nm | 10-, 50-, and 500-nm |
| Magnetic Number | Mn = 0.181, 1.5 | Mn = 2.5 | Mn = 2.5 | Mn = 0.181, 1.5, 2.5 | Mn = 2.5 | Mn = 2.5 |
| Magnet Position 1 | Position 1 | Position 1 | Position 1 | Position 1 | Position 1 | |
| Magnet Position 2 | Position 2 | Position 2 | Position 2 | Position 2 | Position 2 | Position 2 |
| 7.5 lpm | 9 lpm | 15 lpm | 60 lpm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 1 | Position 2 |
| 1-nm | 96.244% | 41.146% | 56.678% | 39.330% | 22.606% | 20.242% | 63.975% | 39.907% |
| 50-nm | 26.201% | 13.871% | 30.779% | 26.820% | 70.724% | 18.203% | 86.918% | 41.595% |
| 100-nm | 30.798% | 11.450% | 21.807% | 7.704% | 44.401% | 13.545% | 62.816% | 52.719% |
| 500-nm | 30.836% | 10.934% | 47.497% | 44.802% | 84.529% | 23.50% | 78.357% | 70.838% |
| Mn | Mn = 0.181 | Mn = 1.5 | Mn = 2.5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 1 | Position 2 |
| 1 nm | 95.275% | 52.828% | 51.116% | 25.080% | 22.606% | 20.242% |
| 10 nm | 90.228% | 15.044% | 64.458% | 13.625% | 27.463% | 15.044% |
| 50 nm | 92.499% | 27.251% | 49.132% | 14.387% | 70.724% | 18.203% |
| 100 nm | 99.404% | 17.146% | 77.095% | 15.427% | 44.401% | 13.545% |
| 500 nm | 91.647% | 0.0193% | 97.729% | 23.278% | 84.529% | 23.500% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, A.; Islam, M.S.; Saha, S.C. Targeted Drug Delivery of Magnetic Nano-Particle in the Specific Lung Region. Computation 2020, 8, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation8010010
Ghosh A, Islam MS, Saha SC. Targeted Drug Delivery of Magnetic Nano-Particle in the Specific Lung Region. Computation. 2020; 8(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation8010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Anusmriti, Mohammad S. Islam, and Suvash C. Saha. 2020. "Targeted Drug Delivery of Magnetic Nano-Particle in the Specific Lung Region" Computation 8, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation8010010
APA StyleGhosh, A., Islam, M. S., & Saha, S. C. (2020). Targeted Drug Delivery of Magnetic Nano-Particle in the Specific Lung Region. Computation, 8(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation8010010







