Machine-Learning Prediction of Underwater Shock Loading on Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Formulation of the Problem
2.1. Governing Equations
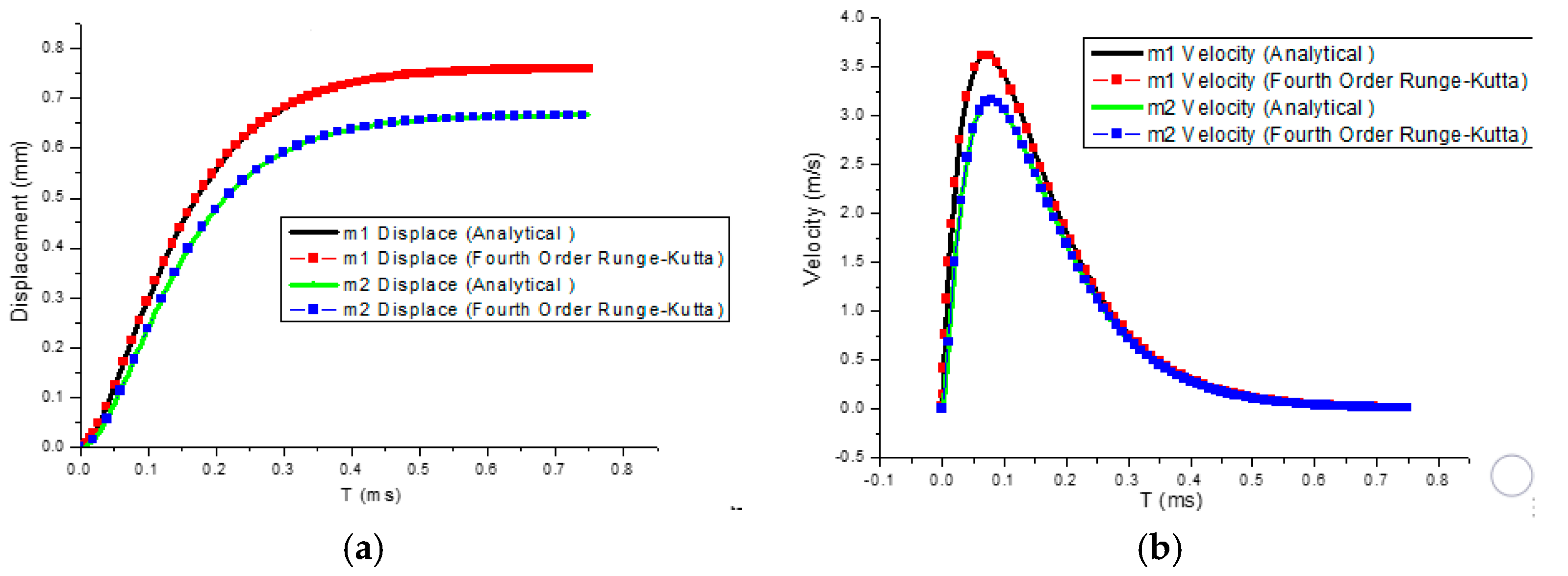
2.2. Analytical Solution
2.3. Numerical Solution
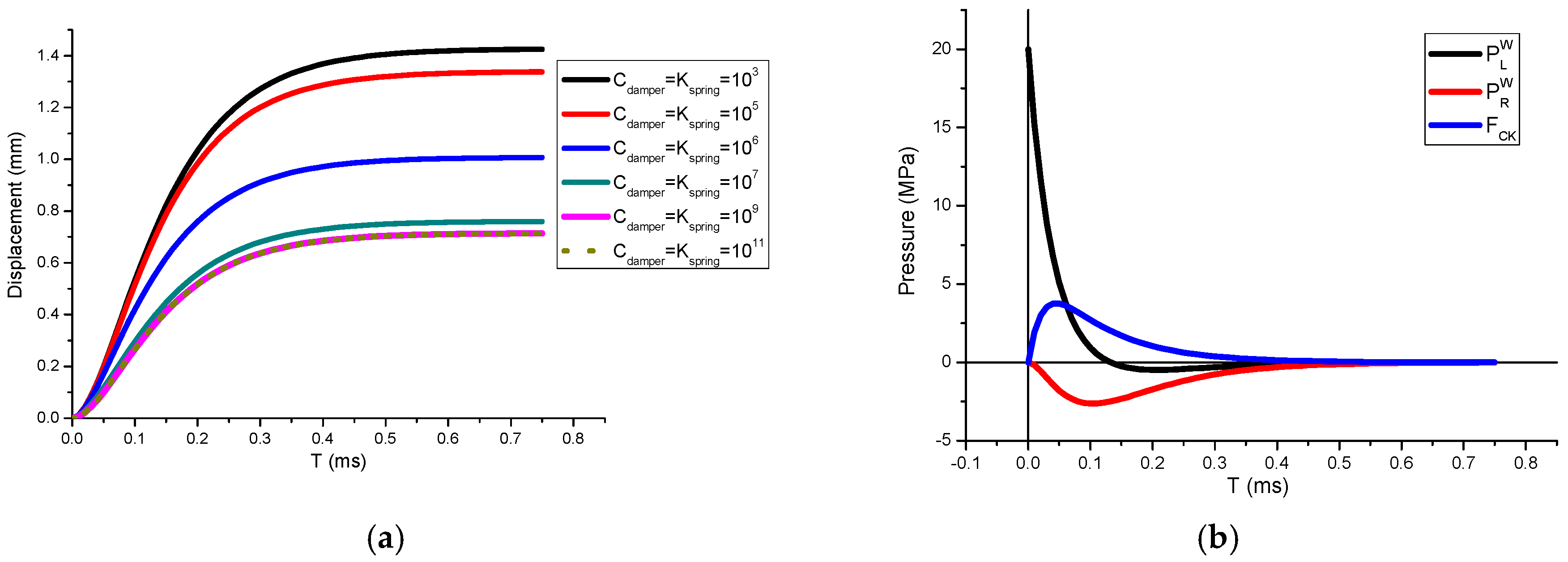
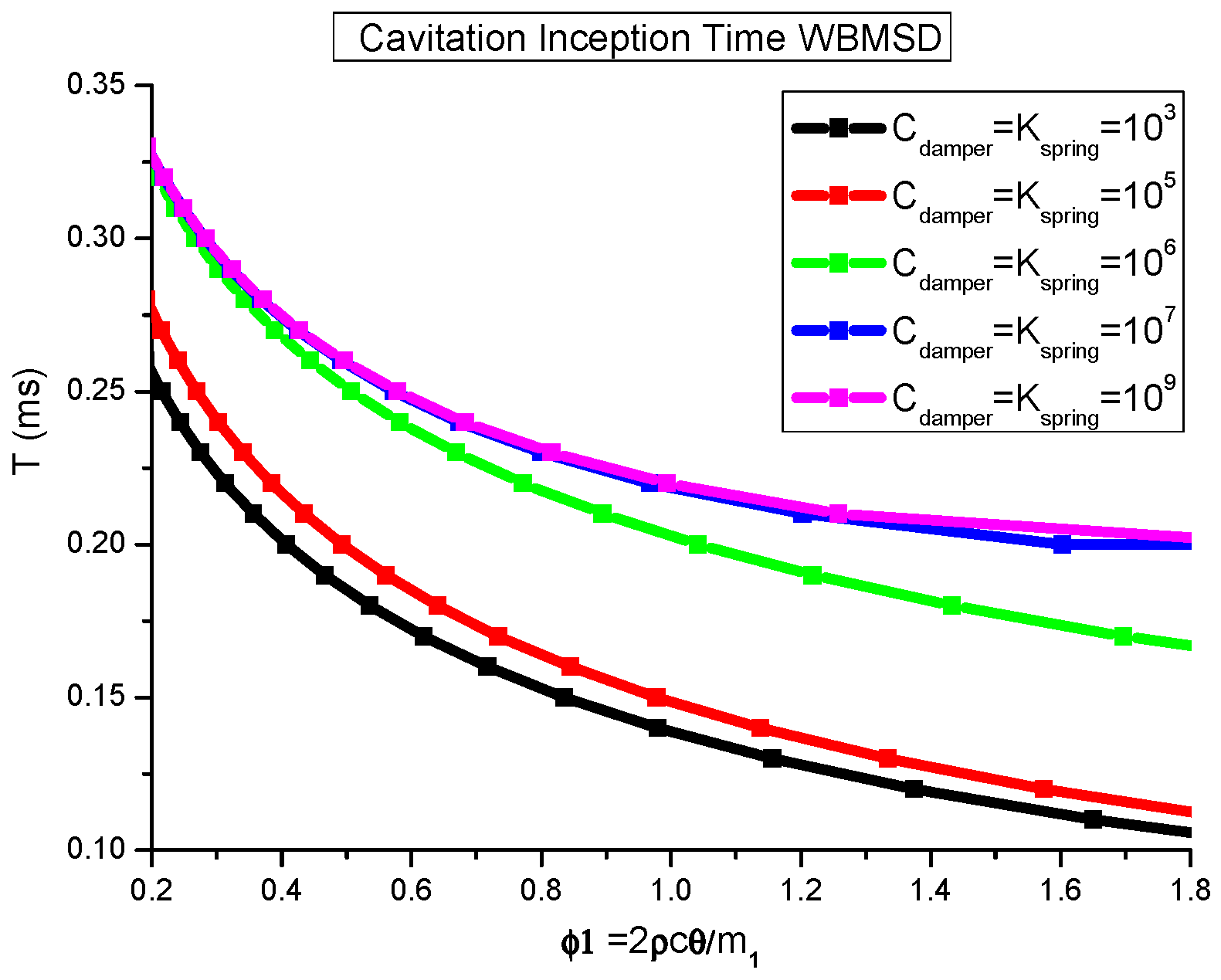
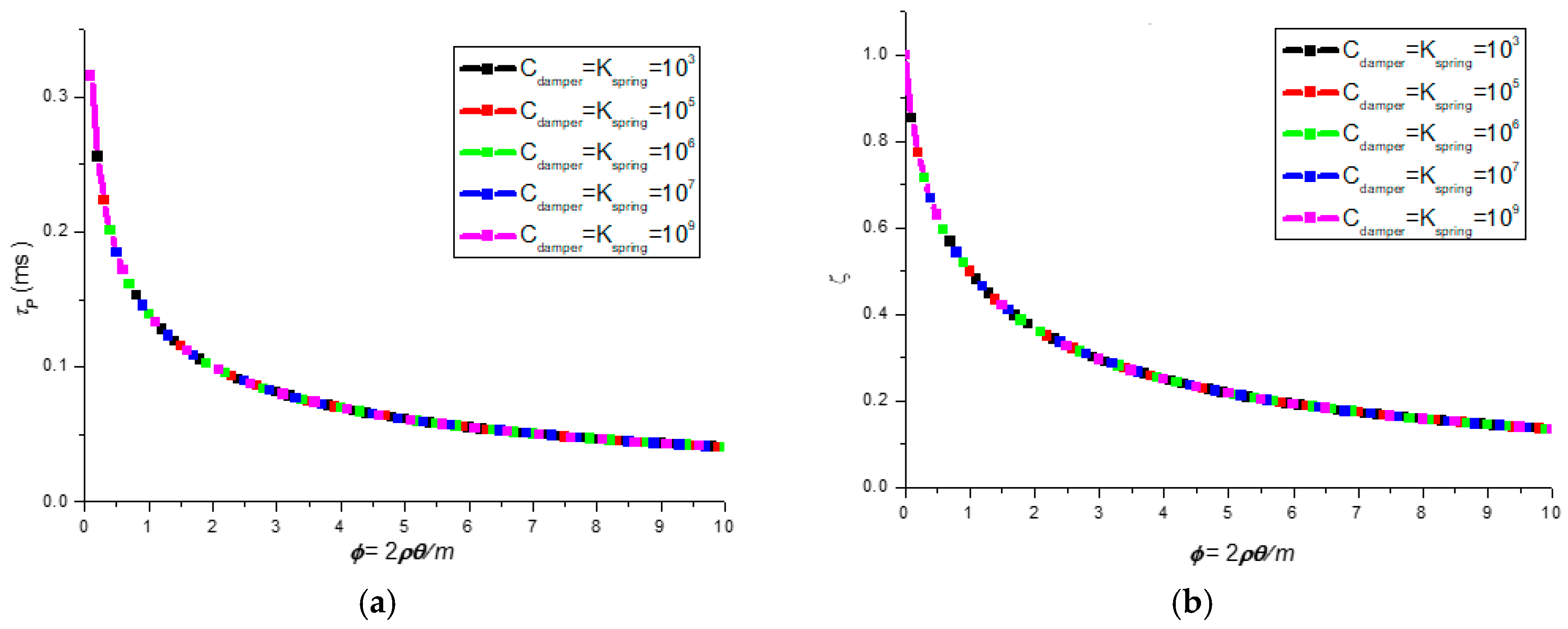
3. Results of Structural Response
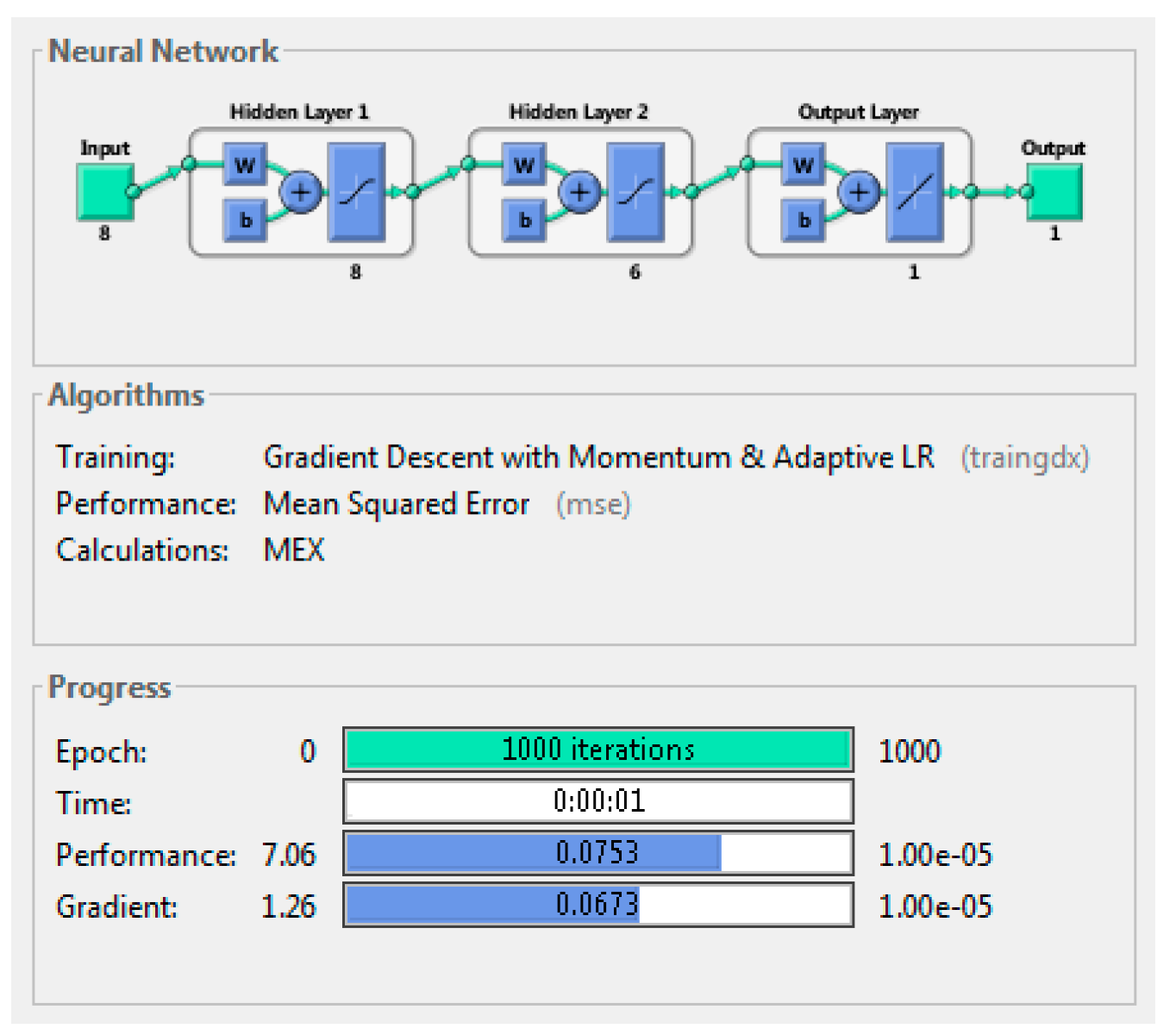
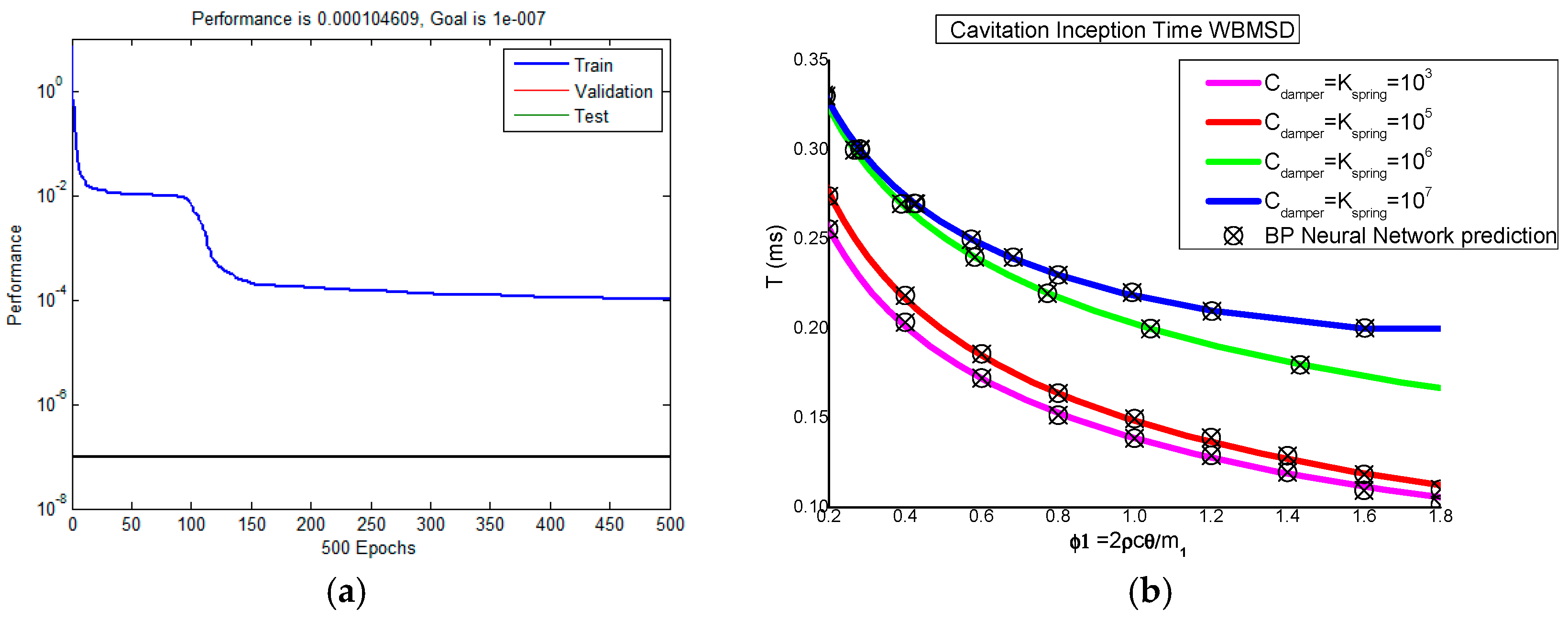
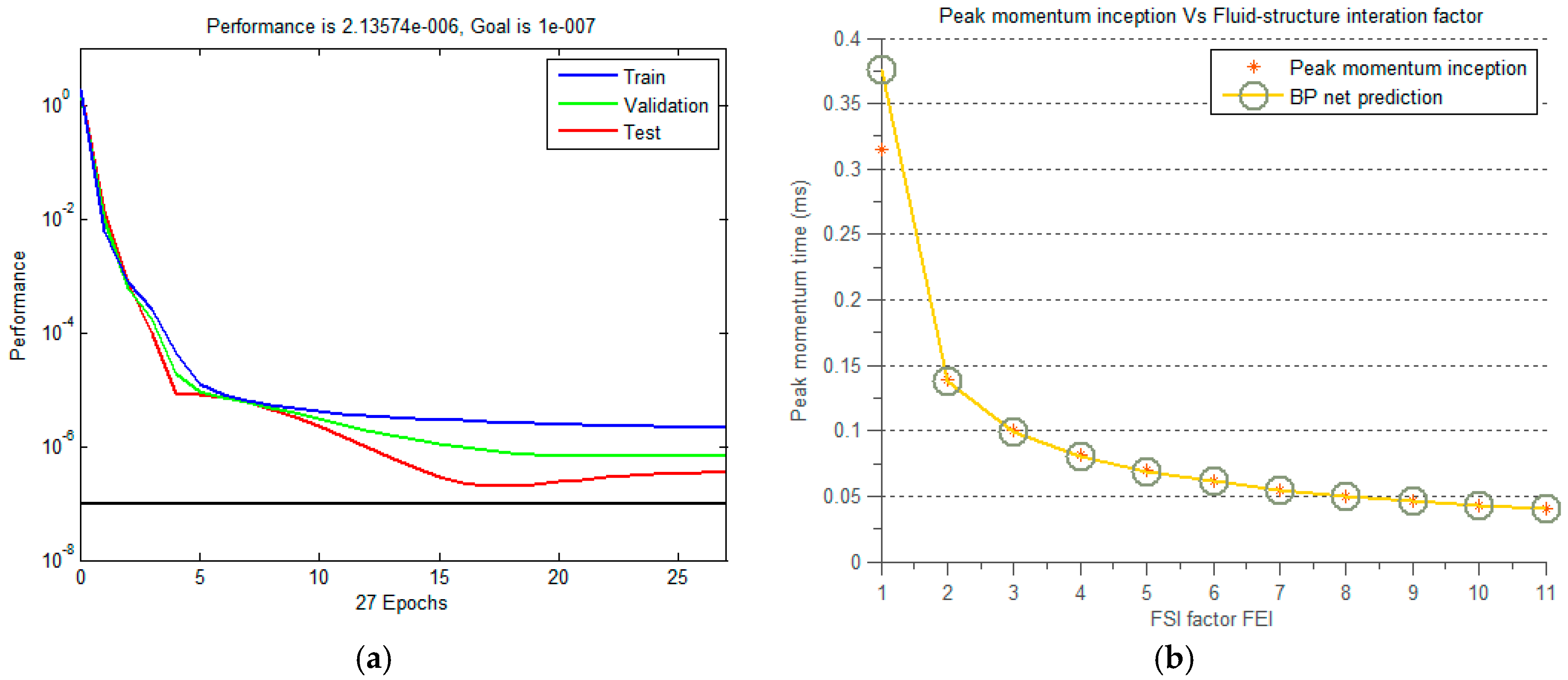
4. Parameter Prediction by BPNN
5. Finite Element Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, G.I. The Pressure and Impulse of Submarine Explosion Waves on Plates; The National Archives: Richmond, UK, 1941; pp. 287–303.
- Liu, Z.; Young, Y.L. Transient Response of a Submerged Plate Subject to Underwater Shock Loading: An Analytical Perspective. J. Appl. Mech. 2008, 75, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambouchev, N.; Noels, L.; Radovitzky, R. Nonlinear Compressibility Effects in Fluid-Structure Interaction and Their Implications on the Air-Blast Loading of Structures. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 063519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambouchev, N.; Radovitzky, R. Fluid-Structure Interaction Effects in the Dynamic Response of Free-Standing Plates to Uniform Shock Loading. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 2007, 74, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambouchev, N.; Noels, L.; Radovitzky, R. Numerical Simulation of the Fluid-Structure Interaction Between Air Blast Waves and Free-Standing Plates. Comput. Struct. 2007, 85, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.J.; Reid, S.R.; Harrigan, J.J. Discussion: The Resistance of Clamped Sandwich Beams to Shock Loading. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 2005, 72, 978–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.W.; Xue, Z. Metal Sandwich Plates Optimized for Pressure Impulses. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2005, 47, 545–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schechter, R.S.; Bort, R.L. The Response of Two Fluid-Coupled Plates to an Incident Pressure Pulse; Technical Report No. 4647; Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hallquist, J.O. LS-DYNA THEORETICAL MANUAL; California, Livermore Software Technology Corporation: Livermore, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mindlin, R.D.; Bleich, H.H. Response of an Elastic Cylindrical Shell to a Transverse Step Shock Wave. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1953, 26, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, J.H. Response of an Elastic Cylindrical Shell to a Pressure Pulse. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1958, 11, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Transient Interaction of Plane Acoustic Waves with a Spherical Elastic Shell. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1969, 45, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. An Exact Analysis of the Transient Interaction of Acoustic Plane Waves with a Cylindrical Elastic Shell. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1970, 37, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Transient Response of Two Fluid-Coupled Spherical Elastic Shells to an Incident Pressure Pulse. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 65, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Geers, T. Excitation of a Fluid-Filled, Submerged Spherical Shell by a Transient Acoustic Wave. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Oliveira, J. Transient Analytic and Numerical Results for the Fluid-Solid Interaction of Prolate Spheroidal Shells. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Veit, A.; Wilber, M.J.; Belongie, S. Residual networks behave like ensembles of relatively shallow networks. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 550–558. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.C.; Huang, D.K.; Xu, J.W. Optimization of Characteristic Parameters of Pipeline Crack Identification Based on BP Neural Network. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 926–930, 3442–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Zhang, Z.R.; Lu, Y.L. The Data Fusion in Multi-Sensors Grain Information Monitoring System Based on Improved BP Neural Networks. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 263–266, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y. Performance Study of BP Neural Network Based on PK Algorithm. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2019, 28, 173–177. [Google Scholar]

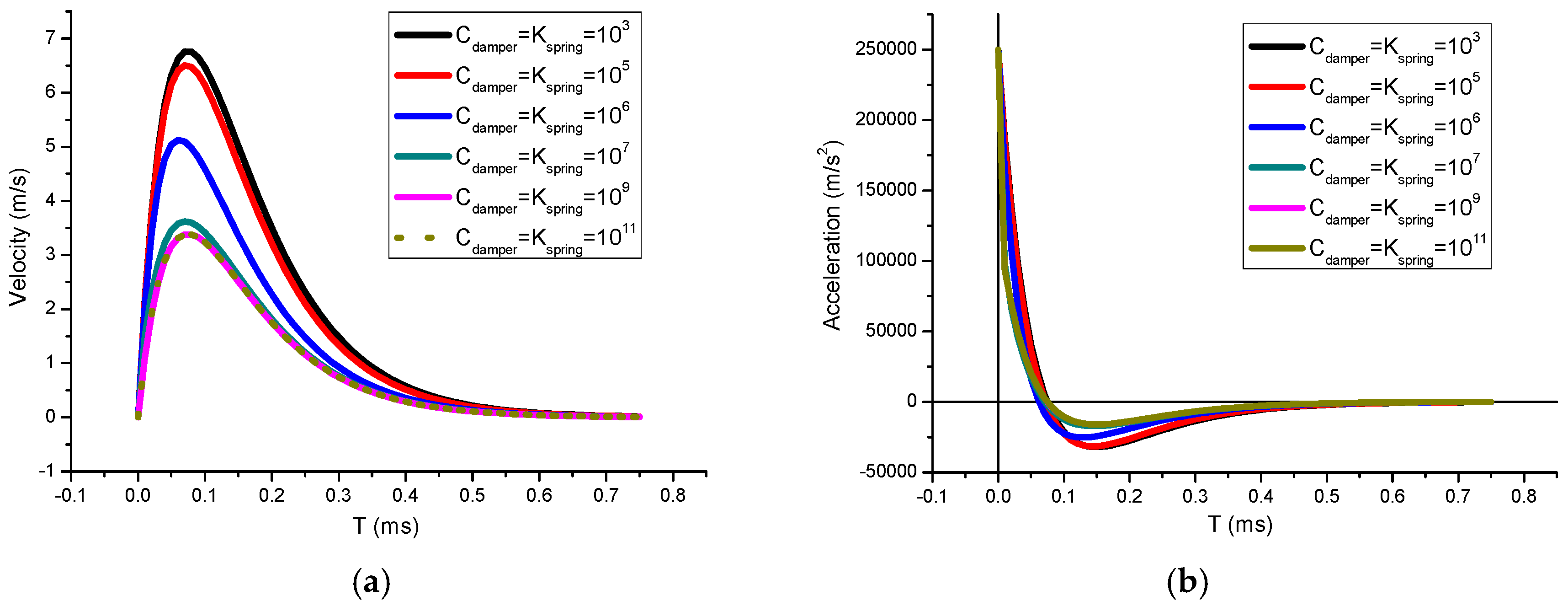
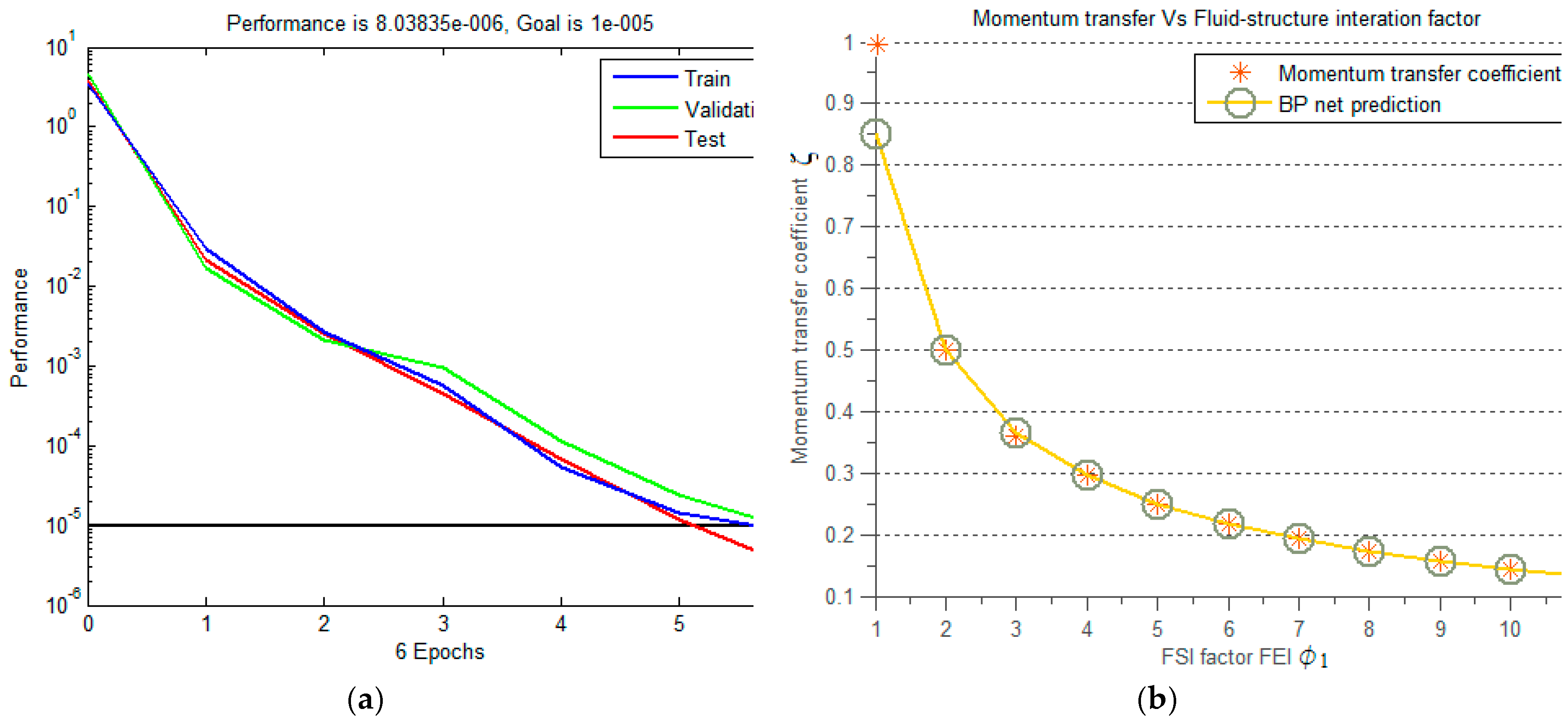


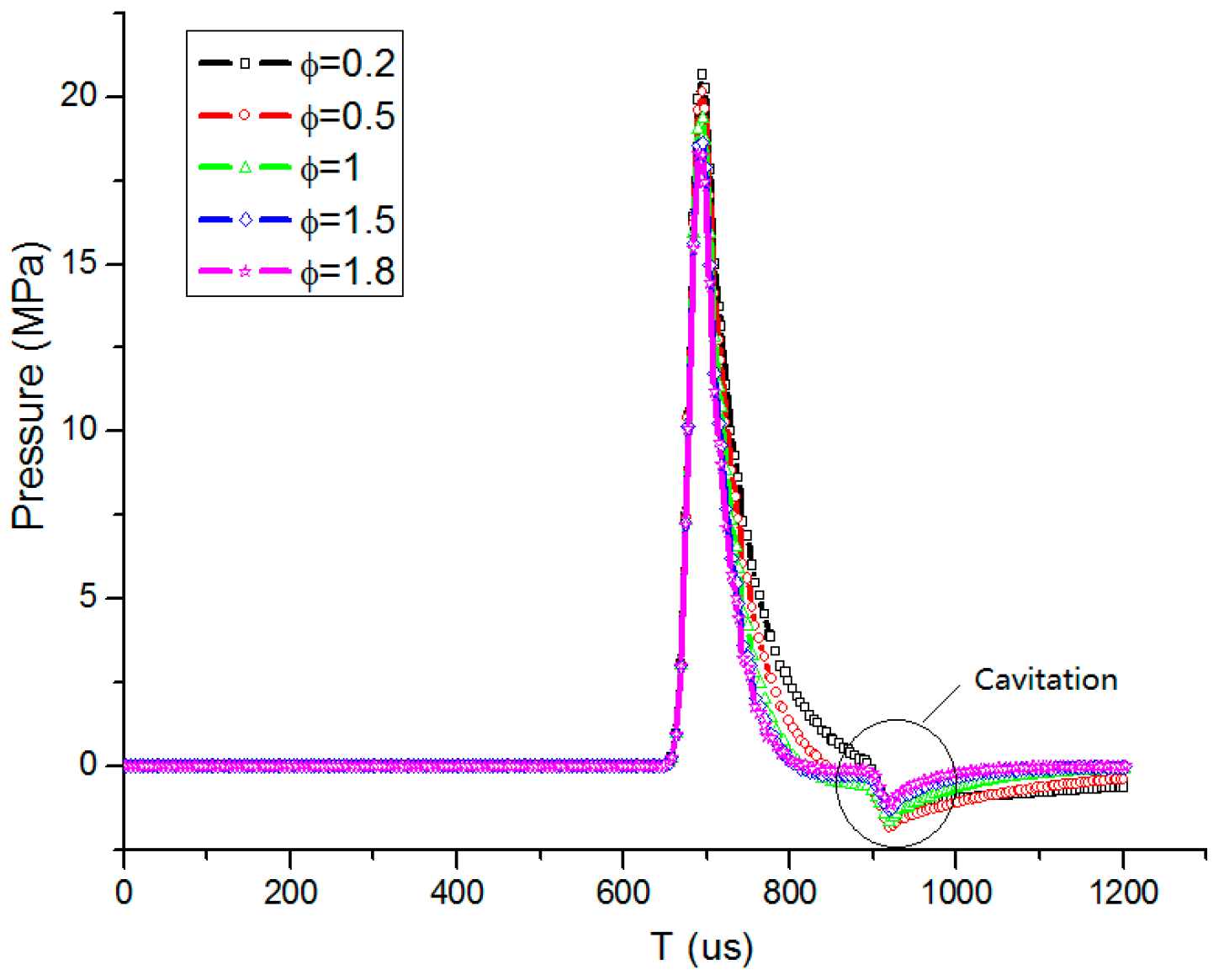
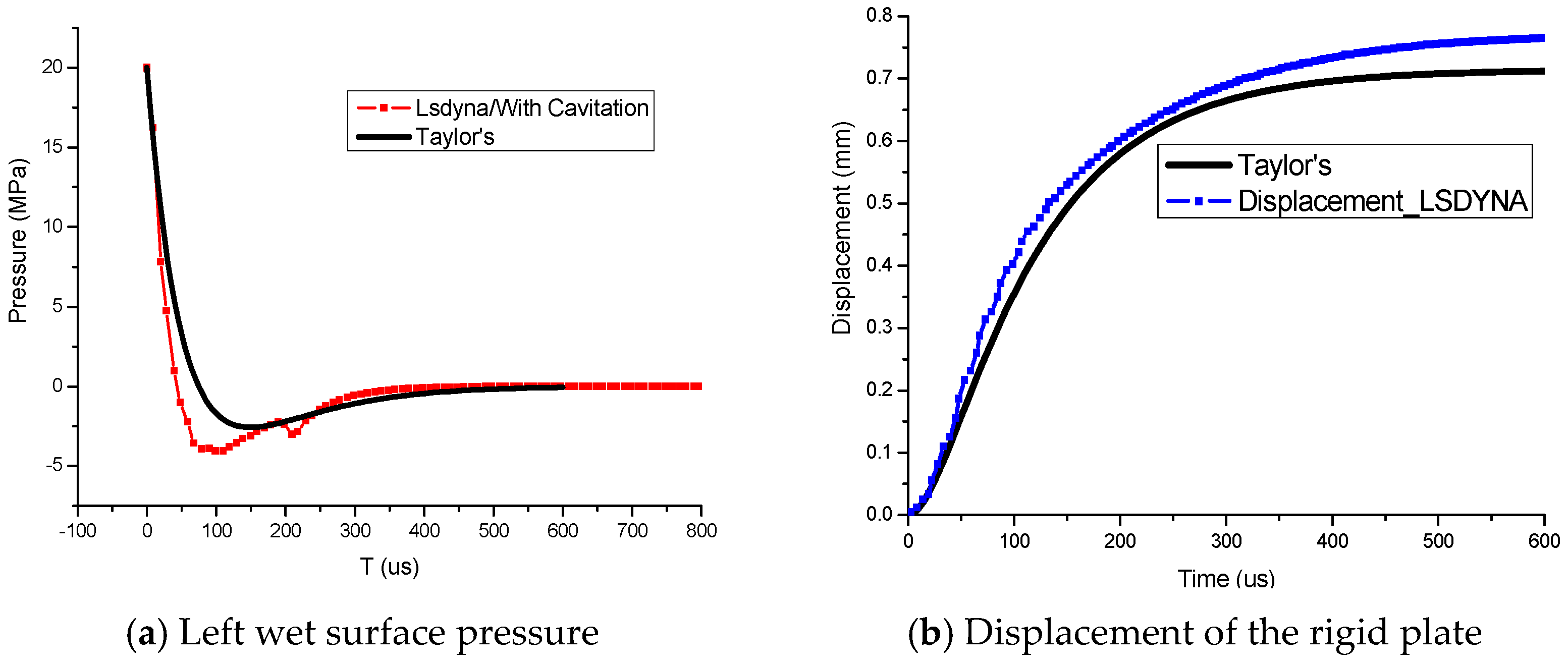
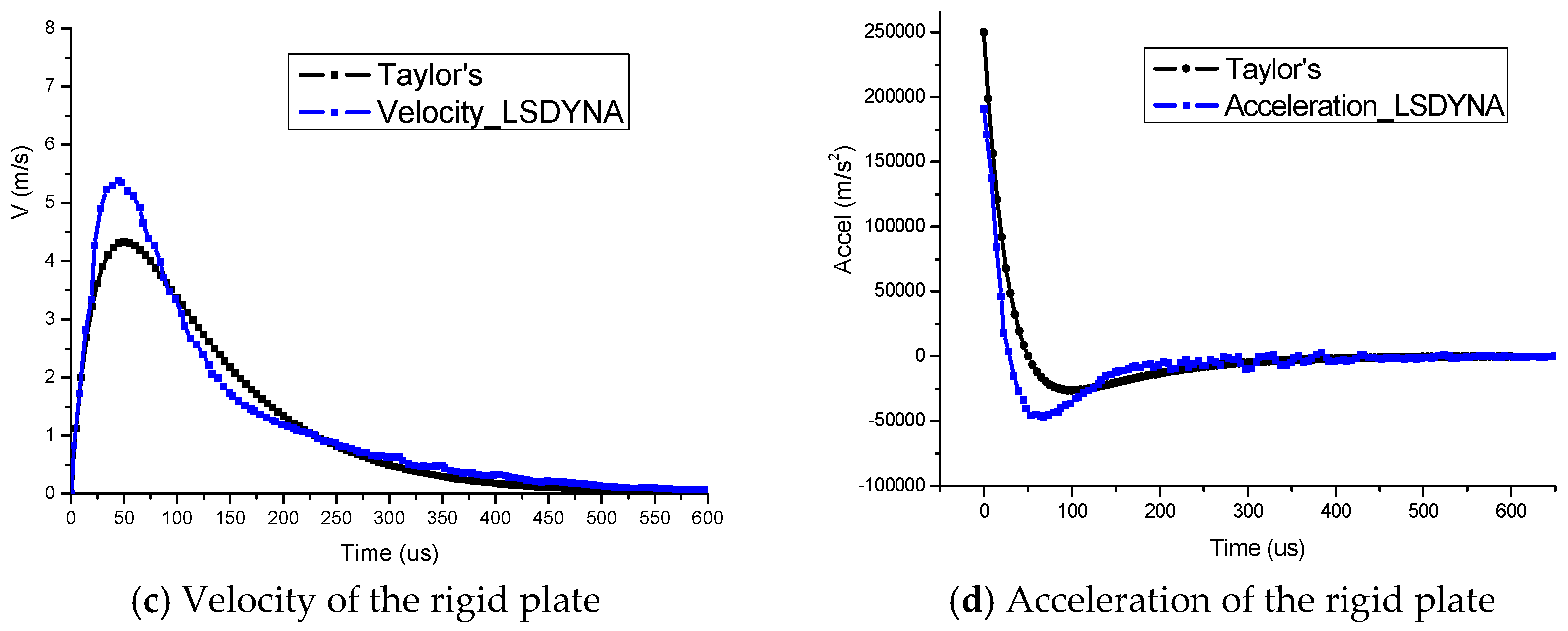
| Algorithm | Layers | Epoch | Stiffness k | Damping C | FSI Parameter ϕ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gradient Descent with Momentum | Input | 500 | 103 | 103 | 0.2 to 20 |
| Hidden layer 1 | 105 | 105 | |||
| Hidden layer 1 | 106 | 106 | |||
| Output layer | 107 | 107 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Drikakis, D.; Li, L.; Yan, X. Machine-Learning Prediction of Underwater Shock Loading on Structures. Computation 2019, 7, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation7040058
Zhang M, Drikakis D, Li L, Yan X. Machine-Learning Prediction of Underwater Shock Loading on Structures. Computation. 2019; 7(4):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation7040058
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mou, Dimitris Drikakis, Lei Li, and Xiu Yan. 2019. "Machine-Learning Prediction of Underwater Shock Loading on Structures" Computation 7, no. 4: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation7040058
APA StyleZhang, M., Drikakis, D., Li, L., & Yan, X. (2019). Machine-Learning Prediction of Underwater Shock Loading on Structures. Computation, 7(4), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation7040058





