Numerical Simulation of the Laminar Forced Convective Heat Transfer between Two Concentric Cylinders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
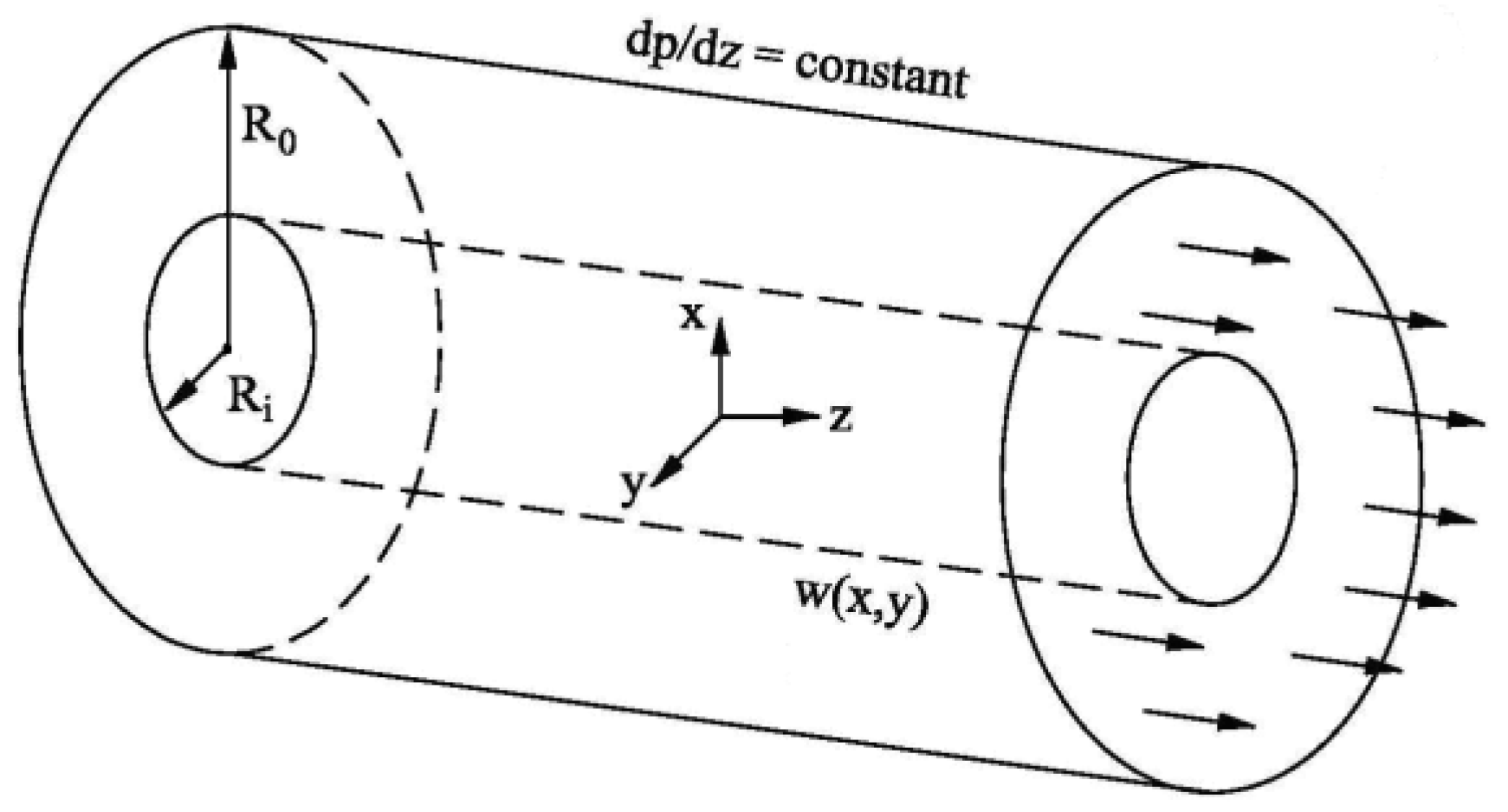
2. Physical Problem and Its Mathematical Formulation
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Boundary Conditions
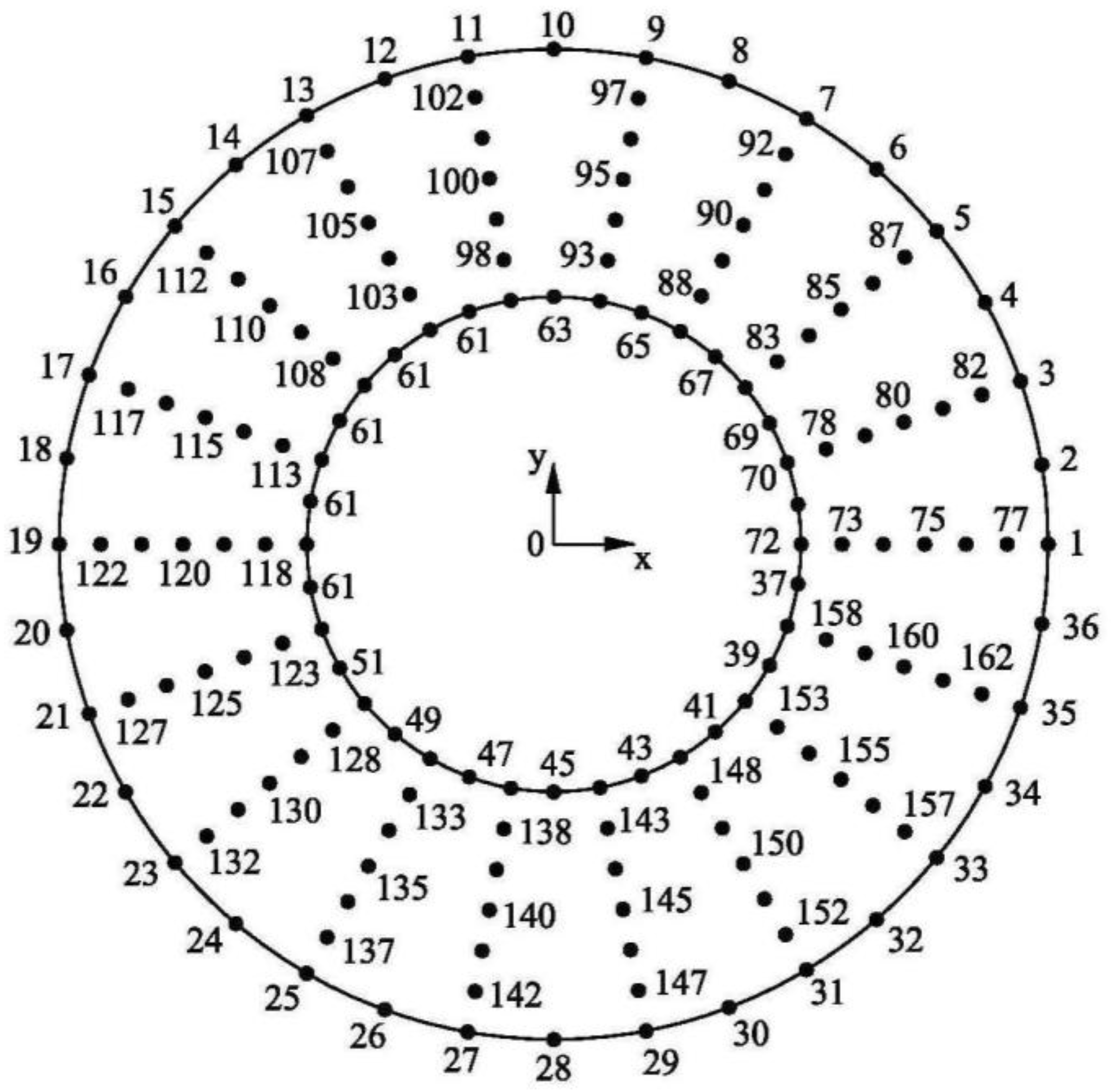
3. Numerical Model
3.1. The DRM Formulation
3.2. Numerical Solution
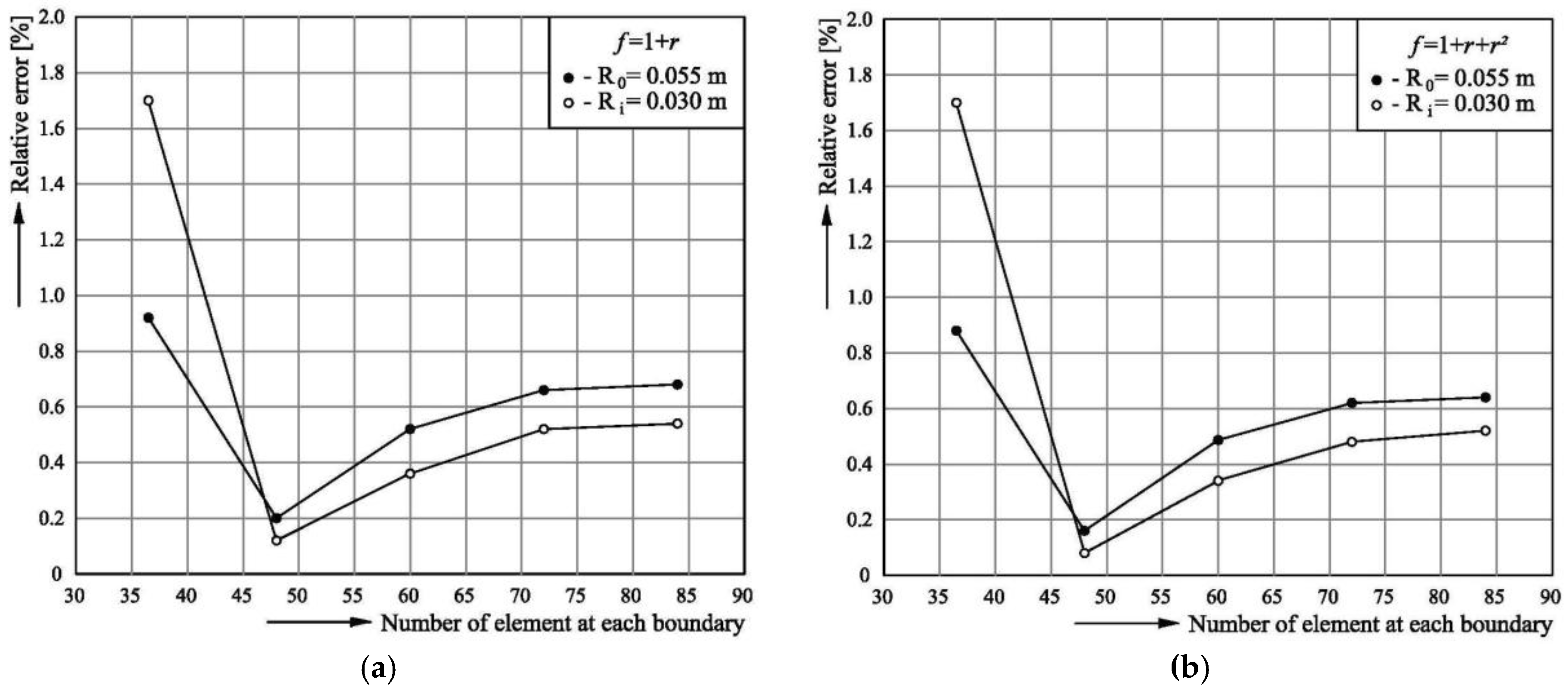
3.3. Testing the Model
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irons, B.M.; Ahmad, S. Techniques of Finite Elements; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S. The Finite Element Method in Engineering; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.J.; Brebbia, A.C. The multiple reciprocity method: A new approach for transforming BEM domain integrals to the boundary. Eng. Anal. 1989, 6, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, W.P.; Brebbia, A.C. Computer implementation of the BEM dual reciprocity method for the solution of general field Equations. Commun. Appl. Numer. Methods 1990, 6, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, J. Boundary Element Methods; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, J.N. An Introduction to the Finite Element Method; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, F.; Cañas, J. Boundary Element Method: Fundamentals and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Power, H.; Mingo, R. The DRM Subdomain decomposition approach to solve the two-dimensional Navier-Stokes system of equations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2000, 24, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, I. Numerical Modelling and Optimizations in Building Services; Polytechnic Publishing House: Timisoara, Romania, 2010. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Lavine, A.S.; Incropera, F.P.; Dewitt, D.P. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, V.; Bui, T.T. A meshless solution to two-dimensional convection-diffusion problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2010, 34, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Lu, W.Q. The selection and assemblage of approximating functions and disposal of its singularity in axisymmetric DRBEM for heat transfer problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2004, 28, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, A.S. Heat transfer on axis symmetric stagnation flow an infinite circular cylinder. In Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Acapulco, Mexico, 25–27 January 2008; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Nekoubin, N.; Nobari, M.R.H. Numerical analysis of forced convection in the entrance region of an eccentric curved annulus. Numer. Heat Transf. Appl. 2014, 65, 482–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.L.; Tian, Y.H. Application of finite element: Finite difference method to the determination of transient temperature field in functionally graded materials. Finite Elements Anal. Des. 2005, 41, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Sheng, A. A Note on finite difference method to analysis an ill-posed problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 182, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakerim, F.; Dehghan, M. A finite volume spectral element method for solving magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 2011, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammouda, H.; Belghith, A.; Surry, C. Finite element simulation of transient natural convection of low-Prandtl-number fluids in heated cavity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 1999, 5, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, I. Numerical analysis of two-dimensional heat conductivity in steady state regime. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 2005, 49, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.L.; Mai, Y.W. Transient one dimensional heat conduction problems solved by finite element. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2005, 47, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebbia, C.A.; Telle, J.C.; Wrobel, I.C. Boundary Element Techniques; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, J.H. Boundary Element Analysis in Engineering Continuum Mechanics; Prentice–Hall: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Chen, C.S.; Bowman, H. Some recent results and proposals for the use of radial basis functions in the BEM. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 1999, 23, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Peng, H.-F.; Cui, M.; Gao, X.-W. New analytical expressions in radial integration BEM for solving heat conduction problems with variable coefficients. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2015, 50, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghatjoo, Z.; Adibi, H. Calculation of domain integrals of two dimensional boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2012, 36, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divo, E.A.; Kassab, A.J. Boundary Element Methods for Heat Conduction: Applications in Non-Homogeneous Media; WIT Press: Southampton, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Žagar, I.; Škerget, L. Boundary elements for time dependent 3-D laminar viscous fluid flow. J. Mech. Eng. 1989, 35, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.Y. Detection of cavities by inverse heat conduction boundary element method using minimal energy technique. J. Korean Soc. Non-Destr. Test. 1997, 17, 237–247. [Google Scholar]
- Garimella, S.; Dowling, W.I.; van der Veen, M.; Killion, J. Heat transfer coefficients for simultaneously developing flow in rectangular tubes. In Proceedings of the ASME 2000 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–10 November 2000; 2, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Skerget, L.; Rek, Z. Boundary-domain integral method using a velocity-vorticity formulation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 1995, 15, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žunič, Z.; Hriberšek, M.; Škerget, L.; Ravnik, J. 3-D boundary element–finite element method for velocity–vorticity formulation of the Navier-Stokes equations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2007, 31, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.L.; Huang, J.L.; Eldho, T.I. Simulation of laminar vortex shedding flow past cylinders using a coupled BEM and FEM model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2001, 190, 5975–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Eldho, T.I. A combined BEM–FEM model for the velocity-vorticity formulation of the Navier-Stokes equations in three dimensions. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2000, 24, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravnik, J.; Škerget, L.; Hriberšek, M. Two-dimensional velocity-vorticity based LES for the solution of natural convection in a differentially heated enclosure by wavelet transform based BEM and FEM. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2006, 30, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, K.J.; Lien, F.S. Numerical modeling of buoyancy-driven turbulent flows in enclosures. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2004, 25, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.W. The radial integration method for evaluation of domain integrals with boundary-only discretization. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2002, 26, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Gao, X.W.; Zhang, J.B. A new approach for the estimation of temperature-dependent thermal properties by solving transient inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 58, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.W.; Peng, H.F. A boundary-domain integral equation method for solving convective heat transfer problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 63, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.F.; Yang, K.; Gao, X.W. Element nodal computation-based radial integration BEM for non-homogeneous problems. Acta Mech. Sin. 2013, 29, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, D.; Brebbia, C.A. A new approach for free vibration analysis using boundary elements. In Boundary Element Methods in Engineering; Computational Mechanics Publications: Southampton, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 312–326. [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel, C.L.; DeFigueiredo, D.B. A dual reciprocity boundary element formulation for convection diffusion problems with variable velocity fields. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 1991, 8, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, P.W.; Brebbia, C.A.; Wrobel, L.C. The Dual Reciprocity Boundary Element Method; Computational Mechanics Publications: Southampton, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Tezer-Sezgin, M.; Bozkaya, C.; Türk, Ö. BEM and FEM based numerical simulations for biomagnetic fluid flow. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2013, 37, 127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Wrobel, L.C.; Power, H. On the convergence of the dual reciprocity boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 1994, 13, 91–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karur, S.R.; Ramachandran, P.A. Radial basis function approximation in the dual reciprocity method. Math. Comput. Model. 1994, 20, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilati, M.; Dehghan, M. The use of radial basis function (RBFs) collocation and RBF-QR methods for solving the coupled nonlinear Sine-Gordon equations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elements 2015, 52, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kays, W.M.; Crawford, M.E. Convective Heat and Mass Transfer; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kakac, S.; Yener, Y.; Pramuanjaroenkij, A. Convective Heat Transfer; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jawarneh, A.M.; Vatistas, G.H.; Ababneh, A. Analytical approximate solution for decaying laminar swirling flows within narrow annulus. Jordan J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2008, 2, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, W.G.; Kim, J.M. Application of spectral collocation method to conduction and laminar forced heat convection in eccentric annuli. KSME Int. J. 1996, 10, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechthler, H.; Browne, M.W.; Bansal, P.K.; Kecman, V. New approach to dynamic modelling of vapour-compression liquid chillers: Artificial neural networks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

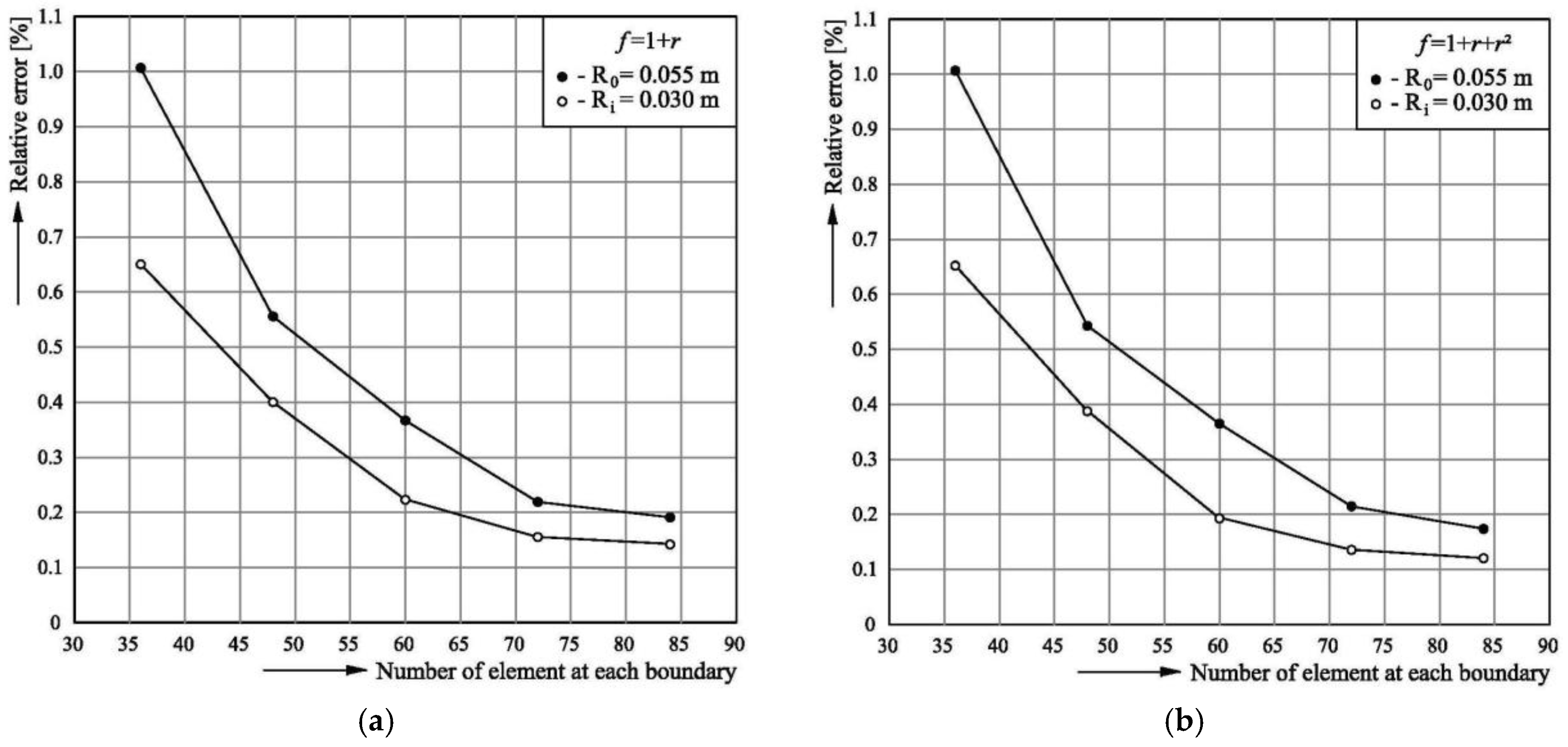
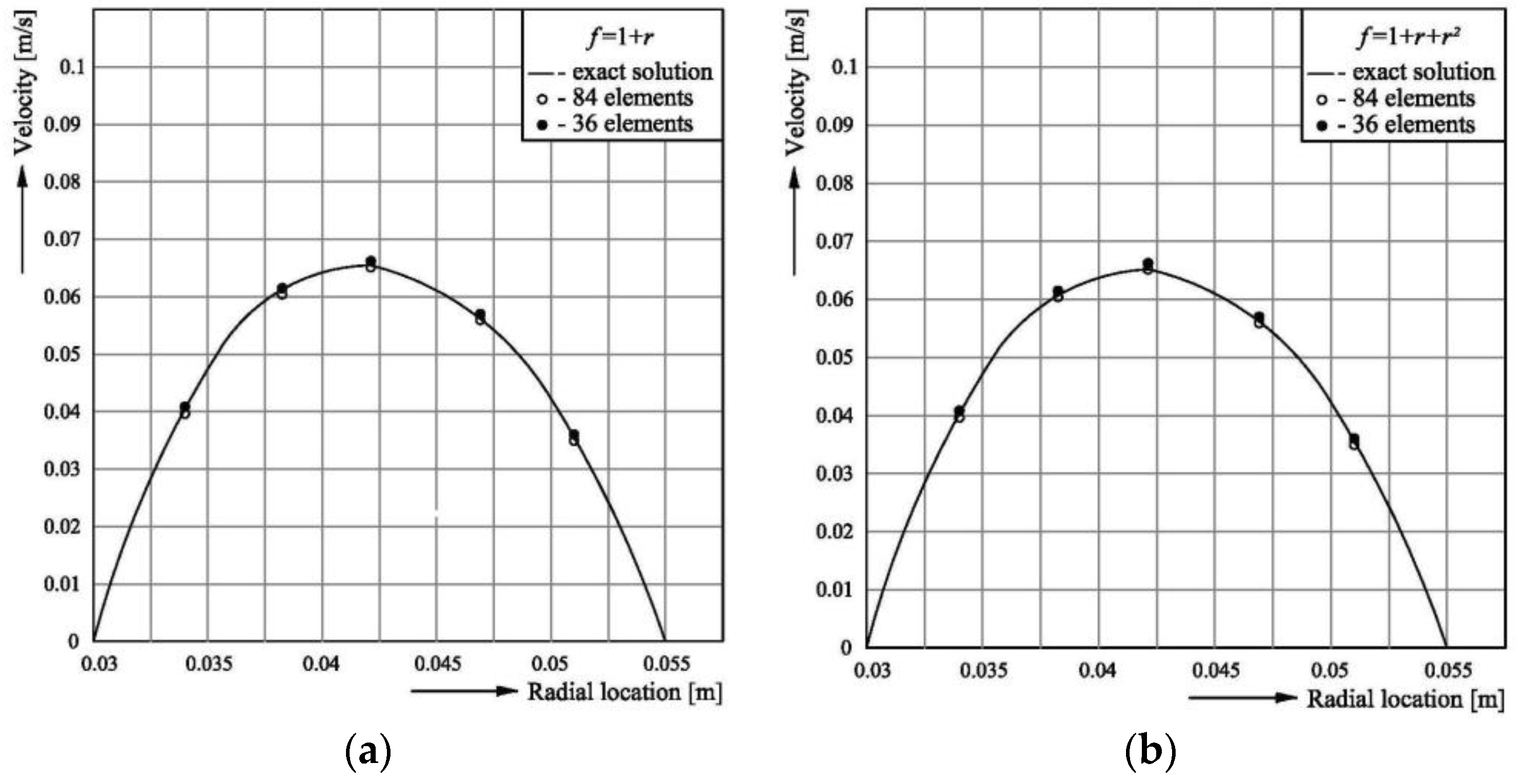


| Variable | Radial Location r [m] | DRM Solution | Analytical Solution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Boundary Elements | |||||||
| 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| ∂w/∂n | 0.055 | −9.570611 | −9.614363 | −9.632446 | −9.646733 | −9.649446 | −9.667904 |
| ∂w/∂n | 0.030 | −11.961390 | −11.931682 | −11.910987 | −11.902295 | −11.900702 | −11.883840 |
| w | 0.0342 | 0.040336 | 0.039937 | 0.039755 | 0.039656 | 0.039614 | 0.039413 |
| w | 0.0383 | 0.061518 | 0.061112 | 0.060926 | 0.060825 | 0.060760 | 0.060591 |
| w | 0.0425 | 0.066727 | 0.066320 | 0.066133 | 0.066030 | 0.065973 | 0.065803 |
| w | 0.0466 | 0.057611 | 0.057196 | 0.057006 | 0.056908 | 0.056853 | 0.056682 |
| w | 0.0508 | 0.035084 | 0.034883 | 0.034733 | 0.034638 | 0.034606 | 0.034439 |
| RMSE | 0.000741 | 0.000427 | 0.000275 | 0.000191 | 0.000149 | − | |
| cv% | 2.018 | 1.162 | 0.749 | 0.521 | 0.405 | − | |
| R2 | 0.999724 | 0.999908 | 0.999962 | 0.999981 | 0.999988 | − | |
| Variable | Radial Location r [m] | DRM Solution | Analytical Solution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Boundary Elements | |||||||
| 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| ∂w/∂n | 0.055 | −9.570477 | −9.615427 | −9.632632 | −9.647164 | −9.651780 | −9.667904 |
| ∂w/∂n | 0.030 | −11.960900 | −11.929878 | −11.906732 | −11.899952 | −11.898130 | −11.883840 |
| w | 0.0342 | 0.040334 | 0.039938 | 0.039754 | 0.039654 | 0.039601 | 0.039413 |
| w | 0.0383 | 0.061519 | 0.061112 | 0.060927 | 0.060820 | 0.060761 | 0.060591 |
| w | 0.0425 | 0.066725 | 0.066321 | 0.066136 | 0.066031 | 0.065974 | 0.065803 |
| w | 0.0466 | 0.057609 | 0.057193 | 0.057012 | 0.056906 | 0.056850 | 0.056682 |
| w | 0.0508 | 0.035080 | 0.034880 | 0.034726 | 0.034635 | 0.034604 | 0.034439 |
| RMSE | 0.000740 | 0.000426 | 0.000276 | 0.000189 | 0.000146 | − | |
| cv% | 2.015 | 1.160 | 0.750 | 0.516 | 0.397 | − | |
| R2 | 0.999725 | 0.9999087 | 0.999961 | 0.999982 | 0.999989 | − | |
| Variable | Radial Location r [m] | DRM Solution | Analytical Solution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Boundary Elements | |||||||
| 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | |||
| ∂T*/∂n | 0.055 | 172056.38 | 170824.22 | 171362.75 | 171600.75 | 171628.56 | 170484.20 |
| ∂T*/∂n | 0.030 | 233420.45 | 229217.02 | 230340.65 | 230698.70 | 230771.22 | 229506.90 |
| T* | 0.0342 | 804.26 | 828.59 | 847.40 | 853.78 | 855.04 | 858.72 |
| T* | 0.0383 | 1268.86 | 1298.52 | 1311.65 | 1315.86 | 1317.26 | 1320.13 |
| T* | 0.0425 | 1383.48 | 1413.28 | 1426.46 | 1429.68 | 1431.26 | 1433.69 |
| T* | 0.0466 | 1180.68 | 1209.26 | 1224.48 | 1230.46 | 1231.92 | 1234.96 |
| T* | 0.0508 | 711.52 | 730.65 | 741.78 | 746.86 | 747.90 | 750.34 |
| RMSE | 42.3739 | 20.1408 | 7.8869 | 3.6070 | 2.4750 | − | |
| cv% | 5.298 | 2.518 | 0.986 | 0.451 | 0.309 | − | |
| R2 | 0.998102 | 0.999571 | 0.99934 | 0.999986 | 0.999993 | − | |
| Variable | Radial Location r [m] | DRM Solution | Analytical Solution | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Boundary Elements | ||||||||
| 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | ||||
| ∂T*/∂n | 0.055 | 171989.88 | 170768.08 | 171293.14 | 171535.45 | 171598.75 | 170484.20 | |
| ∂T*/∂n | 0.030 | 233300.36 | 229286.02 | 230294.05 | 230618.22 | 230708.55 | 229506.90 | |
| T* | 0.0342 | 805.85 | 829.69 | 848.14 | 854.14 | 855.78 | 858.72 | |
| T* | 0.0383 | 1271.14 | 1299.86 | 1312.24 | 1316.04 | 1317.68 | 1320.13 | |
| T* | 0.0425 | 1385.24 | 1414.58 | 1427.24 | 1430.02 | 1431.76 | 1433.69 | |
| T* | 0.0466 | 1182.72 | 1210.64 | 1225.78 | 1230.98 | 1232.04 | 1234.96 | |
| T* | 0.0508 | 713.38 | 731.68 | 742.87 | 747.12 | 748.03 | 750.34 | |
| RMSE | 40.7741 | 19.1179 | 7.1300 | 3.3248 | 2.1458 | − | ||
| cv% | 5.098 | 2.390 | 0.891 | 0.415 | 0.268 | − | ||
| R2 | 0.998243 | 0.999613 | 0.999946 | 0.999988 | 0.999995 | − | ||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarbu, I.; Iosif, A. Numerical Simulation of the Laminar Forced Convective Heat Transfer between Two Concentric Cylinders. Computation 2017, 5, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5020025
Sarbu I, Iosif A. Numerical Simulation of the Laminar Forced Convective Heat Transfer between Two Concentric Cylinders. Computation. 2017; 5(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarbu, Ioan, and Anton Iosif. 2017. "Numerical Simulation of the Laminar Forced Convective Heat Transfer between Two Concentric Cylinders" Computation 5, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5020025
APA StyleSarbu, I., & Iosif, A. (2017). Numerical Simulation of the Laminar Forced Convective Heat Transfer between Two Concentric Cylinders. Computation, 5(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation5020025







