Estimation Parameters of Dependence Meta-Analytic Model: New Techniques for the Hierarchical Bayesian Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Original HBLD Model and Data
2.2. The Hierarchical Bayesian Linear Dependence (HBLD) Model
3. Bayesian Analysis
3.1. Posterior Analysis of HBLD Model Using Gibb Sampler
3.1.1. Conditional Prior Distribution of Given and
3.1.2. Conditional Prior Distribution of Given
3.1.3. Conditional Prior Distribution of
3.1.4. Conditional Posterior Distribution of Given and
3.1.5. Conditional Posterior Distribution of given and
3.1.6. Conditional Posterior Distribution of Given and
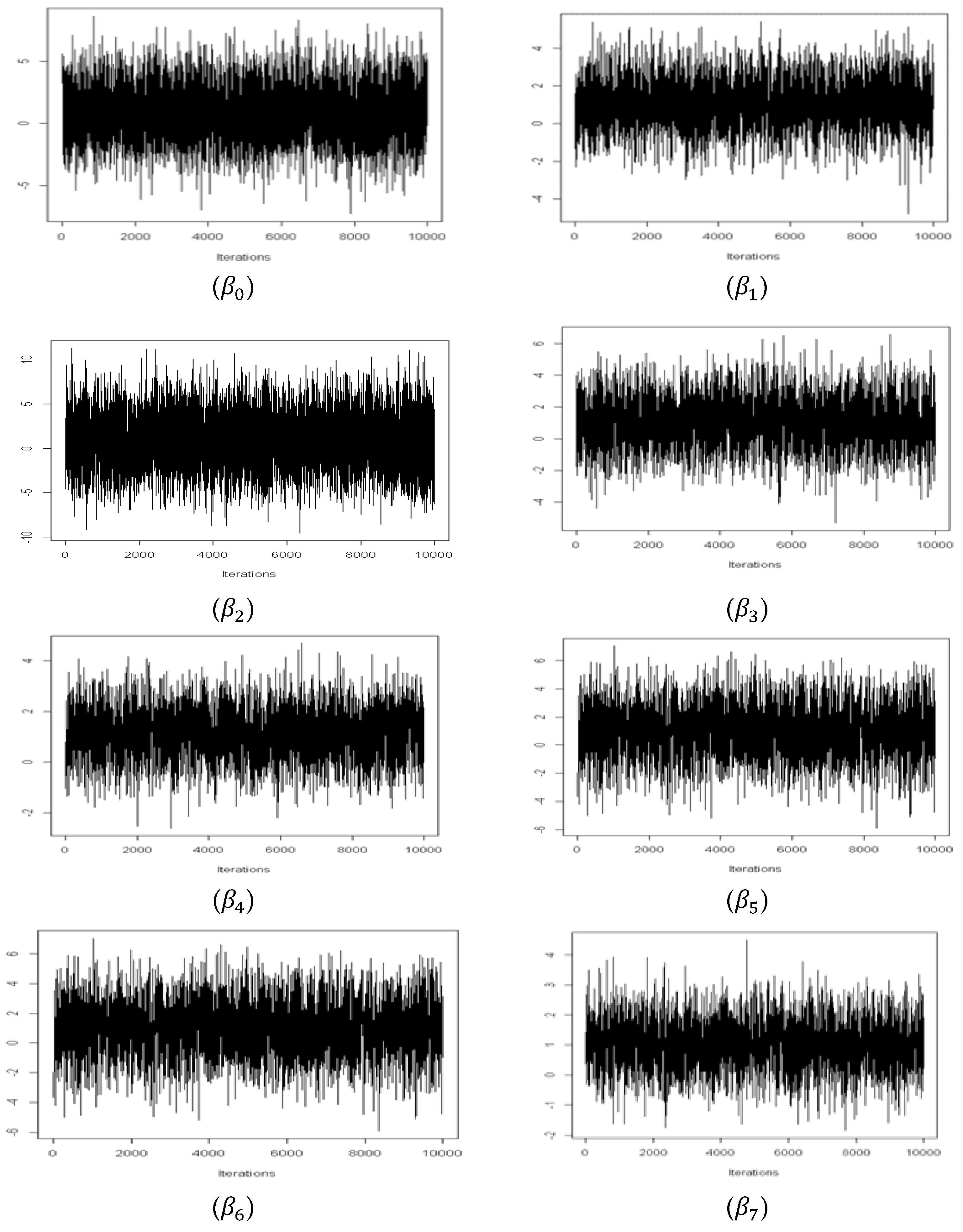
3.2. Gibbs Sampler Algorithm for the HBLD Model
- Let denote the starting point of a Markov chain. The value of these starting points can be randomly drawn from a starting distribution or simply chosen deterministically. Let j = 1, 2, …, t, where t is the number of iterations, i = 1, 2, …, n, n is the number of studies and k = 0, 1, …, p − 1, for p is the number of covariates.
- , given and , is generated using , where and are defined in Equations (14) and (15), respectively. and are defined in Equations (12) and (11).
- , given and , is generated using , where and are defined in Equations (A1) and (A2), respectively. and are defined in Equations (19) and (20).
- , given , is generated using .
- Steps 2–4 are repeated until the chains reached convergence.
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Simulation Study
- We fix the value of a positive real number ().
- We fix matrices and where p is the number of covariates. We then generate the vector of parameters from the multivariate normal distribution. The mean is and the variance–covariance matrix is .
- We construct the matrix and identity matrix (). We then generate parameters from the multivariate normal distribution, with mean and variance–covariance matrix
- Finally, we fix the variance–covariance matrix (). We then generate the effect size vector () from the multivariate normal distribution, with mean and variance–covariance matrix ().
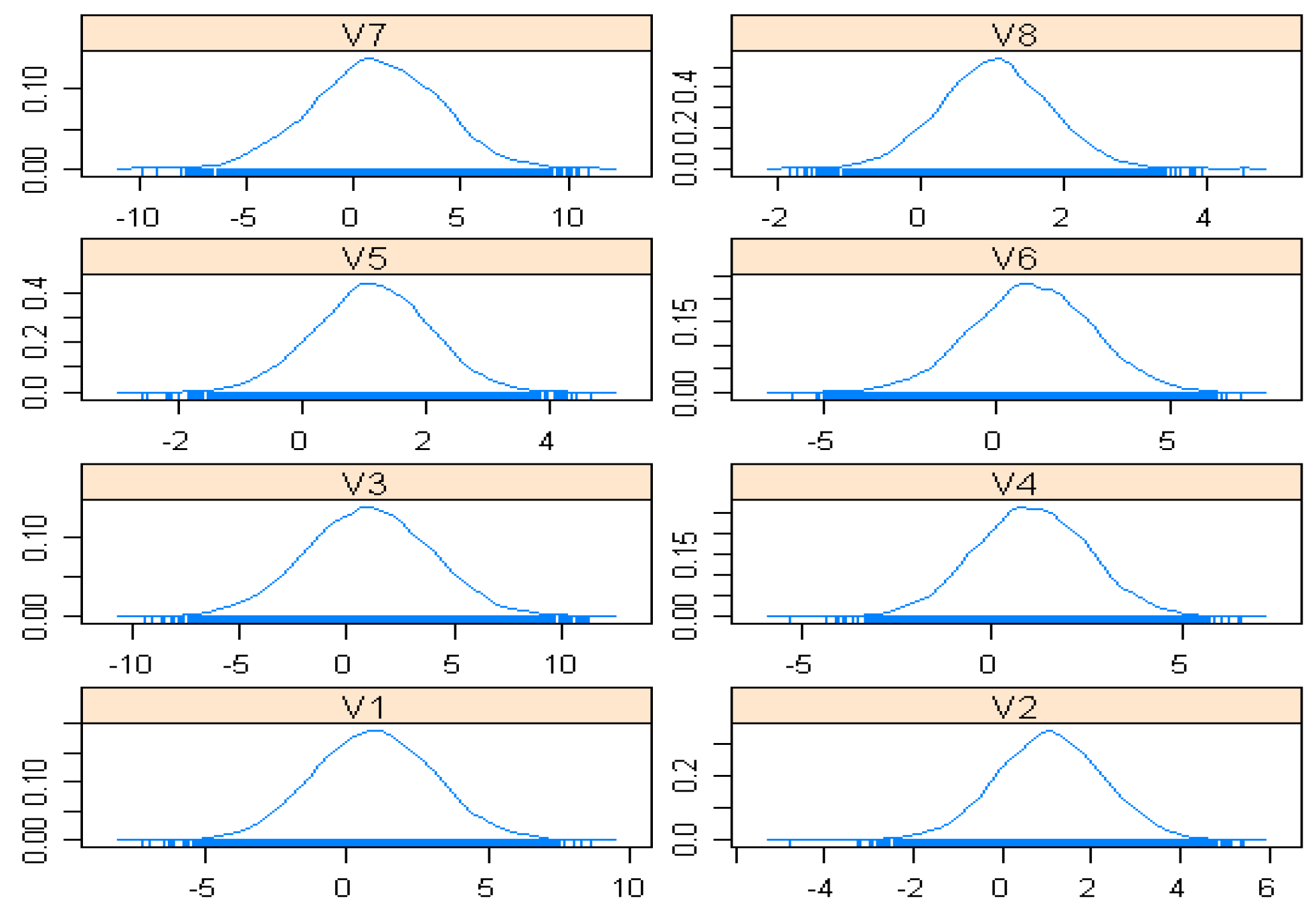
4.1.1. Estimation of Parameters
4.1.2. Estimation Results
4.2. Case Study: Application of the HBLD Model to the Native Language Vocabulary Data
4.2.1. Estimation of Parameters
4.2.2. Estimation Results
5. Prior Sensitivity Analysis
5.1. Sensitivity Analysis of the HBLD Model
5.1.1. Posterior Analysis of the HBLD Model Using Metropolis within Gibbs
- (a)
- It is proposed that ~Gamma ().
- (b)
- The acceptance ratio for the parameter is as follows:
- (c)
- The parameter U is sampled from .
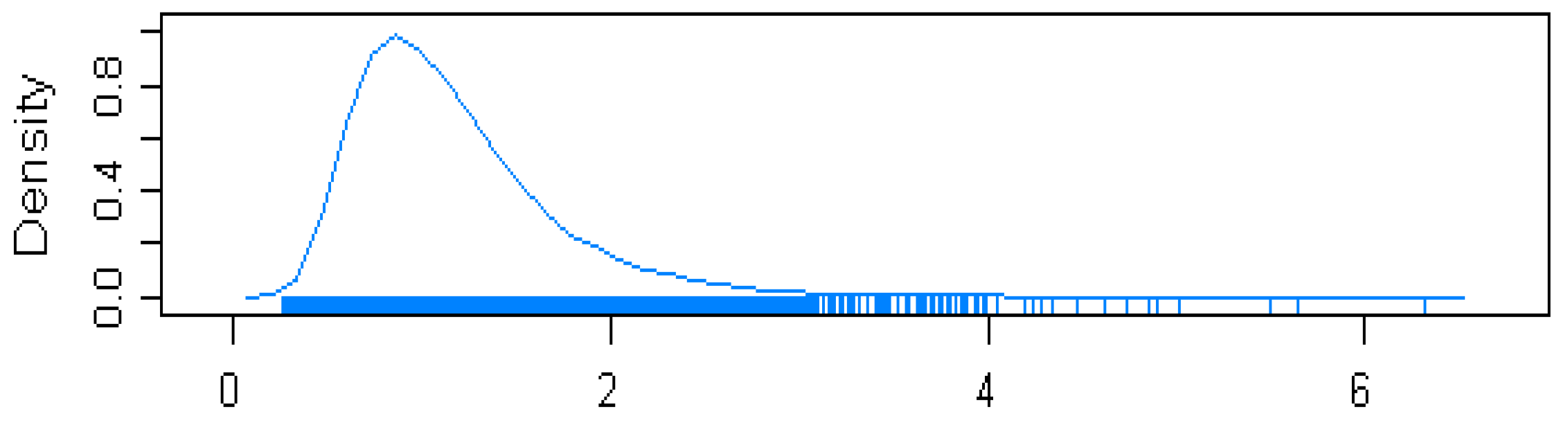
5.1.2. Estimation of Parameters
5.1.3. Estimation Results
5.2. Application of the HBLD Model to the Native Language Vocabulary Data: Metropolis within Gibbs
5.2.1. Estimation of Parameters
5.2.2. Estimation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Cheung, M.W.L. Modeling Dependent Effects Sizes with Three-Level Meta-Analysis: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Psychol. Methods 2014, 19, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noortgate, W.F.; Lopez, J.A.L.; Martinez, F.M.; Meca, J.S. Three Level Meta-Analysis of Dependent Effects Sizes. Behav. Res. 2013, 36, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziani, R.; Venturini, S. A Bayesian Approach to Discrete Multiple Outcome Network Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaidi; Nur, D.; Hudson, I.; Stojanovski, E. Bayesian Analysis of Meta-Analytic Models Incorporating Dependency: New Approaches for the Hierarchical Bayesian Delta-Splitting Model. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.R.; Taylor, A.M. Hierarchical Dependence in Meta-Analysis. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2009, 34, 46–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.R.; Nicholas, G. metahdep: Meta-analysis of hierarchically dependent gene expression studies. Appl. Note 2009, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chib, S.; Greenberg, J. Understanding the Metropolis-Hasting algorithm. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2005, 9, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Carlin, J.B.; Stern, H.S.; Rubin, D. Bayesian Data Analysis; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Junaidi; Nur, D.; Stojanovski, E. Bayesian Estimation of a Meta-analysis model using Gibbs sampler. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual ASEARC Conference, 2–3 February 2012, Wollongong, NSW, Australia; University of Wollongong: Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 2012; Available online: http://ro.uow.edu.au/asearc/6 (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Gilks, W.R.; Richardson, S.; Spiegelhalter, D.J. Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hoff, P.D. A First Course in Bayesian Statistical Methods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, R.B.; Meyer, R. Non-linear state modelling of fisheries biomass dynamics by using Metropolis-Hasting within-Gibbs sampling. Appl. Statist. 2000, 49, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, K.R.; Gillies, C.L.; Lambert, P.C. Meta-Analysis of Heterogeneously Reported Trials Assessing Change from Baseline. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 3823–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pei, J. An assessment of a TNF polymorphic marker for the risk of HCV infection: Meta-analysis and a new clinical study design. Am. Stat. 2009, 49, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohoo, I.; Stryhn, H. Evaluation of underlying risk as a source of heterogeneity in meta-analyses: A simulation study of Bayesian and frequentist implementations of three models. Prev. Vet. Med. 2007, 81, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnisch, J.; Mansmann, U.; Heinrich-Weltzien, R.; Hickel, R. Longevity of materials for pit and fissure sealing-Results from a meta-analysis. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, A.; Loyce, C.; Makowski, D. Assessment of the quality of meta-analysis in agronomy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 148, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengersen, K.L.; Tweedie, R.L.; Biggerstaff, B. The impact of method choice in meta-analysis. Aust. J. Stat. 1995, 37, 19–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.G.; Wang, S.; Smith, B.J.; Jacobson, T.A. Meta-Analysis of the Relationship Between Non-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Reduction and Coronary Heart Disese Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwood, J.M.; Gurian, P.L.; Lee, R.; Thran, B. Variance In Bacillus Anthracis Virulance Assessed Through Bayesian Hierarchical Dose-Response Modelling. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert-Norton, L.; Wilson, R.; Stevens, J.R.; Beard, K.H. A Meta-Analytic Review of Corridor Effectiveness. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, D.; Barrett, J.; Sweeting, M.; Thompson, S. Fully Bayesian hierarchical modelling in two stages, with application to meta-analysis. Appl. Statist. 2013, 62, 551–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.R. Meta-Analytic Approaches for Microarray Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Besag, J.; Green, D.; Higdon, D.; Mengersen, K.L. Bayesian Computation and Stochastic System. Stat. Med. 1995, 14, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, P. Bayesian Statistical Modelling; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dumouchel, W.H.; Harris, J.E. Bayesian methods for combining the results of cancer studies in humans and other species. Bayesian Stat. 1983, 4, 338–341. [Google Scholar]
- Glickman, M.E.; Van Dyk, D.A. Basic Bayesian methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 404, 319–338. [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe, P.J.; Reck, B.H.; Sun, J.; Platek, G.T.; Verzilli, C.; Kader, A.K.; Kim, S.T.; Hsu, F.C.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S.L.; et al. A Comparison of Bayesian and Frequentist Approaches to Incorporating External Information for the Prediction of Prostate Cancer Risk. Genet. Epidemiol. 2012, 36, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.P.; Casella, G. Monte Carlo Statistical Methods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Flury, B. A First Course in Multivariarte Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Geweke, J. Evaluating the accuracy of sampling based approaches to the calculation of posterior moments. In Bayesian Statistics 4; Bernando, J.M., Berger, J.O., Dawid, A.P., Smith, A.F.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 169–193. [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger, P.; Welch, P.D. Simulation run length control in the presence of an initial transient. Oper. Res. 1983, 31, 1109–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E.; Lewis, S.M. How many iterations in the Gibss sampler? In Bayesian Statistics 4; Bernando, J.M., Berger, J.O., Dawid, A.P., Smith, A.F.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 763–773. [Google Scholar]
- Junaidi; Nur, D.; Stojanovski, E. Prior Sensitivity Analysis for a Hierarchical Model. In Proceedings of the Fourth Annual ASEARC Conference, 17–18 February 2011, Parramatta, NSW, Australia; Paper 13; University of Western Sydney: Parramatta, NSW, Australia, 2011; Available online: http://ro.uow.edu.au/asearc/24 (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Lambert, P.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Burton, P.R.; Abrams, K.R.; Jones, D.R. How vague is vague? A simulation study of the impact of the use of vague prior distribution in MCMC using WinBUGS. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 2401–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumouchel, W.H.; Normand, S.L. Computer-modelling and graphical strategies for meta-analysis. In Statistical Methodology in the Pharmeceutical Sciences; Dumouchel, W.H., Berry, D.A., Eds.; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 127–178. [Google Scholar]
- Böhning, D.; Hennig, C.; McLachlan, G.J.; McNicholas, P.D. The 2nd special issue on advances in mixture models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 71, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopantelis, E.; Reeves, D. Performance of statistical methods for meta-analysis when true study effects are non-normally distributed: A simulation study. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2012, 21, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


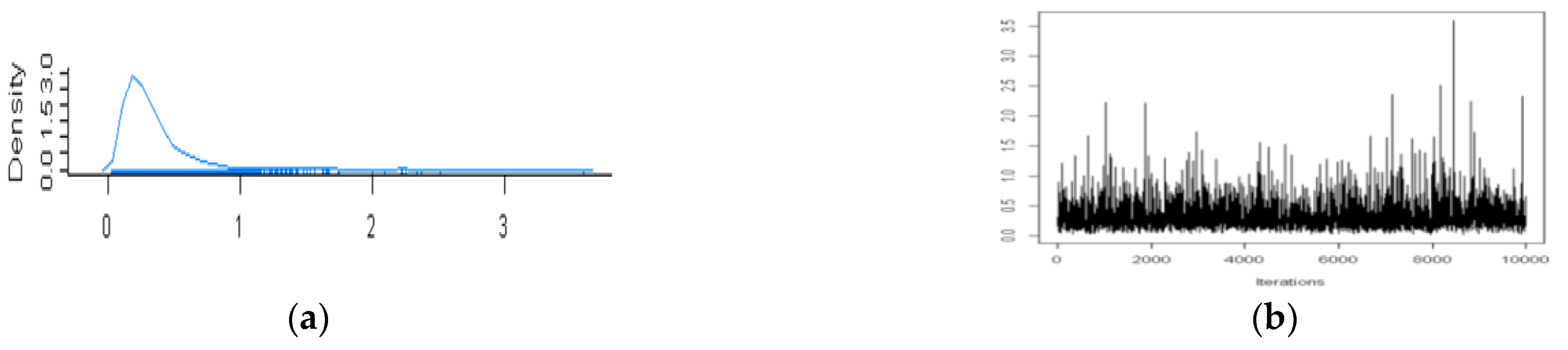
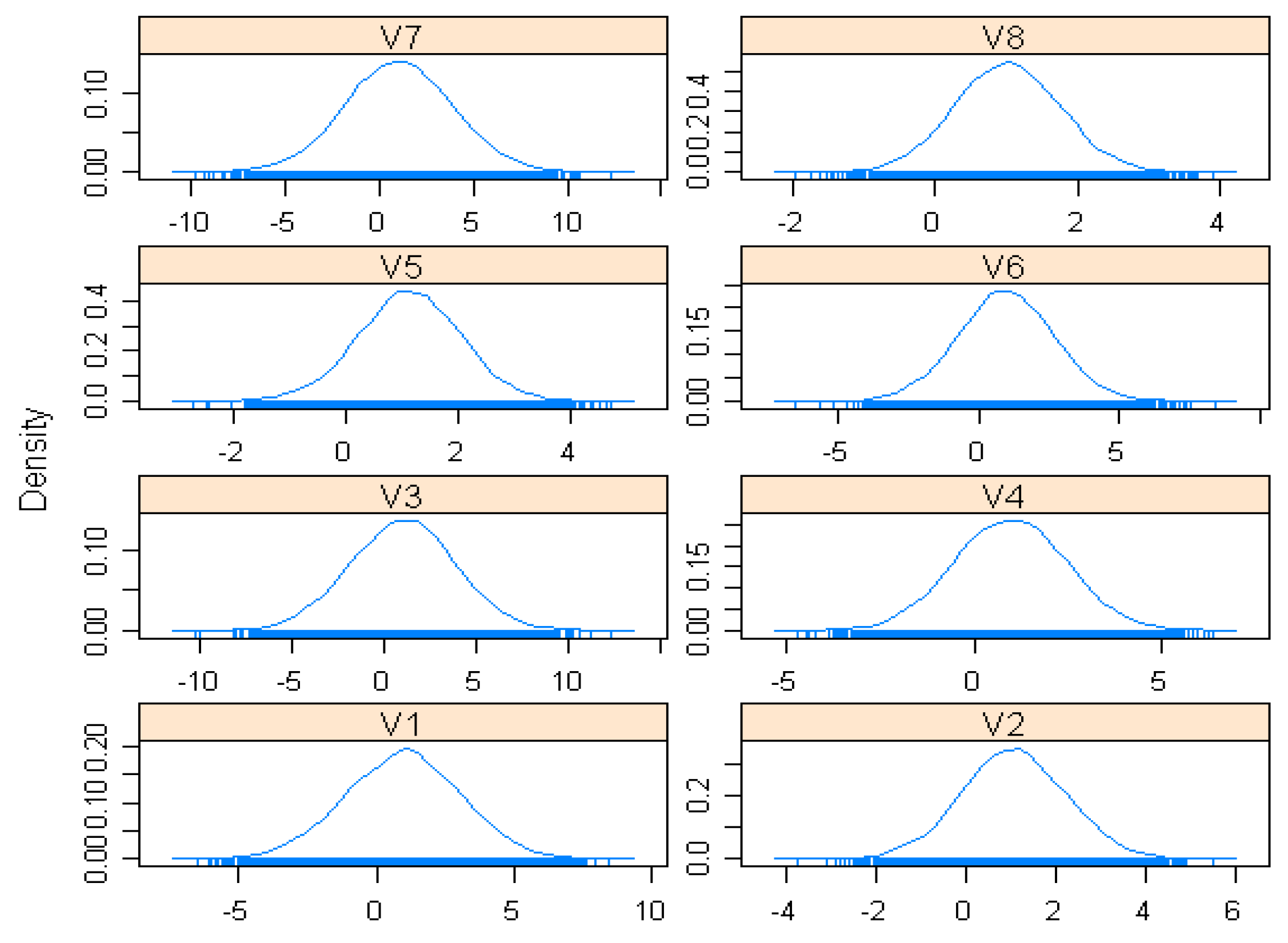
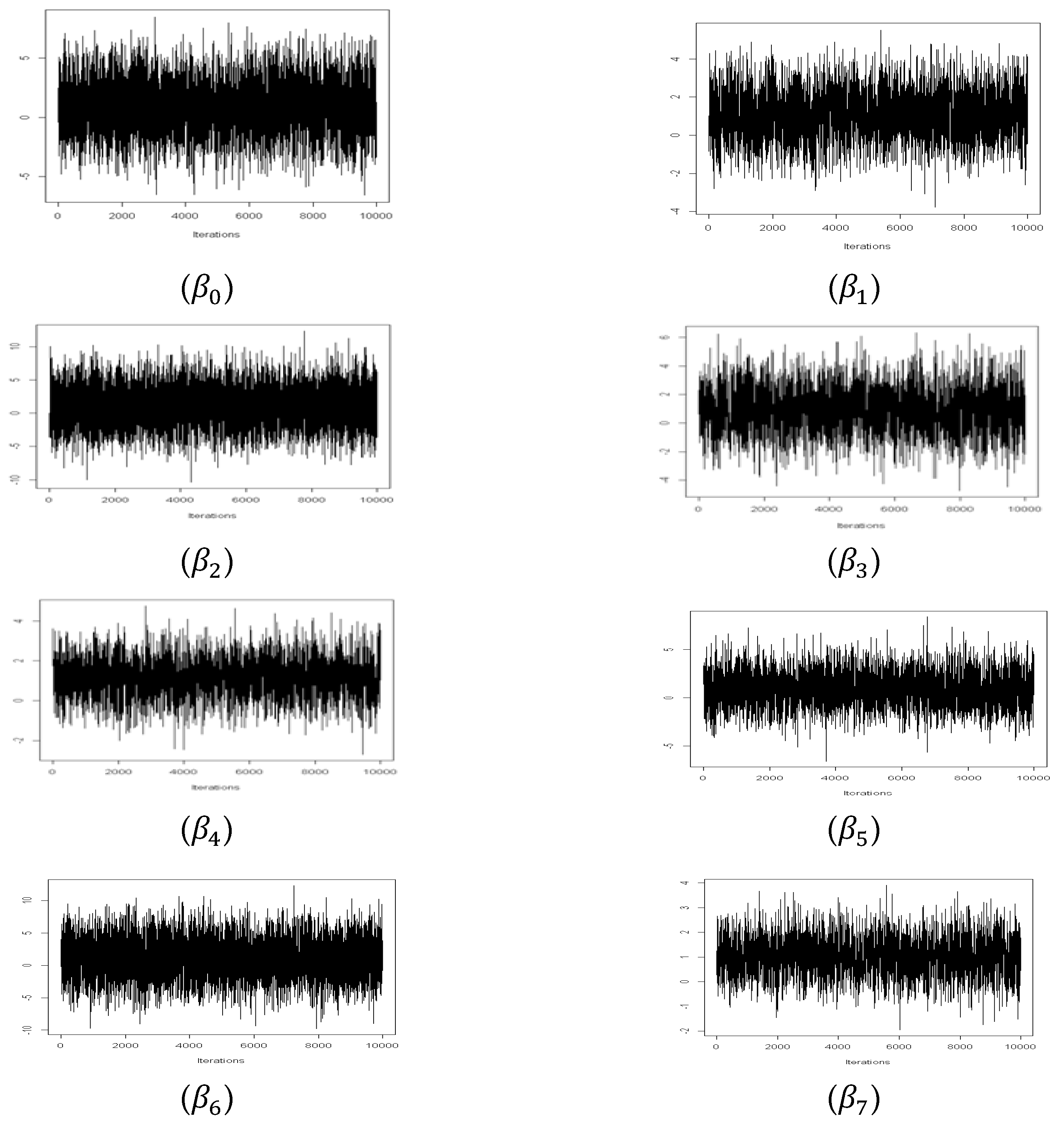


| = 1.2 | |||
| True value of , …, | |||
| = 1.0275 | = 0.9212 | = 0.8836 | = 0.0710 |
| = 1.2837 | = 1.0231 | = 0.8390 | = 1.0911 |
| True value of , …, | |||
| = 4.3449 | = 6.1647 | = 4.3748 | = 4.8439 |
| = 8.5522 | = 8.6170 | = 7.6657 | = 4.4449 |
| = 6.8181 | = 5.0117 | = 5.1228 | = 6.9209 |
| = 4.3826 | = 4.8544 | = 8.0901 | = 7.9717 |
| = 7.7095 | = 4.3726 | = 5.0682 | = 4.9958 |
| = 4.4190 | = 4.3480 | = 4.3539 | = 4.8056 |
| = 8.6780 | = 8.6407 | = 7.6830 | = 4.4835 |
| = 5.0045 | = 5.0403 | ||
| Simulated effect sizes of , …, | |||
| = 4.3774 | 6.1514 | 4.4040 | 4.8722 |
| = 8.6103 | 8.6298 | 7.6647 | 4.4720 |
| 6.7828 | 5.0561 | 5.1507 | 6.9661 |
| = 4.4138 | 4.8214 | 8.0288 | 7.9404 |
| = 7.6861 | 4.3559 | 5.0994 | 5.0429 |
| = 4.3912 | 4.3873 | 4.3688 | 4.8764 |
| = 8.6233 | 8.6188 | 7.6678 | 4.4819 |
| 5.0411 | 5.0351 | ||
| Test Variable | Geweke | H–W | R–L |
|---|---|---|---|
| z-score −0.348 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.867 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.021 | Dependence factor (I) 1.49 | |
| z-score −0.2721 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.8316 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0641 | Dependence factor (I) 1.28 | |
| z-score −1.0362 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.3383 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0486 | Dependence factor (I) 1.65 | |
| z-score −1.0351 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.0643 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0706 | Dependence factor (I) 1.08 | |
| z-score −0.4734 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.1425 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0623 | Dependence factor (I) 1.77 | |
| z-score 0.5459 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.5384 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0391 | Dependence factor (I) 1.68 | |
| z-score 0.5796 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.5736 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0744 | Dependence factor (I) 2.56 | |
| z-score −0.5616 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.5231 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0751 | Dependence factor (I) 1.08 | |
| z-score −0.7367 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.7495 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0352 | Dependence factor (I) 2.84 |
| True Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| = 1.2 | = 1.17 with (0.4911, 2.4756) and 0.5304 | ||
| Estimated value of with the 95% CI and SD | |||
| Parameter estimates | 95 % CI | SD | |
| = 1.0275 | = 0.9488 | (−3.0529, 5.086) | 2.0928 |
| = 0.9212 | = 1.0829 | (−1.3224, 3.461) | 1.2063 |
| = 0.8836 | 1.0041 | (−4.7594, 6.696) | 2.9126 |
| = 1.0701 | 1.0365 | (−1.8536, 3.911) | 1.4685 |
| = 1.1283 | = 1.1428 | (−0.6644, 2.947) | 0.9185 |
| = 1.0231 | = 1.0100 | (−2.4272, 4.338) | 1.7186 |
| = 0.8390 | = 1.0321 | (−4.6317, 6.568) | 2.8615 |
| = 1.0911 | 1.0252 | (−0.4668, 2.517) | 0.7603 |
| , …, | Estimated value of with the 95% CI and SD | ||
| = 4.3449 | = 4.349 | (2.145, 6.535) | 1.1095 |
| = 6.1647 | = 6.081 | (3.563, 8.586) | 1.2684 |
| = 4.3748 | = 4.385 | (2.491, 6.223) | 0.9371 |
| 4.8439 | 4. 864 | (3.012, 6.739) | 0.9396 |
| = 8.5522 | = 8.641 | (6.578, 10.646) | 1.0190 |
| = 8.6170 | = 8.641 | (7.221, 10.046) | 0.7154 |
| = 7.6657 | = 7.624 | (5.763, 9.500) | 0.9375 |
| = 4.4449 | = 4.453 | (2.000, 6.997) | 1.2566 |
| = 6.8181 | = 6.754 | (3.823, 9.767) | 1.5146 |
| = 5.0117 | = 5.050 | (2.739, 7.391) | 1.1675 |
| = 5.1228 | = 5.170 | (3.609, 6.710) | 0.7923 |
| = 6.9209 | = 6.948 | (5.237, 8.691) | 0.8780 |
| = 4.3826 | = 4.416 | (2.316, 6.545) | 1.0711 |
| = 4.8544 | = 4.816 | (2.480, 7.086) | 1.1663 |
| = 8.0901 | = 8.004 | (5.467, 10.610) | 1.2948 |
| = 7.9717 | = 7.895 | (5.233, 10.560) | 1.3355 |
| = 7.7095 | = 7.655 | (5.507, 9.779) | 1.0880 |
| = 4.3726 | = 4.362 | (2.355, 6.352) | 1.0209 |
| = 5.0682 | = 5.105 | (3.413, 6.857) | 0.8603 |
| = 4.9958 | = 5.046 | (3.191, 6.888) | 0.9230 |
| = 4.4190 | = 4.396 | (3.105, 5.717) | 0.6644 |
| = 4.3480 | = 4.388 | (2.714, 6.050) | 0.8451 |
| = 4.3539 | = 4.367 | (2.161, 6.559) | 1.1104 |
| = 4.8056 | = 4.875 | (2.543, 7.324) | 1.1895 |
| = 8.6786 | = 8.621 | (6.908,10.327) | 0.8661 |
| = 8.6407 | = 8.614 | (7.219, 9.975) | 0.7026 |
| = 7.6830 | = 7.634 | (6.102, 9.158) | 0.7738 |
| = 4.4835 | = 4.480 | (1.850, 7.127) | 1.3389 |
| = 5.0045 | = 5.033 | (3.023, 7.089) | 1.0234 |
| = 5.0403 | = 5.017 | (3.610, 6.440) | 0.7170 |
| Test Variable | Geweke | H-W | R-L |
|---|---|---|---|
| z-score −1.527 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.204 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0086 | Dependence factor (I) 3.4 | |
| z-score 0.2917 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.483 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0012 | Dependence factor (I) 1.23 | |
| z-score −0.2912 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.834 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0066 | Dependence factor (I) 1.14 | |
| z-score −0.8820 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.465 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0039 | Dependence factor (I) 2.21 | |
| z-score −0.3594 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.720 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0048 | Dependence factor (I) 1.21 | |
| z-score 0.1667 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.804 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0034 | Dependence factor (I) 1.17 | |
| z-score −0.3995 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.769 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0047 | Dependence factor (I) 1.18 |
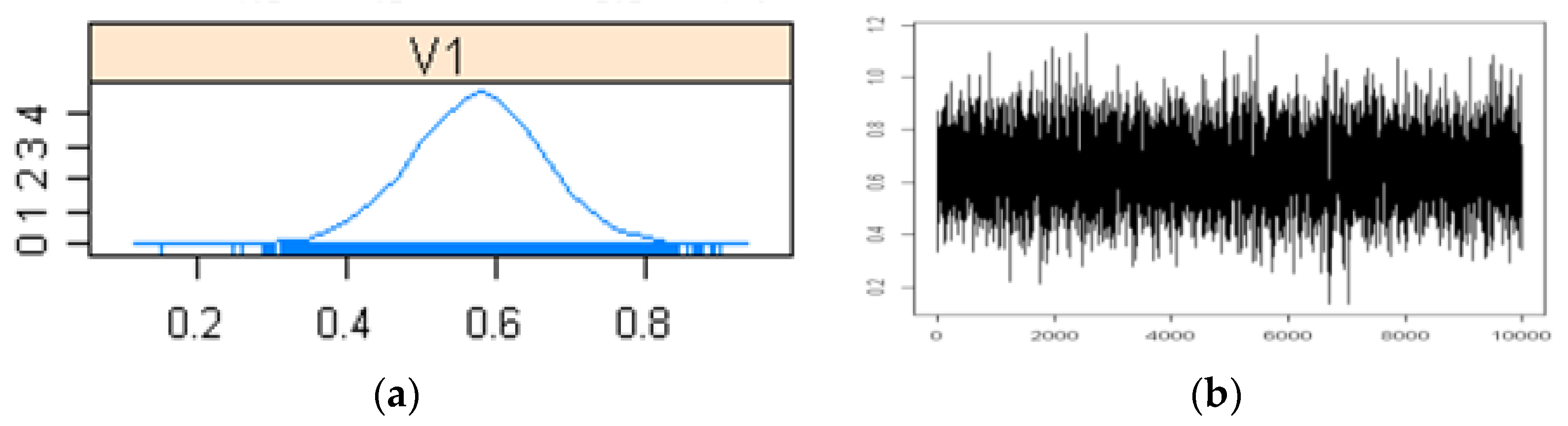
| = 0.3106, CI (0.0764, 0.8201), SD = 0.207 (Gibbs sampler) = 0.3054, CI (−0.0643, 0.6750), SD = 0.1848 ([5]) | ||
| Estimates results of with the 95% CI and SD | ||
| Parameter estimates | 95 % CI | SD |
| = 0.5756 (G-S) = 0.5769 ([5]) | (0.4037, 0.7444) (G-S) (0.2659, 0.8879) (Stevens [5]) | 0.0866 (G-S) 0.1555 ([5]) |
| = −0.9469 | (−1.9459, 0.1328) | 0.5264 |
| −0.2432 | (−0.7733, 0.2608) | 0.2623 |
| 0.2985 | (−0.3606, 0.9554) | 0.3347 |
| = 0.3710 | (−0.1175, 0.8474) | 0.2442 |
| = 0.5545 | (−0.0827, 1.2247) | 0.3329 |
| Test Variable | Geweke | H-W | R-L |
|---|---|---|---|
| z-score −1.702 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.29 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0275 | Dependence factor (I) 26.9 | |
| z-score −0.0771 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.479 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0658 | Dependence factor (I) 1.23 | |
| z-score 0.4396 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.266 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0492 | Dependence factor (I) 2.92 | |
| z-score 1.38061 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.968 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0700 | Dependence factor (I) 1.12 | |
| z-score −0.9961 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.536 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0701 | Dependence factor (I) 2.96 | |
| z-score −0.3347 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.469 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0415 | Dependence factor (I) 2.73 | |
| z-score −0.5931 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.435 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0708 | Dependence factor (I) 1.64 | |
| z-score 0.5017 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.488 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0766 | Dependence factor (I) 1.16 | |
| z-score 0.2488 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.143 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0356 | Dependence factor (I) 2.63 |
| True Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| = 1.2 | = 1.03 with (0.3366, 2.0239) and 0.4416 | ||
| Estimated value of with the 95% CI and SD | |||
| Parameter estimates | 95 % CI | SD | |
| = 1.0275 | = 0.9752 | (−3.2394, 5.074) | 2.1101 |
| = 0.9212 | = 1.0745 | (−1.2130, 3.387) | 1.1644 |
| = 0.8836 | 1.0145 | (−4.5127, 6.652) | 2.8453 |
| = 1.0701 | 0.9565 | (−1.9272, 3.881) | 1.4831 |
| = 1.1283 | = 1.1468 | (−0.6747, 2.914) | 0.9084 |
| = 1.0231 | = 0.9792 | (−2.3408, 4.316) | 1.6892 |
| = 0.8390 | = 1.0569 | (−4.5968, 6.699) | 2.8607 |
| = 1.0911 | 1.0242 | (−0.3861, 2.477) | 0.7322 |
| , …, | Estimated value of with the 95% CI and SD | ||
| = 4.3449 | = 4.352 | (2.330, 6.390) | 1.0198 |
| = 6.1647 | = 6.088 | (3.744, 8.465) | 1.2088 |
| = 4.3748 | = 4.404 | (2.634, 6.233) | 0.8922 |
| 4.8439 | = 4. 834 | (3.080, 6.598) | 0.8933 |
| = 8.5522 | = 8.591 | (6.633, 10.528) | 1.9829 |
| = 8.6170 | = 8.628 | (7.243, 9.985) | 0.7009 |
| = 7.6657 | = 7.644 | (5.842,9.400) | 0.9081 |
| = 4.4449 | = 4.461 | (2.073, 6.826) | 1.1911 |
| = 6.8181 | = 6.742 | (3.762, 9.671) | 1.4920 |
| = 5.0117 | = 5.021 | (2.895, 7.151) | 1.0734 |
| = 5.1228 | = 5.159 | (3.649, 6.688) | 0.7769 |
| = 6.9209 | = 6.950 | (5.280, 8.637) | 0.8628 |
| = 4.3826 | = 4.407 | (2.388, 6.413) | 1.0017 |
| = 4.8544 | = 4.759 | (2.567 6.922) | 1.0826 |
| = 8.0901 | = 8.003 | (5.578, 10.464) | 1.2199 |
| = 7.9717 | = 7.865 | (5.360, 10.309) | 1.2489 |
| = 7.7095 | = 7.682 | (5.671, 9.710) | 1.0331 |
| = 4.3726 | = 4.361 | (2.423, 6.267) | 0.9815 |
| = 5.0682 | = 5.068 | (3.473, 6.697) | 0.8142 |
| = 4.9958 | = 5.024 | (3.243, 6.827) | 0.8984 |
| = 4.4190 | = 4.383 | (3.127, 5.644) | 0.6412 |
| = 4.3480 | = 4.380 | (2.802, 5.975) | 0.8066 |
| = 4.3539 | = 4.358 | (2.217, 6.440) | 1.0441 |
| = 4.8056 | = 4.824 | (2.593, 7.017) | 1.0996 |
| = 8.6786 | = 8.629 | (6.993,10.270) | 0.8288 |
| = 8.6407 | = 8.609 | (7.258, 9.958) | 0.6854 |
| = 7.6830 | = 7.645 | (6.147, 9.132) | 0.7550 |
| = 4.4835 | = 4.459 | (1.893, 6.928) | 1.2707 |
| = 5.0045 | = 5.018 | (3.117, 6.941) | 0.9602 |
| = 5.0403 | = 5.008 | (3.655, 6.379) | 0.6928 |
| Parameters | True Value | Gibbs Sampler Algorithm (Inverse Gamma) | Metropolis within Gibbs (Log-Logistic) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean with CI | SD | Mean with CI | SD | ||
| (intercept) | 1.0275 | 0.9488 (−3.0529, 5.086) | 2.09 | 0.9752 (−3.2394, 5.074) | 2.11 |
| 1.2 | 1.17 (0.4911, 2.4756) | 0.53 | 1.03 (0.3366, 2.0239) | 0.44 | |
| Test Variable | Geweke | H-W | R-L |
|---|---|---|---|
| z-score 1.242 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.343 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0139 | Dependence factor (I) 24.5 | |
| z-score 0.065 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.4156 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0027 | Dependence factor (I) 1.16 | |
| z-score −0.4372 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.0903 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0133 | Dependence factor (I) 1.14 | |
| z-score 1.0128 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.6255 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.008 | Dependence factor (I) 1.15 | |
| z-score −0.9468 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.3958 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0097 | Dependence factor (I) 1.29 | |
| z-score −0.1164 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.5035 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0068 | Dependence factor (I) 1.20 | |
| z-score −0.6779 | Stationarity test: passed p-value: 0.5048 Half-width test: passed Half-width: 0.0095 | Dependence factor (I) 1.18 |
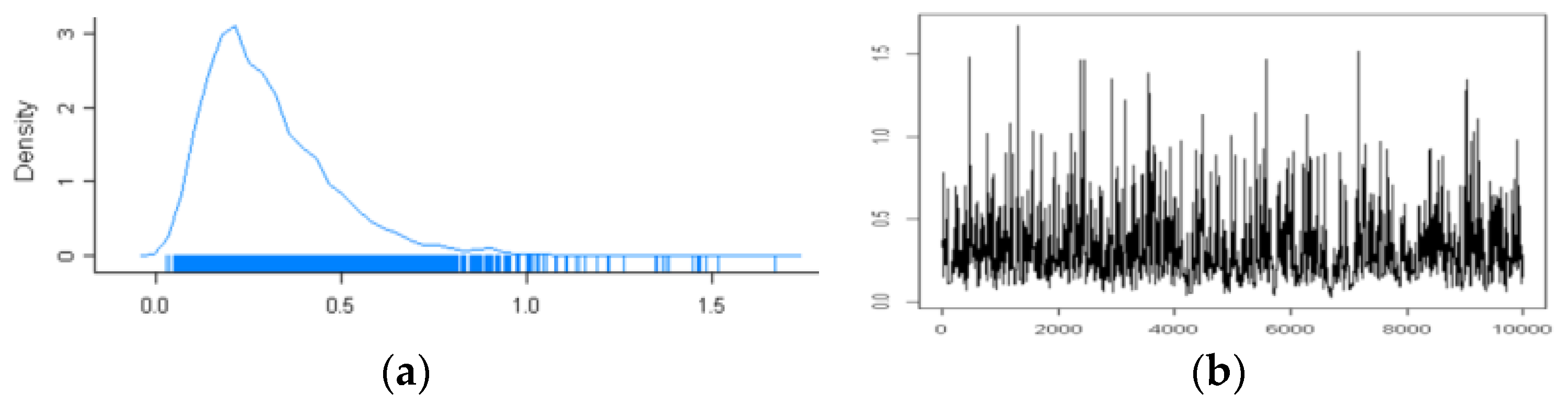
| = 0.3044, CI (0.0817, 0.7446), SD = 0.1743 (Metropolis within Gibbs) = 0.3054, CI (−0.0643, 0.6750), SD = 0.1848 ([5]) | ||
| Estimates results of with the 95% CI and SD | ||
| Parameter estimates | 95 % CI | SD |
| = 0.5758 (MwG) = 0.5769 ([17]) | (0.4025, 0.7481) (MwG) (0.2659, 0.8879) ([17]) | 0.0877 (MwG) 0.1555 ([17]) |
| = −0.9445 | (−1.9556, 0.1406) | 0.5206 |
| −0.2432 | (−0.7781, 0.2676) | 0.2635 |
| 0.3000 | (−0.3740, 0.9483) | 0.3324 |
| = 0.3714 | (−0.1107, 0.8357) | 0.2427 |
| = 0.5590 | (−0.0702, 1.2309) | 0.3301 |
| Parameter | Steven and Taylor [5] | Gibbs Sampler Algorithm (Inverse Gamma) | Metropolis within Gibbs (Log-Logistic) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean with CI | SD | Mean with CI | SD | Mean with CI | SD | |
| (intercept) | 0.5769 (0.2659, 0.8879) | 0.1555 | 0.5756 (0.4036, 0.7444) | 0.0866 | 0.5758 (0.4025, 0.7481) | 0.0877 |
| 0.3054 (−0.0643, 0.6750) | 0.1848 | 0.3106 (0.0764, 0.8201) | 0.207 | 0.3044 (0.0817, 0.744) | 0.1743 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Junaidi; Nur, D.; Hudson, I.; Stojanovski, E. Estimation Parameters of Dependence Meta-Analytic Model: New Techniques for the Hierarchical Bayesian Model. Computation 2022, 10, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10050071
Junaidi, Nur D, Hudson I, Stojanovski E. Estimation Parameters of Dependence Meta-Analytic Model: New Techniques for the Hierarchical Bayesian Model. Computation. 2022; 10(5):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10050071
Chicago/Turabian StyleJunaidi, Darfiana Nur, Irene Hudson, and Elizabeth Stojanovski. 2022. "Estimation Parameters of Dependence Meta-Analytic Model: New Techniques for the Hierarchical Bayesian Model" Computation 10, no. 5: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10050071
APA StyleJunaidi, Nur, D., Hudson, I., & Stojanovski, E. (2022). Estimation Parameters of Dependence Meta-Analytic Model: New Techniques for the Hierarchical Bayesian Model. Computation, 10(5), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10050071






