Model for the Detection of Falls with the Use of Artificial Intelligence as an Assistant for the Care of the Elderly
Abstract
1. Introduction
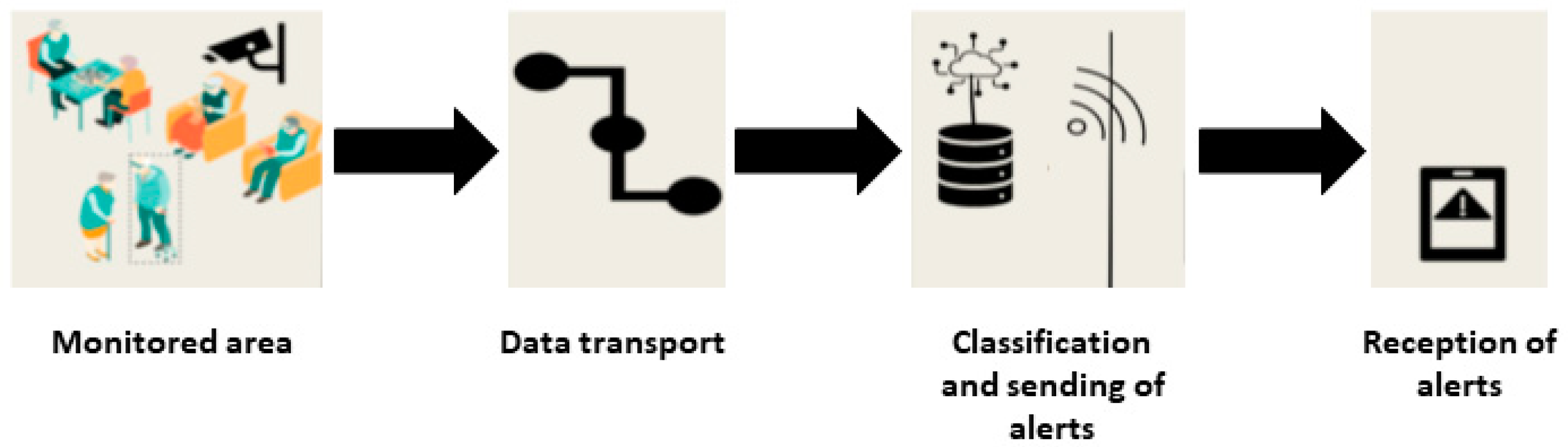
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the Environment and Its Needs
2.2. State of the Matter
2.3. Method
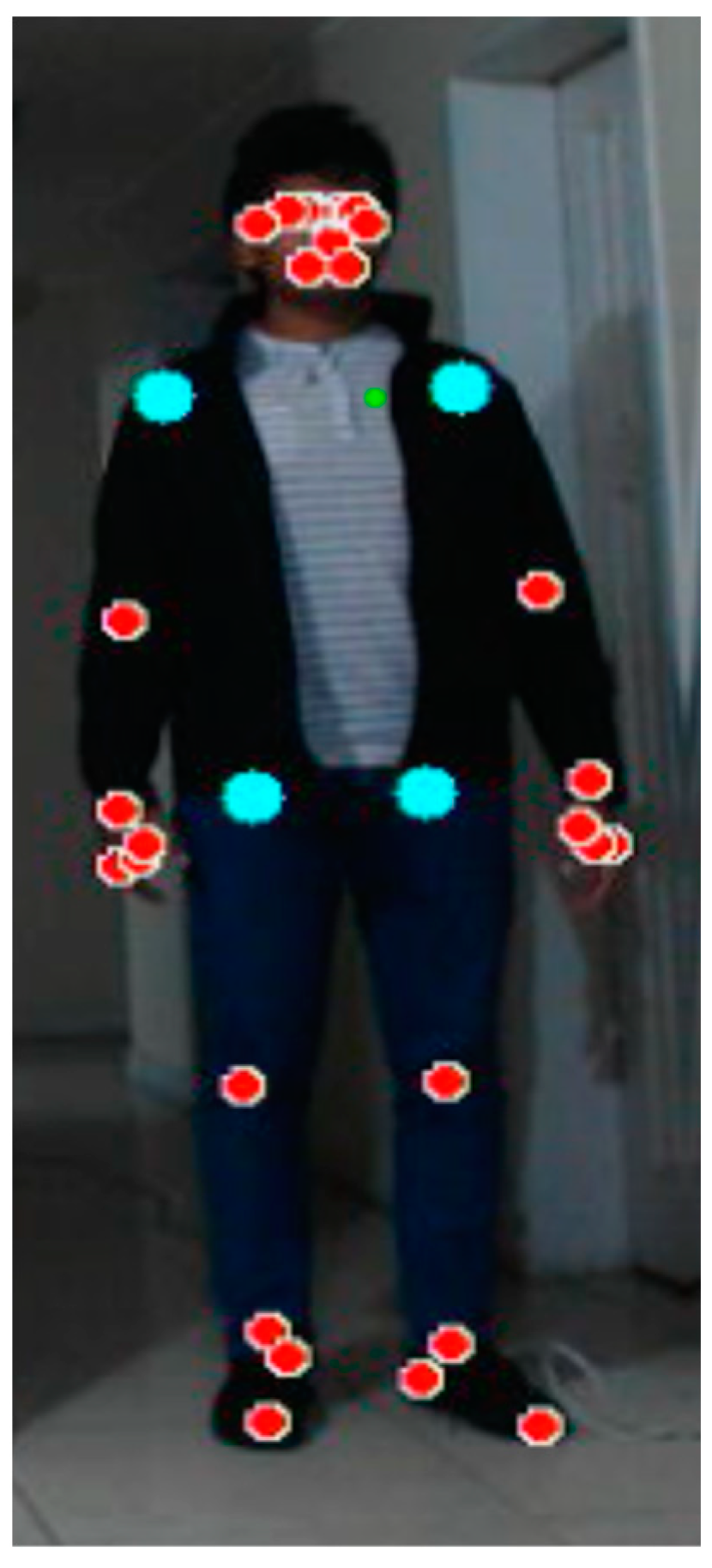
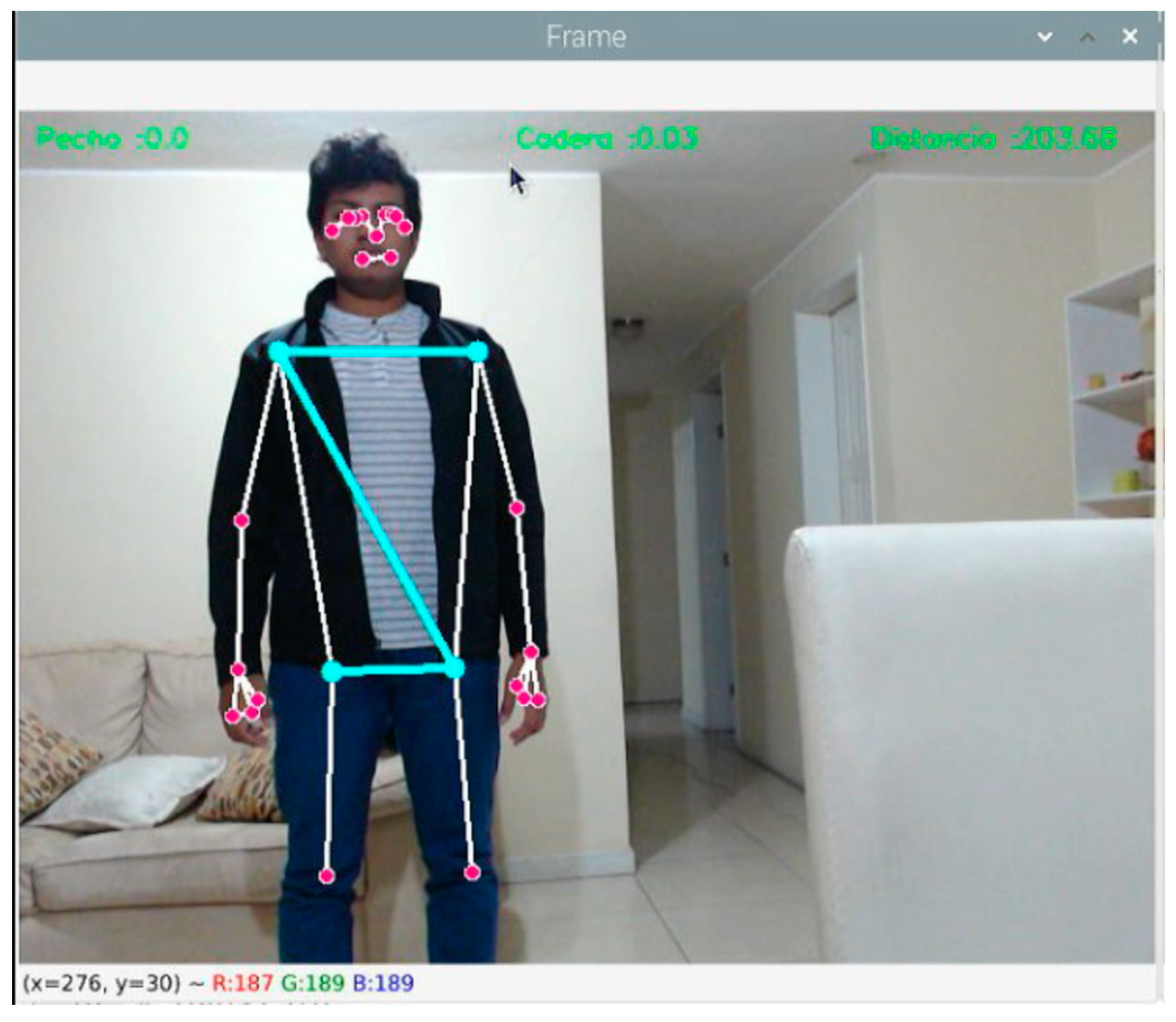
2.4. Development of the Fall Detection Model
- Walking, −90–28 cm/s
- Sit, 25–130 cm/s
- Crouch, 150–300 cm/s
- Falling, 285–535 cm/s
- 1 walk action
- 2 actions sit
- 3 action crouches
- 4 fall action
- print (’Fall detected’)
- cv2.imwrite (’/home/local/Desktop/Program/ImagenGenerada.jpg’, frame)
- cv2.putText (frame, ‘Fall detected’, (10, 100), font, fontScale, (255, 0, 0), thickness, cv2.LINEAA, False)
- bot.send message (chat, ”Fall detected in the room”)
- bot.send message (chat, now)
- bot.send photo (chat, img)
3. Results
- A = Accuracy
- S = Sensitivity
- S1 = Specificity
- TP = True positive
- FP = False positive
- FN = False negative
- TN = True negative
System Evaluation and Adjustments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abobakr, A.; Hossny, M.; Nahavandi, S. A Skeleton-Free Fall Detection System from Depth Images Using Random Decision Forest. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 12, 2994–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Mohanty, M.N.; Patnaik, S. A Comparative Analysis on Edge Detection of Colloid Cyst: A Medical Imaging Approach. Stud. Comput. Intell. 2012, 395, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierleoni, P.; Belli, A.; Maurizi, L.; Palma, L.; Pernini, L.; Paniccia, M.; Valenti, S. A Wearable Fall Detector for Elderly People Based on AHRS and Barometric Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6733–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Georgi, N.; Abbas, M.; le Bouquin Jeannès, R. A Highly Reliable Wrist-Worn Acceleration-Based Fall Detector. In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, A Coruña, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Hong, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Hyeon, T.; Lee, M.; Kim, D.H. Wearable Fall Detector Using Integrated Sensors and Energy Devices. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censos. La Población Adulta Mayor Se Triplicaría En Los Próximos 40 Años. Available online: https://inec.cr/noticias/la-poblacion-adulta-mayor-se-triplicaria-los-proximos-40-anos (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Carmona Valdés, S.E. El Bienestar Personal en el Envejecimiento; Ciencias Sociales de la Universidad Iberoamericana: Distrito Federal, México, 2009; Volume 3, pp. 48–65. [Google Scholar]
- Meeradevi, T.; Vikash Kumar, V.; Subhiksa, S.; Rajhan, V. Wearable Fall Detector for Elderly People; Innovations in Information and Communication Technology Series; Kongu Engineering College: Bengaluru, India, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Lima, A.L.; Smits, T.; Darweesh, S.K.L.; Valenti, G.; Milosevic, M.; Pijl, M.; Baldus, H.; de Vries, N.M.; Meinders, M.J.; Bloem, B.R. Home-Based Monitoring of Falls Using Wearable Sensors in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, C.; Igual, R.; García-Magariño, I.; Plaza, I.; Azuara, G. Combining Novelty Detectors to Improve Accelerometer-Based Fall Detection. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Gomes, D.; Sousa, I.; Cardoso, J.S. Automated Development of Custom Fall Detectors: Position, Model and Rate Impact in Performance. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5465–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaccour, K.; Darazi, R.; el Hassani, A.H.; Andres, E. From Fall Detection to Fall Prevention: A Generic Classification of Fall-Related Systems. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos García, D.; López Ariztegui, N.; Cubo, E.; Vinagre Aragón, A.; García-Ramos, R.; Borrué, C.; Fernández-Pajarín, G.; Caballol, N.; Cabo, I.; Barrios-López, J.M.; et al. Clinical Utility of a Personalized and Long-Term Monitoring Device for Parkinson’s Disease in a Real Clinical Practice Setting: An Expert Opinion Survey on STAT-ONTM. Neurologia 2020, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odunmbaku, A.; Rahmani, A.M.; Liljeberg, P.; Tenhunen, H. Elderly Monitoring System with Sleep and Fall Detector. In Proceedings of the Internet of Things. IoT Infrastructures Second International Summit, IoT 360° 2015, Rome, Italy, 27–29 October 2015; Volume 169. [Google Scholar]
- de Ramón-Fernández, A.; Ruiz-Fernández, D.; Marcos-Jorquera, D.; Gilart-Iglesias, V.; Vives-Boix, V. Monitoring-Based Model for Personalizing the Clinical Process of Crohn’s Disease. Sensors 2017, 17, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeuriot, L.; Pasi, G.; Viviani, M.; Villegas-Ch, W.; Molina, S.; de Janón, V.; Montalvo, E.; Mera-Navarrete, A. Proposal of a Method for the Analysis of Sentiments in Social Networks with the Use of R. Informatics 2022, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; García-Ortiz, J.; Sánchez-Viteri, S. Identification of the Factors That Influence University Learning with Low-Code/No-Code Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Electronics 2021, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, G.; Xu, H. Fall Detection System Based on Deep Learning and Image Processing in Cloud Environment. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Complex, Intelligent, and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS-2018), Matsue, Japan, 4–66 July 2018; Volume 772. [Google Scholar]
- Plechawska-Wójcik, M.; Rybka, J. Assessment and Comparison of Functionalities of Telemedical Applications. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 107, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nho, Y.H.; Lim, J.G.; Kwon, D.S. Cluster-Analysis-Based User-Adaptive Fall Detection Using Fusion of Heart Rate Sensor and Accelerometer in a Wearable Device. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 40389–40401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, M.; Rajendran, P.J.; Kell, S.; Mack, D.; Dalal, S.; Wolfe, M.; Felder, R. A Smart and Passive Floor-Vibration Based Fall Detector for Elderly; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Xue, S. Portable Preimpact Fall Detector with Inertial Sensors. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2008, 16, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.Y.; Jilani, M.T. A Ubiquitous Wheelchair Fall Detection System Using Low-Cost Embedded Inertial Sensors and Unsupervised One-Class SVM. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, H.Y. Development of Pallet Recognition System Using Kinect Camera. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2014, 9, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, G.; Bhuiya, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Bhaumik, S. Kinect Camera Based Gait Data Recording and Analysis for Assistive Robotics-An Alternative to Goniometer Based Measurement Technique. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 133, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudarham, N.; Shkiller, L.; Yovel, G. Face Recognition in Humans and Machines. J. Vis. 2018, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, E.M.; Leme, D.S.; Barbosa, B.H.G.; Rodarte, M.P.; Alvarenga Pereira, R.G.F. A Computer Vision System for Coffee Beans Classification Based on Computational Intelligence Techniques. J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlak, F.; Ozdemir, M.; Melikdglu, M. Computer Vision System Approach in Colour Measurements of Foods: Part I. Development of Methodology. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiel, M.; Słowiński, M. The Use of Computer Vision System to Detect Pork Defects. LWT 2016, 73, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, N.A.; Maharani, W.; Atastina, I. Personality Classification of Facebook Users According to Big Five Personality Using SVM (Support Vector Machine) Method. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 179, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.C.; Bahadori, A.; Zhang, J.; Ahmad, Z. Prediction of Water Quality Index (WQI) Using Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Least Square-Support Vector Machine (LS-SVM). Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, O.; Klenk, J.; Schwickert, L.; Chiari, L.; Becker, C.; Park, E.J.; Mori, G.; Robinovitch, S.N. Validation of Accuracy of SVM-Based Fall Detection System Using Real-World Fall and Non-Fall Datasets. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.C.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsu, S.J.P.; Chan, C.T. Impact of Sampling Rate on Wearable-Based Fall Detection Systems Based on Machine Learning Models. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9882–9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, S.; Alsadoon, A.; Al-Dala’in, T.; Prasad, P.W.C.; Rashid, T.A.; Maag, A. Deep Learning for Vision-Based Fall Detection System: Enhanced Optical Dynamic Flow. Comput. Intell. 2021, 37, 578–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Tayan, O.; Islam, R.; Islam, S.; Nooruddin, S.; Kabir, M.N.; Islam, R. Deep Learning Based Systems Developed for Fall Detection: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 166117–166137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Jácome, D.; Usach, R.; Palau, C.E.; Esteve, M. Highly-Efficient Fog-Based Deep Learning AAL Fall Detection System. Internet Things 2020, 11, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Luna, G.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, D. Relative and Absolute Reliability of a Motor Assessment System Using Kinect® Camera. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos Salazar, G.F. Análisis Del Desempeño Del Sitio Web Del Instituto Ecuatoriano de Seguridad Social (IESS) Para Evaluar Su Accesibilidad y Usabilidad En Los Adultos Mayores de La Asociación de Jubilados de La “Hermandad de Ferroviarios” de La Ciudad de Quito. Propues. De. ComHumanit. Rev. Científica De Comun. 2020, 11, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghifari, H.G.; Darlis, D.; Hartaman, A. Pendeteksi Golongan Darah Manusia Berbasis Tensorflow Menggunakan ESP32-CAM. ELKOMIKA J. Tek. Energi Elektr. Tek. Telekomun. Tek. Elektron. 2021, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahin, N.M.A.; Nasir, H.M.; Jidin, A.Z.; Zulkifli, M.F.; Sutikno, T. Development of Vocabulary Learning Application by Using Machine Learning Technique. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2020, 9, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Accelerated Training and Inference with the Tensorflow Object Detection API; Huang, J., Ed.; Google AI Blog: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, D.C.; Wang, C.J.; Chen, Z.T.; Liaw, J.J. Real-Time Car Detection and Driving Safety Alarm System with Google Tensorflow Object Detection API. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Kobe, Japan, 7–10 July 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aningtiyas, P.R.; Sumin, A.; Wirawan, S. Pembuatan Aplikasi Deteksi Objek Menggunakan TensorFlow Object Detection API Dengan Memanfaatkan SSD MobileNet V2 Sebagai Model Pra-Terlatih. J. Ilm. Komputasi 2020, 19, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manajang, D.J.P.; Sompie, S.R.U.A.; Jacobus, A. Implementasi Framework Tensorflow Object Detection API Dalam Mengklasifikasi Jenis Kendaraan Bermotor. J. Tek. Inform. 2020, 15, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; García-Ortiz, J.; Mullo-Ca, K.; Sánchez-Viteri, S.; Roman-Cañizares, M. Implementation of a Virtual Assistant for the Academic Management of a University with the Use of Artificial Intelligence. Future Internet 2021, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzo, F.; Taqi, A.M.; Milanova, M. Human Related-Health Actions Detection Using Android Camera Based on TensorFlow Object Detection API. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elgendi, M.; Picon, F.; Magnenat-Thalmann, N.; Abbott, D. Arm Movement Speed Assessment via a Kinect Camera: A Preliminary Study in Healthy Subjects. Biomed. Eng. Online 2014, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kim, J.; Sohn, J.C.; Choi, H.J. A Wrist-Type Fall Detector with Statistical Classifier for the Elderly Care. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2011, 5, 1751–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miguel, K.; Brunete, A.; Hernando, M.; Gambao, E. Home Camera-Based Fall Detection System for the Elderly. Sensors 2017, 17, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownsell, S.; Hawley, M. Fall Detectors: Do They Work or Reduce the Fear of Falling? Hous. Care Support 2004, 7, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Person 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | Total Predictions | |||||
| Fall | Crouch | Feel | Walk | Falls | No falls | |
| Fall | 14 | 1 | 0 | 0 | TP 14 | FN 1 |
| Crouch | 1 | 14 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Feel | 0 | 1 | 14 | 0 | FP 3 | TN 39 |
| Walk | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | ||
| Accuracy = 92.9% | Sensitivity = 93% | Specificity = 93% | ||||
| Person 2 | ||||||
| Samples | Total Predictions | |||||
| Fall | Crouch | Feel | Walk | Falls | No falls | |
| Fall | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | TP 15 | FN 0 |
| Crouch | 2 | 13 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Feel | 0 | 2 | 13 | 0 | FP 4 | TN 41 |
| Walk | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | ||
| Accuracy = 93.3% | Sensitivity = 100% | Specificity = 91% | ||||
| Person 3 | ||||||
| Samples | Total Predictions | |||||
| Fall | Crouch | Feel | Walk | Falls | No falls | |
| Fall | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | TP 15 | FN 0 |
| Crouch | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Feel | 0 | 1 | 14 | 0 | FP 1 | TN 44 |
| Walk | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | ||
| Accuracy = 98.3% | Sensitivity = 100% | Specificity = 98% | ||||
| Criterion | Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 68.80% | 74% |
| Error range | 34.20% | 26% |
| Relative error | 3.14% | 11.24% |
| Processing | 110% | 69% |
| Memory | 63% | 15% |
| Storage | 0.038% | 0.006% |
| Cases | Absolute Frecuency | Relative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Falls | 360 | 0.7101 |
| False positives | 136 | 0.2682 |
| False negatives | 11 | 0.0217 |
| Total | 507 | 1 |
| Entorno | Falls | False Positives | False Negatives | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Room | 100 | 25 | 2 | 127 |
| Living room | 260 | 112 | 9 | 382 |
| Total | 360 | 136 | 11 | 507 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villegas-Ch., W.; Barahona-Espinosa, S.; Gaibor-Naranjo, W.; Mera-Navarrete, A. Model for the Detection of Falls with the Use of Artificial Intelligence as an Assistant for the Care of the Elderly. Computation 2022, 10, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10110195
Villegas-Ch. W, Barahona-Espinosa S, Gaibor-Naranjo W, Mera-Navarrete A. Model for the Detection of Falls with the Use of Artificial Intelligence as an Assistant for the Care of the Elderly. Computation. 2022; 10(11):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10110195
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillegas-Ch., William, Santiago Barahona-Espinosa, Walter Gaibor-Naranjo, and Aracely Mera-Navarrete. 2022. "Model for the Detection of Falls with the Use of Artificial Intelligence as an Assistant for the Care of the Elderly" Computation 10, no. 11: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10110195
APA StyleVillegas-Ch., W., Barahona-Espinosa, S., Gaibor-Naranjo, W., & Mera-Navarrete, A. (2022). Model for the Detection of Falls with the Use of Artificial Intelligence as an Assistant for the Care of the Elderly. Computation, 10(11), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation10110195











