Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient and Its Application in Improving CAMShift Tracker in RGBD Video
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient
2.1. Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient
2.2. Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient
3. Improved CAMShift Visual Tracker Based on the Neutrosophic Theory
3.1. Selecting Object Seeds
3.2. Extracting Object
3.3. Calculating the Fused Back-Projection
3.4. Scale Adaption
4. Experiment Results and Analysis
4.1. Setting Parameters
4.2. Evaluation Criteria
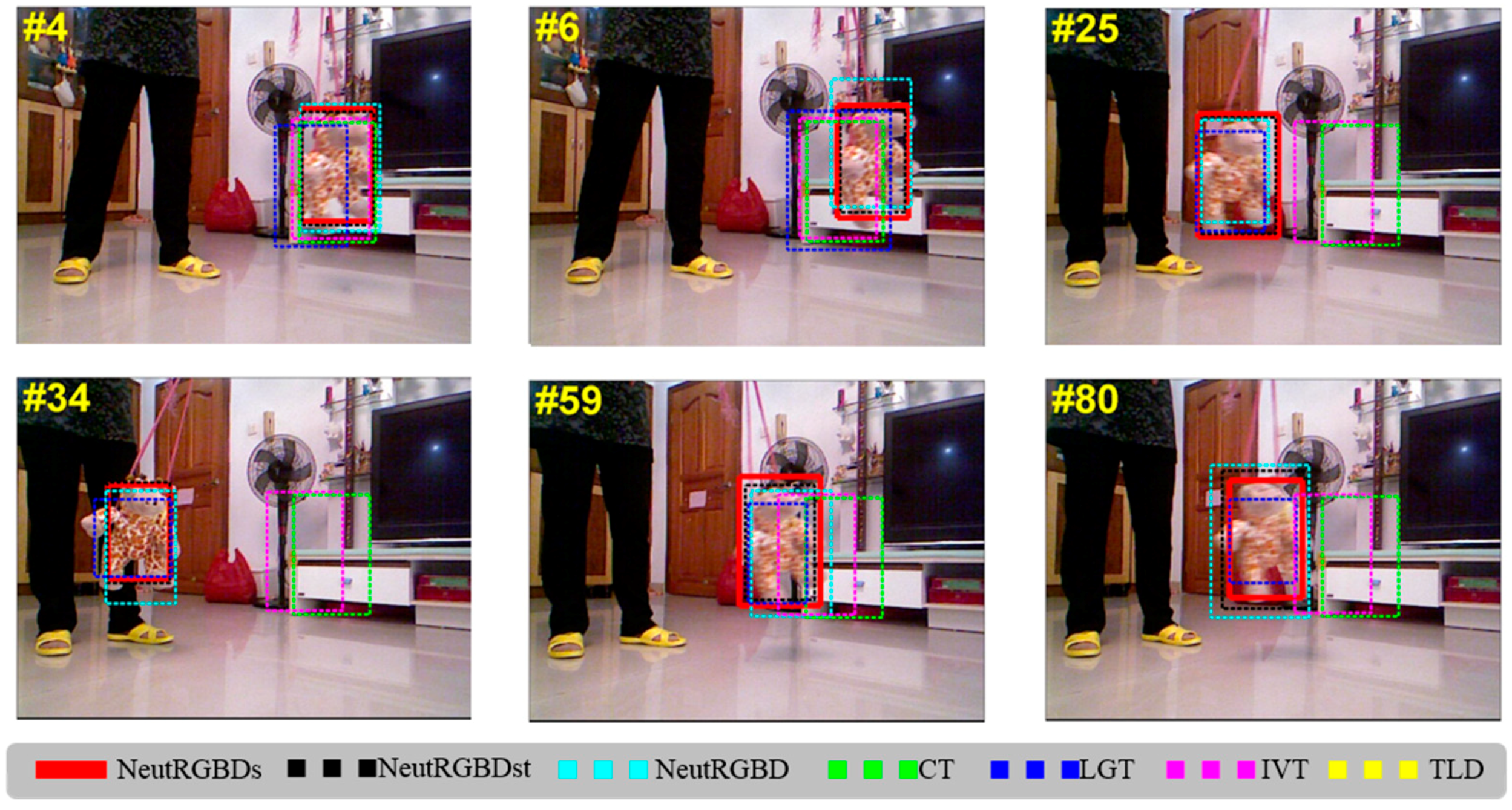
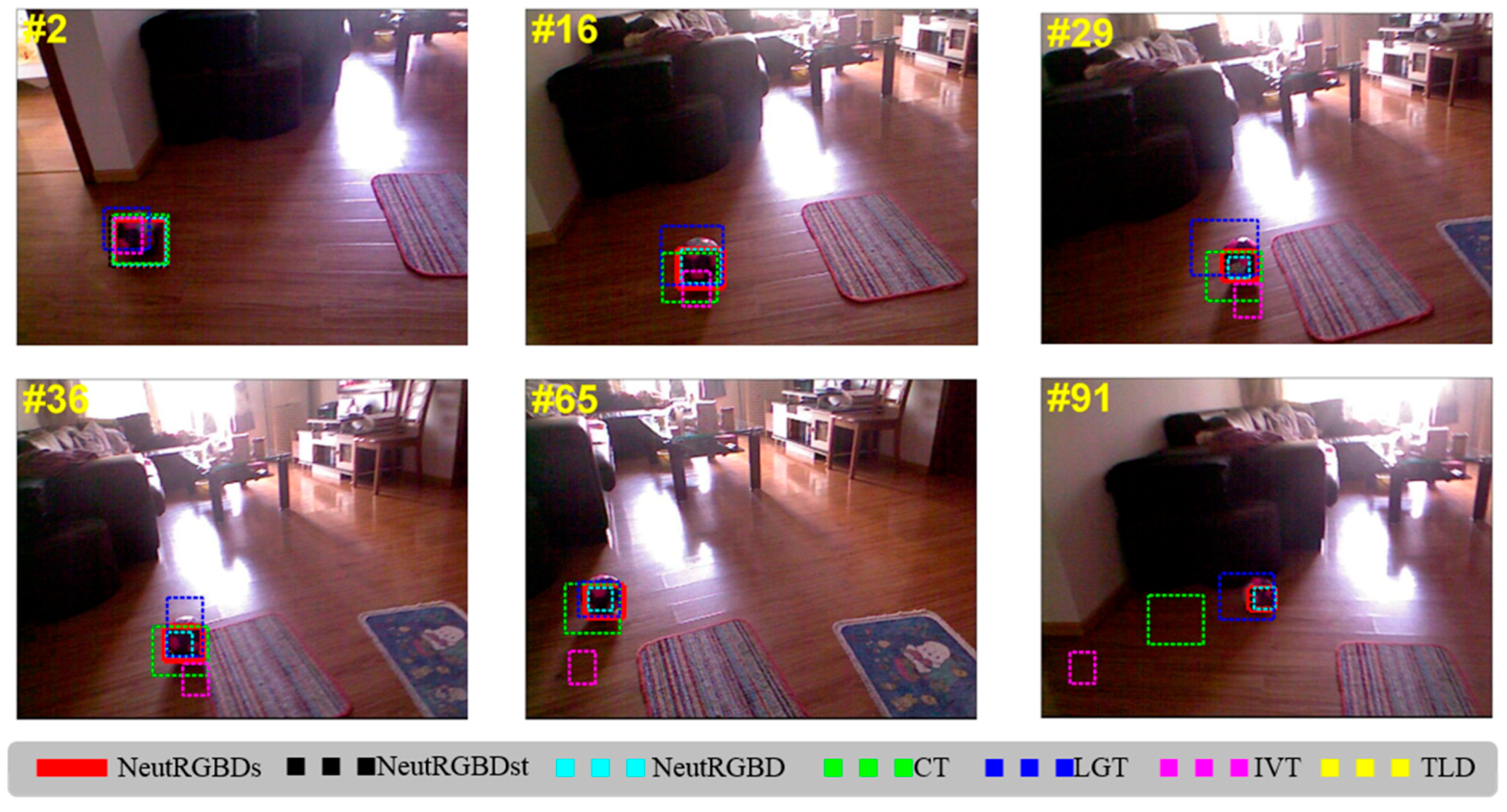
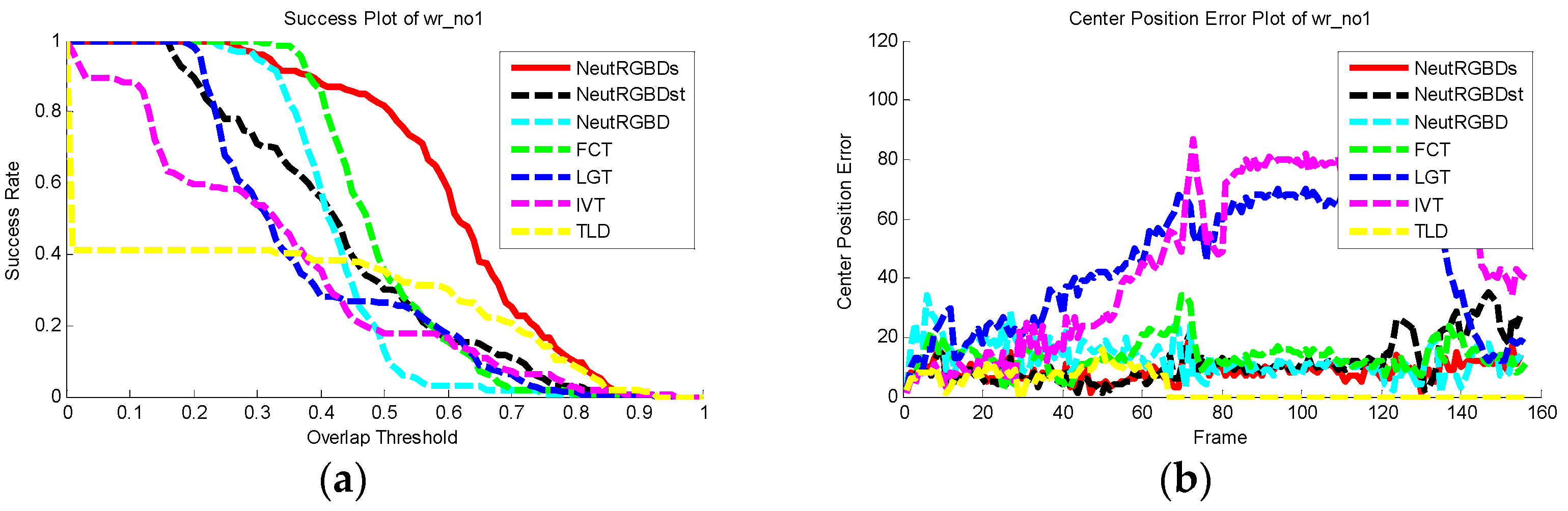
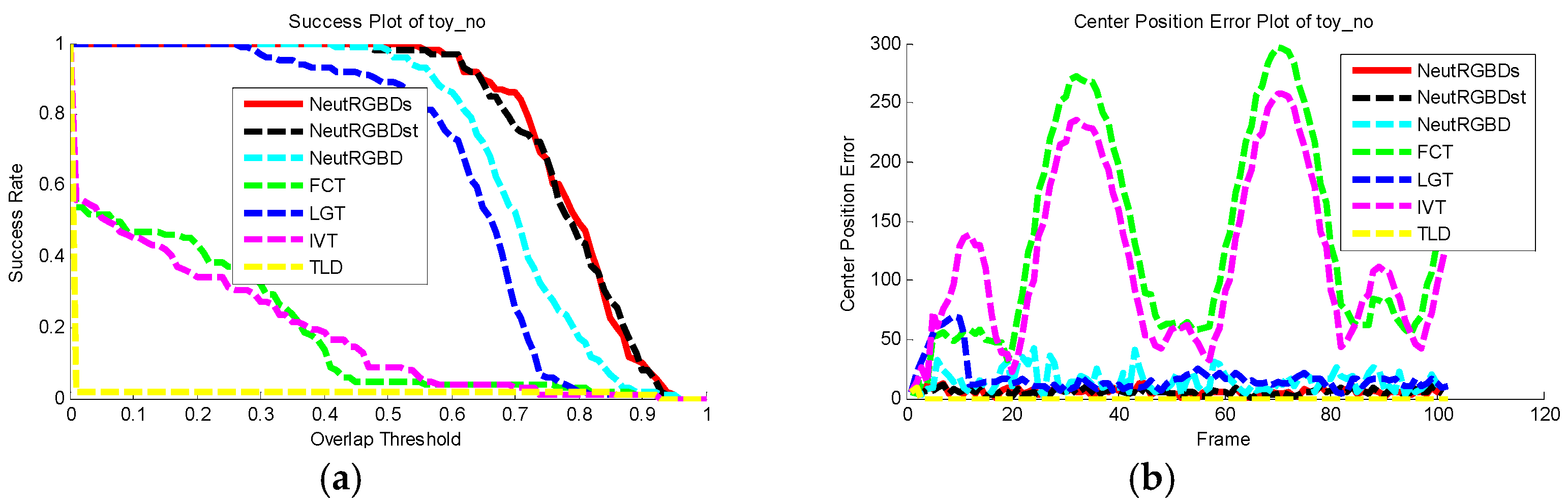
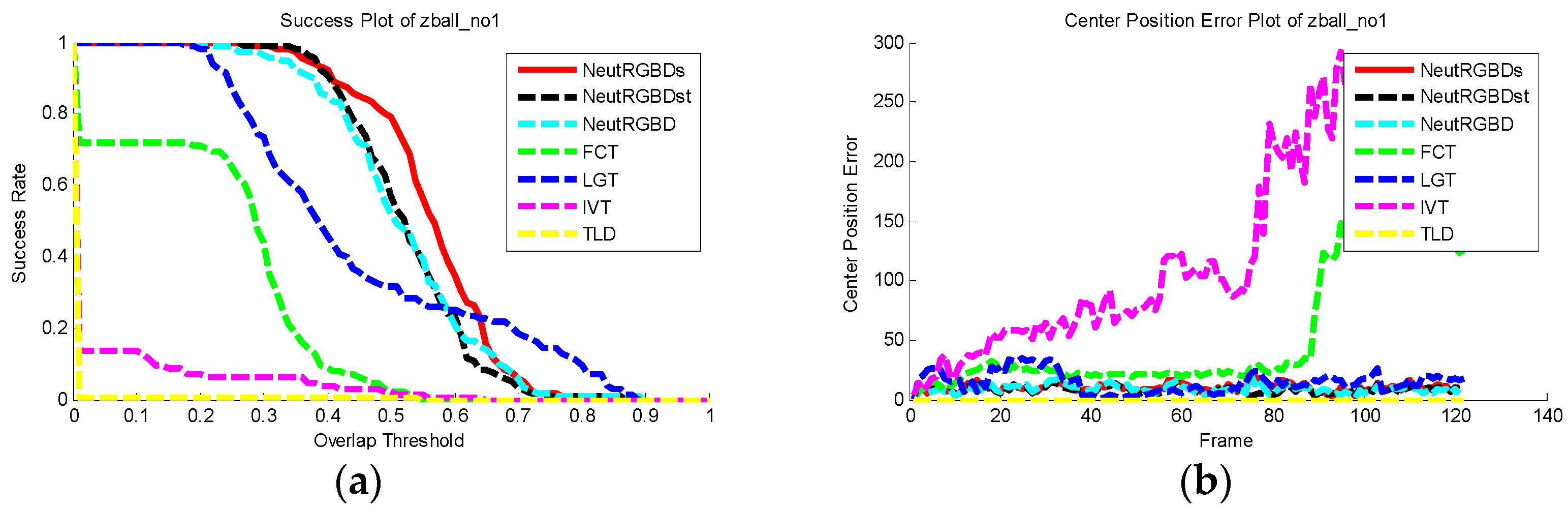
4.3. Tracking Results
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, Delaware, 1998; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sunderraman, R. Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multisp. Multistruct. 2010, 4, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hefenawy, N.; Metwally, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; El-Henawy, I.M. A review on the applications of neutrosophic sets. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2016, 13, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Fu, J. Multi-period medical diagnosis method using a single valued neutrosophic similarity measure based on tangent function. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 123, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Şengür, A. A novel image segmentation algorithm based on neutrosophic similarity clustering. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2014, 25, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, A.M.; Hassanien, A.E.; ElSoud, M.A.A.; Tolba, M.F. Neutrosophic sets and fuzzy c-means clustering for improving ct liver image segmentation. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2014, 303, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Karabatak, E.; Guo, Y.; Sengur, A. Modified neutrosophic approach to color image segmentation. J. Electron. Imaging 2013, 22, 4049–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.D. A neutrosophic approach to image segmentation based on watershed method. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Şengür, A.; Ye, J. A novel image thresholding algorithm based on neutrosophic similarity score. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2014, 58, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sengur, A. A novel 3d skeleton algorithm based on neutrosophic cost function. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 36, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ye, J.; Fan, E.; Shen, S.; Huang, L.; Pi, J. A novel object tracking algorithm by fusing color and depth information based on single valued neutrosophic cross-entropy. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 32, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Fan, E.; Ye, J.; Fan, C.; Shen, S.; Gu, Y. Neutrosophic similarity score based weighted histogram for robust mean-shift tracking. Information 2017, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Pramanik, S.; Giri, B.C. Topsis method for multi-attribute group decision-making under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 27, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharal, A. A neutrosophic multi-criteria decision making method. New Math. Nat. Comput. 2014, 10, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Single valued neutrosophic cross-entropy for multicriteria decision making problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, P. Neutrosophic sets and its applications to decision making. In Adaptation, Learning, and Optimization; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 19, pp. 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. Multicriteria decision-making method using the correlation coefficient under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2013, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baušys, R.; Juodagalvienė, B. Garage location selection for residential house by waspas-svns method. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2017, 23, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Bausys, R.; Juodagalviene, B.; Garnyte-Sapranaviciene, I. Model for residential house element and material selection by neutrosophic multimoora method. Eng. Appl. Artif. Int. 2017, 64, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Bausys, R.; Kaklauskas, A.; Ubarte, I.; Kuzminske, A.; Gudiene, N. Sustainable market valuation of buildings by the single-valued neutrosophic mamva method. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2017, 57, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sengur, A. Ncm: Neutrosophic c-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2710–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeulders, A.W.M.; Chu, D.M.; Cucchiara, R.; Calderara, S.; Dehghan, A.; Shah, M. Visual tracking: An experimental survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1442–1468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Tracking Interacting Objects in Image Sequences; École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Comaniciu, D.; Ramesh, V.; Meer, P. Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradski, G.R. Real time face and object tracking as a component of a perceptual user interface. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, Princeton, NJ, USA, 19–21 October 1998; pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, S. An Fpga Implementation of the Mean-Shift Algorithm for Object Tracking; AUT University: Auckland, New Zealand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leichter, I. Mean shift trackers with cross-bin metrics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C. Video Object Tracking Using Sift and Mean Shift. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bousetouane, F.; Dib, L.; Snoussi, H. Improved mean shift integrating texture and color features for robust real time object tracking. Vis. Comput. 2013, 29, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, B.; Ming-Hsuan, Y.; Belongie, S. Visual tracking with online multiple instance learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 983–990. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Y. Fusing target information from multiple views for robust visual tracking. IET Comput. Vis. 2014, 8, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihua, Z.; Lei, Z.; Ming-Hsuan, Y. Fast compressive tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2002–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cehovin, L.; Kristan, M.; Leonardis, A. Robust visual tracking using an adaptive coupled-layer visual model. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.; Lim, J.; Lin, R.-S.; Yang, M.-H. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalal, Z.; Mikolajczyk, K.; Matas, J. Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazan, E.J.; Jones, G.A. Tracking people across multiple non-overlapping RGB-D sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 831–837. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Pauwels, E.J.; De Zeeuw, P.M.; De With, P.H.N. Employing a RGB-D sensor for real-time tracking of humans across multiple re-entries in a smart environment. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electr. 2012, 58, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, S.; Oulasvirta, A.; Theobalt, C. Interactive markerless articulated hand motion tracking using rgb and depth data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2456–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Camplani, M.; Hannuna, S.; Mirmehdi, M.; Damen, D.; Paiement, A.; Tao, L.; Burghardt, T. Real-time RGB-D tracking with depth scaling kernelised correlation filters and occlusion handling. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Swansea, UK, 7–10 September 2015; pp. 145:1–145:11. [Google Scholar]



| Algorithm 1 NeutRGBDs |
|---|
| Initialization |
| Input: 1st video frame in the RGBD domain |
| (1) Select an object on the image plane |
| (2) Extract object seeds using both color and depth information |
| (3) Extract object region using object seeds and the information of the depth segmentation |
| (4) Calculate the corresponding color and depth histograms as target model |
| Tracking |
| Input: (t+1)-th video frame in the RGBD domain |
| (1) Calculate back-projections in both color (Pc) and depth domain (PD) |
| (2) Calculate fused back-projection (P) using neutrosophic theory |
| (3) Calculate the bounding box of the target in the CAMShift framework |
| (4) Extract object region and update object model and seeds |
| (5) Modify the scale of the bounding box in neutrosophic domain |
| Output: Tracking location |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, K.; Fan, E.; Ye, J.; Pi, J.; Zhao, L.; Shen, S. Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient and Its Application in Improving CAMShift Tracker in RGBD Video. Information 2018, 9, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9050126
Hu K, Fan E, Ye J, Pi J, Zhao L, Shen S. Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient and Its Application in Improving CAMShift Tracker in RGBD Video. Information. 2018; 9(5):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9050126
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Keli, En Fan, Jun Ye, Jiatian Pi, Liping Zhao, and Shigen Shen. 2018. "Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient and Its Application in Improving CAMShift Tracker in RGBD Video" Information 9, no. 5: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9050126
APA StyleHu, K., Fan, E., Ye, J., Pi, J., Zhao, L., & Shen, S. (2018). Element-Weighted Neutrosophic Correlation Coefficient and Its Application in Improving CAMShift Tracker in RGBD Video. Information, 9(5), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9050126





