Residual Recurrent Neural Networks for Learning Sequential Representations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Recurrent Neural Networks and Its Training
2.1. Gradient Issues
2.2. Residual Learning and Identity Mapping
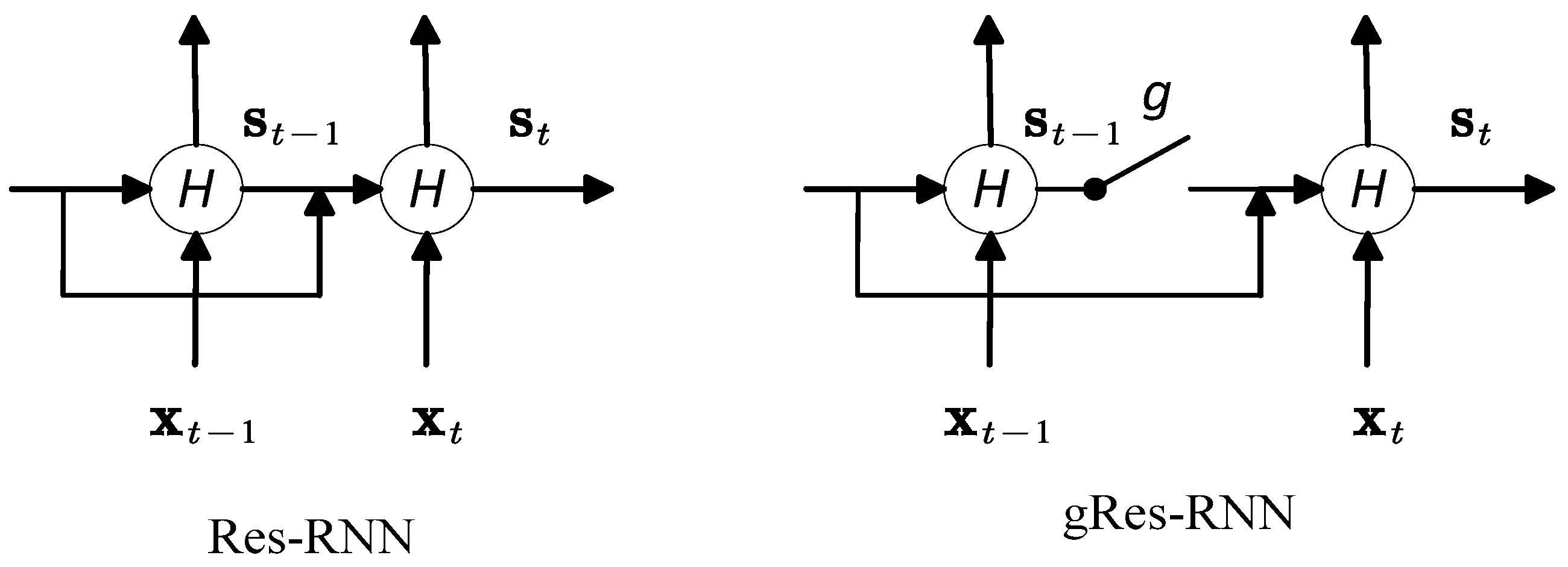
3. Residual Recurrent Neural Network
3.1. Residual-Shortcut Structure
3.2. Analysis of Res-RNN
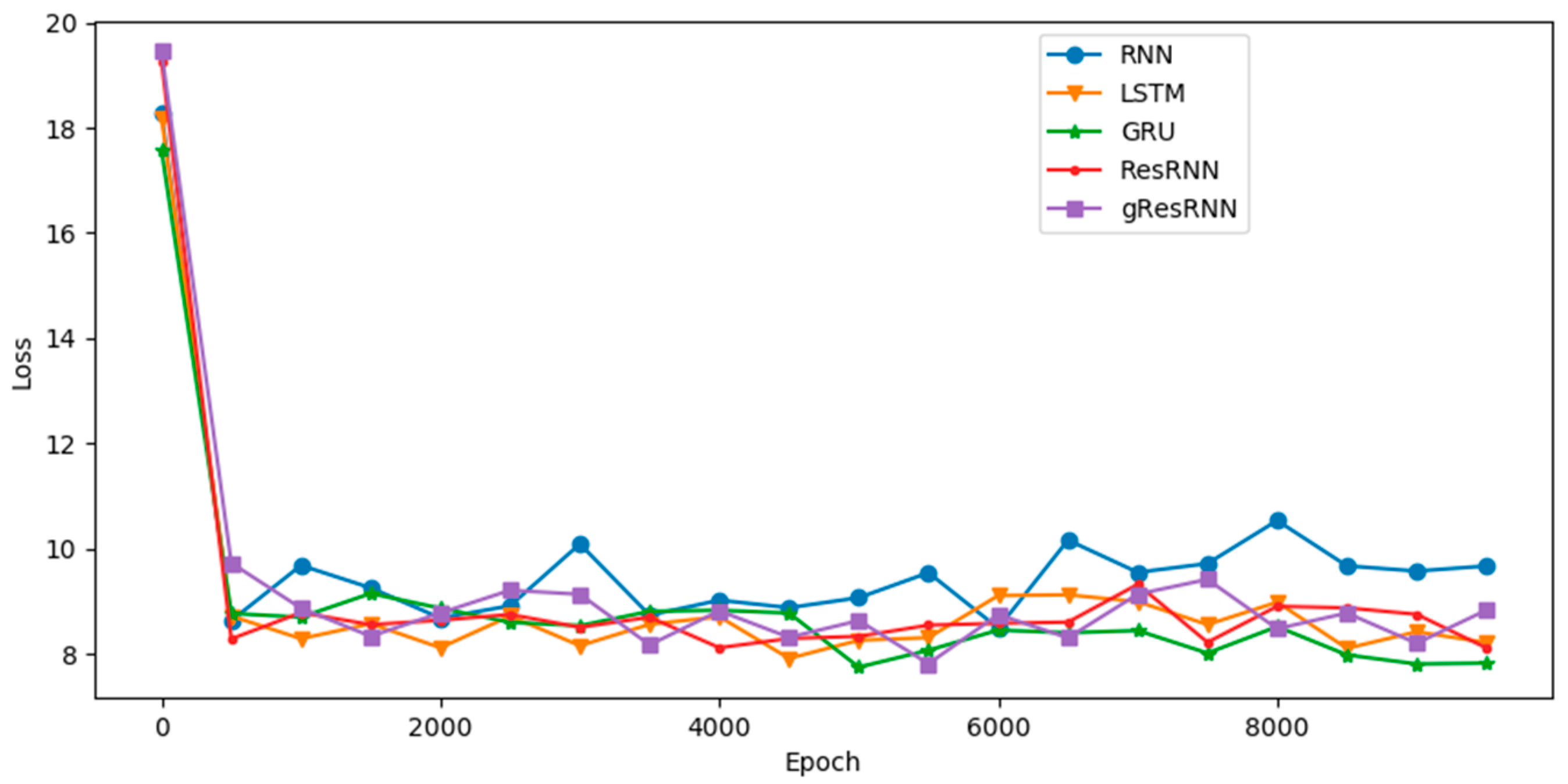
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. ATIS Database
4.2. IMDB Database
4.3. Polyphonic Databases
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Dahl, G.E.; Hinton, G. Acoustic modeling using deep belief networks. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.G.; Patel, R.; Jayatilleke, N.; Kolliakou, A.; Ball, M.; Gorrell, G.; Roberts, A.; Dobson, R.J.; Stewart, R. Natural language processing to extract symptoms of severe mental illness from clinical text: The clinical record interactive search comprehensive data extraction (cris-code) project. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, J.; Koziatek, C.; Theobald, J.; Smith, S.; Iturrate, E. Creation of a simple natural language processing tool to support an imaging utilization quality dashboard. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2017, 101, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaf, H. Automatic Machine Translation Using User Feedback. U.S. Patent US20150248457, 3 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoo, S.; Sumita, K. Machine Translation Apparatus, Machine Translation Method and Computer Program Product. U.S. Patent US20170091177A1, 30 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gallos, L.K.; Potiguar, F.Q.; Andrade, J.S., Jr.; Makse, H.A. Imdb network revisited: Unveiling fractal and modular properties from a typical small-world network. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghina, A.; Breuss, M.; Tsagkias, M.; Rijke, M.D. Predicting imdb movie ratings using social media. In Advances in Information Retrieval, Proceedings of the European Conference on IR Research, ECIR 2012, Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 April 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Elman, J.L. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci. 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I. Serial Order: A Parallel Distributed Processing Approach; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1986; Volume 121, p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Boulanger-Lewandowski, N.; Pascanu, R. Advances in optimizing recurrent networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 8624–8628. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Frasconi, P.; Simard, P. The problem of learning long-term dependencies in recurrent networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 March–1 April 1993; Volume 1183, pp. 1183–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavsson, A.; Magnuson, A.; Blomberg, B.; Andersson, M.; Halfvarson, J.; Tysk, C. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. Comput. Sci. 2013, 52, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I. Training Recurrent Neural Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sepp, H.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Merrienboer, B.V.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Caesars Palace, NE, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Price, P.J. Evaluation of spoken language systems: The atis domain. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Speech and Natural Language, Harriman, NY, USA, 23–26 February 1992; pp. 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, E.B. The internet movie database (imdb). Electron. Resour. Rev. 1999, 3, 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.H.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Jegou, H.; Perronnin, F.; Douze, M.; Sanchez, J.; Perez, P.; Schmid, C. Aggregating local image descriptors into compact codes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perronnin, F.; Dance, C. Fisher kernels on visual vocabularies for image categorization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR ’07), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 18–23 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jégou, H.; Douze, M.; Schmid, C. Product quantization for nearest neighbor search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belayadi, A.; Ait-Gougam, L.; Mekideche-Chafa, F. Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 233–234. [Google Scholar]
- Sermanet, P.; Eigen, D.; Zhang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Fergus, R.; Lecun, Y. Overfeat: Integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1312.6229. [Google Scholar]
- Fahlman, S.E.; Lebiere, C. The cascade-correlation learning architecture. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1991, 2, 524–532. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Greff, K.; Schmidhuber, J. Highway networks. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1505.00387. [Google Scholar]
- Cooijmans, T.; Ballas, N.; Laurent, C.; Gülçehre, Ç.; Courville, A. Recurrent batch normalization. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1603.09025. [Google Scholar]
- Mesnil, G.; He, X.; Deng, L.; Bengio, Y. Investigation of recurrent-neural-network architectures and learning methods for spoken language understanding. In Proceedings of the Interspeech Conference, Lyon, France, 25–29 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Boulangerlewandowski, N.; Bengio, Y.; Vincent, P. Modeling temporal dependencies in high-dimensional sequences: Application to polyphonic music generation and transcription. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 3981–3991. [Google Scholar]



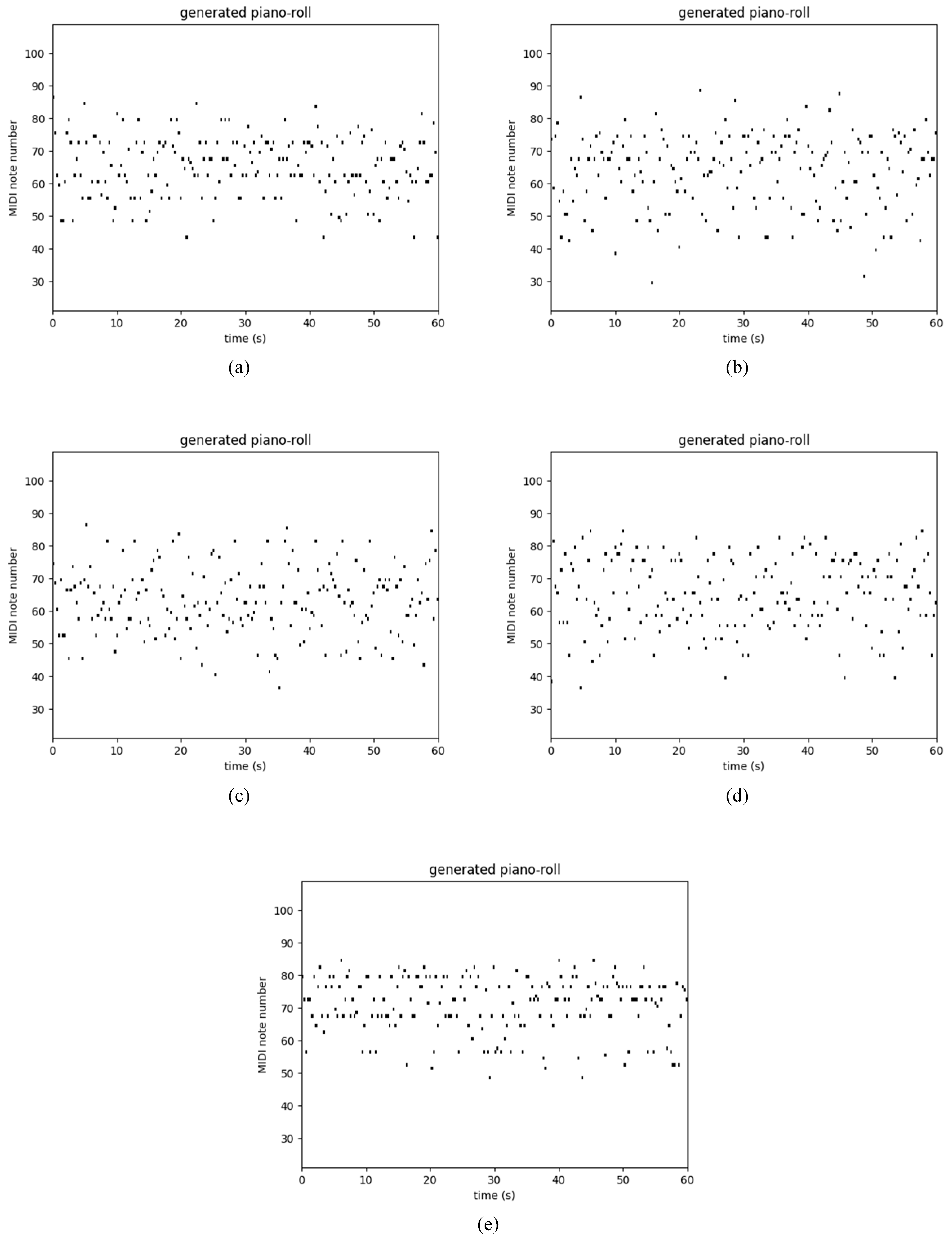
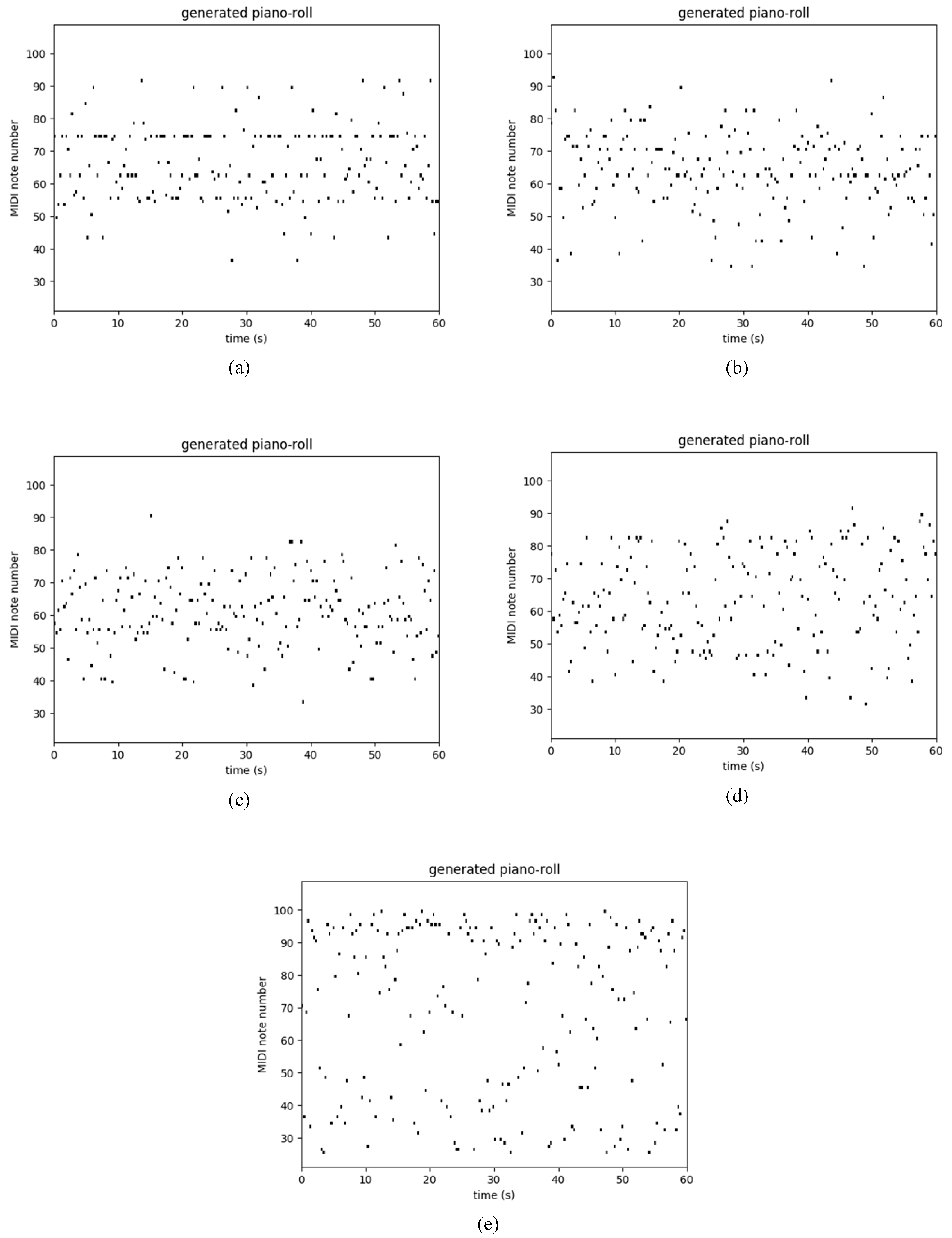
| RNN | LSTM | GRU | Res-RNN | gRes-RNN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid F1 | Mean | 95.63% | 96.58% | 95.63% | 95.87% | 96.53% |
| Std | 0.0142 | 0.0096 | 0.0132 | 0.0115 | 0.0101 | |
| Test F1 | Mean | 92.11% | 93.19% | 92.81% | 92.97% | 93.03% |
| Std | 0.0166 | 0.0092 | 0.0141 | 0.0120 | 0.0110 | |
| Valid Accuracy | Mean | 95.56% | 96.49% | 95.50% | 95.55% | 96.62% |
| Std | 0.0178 | 0.0082 | 0.0122 | 0.0097 | 0.0092 | |
| Test Accuracy | Mean | 91.81% | 92.77% | 92.54% | 92.50% | 92.62% |
| Std | 0.0168 | 0.0077 | 0.0134 | 0.0100 | 0.0083 | |
| Valid Recall | Mean | 95.85% | 96.75% | 96.00% | 96.20% | 96.60% |
| Std | 0.0173 | 0.0056 | 0.0144 | 0.0100 | 0.0099 | |
| Test Recall | Mean | 92.74% | 93.62% | 93.20% | 93.45% | 93.45% |
| Std | 0.0188 | 0.0043 | 0.0112 | 0.0105 | 0.0091 | |
| Time Consumption | 24.10 s | 63.59 s | 56.74 s | 29.10 s | 38.80 s | |
| Training Accuracy | Test Accuracy | Time Consumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | ||
| RNN | 93.91% | 0.0148 | 78.24% | 0.0232 | 51.32 s |
| LSTM | 99.97% | 0.0001 | 85.16% | 0.0023 | 208.44 s |
| GRU | 99.98% | 0.0001 | 85.84% | 0.0038 | 140.10 s |
| Res-RNN | 99.93% | 0.0003 | 84.78% | 0.0042 | 90.08 s |
| Res-RNN with gate | 99.95% | 0.0002 | 85.33% | 0.0029 | 123.22 s |
| RNN | LSTM | GRU | Res-RNN | gRes-RNN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nottingham | Loss | 9.62 | 7.37 | 8.50 | 8.26 | 8.60 |
| Std | 1.63 | 0.54 | 0.72 | 0.89 | 0.66 | |
| Time | 10.45 s | 35.48 s | 27.32 s | 19.06 s | 25.01 s | |
| JSB Chorales | Loss | 9.04 | 7.43 | 8.54 | 7.60 | 7.77 |
| Std | 1.01 | 0.67 | 0.96 | 0.55 | 0.23 | |
| Time | 10.62 s | 35.50 s | 27.14 s | 18.92 s | 25.42 s | |
| MuseData | Loss | 10.42 | 9.62 | 9.86 | 9.31 | 8.93 |
| Std | 1.45 | 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.33 | 0.30 | |
| Time | 10.33 s | 35.39 s | 27.33 s | 19.13 s | 25.01 s | |
| Piano-midi | Loss | 11.71 | 9.57 | 9.62 | 8.22 | 9.26 |
| Std | 1.92 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.24 | 0.68 | |
| Time | 10.52 s | 35.44 s | 27.20 s | 19.44 s | 25.01 s | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, B.; Fu, J.; Liang, J. Residual Recurrent Neural Networks for Learning Sequential Representations. Information 2018, 9, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9030056
Yue B, Fu J, Liang J. Residual Recurrent Neural Networks for Learning Sequential Representations. Information. 2018; 9(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Boxuan, Junwei Fu, and Jun Liang. 2018. "Residual Recurrent Neural Networks for Learning Sequential Representations" Information 9, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9030056
APA StyleYue, B., Fu, J., & Liang, J. (2018). Residual Recurrent Neural Networks for Learning Sequential Representations. Information, 9(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9030056





