Mean-Variance Analysis of Retailers Deploying RFID-Enabled Smart Shelves
Abstract
1. Introduction
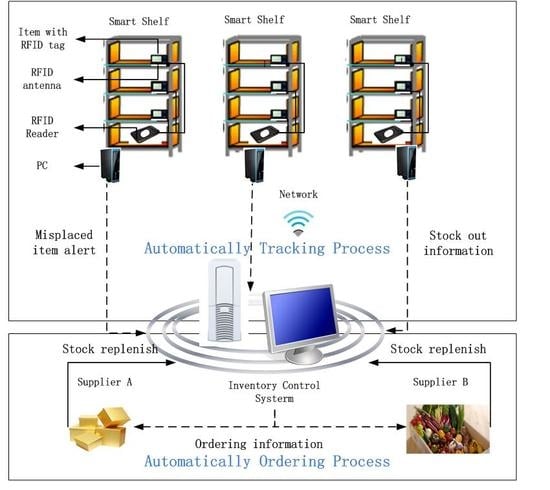
2. Problem Description
3. Inventory Models for the Retailer
3.1. Inventory Model without the Smart Shelf System
3.2. Inventory Model with the Smart Shelf System
4. The Condition for Investing in Smart Shelves
5. Numerical Analysis
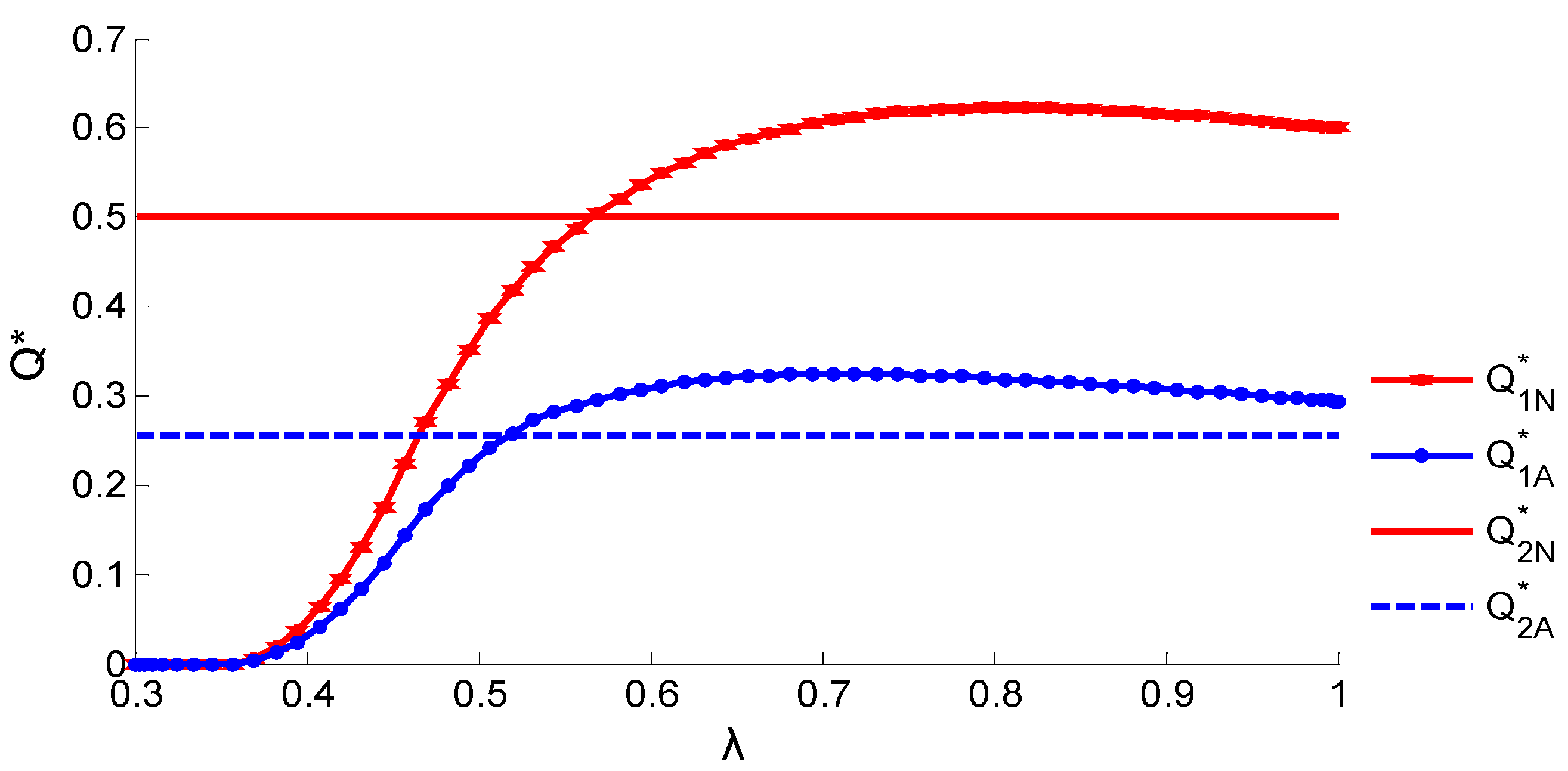
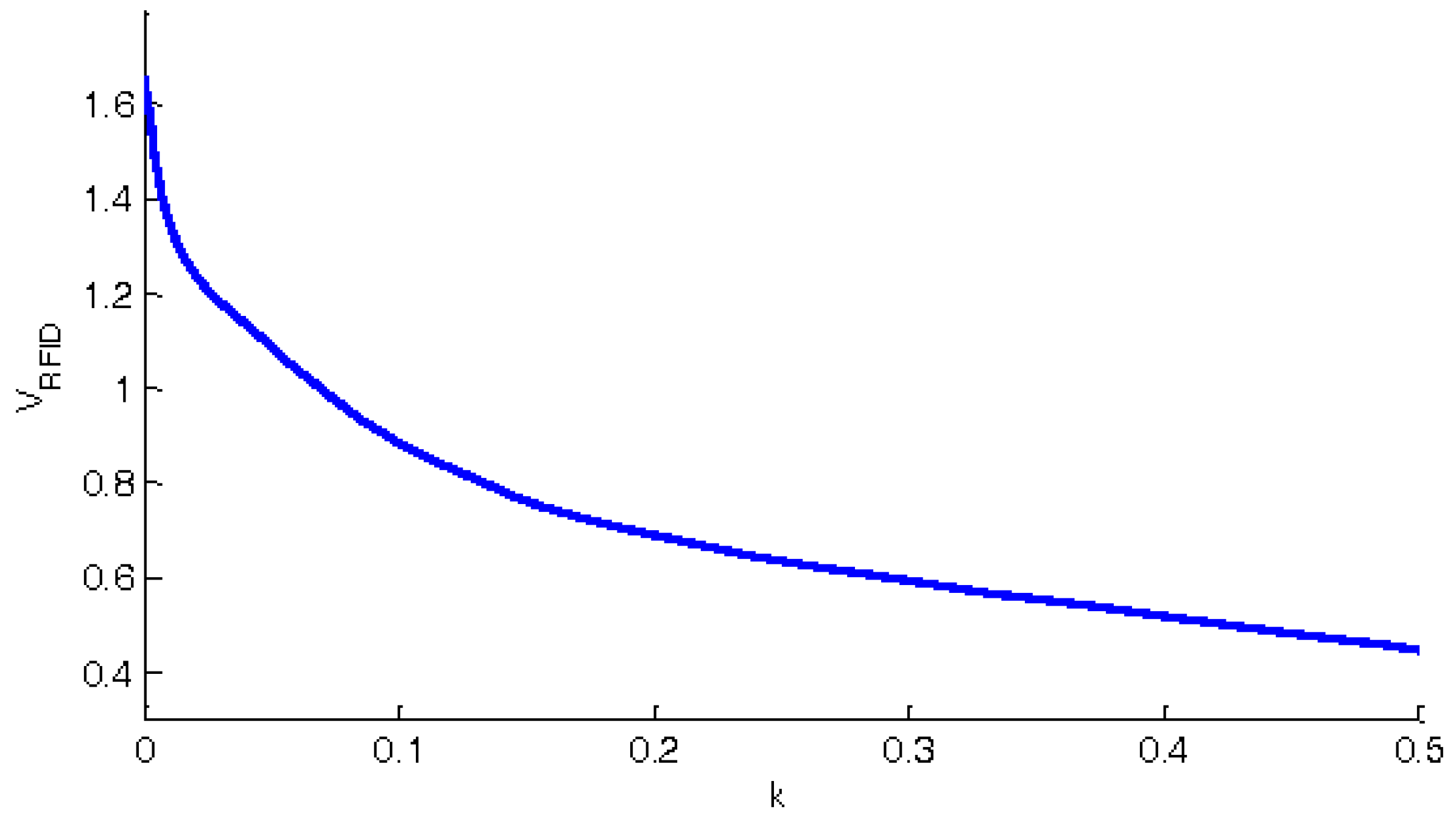
5.1. Impact of Inventory Inaccuracy on the Retailer’s Ordering Policy
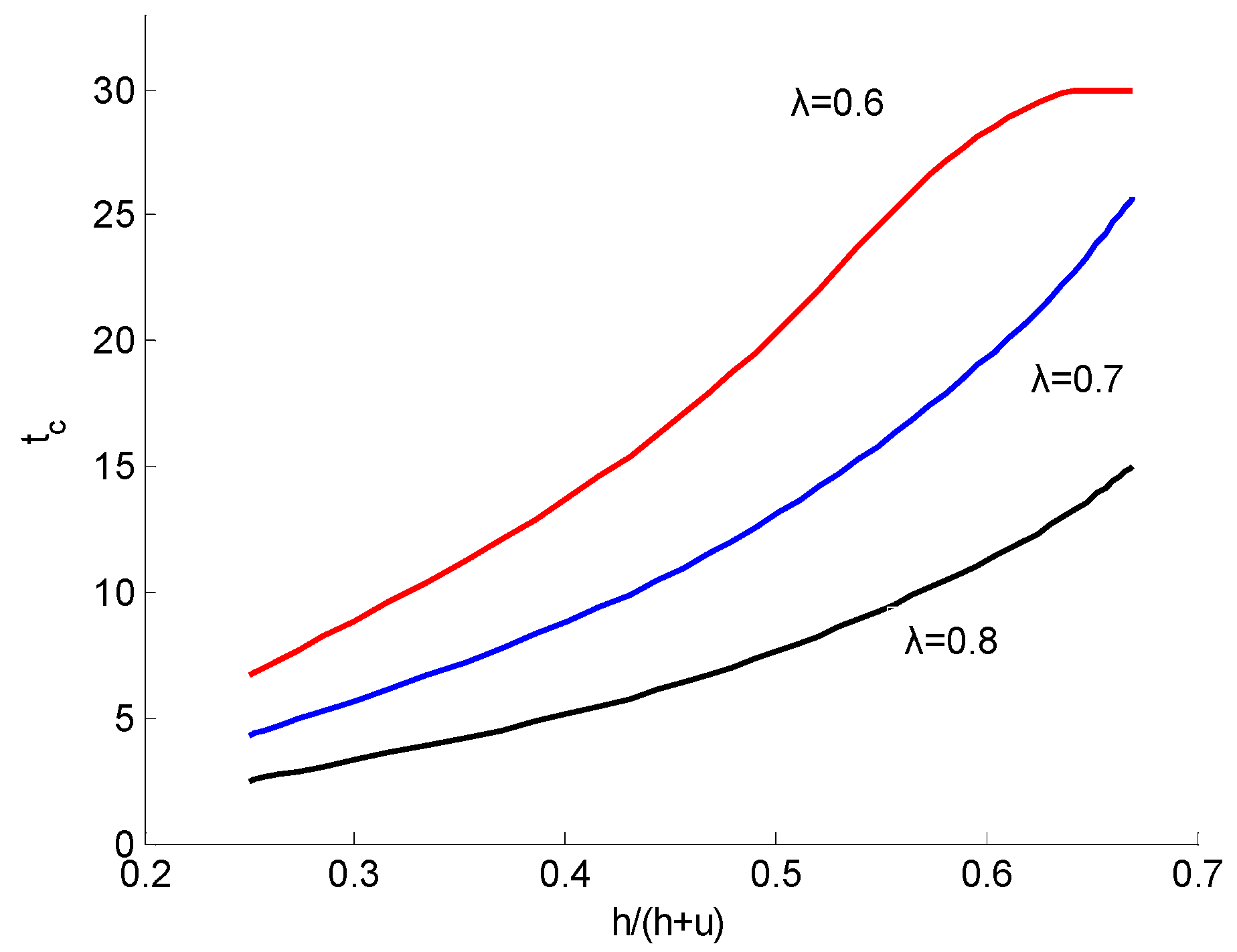
5.2. Impact of Risk Attitude on the Benefit of Smart Shelves
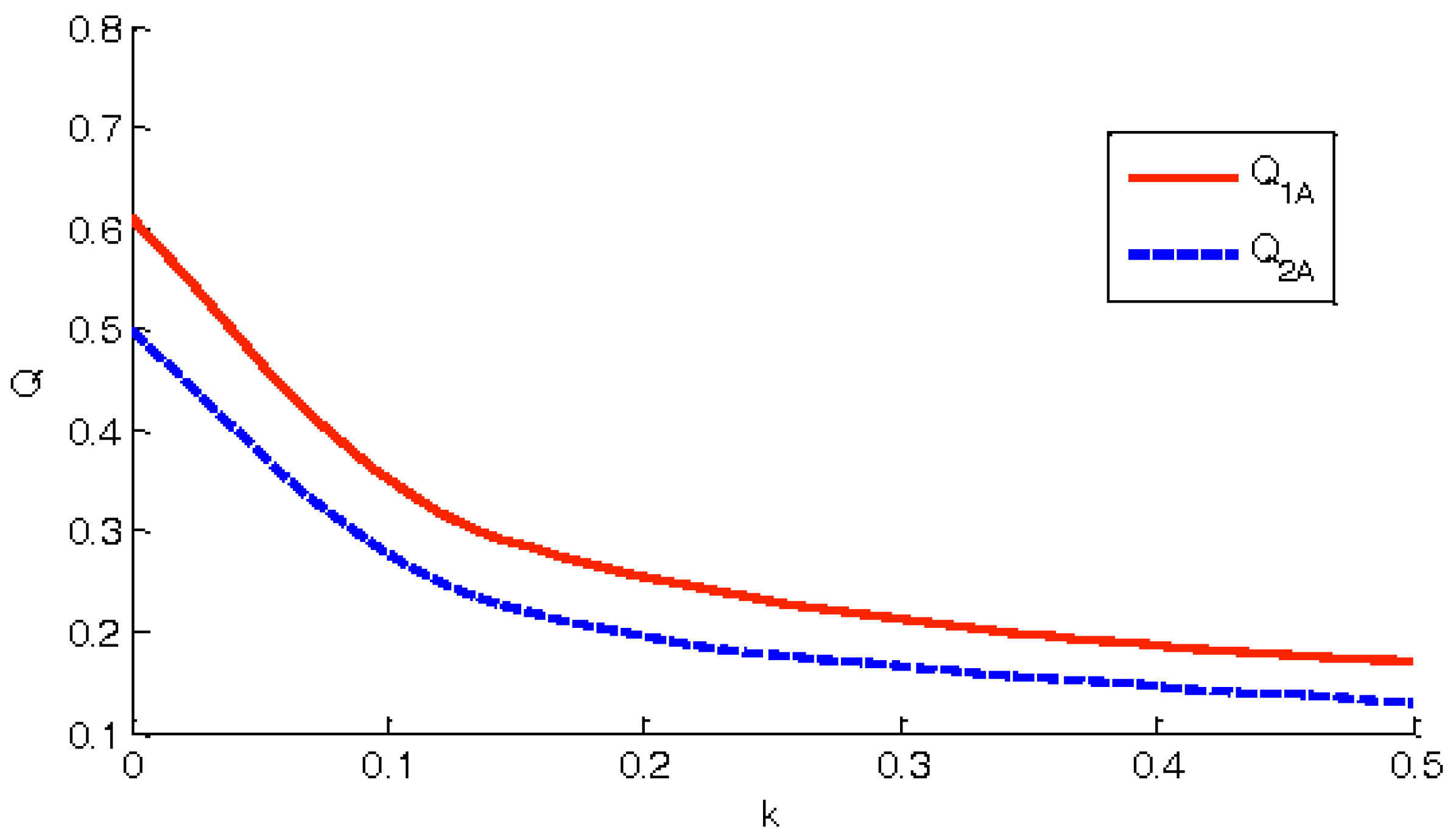
5.3. Sensitivity of the Cost Parameters to the Investment Decisions
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| R | Selling price per item |
| s | Salvage price per item |
| w | Purchasing cost per item |
| t | RFID tag cost per item |
| k | Parameter that reflects the retailer’s degree of risk aversion |
| x | Random demand |
| Probability density function (pdf) of x | |
| Cumulative distribution function (CDF) of x | |
| Ratio between the available quantity for sale and the total physical quantity in the store | |
| Profit of the retailer with random demand | |
| Mean of the profit | |
| Variance of the profit | |
| Utility of the profit | |
| Optimal order quantity (decision variable) ( denotes approach 1 and approach 2 respectively denotes risk-neutral and risk-averse respectively) |
References
- Zhu, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Kurata, H. A review of RFID technology and its managerial applications in different industries. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2012, 29, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uckelmann, D.; Romagnoli, G. Rf-based locating of mobile objects. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Internet of Things, Linz, Austria, 22–25 October 2017; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Chang, K.H. Cost-benefit analysis of RFID application in apparel retailing for SME: A case from taiwan. Transp. J. 2010, 49, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bottani, E.; Montanari, R.; Romagnoli, G. Improving sales turnover in fashion retailing by means of an RFID-based replenishment policy. Int. J. RF Technol. Res. Appl. 2016, 7, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Yang, B.; Cheung, H.H. Item-level RFID for enhancement of customer shopping experience in apparel retail. Comput. Ind. 2015, 71, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragg, J. The Emergence of RFID Technology in Modern Society; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, C.R.; Costa, J.R.; Fernandes, C.A. RFID smart shelf with confined detection volume at UHF. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Chen, Z.N. Characteristics of a metal-backed loop antenna and its application to a high-frequency RFID smart shelf. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2009, 51, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Liu, P.; Bai, Y. Bridging physical and virtual worlds: Complex event processing for RFID data streams. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Database Technology, Munich, Germany, 26–31 March 2006; pp. 588–607. [Google Scholar]
- Atali, A.; Lee, H.L.; Özer, Ö. If the Inventory Manager Knew: Value of Visibility and RFID under Imperfect Inventory Information. 2009. Available online: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1351606 (accessed on 11 February 2018).
- Xu, J.; Wei, J.; Tian, J. Comparing improvement strategies for inventory inaccuracy in a two-echelon supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 221, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Gershwin, S.B. Information inaccuracy in inventory systems: Stock loss and stockout. IIE Trans. 2005, 37, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehoratius, N.; Raman, A. Inventory record inaccuracy: An empirical analysis. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cost Reduction in Retailing & Products Using Rfid. Available online: http://www.idtechex.com/research/articles/cost_reduction_in_retailing_and_products_using_rfid_00000205.asp (accessed on 16 April 2008).
- Zipkin, P. Om forumthe best things in life were free: On the technology of transactions. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2006, 8, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lee, C. Risk analysis of a two-level supply chain subject to misplaced inventory. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Özer, Ö. Unlocking the value of RFID. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2007, 16, 40–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, Y.; Sahin, E.; Dallery, Y. Analysis of the impact of the rfid technology on reducing product misplacement errors at retail stores. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 112, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heese, H.S. Inventory record inaccuracy, double marginalization, and RFID adoption. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2007, 16, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.M.; Li, D.; Yan, H.; Chiu, C.H. Channel coordination in supply chains with agents having mean-variance objectives. Omega 2008, 36, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Sethi, S.P.; Yan, H. Channel coordination with a risk-neutral supplier and a downside-risk-averse retailer. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2010, 14, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Yang, D. Price and service competition of supply chains with risk-averse retailers under demand uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 114, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y. Mean-variance utility. J. Econ. Theory 2015, 160, 536–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, T.C.E. Mean–variance analysis of the newsvendor model with stockout cost. Omega 2009, 37, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, A.A. Risk sensitivity in distribution channel partnerships: Implications for manufacturer return policies. J. Retail. 2002, 78, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Impact of inventory inaccuracies on products with inventory-dependent demand. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 177, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camdereli, A.Z.; Swaminathan, J.M. Misplaced inventory and radio-frequency identification (rfid) technology: Information and coordination. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2010, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Deng, F.; Wu, X. Design of a quaternary query tree aloha protocol based on optimal tag estimation method. Information 2016, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, Z.; Wu, F. An improved particle swarm optimization-based feed-forward neural network combined with RFID sensors to indoor localization. Information 2017, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.; Wu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J. A split-path schema-based RFID data storage model in supply chain management. Sensors 2013, 13, 5757–5776. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L. Economic analysis of a traceability system for a two-level perishable food supply chain. Sustainability 2017, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. A lightweight rfid grouping-proof protocol based on parallel mode and DHCP mechanism. Information 2017, 8, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, H.M. Portfolio Selection: Efficient Diversification of Investments, 2nd ed.; Yale University Press: City of New Haven, CT, USA, 1991; Volume 35, pp. 243–265. [Google Scholar]
- Inderfurth, K. Analytical solution for a single-period production-inventory problem with uniformly distributed yield and demand. Cent. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 12, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sahina, E.; Dallery, Y. Analysis of a newsvendor which has errors in inventory data records. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 188, 370–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.L.; Ngai, E.W.T. The adoption of rfid in fashion retailing: A business value-added framework. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2008, 108, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaukler, G.M.; Seifert, R.W.; Hausman, W.H. Item-level rfid in the retail supply chain. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2007, 16, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, S. Inference Electronic Shelf Life Dating System for Perishables. U.S. Patent US9710754 B2, 18 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | 9 | 5.008 | 0 |
| 0.9 | 7.716 | 4.373 | 2.222 |
| 0.8 | 6.25 | 3.632 | 5 |
| 0.7 | 4.591 | 2.767 | 8.571 |
| 0.6 | 2.778 | 1.774 | 13.333 |
| 0.5 | 1 | 0.712 | 20 |
| 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
| 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 30 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Wang, P.; Xi, S. Mean-Variance Analysis of Retailers Deploying RFID-Enabled Smart Shelves. Information 2018, 9, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020040
Zhu L, Wang P, Xi S. Mean-Variance Analysis of Retailers Deploying RFID-Enabled Smart Shelves. Information. 2018; 9(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Lijing, Peize Wang, and Sha Xi. 2018. "Mean-Variance Analysis of Retailers Deploying RFID-Enabled Smart Shelves" Information 9, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020040
APA StyleZhu, L., Wang, P., & Xi, S. (2018). Mean-Variance Analysis of Retailers Deploying RFID-Enabled Smart Shelves. Information, 9(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9020040