Personal Identification and the Assessment of the Psychophysiological State While Writing a Signature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Further increase in the signer's identification reliability can be achieved if the signer's psychophysiological states at the moments of template creation and identification are the same.
- (2)
- Results of the signer's psychophysiological state evaluation can be used to make a suggestion about the signer's admission to specific information.
2. Proposed Approach
2.1. Identification and Training Procedures
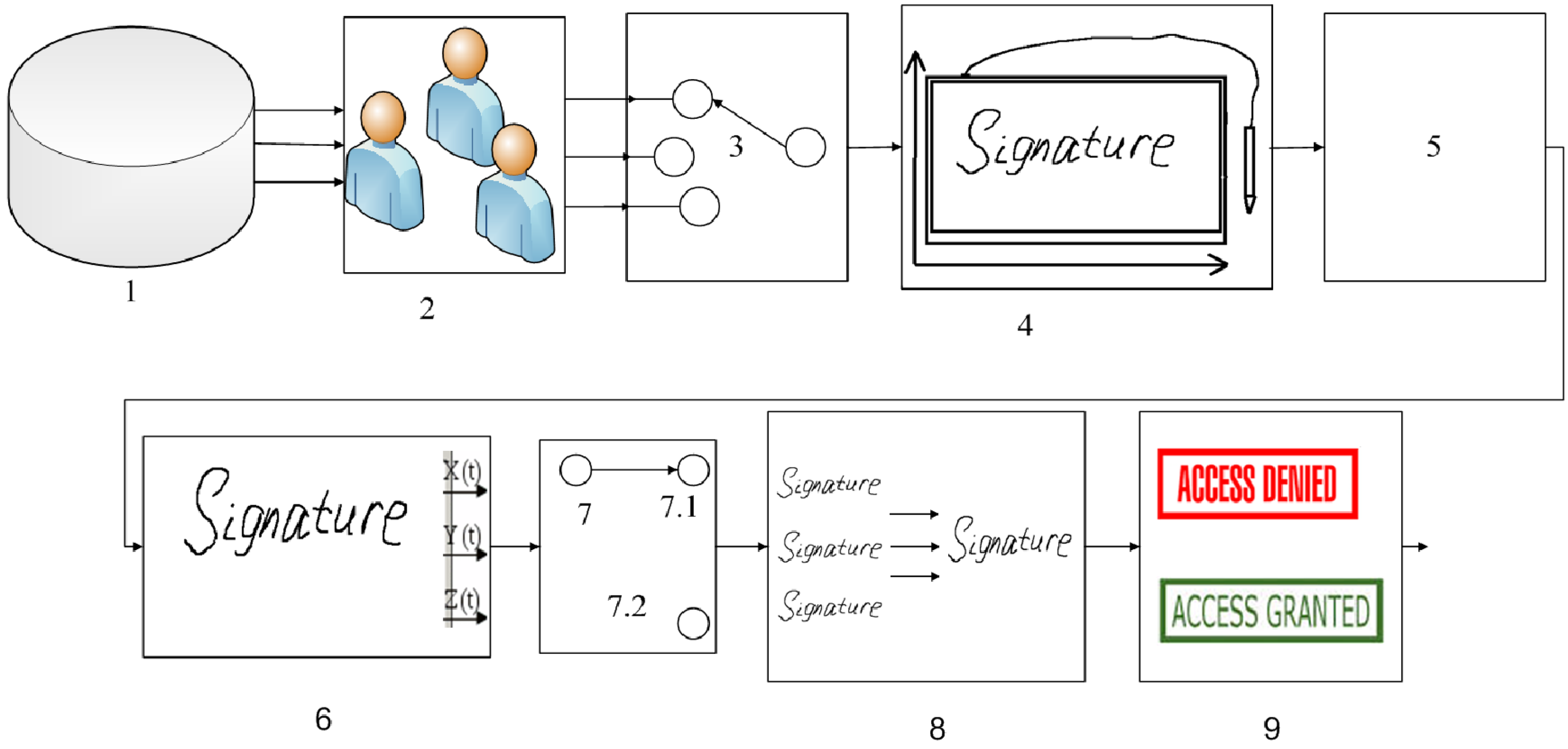
- To create signature etalons for each subject psychophysiological state separately;
- To perform the subject psychophysiological state recognition during his/her identification and to use etalon signature descriptions for corresponding psychophysiological state.
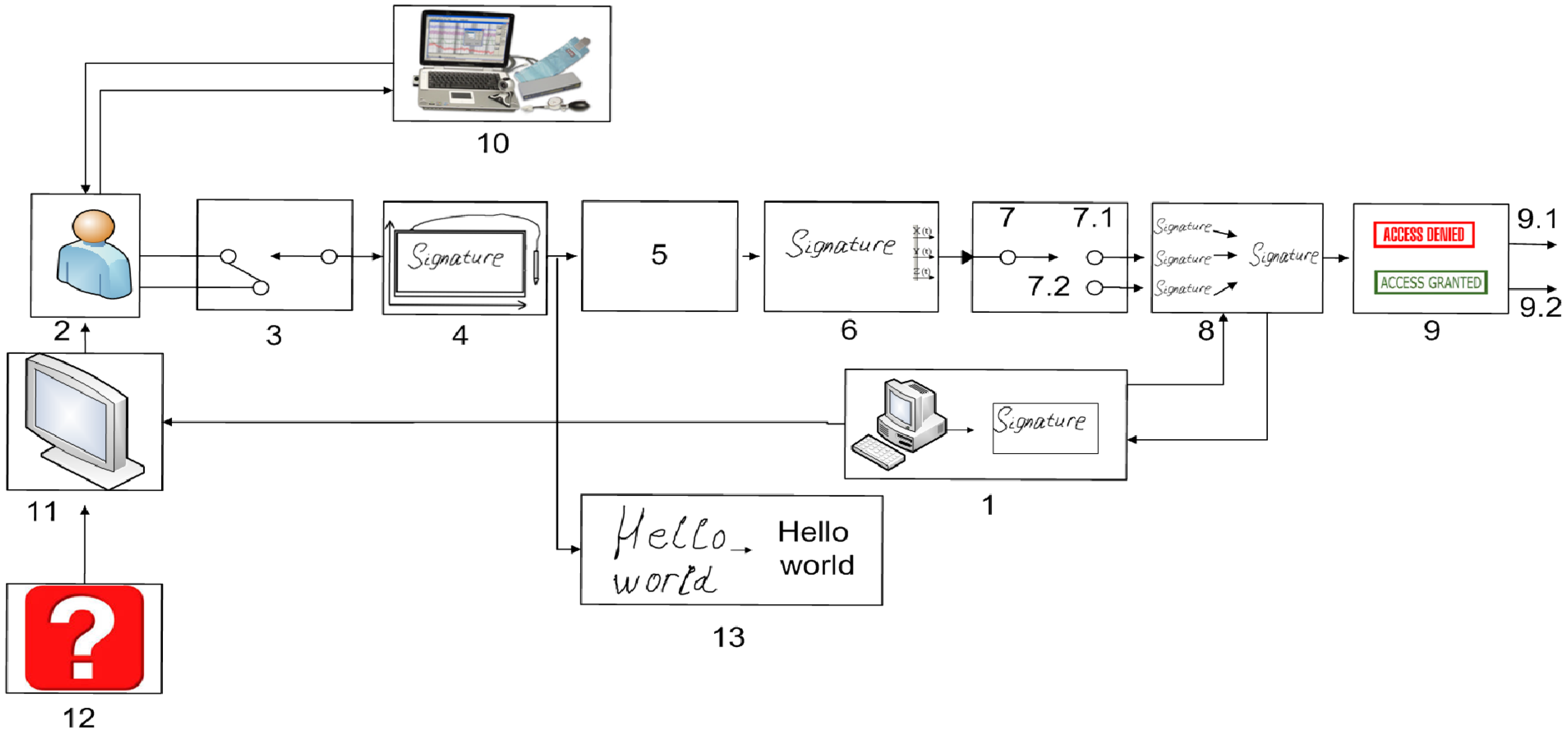
2.2. Usage of Information about the Psychophysiological State
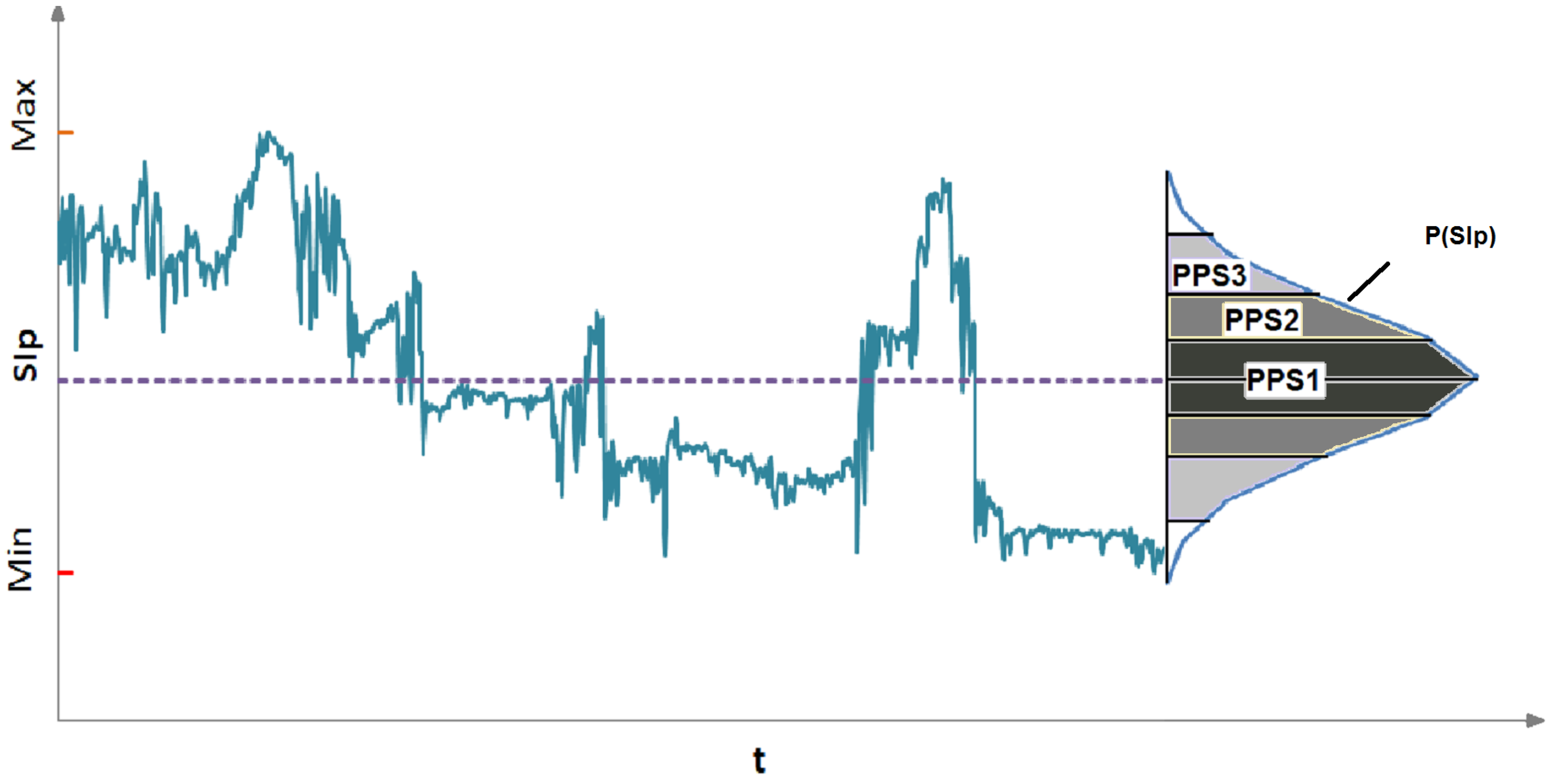
2.3. Decision-Making Algorithm
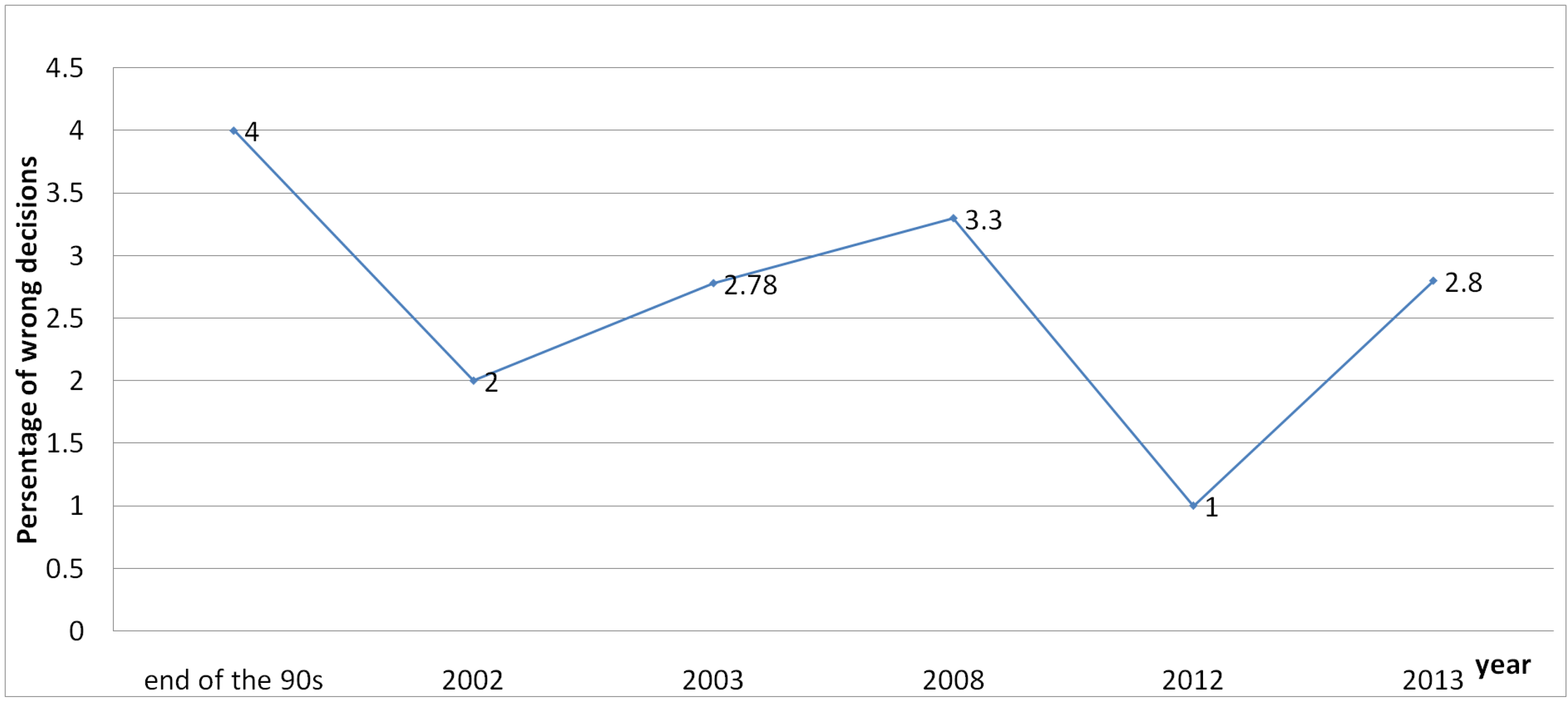
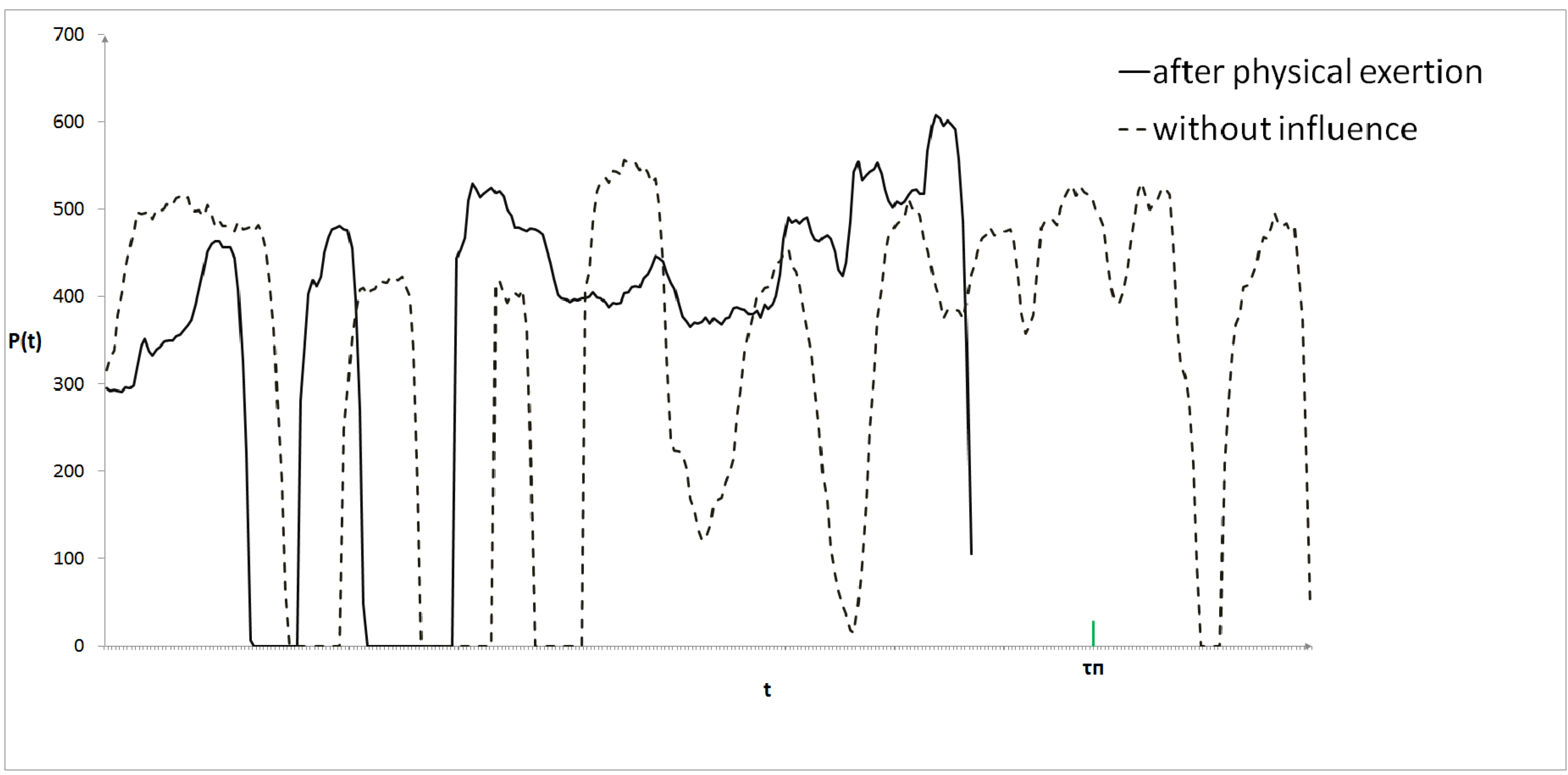
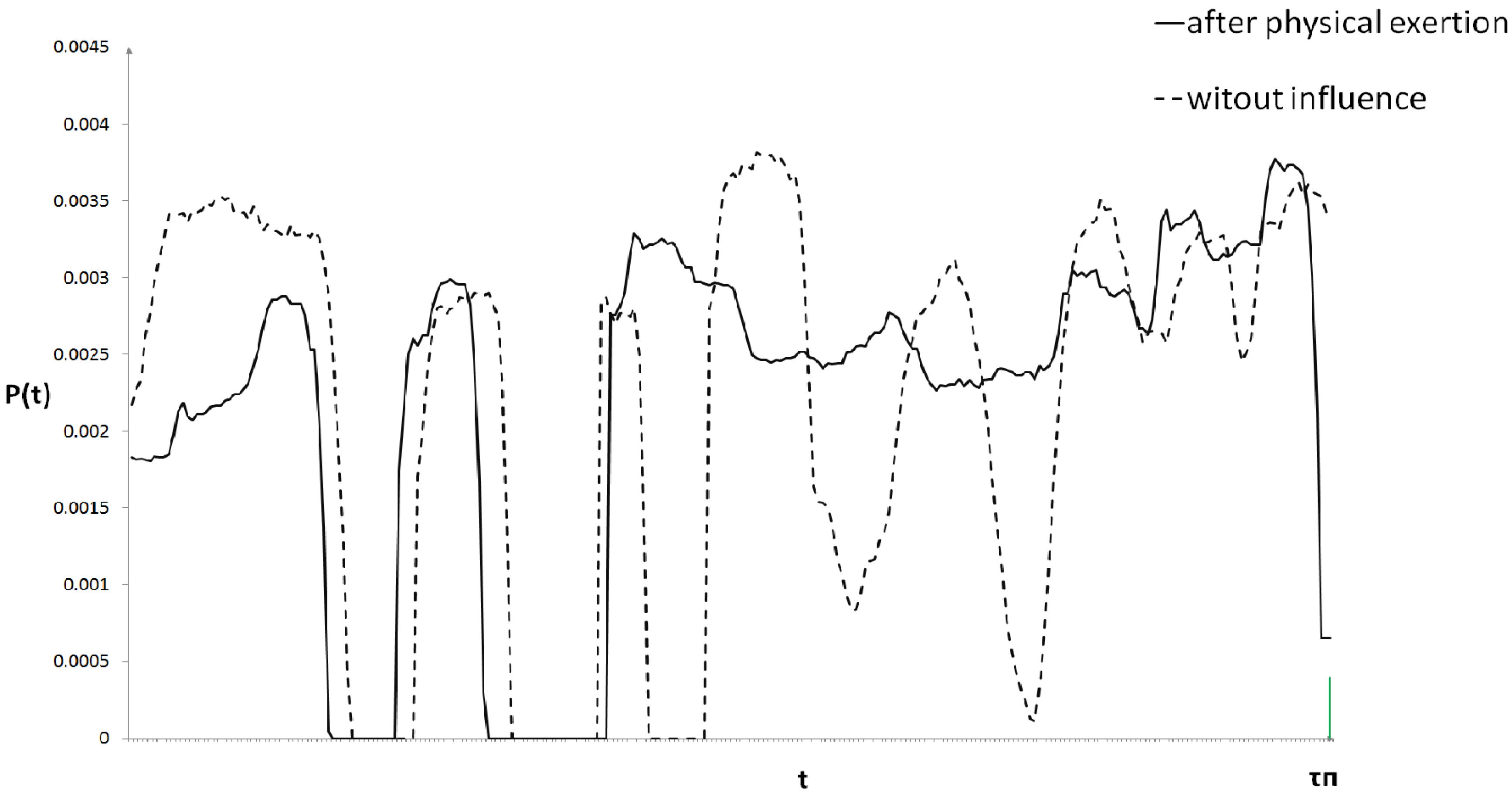
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Epifantsev, B.N.; Lozhnikov, P.S.; Kovalchuk, A.S. Hidden identification for operators of information-processing systems by heart rate variability in the course of professional activity. In Proceedings of the Dynamics of Systems, Mechanisms and Machines (Dynamics) 2014, Omsk, Russian, 11–13 November 2014; pp. 1–4.
- Xiao, X.H.; Leedham, G. Signature verification by neural networks with selective attention. Appl. Intell. 1999, 11, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Lee, I.Y.; Yang, H.S. An on-line signature verification system using hidden Markov model in polar space. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Workshop on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition, Ontario, Canada, 6–8 August 2002; pp. 329–333.
- Miramatsu, D.; Matsumoto, T. An HMM on-line signature verification algorithm. In Audio- and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference, AVBPA 2003, Guildford, UK, 9–11 June 2003; pp. 233–241.
- McCabe, A. Neural network—Based handwritten signature verification. J. Comput. 2008, 3, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshir, M.; Kempf, F. Advanced biometric pen system for recording and analyzing handwriting. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2012, 68, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutellaa, E. Improving online signature verification by user-specific likelihood ratio score normalization. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th International Workshop on Systems, Signal Processing and Their Application (WoSSPA), Algiers, Algeria, 12–15 May 2013; pp. 296–300.
- Impedovo, D.; Pirloi, G. Automatic Signature Verification: The State of the Art. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. C Appl. Rev. 2008, 38, 609–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, L.; Deka, A. A Study on Handwritten Signature. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 79, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Rindtorff, K.; Rudolph, V. Method for Verification of Signatures and Handwriting Based on Comparison of Extracted Features. U.S. Patent No. 5,995,953, 30 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Black, G.R. Security Authentication Method and System. U.S. Patent No. 7,363,505, 22 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, R. A Prototype System for Off-line Signature Verification Using Multilayered Feedforward Neural Networks. Master's Thesis, RMIT, Melbourne, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Tassinary, L.G.; Berntson, G. Handbook of Psychophysiology, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, G.; Hockey, J.; Burov, O. Operator Functional State: The Assessment and Prediction of Human Performance Degradation in Complex Tasks; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vendemia, J.M.C. Detection of Deception. Polygraph 2003, 32, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Yeo, H.S.; Yoon, G.W. Method and Apparatus for Evaluating Human Stress Using Photoplethysmography. U.S. Patent No. 7,613,486, 3 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Masakov, L.V.; Larionov, V.B. Apparatus and Method for Non-Invasive Measurement of Current Functional State and Adaptive Response in Humans. U.S. Patent No. 6,572,558, 3 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai, H.; Oliver, D.; Rohrbangh, J.; Papadopoulos, C. Novel Applications of Laser Doppler Vibration Measurements to Medical Imaging. Sens. Imaging Int. J. 2013, 14, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Berilla, J. An Innovative Non-invasive ECG Sensor and Comparison Study with Clinic System. In Proceedings of the 2013 Bioengineering Conference (NEBEC), Syracuse, NY, USA, 5–7 April 2013; Volume 39, pp. 163–164.
- Bayevsky, R.M.; Ivanov, G.G.; Chireykin, L.V.; Gavrilushkin, A.P.; Dovgalevsky, P.Ya.; Kukushkin, U.A.; Mironova, T.F.; Priluzkiy, D.A.; Semenov, U.N.; Fedorov, V.F.; et al. HRV Analysis under the Usage of Different Electrocardiography Systems (Methodical Recommendations). Available online: http://www.drkucera.eu/upload_doc/hrv_ analysis_%28methodical_recommendations%29.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2015).
- Malik, M.; Bigger, J.T.; Camm, A.J. Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Eur. Heart J. 1996, 17, 354–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Rau, L.F.; Wang, P.S.P. (Eds.) Handbook of Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, Singapore, 1995.
- Vrij, A. Detecting Lies and Deceit: The Psychology of Lying and Implications for Professional Practice; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lozhnikov, P.S.; Sulavko, A.E.; Volkov, D.A. Application of noise tolerant code to biometric data to verify the authenticity of transmitting information. In Proceedings of the Control and Communications (SIBCON), Omsk, Russia, 20–22 May 2015.
- Epifantsev, B.N.; Lozhnikov, P.S.; Sulavko, A.Y. An algorithm of hypotheses identification in an uninformative attribute space based on consistent bayes' law. Interindustry Inf. Serv. IIS 2013, 2, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Eremenko, A.; Sulavko, A.Y.; Samotuga, A.Y. Exceptions gross mistakes of biometric data before creating measurement standards of people in biometric identification systems. Inf. Technol. Comput. Syst. 2013, 3, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Eremenko, A.; Sulavko, A.Y. Compression method of own areas of identified classes of images in the space of signs that contains small portions of information. Artif. Intell. Decis. Mak. 2014, 2, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kolers, P.; Eden, M. Recognizing Patterns. Studies in Living and Automatic Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lozhnikov, P.; Sulavko, A.; Samotuga, A. Personal Identification and the Assessment of the Psychophysiological State While Writing a Signature. Information 2015, 6, 454-466. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6030454
Lozhnikov P, Sulavko A, Samotuga A. Personal Identification and the Assessment of the Psychophysiological State While Writing a Signature. Information. 2015; 6(3):454-466. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6030454
Chicago/Turabian StyleLozhnikov, Pavel, Alexey Sulavko, and Alexander Samotuga. 2015. "Personal Identification and the Assessment of the Psychophysiological State While Writing a Signature" Information 6, no. 3: 454-466. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6030454
APA StyleLozhnikov, P., Sulavko, A., & Samotuga, A. (2015). Personal Identification and the Assessment of the Psychophysiological State While Writing a Signature. Information, 6(3), 454-466. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6030454





