Immune-Based Botnet Defense System: Multi-Layered Defense and Immune Memory †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Proposal of an IoT Botnet Defense Mechanism mimicking the bioimmune system: Focusing on the roles of antibodies and phagocyte cells in the bioimmune system, we developed two types of worms, antibody worms and phagocyte worms, and proposed utilizing them to apply a multi-layered defense mechanism, consisting of innate immunity and adaptive immunity, in IoT botnet defense.
- Development of an immune memory function for repeated infections: For botnets that repeatedly infect systems, we developed an immune memory function. This function enables the system to respond more quickly and effectively, and it improves defense efficiency and robustness.
- Implementation and evaluation of an iBDS prototype: To demonstrate the concept of our proposed iBDS, we implemented a prototype. Its effectiveness has been confirmed through simulations and experiments in actual IoT environments.
2. Bioimmune-Inspired Cybersecurity: Overview and Research Positioning
2.1. Bioimmune System
2.2. Bioimmune-Inspired Cybersecurity Research Overview
2.3. Uniqueness of This Research
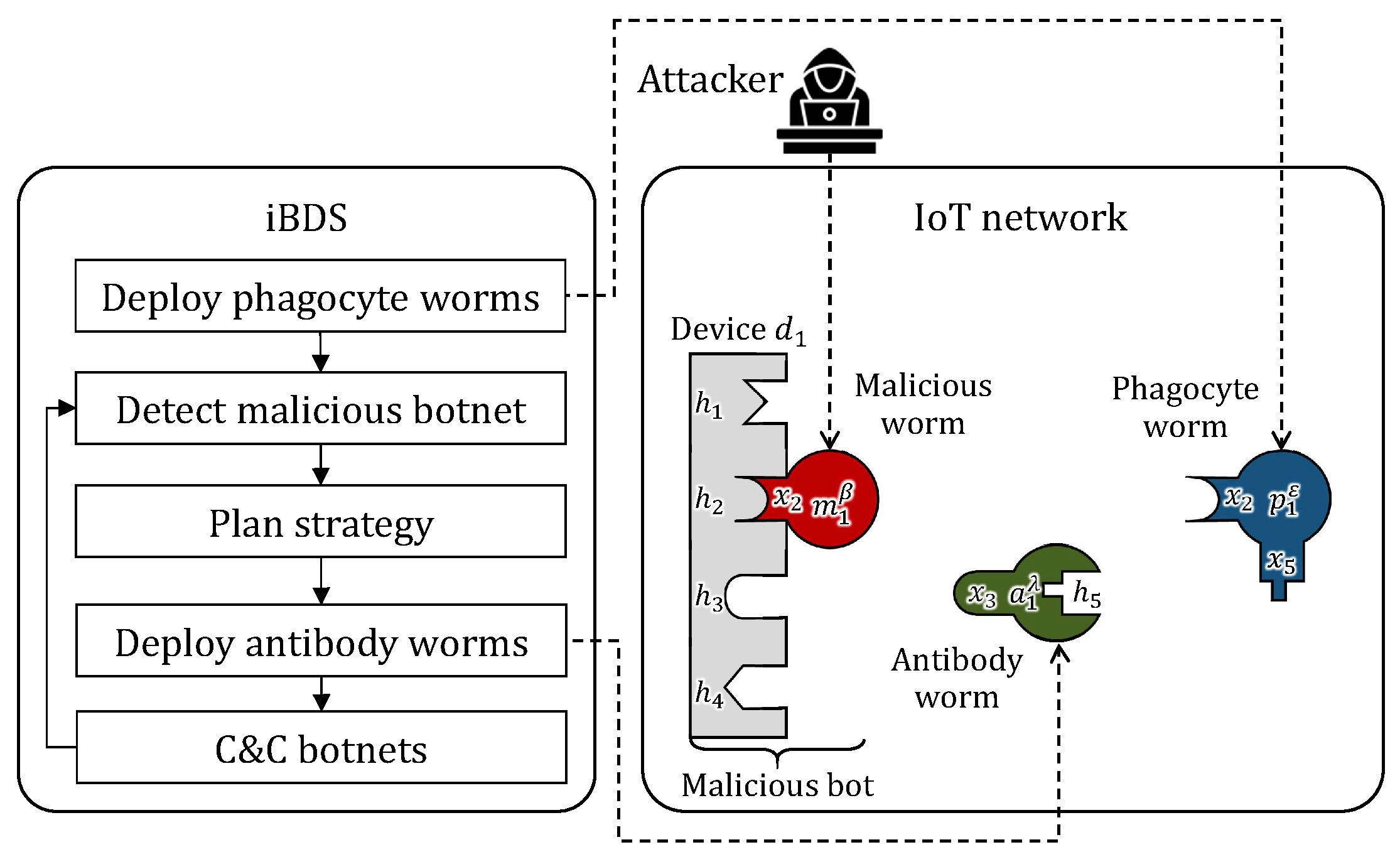
3. Basic Concept of iBDS and Cooperation Between Phagocyte Worms and Antibody Worms
3.1. Basic Concept of iBDS
- Phagocyte worms: These worms directly eliminate malicious botnets. They infect malicious bots and remove malicious worms from them.
- Antibody worms: These worms help phagocyte worms eliminate malicious botnets. When phagocyte worms cannot directly infect malicious bots, antibody worms, instead, infect the bots and change their vulnerabilities to allow phagocyte worms to infect them.
- Deploy phagocyte worms: iBDS deploys phagocyte worms on the IoT network and establishes a resident phagocyte botnet.
- Detect malicious botnet: iBDS continuously monitors the network to detect a malicious botnet that an attacker creates using malicious worms.
- Plan strategy: iBDS plans a strategy to effectively eliminate the detected malicious botnet.
- Deploy antibody worms: iBDS deploys the antibody worm and builds an antibody botnet based on the developed strategy.
- Command and control botnets: iBDS commands and controls the antibody and phagocyte botnets to effectively eliminate the malicious botnet.
3.2. Design of Phagocyte Worms and Antibody Worms
4. Innate and Acquired Immunity and Immune Memory of iBDS
4.1. Innate Immunity
- At startup: iBDS makes 10 -type phagocyte worms resident on the IoT network.
- Step 5: The attacker infects the network with 10 -type malicious worms. This represents the first attack.
- Step 30: The attacker infects the network again with 10 -type malicious worms. This represents the second attack.
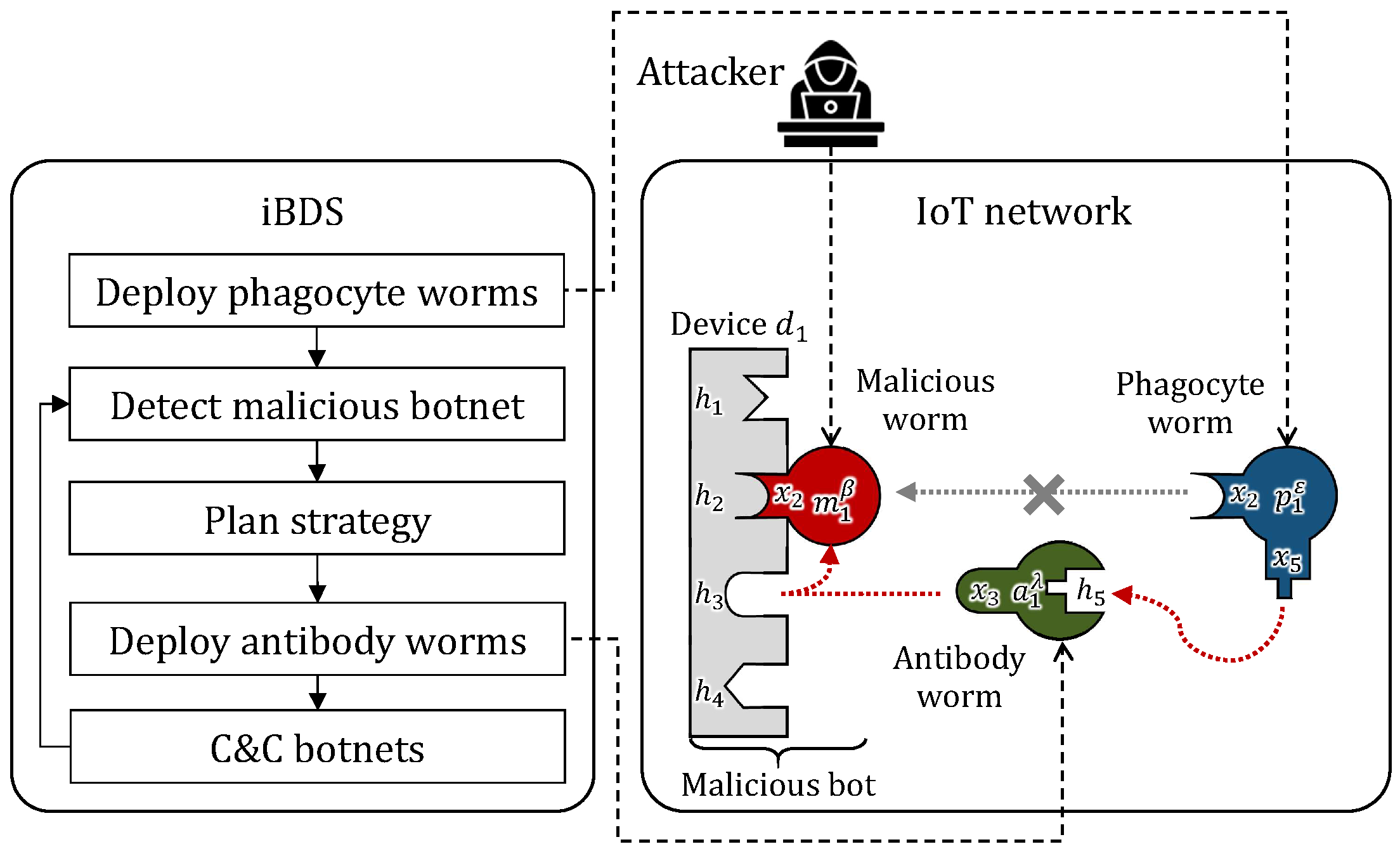
4.2. Acquired Immunity
- At startup: iBDS makes 10 -type phagocyte worms that are resident on the IoT network.
- Step 5: The attacker infects the network with 10 -type malicious worms.
- Step 10: iBDS detects 10 () malicious bots and deploys 20 () -type antibody worms as the primary immune response.
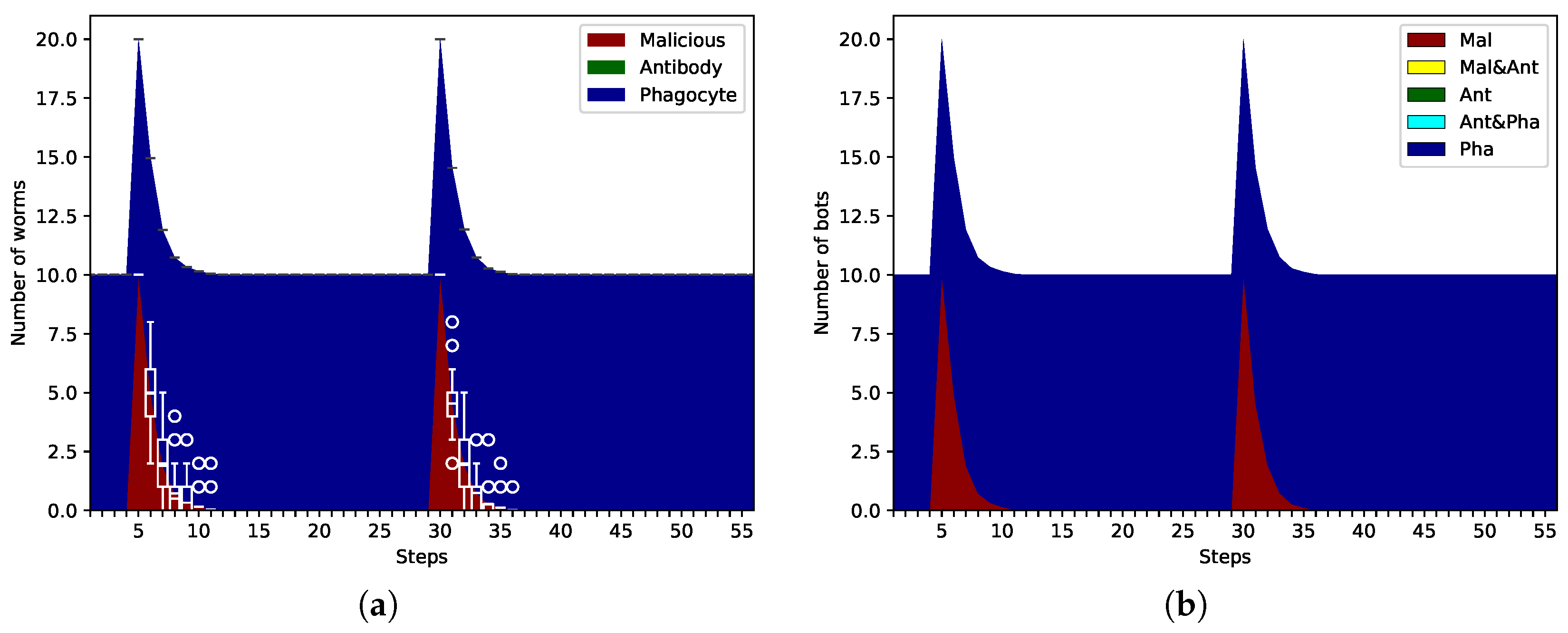
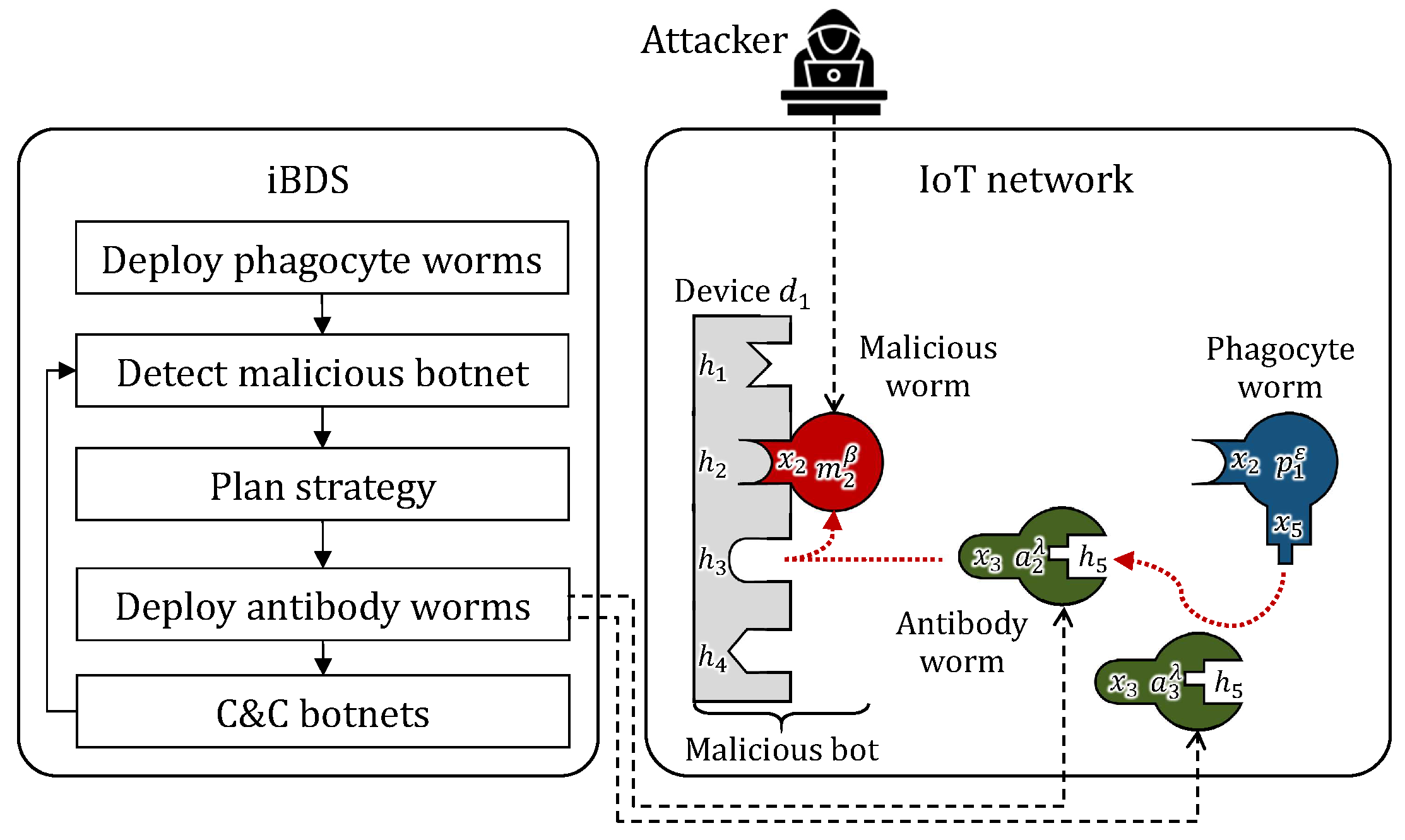
4.3. Immune Memory
- At startup: iBDS makes 10 -type phagocyte worms that are resident on the IoT network.
- Step 5: The attacker infects the network with 10 -type malicious worms as the first attack.
- Step 10: iBDS detects 10 () malicious bots and deploys 20 () -type antibody worms as the primary immune response.
- Step 30: The attacker infects the network again with 10 -type malicious worms as the second attack.
- Step 35: iBDS detects 10 () malicious bots and deploys 30 () -type antibody worms as the secondary immune response.
5. Prototype Implementation and Experimental Evaluation
5.1. Prototype Implementation
- DNS and DHCP server: 192.168.0.1;
- C&C, Web, Loader server for malicious botnet: 192.168.0.4;
- C&C, Web, Loader server for phagocyte botnet: 192.168.0.14;
- C&C, Web, Loader server for antibody botnet: 192.168.0.24;
- A total of 22 vulnerable devices: 192.168.0.100 ∼ 192.168.0.250.
5.2. Experimental Evaluation
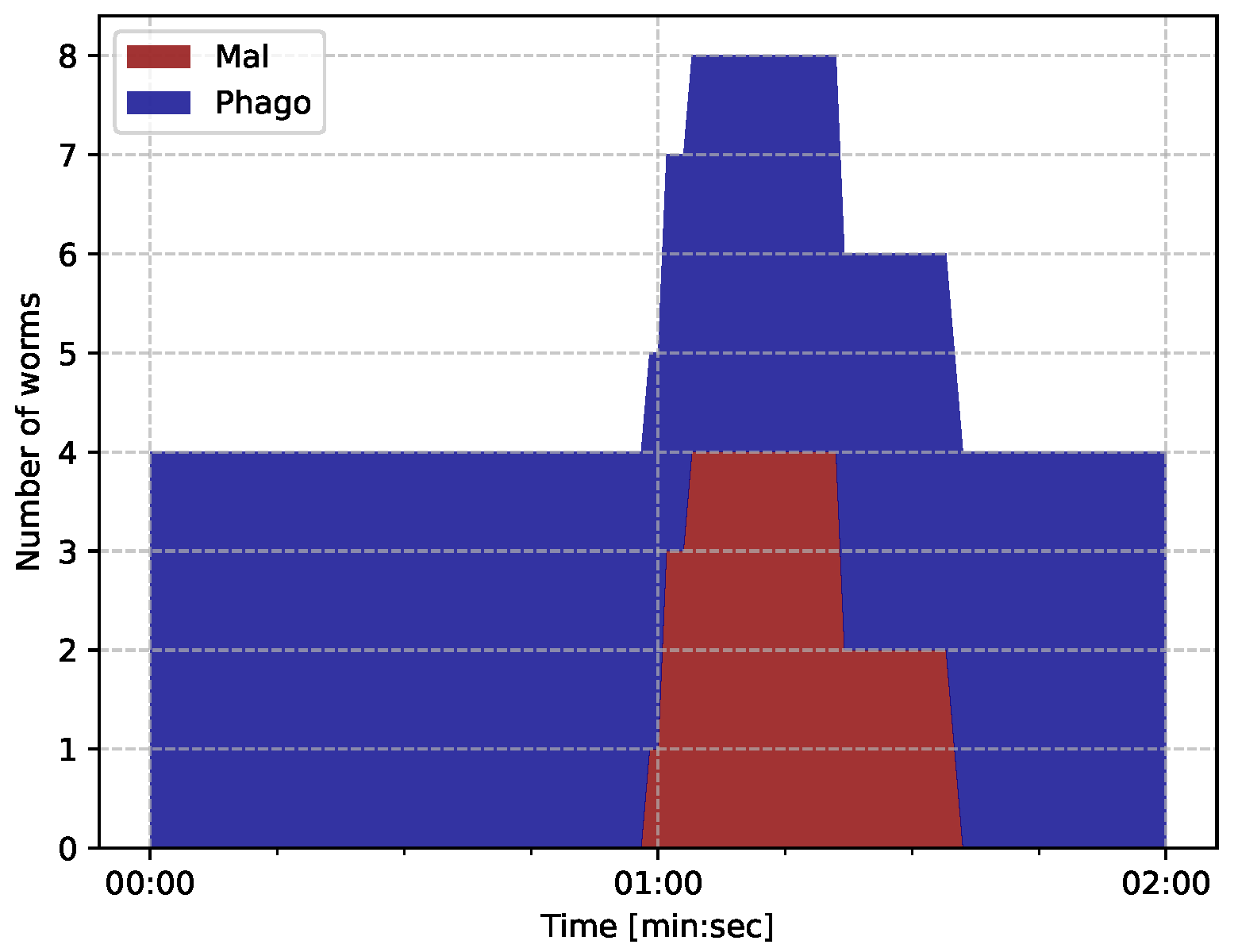
- iBDS makes 4 -type phagocyte worms that are resident on the IoT network at startup;
- The attacker infects the network with 4 -type malicious worms at about 01:00 (min:sec).
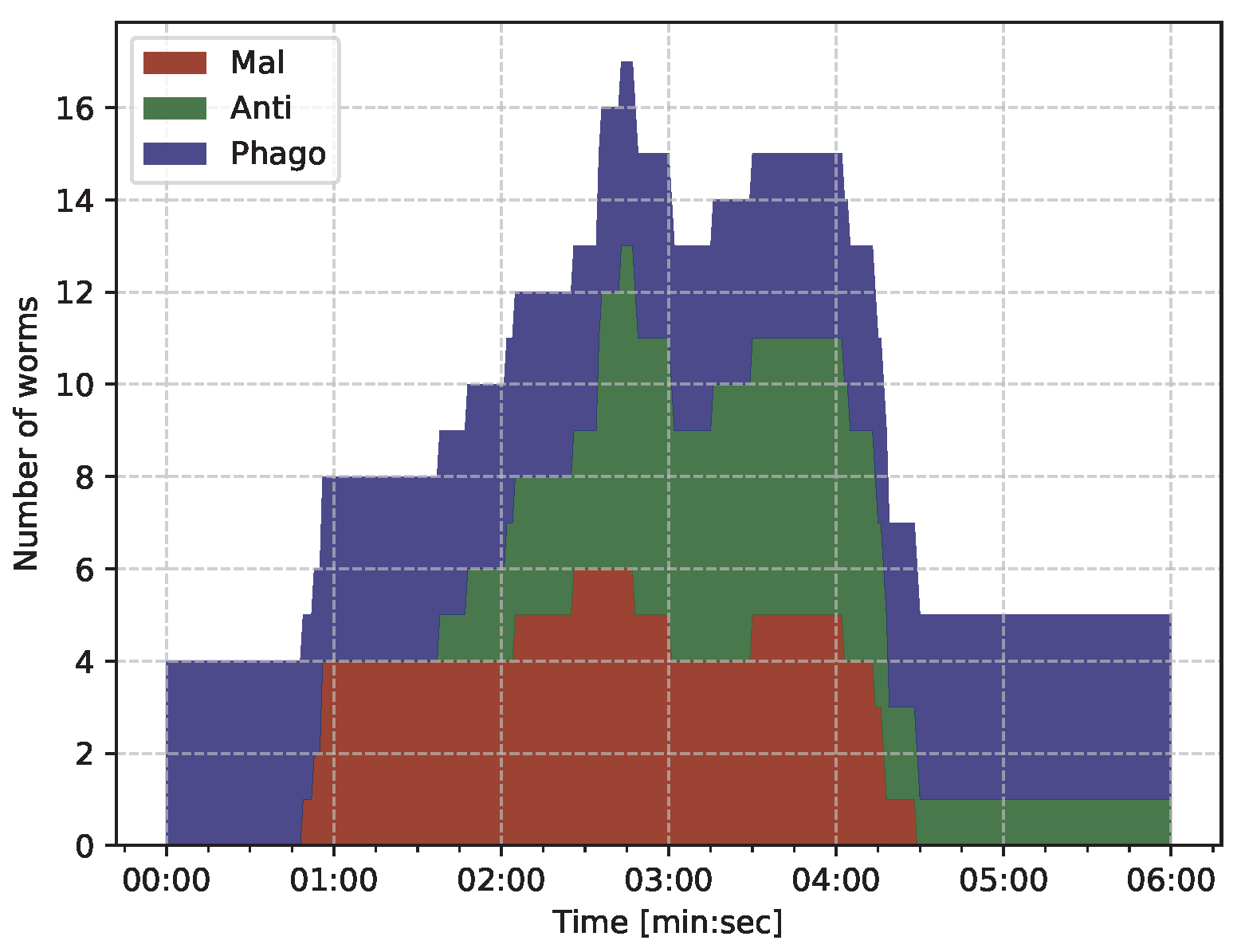
- iBDS makes 4 -type phagocyte worms that are resident on the IoT network at starup;
- The attacker infects the network with 3 -type malicious worms at about 01:00;
- When iBDS detects 4 () malicious bots, it deploys 8 () -type antibody worms as the primary immune response.
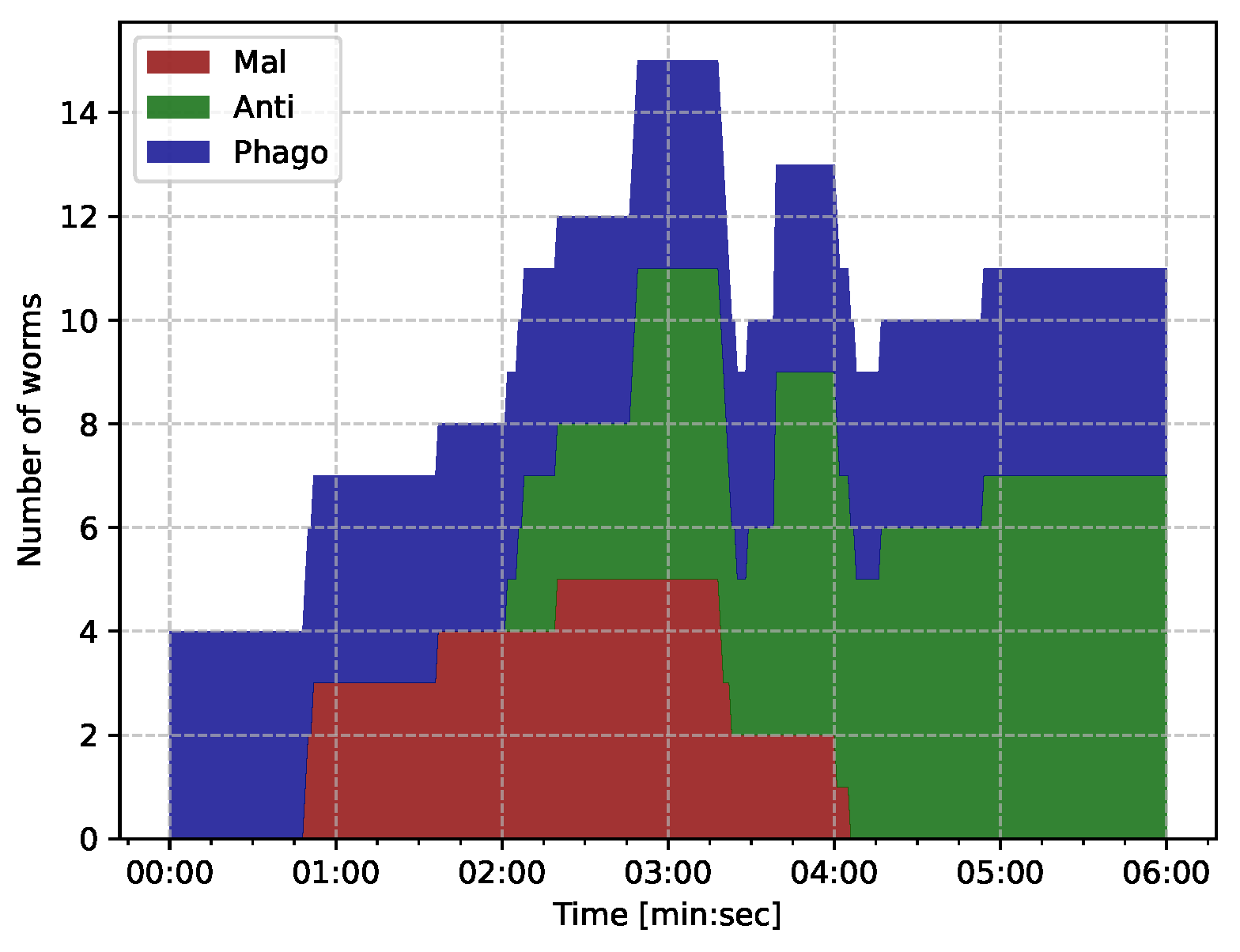
- iBDS makes 4 -type phagocyte worms that are resident on the IoT network at startup;
- The attacker infects the network again with 3 -type malicious worms at about 01:00;
- When iBDS detects 4 () malicious bots, it deploys 8 () -type antibody worms as the secondary immune response.
5.3. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Douligeris, C.; Raghimi, O.; Lourenço, M.B.; Marinos, L.; Sfakianakis, A.; Doerr, C.; Armin, J.; Riccardi, M.; Wim, M.; Thaker, N.; et al. ENISA Threat Landscape 2020—Botnet. Available online: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/enisa-threat-landscape-2020-botnet (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Owen, H.; Zarrin, J.; Pour, S.M. A Survey on Botnets, Issues, Threats, Methods, Detection and Prevention. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2022, 2, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolias, C.; Kambourakis, G.; Stavrou, A.; Voas, J. DDoS in the IoT: Mirai and other botnets. IEEE Comput. 2017, 50, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence Experts. Kaspersky Finds Botnet Prices Starting at $100 on Dark Web Market. Available online: https://www.kaspersky.co.uk/about/press-releases/kaspersky-finds-botnet-prices-starting-at-100-on-dark-web-market (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Ashraf, J.; Keshk, M.; Moustafa, N.; Abdel-Basset, M.; Khurshid, H.; Bakhshi, A.D.; Mostafa, R.R. IoTBoT-IDS: A Novel Statistical Learning-Enabled Botnet Detection Framework for Protecting Networks of Smart Cities. In Sustainable Cities and Society; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 72, p. 103041. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Du, Y. Towards Effective Feature Selection for IoT Botnet Attack Detection Using a Genetic Algorithm. Electronics 2023, 12, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.-A.; Chao, C.-S. Real-Time Dynamic Configuration of Firewall Rules for High-Speed IoT Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 4th Eurasia Conference on IOT, Communication and Engineering (ECICE), Yunlin, Taiwan, 28–30 October 2022; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.S.; Lee, J.E.; Oh, S.H. Stage-Specific Reinforcement Learning-Based Firewall for IoT Security Against Okiru Botnet. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Cyberworlds, Yamanashi, Japan, 29–31 October 2024; pp. 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Computer Emergency Readiness Team. Heightened DDoS Threat Posed by Mirai and Other Botnets. alert TA16-288A. Available online: https://www.us-cert.gov/ncas/alerts/TA16-288A (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Yamaguchi, S. Botnet Defense System: A System to Fight Botnets with Botnets. In Malware; Gritzalis, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, S. An Antibody-Mediated Immune Mechanism in Botnet Defense System. In Proceeding of the 2024 International Conference on Future Technologies for Smart Society (ICFTSS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 7–8 August 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Weaver, C. Janeway’s Immunobiology, 9th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alrubayyi, H.; Goteng, G.; Jaber, M.; Kelly, J. Challenges of Malware Detection in the IoT and a Review of Artificial Immune System Approaches. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.; Perelson, A.S.; Allen, L.; Cherukuri, R. Self-Nonself Discrimination in a Computer. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE Computer Society Symposium on Research in Security and Privacy, Oakland, CA, USA, 16–18 May 1994; pp. 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, L.N.; Von Zuben, F.J. The Clonal Selection Algorithm with Engineering Applications. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO ’00), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–12 July 2000; pp. 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro, L.N.; Timmis, J. An Artificial Immune Network for Multimodal Function Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; Volume 1, pp. 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Pamukov, M.E.; Poulkov, V.K.; Shterev, V.A. Negative Selection and Neural Network Based Algorithm for Intrusion Detection in IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing, Athens, Greece, 4–6 July 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereta, M. Negative Selection Algorithm for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.; Tan, Y. A Virus Detection System Based on Artificial Immune System. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Beijing, China, 11–14 December 2009; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Application of Clonal Selection Clustering Algorithm for Anomaly Detection in Network Security Management. Open Autom. Control Syst. J. 2015, 7, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, M.; Luo, A.; He, J. Improved Clonal Selection Algorithm Based on the Directional Update Strategy. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 19312–19331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassam, M.A. Artificial Immune Network Clustering Approach for Anomaly Intrusion Detection. J. Adv. Inf. Technol. 2012, 3, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.H.; Vu, N.T.; Le, T. A Smart System of Malware Detection Based on Artificial Immune Network and Deep Belief Network. Int. J. Inf. Secur. Priv. 2021, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, H. Unsupervised Anomaly Detection for Network Traffic Using Artificial Immune Network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 13007–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSobeh, A.M.R.; Gaber, K.; Hammad, M.M. Android Malware Detection Using Time-Aware Machine Learning Approach. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 12627–12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Caldas Filho, F.; Soares, S.; Oroski, E.; de Oliveira Albuquerque, R.; da Mata, R.; de Mendonça, F.; de Sousa Júnior, R. Botnet Detection and Mitigation Model for IoT Networks Using Federated Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, P.P.; Truong-Huu, T.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Teo, S.G. Detection and Classification of Botnet Traffic Using Deep Learning with Model Explanation. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Makihara, D. On Resident Strategy for White-Hat Botnet in Botnet Defense System. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2022 International Conference on Consumer Electronics—Taiwan (ICCE-TW), Taipei, Taiwan, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, S. BDSsim: A Mesa-Based Simulator for Botnet Defense System. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers, and Communications (ITC-CSCC), Okinawa, Japan, 2–5 July 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- ter Hoeven, E.; Kwakkel, J.; Hess, V.; Pike, T.; Wang, B.; Kazil, J. Mesa 3: Agent-Based Modeling with Python in 2025. J. Open Source Softw. 2025, 10, 7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, A.A.; Schult, D.A.; Swart, P.J. Exploring Network Structure, Dynamics, and Function Using NetworkX. In Proceedings of the 7th Python in Science Conference, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–24 August 2008; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Fukushima, A.; Yamaguchi, S. Implementation of White-Hat Worms Using Mirai Source Code and Its Optimization through Parameter Tuning. Future Internet 2024, 16, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamblin, J. GitHub-Jgamblin/Mirai-Source-Code: Leaked Mirai Source Code for Research/IoC Development Purposes. Available online: https://github.com/jgamblin/Mirai-Source-Code (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- EC-Council. Code of Ethics|EC-Council. Available online: https://www.eccouncil.org/code-of-ethics (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- OpenWrt Website. Available online: http://openwrt.org/ (accessed on 20 July 2024).
- Patel, R.; Kaki, M.; Potluri, V.; Kahar, P.; Khanna, D. A Comprehensive Review of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Pfizer, Moderna & Johnson & Johnson. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2002083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Research | Purpose | Contributution | Negative Selection | Clonal Selection | Immune Network | Immune Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M.E. Pamukov et al. (2018) [17] | Detection | Integration of negative selection algorithm and neural networks | ✓ | |||
| M. Bereta et al. (2024) [18] | Detection | Integration of negative selection algorithm and unsupervised learning | ✓ | |||
| R. Chao et al. (2009) [19] | Detection | Proposal of a hybrid algorithm of negative selection and clonal selection | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Q. Zhang et al. (2015) [20] | Detection | Integration of clonal selection algorithm and clustering | ✓ | |||
| C. Yang et al. (2023) [21] | Detection | Proposal of algorithm for leading global optimal solution in a clonal selection algorithm | ✓ | |||
| M. Rassam (2012) [22] | Detection | Integration of immune network algorithm and rough set theory | ✓ | |||
| D.H. Le (2021) [23] | Detection | Virus detection system based on immune network algorithm | ✓ | |||
| Y. Shi et al. (2022) [24] | Detection | Proposal of an unsupervised anomaly-detection method based on immune network | ✓ | |||
| BDS (2020) [10] | Elimination | Proposal of disinfection method for single infections of botnets | ||||
| This paper iBDS | Elimination | Proposal of disinfection method for multiple infections of botnets | ✓ |
| Worm | Exploit | Vulnerability to Be | Vulnerability to Be | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removed | Added | |||
| -type malicious worm | ∅ | ∞ | ||
| -type malicious worm | ∅ | ∞ | ||
| -type phagocyte worm | ∅ | ∞ | ||
| -type antibody worm | 15 steps |
| Worm | Exploit | Vulnerability to Be | Vulnerability to Be |
|---|---|---|---|
| Removed | Added | ||
| -type malicious worm | |||
| -type phagocyte worm | |||
| -type phagocyte worm | |||
| -type antibody worm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaguchi, S. Immune-Based Botnet Defense System: Multi-Layered Defense and Immune Memory. Information 2025, 16, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080680
Yamaguchi S. Immune-Based Botnet Defense System: Multi-Layered Defense and Immune Memory. Information. 2025; 16(8):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080680
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaguchi, Shingo. 2025. "Immune-Based Botnet Defense System: Multi-Layered Defense and Immune Memory" Information 16, no. 8: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080680
APA StyleYamaguchi, S. (2025). Immune-Based Botnet Defense System: Multi-Layered Defense and Immune Memory. Information, 16(8), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080680







