AI-Based Detection of Optical Microscopic Images of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Planktonic and Biofilm States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
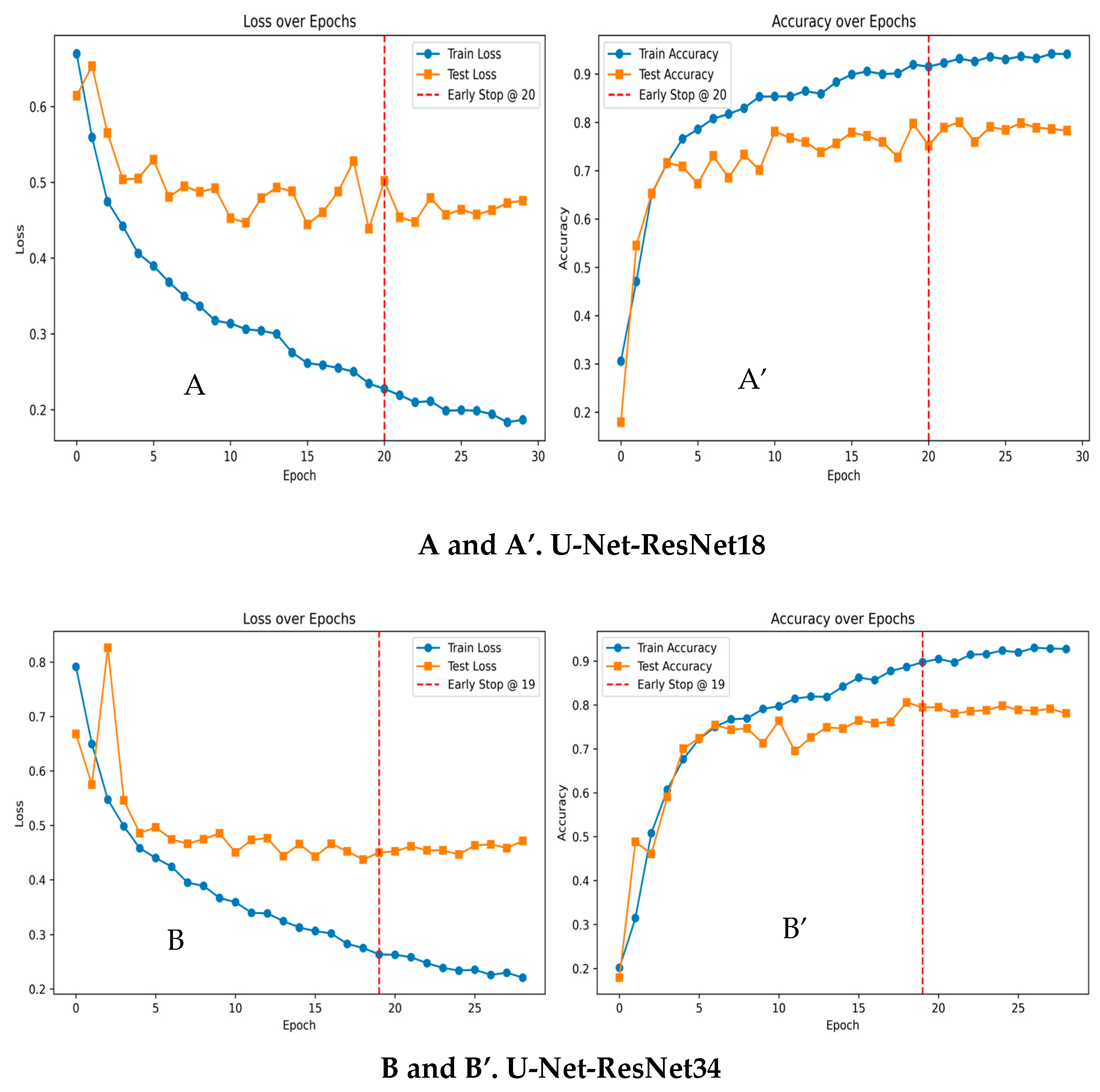
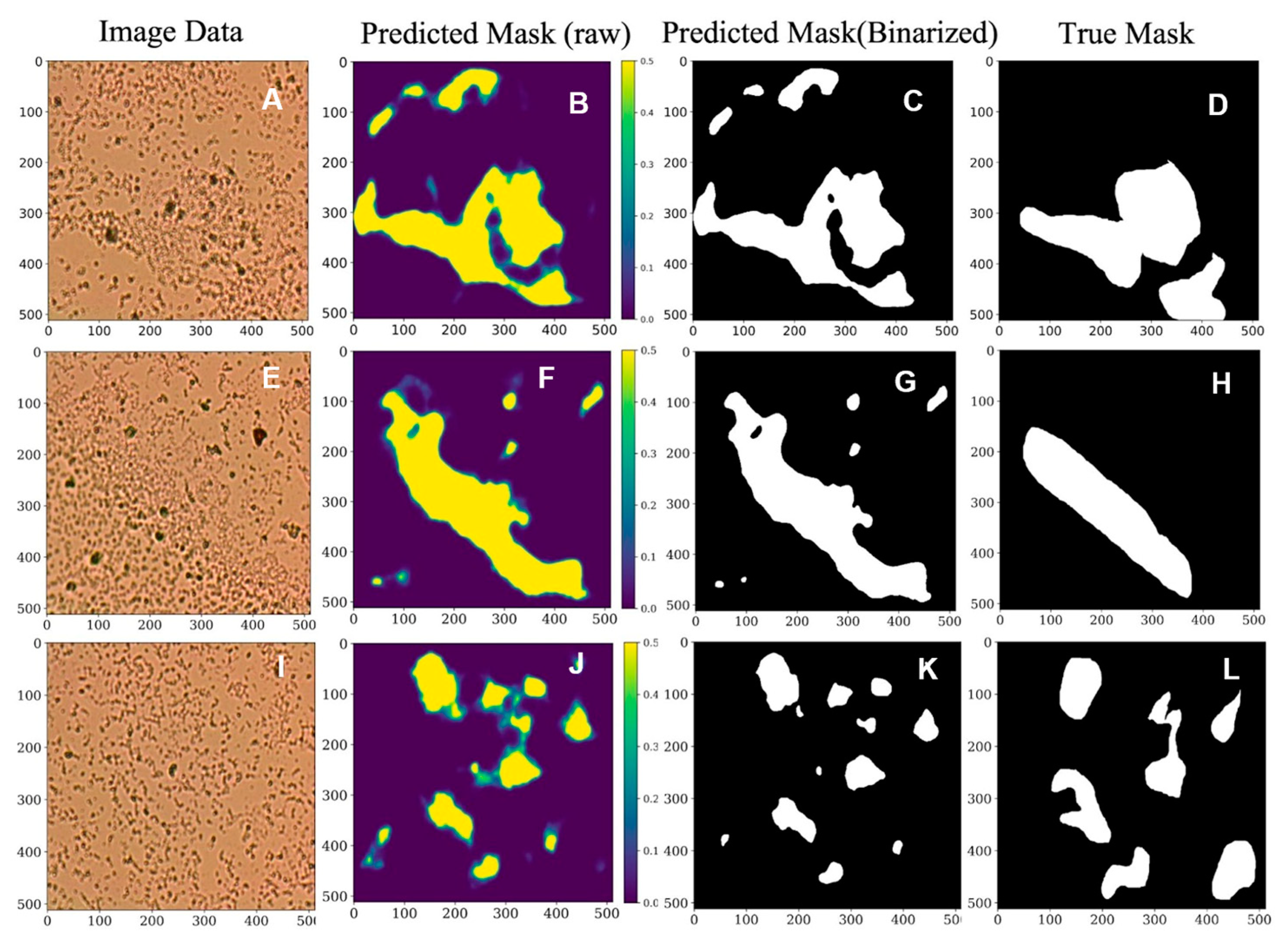
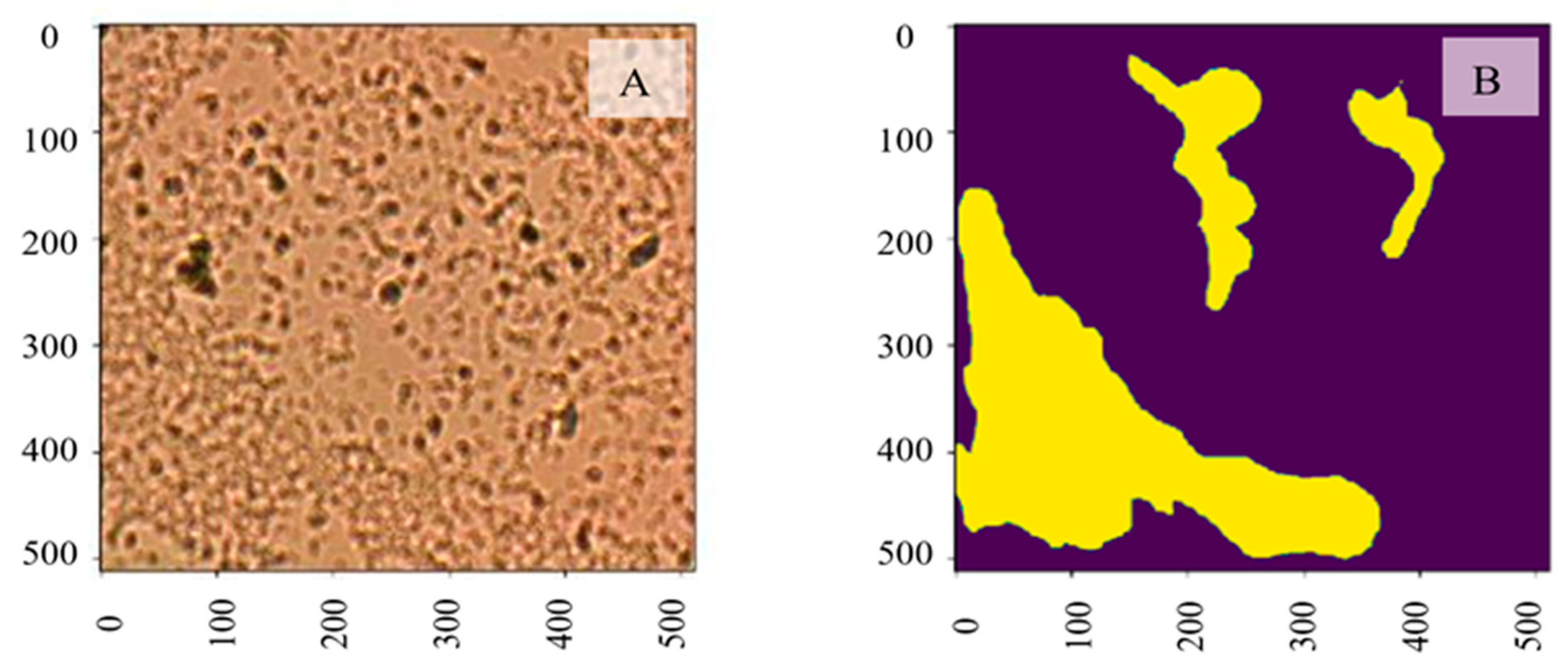
Machine Learning Results for Biofilm Segmentation
3. Experimental Methodology and Instrumentation
3.1. Preparation of DNA-Templated Silver Nanocluster
3.2. Preparation of Bacterial Samples for Biofilm Study
3.3. Steady-State Absorption, Fluorescence
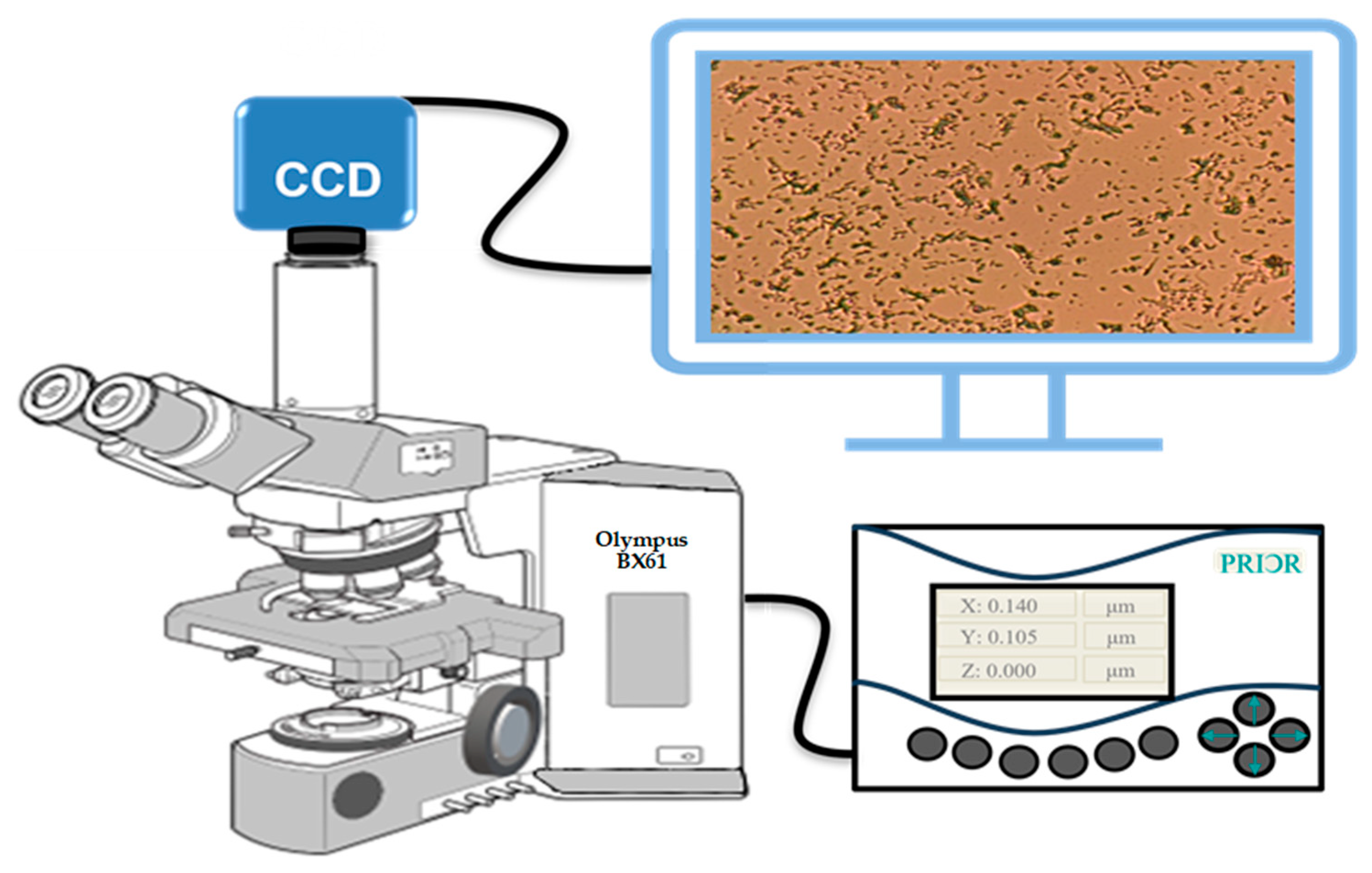
3.4. Instrumentation
3.5. Scanning Method
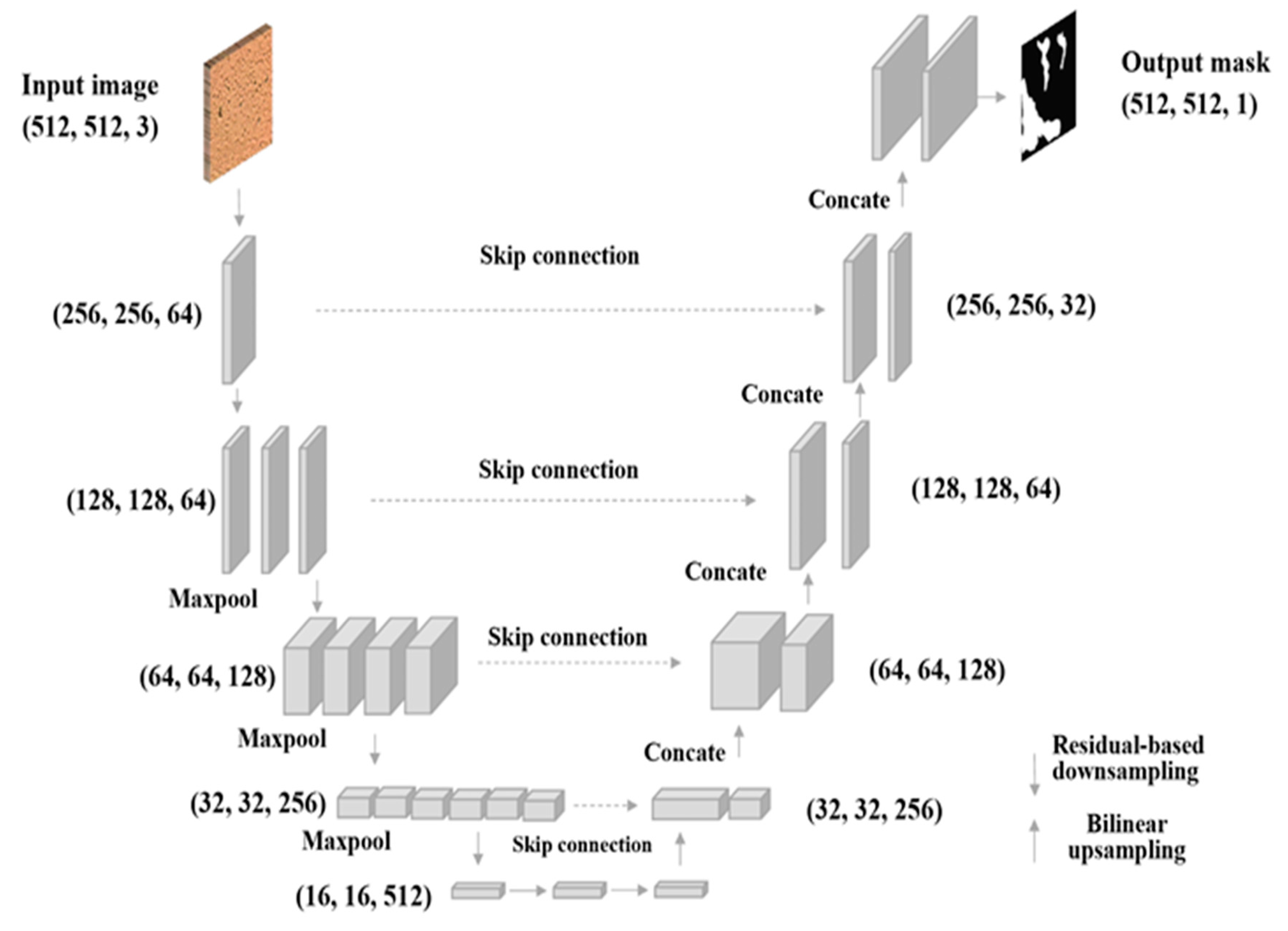
3.6. AI: ResNet-Based U-Net Biofilm Segmentation
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Characterization of the Aptamer-Templated Ag-Nc Using the Absorption and Fluorescence Spectroscopy
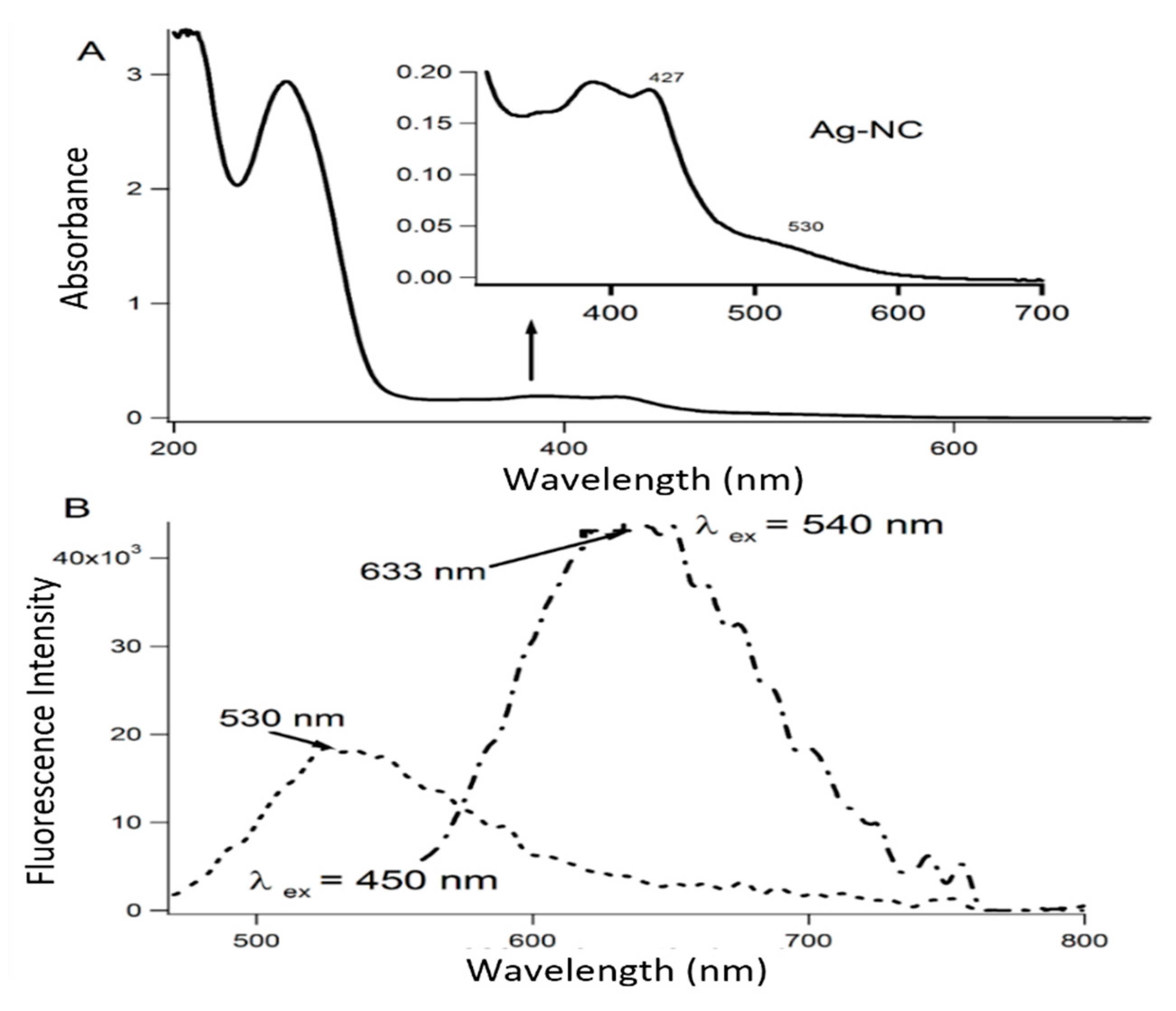
References
- Cohn, F. Beiträge Zur Biologie Der Bacillen; (Beiträge zur Biologie der Pflanzen. Untersuchungen über Bacterien, 1877); Duncker & Humblot: Berlin, Germany, 1877; Volume IV, pp. 249–276. [Google Scholar]
- Vlamakis, H.; Chai, Y.; Beauregard, P.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Sticking together: Building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samrot, A.V.; Mohamed, A.A.; Faradjeva, E.; Jie, L.S.; Sze, C.H.; Arif, A.; Sean, T.C.; Michael, E.N.; Mun, C.Y.; Qi, N.X.; et al. Mechanisms and Impact of Biofilms and Targeting of Biofilms Using Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, S.; Ramarao, N.; Faille, C.; Fouet, A.; Aymerich, S.; Gohar, M. Biofilm Formation and Cell Surface Properties among Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Strains of the Bacillus cereus Group. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6616–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemesh, M.; Ostrov, I. Role of Bacillus species in biofilm persistence and emerging antibiofilm strategies in the dairy industry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.; Borges, A.; Teodósio, J.; Araújo, P.; Mergulhão, F.; Melo, L.; Simões, M. The effects of ferulic and salicylic acids on Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas fluorescens single- and dual-species biofilms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 86, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, B.; Sinha, S.S.; Garner, B.L.; Arany, I.; Corley, C.; Cobb, K.; Brown, E.; Ray, P.C. Influence of Aptamer-Enclosed Silver Nanocluster on the Prevention of Biofilm by Bacillus thuringiensis. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2016, 8, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, B.; Adhikari, P.; Mallet, E.; Havner, R.; Pradhan, P. Spectroscopic Study on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm in the Presence of the Aptamer-DNA Scaffolded Silver Nanoclusters. Molecules 2020, 25, 3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, M.T.T.; Wibowo, D.; Rehm, B.H.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, G.; Williams, C. The Clinical Importance of Fungal Biofilms. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 84, pp. 27–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, T.V.M.; Rozental, S. Biofilm Formation as a Pathogenicity Factor of Medically Important Fungi. In Fungal Pathogenicity. 2016, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fanning, S.; Mitchell, A.P. Fungal Biofilms. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovská, Z.; Čonková, E.; Váczi, P. Biofilm Formation in Medically Important Candida Species. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, J.; Abreu, A.C.; Borges, A.; Simões, L.C.; Simões, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Selected Phytochemicals against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus and Their Biofilms. Pathogens 2014, 3, 473–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondil, V.S.; Subhadra, B. Biofilms and their role on diseases. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. Risk factors for chronic biofilm-related infection associated with implanted medical devices. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, G.M. The Role of Bacterial Biofilm in Antibiotic Resistance and Food Contamination. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1705814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, P.; O’Flaherty, V.; Moran, A.; Stoodley, P.; Mahony, T. Biofilms in Medicine, Industry and Environmental Biotechnology—Characteristics, Analysis and Control. Water Intell. Online 2015, 6, 9781780402161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Khan, F. Medical Device-Associated Infections Caused by Biofilm-Forming Microbial Pathogens and Controlling Strategies. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Jiménez, E.; Del Campo, R.; Toledano, V.; Vallejo-Cremades, M.T.; Muñoz, A.; Largo, C.; Arnalich, F.; García-Rio, F.; Cubillos-Zapata, C.; López-Collazo, E. Biofilm vs. planktonic bacterial mode of growth: Which do human macrophages prefer? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETaylor, E.N.; Webster, T.J. The Use of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Prosthetic Biofilm Prevention. Int. J. Nanomed. 2009, 4, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Wu, Z.; Yu, T.; Jiang, C.; Kim, W.-S. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, M.P. Advanced Nanotechnological Approaches for Biofilm Prevention and Control. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaure, P.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Recent Advances in Surface Nanoengineering for Biofilm Prevention and Control. Part I: Molecular Basis of Biofilm Recalcitrance. Passive Anti-Biofouling Nanocoatings. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Kwon, D.-N.; Kim, J.-H. Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.S.; Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Interactions of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles with Bacterial Biofilms: Molecular Interactions behind Inhibition and Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żyro, D.; Sikora, J.; Szynkowska-Jóźwik, M.I.; Ochocki, J. Silver, Its salts and application in medicine and pharmacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, Y.K.; Biswas, K.; Jena, S.K.; Hashem, A.; Abd, E.F.; Mohanta, T.K. Anti-biofilm and antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized by the reducing activity of phytoconstituents present in the Indian medicinal Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosnedlova, B.; Kabanov, D.; Kepinska, M.; Narayanan, V.H.B.; Parikesit, A.A.; Fernandez, C.; Bjørklund, G.; Nguyen, H.V.; Farid, A.; Sochor, J.; et al. Effect of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on bacterial biofilm changes in S. aureus and E. coli. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, P.R.; Pandit, S.; Filippis, A.D.; Franci, G.; Mijakovic, I.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles: Bactericidal and mechanistic approach against drug resistant pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.G.; Carrillo, M.P. development of aptamer beacons for rapid presumptive detection of Bacillus Spores. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikanovic, M.; Rudzinski, W.E.; Bruno, J.G.; Allman, A.; Carrillo, M.P.; Dwarakanath, S.; Bhahdigadi, S.; Rao, P.; Kiel, J.L.; Andrews, C.J. Fluorescence assay based on aptamer-quantum dot binding to Bacillus thuringiensis Spores. J. Fluoresc. 2007, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsicova, M.; Korcekova, J.; Poturnayova, A.; Breier, A. New insights into aptamers: An alternative to antibodies in the detection of molecular biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, H.R.; Im, S.J.; Nguyen, D.V.; Jeong, S.P.; Jang, A. Real-time diagnosis and monitoring of biofilm and corrosion layer formation on different water pipe materials using non-invasive imaging methods. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdzal, M.; Vorontsov, E.; Chartrand, G.; Kadoury, S.; Pal, C. The Importance of Skip Connections in Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimauro, G.; Deperte, F.; Maglietta, R.; Bove, M.; La Gioia, F.; Renò, V.; Simone, L.; Gelardi, M. A novel approach for biofilm detection based on a convolutional neural network. Electronics 2020, 9, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrastia, J.L.; Heilenkötter, N.; Baguer, D.O.; Hauberg-Lotte, L.; Boskamp, T.; Hetzer, S.; Duschner, N.; Schaller, J.; Maass, P. Deeply Supervised UNet for Semantic Segmentation to Assist Dermatopathological Assessment of Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from sray-level Hhstograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Dhiman, A.; Kapil, A.; Bansal, V.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamer-mediated colorimetric and electrochemical detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa utilizing peroxidase-mimic activity of gold NanoZyme. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, B.; Ritchie, C.M.; Buckman, J.G.; Johnsen, K.R.; Goodwin, P.M.; Petty, J.T. Base-directed formation of fluorescent silver clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 18776–18782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, E.; Trimble, M.; Cheng, J.; Vallé, Q.; Hancock, R. Critical assessment of methods to quantify biofilm growth and evaluate antibiofilm activity of host defence peptides. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatli, U.; Budak, C. Biomedical image segmentation with modified U-Net. Traitement du Signal 2023, 40, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xue, C.; Shao, Y.; Chen, K.; Xiong, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, L. Semantic segmentation of litchi branches using DeepLabV3+ Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 164546–164555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, P.; Chen, C. A robust iris segmentation using fully convolutional network with dilated convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), Taichung, Taiwan, 10–12 December 2018; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Fan, D.; Huang, C.; Diagne, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sant, A.C.; Suàrez, A.; Jagersand, M.; Shao, L. Boundary-Aware segmentation network for mobile and web applications. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.04704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F-1 Score | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabV3+ | 0.9042 | 0.7491 | 0.7949 | 0.7713 | 0.6278 |
| F-CN | 0.8160 | 0.7554 | 0.8160 | 0.7338 | 0.6661 |
| BASNet | 0.8160 | 0.6659 | 0.8160 | 0.7333 | 0.6659 |
| Attention U-net | 0.8636 | 0.6138 | 0.8867 | 0.7254 | 0.5691 |
| U-Net-ResNet34 | 0.8840 | 0.6766 | 0.8220 | 0.7422 | 0.5901 |
| U-Net-ResNet18 | 0.9074 | 0.7598 | 0.7957 | 0.7774 | 0.6358 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sengupta, B.; Alrubayan, M.; Kolla, M.; Wang, Y.; Mallet, E.; Torres, A.; Solis, R.; Wang, H.; Pradhan, P. AI-Based Detection of Optical Microscopic Images of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Planktonic and Biofilm States. Information 2025, 16, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040309
Sengupta B, Alrubayan M, Kolla M, Wang Y, Mallet E, Torres A, Solis R, Wang H, Pradhan P. AI-Based Detection of Optical Microscopic Images of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Planktonic and Biofilm States. Information. 2025; 16(4):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040309
Chicago/Turabian StyleSengupta, Bidisha, Mousa Alrubayan, Manideep Kolla, Yibin Wang, Esther Mallet, Angel Torres, Ravyn Solis, Haifeng Wang, and Prabhakar Pradhan. 2025. "AI-Based Detection of Optical Microscopic Images of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Planktonic and Biofilm States" Information 16, no. 4: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040309
APA StyleSengupta, B., Alrubayan, M., Kolla, M., Wang, Y., Mallet, E., Torres, A., Solis, R., Wang, H., & Pradhan, P. (2025). AI-Based Detection of Optical Microscopic Images of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Planktonic and Biofilm States. Information, 16(4), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16040309







