Abstract
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) are central to the modern healthcare system. Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), have opened new opportunities for the advancement of EMRs. This scoping review aims to explore the current real-world applications of GenAI within EMRs to support an understanding of AI applications in healthcare. A literature search was conducted following PRISMA-ScR guidelines. The search was conducted using Ovid MEDLINE, up to 28 October 2024, using a peer-reviewed search strategy. Overall, 55 studies were included. A list of five themes was generated by human reviewers based on the literature review: data manipulation (24), patient communication (9), clinical decision making (8), clinical prediction (8), summarization (4), and other (2). The majority of studies originated from the United States (35). Both proprietary and commercially available models were tested, with ChatGPT being the most commonly referenced LLM. As these models continue to be developed, their diverse use cases within EMRs have the potential to improve patient outcomes, enhance access to medical data, streamline hospital workflows, and reduce physician workload. However, continued problems surrounding data privacy, trust, bias, model hallucinations, and the need for robust evaluation remain. Further research considering the ethical, medical, and societal implications of GenAI applications in EMRs is essential to validate these findings and address existing limitations to support healthcare advancement.
1. Introduction
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) are an integral part of the modern healthcare system, providing healthcare workers with an effective platform for documentation, clinical decision support, record keeping, and communication. As these digital repositories of patient health information have become widespread, healthcare workers now have access to increasingly large numbers of data surrounding each patient interaction. While this presents providers with many new opportunities, the quantity and unstructured nature of EMR data present numerous challenges. Recently, with advances in generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), new methods of interacting with and understanding textual data have become available. More specifically, the use of large language models (LLMs) has, in particular, drawn consideration for use in medical practice since the public launch of ChatGPT (OpenAI, CA, USA) in November 2022 [1].
While AI in medicine has been an intense subject of study for many years, past AI techniques relied on using gold-standard data to train hyper-specialized models to classify or predict accurately. This was not only prohibitively costly, but also involved developing and testing new models for each desired usage case. In contrast, since their release, LLMs have proven to be a cost-effective, rapidly improving, and versatile method of interacting with text and generating coherent, context-specific text with striking similarity to humans. Although these tools are in their infancy, they hold significant potential to address major ongoing challenges in the healthcare system.
Despite the growth and scholarly interest surrounding GenAI and medicine, the recent and rapid development of these models has outpaced the broader healthcare community’s capacity to fully understand and evaluate the potential impacts of these tools on clinical workflows. Considering the nascent state of research in this field, there is limited comprehensive background literature, and, thus, most of the cited references directly reflect studies reviewed in this article. To address this gap, we conducted this scoping review, following the PRISMA-ScR guidelines, to further clarify the current state of evidence, categorize various use cases, and highlight areas of promise—providing valuable insights to physicians, administrators, EMR providers, and the broader healthcare community.
2. Materials and Methods
This scoping review was developed in line with the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines (See Supplementary S1 for checklist). Previous literature searches indicated the lack of a recent review exploring our research question. Considering the rapid advancements in GenAI and EMR literature, we undertook this scoping review promptly to provide timely results without registration.
Our peer-reviewed search strategy encompassed two concepts: generative artificial intelligence and Electronic Medical Records. Our search design involved the identification of synonyms for these concepts, as well as Boolean operators. The search strategy primarily used keywords. No search filters were used to limit the search results. The search was conducted using Ovid MEDLINE(R) <1946 to 28 October 2024>.
- Search:
- (LLM or “large language model*” or (GenAI or “generative AI” or “generative artificial intelligence”) or ChatGPT).ab,tw,kf,kw.
- (“electronic health record*” or “medical records system*” or “electronic medical record*” or “health information system*” or “decision support system*” or “EHR*” or “EMR*” or “CDSS*”).ab,tw,kf,kw.
- 1 and 2
Search results were inputted into the software Covidence for title/abstract screening, full-text review, and extraction. Studies that used at least one form of GenAI (including, but not limited to, large language models, natural language processing, and machine learning with generative outputs), incorporated use with EMRs, and were published in English were included. Studies that used fictional data, did not involve the application of GenAI, or were not original research were excluded. Duplicates were removed. Title/abstract screening and full-text review were completed by two reviewers, and extraction was completed by one reviewer. The extracted data are included in the attached Supplementary S2. Any conflicts were discussed by all reviewers until a consensus was reached. A quality appraisal was not conducted per PRISMA-ScR guidelines. Studies included in this review were extracted for information including country, methods, funding, conflicts of interest, study design, population, objectives, and GenAI use/application.
A list of 5 themes was generated by the study team based on the literature review. These themes were data manipulation, patient communication, clinical decision making, clinical prediction, and summarization. Each study was classified in duplicate by two reviewers into specific themes, with each study assigned to only one theme. Any conflicts or discrepancies between reviewers were resolved through discussion until a consensus was reached. Studies that could not be assigned to a specific theme were placed in the ‘other’ category.
3. Results
We identified 249 studies from databases through our search strategy, of which 121 (48.6%) duplicates were removed; 128 studies were screened, with 67 (52.3%) excluded during title/abstract screening and 6 (4.7%) excluded during full-text review per our exclusion criteria. Ultimately, 55 (43.0%) studies were extracted and included in the review (see Figure 1).
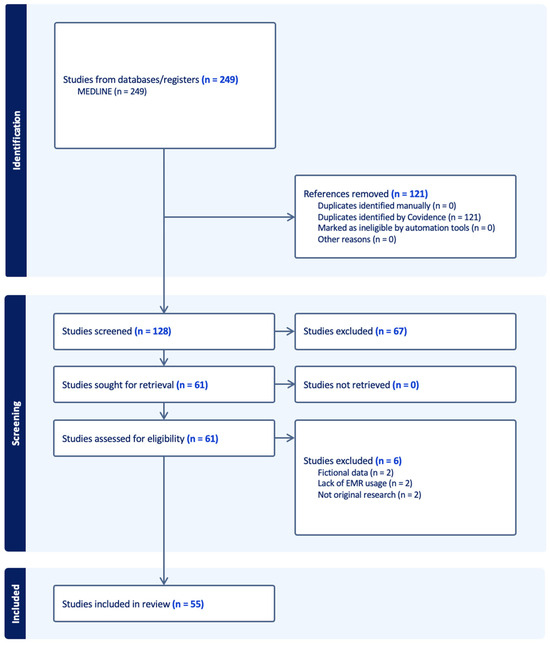
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) flow chart.
Of the 55 included studies, the majority were from the United States (35), with a minority from the United Kingdom (2), Australia (2), and Canada (1). The remaining studies were categorized as “Other” (15), encompassing multiple regions and multinational collaborations. The majority of included studies were comparative studies (29), followed by cross-sectional studies (9), other designs (11), diagnostic test accuracy studies (3), non-randomised experimental studies (2), and a single cohort study (1). Patient populations and data volumes varied substantially, with sample sizes ranging from as few as 10 to over 7 million records, and a median of approximately 8000 patient records per study. Data sources for the included studies varied extensively. Many leveraged well-known publicly available datasets, such as MIMIC-III (2001–2012) and MIMIC-IV (2008–2019), while others utilized diverse repositories for imaging reports. Additional datasets encompassed institutional EHRs from large tertiary care centers, specialized registries, outpatient clinical notes, emergency department visits, and patient-generated messages. Some studies combined multiple datasets, others focused on single-center sources, and a subset employed specialized curated data. Across all studies, the time frame generally extended from the early 2000s through to the mid-2020s. A wide array of both commercially available and proprietary GenAI models were evaluated, including, but not limited to, ChatGPT (GPT-3.5, GPT-4), Claude, Microsoft Co-Pilot, LLaMA-based models, Flan-T5, Vicuna, Med-Alpaca, and domain-adapted BERT variants (ClinicalBERT, BioBERT), as well as proprietary hospital-integrated systems. ChatGPT was the most commonly evaluated AI model, being tested in over half of the included studies.
Our review shows that GenAI is being used broadly within EMRs. We found that the most common uses were data manipulation and patient communication. A variety of GenAI models, including commercial models like ChatGPT and proprietary models, were used to achieve these applications across all studies. From identifying cancer symptoms in clinical notes [2] to extracting thyroid nodule characteristics [3], GenAI has been applied in multiple medical disciplines. In addition, applications that were both patient-centered and provider-centered were identified.
A diverse range of themes emerged across the included studies, reflecting the varied applications of generative AI in healthcare: Data Manipulation (24), Patient Communication (9), Clinical Decision Making (8), Clinical Prediction (8), Summarization (4), and Other (2) (See Supplementary S3).
3.1. GenAI for Data Manipulation
Electronic medical records are filled with a wealth of medical data. However, given the variation in data recording and the vast numbers of records within EMRs, it can be difficult to make sense of these data. The application of GenAI in this area has allowed for the extraction and identification of large quantities of information to allow for further analysis. Of the 55 studies reviewed, 24 used GenAI for data manipulation. Uses ranged from disease phenotyping [4] to lung cancer staging descriptor extraction [5] and data mining to support the identification of HIV patients [6]. The vast majority of studies showed that GenAI was both faster and more effective at manipulating data items compared to humans, especially with larger datasets. Zero-shot data extraction (i.e., extracting data in a format or content that was not part of model training) was also shown to be feasible [7].
3.2. GenAI for Patient Communication
A rapidly growing body of evidence suggests that a powerful usage case for GenAI within the context of EMRs is to improve the quality and efficiency of patient-facing communication. In fact, 9 of the 55 studies used GenAI for patient communication. For example, a study examining GenAI responses to patient queries in a urology setting found that nearly half of ChatGPT-generated responses were considered acceptable for patient messaging [8]. Similarly, another study conducted in breast reconstruction surgery clinics showed that ChatGPT exhibited strengths in terms of empathy and accuracy [9]. Our review also shows that, in a broad number of specialties and clinical practices, AI integration mitigates physician burnout or perceived task load, even when objective time metrics remain unchanged [8,10,11]. While a subset of studies identified GenAI responses as more empathetic, direct, or clear when compared to those written by physicians [9,12], other researchers found that AI-generated messages were in some cases more difficult to read and that physician-generated messages were still strongly preferred [9,13]. Overreliance, personalization, and factual errors are also cited as barriers to a larger-scale deployment of GenAI for patient communication [8,11,13].
3.3. GenAI for Clinical Decision Making
In our review, 8 of the 55 included studies used GenAI for clinical decision making. While a subset of these studies indicated that GenAI was able to accurately diagnose and perform at levels comparable to physicians, numerous studies have also raised concerns about the risks and downsides of GenAI being used for clinical decision making. For example, when tested in emergency department cohorts, GenAI showed suboptimal accuracy [14] and produced unsafe triage recommendations in a substantial number of cases [15]. Additionally, GenAI models also performed poorly in guiding renal dose interventions for hospitalized patients [16]. Another mentioned shortfall of this technology was the propensity of these models to hallucinate and occasionally fabricate references or diagnoses [17].
3.4. GenAI for Clinical Prediction
In our review, 8 of the 55 included studies used GenAI for clinical prediction, highlighting both the promise and limitations of GenAI as a clinical predictor. Several investigations have shown that, with careful design and thoughtful integration, GenAI can excel at certain prediction tasks. For example, in a perioperative context, GenAI accurately classified whether patients required hospital or ICU admission [18]. Furthermore, in predicting seizure recurrences, LLMs also achieved accuracy superior to models relying solely on structured data [19]. Overall, these findings show that GenAI in its current form has the potential to serve as an accurate predictor in a variety of clinical uses.
3.5. GenAI for Summarization
GenAI’s role in medical communication is not limited to responding to patient queries, however. These new models also show significant promise in summarizing reports and simplifying complex medical language. In our review, 4 of the 55 included studies used GenAI for summarization. From transforming inpatient discharge summaries into more readable formats [20], to “translating” radiology reports to lower reading levels [21], GenAI is now being used to try and enhance patient comprehension and improve health literacy.
3.6. GenAI for Other Use Cases
Of the 55 studies, 2 were classified as ‘other’ due to their unique applications that did not fit within the predefined five themes. One study examined the use of an LLM for the summarization of notes, patient data extraction, and drafting of referral letters or memos [22]. Due to its broad scope, spanning multiple categories, it was not placed into a single theme. The second study explored how GenAI could support health equity research, specifically examining how LLMs could be used to assess disparities in seizure outcomes [23]. While not focused on a direct EMR function, this study further explored a possible future use case for integrating LLMs into EMRs to support healthcare analytics and decision making.
4. Discussion
AI in medicine has been a large and promising area of research over the last decade, though there have been relatively few large-scale and widespread implementations in clinical practice. Prior to LLMs, the majority of progress for AI in medicine occurred in fields with well-defined problems and large numbers of available, gold-standard data, such as radiology and pathology [24]. However, with recent technological advances in transformer architecture, commercially available LLMs are capable of producing coherent and contextually relevant text with increasing levels of accuracy. If properly integrated into the clinical environment, GenAI’s specific attributes offer the potential for increased efficiency, scalability, consistency, and a reduction in clinical workload.
The study of EMRs has allowed them to be a centre for innovation in healthcare for many years. Although most early AI research in EMRs relied on conventional ML approaches requiring large, well-curated datasets, several studies in our review indicate that modern generative models can match or even surpass these older techniques. For instance, a health system–scale LLM, known as NYUTron, outperformed traditional risk stratification methods in tasks such as mortality prediction, hospital readmission, and insurance denial [25]. Another group leveraged LLMs to forecast seizure recurrence more accurately than classical predictive algorithms, underscoring the value of unstructured text in improving performance beyond what structured EHR data alone can achieve [19]. Hybrid strategies also stand out, such as a framework combining dictionary-based NLP with LLM-based rare disease phenotyping that significantly outperformed existing ontological or rule-based methods [4]. Meanwhile, zero-shot or few-shot prompting in LLMs has shown promising results for data extraction [7] and cancer symptom detection [2] with minimal annotation requirements, exceeding the capabilities of older approaches reliant on manual feature engineering.
Collectively, these findings suggest that the long-standing paradigm of “gold standard” ML models—dependent on static training sets and meticulously curated features—may be giving way to more flexible, generalist LLMs that adapt to varied clinical tasks with little additional fine-tuning. Although specialized ML algorithms still have a place in well-defined domains, the ability of generative models to process large volumes of unstructured text and extract or synthesize information at scale offers a novel advantage, albeit with risks such as hallucinations. This shift could allow EMRs to serve broader applications—from advanced risk prediction to real-time data extraction—under a single, more adaptable architecture.
GenAI integration in EMRs may lead to improved patient outcomes directly, for example, through GenAI-based clinical decision support systems that can suggest appropriate treatments and potentially reduce medical errors. Data manipulation, clinical prediction, or summarization through GenAI can indirectly benefit patients by improving physician efficiency, allowing for better prioritization, and saving overall time that can be used with patients, rather than administrative tasks. An example of this is the automation of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) diagnosis based on the Berlin criteria, a tool that can increase physician efficiency and allow for improved management approaches [26]. Fundamentally, this can support a long-term shift in the role of a physician, allowing for more patient-facing time and focus on more complex issues.
The promising early work conducted in the studies included in our review has also validated the ongoing commitment by both large technology providers and healthcare organizations to integrate AI into EMRs. Recently, several enterprise-level collaborations have begun with the aim of delivering real-time cloud-based solutions for healthcare analytics and automation. For instance, Epic recently announced new generative AI features to enhance clinical documentation and intelligent chart review [27]. However, innovation is not limited to the major EMR providers. Both startups and tech giants have committed to investing in the development of GenAI-empowered healthcare solutions [28]. These early forays into large-scale deployments offer compelling glimpses into how LLMs could be embedded into routine practice.
The successful integration of GenAI into EMRs is not only a technical problem. There also exist many ethical considerations, including, but not limited to, accountability for AI-generated recommendations, patient consent for AI-enabled healthcare, and potential risks with regards to the security of patient medical information. Patient and physician education, particularly around understanding an AI model’s strengths and limitations and safeguarding patient privacy, remains a crucial step in their successful integration. Additionally, the current literature surrounding this area remains nascent. Ultimately, as GenAI tools continue to evolve and gain popularity, they will be integrated into EMRs, catalyzing tremendous innovation that fundamentally shifts how clinicians document, analyze, and act upon the ever-growing volume of patient data.
Despite the promising prospects of GenAI and its application in EMRs, this technology is still largely infant within healthcare. Due to this, as well as variable performance on higher-level tasks such as clinical decision making, many clinicians lack trust in the capability of GenAI. Fears generally exist around breaches of patient confidentiality that can occur with commercial cloud-based LLMs and safety concerns about GenAI producing inaccurate responses. Medical errors made while using GenAI may also lack legal clarity in certain jurisdictions, leading to further concerns. Currently, liability remains an unresolved issue, with debate ongoing as to which of the three stakeholders—clinicians, model developers, or healthcare institutions—should be held responsible. This underscores the need for clear regulatory frameworks to govern AI use in medical decision making. However, it is important to note that GenAI in its current form is only useful to empower physicians, not replace them. As demonstrated by the studies we have analyzed, GenAI within EMRs can support physicians in providing effective healthcare, but still lacks the ability to act independently. For example, a study exploring the use of ChatGPT to respond to clinical decision support system alerts for renal dysfunction patients found that ChatGPT is not currently appropriate for EHR integration due to its poor performance—in various scenarios, ChatGPT provided correct and identical responses for less than 20% of alerts [16]. Even with this notion, however, significant limitations surrounding this technology persist. More specifically, there remain concerns around overreliance on such supports, particularly due to GenAI’s potential for hallucinations, inaccuracies, or contextually inappropriate outputs that can undermine clinical reliability, and, in severe cases, risk patient safety. Additionally, since these models were trained on the entirety of the internet, intrinsic biases embedded within the training data may perpetuate existing disparities and exacerbate inequities in healthcare access and treatment decisions, particularly for historically underserved populations. Finally, due to the “black box” nature of GenAI models, interpretability issues pose additional risks, as clinicians may struggle to fully grasp how these models arrive at their prediction or recommendation. Nearly all studies reviewed acknowledge at least one of these limitations, underscoring the need for robust safeguards and continued human oversight to ensure that GenAI integration enhances, rather than undermines, patient care. These concerns are important to consider and study as the use of GenAI becomes more widespread and central to EMRs. Ultimately, as GenAI continues to be further integrated into EMRs, addressing the ethical, medical, and societal implications of this new technology will be equally as important as advancing the underlying technology. A proactive, measured, and thoughtful approach to regulation, bias mitigation, safety measures, physician oversight, and stakeholder involvement will ensure that GenAI enhances, rather than undermines, effective, equitable, and safe healthcare delivery.
Study Limitations
Although our scoping review offers many valuable insights into the current landscape of GenAI and its integration into EMRs, several limitations should be considered. Firstly, over 63% of included studies originate from the United States. Although studies from other regions were included, this geographic focus may potentially limit the generalizability of findings to other healthcare systems. Secondly, as this area of research is in its infancy, the majority of included studies were structured as proof-of-concept or exploratory studies. As a result, these findings are unable to fully assess both the long-term and second-order effects of such integrations, and the sample sizes are consequently limited. Thirdly, due to the rapid evolution of these models, the included studies evaluated various AI model generations, many of which are now outdated. Consequently, the conclusions drawn may underestimate the current capabilities of GenAI and may not reflect the outcomes associated with the most up-to-date models. Fourthly, the vast majority of models tested in the included studies were commercially available. While this is beneficial for reproducibility, our review does not capture the challenges and opportunities that may arise from using proprietary, medically trained models in EMRs. Additionally, given the preliminary nature and methodological diversity of the included studies, an extensive critical evaluation of the evidence was not included in this article. However, we have included a detailed Supplementary Materials, outlining each study’s objectives, methods, results, and thematic categorization. Overall, future research should focus on larger-scale, multisite, multi-model, and international studies to address these limitations and better assess the full potential and implications of GenAI integration within EMRs.
5. Conclusions
GenAI is a rapidly growing technology that healthcare has slowly begun to incorporate, especially within EMRs, an ideal environment for such implementation, since it is text-based. GenAI has been used within EMRs in a wide variety of ways, including for data manipulation, patient communication, clinical decision making, clinical prediction, and summarization. These applications highlight the potential of GenAI to significantly enhance existing EMRs to improve patient outcomes and reduce physician workload. Clinicians should continue to explore and implement the use of GenAI within EMRs as aides of the healthcare team. Further research considering the ethical, medical, and societal implications of GenAI applications within EMRs are essential to validate these findings in order to promote healthcare advancement and address the limitations currently inherent in these technologies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/info16040284/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M. and M.S.; methodology, L.M., M.S. and B.G.; investigation and data curation, N.H., M.M., L.M. and B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M. and B.G.; writing—review and editing, L.M., B.G. and M.S.; visualization, B.G.; project administration, L.M. and M.S.; supervision, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and its Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| EMR | Electronic Medical Record |
| GenAI | Generative Artificial Intelligence |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| ML | Machine Learning |
References
- Introducing ChatGPT. OpenAI Blog. Available online: https://openai.com/index/chatgpt/ (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Zeinali, N.; Albashayreh, A.; Fan, W.; White, S.G. Symptom-BERT: Enhancing Cancer Symptom Detection in EHR Clinical Notes. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2024, 68, 190–198.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Yu, Z.; Paredes, D.; Monsour, E.P.; Rocha, A.O.; Brito, J.P.; Ospina, N.S.; Wu, Y. Extracting Thyroid Nodules Characteristics from Ultrasound Reports Using Transformer-based Natural Language Processing Methods. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2023, 2023, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Dong, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, R.; Patra, A.; Dai, C.; Ali, W.; Scordis, P.; Wu, H. A hybrid framework with large language models for rare disease phenotyping. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Yoo, S.; Kim, B.; Jang, S.; Sunwoo, L.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.; Nam, S.; Chung, J.-H. Extracting lung cancer staging descriptors from pathology reports: A generative language model approach. J. Biomed. Inform. 2024, 157, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Sánchez, R.; Montalvo, S.; Riaño, A.; Martínez, R.; Velasco, M. Early diagnosis of HIV cases by means of text mining and machine learning models on clinical notes. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 179, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, N. Zero-shot information extraction from radiological reports using ChatGPT. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2024, 183, 105321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.; Muncey, W.; Seranio, N.; Belladelli, F.; Del Giudice, F.; Li, S.; Ha, A.; Glover, F.; Zhang, C.A.; Eisenberg, M.L. Assessing Artificial Intelligence–Generated Responses to Urology Patient In-Basket Messages. Urol. Pract. 2024, 11, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroudi, D.B.; Gozali, A.M.; Knox, J.A.; Parmeshwar, N.; Sadjadi, R.; Wilson, J.C.B.; Lee, S.A.; Piper, M.L. Comparing Provider and ChatGPT Responses to Breast Reconstruction Patient Questions in the Electronic Health Record. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2024, 93, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; McCoy, A.B.; Wright, A.P.; Carew, B.; Genkins, J.Z.; Huang, S.S.; Peterson, J.F.; Steitz, B.; Wright, A. Leveraging large language models for generating responses to patient messages—A subjective analysis. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2024, 31, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Ma, S.P.; Shah, S.; Smith, M.; Jeong, Y.; Devon-Sand, A.; Tai-Seale, M.; Takazawa, K.; Clutter, D.; Vogt, K.; et al. Artificial Intelligence–Generated Draft Replies to Patient Inbox Messages. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e243201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, W.R.; Wiesenfeld, B.; Brandfield-Harvey, B.; Jonassen, Z.; Mandal, S.; Stevens, E.R.; Major, V.J.; Lostraglio, E.; Szerencsy, A.; Jones, S.; et al. Large Language Model–Based Responses to Patients’ In-Basket Messages. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2422399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, K.; Nadelman, D.; Durgin, J.; Ansah-Addo, S.; Cole, D.; Fayne, R.; Harrell, J.; Ratycz, M.; Runge, M.; Shepard-Hayes, A.; et al. Comparing the quality of ChatGPT- and physician-generated responses to patients’ dermatology questions in the electronic medical record. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.Y.K.; Miao, B.Y.; Kornblith, A.E.; Butte, A.J. Evaluating the use of large language models to provide clinical recommendations in the Emergency Department. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, H.; Crossland, D.; Bacher, I.; Ranney, M.; Madsen, T.; Hilliard, R. Comparison of Diagnostic and Triage Accuracy of Ada Health and WebMD Symptom Checkers, ChatGPT, and Physicians for Patients in an Emergency Department: Clinical Data Analysis Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2023, 11, e49995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nuland, M.; Snoep, J.D.; Egberts, T.; Erdogan, A.; Wassink, R.; van der Linden, P.D. Poor performance of ChatGPT in clinical rule-guided dose interventions in hospitalized patients with renal dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, J.M. Computerized diagnostic decision support systems—A comparative performance study of Isabel Pro vs. ChatGPT4. Diagnosis 2024, 11, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.; Fong, C.T.; Walters, A.M.; Aghaeepour, N.; Yetisgen, M.; O’reilly-Shah, V.N. Large Language Model Capabilities in Perioperative Risk Prediction and Prognostication. JAMA Surg. 2024, 159, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu-Jones, B.K.; Villamar, M.F.; Scordis, P.; Bartmann, A.P.; Ali, W.; Wissel, B.D.; Alsentzer, E.; de Jong, J.; Patra, A.; Kohane, I. Predicting seizure recurrence after an initial seizure-like episode from routine clinical notes using large language models: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2023, 5, e882–e894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaretsky, J.; Kim, J.M.; Baskharoun, S.; Zhao, Y.; Austrian, J.; Aphinyanaphongs, Y.; Gupta, R.; Blecker, S.B.; Feldman, J. Generative Artificial Intelligence to Transform Inpatient Discharge Summaries to Patient-Friendly Language and Format. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e240357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, R.; Amin, K.S.; Khosla, P.; Bajaj, S.; Chheang, S.; Forman, H.P. Quantitative Evaluation of Large Language Models to Streamline Radiology Report Impressions: A Multimodal Retrospective Analysis. Radiology 2024, 310, e231593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.E.S.; Teo, W.Z.W.; Puhaindran, M.E. Artificial Intelligence in Hand Surgery–How Generative AI is Transforming the Hand Surgery Landscape. J. Hand Surg. 2024, 29, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Ojemann, W.K.S.; Gallagher, R.S.; Shinohara, R.T.; Lucas, A.; Hill, C.E.; Hamilton, R.H.; Johnson, K.B.; Roth, D.; Litt, B.; et al. Disparities in seizure outcomes revealed by large language models. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2023, 31, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alowais, S.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsuhebany, N.; Alqahtani, T.; Alshaya, A.I.; Almohareb, S.N.; Aldairem, A.; Alrashed, M.; Bin Saleh, K.; Badreldin, H.A.; et al. Revolutionizing healthcare: The role of artificial intelligence in clinical practice. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Pour Nejatian, N.; Nasir-Moin, M.; Wang, D.; Abidin, A.; Eaton, K.; Riina, H.A.; Laufer, I.; Punjabi, P.; et al. Health system-scale language models are all-purpose prediction engines. Nature 2023, 619, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, A.; Wu, P.; Clement, D.R.; Xing, J.; Aviv, R.; Federbush, M.; Yuan, Z.; Jing, Y.; Wei, G.; Hajizadeh, N. ARDSFlag: An NLP/machine learning algorithm to visualize and detect high-probability ARDS admissions independent of provider recognition and billing codes. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capoot, A. Epic Systems is building more than 100 new AI features for doctors and patients. Here’s what’s coming. CNBC, 21 August 2024. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2024/08/21/epic-systems-ugm-2024-ai-tools-in-mychart-cosmos-.html (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Milliard, M. New Oracle EHR Promises AI-Enabled Reinvention. Healthcare IT News, 30 October 2024. Available online: https://www.healthcareitnews.com/news/new-oracle-ehr-promises-ai-enabled-reinvention (accessed on 13 November 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).