Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Detection with Dual-Port Textile UWB MIMO Bra-Tenna System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Wearable Orthogonal-Polarized MIMO Bra-Tenna System
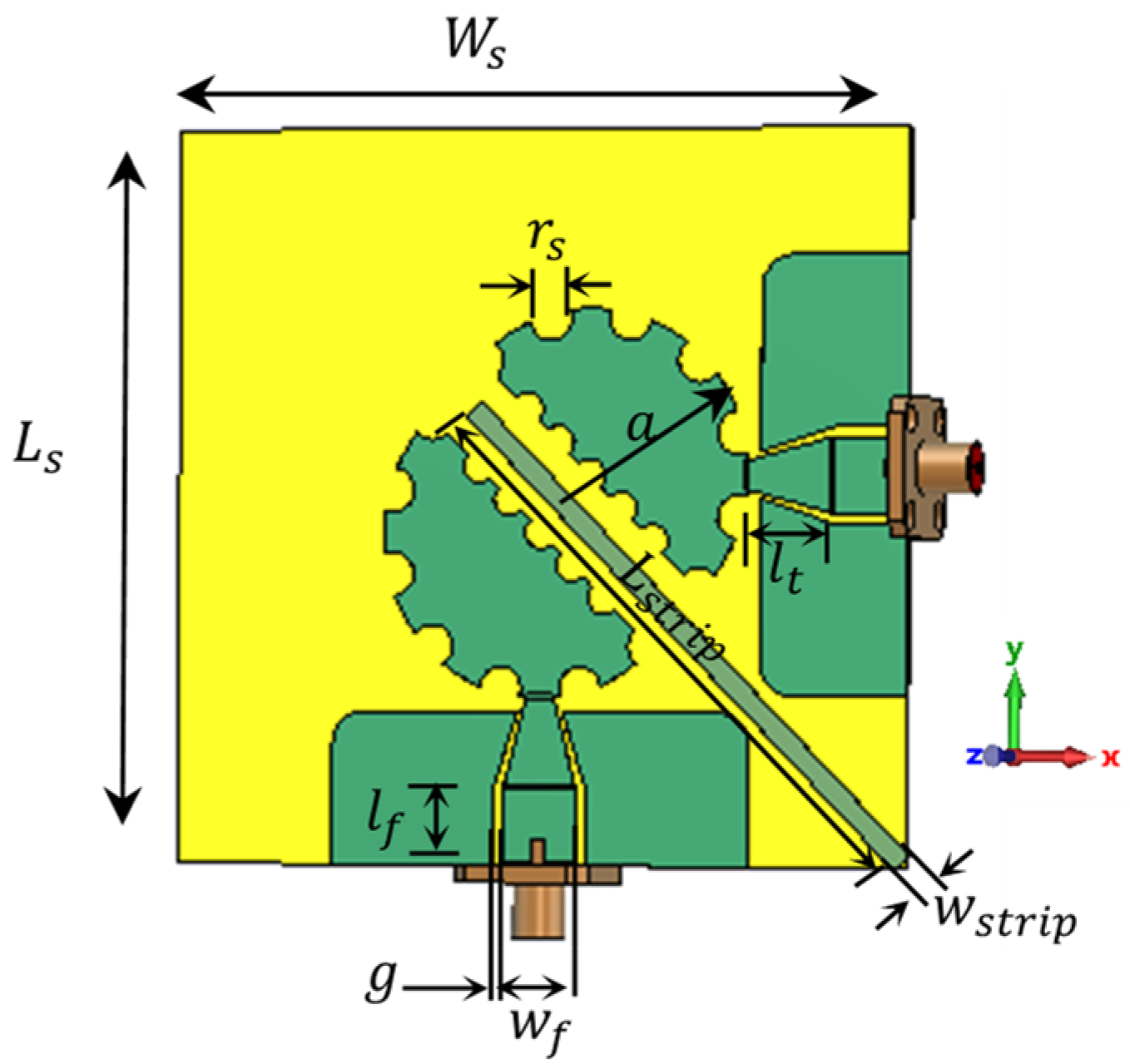
2.1. Sensor Design
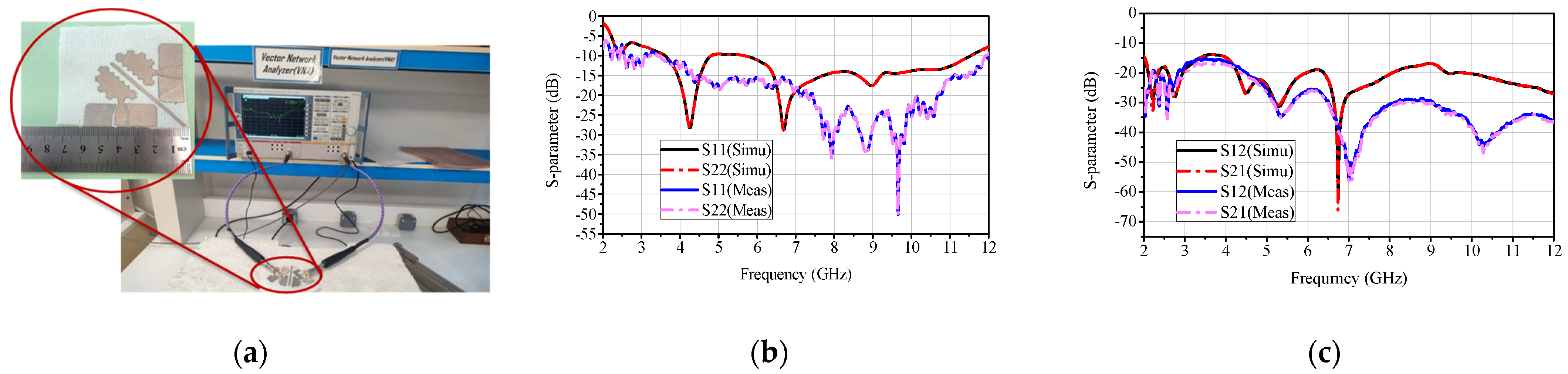
2.2. Sensor Fabrication and Results
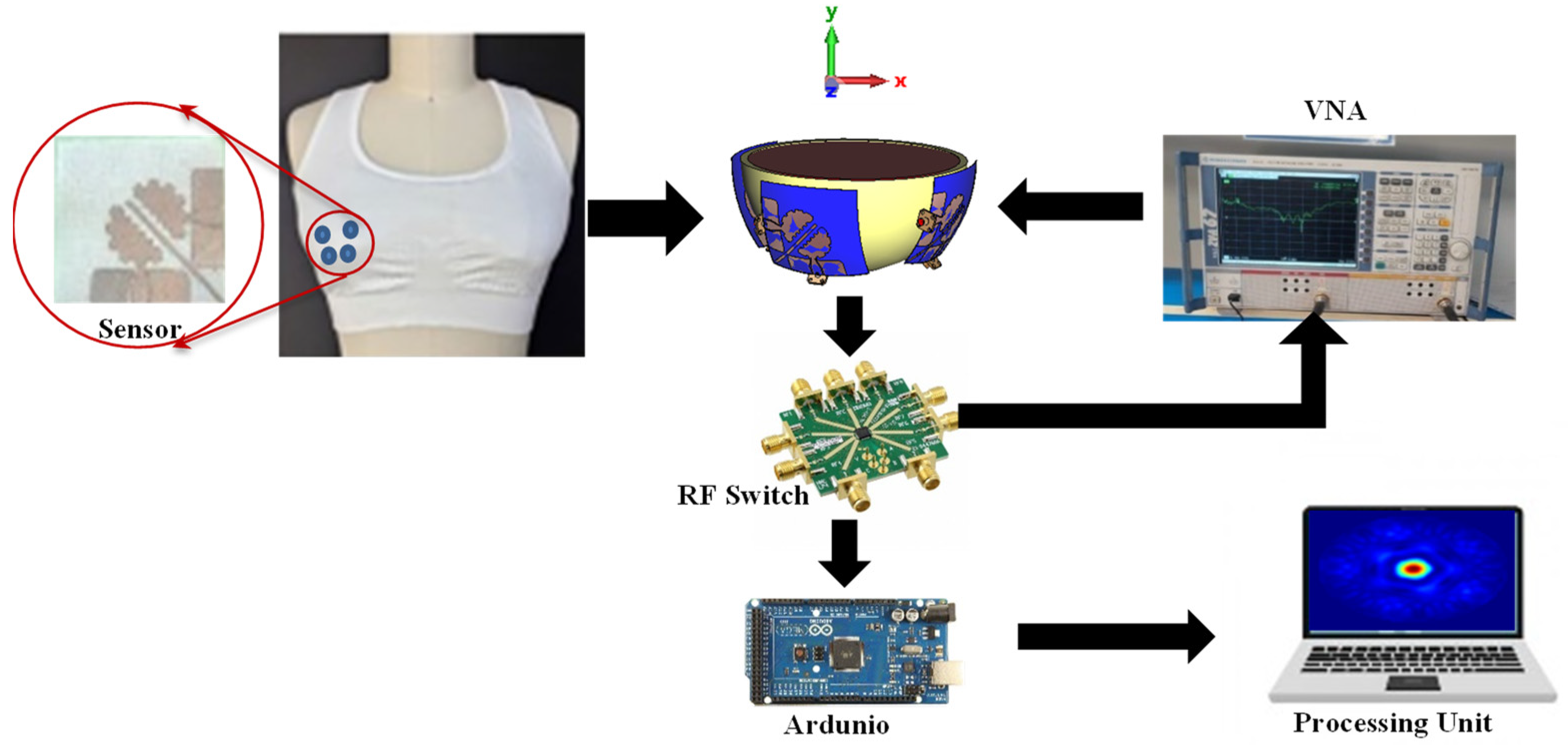
2.3. Wearable BC Monitoring System
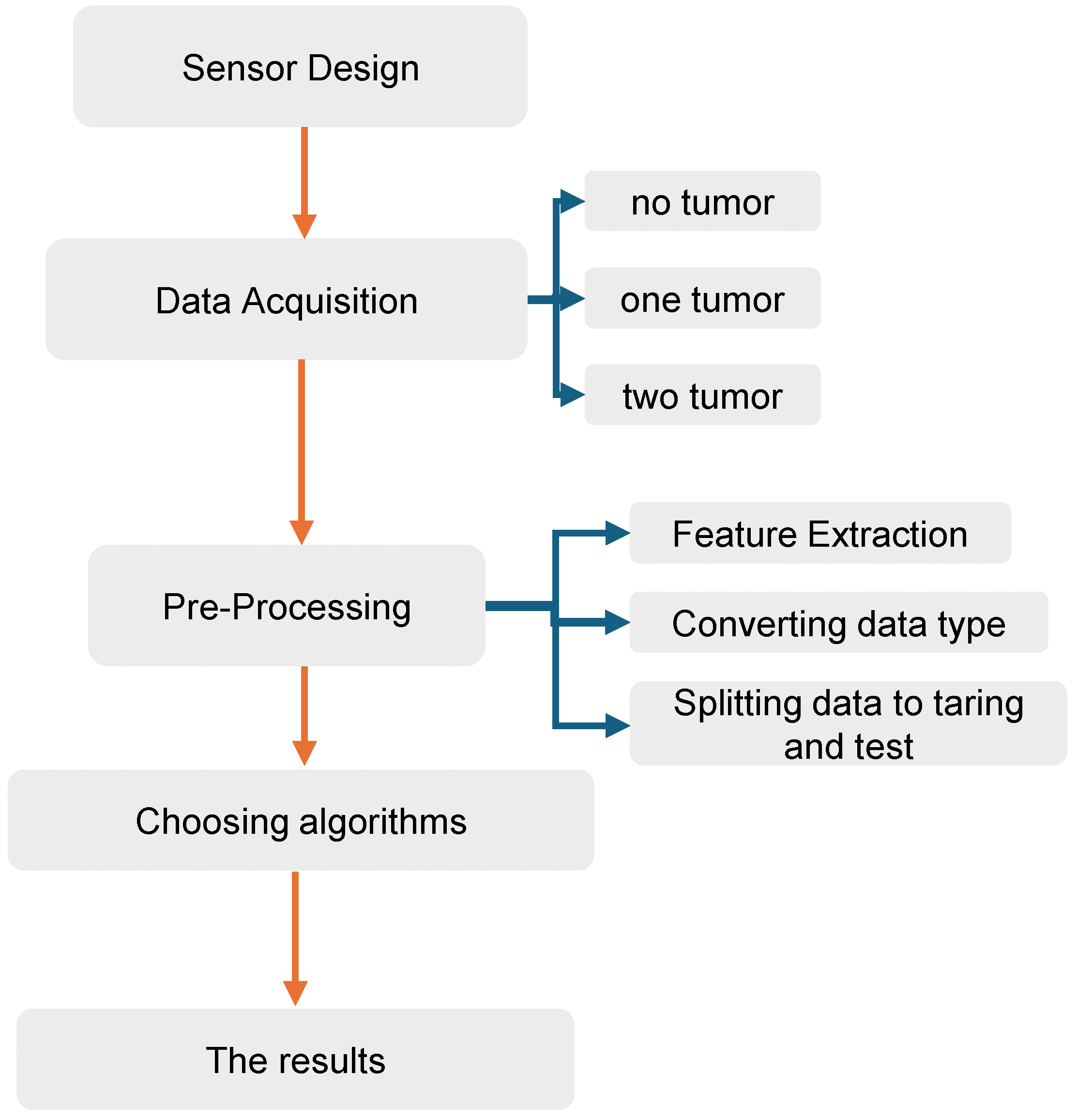
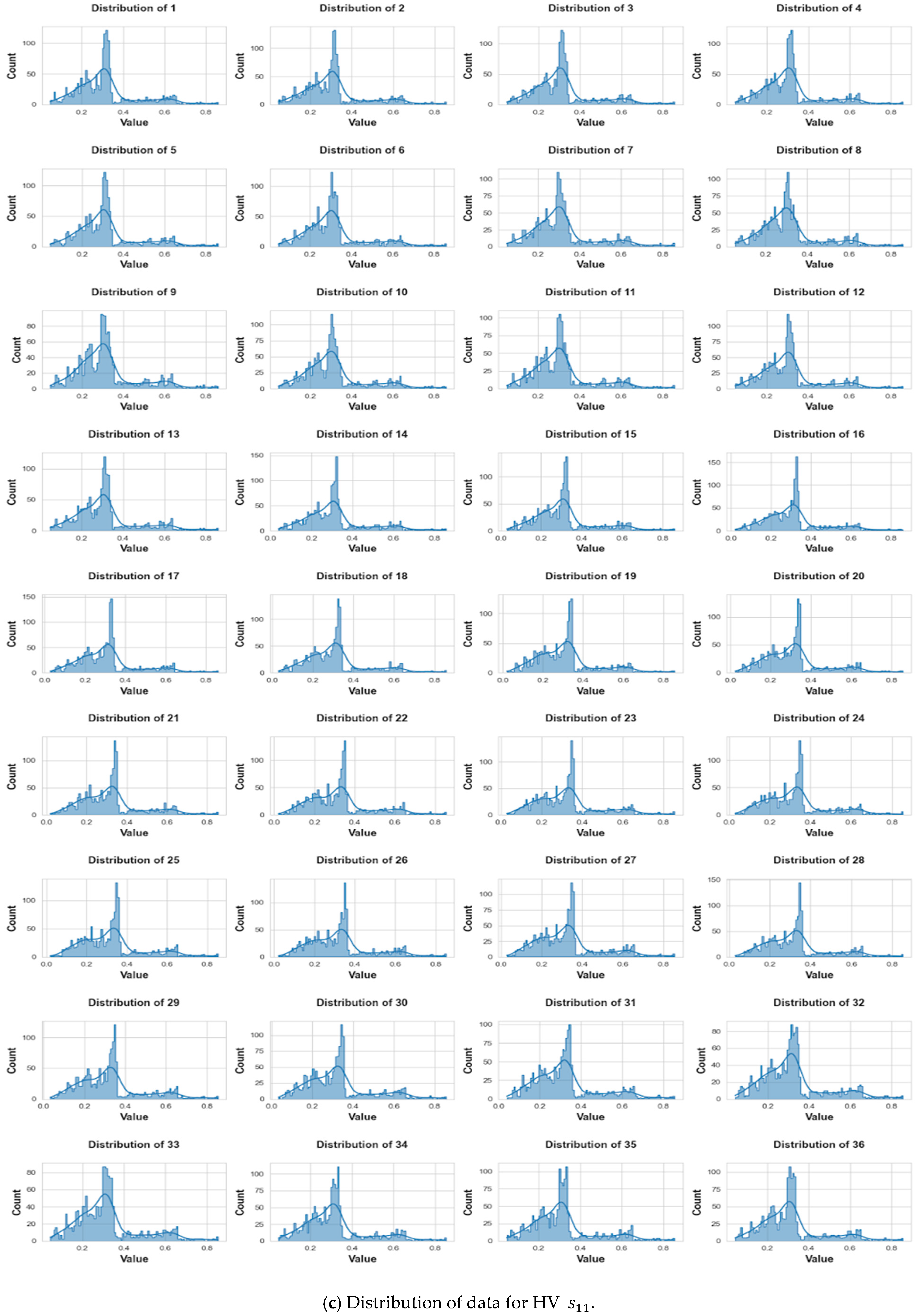
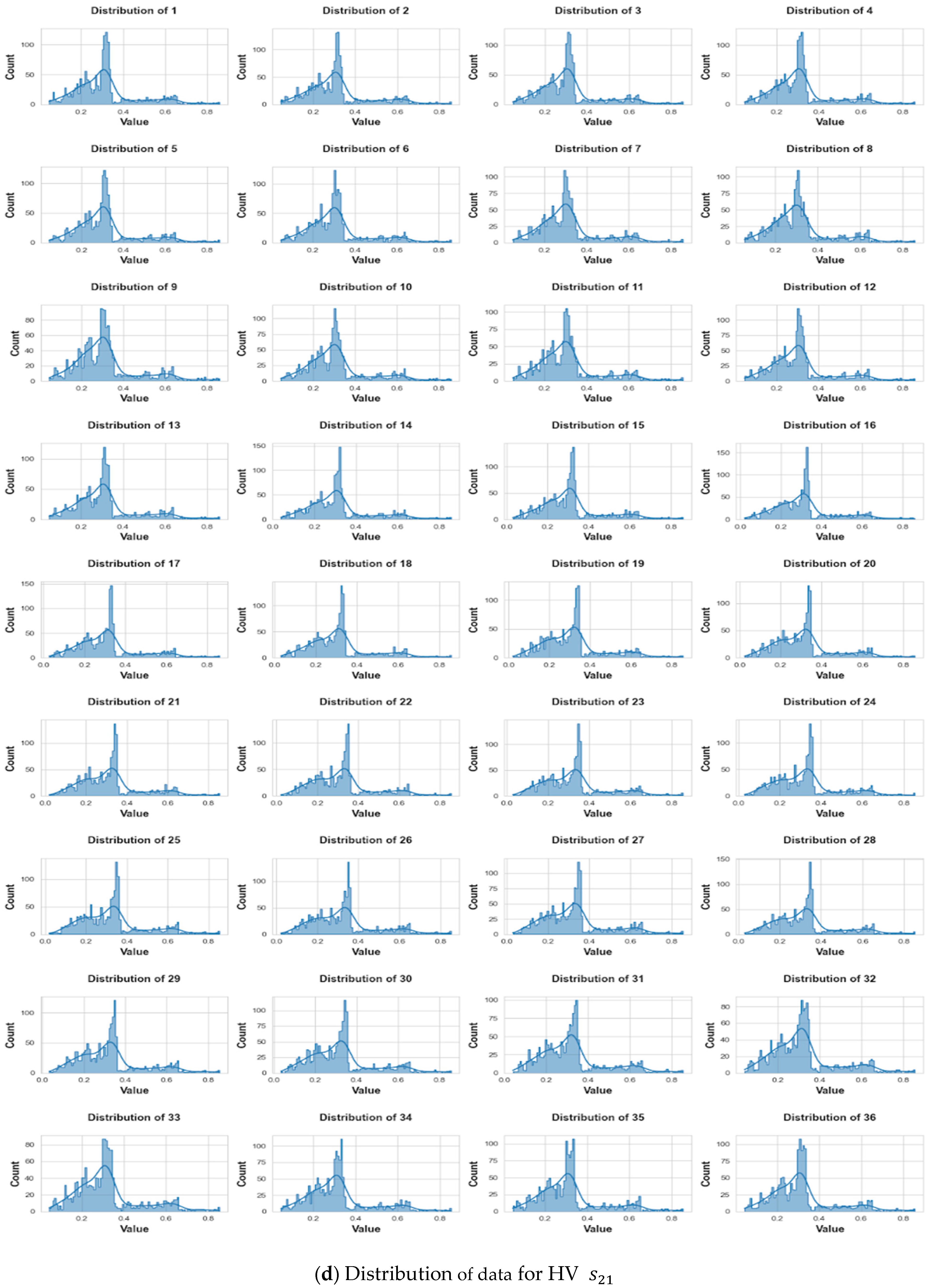
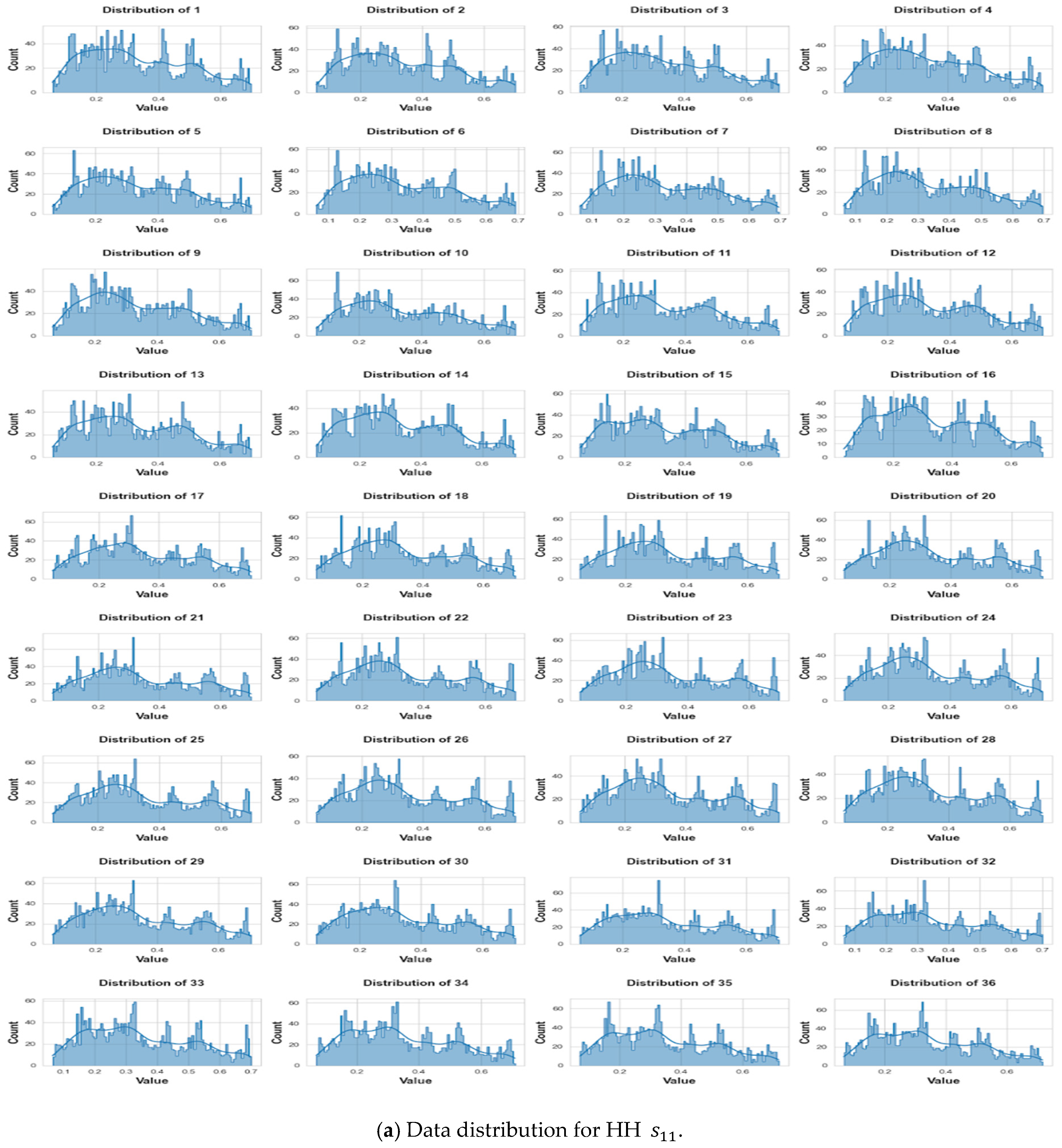
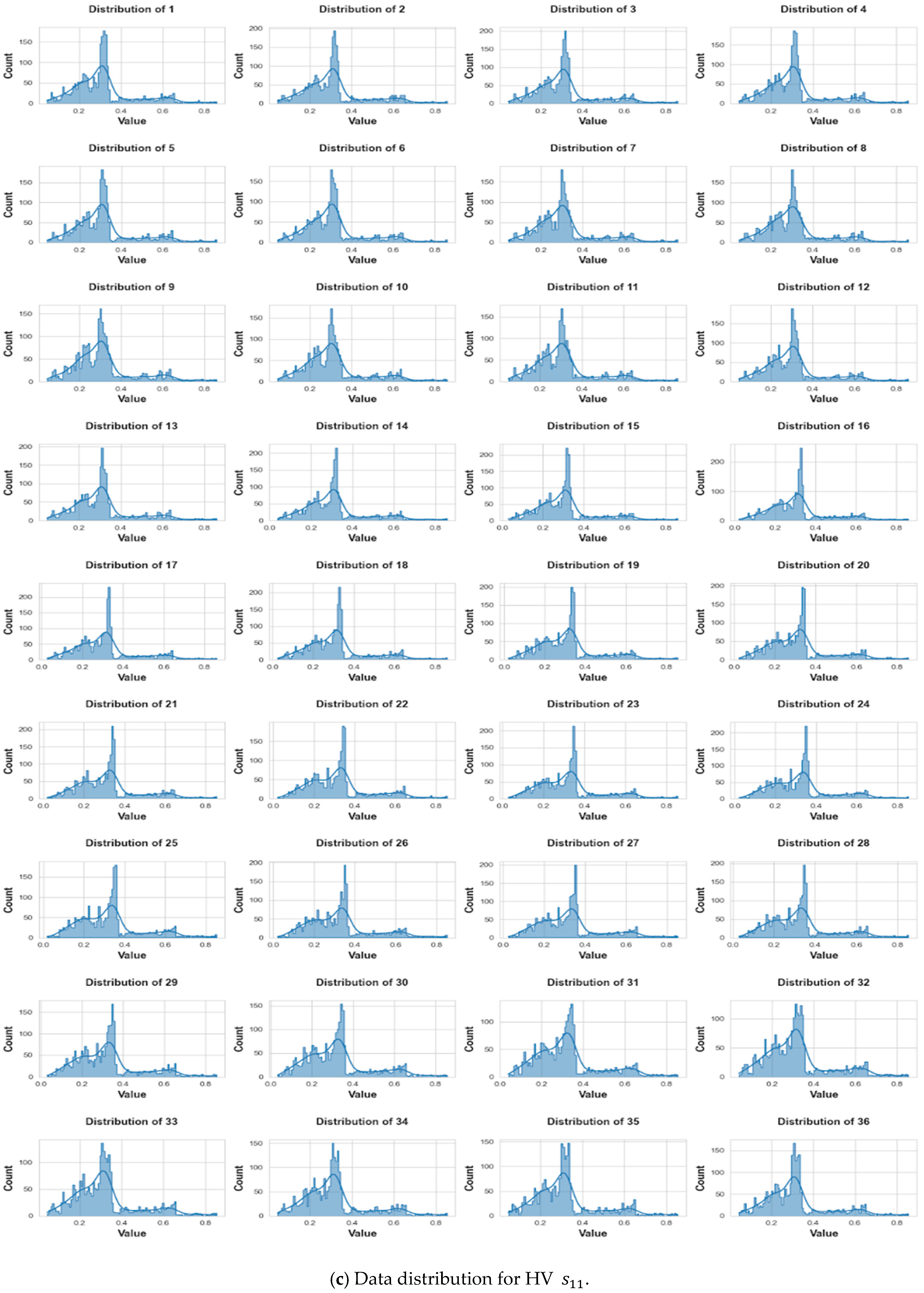
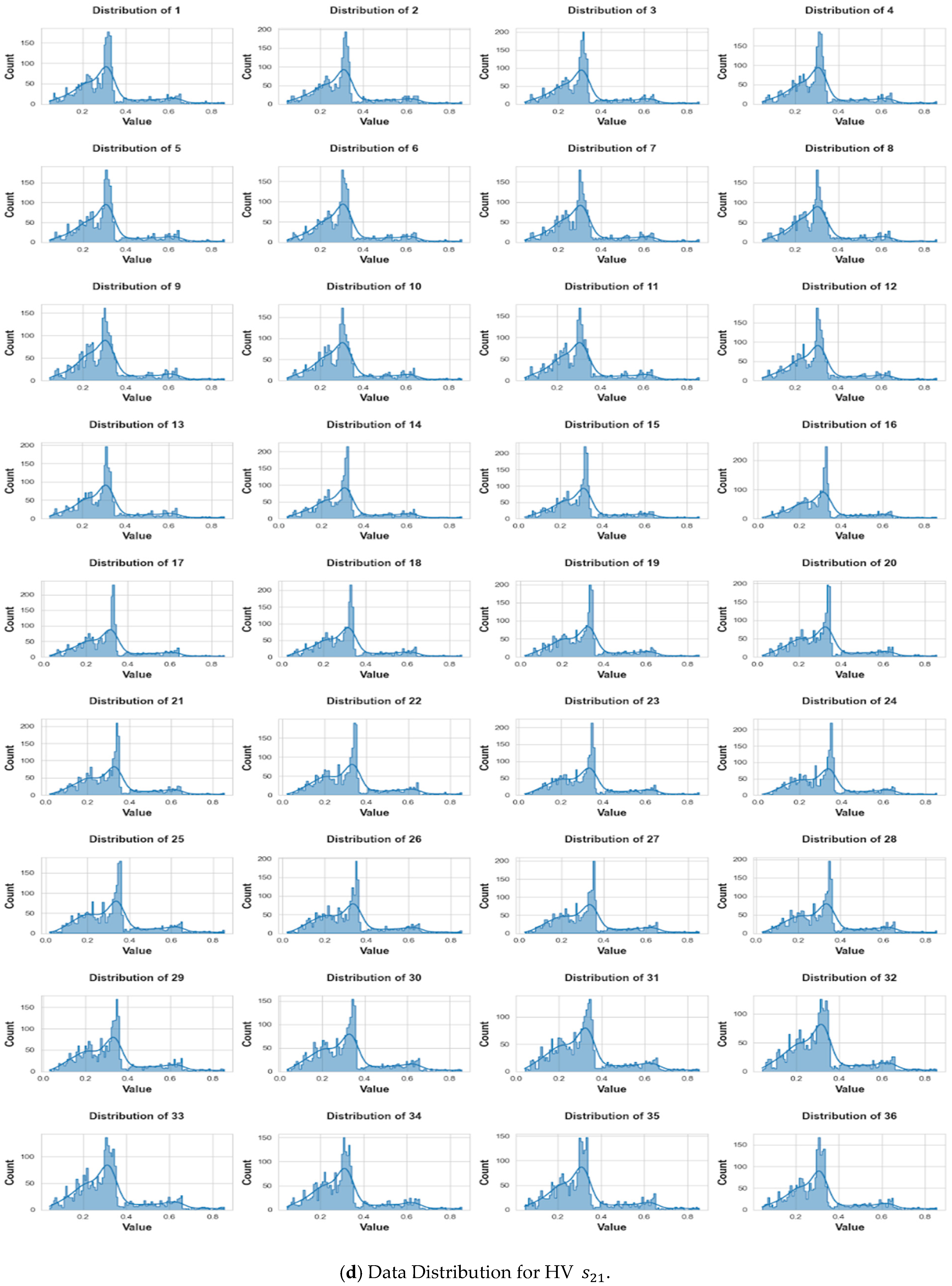
3. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
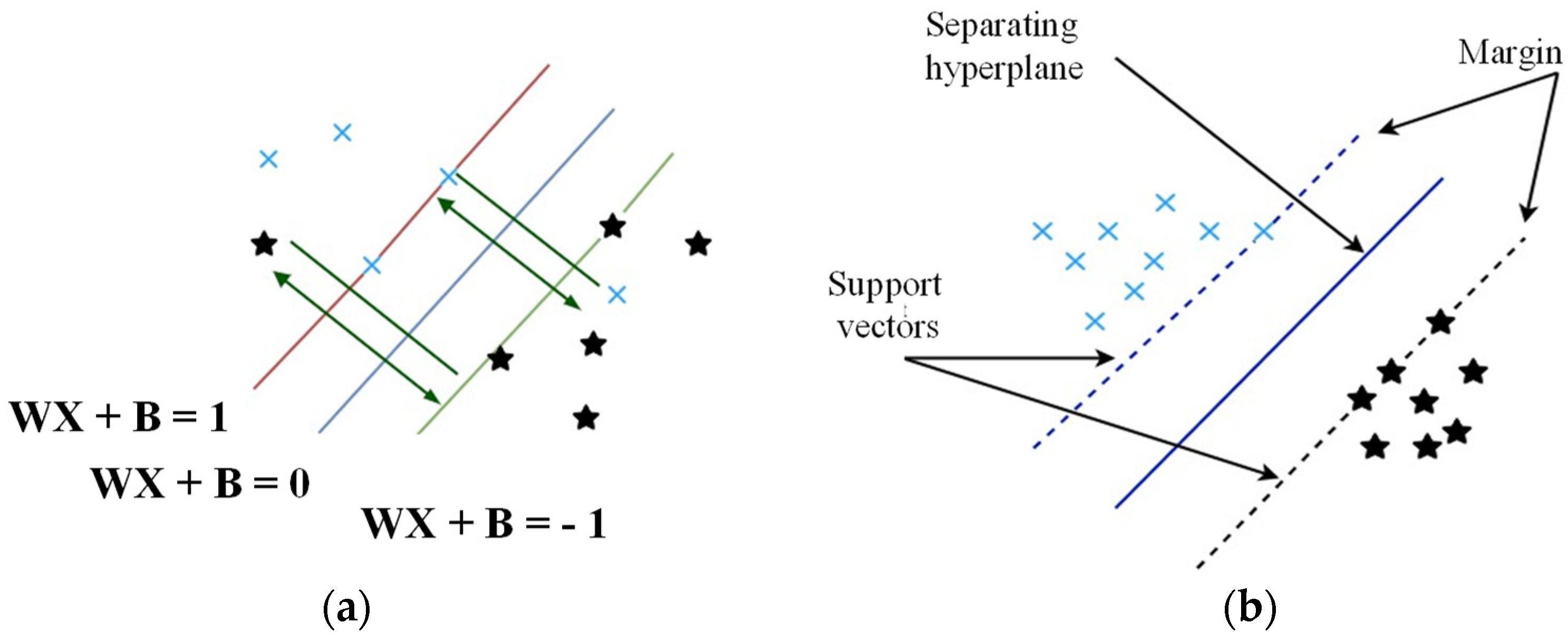
3.1. Machine Learning Algorithms and Evaluation Metrics
- 1.
- Logistic Regression (LR)
- 2.
- Support Vector Machine (SVM)
- 3.
- Decision Trees (DTs)
- 4.
- Random Forest (RF)
- 5.
- Gradient Boosting Methods (GBMs)
- 6.
- Categorical Boost (“CatBoost”)
- 7.
- Adaptive Boosting (Ada Boost)
- 8.
- Extreme Gradient Boosting (XG Boost)
3.2. Dataset of BC
3.3. Pre-Processing
3.3.1. Scenario 1: One Tumor or No Tumor
3.3.2. Scenario 2: One or Two Tumors vs. No Tumor
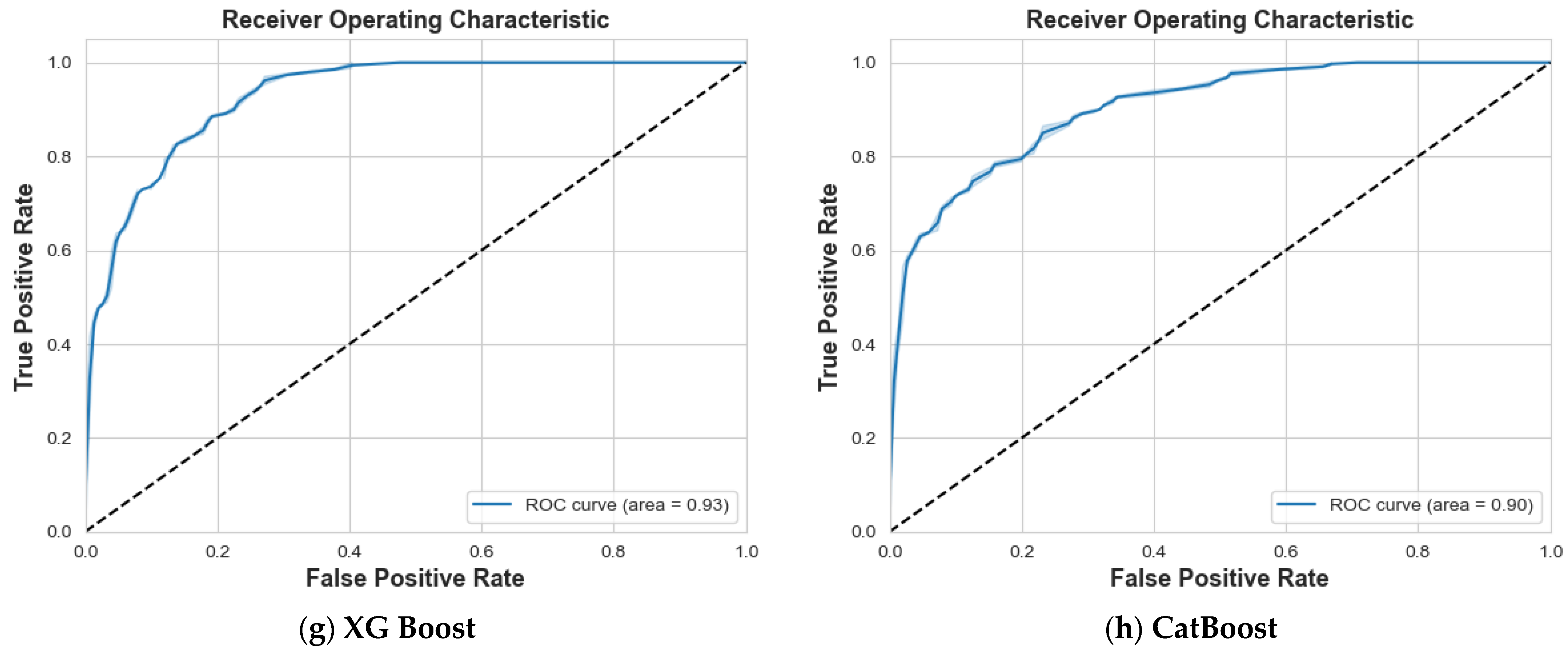
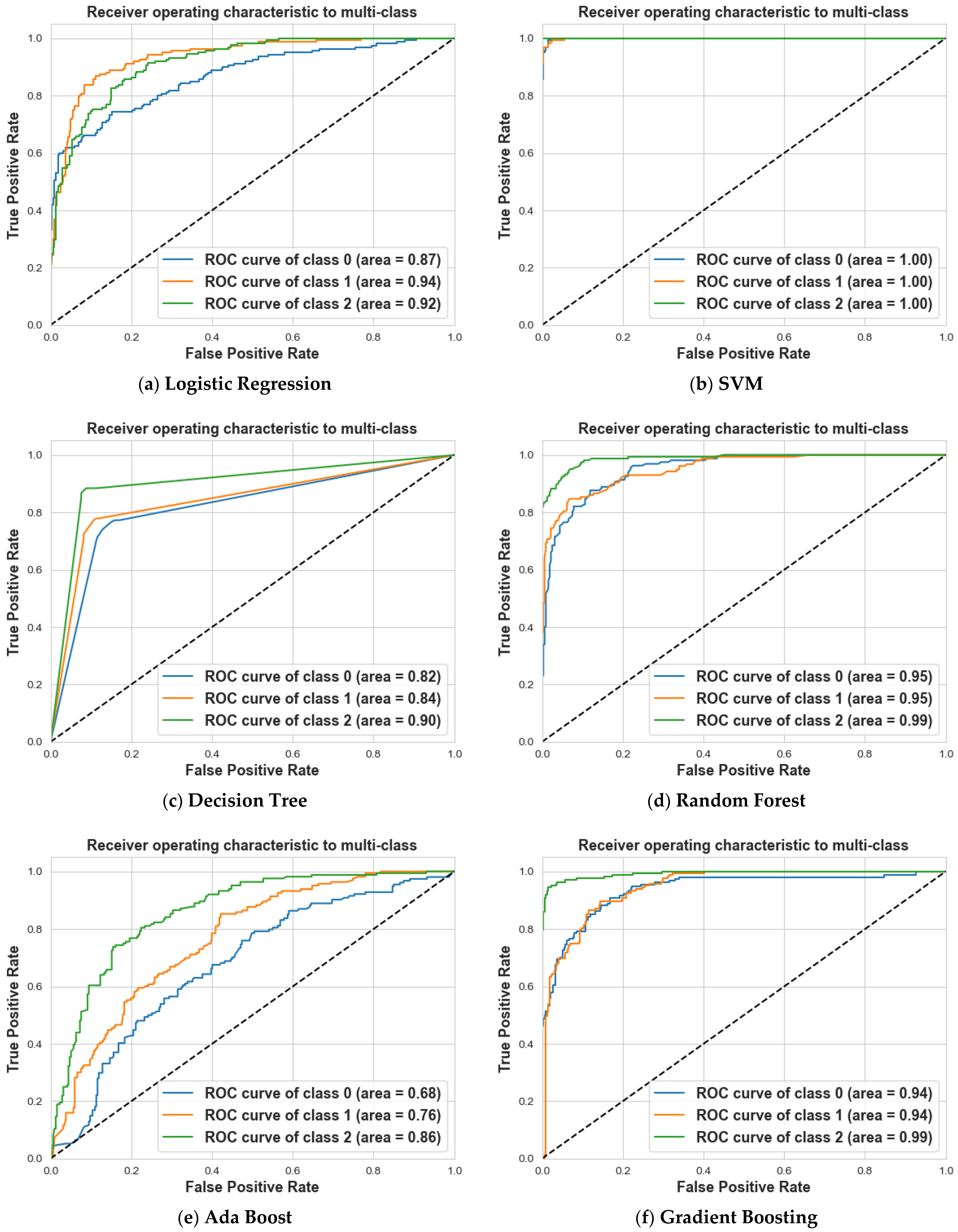
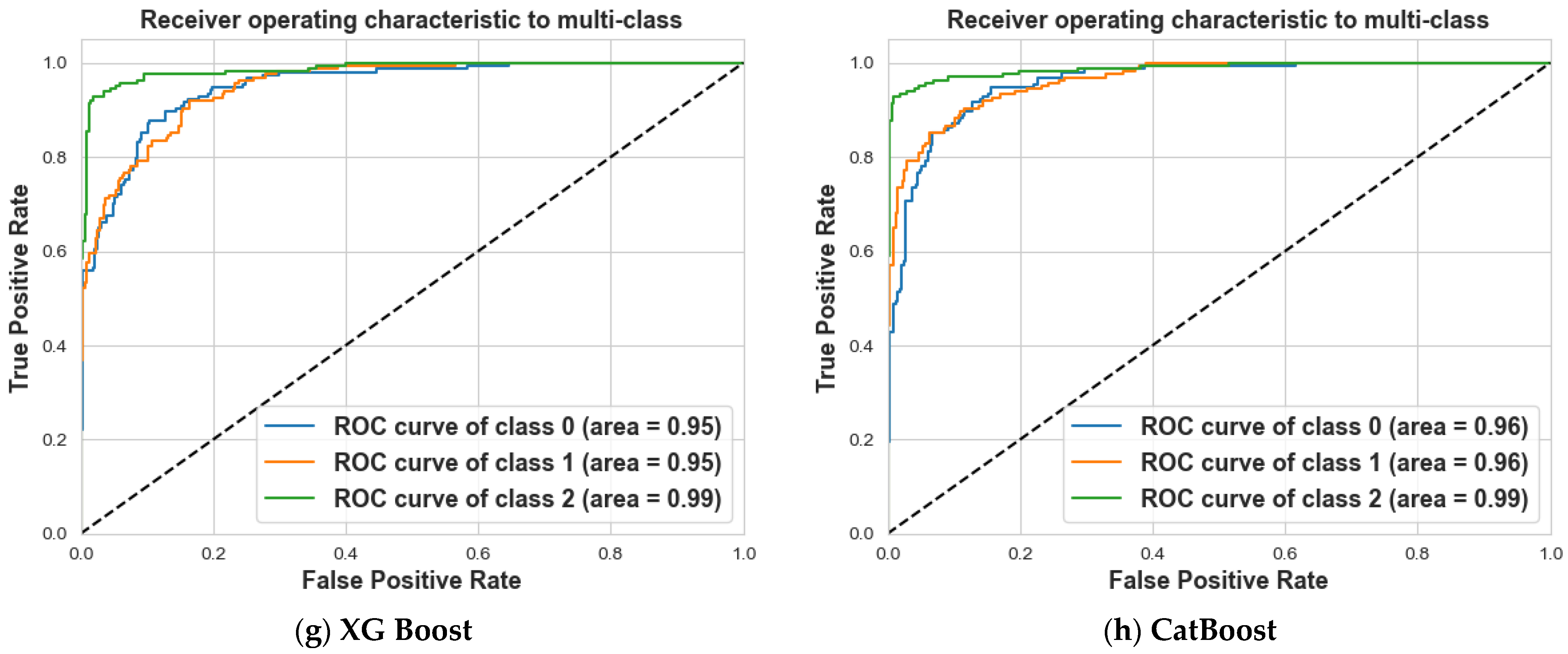
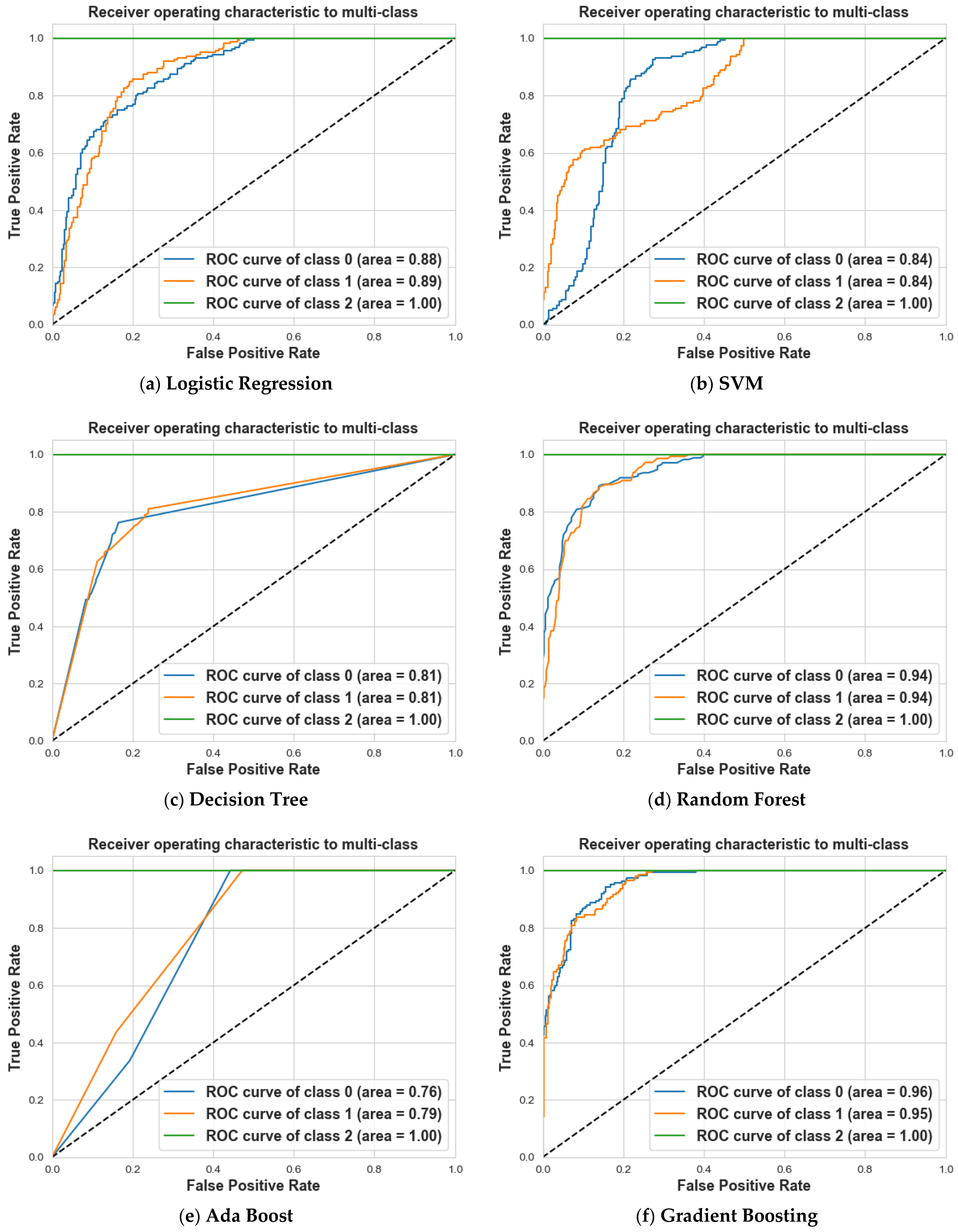
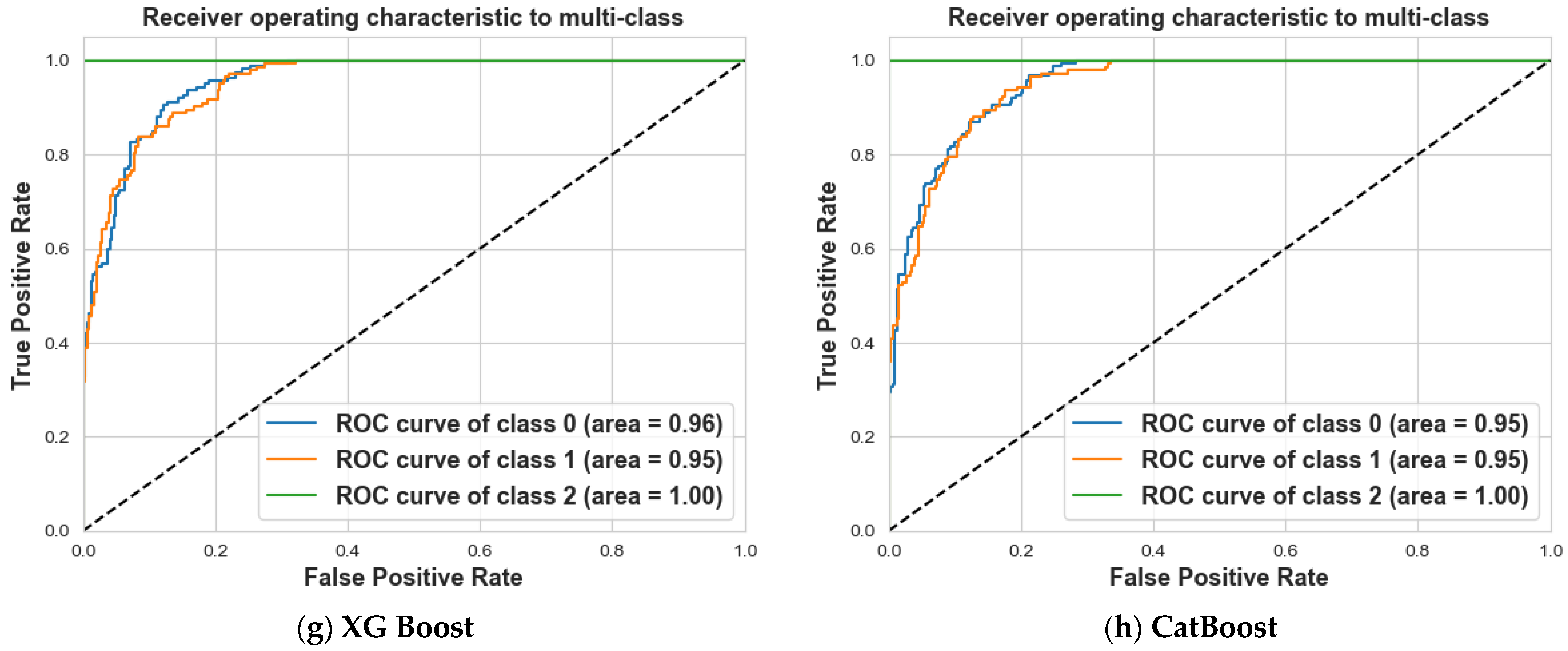
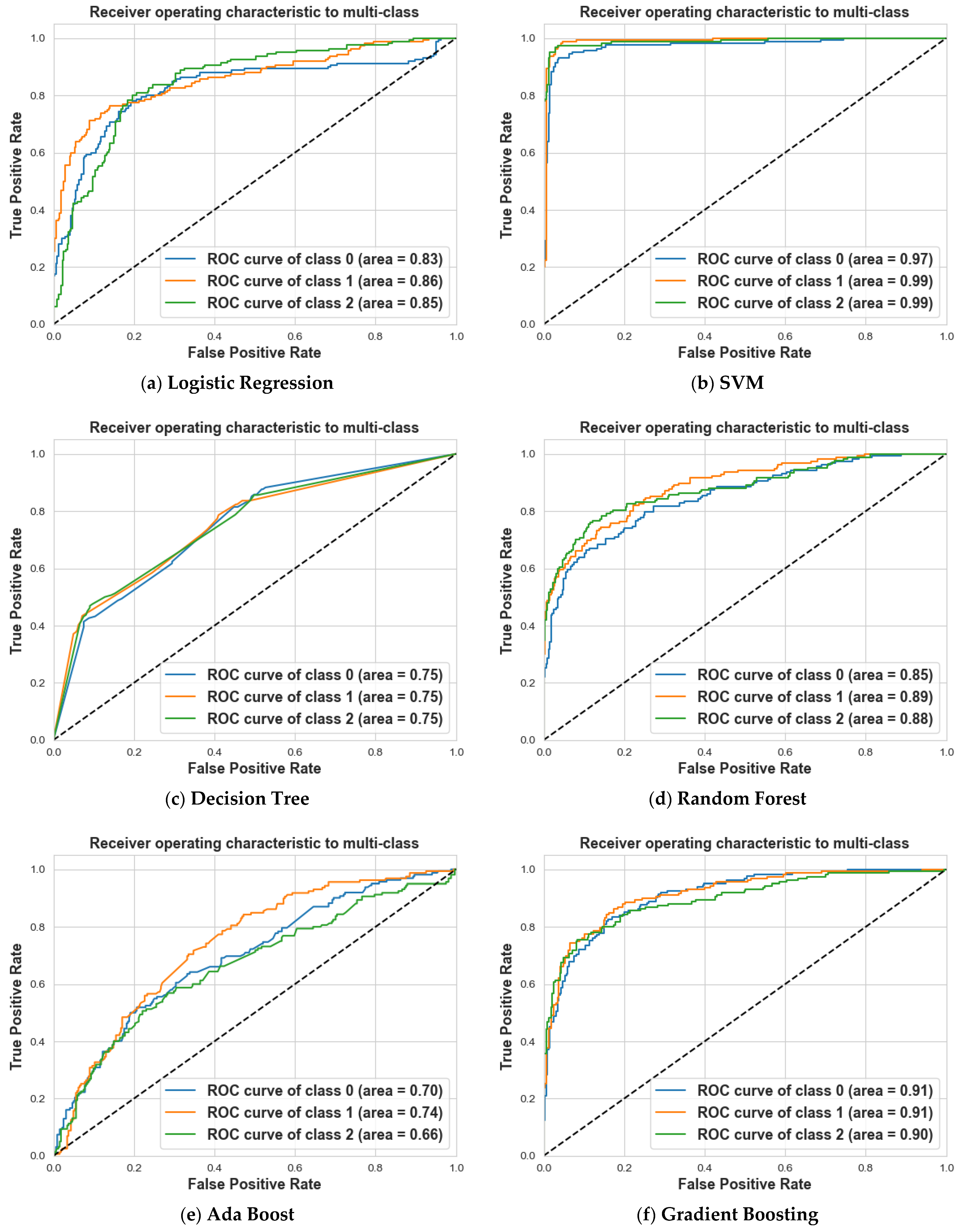
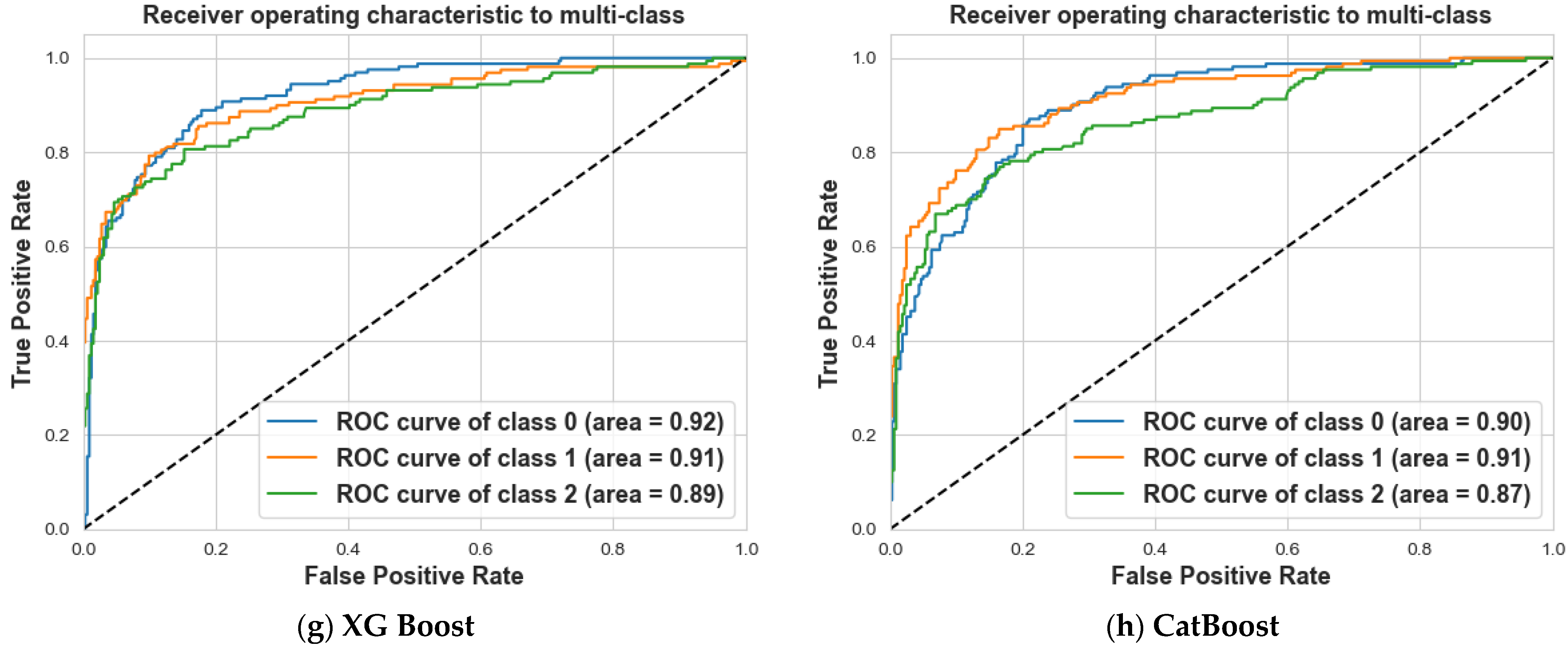
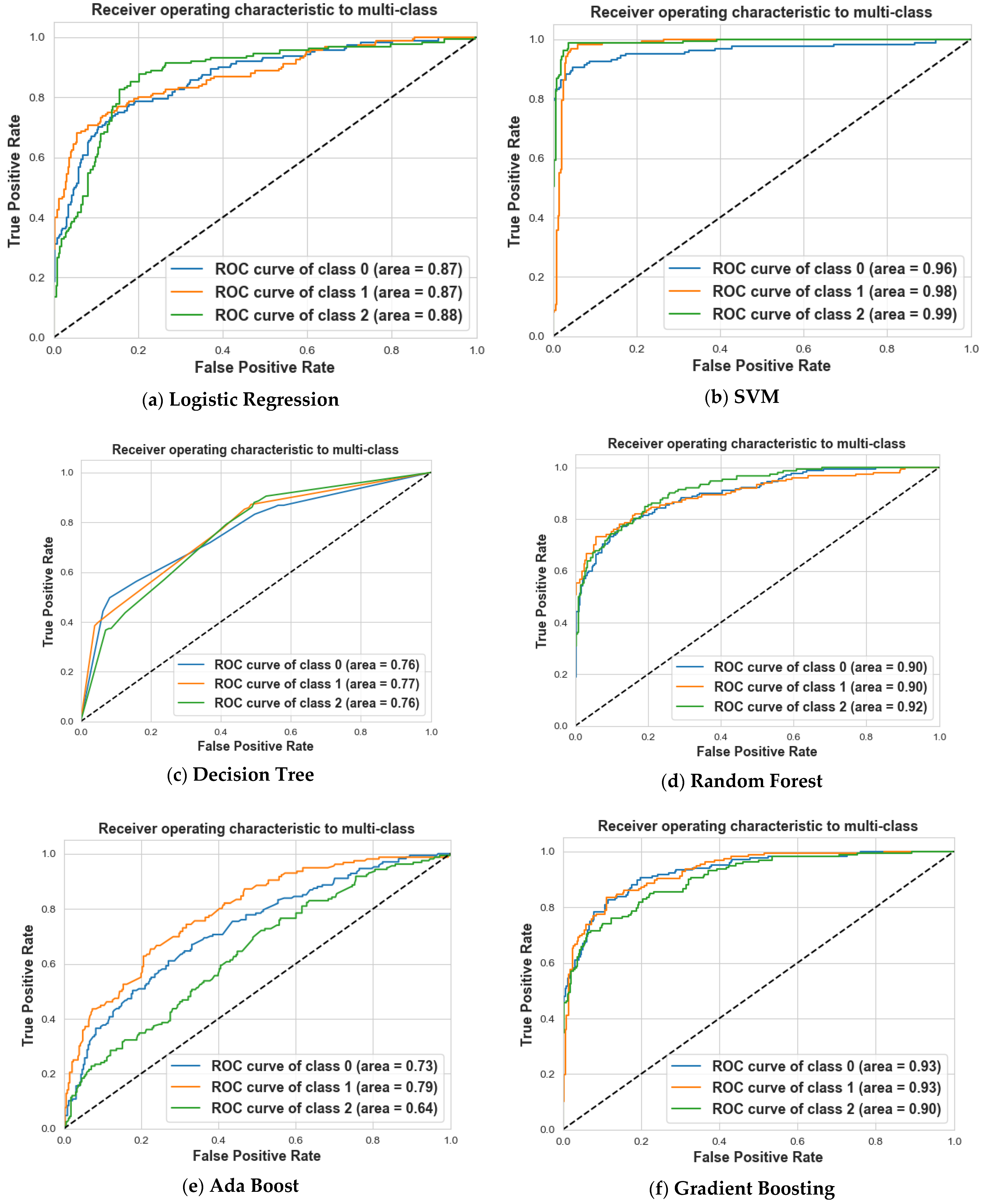
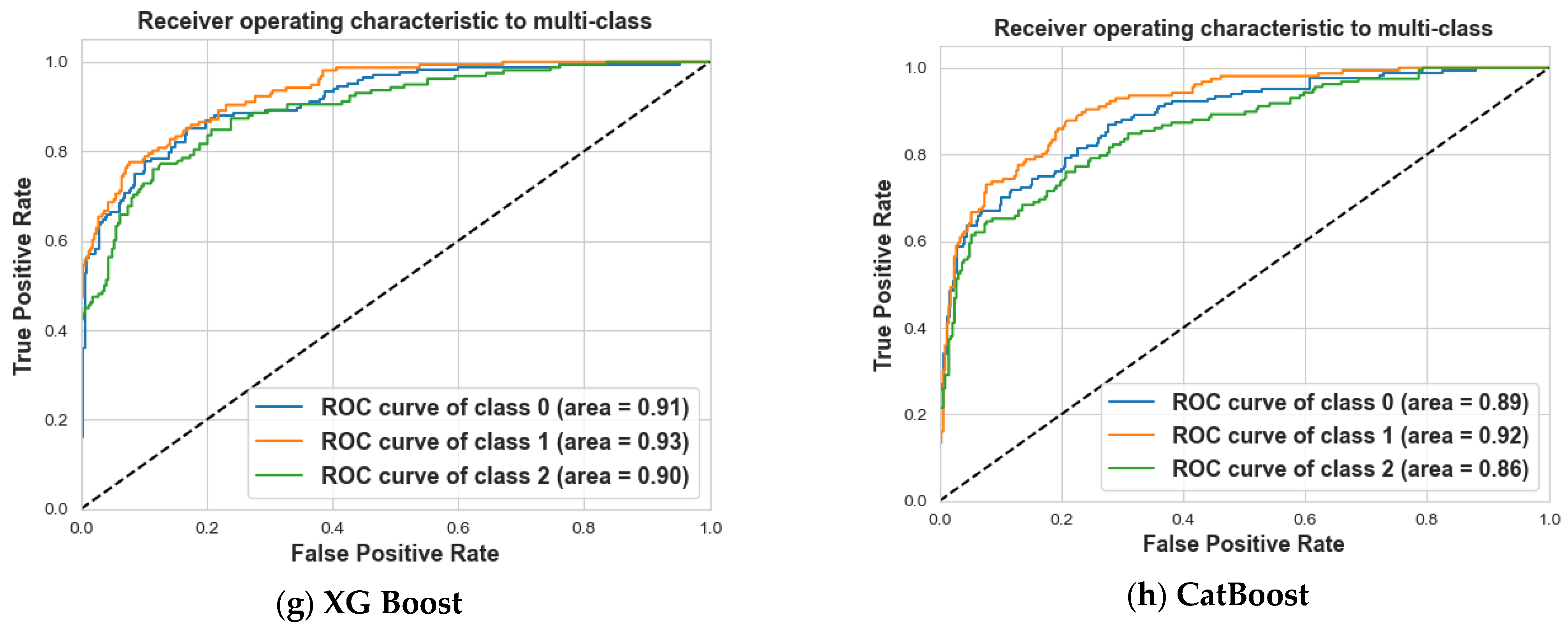
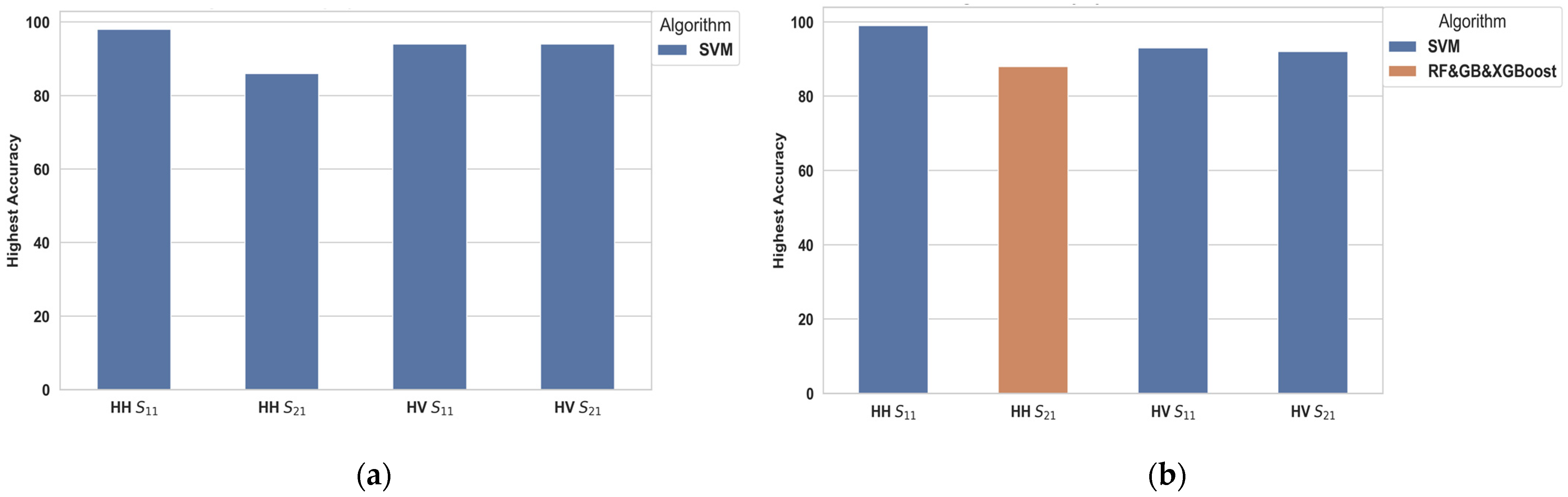
4. Results and Discussion
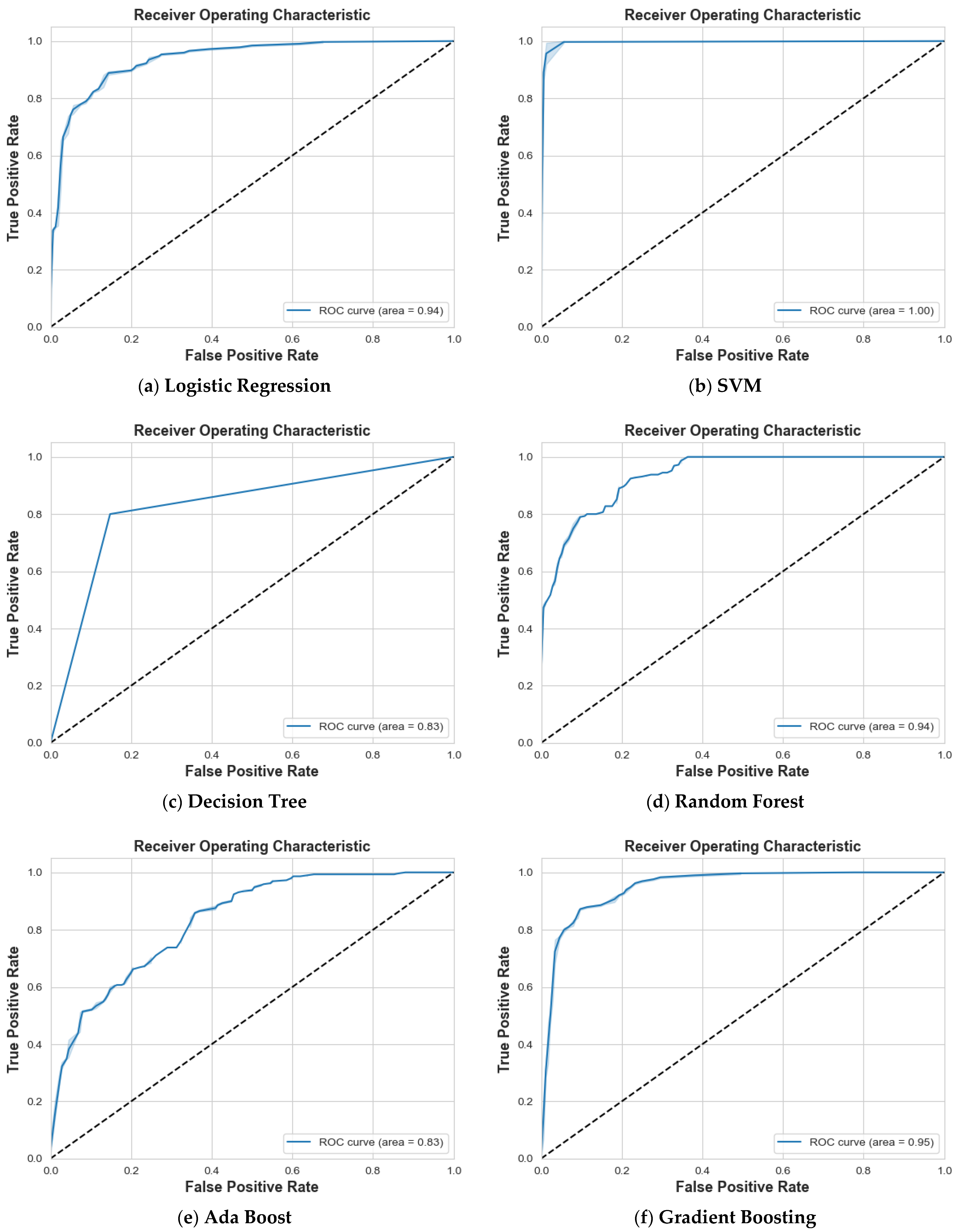
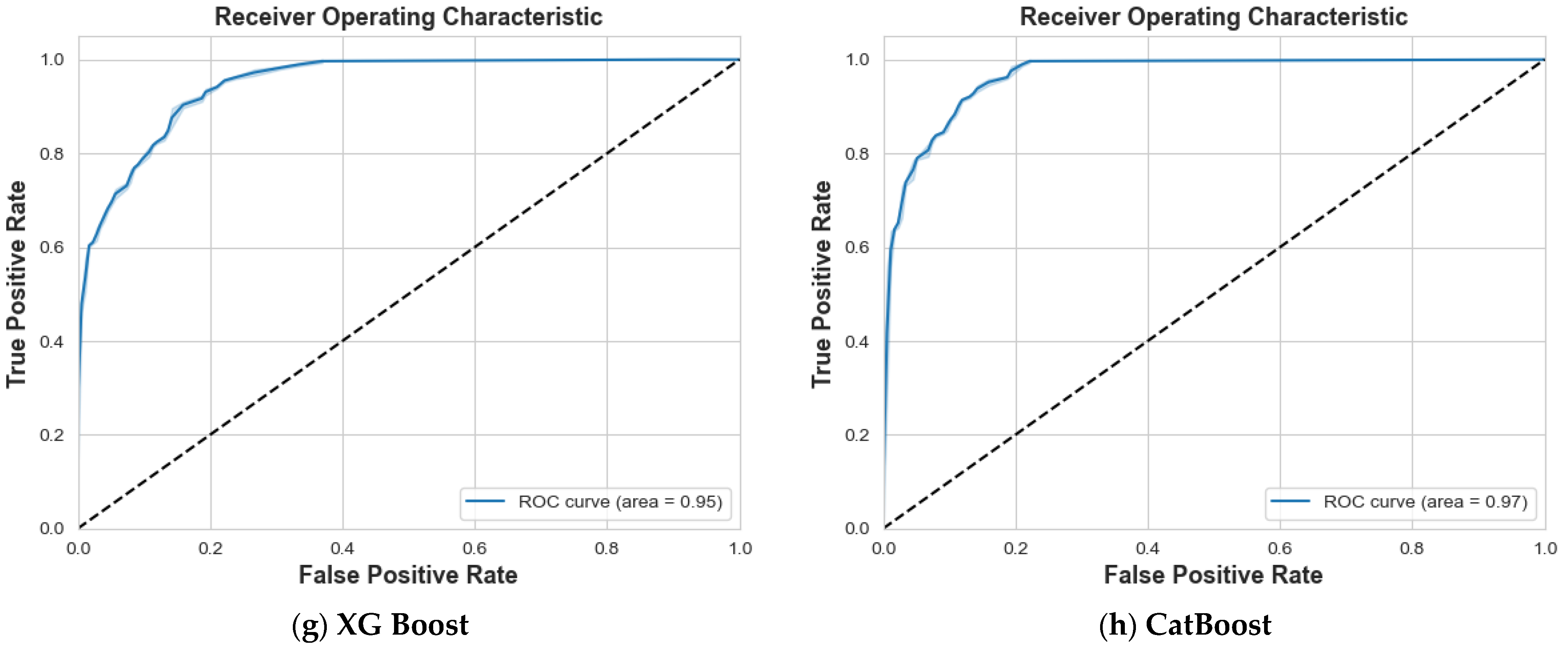
4.1. Scenario 1: One Tumor or Not
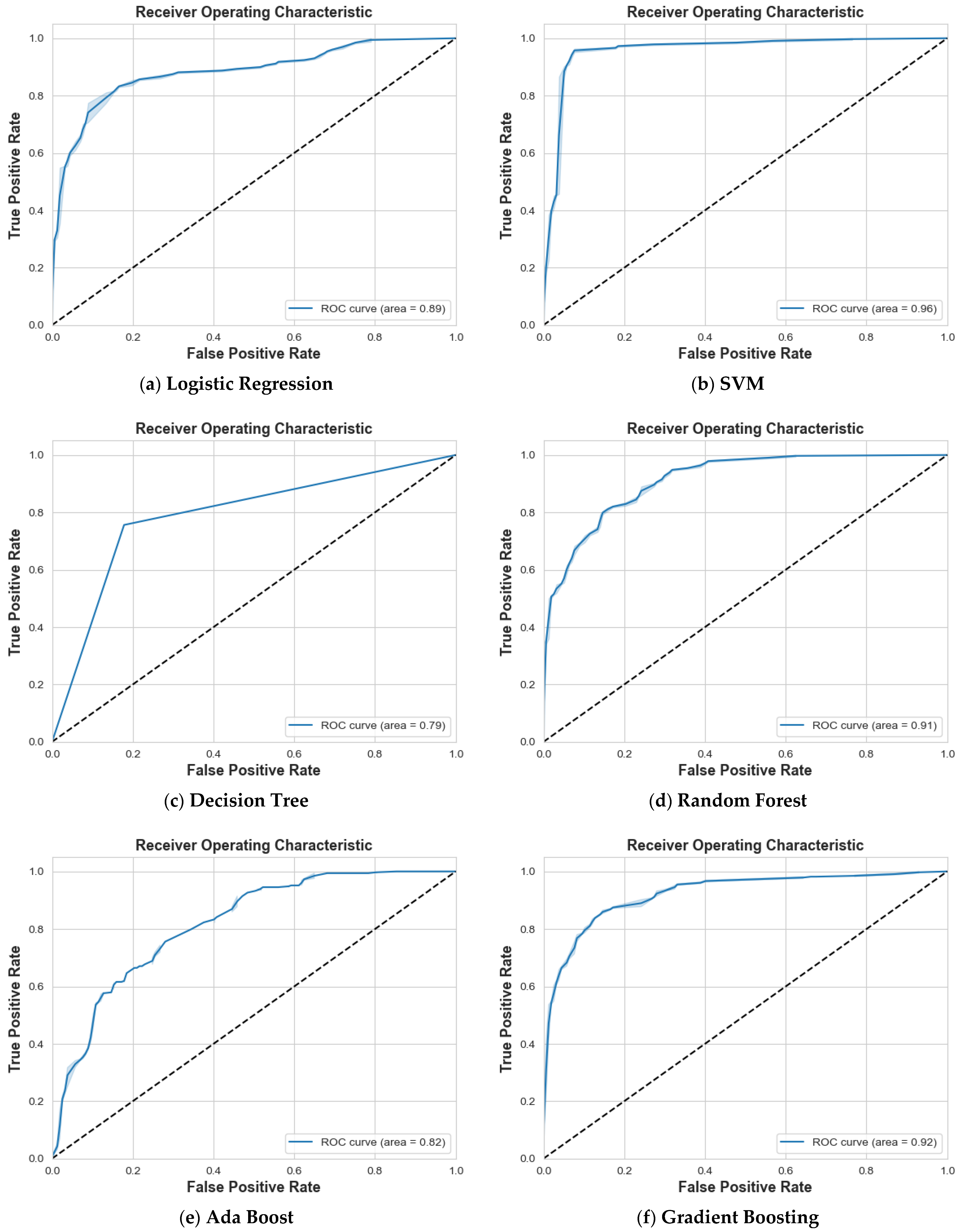
4.2. Scenario 2: One, Two, and No Tumors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tayel, M.; Abouelnaga, T.; Elnagar, A.H. Pencil Beam Grid Antenna Array for Hyperthermia Breast Cancer Treatment System. Circuits Syst. 2017, 8, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L. Microwave Imaging and Sensing Techniques for Breast Cancer Detection. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, I.H. Ai-driven cyber security: An overview, security intelligence modeling and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H.; Hoque, M.M. Mobile data science and intelligent apps: Concepts, AI-based modeling and research directions. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H.; Kayes, A.S.M.; Badsha, S.; Alqahtani, H.; Watters, P.; Ng, A. Cybersecurity data science: An overview from machine learning perspective. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Khan, M.B. Machine Learning: Algorithms and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4987-0538-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kamber, M. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann 2006, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H.; Watters, P. Effectiveness analysis of machine learning classification models for predicting personalized con text-aware smartphone usage. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazzam, B.; Mansour, M.; Hammam, H. Machine Learning of Medical Applications Involving Complicated Proteins and Genetic Measurements. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2023, 2023, 9839162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Rahman, S. A Comprehensive Review on Machine Learning in Healthcare Industry: Classification, Restrictions, Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors 2023, 23, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Ayub, H.; Khan, J.A.; Ahmad, I.; Salama, A.S.; Daradkeh, Y.I.; Javeed, D.; Ur Rehman, A.; Hamam, H. A Hybrid Deep Learning-Based Approach for Brain Tumor Classification. Electronics 2022, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanmaran, R.; Srimathi, S.; Yamuna, G.; Thanigaivel, S.; Vickram, A.S.; Priya, A.K.; Karthick, A.; Karpagam, J.; Mohanavel, V.; Muhibbullah, M. Investigating the Role of Image Fusion in Brain Tumor Classification Models Based on Machine Learning Algorithm for Personalized Medicine. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 7137524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslehi, S.; Rabiei, N.; Soltanian, A.R.; Mamani, M. Application of Machine Learning Models Based on Decision Trees in Classifying the Factors Affecting Mortality of COVID-19 Patients in Hamadan, Iran. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A.; Dhilip Kumar, V.; Asghar, J.; Hemalatha, D.; Arulkumaran, G. A Combined Deep CNN: LSTM with a Random Forest Approach for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Complexity 2022, 2022, 9299621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhof, K.; Eckhart, L.; Gerstner, N.; Kehl, T.; Lenhof, H.-P. Simultaneous Regression and Classification for Drug Sensitivity Prediction Using an Advanced Random Forest Method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wu, Z. The Application of Wearable Sensors and Machine Learning Algorithms in Rehabilitation Training: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Hameed, A.S.; Elsheakh, D.M.; Elashry, G.M.; Abdallah, E.A. A comparative Study of Narrow/Ultra-wideband Micro-wave Sensors for Continuous Monitoring of Vital Signs and Lung Water Level. Sensors 2024, 24, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabrah, A.; Alkhamees, B.F.; Amin, F.; AlSalman, H.; Choi, G.S. Breast Breast Cancer Detection and Prevention Using Machine Learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3113. [Google Scholar]
- Soumya, A.; Krishna Mohan, C.; Cenkeramaddi, L.R. Recent Advances in mmWave-Radar-Based Sensing, Its Applications, and Machine Learning Techniques: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 8901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Choudhury, T. Breast Cancer Detection Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computational Techniques, Electronics and Mechanical Systems (CTEMS), Belgaum, India, 21–22 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshan, M.S.A.; Amin, S.; Zeb, M.A.; Sulaiman, A.; Alshahrani, H.; Azar, A.T.; Shaikh, A. Enhancing Breast Cancer Detection and Classification Using Advanced Multi-Model Features and Ensemble Machine Learning Techniques. Life 2023, 13, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syversen, A.; Dosis, A.; Jayne, D.; Zhang, Z. Wearable Sensors as a Preoperative Assessment Tool: A Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, E.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Qi, S. An Optimized Framework for Breast Cancer Classification Using Machine Learning. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8482022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorogush, A.V.; Ershov, V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Gradient boosting with categorical features support. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.11363. [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 6639–6649. [Google Scholar]
- Vakaa, A.R.; Sonia, B.; Reddy, K.S. Breast cancer detection by leveraging Machine Learning. ICT Express 2020, 6, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, Y.; Waruwu, I. Early detection of breast cancer using ultra wide band slot antenna. SINERGI 2019, 23, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.; Bahrami, H.; Santorelli, A.; Gosselin, B.; Rusch, L.A.; Popovic, M. A Wearable Microwave Antenna Array for Time-Domain Breast Tumor Screening. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, D.; Gopalakrishnan, M. Breast Cancer Detection Using Adaptable Textile Antenna Design. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, B.M.; O’Loughlin, D.; Abd Elwahab, S.; Kerin, M.J. Breast Cancer Detection—A Synopsis of Conventional Modalities and the Potential Role of Microwave Imaging. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, D.; O’Halloran, M.; Moloney, B.M.; Glavin, M.; Jones, E.; Elahi, M.A. Microwave Breast Imaging: Clinical Advances and Remaining Challenges. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, Z.A.; Abduljabbar, Z.H.; Taher, H.A.; Sallow, A.B.; Almufti, S.M. Exploring the Power of eXtreme Gradient Boosting Algorithm in Machine Learning: A Review. Acad. J. Nawroz Univ. 2023, 12, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarap, A.F.M. On Breast Cancer Detection: An Application of Machine Learning Algorithms on the Wisconsin Diagnostic Dataset. In Proceedings of the ICMLSC 2018, 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Soft Computing, Phuoc Island, Vietnam, 2–4 February 2018; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathri, B.M.; Sumathi, C.P. Breast cancer diagnosis using machine learning algorithms—A survey. Int. J. Distrib. Parallel Syst. 2013, 4, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Bhise, S.; Bepari, S. Breast Cancer Detection using Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 2278-0181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Yang, F.; Xu, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, H. A feasibility study of 2-D microwave thorax imaging based on the supervised descent method. Electronics 2021, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheakh, D.N.; Mohamed, R.A. Complete breast cancer detection and monitoring system by using microwave textile based antenna sensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, T.R.; Vinoth Kumar, V.; Muthukumaran, V.; Shashikala, H.K.; Swapna, B.; Guluwadi, S. Performance Analysis of XGBoost Ensemble Methods for Survivability with the Classification of Breast Cancer. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 4649510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Mehta, D.A. Comparative Analysis of Various Machine Learning Techniques for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 8, 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Fatih, M. A Comparative Analysis of Breast Cancer Detection and Diagnosis Using Data Visualization and Machine Learning Applications. Healthcare 2020, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asria, H.; Mousannifb, H.; Al Moatassime, H. Using Machine Learning Algorithms for Breast Cancer Risk Prediction and Diagnosis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 83, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazazeh, D.; Shubair, R. Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms for Breast Cancer Detection and Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Electronic Devices, Systems and Applications (ICEDSA), Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, 6–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, A.H.; Abd El-Hameed, A.S.; Yakout, M.A.; Areed, N.F. Development and comprehensive evaluation of a dual-port textile UWB MIMO antenna for biomedical use. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hameed, A.S.; Wahab, M.G.; Elpeltagy, M. Quad-port UWB MIMO antenna based on LPF with vast rejection band. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 134, 153712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, G.; Zurcher, J.-F.; Skrivervik, A.K. System fidelity factor: A new method for comparing UWB antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 59, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar]
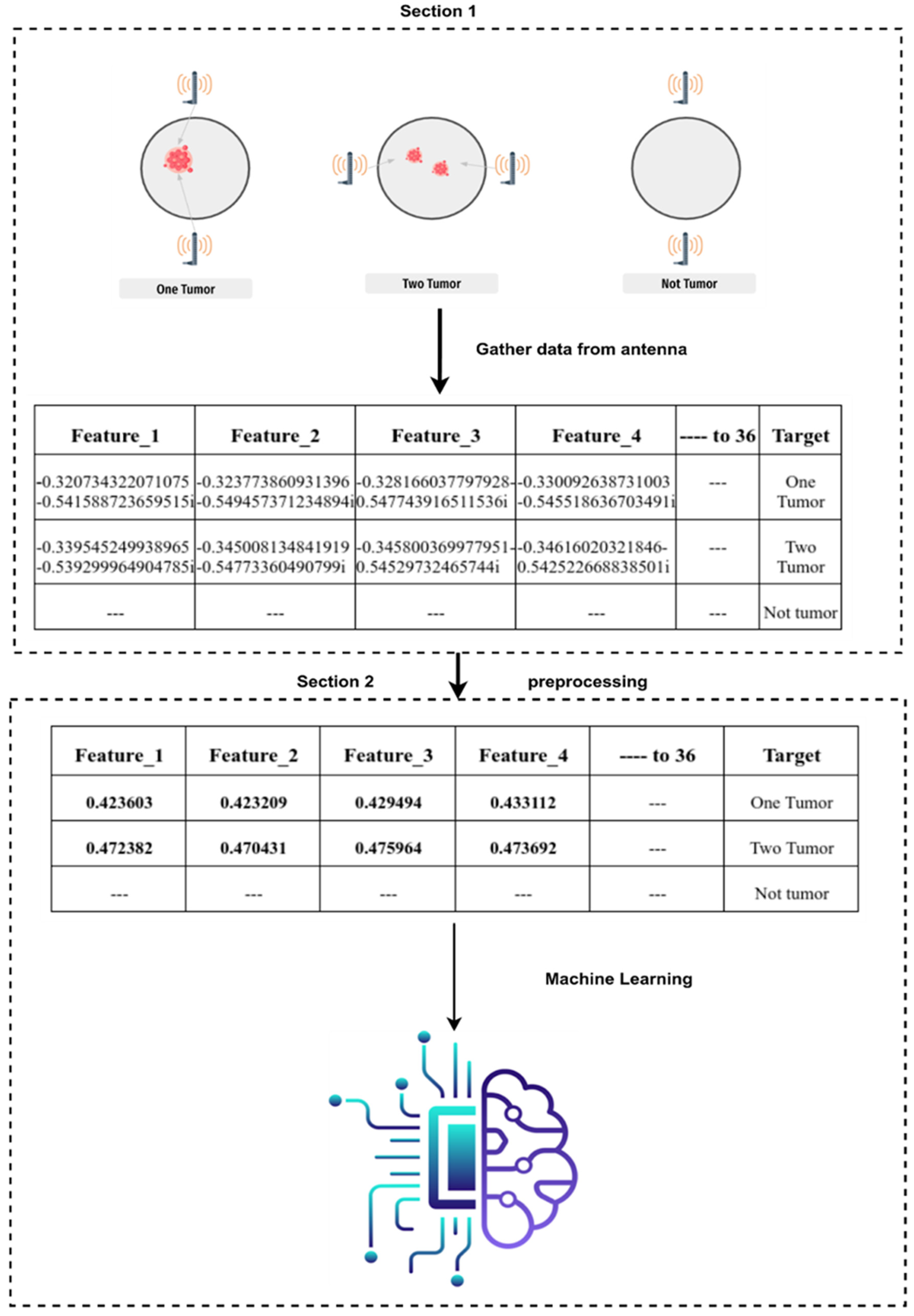

| Feature_1 | Feature_2 | Feature_3 | Feature_4 | Feature_5 | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.320734322071075–0.541588723659515i | −0.323773860931396–0.549457371234894i | −0.328166037797928–0.547743916511536i | −0.330092638731003–0.545518636703491i | −0.328741282224655–0.546375811100006i | … |
| −0.339545249938965–0.539299964904785i | −0.345008134841919–0.54773360490799i | −0.345800369977951–0.54529732465744i | −0.34616020321846–0.542522668838501i | −0.347417116165161–0.547296822071075i | … |
| Feature_1 | Feature_2 | Feature_3 | Feature_4 | Feature_5 | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.423603 | 0.423209 | 0.429494 | 0.433112 | 0.436930 | … |
| 0.472382 | 0.470431 | 0.475964 | 0.473692 | 0.475052 | … |
| 0.251808 | 0.254344 | 0.249489 | 0.248362 | 0.242685 | … |
| 0.400151 | 0.398328 | 0.403605 | 0.40977 | 0.41290 | … |
| 0.249165 | 0.251867 | 0.250815 | 0.23965 | 0.24348 | … |
| 1. IMPORT LIBRARIES: numpy, pandas, sklearn.model_selection 2. DEFINE FILE PATHS: PATH_with, PATH_without 3. READ CSV FILES: df_with, df_without = read_csv(PATH_with, PATH_without) 4. CONVERT TO COMPLEX NUMBERS: df_with, df_without = convert_to_complex(df_with, df_without) 5. CALCULATE MAGNITUDES: df_with, df_without = calculate_magnitudes(df_with, df_without) 6. ADD TUMOR COLUMN: df_with[‘tumor’] = 1, df_without[‘tumor’] = 0 7. CONCATENATE DATAFRAMES: df = concatenate(df_with, df_without) 8. SHUFFLE ROWS: df = shuffle(df) 9. SPLIT DATA: train, test = split(df), test_size = 0.2 |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1 | Precision | Recall | F1 | Accuracy | AUC |
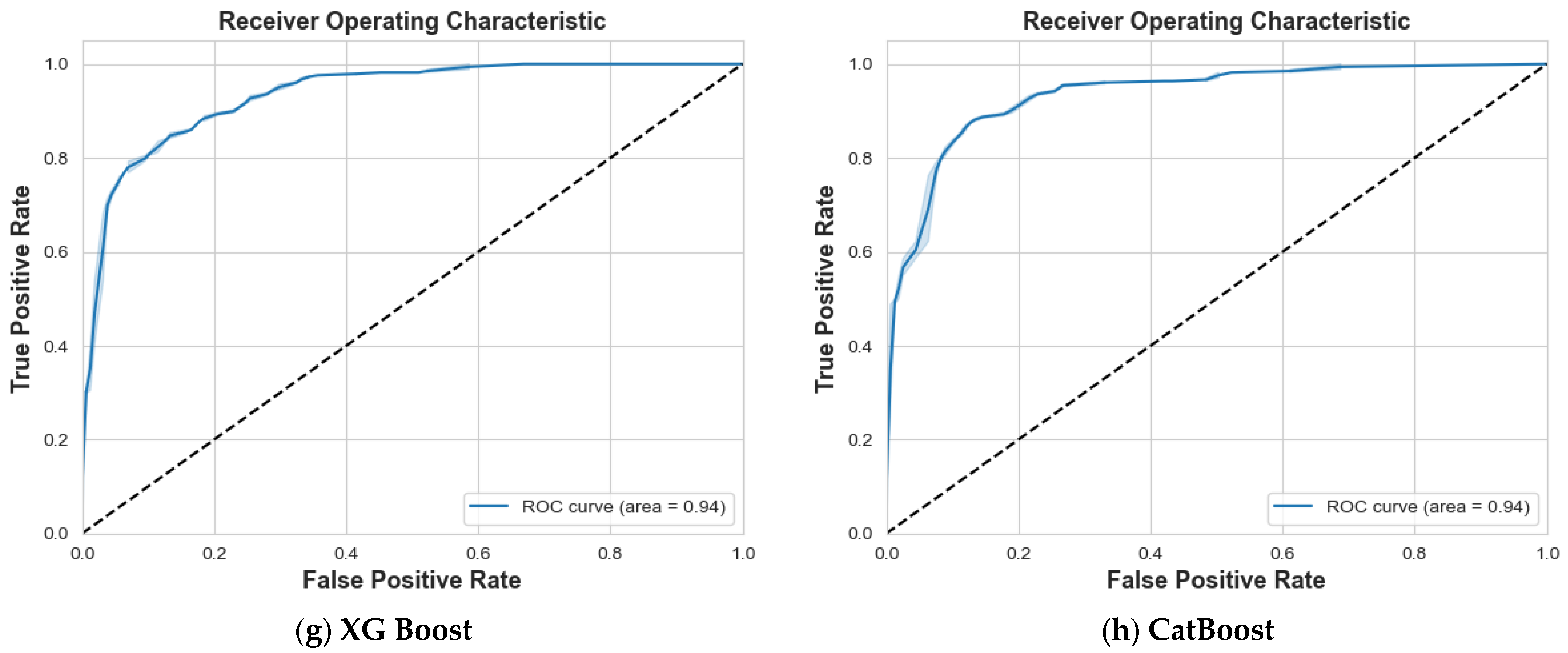
| Logistic Regression | 87% | 87% | 87% | 87% | 88% | 87% | 87% | 0.94 |
| SVM | 97% | 99% | 98% | 99% | 97% | 98% | 98% | 1 |
| Decision Tree | 84% | 85% | 85% | 82% | 80% | 81% | 83% | 0.83 |
| Random Forest | 86% | 84% | 85% | 81% | 83% | 82% | 83% | 0.94 |
| Ada Boost | 74% | 77% | 75% | 71% | 68% | 69% | 73% | 0.83 |
| Gradient Boosting | 90% | 88% | 89% | 85% | 88% | 87% | 88% | 0.95 |
| XG Boost | 87% | 86% | 87% | 84% | 85% | 84% | 86% | 0.95 |
| CatBoost | 92% | 89% | 90% | 87% | 91% | 89% | 90% | 0.97 |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1 | Precision | Recall | F1 | Accuracy | AUC |
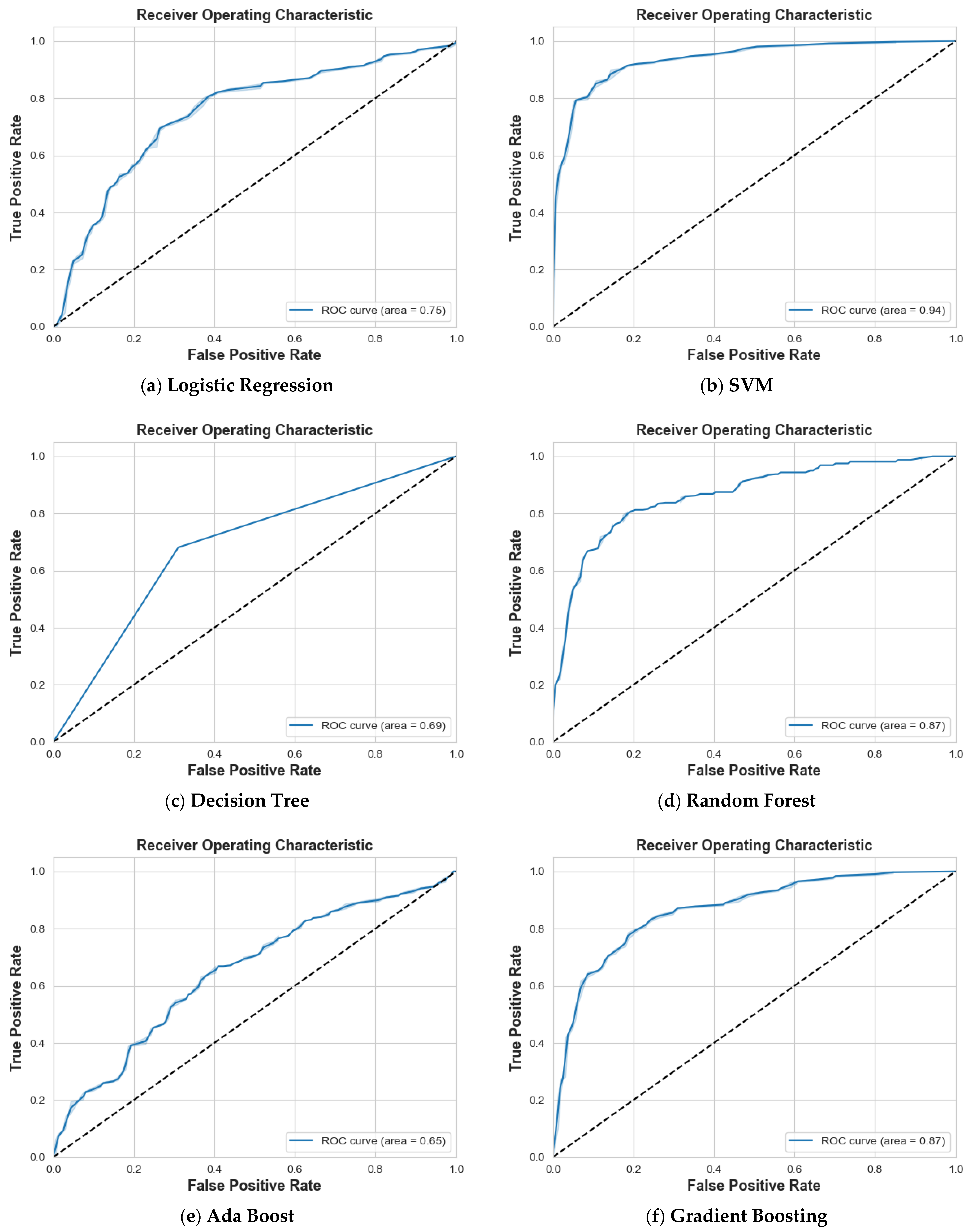
| Logistic Regression | 81% | 87% | 84% | 86% | 81% | 84% | 84% | 0.89 |
| SVM | 95% | 92% | 94% | 93% | 96% | 94% | 94% | 0.96 |
| Decision Tree | 76% | 82% | 79% | 82% | 76% | 78% | 79% | 0.79 |
| Random Forest | 81% | 85% | 83% | 85% | 80% | 83% | 83% | 0.91 |
| Ada Boost | 71% | 73% | 72% | 74% | 72% | 73% | 73% | 0.82 |
| Gradient Boosting | 84% | 87% | 86% | 87% | 84% | 86% | 86% | 0.92 |
| XG Boost | 85% | 83% | 84% | 84% | 86% | 85% | 85% | 0.94 |
| CatBoost | 85% | 89% | 87% | 89% | 85% | 87% | 87% | 0.94 |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1 | Precision | Recall | F1 | Accuracy | AUC |
| Logistic Regression | 60% | 78% | 68% | 78% | 60% | 68% | 68% | 0.75 |
| SVM | 80% | 91% | 85% | 92% | 82% | 87% | 86% | 0.94 |
| Decision Tree | 69% | 69% | 69% | 69% | 68% | 68% | 69% | 0.69 |
| Random Forest | 81% | 77% | 79% | 78% | 81% | 80% | 79% | 0.87 |
| Ada Boost | 63% | 61% | 62% | 62% | 64% | 63% | 63% | 0.65 |
| Gradient Boosting | 79% | 81% | 80% | 81% | 79% | 80% | 80% | 0.87 |
| XG Boost | 78% | 76% | 77% | 76% | 79% | 78% | 77% | 0.86 |
| CatBoost | 83% | 80% | 82% | 81% | 84% | 82% | 82% | 0.89 |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Precision | Recall | F1 | Precision | Recall | F1 | Accuracy | AUC |
| Logistic Regression | 87% | 82% | 84% | 83% | 88% | 85% | 85% | 0.91 |
| SVM | 98% | 91% | 94% | 91% | 98% | 95% | 94% | 0.96 |
| Decision Tree | 75% | 78% | 76% | 80% | 76% | 78% | 77% | 0.79 |
| Random Forest | 80% | 81% | 81% | 83% | 82% | 82% | 81% | 0.91 |
| Ada Boost | 72% | 72% | 72% | 75% | 75% | 75% | 74% | 0.81 |
| Gradient Boosting | 84% | 85% | 85% | 87% | 86% | 86% | 83% | 0.92 |
| XG Boost | 80% | 87% | 83% | 87% | 81% | 84% | 84% | 0.93 |
| CatBoost | 77% | 80% | 79% | 82% | 79% | 80% | 79% | 0.90 |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | Class 2: Two Tumors | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Accuracy |
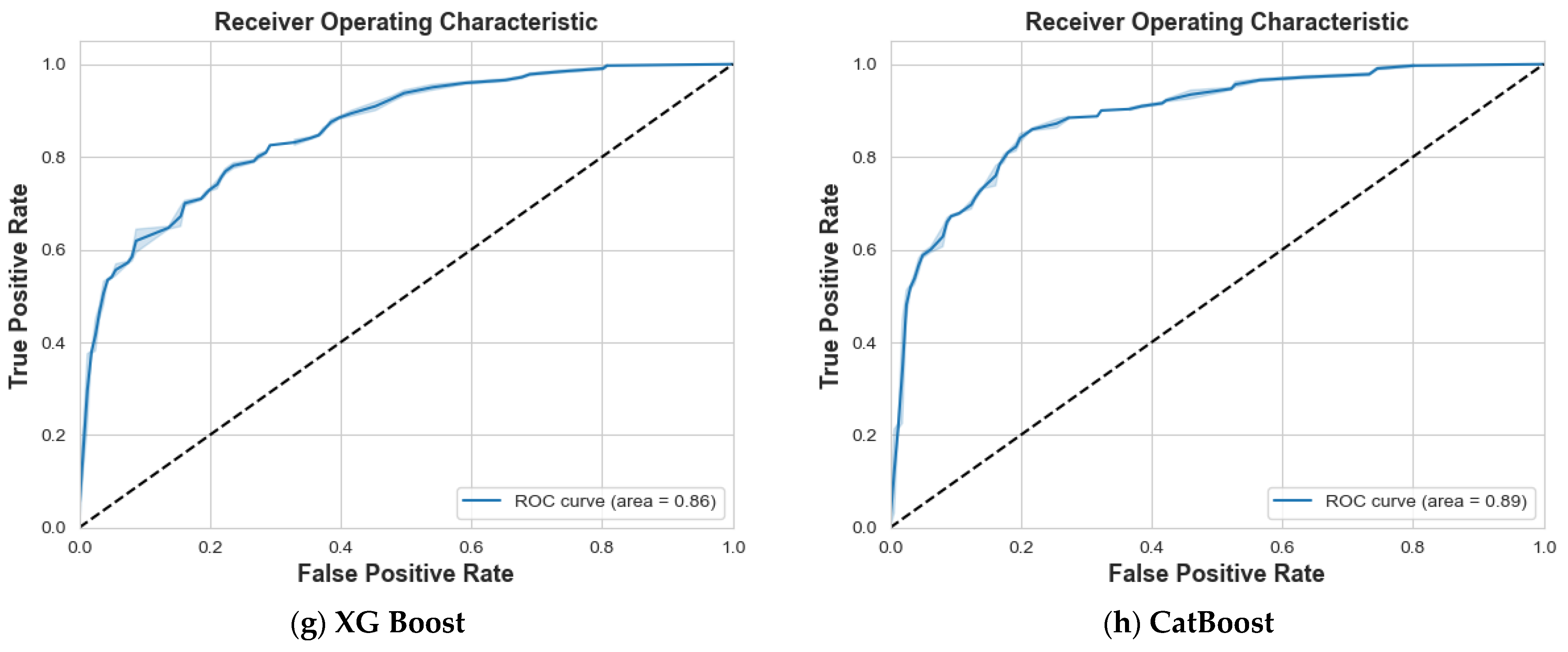
| Logistic Regression | 85% | 66% | 75% | 70% | 87% | 78% | 75% | 74% | 74% | 76% |
| SVM | 97% | 99% | 98% | 99% | 97% | 98% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 99% |
| Decision Tree | 71% | 77% | 74% | 82% | 73% | 77% | 85% | 87% | 86% | 79% |
| Random Forest | 83% | 78% | 81% | 83% | 83% | 83% | 90% | 94% | 92% | 85% |
| Ada Boost | 52% | 53% | 52% | 58% | 52% | 55% | 65% | 70% | 67% | 58% |
| Gradient Boosting | 81% | 79% | 80% | 81% | 80% | 80% | 92% | 96% | 94% | 85% |
| XG Boost | 82% | 79% | 81% | 81% | 79% | 80% | 90% | 95% | 93% | 85% |
| CatBoost | 84% | 84% | 84% | 85% | 85% | 85% | 95% | 95% | 95% | 88% |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | Class 2: Two Tumors | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Accuracy |
| Logistic Regression | 67% | 76% | 71% | 72% | 63% | 67% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 80% |
| SVM | 58% | 94% | 71% | 83% | 31% | 45% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 75% |
| Decision Tree | 72% | 58% | 64% | 61% | 74% | 67% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 78% |
| Random Forest | 86% | 78% | 82% | 76% | 85% | 80% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 88% |
| Ada Boost | 57% | 66% | 61% | 53% | 44% | 48% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 72% |
| Gradient Boosting | 84% | 78% | 81% | 77% | 84% | 80% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 88% |
| XG Boost | 85% | 77% | 81% | 77% | 85% | 81% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 88% |
| CatBoost | 81% | 79% | 80% | 77% | 80% | 78% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 87% |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | Class 2: Two Tumors | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Accuracy |
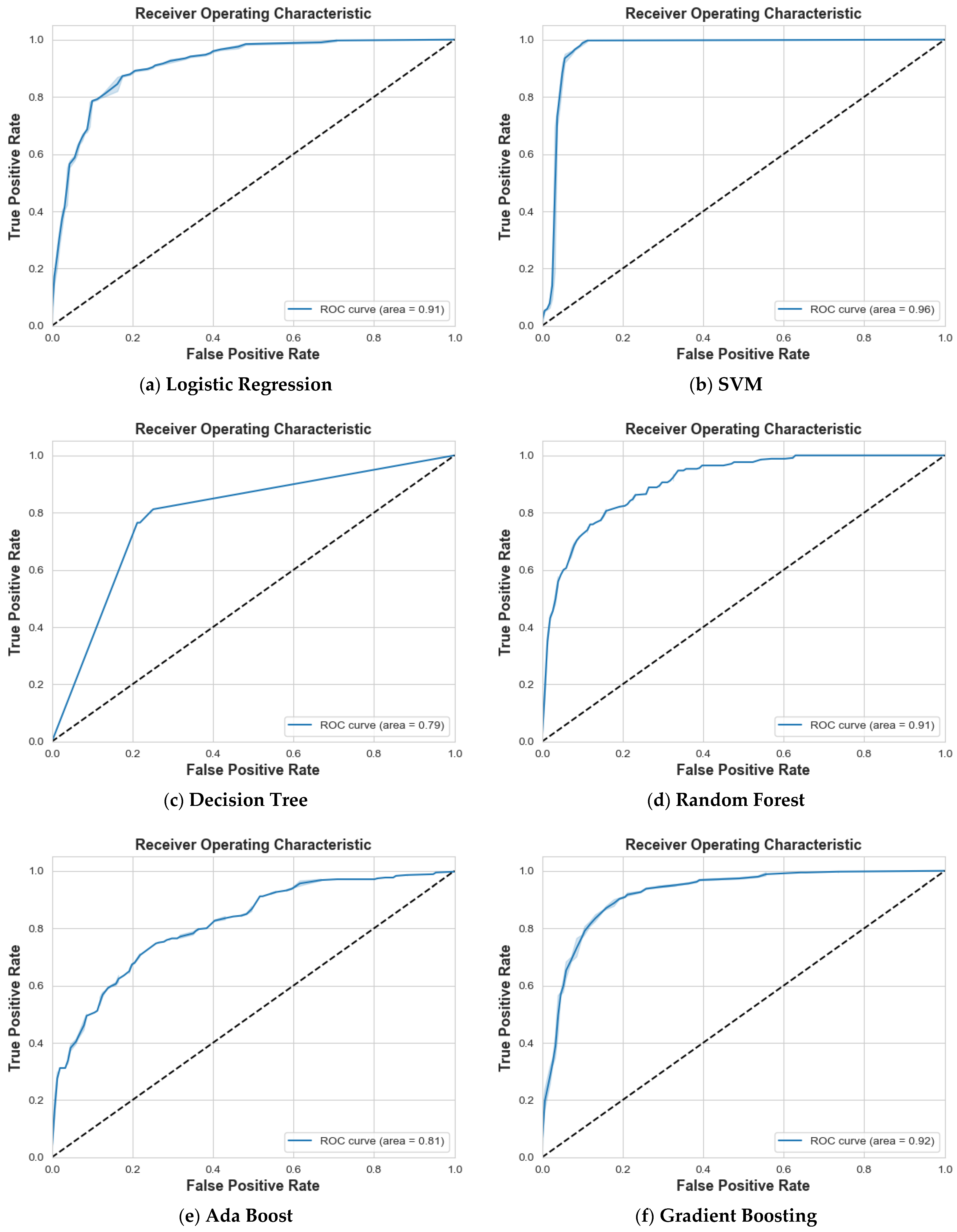
| Logistic Regression | 73% | 74% | 74% | 76% | 72% | 74% | 71% | 75% | 73% | 74% |
| SVM | 87% | 93% | 90% | 97% | 90% | 93% | 96% | 95% | 95% | 93% |
| Decision Tree | 52% | 61% | 56% | 54% | 57% | 55% | 66% | 50% | 57% | 56% |
| Random Forest | 73% | 67% | 70% | 75% | 72% | 73% | 72% | 80% | 76% | 73% |
| Ada Boost | 51% | 46% | 49% | 54% | 53% | 54% | 46% | 51% | 49% | 50% |
| Gradient Boosting | 73% | 78% | 75% | 79% | 77% | 78% | 79% | 76% | 77% | 77% |
| XG Boost | 76% | 80% | 78% | 77% | 79% | 78% | 80% | 72% | 76% | 77% |
| CatBoost | 71% | 74% | 72% | 75% | 75% | 75% | 74% | 70% | 72% | 73% |
| Class 0: Non-Tumor | Class 1: One Tumor | Class 2: Two Tumors | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Prec. | Recall | F1 | Accuracy |
| Logistic Regression | 72% | 76% | 74% | 77% | 69% | 73% | 74% | 78% | 76% | 74% |
| SVM | 93% | 88% | 90% | 94% | 93% | 93% | 92% | 98% | 95% | 92% |
| Decision Tree | 95% | 56% | 60% | 48% | 77% | 59% | 68% | 37% | 48% | 57% |
| Random Forest | 79% | 74% | 77% | 82% | 71% | 76% | 69% | 84% | 76% | 76% |
| Ada Boost | 57% | 54% | 56% | 56% | 58% | 57% | 47% | 47% | 47% | 53% |
| Gradient Boosting | 77% | 83% | 80% | 83% | 77% | 80% | 75% | 74% | 75% | 78% |
| XG Boost | 75% | 80% | 77% | 81% | 78% | 79% | 76% | 73% | 75% | 77% |
| CatBoost | 71% | 74% | 72% | 75% | 77% | 76% | 71% | 66% | 69% | 72% |
| Parameter | Time Complexity (Training Phase) | Problem Type | Model Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Models | |||
| LR | n(O(d)) = O(nd) | Classification | Parametric |
| SVM | O( × d) or O() | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
| DT | O(m · ) | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
| RF | O(v × n log(n)) | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
| Ada Boost | O(Tf) | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
| GBM | O(Td) | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
| XG Boost | O(tdxlogn) | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
| CatBoost | O(sn2) | Classification and regression | Non-parametric |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elnaggar, A.H.; El-Hameed, A.S.A.; Yakout, M.A.; Areed, N.F.F. Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Detection with Dual-Port Textile UWB MIMO Bra-Tenna System. Information 2024, 15, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15080467
Elnaggar AH, El-Hameed ASA, Yakout MA, Areed NFF. Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Detection with Dual-Port Textile UWB MIMO Bra-Tenna System. Information. 2024; 15(8):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15080467
Chicago/Turabian StyleElnaggar, Azza H., Anwer S. Abd El-Hameed, Mohamed A. Yakout, and Nihal F. F. Areed. 2024. "Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Detection with Dual-Port Textile UWB MIMO Bra-Tenna System" Information 15, no. 8: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15080467
APA StyleElnaggar, A. H., El-Hameed, A. S. A., Yakout, M. A., & Areed, N. F. F. (2024). Machine Learning for Breast Cancer Detection with Dual-Port Textile UWB MIMO Bra-Tenna System. Information, 15(8), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15080467







