A Novel Predictor for the Analysis and Prediction of Enhancers and Their Strength via Multi-View Features and Deep Forest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- NEPERS formulates the prediction of enhancers and their strength as a binary classification problem and solves it using a cascade deep forest algorithm.
- It takes advantage of multi-view features, such as position-specific trinucleotide propensity based on single-stranded (PSTNPss) characteristics, position-specific trinucleotide propensity based on double-stranded (PSTNPdss) characteristics, the composition of k-spaced nucleic acid pairs (CKSNAP), and nucleotide chemical properties (NCP), to incorporate biological sequences into nominal descriptors.
- A block-wise deep forest algorithm was applied, and a quantitative score was derived using metrics including accuracy (ACC), specificity (Spe), sensitivity (Sen), and Mathew’s correlation coefficient (MCC) with five-fold cross-validation (5CV), and independent dataset tests are utilized to evaluate the performance of NEPERS.
- Our method outperformed existing predictors by achieving high predictive rates.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Feature Engineering
3.2.1. PSTNPss
3.2.2. PSTNPdss
3.2.3. CKSNAP
- NA∗A represents the count of ‘AA’ pairs;
- NA∗C represents the count of ‘AC’ pairs;
- NA∗G represents the count of ‘AG’ pairs;
- and so on for all 16 possible nucleic acid pairs.
- NTotal is the total count of one-spaced nucleic acid pairs in the sequence.
3.2.4. Nucleotide Chemical Property (NCP)
3.3. Model Training and Evaluation
3.3.1. Deep Forest
3.3.2. Two-Layer Classification Framework
4. Evaluation Parameters
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. Feature Analysis (Individual vs. Fusion)
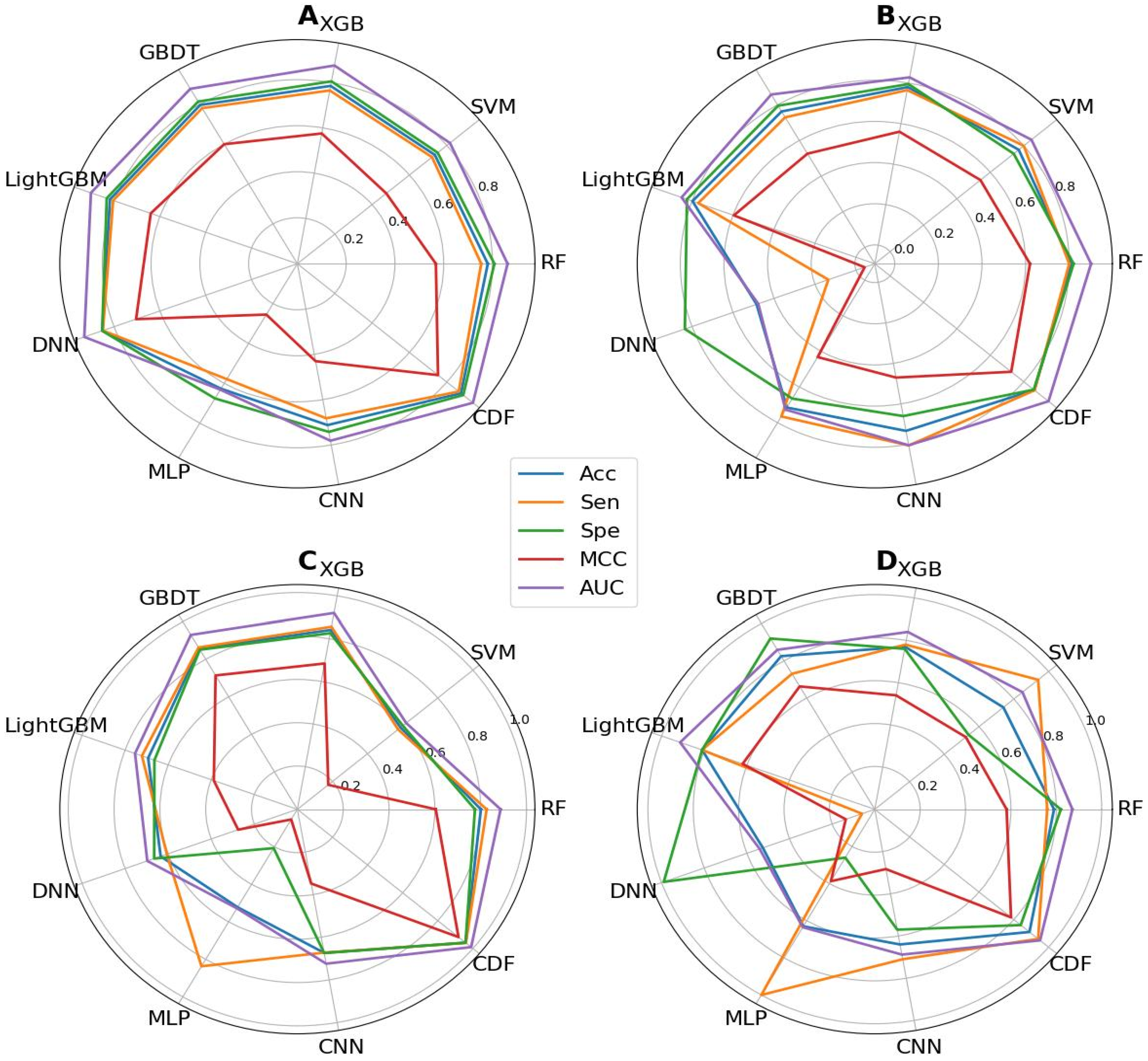
5.2. Analysis of Various Classifiers
5.3. Comparison with Existing Methods via 10-Fold CV
5.4. Independent Test Comparison with Existing Methods
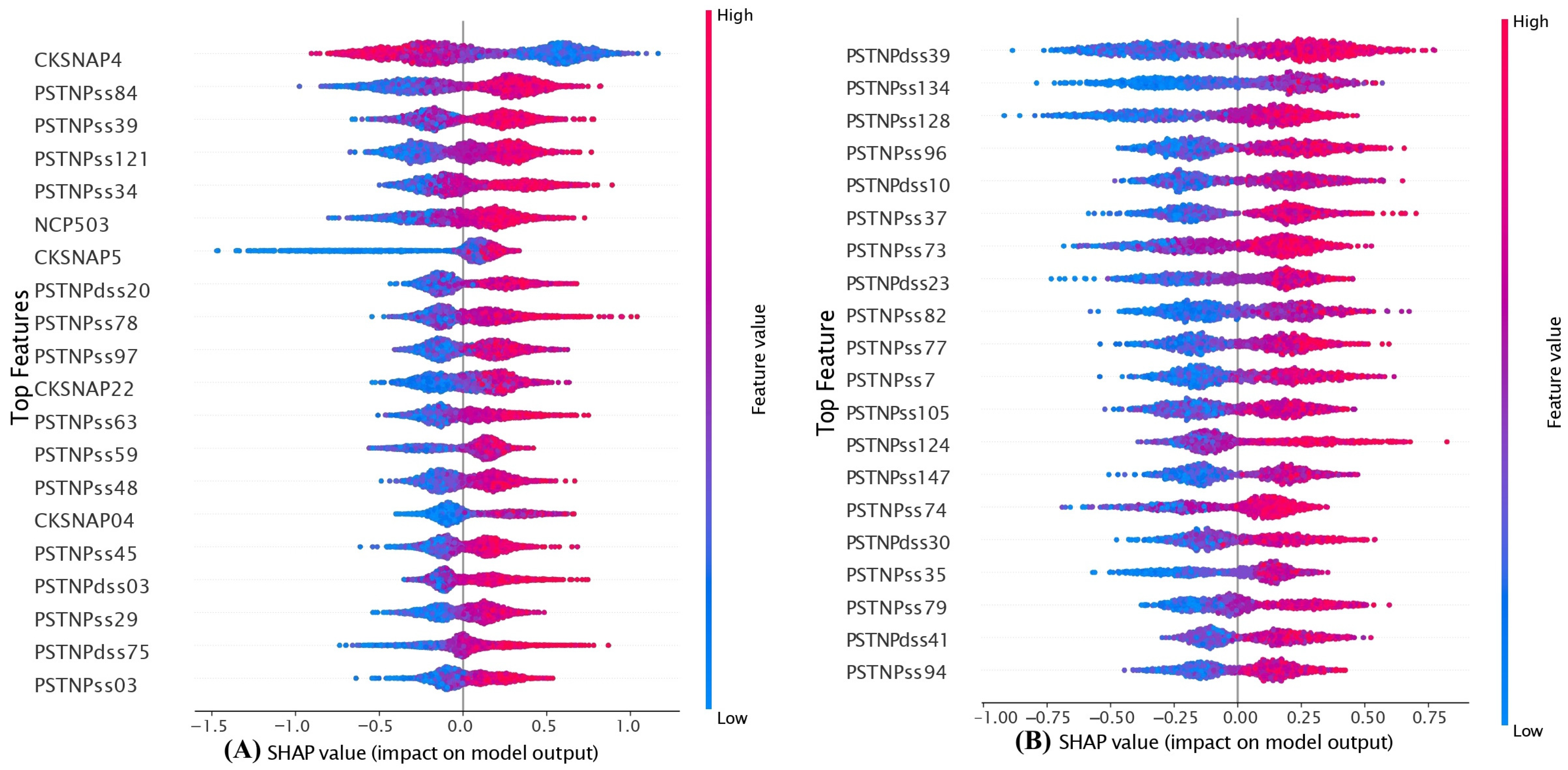
5.5. Model Interpretation
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahir, M.; Hayat, M. Inuc-stnc: A sequence-based predictor for identification of nucleosome positioning in genomes by extending the concept of saac and chou’s pseaac. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akui, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Sato, G.; Takinoue, M.; Shin-ichiro, M.N.; Doi, N. System concentration shift as a regulator of transcription-translation system within liposomes. Iscience 2021, 24, 102859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Tee, W.W. Enhancers and chromatin structures: Regulatory hubs in gene expression and diseases. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20160183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Fang, L.; Long, R.; Lan, X.; Chou, K.-C. Ienhancer-2l: A two-layer predictor for identifying enhancers and their strength by pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; He, W. Enhancerpred: A predictor for discovering enhancers based on the combination and selection of multiple features. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M.; Hayat, M.; Kabir, M. Sequence based predictor for discrimination of enhancer and their types by applying general form of chou’s trinucleotide composition. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 146, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Yapp, E.K.Y.; Ho, Q.-T.; Nagasundaram, N.; Ou, Y.-Y.; Yeh, H.-Y. Ienhancer-5step: Identifying enhancers using hidden information of DNA sequences via chou’s 5-step rule and word embedding. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 571, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S. Identifying Enhancers and Their Strength Based on pcwm Feature by a Two-Layer Predictor. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Biological Information and Biomedical Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 20–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.Y.; Khanal, J.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K.T. Ienhancer-rf: Identifying enhancers and their strength by enhanced feature representation using random forest. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 212, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, H.; Cheng, Y. Ienhancer-mfgbdt: Identifying enhancers and their strength by fusing multiple features and gradient boosting decision tree. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 8797–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, K.; Huang, D.-S.; Chou, K.-C. Ienhancer-el: Identifying enhancers and their strength with ensemble learning approach. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3835–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ren, X.; Fu, X.; Peng, L.; Gao, M.; Zeng, X. Ienhancer-xg: Interpretable sequence-based enhancers and their strength predictor. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, K.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S.; Teng, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y. Ienhancer-eblstm: Identifying enhancers and strengths by ensembles of bidirectional long short-term memory. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Nguyen-Vo, T.-H.; Le, N.Q.K.; Do, T.T.; Rahardja, S.; Nguyen, B.P. Ienhancer-ecnn: Identifying enhancers and their strength using ensembles of convolutional neural networks. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L. Identification and classification of enhancers using dimension reduction technique and recurrent neural network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 8852258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asim, M.N.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Malik, M.I.; Dengel, A.; Ahmed, S. Enhancer-dsnet: A Supervisedly Prepared Enriched Sequence Representation for the Identification of Enhancers and Their Strength. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Bangkok, Thailand, 23–27 November 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Huang, L.; Zhou, F. A novel position-specific encoding algorithm (seqpose) of nucleotide sequences and its application for detecting enhancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Xia, X. Ienhancer-rd: Identification of enhancers and their strength using rkpk features and deep neural networks. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 630, 114318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Ho, Q.-T.; Nguyen, T.-T.-D.; Ou, Y.-Y. A transformer architecture based on bert and 2d convolutional neural network to identify DNA enhancers from sequence information. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, N.; Khan, M.; Iqbal, N.; Khan, S.; Raza, M.; Khan, D.M.; Khan, A.; Wei, D.Q. Ienhancer-dhf: Identification of enhancers and their strengths using optimize deep neural network with multiple features extraction methods. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 40783–40796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPhillamy, C.; Alinejad-Rokny, H.; Pitchford, W.S.; Low, W.Y. Cross-species enhancer prediction using machine learning. Genomics 2022, 114, 110454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, F.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Leier, A.; Revote, J.; Zhu, Y.; Powell, D.R.; Akutsu, T.; Webb, G. Ilearn: An integrated platform and meta-learner for feature engineering, machine-learning analysis and modeling of DNA, rna and protein sequence data. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H. Bioseq-analysis2. 0: An updated platform for analyzing DNA, rna and protein sequences at sequence level and residue level based on machine learning approaches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Jia, C.; Duan, Y.; Zou, Q. 70propred: A predictor for discovering sigma70 promoters based on combining multiple features. BMC Syst. Biol. 2018, 12, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, F.; Leier, A.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Webb, G.I.; Smith, A.I.; Daly, R.J.; Chou, K.-C. Ifeature: A python package and web server for features extraction and selection from protein and peptide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2499–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Jia, P.; Zhao, Z. Deep4mc: Systematic assessment and computational prediction for DNA n4-methylcytosine sites by deep learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M.; Tayara, H.; Hayat, M.; Chong, K.T. Kdeepbind: Prediction of rna-proteins binding sites using convolution neural network and k-gram features. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 208, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Xiang, D.; Ge, Z.; Li, F.; Jia, C.; Song, J. An interpretable prediction model for identifying n7-methylguanosine sites based on xgboost and shap. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Feng, P.; Ding, H.; Lin, H. Idna4mc: Identifying DNA n4-methylcytosine sites based on nucleotide chemical properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3518–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, J.-W.; Liu, Z.; Ren, M.-W.; Shen, H.-B.; Yu, D.-J. Improving n6-methyladenosine site prediction with heuristic selection of nucleotide physical–chemical properties. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 508, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Vo, T.-H.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, T.-N.; Rahardja, S.; Nguyen, B.P. Ipseu-ncp: Identifying rna pseudouridine sites using random forest and ncp-encoded features. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Tayara, H.; Hayat, M.; Chong, K.T. Intelligent and robust computational prediction model for DNA n4-methylcytosine sites via natural language processing. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 217, 104391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-H.; Feng, J. Deep forest: Towards an Alternative to Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Shang, X. Bcdforest: A boosting cascade deep forest model towards the classification of cancer subtypes based on gene expression data. MC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Kabir, M.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, A.; Ge, F.; Khelifi, A.; Yu, D.-J. Deepcppred: A deep learning framework for the discrimination of cell-penetrating peptides and their uptake efficiencies. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 19, 2749–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, F.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, S. Predpromoter-mf (2l): A novel approach of promoter prediction based on multi-source feature fusion and deep forest. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2022, 14, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Bi, Y.; Chen, J.; Leier, A.; Li, F.; Song, J. Passion: An ensemble neural network approach for identifying the binding sites of rbps on circrnas. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4276–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Basith, S.; Pitti, T.; Lee, G.; Manavalan, B. Throne: A new approach for accurate prediction of human rna n7-methylguanosine sites. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenkwan, P.; Ahmed, S.; Nantasenamat, C.; Quinn, J.M.W.; Moni, M.A.; Lio’, P.; Shoombuatong, W. Amypred-frl is a novel approach for accurate prediction of amyloid proteins by using feature representation learning. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Shoombuatong, W. Meta-iavp: A sequence-based meta-predictor for improving the prediction of antiviral peptides using effective feature representation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Q.; Liu, Z.; Shen, H.-B.; Yu, D.-J. Targetm6a: Identifying n 6-methyladenosine sites from rna sequences via position-specific nucleotide propensities and a support vector machine. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2016, 15, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble methods in machine learning. In International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems, 2000; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?” Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Domingos, P. A few useful things to know about machine learning. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A. An introduction to variable and feature selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 1157–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Charoenkwan, P.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Lio’, P.; Shoombuatong, W. Scorpion is a stacking-based ensemble learning framework for accurate prediction of phage virion proteins. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Type | Dataset | Samples | CD-HIT Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhancer | (layer-1) | 1484 | 0.8 |
| Non-enhancer | 1484 | ||
| Strong Enhancer | (layer-2) | 742 | |
| Weak Enhancer | 742 | ||
| Enhancer | (layer-1) | 200 | 0.8 |
| Non-enhancer | 200 | ||
| Strong Enhancer | (layer-2) | 100 | |
| Weak Enhancer | 100 |
| Layers | Features | Benchmark Dataset | Independent Testing | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | ||
| Layer_1 | PSTNPss | 0.810 | 0.800 | 0.820 | 0.630 | 0.890 | 0.853 | 0.845 | 0.850 | 0.715 | 0.948 |
| PSTNPdss | 0.801 | 0.837 | 0.763 | 0.607 | 0.874 | 0.778 | 0.835 | 0.720 | 0.559 | 0.852 | |
| CKSNAP | 0.761 | 0.713 | 0.809 | 0.528 | 0.839 | 0.748 | 0.700 | 0.795 | 0.497 | 0.822 | |
| NCP | 0.744 | 0.711 | 0.777 | 0.493 | 0.827 | 0.503 | 1.000 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.798 | |
| All features | 0.876 | 0.864 | 0.888 | 0.753 | 0.940 | 0.863 | 0.865 | 0.860 | 0.725 | 0.949 | |
| Layer_2 | PSTNPss | 0.916 | 0.939 | 0.892 | 0.833 | 0.973 | 0.855 | 0.800 | 0.910 | 0.714 | 0.934 |
| PSTNPdss | 0.658 | 0.751 | 0.565 | 0.322 | 0.710 | 0.805 | 0.760 | 0.850 | 0.612 | 0.910 | |
| CKSNAP | 0.635 | 0.733 | 0.536 | 0.276 | 0.688 | 0.655 | 0.780 | 0.530 | 0.320 | 0.713 | |
| NCP | 0.606 | 0.684 | 0.527 | 0.216 | 0.646 | 0.650 | 0.800 | 0.500 | 0.314 | 0.730 | |
| All features | 0.959 | 0.960 | 0.958 | 0.918 | 0.990 | 0.890 | 0.940 | 0.840 | 0.784 | 0.951 | |
| Layers | Classifiers | 10CV | Independent Testing | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | ||
| Layer_1 | RF | 0.781 | 0.754 | 0.808 | 0.568 | 0.862 | 0.810 | 0.800 | 0.820 | 0.620 | 0.900 |
| SVM | 0.736 | 0.721 | 0.751 | 0.476 | 0.817 | 0.770 | 0.800 | 0.740 | 0.541 | 0.846 | |
| XGB | 0.785 | 0.765 | 0.805 | 0.575 | 0.875 | 0.780 | 0.765 | 0.795 | 0.560 | 0.828 | |
| GBDT | 0.797 | 0.781 | 0.814 | 0.600 | 0.878 | 0.763 | 0.730 | 0.795 | 0.526 | 0.858 | |
| LightGBM | 0.818 | 0.804 | 0.832 | 0.640 | 0.901 | 0.798 | 0.770 | 0.825 | 0.596 | 0.851 | |
| DNN | 0.851 | 0.849 | 0.852 | 0.704 | 0.930 | 0.485 | 0.135 | 0.835 | -0.042 | 0.477 | |
| MLP | 0.627 | 0.579 | 0.676 | 0.255 | 0.632 | 0.715 | 0.765 | 0.665 | 0.432 | 0.727 | |
| CNN | 0.712 | 0.682 | 0.742 | 0.430 | 0.781 | 0.733 | 0.805 | 0.660 | 0.470 | 0.804 | |
| CDF | 0.876 | 0.864 | 0.888 | 0.753 | 0.940 | 0.863 | 0.865 | 0.860 | 0.725 | 0.948 | |
| Layer_2 | RF | 0.801 | 0.826 | 0.775 | 0.604 | 0.887 | 0.790 | 0.760 | 0.820 | 0.581 | 0.871 |
| SVM | 0.588 | 0.574 | 0.601 | 0.176 | 0.620 | 0.740 | 0.940 | 0.540 | 0.524 | 0.850 | |
| XGB | 0.841 | 0.856 | 0.826 | 0.684 | 0.920 | 0.770 | 0.780 | 0.760 | 0.540 | 0.840 | |
| GBDT | 0.857 | 0.863 | 0.851 | 0.714 | 0.930 | 0.825 | 0.730 | 0.920 | 0.662 | 0.859 | |
| LightGBM | 0.693 | 0.722 | 0.664 | 0.388 | 0.754 | 0.810 | 0.810 | 0.810 | 0.620 | 0.913 | |
| DNN | 0.635 | 0.606 | 0.665 | 0.275 | 0.697 | 0.525 | 0.060 | 0.990 | 0.136 | 0.540 | |
| MLP | 0.522 | 0.837 | 0.207 | 0.054 | 0.528 | 0.630 | 1.000 | 0.260 | 0.387 | 0.635 | |
| CNN | 0.673 | 0.672 | 0.674 | 0.348 | 0.724 | 0.640 | 0.710 | 0.570 | 0.283 | 0.688 | |
| CDF | 0.959 | 0.960 | 0.958 | 0.918 | 0.990 | 0.890 | 0.940 | 0.840 | 0.784 | 0.951 | |
| Predictors | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | |
| iEnhancer-2L | 0.769 | 0.781 | 0.759 | 0.540 | 0.850 | 0.619 | 0.622 | 0.618 | 0.240 | 0.660 |
| EnhancerPred | 0.773 | 0.719 | 0.828 | 0.550 | - | 0.682 | 0.712 | 0.652 | 0.360 | - |
| Enhancer-TNC | 0.773 | 0.758 | 0.786 | 0.550 | - | 0.647 | 0.720 | 0.544 | 0.300 | - |
| iEnhancer-5Step | 0.823 | 0.811 | 0.835 | 0.650 | - | 0.681 | 0.753 | 0.608 | 0.370 | - |
| Enhancer-PCWM | 0.815 | 0.816 | 0.814 | 0.631 | 0.895 | 0.631 | 0.829 | 0.434 | 0.286 | 0.692 |
| iEnhancer-RF | 0.762 | 0.736 | 0.787 | 0.526 | 0.840 | 0.625 | 0.684 | 0.566 | 0.253 | 0.670 |
| iEnhancer-EL | 0.781 | 0.756 | 0.804 | 0.561 | 85.470 | 0.651 | 0.690 | 0.611 | 0.315 | 0.696 |
| iEnhancer-XG | 0.811 | 0.757 | 0.865 | 0.626 | - | 0.668 | 0.749 | 0.585 | 0.334 | - |
| iEnhancer-EBLSTM | 0.772 | 0.755 | 0.795 | 0.534 | 0.835 | 0.658 | 0.812 | 0.536 | 0.324 | 0.688 |
| iEnhancer-MFBGDT | 0.787 | 0.775 | 0.798 | 0.574 | 0.862 | 0.660 | 0.706 | 0.616 | 0.323 | 0.719 |
| iEnhancer-ECNN | 0.769 | 0.782 | 0.752 | 0.537 | 0.832 | 0.678 | 0.791 | 0.564 | 0.368 | 0.748 |
| Enhancer-RNN | 0.767 | 0.733 | 0.801 | 0.699 | - | 0.849 | 0.858 | 0.840 | 0.699 | - |
| Enhancer-DSNet | 0.760 | 0.760 | 0.760 | 0.520 | - | 0.630 | 0.630 | 0.670 | 0.260 | - |
| spEnhancer | 0.779 | 0.708 | 0.850 | 0.523 | 0.846 | 0.642 | 0.850 | 0.305 | 0.211 | 0.614 |
| iEnhancer-RD | 0.788 | 0.810 | 0.570 | 0.576 | 0.844 | 0.705 | 0.840 | 0.570 | 0.426 | 0.792 |
| Enhancer-BERT-2D | 0.800 | 0.765 | 0.729 | 0.531 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| iEnhancer-DHF | 0.801 | 0.858 | 0.863 | 0.722 | 0.910 | 0.696 | 0.696 | 0.693 | 0.392 | 0.720 |
| NEPERS | 0.876 | 0.864 | 0.888 | 0.753 | 0.940 | 0.959 | 0.960 | 0.958 | 0.918 | 0.990 |
| Predictors | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | ACC | Sen | Spe | MCC | AUC | |
| iEnhancer-5Steps | 0.790 | 0.820 | 0.760 | 0.580 | - | 0.635 | 0.740 | 0.530 | 0.280 | - |
| Enhancer-PCWM | 0.770 | 0.785 | 0.755 | 0.540 | 0.821 | 0.695 | 0.810 | 0.580 | 0.401 | 0.756 |
| iEnhancer-RF | 0.797 | 0.785 | 0.810 | 0.595 | - | 0.850 | 0.930 | 0.770 | 0.709 | - |
| iEnhancer-EL | 0.747 | 0.710 | 0.785 | 0.496 | 0.817 | 0.610 | 0.540 | 0.680 | 0.222 | 0.680 |
| iEnhancer-XG | 0.757 | 0.740 | 0.775 | 0.515 | - | 0.635 | 0.700 | 0.570 | 0.272 | - |
| iEnhancer-EBLSTM | 0.728 | 0.774 | 0.726 | 0.498 | 0.788 | 0.622 | 0.740 | 0.572 | 0.310 | 0.664 |
| iEnhancer-MFGBDT | 0.775 | 0.768 | 0.796 | 0.561 | 0.859 | 0.685 | 0.726 | 0.668 | 0.386 | 0.752 |
| iEnhancer-ECNN | 0.769 | 0.785 | 0.752 | 0.537 | 0.832 | 0.678 | 0.791 | 0.564 | 0.368 | 0.748 |
| iEnhancer-DSNet | 0.780 | 0.780 | 0.770 | 0.560 | - | 0.830 | 0.830 | 0.670 | 0.700 | - |
| spEnhancer | 0.772 | 0.830 | 0.715 | 0.579 | 0.824 | 0.620 | 0.910 | 0.330 | 0.370 | 0.625 |
| iEnhancer-RD | 0.788 | 0.810 | 0.765 | 0.576 | 0.844 | 0.705 | 0.840 | 0.570 | 0.892 | 0.792 |
| Enhancer-BERT-2D | 0.756 | 0.800 | 0.712 | 0.514 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| iEnhancer-DHF | 0.832 | 0.821 | 0.844 | 0.711 | - | 0.675 | 0.659 | 0.687 | 0.312 | - |
| NEPERS | 0.863 | 0.865 | 0.860 | 0.725 | 0.948 | 0.890 | 0.940 | 0.840 | 0.784 | 0.951 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gill, M.; Ahmed, S.; Kabir, M.; Hayat, M. A Novel Predictor for the Analysis and Prediction of Enhancers and Their Strength via Multi-View Features and Deep Forest. Information 2023, 14, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14120636
Gill M, Ahmed S, Kabir M, Hayat M. A Novel Predictor for the Analysis and Prediction of Enhancers and Their Strength via Multi-View Features and Deep Forest. Information. 2023; 14(12):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14120636
Chicago/Turabian StyleGill, Mehwish, Saeed Ahmed, Muhammad Kabir, and Maqsood Hayat. 2023. "A Novel Predictor for the Analysis and Prediction of Enhancers and Their Strength via Multi-View Features and Deep Forest" Information 14, no. 12: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14120636
APA StyleGill, M., Ahmed, S., Kabir, M., & Hayat, M. (2023). A Novel Predictor for the Analysis and Prediction of Enhancers and Their Strength via Multi-View Features and Deep Forest. Information, 14(12), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14120636







