Abstract
Neo4j is a graph database that can use not only data, but also data relationships. Crop portraits, a kind of property graph, model the crop entity in the real world based on data to realize the networked management of crop knowledge. The existing crop knowledge base has shortcomings such as single crop variety, incomplete description, and lack of agricultural knowledge. Constructing crop portraits can provide a comprehensive description of crops and make up for these shortcomings. This research used agricultural question-and-answer data and popular science data obtained by text crawling as the original data, selected labels to establish a crop portrait that including three categories (crops, pesticides, and diseases and pests), and used the graph database (Neo4j) to store and display these portrait data. Information mining found that the crop portrait revealed the occurrence trend of diseases and pests, exhibited a nonintrinsic connection between different diseases and pests, and provided a variety of pesticides to choose from for control of diseases and pests. The results showed that constructing crop portraits is beneficial to agricultural analysis, and has practical application values and theoretical research prospects in the field of big data analytics.
1. Introduction
Crop production is the basis of agricultural production, and agricultural production is the foundation for human survival. In the era of big data, the problems of information overload and lost information have attracted more and more attention of researchers [1]. Agriculture is an obvious and important target of big data, and data-mining technology provides accurate crop-yield estimates for agricultural production [2]. The use of data-mining technology to integrate agricultural information to realize the transformation from traditional agriculture to digital agriculture is an inevitable trend in the development of modern agriculture.
Big data analytics (BDA) is an essential part of modern data science. In the agricultural field, BDA enables practitioners to acquire a large amount of commercial and scientific knowledge to improve their operating procedures and product quality [3]. However, traditional data technologies and platforms are unable to obtain the required information from large amounts of data due to their scalability issues, limited storage, and performance capacity [4]. Graph databases (such as Neo4j) that use graph theory to store, map, and query relationships provide a more powerful platform for deep analysis, and provide more accurate and reliable results for extracting information. A knowledge graph (KG) represents a network of real-world entities, illustrates the entities’ relationships, stores entities’ information in a graph database, and visualizes the information as a graph [5]. Since Google announced KGs that represent the general world knowledge, KGs have become one of the most effective and efficient knowledge integration technologies, but KGs still face many problems such as data insufficiency, explainability, incomplete and incorrect knowledge, inconsistencies, and many others [6]. A user portrait, which is a collection of user feature tags that best represent users, has been widely applied in the fields of e-commerce, tourism, Internet finance, news media, social networks, healthcare, etc. [7]. In addition, user portrait technology has been applied in agriculture to recommend personalized agricultural information resources [7]. However, neither the knowledge graph nor the user portrait can fully describe the crops in agricultural analysis.
In this study, we employed property graphs to comprehensively describe crops. With reference to the concept of user portrait, we call this property graph a “crop portrait”. Constructing crop portraits based on graph databases can realize crop-centric labeling and description of crops; can be applied to the efficient extraction, management, and sharing of agricultural knowledge; and achieve in-depth and accurate analysis of agricultural affairs. The research on crop portraits is still blank, so crop portraits have considerable research value and can provide new ideas for the development of smart agriculture. Based on the graph theory, this research used Neo4j as the storage method and display form to construct crop portraits. Further, information was mined from five aspects: the basic nature of the crop portrait, the relative importance of different crop entities, the occurrence trend of diseases and pests, the interconnection within crop diseases and pests, and the non-one-to-one relation between pesticides and diseases and pests. The results showed that the crop portrait based on graph databases provides good guidance on agricultural production, and solves problems that are difficult to directly display with general science data.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces some related work of graphics technology applied in agriculture. Section 3 introduces the construction of crop portraits. Section 4 introduces agricultural data mining based on the crop portrait. Section 5 presents a discussion of the paper, and Section 6 provides the conclusions.
2. Related Work
Ontology is a standardized description of the relationship between concepts and is a method that enables computers to recognize human knowledge. It is a practical and systematic way of conceptualization that can enhance the consensus of expressing things and provide interoperability between various software applications. Conceptualization refers to combining the associations between objects by providing a set of objects, concepts, and various entities for explaining knowledge [8]. A knowledge graph is based on an ontology. When we apply the ontology to the data set of a single data point and apply the reasoning program to obtain new knowledge, the knowledge graph will be constructed [9].
Agricultural ontology organizes the relationship between concepts in agricultural domain knowledge in a computer-recognizable formal description language. Currently, many applications of ontology and/or knowledge graphs in the agricultural field have been reported. Lange et al. [10] suggested a multiontology-based foods-for-health knowledge system. Brožová et al. [11] studied the optimization of agricultural production structure using knowledge graphs. Zheng et al. [12] proposed an ontology-based system for agricultural knowledge management. Qi et al. [13] proposed a method for constructing meteorology and agriculture knowledge graphs. Chen et al. [14] proposed an agricultural knowledge graph to automatically integrate massive agricultural data from the Internet. Lagos-Ortiz et al. [15] constructed a knowledge-based platform to help crop insect pest diagnosis and management. Qiao et al. [16] proposed an agricultural entity relationship joint extraction model for the construction of knowledge graphs. All these applications illustrate the importance of ontology and/or knowledge graphs in agricultural research.
Neo4j was launched in 2010 and stores data in the form of nodes, attributes, and edges, where each node and edge can have multiple attributes [17]. Neo4j implements a property graph that is made up of nodes, relationships, and properties. Property graphs are quite different from knowledge graphs because they are provided in mature implementations (such as Neo4j), and thus are easy to get started with. Another difference between the two graphs is that knowledge graphs require reasoning rules, while property graphs do not [9]. However, there is conceptual confusion between these two graphs, so only a few of the studied graphs are called property graphs [18].
In this research, the labeled property graph model, together with Neo4j platform, were used to construct the property graph of crops, and we called the property graph a crop portrait. Neo4j is one of the most effective data-mining models. The model uses Cypher for expressive and efficient data querying and visualization in a property graph model, and brings ease of use and intuitive user experience [19,20]. Neo4j can reveal the hidden patterns and structures stored in connection data with almost no coding, and it can be run through a web browser [21]. All these features make Neo4j an ideal tool for representing, visualizing, and analyzing complex data. Currently, this study is the only crop portrait study based on Neo4j.
3. Crop Portrait Model Based on Graph Databases
There are many ways to constructing knowledge graphs; however, all approaches contain the following four constructing parts: data acquisition, knowledge extraction, knowledge fusion, and graph construction [22,23]. The process of crop portrait construction is similar to the process of knowledge graph construction. Figure 1 shows the construction framework for crop portraits employed in this study.
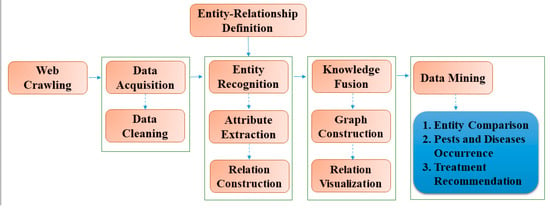
Figure 1.
Framework of crop portrait construction.
3.1. Data Collection
Python 3, combined with the Requests library, was used to crawl the text content of the question-and-answer (Q&A) platform of the “NongGuanJia” (in Chinese, available at: http://www.laodao.so, accessed on 25 September 2020) and of the popular science data of “FuNongLu” website (in Chinese, available at: http://www.funonglu.com, accessed on 20 February 2020). We took the “NongGuanJia” platform as an example; the source code of the Q&A interface of each crop is stored in JSON format similar to http://ngjv4.laodao.so/ASHX/bbs_card.ashx?action=jzlist&version=pc&CropID=7&lastid=710530&pgsize=20 (accessed on 26 September 2020). In the link, “CropID” represents the type of crop. Since the Q&A data was paginated, “lastid” recorded the web page ID of the next part of the Q&A data of the crop. Therefore, a crawling program was designed accordingly.
The data set obtained included 15 crops, 28 pesticides, 93 diseases and pests, and a total of more than 67,000 Q&A data and popular science data. There were four crops with less than 1000 data, three crops with 1000–5000 data, seven crops with 5000–10,000 data, and one crop with more than 10,000 data (Table 1). An example of the collected corpus is showed in Table 2 (only the first two answers of the Q&A data are listed).

Table 1.
Statistical table of question-and-answer (Q&A) data and popular science data.

Table 2.
Examples of Q&A data and popular science data.
3.2. Entity-Relationship Definition
Building a portrait is a process of labeling entities. An instance of a label refers to the specific content contained in a label, which is characterized by conforming to the MECE principle. The MECE principle is a thinking tool proposed by Barbara Minto in the Minto Pyramid Principle. It is the abbreviation of Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive, which means that each part is independent of each other and all parts are completely exhausted [24].
The Entity-Relationship (ER) model is the basis for unification of different views of data [25], and connects numerous entities through different relationships [26]. The ER model focuses on three main elements: entities (sets of things used to store information), attributes (information collected for an entity), and relationships (relations between entities). In this work, we defined model ER = <C, A, R, I>. Among these, C stands for category entities, A stands for attributes, R stands for relations, and I stands for instance entities. We also established the following five definitions for model ER:
1. We defined the triplet M = <e1, r, e2>, where e1 and e2 represent two entities, and r represents a semantic relationship. The entities of the triplet are connected with each other through relationships, forming a networked knowledge structure.
2. We defined C = <Ccro, Cpes, Cdis> to mean that the model contains three categories: Ccro represents crops, Cpes represents pesticides, and Cdis represents diseases and pests. These three are important entities in the agricultural field and run through the entire process of agricultural production.
3. We defined A = <Acro, Apes, Adis> to represent the attribute sets of the three categories, among which:
- Acro = {id, name, alias, susceptible disease, nutrients, fertilizer, place of production}
- Apes = {id, name, alias, susceptible crops}
- Adis = {id, name, alias, effect}
Note: In order to avoid duplication after importing into Neo4j and to facilitate the addition of the relationship between categories, a number (ID) was set for each instance. This model was built by focusing on crops, and six attributes of crops (name, alias, susceptible disease, nutrients, fertilizer, place of production) were selected. These attributes have a wide dimension and clear characteristics. They are frequently involved in agricultural affairs and can describe crops in all directions. This model did not select appearance features, selling prices, etc. as attributes of crops, because these attributes are difficult to accurately quantify, and few users want to understand them, so they are of little practical significance. Three attributes were selected for the pest category: name, alias, and susceptible crops; and three attributes were selected for the pesticide category: name, alias, and effect. The purpose of selecting these attributes was to associate with the crop entity and assist in the description of the crops.
4. We defined R = <r1, r2, r3>. Among these, r1 = {infect, treat} represents the relationship between categories. Infect is the relationship between crops and diseases and pests; and treat is the relationship between pesticides and diseases and pests. r2 = {instance} represents the attribution relationship; that is, the relationship between the category and the instance. r3 = {A} represents the attribute relationship; that is, the relationship between the instance and the attribute value.
5. We defined I = <I1, I2, I3> to represent the instances of the three categories, where I1 represents the instance collection of crops, a total of 15 crop elements; I2 represents the instance collection of pesticides, a total of 28 pesticide elements; and I3 represents the instance collection of diseases and pests, a total of 93 diseases and pests elements.
3.3. Named Entity Recognition
This portrait model used named entity recognition technology to extract instances and their corresponding tags. Named entity recognition belongs to a branch of natural language processing and is relatively mature. The raw data to be recognized had two types: Q&A corpus and popular science corpus. For Q&A corpus and irregular science corpus, machine learning could be used for feature extraction. This model selected the Conditional Random Field (CRF) model, and selected delimiting words, part of speech, left bounding words, and radicals as features to label each corpus and its context in the observed corpus sequence [27]. The above features had a good degree of discrimination, and it was easy to realize automatic labeling through programs [27]. For some simple and standardized crop science corpora, feature extraction was performed by manually compiling a dictionary to obtain the nutrients, place of production, and other attributes of crops, which improved not only the accuracy, but also the time and space limitations of the algorithm.
The CRF++ toolkit was used to identify the named entities of the original corpus, to find out the instances in each category and their corresponding attributes, and to sort them separately. When using the CRF++ tool, the data set was divided into a training set and a test set at a ratio of 7 to 3. Entities labeling and recognition were carried out with reference to the results of reference [27]. In order to facilitate display, the data in the result list were separated by “/”.
In the Ccro category, we took strawberry as an example. Strawberry ∈ I1, established the triplet M form relationship according to its attributes (Table 3): strawberry is an instance of the Ccro category, conforms to the relation r2, expressed as M = <Ccro, instance, strawberry>; Vitamin C is a nutrient attribute of strawberry, which conforms to the relationship r3, expressed as M = <strawberry, nutrition, vitamin C>.

Table 3.
Strawberry-related attribute recognition.
In the Cpes category, we took pyridaben (“SuManTong” in Chinese) as an example. Pyridaben ∈ I2, established the triplet M form relationship according to its attributes (Table 4): pyridaben is an instance of the Cpes category, conforms to the relationship r2, expressed as M = <Cpes, instance, pyridaben>; “DaManTong” (in Chinese) is an alias attribute of SuManTong, in accordance with the relationship r3, expressed as M = <SuManTong, alias, DaManTong>.

Table 4.
Pyridaben (“SuManTong” in Chinese)-related attribute recognition.
In the Cdis category, we took thrip (“JiMa” in Chinese) as an example. Thrip ∈ I3, established the triplet M form relationship according to its attributes (Table 5): thrip is an instance of the Cdis category, conforms to the relationship r2, expressed as M = <Cdis, instance, thrip>; “JiChong” (in Chinese) is an alias attribute of JiMa, conforms to the relationship r3, expressed as M = <JiMa, alias, JiChong>. The relationship between thrip and strawberry was infection and being infected, which was consistent with the relationship r1, expressed as M = <thrip, infect, strawberry>. The relationship between pyridaben and thrip was prevention and being prevented, and the relationship was consistent with relationship r1, expressed as M = <pyridaben, treat, thrip>.

Table 5.
Thrip (“JiMa” in Chinese)-related attributes recognition.
3.4. Crop Portrait Storage and Visualization
Neo4j, created by Neo Technology, is a native graph database platform (http://neo4j.com, accessed on 25 September 2020). It provides a query language called Cypher, which can query and update graph databases, similar to the structured query language of relational databases.
The crop portrait established by this model was an undirected graph that was defined as G = (V, E). In the definition, vertex V represents the entity, corresponding to e1 and e2 in the triplet M, while edge E represents the relationship between the entities, corresponding to r in the triplet M. To establish the crop portrait, we performed the following sequential operations:
1. We used the statement “LOAD CSV WITH HEADERS FROM ‘file:///crops.csv’ AS line FIELDTERMINATOR ‘,’ MERGE (: crop{id: line.crops_id, name: line.crops_name, alia: line.crops_alias, nutrient: line.nutrients, disease: line.disease, fertilizer: line.fertilizer, producer: line.producer})” to import the csv file that stores crops and attribute data.
2. We used the statement “CREATE (n: category {name: ‘crop’}) RETURN n” to create the nodes of crops.
3. We used the statement “MATCH (a: crop), (b: class {name: ‘crop’}) MERGE (a)-[: instance]->(b)” to establish the relationship between the nodes of “crop” and crop instances.
4. We imported the data of examples (strawberry, pyridaben, and thrip) described in Section 3.1 into Neo4j in the form of triplet M to obtain a visualized portrait of strawberry (Figure 2).
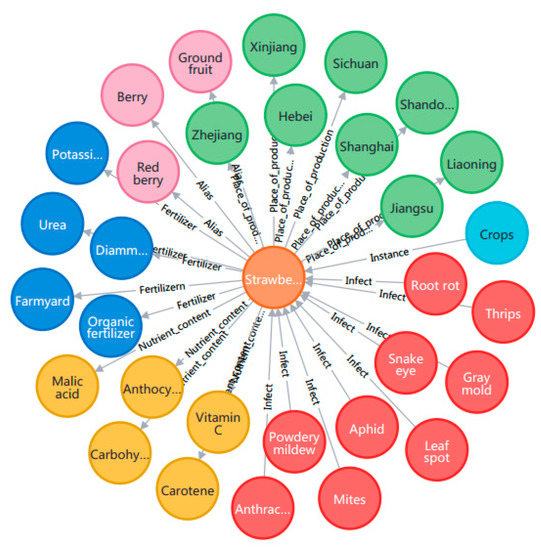
Figure 2.
The portrait of strawberry based on graph databases. The light blue circle represents the crop entity, the orange circle represents the strawberry instance, the purple circles represent aliases, the dark blue circles represent fertilizers, the yellow circles represent nutrient contents, the red circles represent diseases and pests, and the green circles represent places of production.
5. We imported all finished data into Neo4j in the form of triplet M for storage and obtained a visualized portrait of all 15 crops (Figure 3).
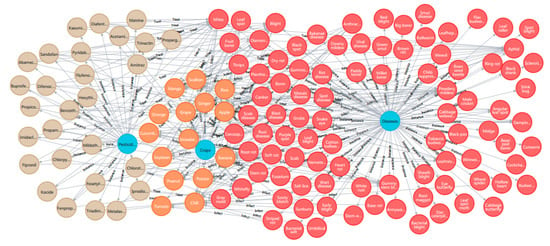
Figure 3.
The relations of entities and their instances in the portrait. The light blue circles represent the three entities, the orange circles represent instances of crops, the light gray circles represent instances of pesticides, and the red circles represent instances of diseases and pests.
4. Data Mining Based on the Crop Portrait
4.1. Basic Properties of the Crop Portrait Graph
Based on the crop portrait G, we established the following definitions:
1. Dv, the degree of vertex entity v;
2. Dv_max, the maximum value of Dv in a certain type of entity, indicating that the vertex entity had the highest importance in the crop portrait;
3. Dv_min, the minimum value of Dv in a certain type of entity, indicating that the vertex entity had the lowest importance in the crop portrait;
4. Davg, the average value of Dv in certain types of entities;
5. AN, the adjacent node of vertex entity v.
The Dv of crops, diseases and pests, and pesticides were counted (Figure 4). The fluctuations (range, R) of Dv of crops, pesticides, and diseases and pests were 21, 7, and 17, respectively. Compared with pesticides and diseases and pests, the Dv of crops were larger (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001, respectively), all not less than 14; and the Dv of pesticides and of diseases and pests were smaller, not greater than 10 and 18, respectively. However, there was no statistically significant difference between the Dv of pesticides and the Dv of diseases and pests (p = 0.9751). These results indicated that crops were more important than pesticides and diseases and pests in the portrait.
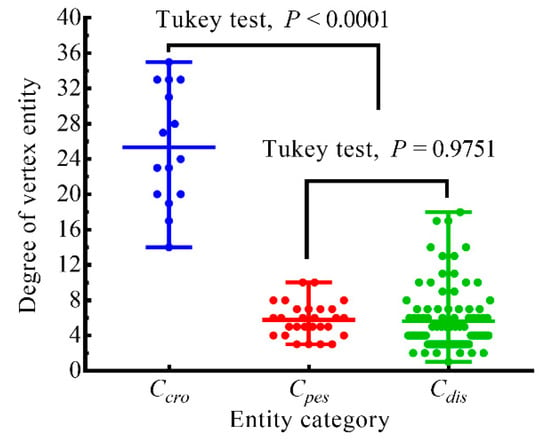
Figure 4.
Comparison of the degree of vertex entity (Dv).
In the crop category (Ccro), Dv_max = 35 (mango), Dv-min = 14 (rice), and Davg = 25.3 (s = 6.651). In the pesticide category (Cpes), Dv-max = 10 (abamectin and chlorothalonil), Dv-min = 3 (flufenoxuron, hexythiazox and propargite), and Davg = 5.8 (s = 1.931). In the diseases and pests category (Cdis), Dv-max = 18 (mites), Dv-min = 1 (white rust), and Davg = 5.6 (s = 3.539). Generally, for an entity, the larger the Dv of the instance it contained, the greater the importance of the instance in the portrait. Conversely, the smaller the Dv of the instance, the smaller the importance of the instance in the portrait.
4.2. Relative Importance of Different Crop Entities
The numbers of adjacent nodes of 15 crop instances were counted to represent the numbers of their diseases and pests (Figure 5a). In the model, the number of diseases and pests that for each crop was prone to occur, the highest was AN = 18, and the lowest was AN = 4. Mangoes were the most susceptible to diseases and pests, while bananas and chilies also were more susceptible to diseases and pests, and 10 crops had less than 10 diseases and pests.
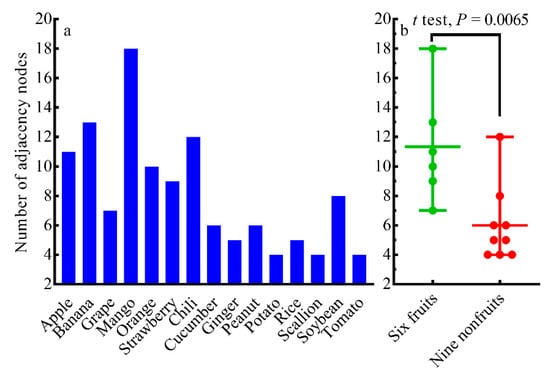
Figure 5.
Numbers of adjacent nodes: (a) compared across all 15 crops; (b) compared between six fruits and nine nonfruits.
Further, the adjacent nodes of fruits and not-fruits were counted to represent the numbers of their diseases and pests, respectively (Figure 5b). In the model, the numbers of susceptible diseases and pests for six fruits were at most AN = 18, while the least was AN = 7, and the average was AN = 11.3 (s = 3.830); the numbers of susceptible diseases and pests of nine non-fruits were at most AN = 12, while the least was AN = 4, and the average was AN = 6.0 (s = 2.598). These results indicated that people pay more attention to fruit diseases and pests than to nonfruit diseases and pests, because the ANs of fruits were significantly greater than the ANs of nonfruits (p = 0.0065), which may be related to the fact that economic value of fruits is higher than that of nonfruits.
4.3. Occurrence Trend of Crop Diseases and Pests
In a certain time span, the change in the numbers of Q&A about a certain crop disease or pest can reflect the occurrence trend of this disease or pest. We defined qn to represent the quantity of Q&A about a certain disease or pest for n consecutive days. We took root rot disease of strawberry as an example, and selected a total of 210 days (1 February 2019–29 August 2019) of data for analysis. The quantities of Q&A were summed every seven consecutive days (q7), and hence 30 weeks of data were obtained. When we took 1 February 2019 as the starting date and seven days (n = 7) as the time interval, the Q&A quantities for root rot reached a peak around the 10th week, and then gradually stabilized until a small increase occurred again around the 25th week (Figure 6). Therefore, the root rot disease of strawberry was estimated to occur concentratedly around mid-April, consistent with the result that red heart root rot disease of strawberry mostly occurs from mid-March to mid-May [28].
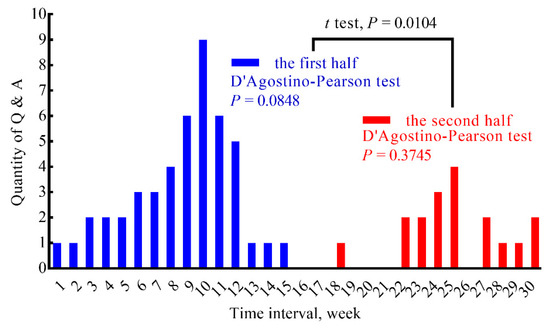
Figure 6.
Trend in the quantities of Q&A on root rot disease of strawberry.
Further, the 30 weeks of data were divided into two parts, the first half contained the first 15 weeks of data (colored blue in Figure 6), and the second half contained the last 15 weeks of data (colored red in Figure 6). The Q&A quantities of the two halves both were in accordance with the normal distribution (p = 0.0848 and p = 0.3745, respectively). The Q&A quantities of the first half were higher than those of the second half (p = 0.0104), indicating that the first 15 weeks was the main occurrence period of root rot disease of strawberry.
4.4. Interconnection within Crop Diseases and Pests
The link between two diseases and pests that can infect the same crop was measured due to the possibility of some internal links. We took diseases and pests data of strawberry as an example, and divided the 210 days (1 February 2019–29 August 2019) into 30 statistical periods with an interval of seven days. The quantities q7 of different diseases and pests were calculated. The similarity index, Sim ϵ [0, 1], was defined as Formula (1) with a precision of two decimals:
where xi represents the quantity of occurrence of disease or pest x in the ith statistical interval, and yi represents the quantity of occurrence of disease or pest y in the ith statistical interval. When two diseases and pests had Q&A data in a same statistical period, the closer the two Q&A quantities were, the closer the relationship between the two diseases and pests was.
In the model, we obtained the similarity index (Sim) of root rot, anthracnose, thrips, leaf spot, and aphid damage of strawberry (Figure 7). Root rot and anthracnose are both fungal diseases with similar harmful symptoms, mainly wilting and death, and both are devastating diseases of strawberry [29,30]. Therefore, the similarity index between the two diseases and pests in this model was relatively high (Sim = 0.41). Thrips and leaf spot disease have similar harmful symptoms, and both cause gray spots on the leaves [31,32]. The similarity index between the two diseases and pests in this model also was high (Sim = 0.46). These results indicated that when two diseases and pests occurred at the same time, even if the symptoms were similar, the causes can be similar or different. Therefore, the similarity index was only related to the symptoms and not related to the cause of the disease or pest. This result suggested that it is very important to confirm the causes of diseases and pests. When diagnosing diseases and pests, it is necessary to consider a variety of diseases and pests with a high similarity index at the same time to prevent diagnostic errors.
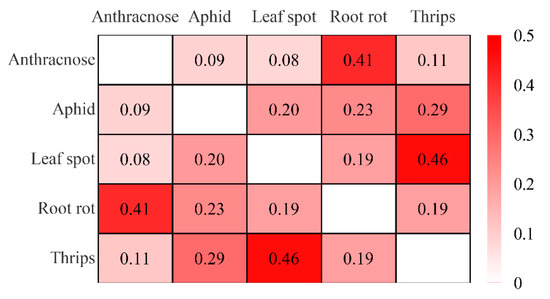
Figure 7.
Similarity indexes between diseases and pests of strawberry.
4.5. Non-One-to-One Relation between Pesticides and Diseases and Pests
Providing accurate information for control of diseases and pests is an important purpose of constructing crop portraits. By analyzing the diseases and pests involved in this study and the pesticides recommended for the control of these diseases and pests, we found that out of 28 pesticides, there were four pesticides that each could be used for control of only one disease or pest. The one pesticide with the broadest control spectrum could be used to control six diseases and pests, and each of the other 23 pesticides also could control more than one disease and pest (Figure 8a). On the other hand, there were 11 pesticides for control of mites. There were 8, 8, 7, 7, 6, and 5 pesticides for blight, gummy stem blight, aphid, whitefly, anthracnose, and diamondback moth control, respectively (Figure 8b). These results indicated that broad-spectrum pesticides have been widely used in crop production. These broad-spectrum pesticides can simultaneously control target and nontarget diseases and pests, and help improve the efficiency of management of diseases and pests. However, the environmental pressure brought by broad-spectrum pesticides is relatively greater. For some diseases and pests, there are a variety of pesticides to choose from for control, which is beneficial to giving priority to environmentally compatible pesticides with high efficiency and low toxicity.
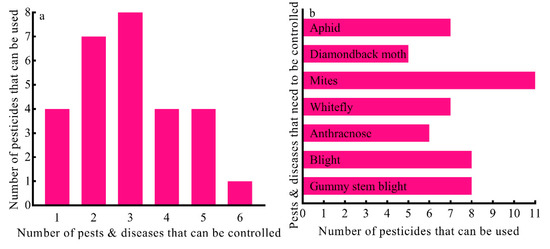
Figure 8.
Non-one-to-one relation of pesticides against diseases and pests. (a) Broad spectrum of some pesticides. (b) There are many pesticides available against one disease or pest.
5. Discussion
We constructed a property graph of crops using graph theory and called the property graph a crop portrait. Crop portraits have good development prospects and will play an important role in the age of digital agriculture for data mining. Our crop portrait contained three types of entities (crops, pesticides, and diseases and pests), as well as their corresponding attributes and the relationships between them.
Based on the portrait, we found that crop entities were more important than pesticide entities and disease and pest entities, and fruit entities were more important than nonfruit entities. These results were consistent with the fact that crops are the core of agricultural production, and the economic value of fruits is higher than that of nonfruits nowadays. Through data mining, we found that diseases and pests with the same symptoms may be caused by completely different pathogenic factors. Therefore, the control of these diseases and pests should be based on the cause, not on the symptoms, which would comply with the principles of disease or pest control in phytopathology. Although the crop portrait revealed that broad-spectrum pesticides are widely recommended for use in production, the impact of pesticides on the environment, rather than control effects, should be considered first in control of diseases and pests, and environmentally friendly pesticides should be given priority.
At present, there is a lack of research reports on the construction of crop portraits. This study successfully constructed a crop portrait based on the graph database Neo4j, and evaluated the constructed crop portraits through data mining. The results showed that the construction of crop portraits based on graph theory is very necessary and useful for agricultural data mining, which is helpful for agricultural analysis and guiding agricultural production. This research provides a simpler and more effective method for the analysis of agricultural big data. Although this method is based on Chinese data, the methods involved are also applicable to other data, except the named entity recognition method.
6. Conclusions
In this research, a crop portrait containing 15 crops, 28 pesticides, and 93 diseases and pests was constructed based on the graph database Neo4j, and detailed information was mined. The crop portrait could describe crops in an all-around way.
In the crop portrait, crops were more important than both pesticides and diseases and pests when measured by the Dv of vertex entities, and people paid more attention to fruits than nonfruits among the 15 crops. Taking strawberry as an example, we successfully predicted the occurrence period of its root rot disease. It was found that two kinds of diseases and pests that occurred at the same time with similar symptoms may have different causes. Broad-spectrum pesticides were widely recommended for the control of diseases and pests.
Our work filled the gaps in the field of crop portraits to a certain extent, and opened up a new path for agricultural analysis. In the future, this research will further optimize the image label selection of crop portraits, improve the recognition method of named entities in the agricultural field, and incorporate more crops into the crop portrait by increasing the amount of data. In addition, the labels of the crop portrait are currently defined as static labels. When applied to the intelligent agricultural knowledge question-answering system, certain tags need to be defined as dynamic tags in order to update them in time and provide accurate recommendation services.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.-X.S. and B.-K.Z.; software, Y.-X.S. and Y.-X.W.; validation, Y.-X.S. and B.-K.Z.; data curation, H.-Q.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-X.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.-X.S. and X.L.; visualization, Y.-X.S.; supervision, X.L.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), grant number 61601471.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and editors for their constructive comments and helpful suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Shao, B.; Li, X.; Bian, G. A Survey of Research Hotspots and Frontier Trends of Recommendation Systems from the Perspective of Knowledge Graph. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, J.; Naraseeyappa, S.; Ankalaki, S. Analysis of Agriculture Data Using Data Mining Techniques: Application of Big Data. J. Big Data 2017, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo Vuong, M.; Kechadi, M.-T. Crop Knowledge Discovery Based on Agricultural Big Data Integration. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Machine Learning and Soft Computing, Haiphong City, Vietnam, 17–19 January 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldırım, M.; Okay, F.Y.; Özdemir, S. Big Data Analytics for Default Prediction Using Graph Theory. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 176, 114840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiong, N.N.; Guo, W. A Survey on Knowledge Graph Embedding: Approaches, Applications and Benchmarks. Electronics 2020, 9, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Al-Aswadi, F.N.; Gaurav, D. Recent Trends in Knowledge Graphs: Theory and Practice. Soft Comput. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qin, X.; Zheng, H. Research on Contextual Recommendation System of Agricultural Science and Technology Resource Based on User Portrait. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1693, 012186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, M.N. Ontology-Based Data Acquisition Model Development for Agricultural Open Data Platforms and Implementation of Owl2mvc Tool. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Xiang, Y. A Review: Knowledge Reasoning over Knowledge Graph. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.C.; Lemay, D.G.; German, J.B. A Multi-Ontology Framework to Guide Agriculture and Food towards Diet and Health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brožová, H.; Šubrt, T.; Bartoška, J. Knowledge Maps in Agriculture and Rural Development. Agric. Econ. 2008, 54, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.L.; He, Q.Y.; Ping, Q.I.A.N.; Ze, L.I. Construction of the Ontology-Based Agricultural Knowledge Management System. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Song, Q.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, H. Cn-Makg: China Meteorology and Agriculture Knowledge Graph Construction Based on Semi-Structured Data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACIS 17th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Singapore, 6–8 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Kuang, J.; Cheng, D.; Zheng, J.; Gao, M.; Zhou, A. Agrikg: An Agricultural Knowledge Graph and Its Applications. In Complexity in Polish Phonotactics; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 533–537. [Google Scholar]
- Lagos-Ortiz, K.; Salas-Zárate, M.D.P.; Paredes-Valverde, M.A.; García-Díaz, J.A.; Valencia-García, R. Agrient: A Knowledge-Based Web Platform for Managing Insect Pests of Field Crops. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Zou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Fang, K.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y. A Joint Model for Entity and Relation Extraction Based on Bert. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, P.; Sachin, B.; Anuj, S. Neo4j Graph Database Implementation for Linkedin. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2020, 1, 339–342. [Google Scholar]
- Abad-Navarro, F.; Bernabé-Diaz, J.A.; García-Castro, A.; Fernandez-Breis, J.T. Semantic Publication of Agricultural Scientific Literature Using Property Graphs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothers, J.; Andrew, N. Can Neo4j Replace Postgresql in Healthcare? AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. 2020, 2020, 646–653. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Mehta, A.; Ganguli, R.; Sen, S. Recommendation of Influenced Products Using Association Rule Mining: Neo4j as a Case Study. Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulias, K.; Palaiokrassas, G.; Fragkos, G.; Litke, A.; Varvarigou, T.A. A Graph Model Based Blockchain Implementation for Increasing Performance and Security in Decentralized Ledger Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 130952–130965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Arias, P.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.J.; Morlán-Plo, V.; Notivol-Bezares, R.; Oscar, C. The Zaragoza’s Knowledge Graph: Open Data to Harness the City Knowledge. Information 2020, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Kolmanič, S. Preliminary Study on the Knowledge Graph Construction of Chinese Ancient History and Culture. Information 2020, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mece Principle. Available online: https://wikimili.com/en/MECE_principle (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Chen, P.P.S. The Entity-Relationship Model—Toward a Unified View of Data. ACM Trans. Database Syst. 1976, 1, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, M.; Peng, C.; Ni, S.; Shen, S. Scenario-Entity Analysis Based on an Entity-Relationship Model: Revisiting Crime Reconstruction. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 302, 109923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wei, X.H.; Jia, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.E. Recognition of Crops, Diseases and Pesticides Named Entities in Chinese Based on Conditional Random Fields. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2017, 48, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.L. The Characteristics and Prevention of Strawberry Root Rot. Rural. Sci. Technol. 2017, 12, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.R.; Liu, C.F. Occurrence and Control of Strawberry Anthracnose and Root Rot. Jilin Veg. 2009, 1, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Q. Symptoms and Control Measures of Strawberry Root Rot and Anthracnose. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2012, 18, 94–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.N.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.P.; Shang, Q.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wei, Y.M. Pestalotiopsis Clavispora Causing Leaf Spot on Strawberry. Mycosystema 2016, 35, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Han, H.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, L.H. Common Diseases and Pests of Strawberry in Northern Jiangsu Province and Their Comprehensive Control. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 26, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).