Abstract
The effective detection of driver drowsiness is an important measure to prevent traffic accidents. Most existing drowsiness detection methods only use a single facial feature to identify fatigue status, ignoring the complex correlation between fatigue features and the time information of fatigue features, and this reduces the recognition accuracy. To solve these problems, we propose a driver sleepiness estimation model based on factorized bilinear feature fusion and a long- short-term recurrent convolutional network to detect driver drowsiness efficiently and accurately. The proposed framework includes three models: fatigue feature extraction, fatigue feature fusion, and driver drowsiness detection. First, we used a convolutional neural network (CNN) to effectively extract the deep representation of eye and mouth-related fatigue features from the face area detected in each video frame. Then, based on the factorized bilinear feature fusion model, we performed a nonlinear fusion of the deep feature representations of the eyes and mouth. Finally, we input a series of fused frame-level features into a long-short-term memory (LSTM) unit to obtain the time information of the features and used the softmax classifier to detect sleepiness. The proposed framework was evaluated with the National Tsing Hua University drowsy driver detection (NTHU-DDD) video dataset. The experimental results showed that this method had better stability and robustness compared with other methods.
1. Introduction
Fatigued driving is causing increased traffic accidents, and has become a serious social problem. According to a survey published by the National Highway Transportation Administration, 7.277 million traffic accidents occurred in the United States in 2016, causing 37,461 deaths and 3.144 million injuries, of which fatigued driving caused approximately 20–30%. Studies demonstrated that fatigued driving impairs a driver’s responsiveness and information processing ability, thus causing the driver to lose control of the vehicle and eventually deviate from the lane or cause a tail chase [1,2]. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to design an effective driver fatigue identification method to improve road traffic safety.
With the rapid development of computer vision technology, the method of detecting the driver’s drowsiness state by analyzing the driver’s facial behavior characteristics has attracted widespread attention of researchers. The researchers extracted different facial fatigue features to detect the driver’s sleepiness. Zhao et al. [3] used the Deep Belief Network (DBN) to extract different facial fatigue features from the dataset and respectively verified the accuracy of driver drowsiness detection. Zhang et al. [4] used the local binary pattern (LBP) and support vector machine (SVM) fatigue expression reorganization algorithm to estimate the fatigue degree of drivers. However, this detection method based on a single facial feature has some limitations in robustness and reliability, and does not consider the time change characteristics of the driver’s drowsiness, thereby reducing the recognition accuracy.
To overcome the limitations associated with the use of a single source of information, some methods have combined multiple sources to detect sleepiness. Wang et al. [5] combined the eye and mouth states and proposed a method to discriminate the driver fatigue state when wearing glasses. The Deep Drowsiness Detection (DDD) framework proposed by Park et al. [6] used three deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN) to extract drowsiness-related behavioral features such as facial and head movements. In addition, two fusion strategies of independent average architecture (IAA) and feature fusion architecture (FFA) are used to perform linear fusion of fatigue features, which improved the accuracy of driver drowsiness detection.
However, most of the above methods of combining multiple information sources for drowsiness detection simply use a linear model to fuse the fatigue features. Since the distribution of multimodal features may change significantly, the feature vectors obtained by this linear fusion cannot adequately express the complex correlations between the driver’s facial feature areas, thus limiting the final detection performance.
To solve these problems, we propose a driver drowsiness estimation model based on factorized bilinear feature fusion and a long-short-term recurrent convolutional network to detect driver sleepiness effectively, as shown in Figure 1. First, we designed two kinds of DCNN, which were used to extract the deep features of the driver’s eyes and mouth and to detect their states. Then, we used the factorized bilinear feature fusion method to fuse the deep feature representation of the eyes and mouth. Finally, we used the recurrent network LSTM to model the time variation of the drivers’ drowsiness to provide accurate detection of the drivers’ drowsiness under various driving conditions.
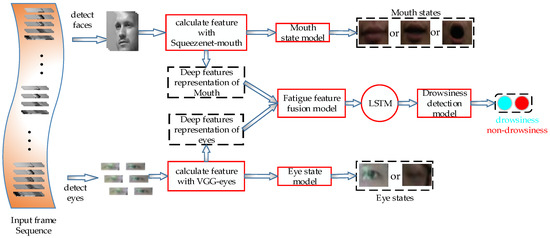
Figure 1.
Overall architecture of the proposed framework. The red boxes denote the models, and the black boxes drawn with dotted lines define the extracted features or outputs of each model.
To fully extract the correlation characteristics between driver fatigue features, we improved the homogeneous feature fusion method in [7] and proposed a factorized bilinear feature fusion method suitable for multi-modal feature input. In addition, the factorized parameterization and the adoption of the dropout layer effectively solved the problem of excessive parameters in the fusion process.
The main contributions of this study are as follows: (1) We proposed a new multi-level driver drowsiness estimation system. The system has three main components: ➀ extraction of deep feature representations related to the driver’s eyes and mouth in the dataset, ➁ fatigue feature fusion, ➂ record the time information of fatigue features through LSTM. (2) Regarding fatigue feature fusion, we proposed a new factorized bilinear feature fusion model suitable for multi-modal feature input and performed bilinear fusion of the extracted deep feature representations of eyes and mouth to solve the limitations of the feature linear fusion process.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. The second part summarizes the related work. The third part introduces the overall framework of driver drowsiness detection. The fourth part provides the details of the experiment and the experimental results to evaluate the performance of the proposed method. The last part gives the conclusion and discusses future work.
2. Related Work
The objective of the different techniques used in the field of driver drowsiness detection is to represent and detect the signs of the driver’s drowsiness. In the literature, driver fatigue has been identified based on vehicle behavior as well as the driver’s physiological state and facial expression. The technology based on the driver’s physiological signals is mainly to detect specific electrophysiological signals generated by the driver during driving fatigue, including Electroencephalogram (EEG) [8,9], Electrocardiogram (ECG) [10,11], etc. Khushaba et al. [12] used a wavelet packet transform model based on fuzzy mutual information to extract information related to drowsiness from a group of EEG, electrooculogram (EOG), and ECG signals to detect driver drowsiness. Li et al. [10] extracted the heart rate variability (HRV) from an ECG signal, performed a wavelet transform on it to obtain discriminant features, and then used a classifier to identify the fatigue state. These signals can provide stricter and more accurate discriminative information when analyzing driver fatigue. However, drivers need to wear invasive detection devices that affect the driver’s driving experience.
Fatigue detection methods based on vehicle behavior mainly measure the vehicle’s speed, turning angle, and deviation from the center line of the vehicle to detect driving fatigue [13,14]. Wang et al. [15] used a random forest classifier to study the relationship between the vehicle steering wheel lateral acceleration, longitudinal acceleration and steering angle and the accuracy of driver fatigue recognition under different time window sizes. This method is easily influenced by factors, such as the driver’s driving experience, vehicle condition, and road environment, thus reducing the accuracy of the driver’s sleep awareness.
Methods based on the driver’s facial behavior mainly analyze the facial features to detect fatigued driving, such as PERCLOS (eyelid closure rate exceeds the pupil percentage per unit time), mouth opening, head posture, facial expression, etc. [16,17,18]. This method does not interfere with driving, and is therefore more acceptable to drivers. Garcia et al. [19] proposed a three-step system. Their system first detects and tracks faces and eyes. Then, to analyze the performance of the eyes under different illumination conditions, the system performs image filtering. The system uses PERCLOS measurements to assess eye closure. Jie et al. [2] proposed an automatic yawn detection method based on extracting the geometric and appearance features of the eye and mouth regions. This method can successfully detect hand covered and uncovered yawns, and achieve high accuracy.
At the same time, to overcome the limitation of extracting single facial cues in driver fatigue detection, researchers combined multiple information sources to detect fatigue in two aspects: fatigue feature extraction and fusion model construction. Du et al. [20] proposed a multimodal fusion recurrent neural network (MFRNN) framework. They used RGB-D cameras and infrared video to extract the driver’s eye opening degree, mouth opening degree, and heart rate information, and at the same time, extracted time information related to each fatigue feature to improve the performance of driver fatigue detection.
Sun et al. [21] proposed a two-level fusion method of context features based on a multi-class support vector machine (MCSVM). Deng et al. [22] proposed three criteria to judge the driver’s sleepiness, including the blinking frequency, closed time, and yawning time, and fused the three criteria at the decision level to detect a driver’s sleepiness. Donahue et al. [23] proposed a long short-term recurrent convolutional network (LRCN) model. By using the LSTM units in the convolutional neural network, the model combined learning time dynamics and convolution perception representation, effectively improving the recognition accuracy of the model.
Parkhi et al. [24] proposed a VGG-faceNet for face recognition, and achieved a large number of advanced experimental results using the above training dataset and a simpler network structure. Shih and Hsu [25] proposed a multi-stage spatio-temporal network (MSTN), in which the characteristic graph of each convolutional layer was cascaded with a parallel connected structure, and the full connection layer used the cascaded characteristic graph to estimate the driver’s drowsiness.
To fully model the problem of the complex correlation between two modal features in the process of computer vision tasks, Hong et al. [26] observed that the correlation between related features can be captured using the element-wise multiplication interaction between the feature maps. Therefore, Yu et al. [27] fused the spatio-temporal feature representation obtained from 3D-DCNN with the related scene annotation by element-wise multiplication interaction, and added a set of conditional adaptive representation to effectively distinguish driver drowsiness.
Parkd et al. [6] respectively used two fatigue feature fusion strategies, IAA and FFA, to fuse the extracted multi-mode driver fatigue features to improve the accuracy of driver drowsiness detection. Lin et al. [28] proposed a bilinear pooling method to calculate the vector outer product of the feature vectors at each position in the feature mapping obtained by convolution, and then used this for classification.
To solve the problem of higher feature dimensions after fusion, Li et al. [7] used the method of unimodal matrix factorization and DropFactor to cut the parameters of the model; thereby, the parameter size was reduced by dozens of times compared with the bilinear pooling method. At the same time, they also added a factorized bilinear network (FBN) in different convolutional layers of the concept network, which further proves that FBNs can effectively improve the accuracy of image recognition and classification tasks.
3. Proposed Work
Figure 1 shows the proposed fatigue detection framework, which is mainly composed of three models: fatigue feature extraction, fatigue feature fusion, and driver drowsiness detection. In Section 3.1, we describe the established CNN network structures for the driver’s eye and mouth state detection to extract deep feature representation of the eye and mouth features from the input data. In Section 3.2, we introduce the factorized bilinear feature fusion for deep feature fusion of the eyes and mouth to obtain the fusion representation of the driver fatigue features. In Section 3.3, we input the feature fusion representation into the LSTM according to the time series of the input data to identify the driver’s drowsiness.
3.1. Fatigue Feature Extraction
In this section, we describe a learning model for extracting the deep feature representation of the driver’s eyes and mouth from a given consecutive frame. When the driver is sleepy, the infrared camera in front of the driver can capture various changes in the driver’s facial expressions (such as the eyes and mouth), which are interpreted as shape changes or movement changes. In view of this change, we propose two separate CNN network models for eye and mouth fatigue feature extraction and state identification.
3.1.1. Mouth State Model
To effectively extract the deep feature representation of the mouth, we have made certain improvements to the Squeezenet network in [29], adjusting the input of the network to a 128 × 128 pixel image, and reducing the number of Fire module blocks. The framework of the Fire module is shown in Figure 2. We named the improved network Squeezenet-mouth network to identify the driver’s mouth state effectively. Figure 3 shows the structure of our proposed mouth state detection model.
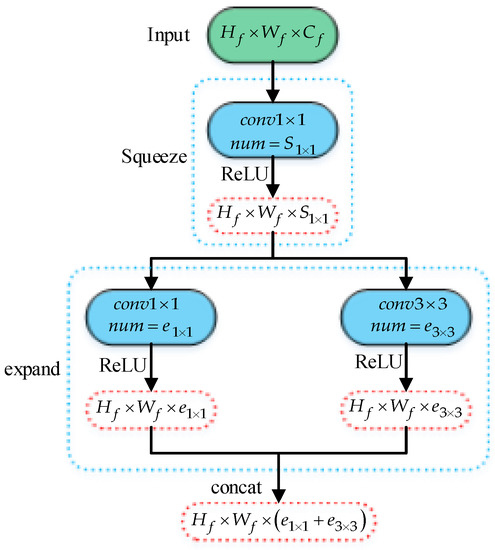
Figure 2.
The organization of the convolution filters in the Fire module. The red boxes drawn with a dotted line defines the dimension of the output characteristics of each convolution layer.
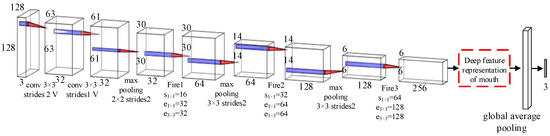
Figure 3.
Illustration of the mouth state detection model. The red boxes drawn with a dotted line define the extracted deep features representation of the mouth. The numbers next to the boxes illustrate the dimensionality and structural detail of the kernel in each convolutional layer.
First, the input image with a size of is input into a convolution layer according to the time sequence, and the image size is initially reduced. Then, through multiple Fire modules and max-pooling layers, the size of the detected face image is reduced from 128 × 128 to 6 × 6. Finally, the mouth state related feature representation is further extracted through average pooling and full connection layers and we use the softmax layer of the model to effectively identify the mouth state. The convolutional layer hidden unit of the network model adopts a Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function. The layer marked “V” in Figure 3 represents the padding of “valid.”
Let denote the face image input according to the time series, where H, W, and C represent the height, width, and channel number of the input face image, respectively. For a given input face image , based on the proposed mouth state model, the deep feature representation is extracted as follows:
where is the parameter vector of the deep feature representation of the mouth state, and is the deep feature representation of mouth state. The deep representation of the mouth state is defined as the activation value of the hidden unit in the last convolutional layer of the mouth state detection model. , , and denote the height, width, and channel number, respectively, of
.
3.1.2. Eye State Model
When the driver is drowsy during driving, the eye state will change significantly, which is mainly manifested in the faster blinking frequency or the longer duration of closed eyes. Based on the VGG-16 [30] network structure, we propose an improved VGG-eye network model to effectively identify the driver’s eye state. Figure 4 illustrates the structure of the modified eye state detection model. The eye state detection model includes eight convolution layers, three max-pooling layers, one global average pooling layer, and full connection layers.
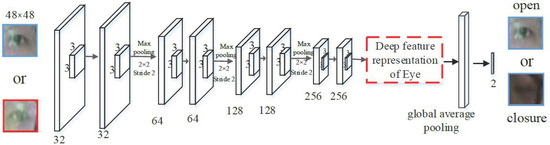
Figure 4.
Illustration of the eyes state detection model. The red boxes drawn with a dotted line define the extracted deep features representation of the eyes. The numbers next to the boxes illustrate the dimensionality and structural detail of the kernel in each convolutional layer.
Similar to the mouth state model, the convolutional layer hiding unit of VGG-eye model adopts a ReLU activation function. We input the 48 × 48 eye image into the network model in the time sequence and extract the driver’s eye state features through CNN to effectively identify the driver’s eye state. At the same time, referring to the deep feature representation of the mouth state, the deep feature representation of driver’s eye state is extracted as follows:
where is the input image of the given eye, is the parameter vector of the deep representation of eye state, and is the deep feature representation of the eye state. The deep representation of eye state is defined as the activation value of the hidden unit in the last convolution layer of eye state model. , , and denote the height, width, and channel number, respectively, of .
3.2. Fatigue Feature Fusion
In the previous stage, we have trained two models to extract the deep feature representations of the driver’s eyes and mouth. To obtain the correlation of fatigue features between different facial regions, it is necessary to fuse the fatigue features of different facial regions when detecting the drowsiness of drivers.
Therefore, we propose a factorized bilinear feature fusion model suitable for multi-modal feature input to fuse the deep feature representations of the driver’s eyes and mouth. It solves the limitation of [7] that can only perform feature fusion for homologous feature input, and improves the versatility of the feature fusion model. For the two feature maps of eyes and mouth on position, the fusion model is defined as follows:
where is the feature mapping of the deep mouth features at position , is the feature mapping of deep eye features at position , and represents the location set in the feature mapping. is equivalent to the acquired deep features of the eyes and mouth models. and denotes the feature vector dimension of the deep feature representation of the mouth and eyes at position , respectively, denotes the global feature descriptor. Then, the full connection layer of the feature fusion model can be expressed as:
where is the vectorization operator that converts a matrix into a column vector, and are the weight and bias of the full connection layer, respectively. is the output of the feature fusion model, is the dimension of the output of the feature fusion model. For feature fusion model, an output unit can be expressed as:
where is a matrix reshaped from ,is the j-th row of .
It is easy to see that the size of the global feature descriptor can become large, which introduces a large number of parameters, which may lead to a high computational cost and the risk of overfitting. Inspired by the matrix decomposition technique of unimodal data, we can decompose the matrix in Equation (5) into two low rank matrices:
where and represent the two low-rank factorized matrices. is the factor or the latent dimensionality, and is an all-one vector. To obtain the output features through Equation (6), the weights to be learned are two three-order tensors and accordingly. At the same time, to further prevent the model from overfitting, a dropout layer is added after the element-wise multiplication interaction. The purpose of the dropout layer is to avoid overfitting of the model by randomly discarding some neurons in the feature fusion and output layer. Finally, an average pooling layer is used to gather the scores around the spatial position. Therefore, Equation (6) can be reformulated as follows:
We named our feature fusion model factorized bilinear feature fusion (FBFF). Figure 5 shows the detailed program of the FBFF model. Then, we used the output of the feature fusion model as input for the LSTM model to identify the driver’s drowsiness, which will be explained in the next section.
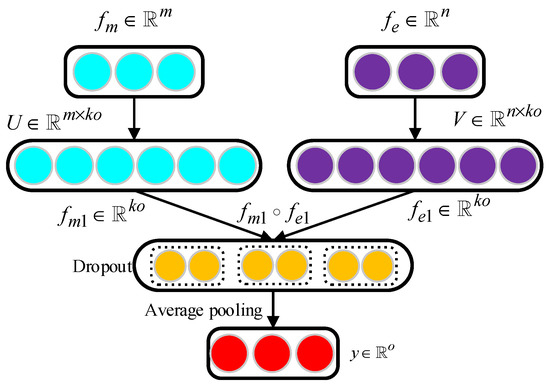
Figure 5.
The flowchart of factorized bilinear feature fusion (FBFF).
3.3. Driver Drowsiness Detection
In the previous sections, we extracted the feature representation of different facial regions by the established network model. At the same time, we used the factorized bilinear feature fusion model to fuse the sleepiness features of the eyes and mouth. However, to detect the drowsiness of drivers, the spatial information (facial feature state) and temporal information of the drivers’ facial features must be considered at the same time.
It is not possible to estimate the driver’s drowsiness through a single frame, because a single frame cannot contain the temporal sequence of a driver’s facial state. Therefore, to obtain the temporal relationship of feature mapping in the proposed drowsiness detection model, we first used the LSTM unit to obtain the time change of the sleeping state from the frame level fusion feature sequence. The time network we used was a one-way single-layer LSTM architecture with 128 hidden units. Then, we input the output of the LSTM unit into a softmax layer to accurately predict the drowsiness of the driver in each frame.
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
We used the National Tsing Hua University drowsy driver detection (NTHU-DDD) dataset [31] collected by the NTHU computer laboratory to train and evaluate the proposed driver drowsiness detection framework. The dataset recorded the driver’s face state changes (including normal driving, yawning, and slow blinking) through the use of visual sensors in a simulated driving environment. The whole dataset (including training, validation, and the test dataset) contains 36 subjects. Each subject recorded video data in five different scenes (no glasses, glasses, night (no glasses), night (glasses), and sunglasses). The training dataset includes 360 video clips of 18 subjects, the evaluation dataset includes 20 video clips of 4 subjects, and the test dataset includes 70 video clips of 14 subjects.
For the training and evaluation datasets, frame level annotation of the sleepiness state, eye state, mouth state, and head posture were provided. As the basic authenticity label of the test dataset has not been disclosed, we only used the training and evaluation dataset in this work. The data video of night (glasses) and night (no glasses) were shot at the speed of 15 frames per second, and the video data of other scenes were shot at the speed of 30 frames per second. All video frames are grayscale images with a resolution of 640 × 480 and do not contain audio information. Figure 6 shows various examples of facial state changes in the NTHU-DDD dataset.

Figure 6.
Example frames of the National Tsing Hua University drowsy driver detection (NTHU-DDD) video dataset with different situations. (a) Examples of changes in different facial states in the same scenario; (b) Examples of state changes under different scenarios.
4.2. Experimental Details
4.2.1. Dataset Preprocessing
We divided the training dataset and evaluation dataset of NTHU-DDD into three subsets: sleepiness state detection, eye state detection, and mouth state detection. Each subset contains video data collected from five different scenes and the corresponding frame level annotations. For the collected video data, we first used the Viola and Jones algorithm [32] to detect the driver’s face area, and then used the bilinear interpolation method in OpenCV to adjust the cropped face image to a uniform size of 128 × 128 pixels to improve the operation efficiency of the model. At the same time, we used one-hot vectors to redefine the frame level annotation of the facial element state. A detailed description of the redefined frame level annotation is shown in Table 1. To increase the data capacity of each subset, we enhanced the processed facial images by random cropping and horizontal flipping to prevent overfitting in the process of model training.

Table 1.
A detailed explanation of transforming the NTHU-DDD dataset frame level annotation into one-hot vectors.
4.2.2. Model Training
Eye state detection model: We first used FER2013 [33] to pre-train the VGG-eye model. Then, we selected the eye state detection subset of the NTHU-DDD dataset to fine-tune the pre-trained network model, and the weight of the new layer was randomly initialized by a Gaussian function. To ensure that the model can fully learn the features related to the eye state, we studied the method in [23], which located and cuts the eye region of the face image in the dataset, and adjusted the cropped eye image to 48 × 48 pixels. We chose the RMSProp [34] optimization algorithm to train the eye state detection model, and carried out 40,000 iterations on the VGG-eye model. The mini-batch size was 48. The learning rate was updated by exponential decay. The initial learning rate was set as 0.0005, and the decay rate was 0.9. At the same time, batch normalization was added after the convolutional layer of the model to further accelerate the operation speed of the model.
Mouth state detection model: We used the mouth state detection subset to train the proposed network model. To fully consider the influence of the eyes, mouth, nose, and other facial features on yawning behavior, we took the whole face image of the driver as input. We input a 128 × 128 pixel face image into the mouth state detection model. Similar to the eye state detection model, we choose the RMSProp optimization algorithm to train and optimize the Squeezenet-mouth model. The model was iterated 10,000 times, and the mini-batch size was 48. The learning rate was also updated by exponential decay. Apart from the initial learning rate that was changed to 0.001, the other parameter settings were the same as the eye state detection model.
Drowsiness detection model: We clipped the video data from the sleepiness detection subset into a fixed 30 frame video clip, which was used as the input of the drowsiness detection model to train the model. The video segments were input into the eye state detection model and the mouth state detection model according to the time series to obtain the related deep feature representation. After that, the FBFF feature fusion model was used to fuse the deep features related to the mouth and eyes. The feature fusion results were input into the LSTM unit to record the time information of the video sequence. Finally, the softmax layer was used to record the time information of the video sequence to accurately predict the drowsiness score of the drivers in each frame. We choose Adam’s [35] optimization algorithm to train and optimize the drowsiness detection model, with and of 0.9 and 0.999, respectively, was 1 × 10−8, the initial learning rate was set at 0.001, and the learning rate was updated by exponential decay. We used the cross entropy loss to optimize the prediction effect of the model.
4.2.3. Environment
The computer running the network model was configured with a NVIDIA GTX 1080Ti graphics card, Intel Core i7-7700 CPU processor with 3.6 GHz and 16 GB RAM. The software used was tensorflow under a Spyder environment, and the computer was a Windows7 system.
4.3. Performance of Proposed Method
We used the evaluation dataset of the NTHU-DDD dataset to verify the effectiveness of our framework. The evaluation dataset consisted of 20 videos collected by four subjects in five different scenes. At the same time, the evaluation dataset also included a number of one-hot vector frame level annotations related to the scene conditions and drowsiness. We evaluated the performance of the state detection model and drowsiness detection model.
First, we used the evaluation dataset and the frame level annotation for eye state and mouth state to evaluate and verify the trained eye state detection model and mouth state detection model. The results of the evaluation and validation are shown in Table 2. For the verification accuracy of the two models in different scenarios, the ratio of the number of correct classifications of each state detection model on the evaluation dataset to the total number of evaluation samples was obtained. Finally, the arithmetic mean of the verification accuracy of each scene was calculated as the average accuracy of the training state detection model on the evaluation dataset.

Table 2.
The evaluation dataset of the NTHU-DDD dataset was used to verify the average accuracy of the eye and mouth state detection model in different scenes.
The experimental results in Table 2 show that the proposed mouth state detection model achieved good classification results in different scenarios, and the average verification accuracy reached 93.3%. However, the classification results of the eye state detection model were relatively low, especially in the two scenes of sunglasses and night (glasses), the verification accuracy was only close to 80%. Considering that the model’s understanding of the scene will be affected by the size of the object’s feature area and the problem of light, in the evaluation dataset, the eyes in the above two scenes were blocked to a certain extent and the light was insufficient, which affects the extraction of eye state features from the VGG-eye model, and further affects the accuracy of the model verification.
We evaluated and verified the proposed drowsiness detection model using the evaluation dataset and the frame level annotation of the sleepiness state. In [36], the convolutional neural network structure at a lower level typically responded to simple low-level features; therefore, linear transformation was enough to abstract the concepts in the image. Therefore, as shown in Figure 7, we studied the influence of different high-level CNN feature fusion structures on the accuracy of sleepiness detection. The last convolutional layer of the state detection model and the convolutional layer after global average pooling were fused using FBFF. At the same time, in the process of training the sleepiness detection model, we clipped the video data from the sleepiness detection subset into a fixed length of 30 frames. To test the accuracy of the drowsiness detection model, we used the data of different frames (frames = 30, 40, and 50) as the input of the LSTM in the test.
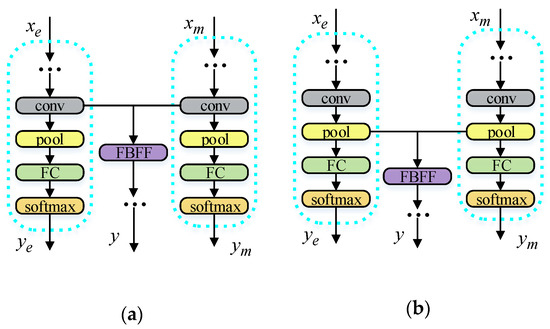
Figure 7.
Structure chart of the feature fusion of different convolution layers. (a) The feature fusion of the convolutional layer before global average pooling. (b) The feature fusion of the convolutional layer after global average pooling.
We used the F1-score to quantitatively evaluate the proposed drowsiness detection framework. The F1-score is the harmonic average of Precision and Recall; therefore, the definition of the F1-score is as follows:
where Precision represents the proportion of the real sleepy samples judged by the classifier, and Recall represents the proportion of the predicted sleepy samples to the total sleepy samples in the evaluation dataset. Table 3 shows the average detection accuracy of the training sleepiness detection model on the evaluation dataset under the condition of feature fusion for different high-level neural networks and the selection of different frame length sequence data segments. The results show that, under the premise of selecting the same high-level convolutional neural network for feature fusion, the accuracy of sleepiness detection model in the evaluation dataset was gradually improved with the increase in the number of input sequence frames.

Table 3.
The evaluation dataset of the NTHU-DDD dataset was used to compare the average accuracy of the drowsiness and non-drowsiness state.
This indicates that the ability of the network LSTM to simulate the time change of the drowsiness state was related to the length of the input sequence to a certain extent. With more frames of the input sequence, the detection accuracy of the model improved correspondingly, but the operation time and cost of the model also increased correspondingly. However, when the number of input frames were all 30 frames, the drowsiness detection accuracy of feature fusion in the last convolutional layer was 0.758, which was significantly higher than the average accuracy of the feature fusion after global average pooling.
Considering that texture attributes are usually translation invariant, most texture representations were based on the unordered aggregation of local image features, such as global average pooling. Therefore, compared with the feature fusion of the convolutional layer after global average pooling, feature fusion in the last layer of the model retained the texture attributes of the image and improved the robustness and accuracy of driver drowsiness predictions.
Due to the lack of available public datasets to compare the performance of drowsiness detection, we used the NTHU-DDD dataset to compare the performance of the proposed drowsiness detection model with several sleepiness detection models. We used the same training dataset and frame level annotation to fine-tune the training of five network models: DBN [3], MSTN [25], VGG-faceNet [24], LRCN [23] and DDD [6]. At the same time, we evaluated and tested the performance of the network model drowsiness detection on the evaluation dataset.
These methods use the same training and evaluation procedures as our proposed framework. Table 4 shows the comparison results of using NTHU-DDD to detect drivers’ drowsiness. Among them, the two network models of DBN and VGG-faceNet only extracted a single facial feature to detect the driver’s drowsiness, and did not consider the time change characteristics of the driver’s drowsiness, so the detection accuracy of the driver’s drowsiness is low.

Table 4.
The average accuracy of the drowsiness detection methods under different conditions was compared with the evaluation dataset of the NTHU-DDD dataset.
Although the two network models of MSTN and LRCN consider the time change of driver’s drowsiness, the detection accuracy of driver’s drowsiness is low due to the depth of the network model and the limitations of single facial features. The DDD network model proposed by Park et al. [6] used two fusion strategies of IAA and FFA to perform the linear fusion of fatigue features, which improves the accuracy of driver drowsiness detection. However, the drowsiness detection framework does not consider the time change characteristics of driver drowsiness, and the feature fusion stage is simply linear fusion, which has certain limitations.
Our multi-level driver drowsiness estimation system uses two DCNNs to extract the deep features of the eyes and mouth, and uses the FBFF model to fuse the fatigue features, and finally uses the LSTM unit to capture the time variation of drowsiness features, which improves the driver Drowsiness detection accuracy. It can be seen from the results in Table 4, compared with other drowsiness detection methods that this framework can provide an accurate and effective driver drowsiness detection method in most cases.
To further verify the robustness of the proposed driver drowsiness detection framework, we have made the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of several network models on the evaluation dataset, as shown in Figure 8. The ordinate True Positive Rate represents the proportion of truly sleepy samples in the classifier judged as sleepy, and the abscissa False Positive Rate represents the proportion of all non-drowsy samples predicted to be sleepy. It can be seen from the ROC graph that compared with other network models, the proposed driver drowsiness detection framework has a larger the area under curve (AUC) on the evaluation dataset, which indicates that the proposed driver drowsiness detection system has a stronger ability to judge whether the driver is drowsy. The classification effect further proves the superiority and robustness of the proposed framework.
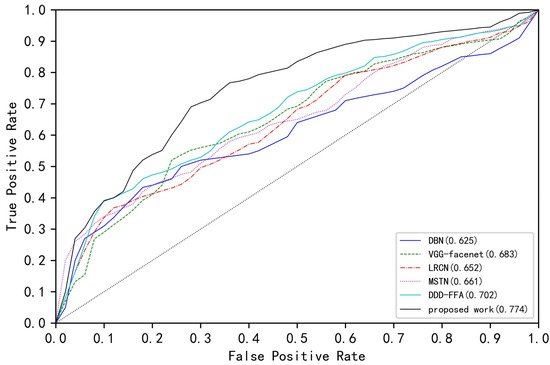
Figure 8.
The receiver operating characteristics (ROCs) for the driver drowsiness detection. Figures in parentheses indicate the area under curves (AUCs).
The experimental results show that the proposed factorized bilinear feature fusion method is helpful to find driver drowsiness features with strong recognition and rich content. At the same time, when combined with the LSTM unit, the method can effectively capture the time information of the input image sequence, which plays an important role in providing high-quality drowsiness detection in various situations.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, we proposed a driver drowsiness estimation model based on factorized bilinear feature fusion and a long-short-term recurrent convolutional network to effectively detect driver drowsiness. First, we designed two kinds of CNN, which were used to extract the deep features of the driver’s eyes and mouth and to detect their states. Then, we used the FBFF method to fuse the deep feature representation of the eyes and mouth. Finally, we used the recurrent network LSTM to model the time variation of the drivers’ drowsiness to provide accurate detection of the drivers’ drowsiness under various driving conditions. The experimental results showed that the proposed drowsiness detection framework had good reliability, robustness, and accuracy under various driving conditions.
In future research, we will further optimize the network structure in the proposed framework to improve the operational efficiency of the model without reducing the detection performance. At the same time, we will study a combination of drivers’ facial fatigue features and physiological signals, such as the heart rate, to further improve the accuracy of driver drowsiness detection.
Author Contributions
Methodology, software, and validation: S.C. and W.C.; data curation: W.C.; review, editing, and supervision: S.C., Z.W., and W.C. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant no. ZR2018MEE015).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data was obtained from [Computer Vision Lab, National Tsuing Hua University] and are available [at http://cv.cs.nthu.edu.tw/php/callforpaper/datasets/DDD/] with the permission of [Computer Vision Lab, National Tsuing Hua University].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- He, J.; Choi, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Peng, K. Detection of driver drowsiness using wearable devices: A feasibility study of the proximity sensor. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 65, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, Z.; Mahmoud, M.; Stafford-Fraser, Q.; Robinson, P.; Dias, E.; Skrypchuk, L. Analysis of Yawning Behaviour in Spontaneous Expressions of Drowsy Drivers. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.C.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, Q. Driver drowsiness detection using facial dynamic fusion information and a DBN. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 12, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hua, C.J. Driver fatigue recognition based on facial expression analysis using local binary patterns. Optik 2015, 126, 4501–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Shen, L. A method of detecting driver drowsiness state based on multi-features of face. In Proceedings of the 2012 5th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Chongqing, China, 16–18 October 2012; pp. 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Pan, F.; Kang, S.; Yoo, C.D. Driver Drowsiness Detection System Based on Feature Representation Learning Using Various Deep Networks. In Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; pp. 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, N.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Hou, X.D. Factorized Bilinear Models for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2098–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.R.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.B. Dynamic driver fatigue detection using hidden Markov model in real driving condition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 63, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.G.; Lee, B.L.; Chung, W.Y. Mobile Healthcare for Automatic Driving Sleep-Onset Detection Using Wavelet-Based EEG and Respiration Signals. Sensors 2014, 14, 17915–17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chung, W.Y. Detection of Driver Drowsiness Using Wavelet Analysis of Heart Rate Variability and a Support Vector Machine Classifier. Sensors 2013, 13, 16494–16511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromer, M.; Salb, D.; Walzer, T.; Madrid, N.M.; Seepold, R. ECG sensor for detection of driver’s drowsiness. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 159, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Kodagoda, S.; Lal, S.; Dissanayake, G. Driver Drowsiness Classification Using Fuzzy Wavelet-Packet-Based Feature-Extraction Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, P.M.; Vila, B.J.; Short, R.A.; Mott, C.G.; Dongen, H.P.V. Efficient driver drowsiness detection at moderate levels of drowsiness. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2013, 50, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.M.; Pilcher, J.J.; Switzer, F.S., III. Lane heading difference: An innovative modal for drowsy driving detection using retrospective analysis around curves. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2015, 80, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.S.; Jeong, N.T.; Kim, K.S. Drowsy behavior detection based on driving information. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2016, 17, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lodewijks, G. Detecting fatigue in car drivers and aircraft pilots by using non-invasive measures: The value of differentiation of sleepiness and mental fatigue. J. Saf. Res. 2020, 72, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abtahi, S.; Hariri, B.; Shirmohammadi, S. Driver Drowsiness Monitoring Based on Yawning Detection. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Binjiang, China, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1206–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, K.; Martin, S.; Trivedi, M.M. Looking at Faces in a Vehicle: A Deep CNN Based Approach and Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, I.; Bronte, S.; Bergasa, L.M.; Almazan, J.; Yebes, J. Vision-based drowsiness detector for Real Driving Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposiu, Alcala de Henares, Spain, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Liu, P.X.; Li, D. Vision-Based Fatigue Driving Recognition Method Integrating Heart Rate and Facial Features. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, X.R.; Peeta, S.; He, X.Z.; Li, Y.F. A Real-Time Fatigue Driving Recognition Method Incorporating Contextual Features and Two Fusion Levels. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 3408–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.H.; Wu, R.X. Real-Time Driver-Drowsiness Detection System Using Facial Features. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 118727–118738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, J.; Hendricks, L.A.; Rohrbach, M.; Venugopalan, S.; Guadarrama, S.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Long-Term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition and Description. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhi, O.M.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep face recognition. Proc. BMVC 2015, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, T.H.; Hsu, C.T. MSTN: Multistage Spatial-Temporal Network for Driver Drowsiness Detection. In Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; pp. 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Oh, J.; Lee, H.; Han, B. Learning Transferrable Knowledge for Semantic Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3204–3212. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Jeon, M. Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Condition-Adaptive Representation Learning Framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 4206–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; RoyChowdhury, A.; Maji, S. Bilinear CNN Models for Fine-Grained Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-Level Accuracy with 50× Fewer Parameters and <0.5 MB Model Size. Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=S1xh5sYgx (accessed on 4 November 2016).
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, C.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Lai, S.H. Driver Drowsiness Detection via a Hierarchical Temporal Deep Belief Network. In Proceedings of the 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; pp. 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR 2001, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Erhan, D.; Luc Carrier, P.; Courville, A.; Mirza, M.; Hamner, B.; Bengio, Y. Challenges in representation learning: A report on three machine learning contests. Neural Netw. 2015, 64, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieleman, T.; Hinton, G. Rmsprop: Divide the Gradient by a Running Average of Its Recent Magnitude. Coursera: Neural Networks for Machine Learning; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Yim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Joint Fine-Tuning in Deep Neural Networks for Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2983–2991. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).