Classroom Attendance Systems Based on Bluetooth Low Energy Indoor Positioning Technology for Smart Campus
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We record the attendance of students with their positions in the classroom using our proposed system.
- We store all of the gathered information in a database and display it in a web application each course (including calculations for absence or late attendance, per week, and per term).
2. Related Work
2.1. Class Attendance
2.2. Indoor Location Positioning
2.2.1. Bluetooth Based Indoor Positioning
- Devices with Bluetooth capability are commonplace today, such as mobile phones, smart watches, Bluetooth tags, and smart wearable devices.
- Bluetooth is able to transmit a small amount of data with ultra-low power consumption.
2.2.2. Trilateration
2.2.3. Fingerprinting
3. Materials and Methods
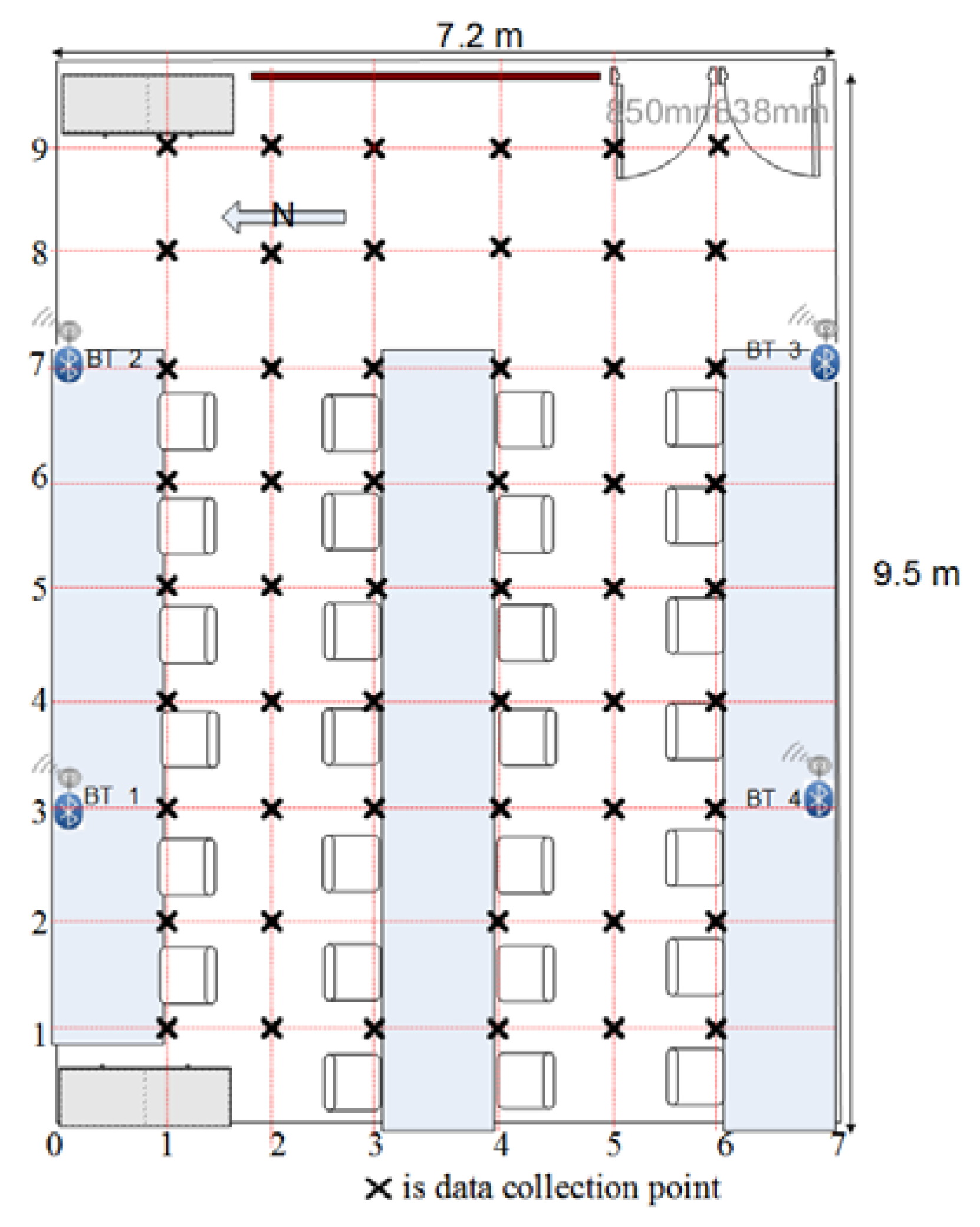
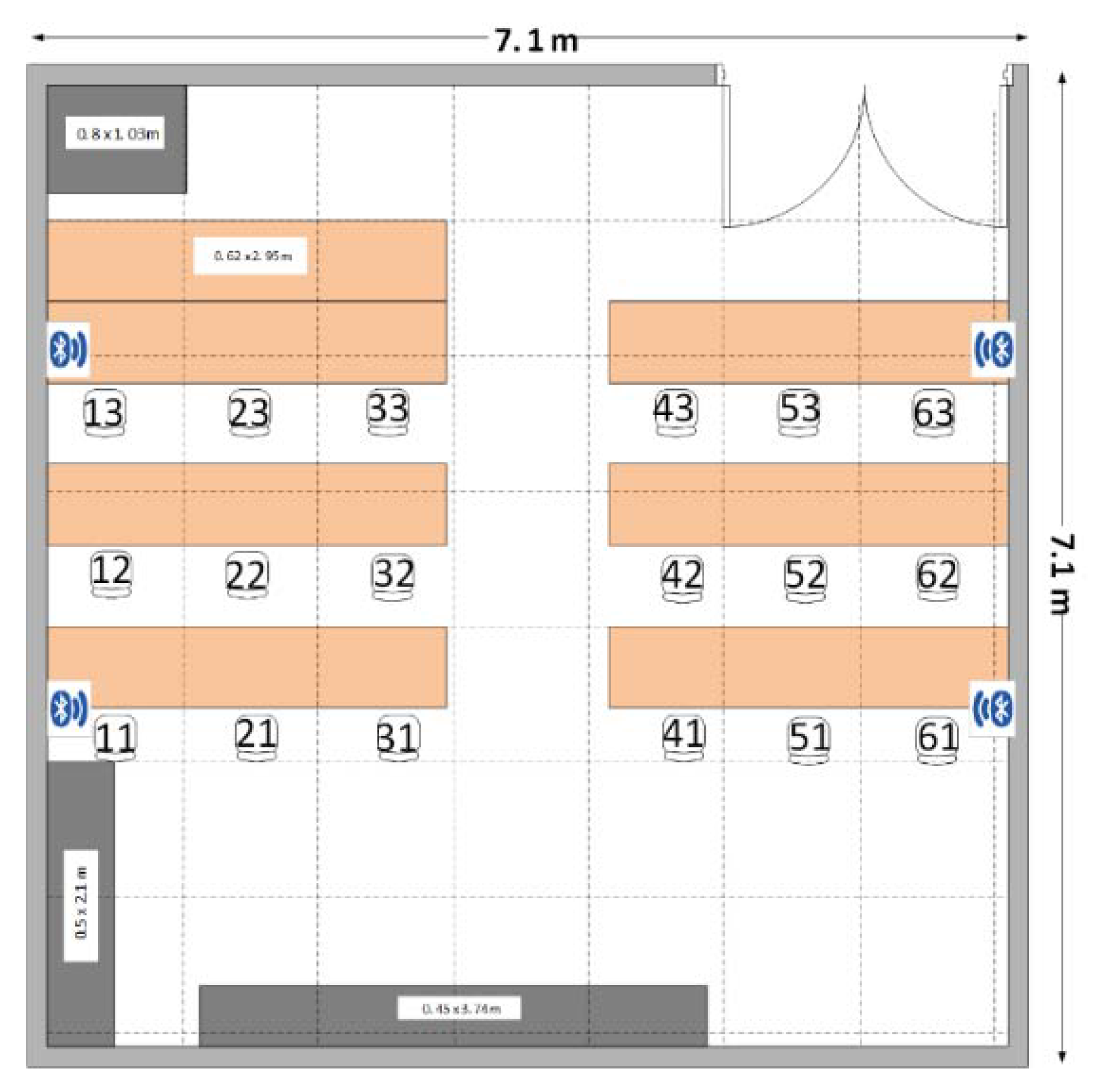
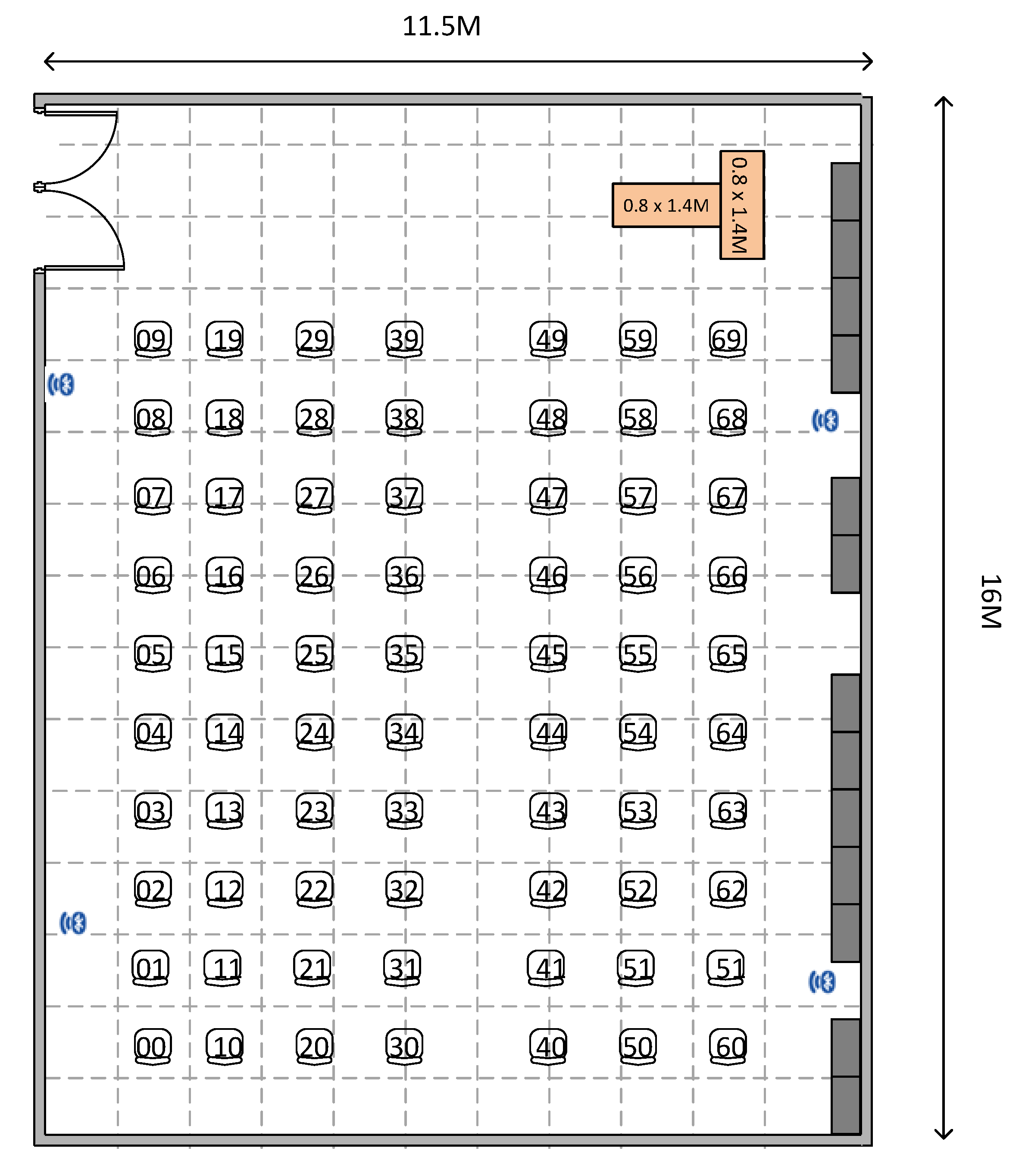
3.1. Experiment Environment
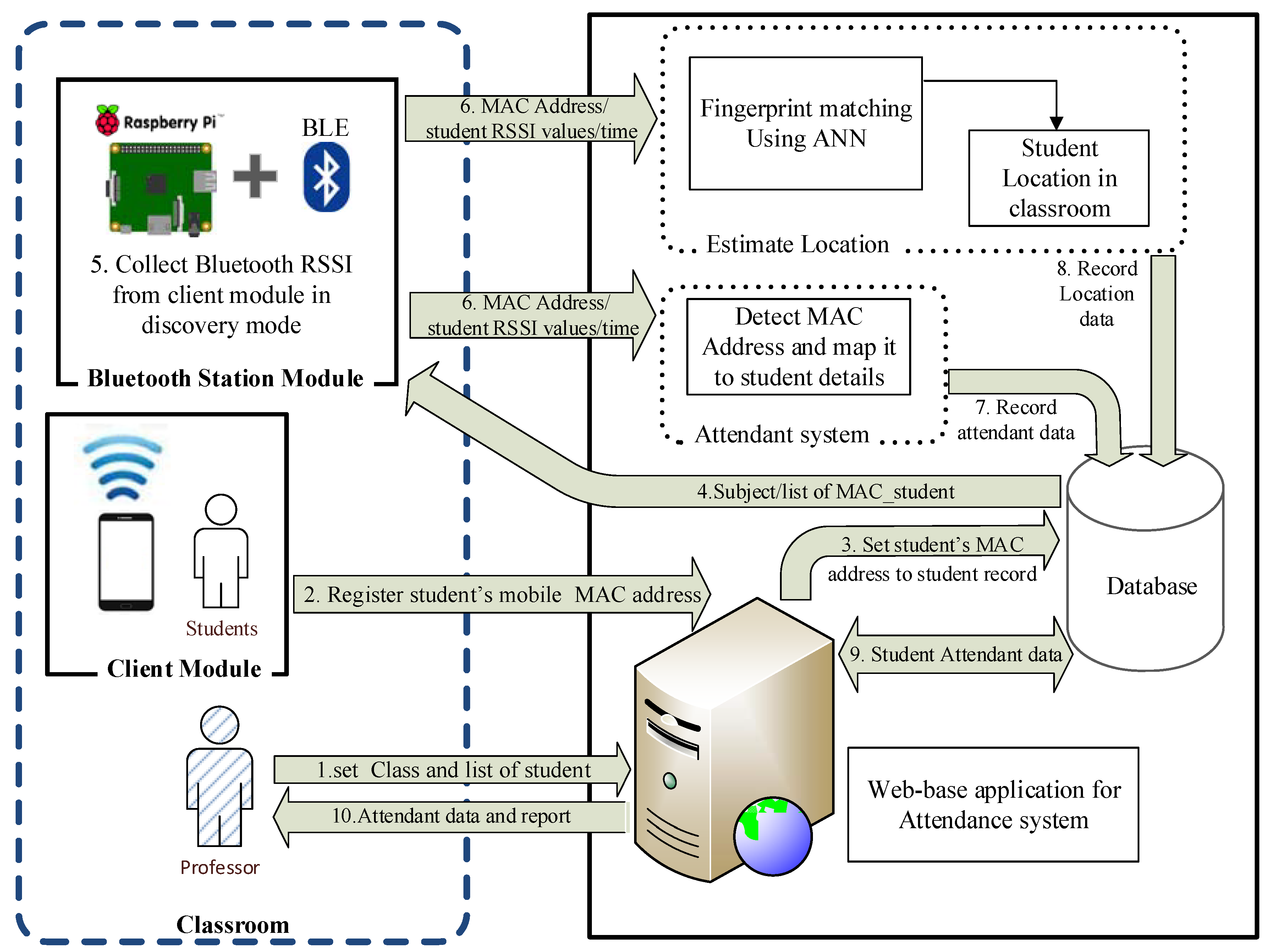
3.2. System Architecture
3.2.1. Server Module
3.2.2. Bluetooth Station Module
3.2.3. Client Module
3.3. Participant
3.4. Student Attendance Mechanism
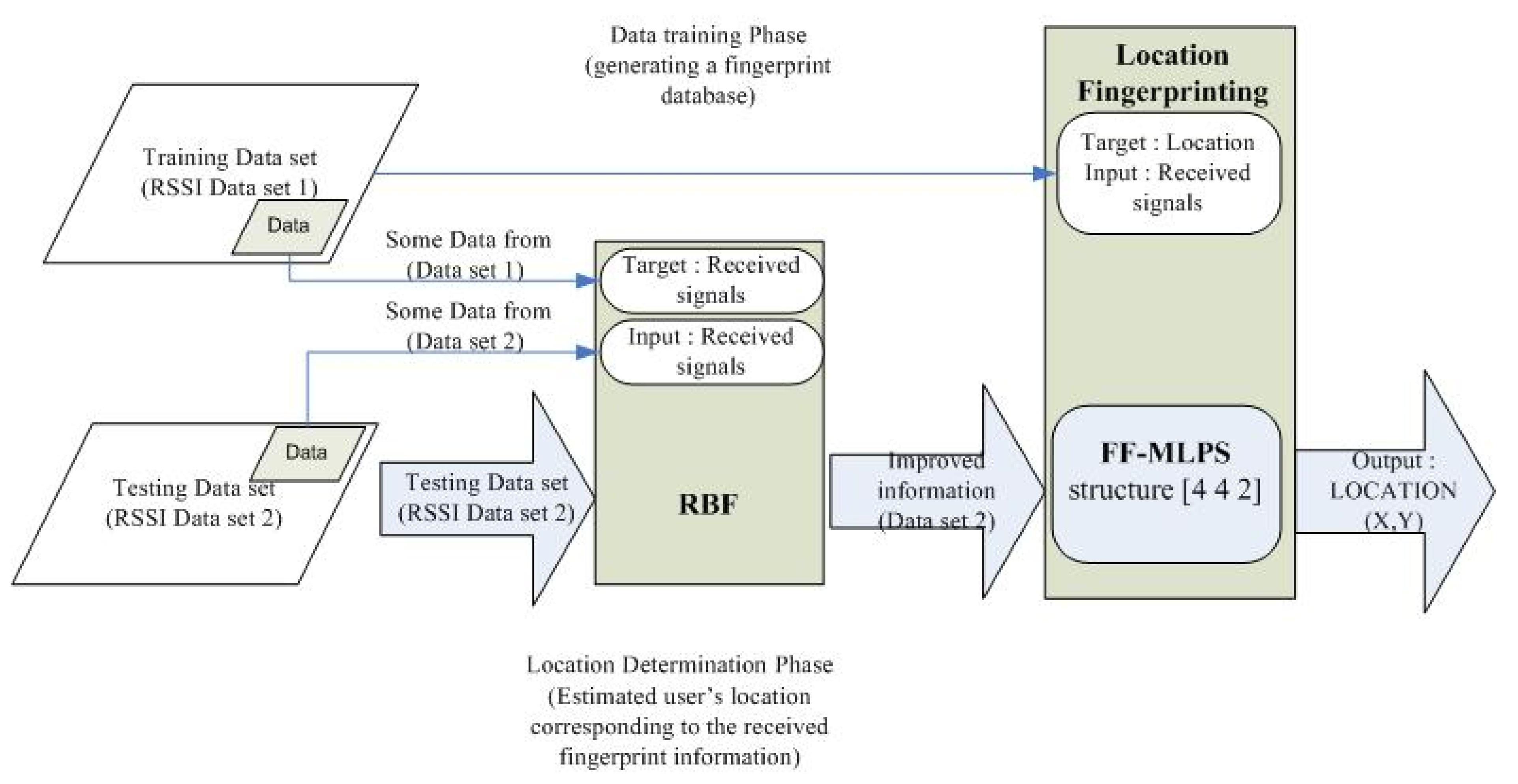
3.5. Location Estimation Framework
3.5.1. Data Collection
- The RSSI data for every point in the experimental site were collected with the four Bluetooth reference nodes.
- At each point, the RSSI was collected by moving the mobile around (the experimenter hold the receiver in front and turns toward north, south, east, and west).
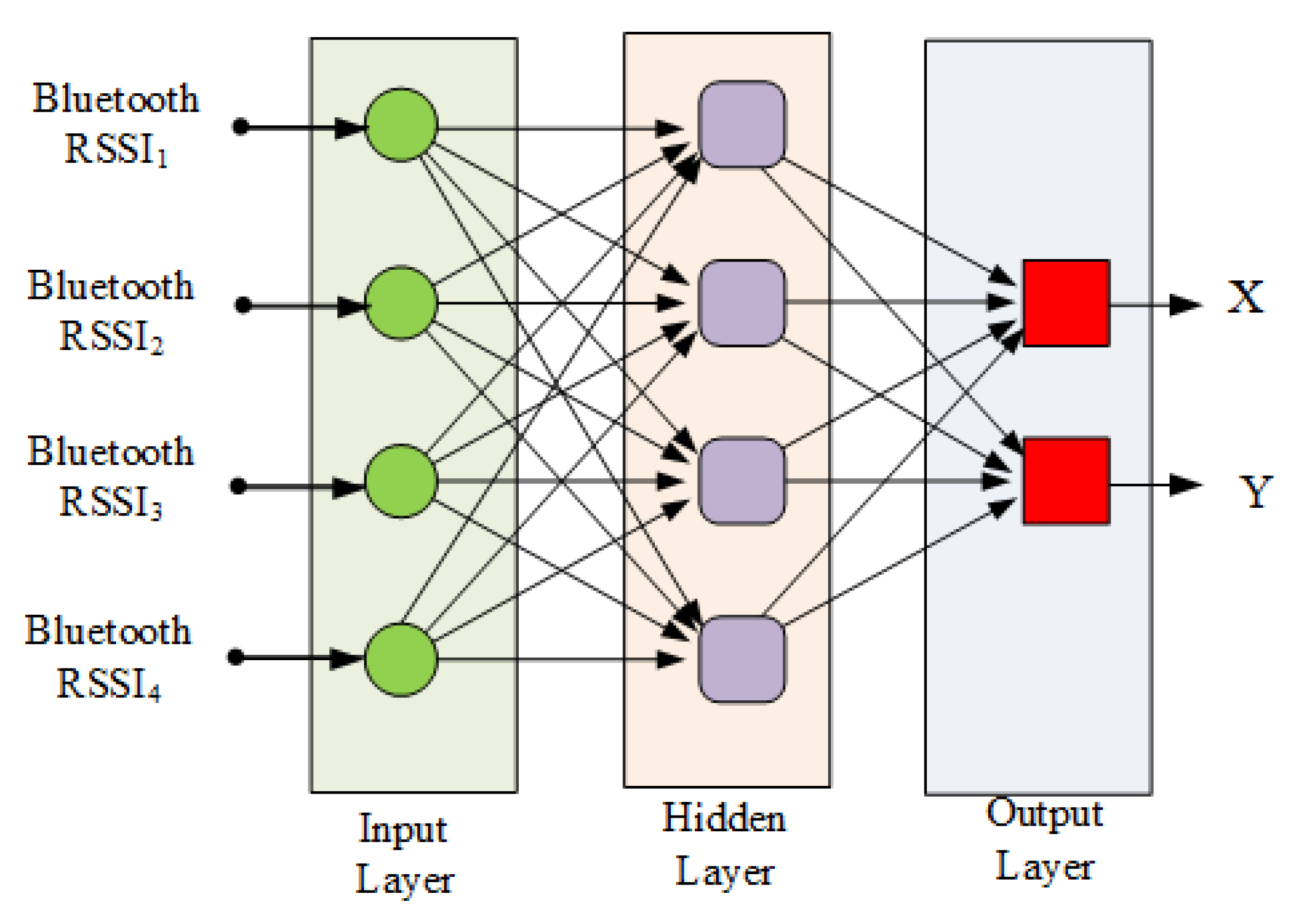
3.5.2. Location Estimation Module Structure
3.6. Database and Web-Based Application for Classroom Attendance Systems
4. Result and Discussion
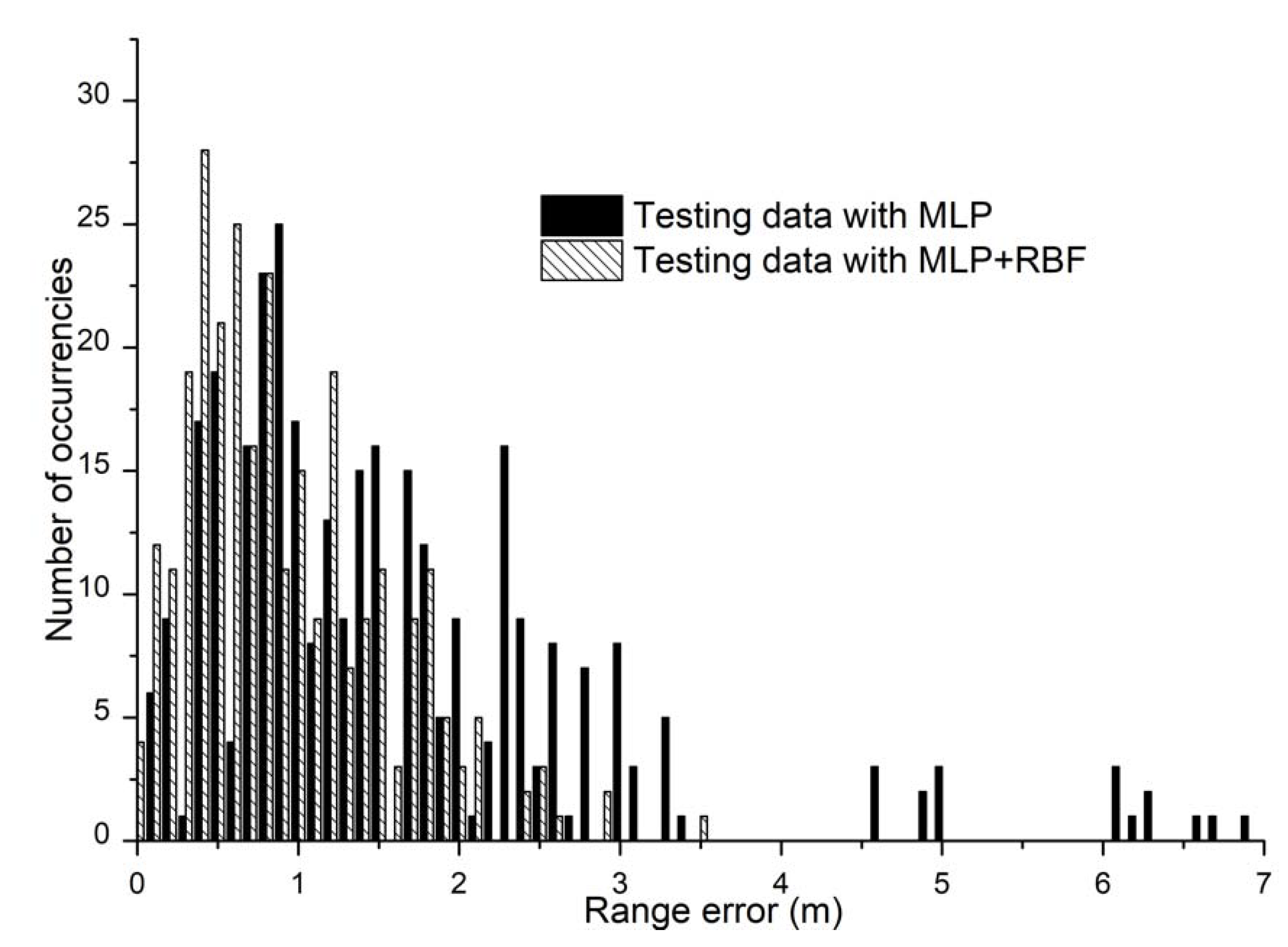
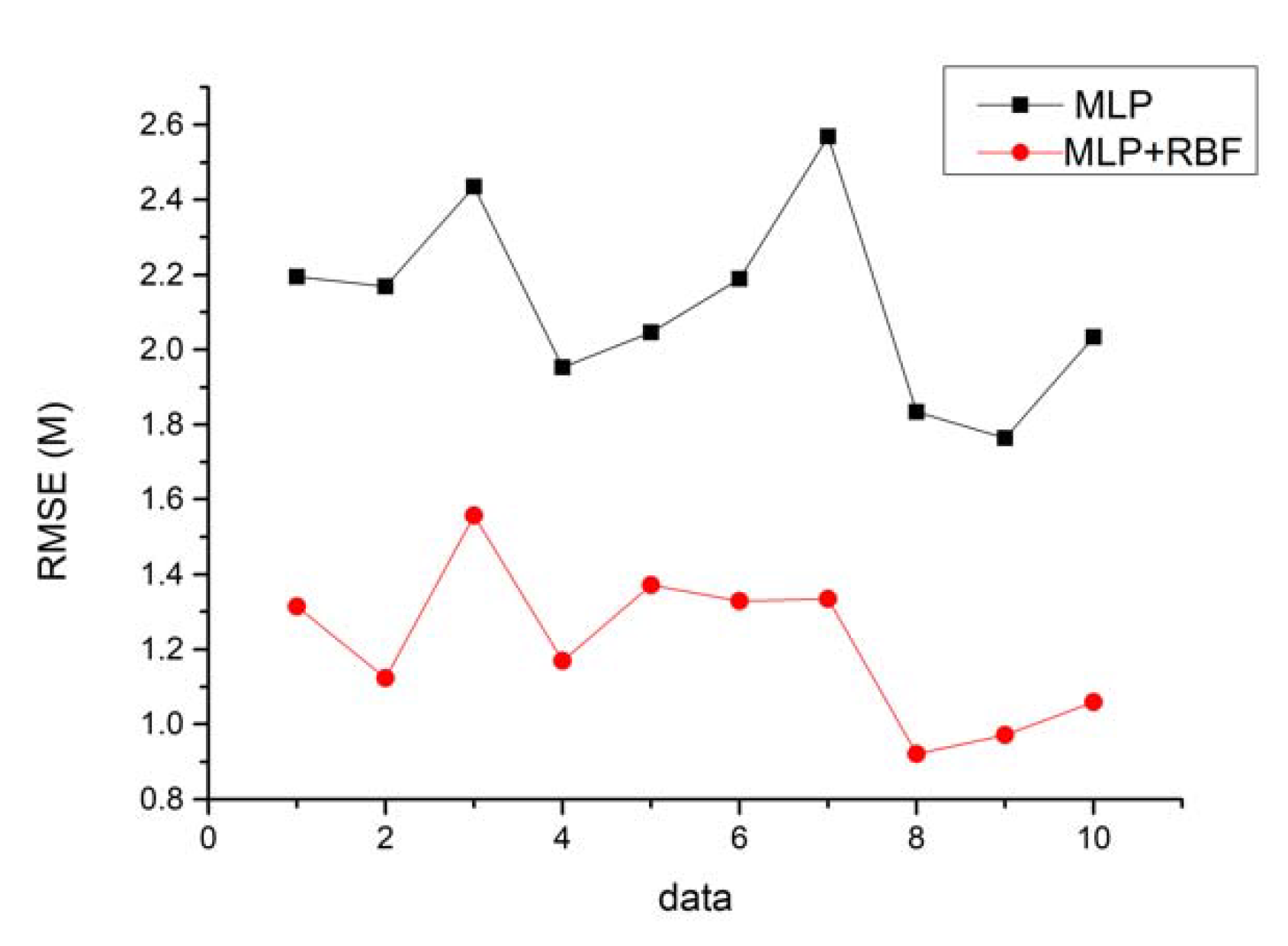
4.1. Results from Location Estimation Framework
4.2. Computation of Student Positioning in Classroom
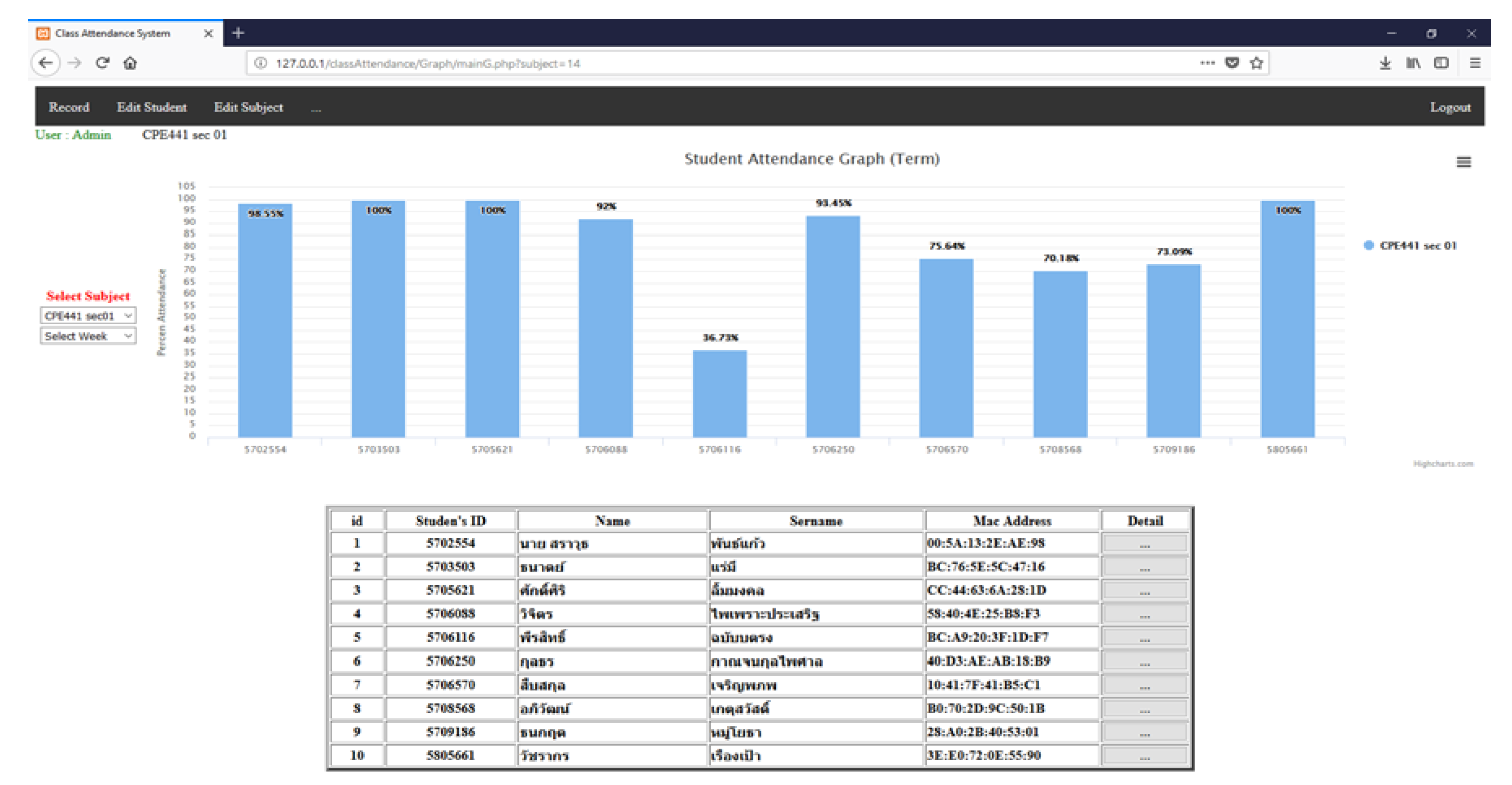
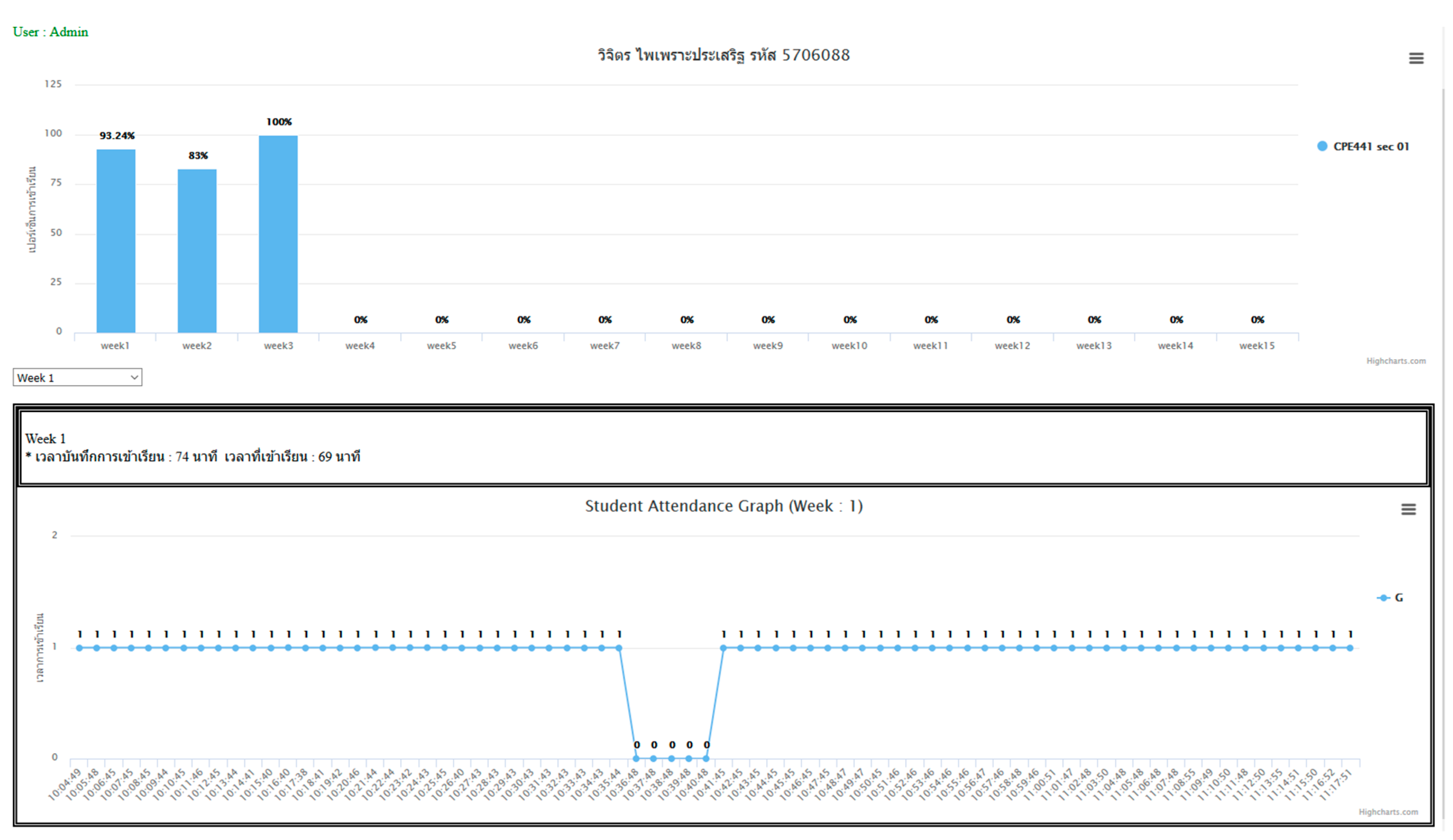
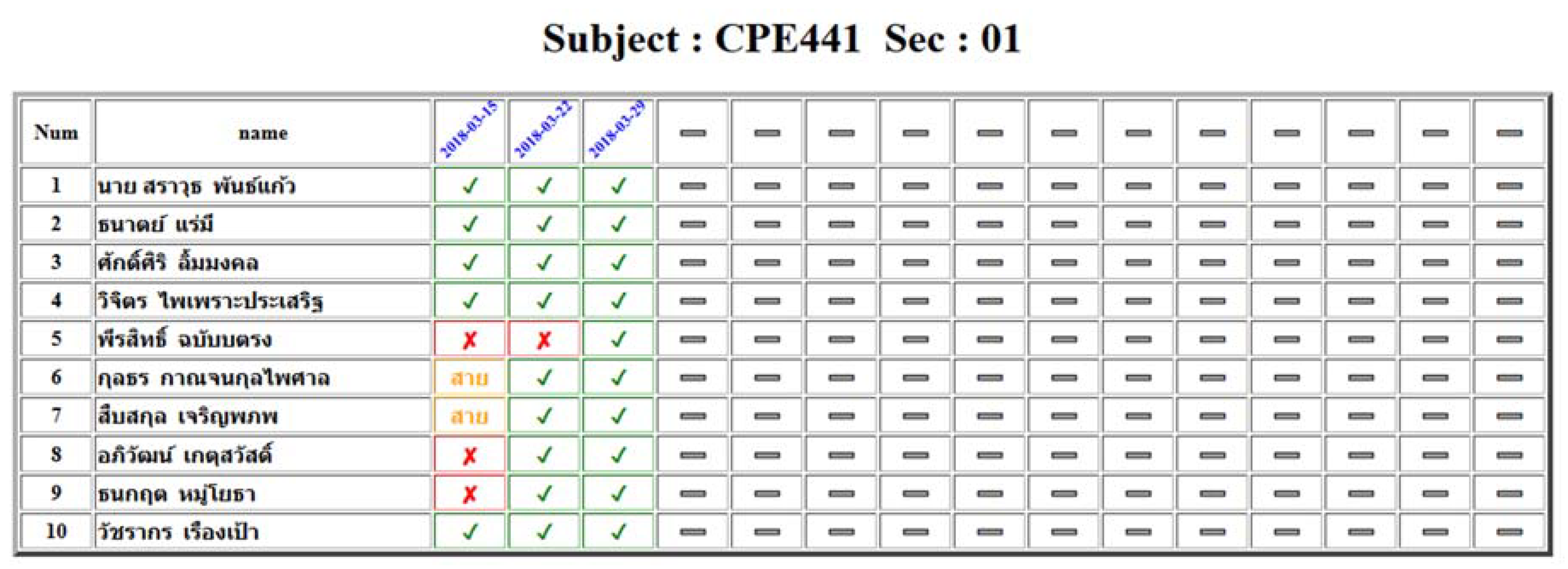
4.3. Web Attendance System Testing
4.4. Cost and Benefit
- the percentage of the classes attended in the semester;
- preference of siting location of each student; and,
- walk-in and walk-out behavior.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raj, R.; Das, A.; Gupta, S.C. Proposal of an efficient approach to attendance monitoring system using Bluetooth. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 10–11 January 2019; pp. 611–614. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, E.; Price, T.; Lloyd, S.; Thomas, S. Improving the quantity and quality of attendance data to enhance student retention. J. Furth. High. Educ. 2005, 29, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, B. The Surveillance of Learning: A Critical Analysis of University Attendance Policies. High. Educ. Q. 2013, 67, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marburger, D.R. Does Mandatory Attendance Improve Student Performance? J. Econ. Educ. 2006, 37, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.; Meeder, L.; Voskuil, V.R. Chronic Student Absenteeism: The Critical Role of School Nurses. NASN Sch. Nurse 2016, 31, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, R. The Effect of Classroom Environment on Student Learning. Honors Thesis, Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, MI, USA, 2013; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, Y.; Varshney, A.; Aggarwal, P.; Matani, K.; Mittal, V. Fingerprint biometric based Access Control and Classroom Attendance Management System. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hoo, S.C.; Ibrahim, H. Biometric-Based Attendance Tracking System for Education Sectors: A Literature Survey on Hardware Requirements. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 7410478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhoseny, H.; Elhoseny, M.; Abdelrazek, S.; Riad, A.M. Evaluating Learners’ Progress in Smart Learning Environment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-64860-6. [Google Scholar]
- De Blasio, G.S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.C.; García, C.R.; Quesada-Arencibia, A. Beacon-Related Parameters of Bluetooth Low Energy: Development of a Semi-Automatic System to Study Their Impact on Indoor Positioning Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Bijlani, K.; Suresh, S.; Praphul, P. Attendance Monitoring in Classroom Using Smartphone & Wi-Fi Fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Eighth International Conference on Technology for Education (T4E), Mumbai, India, 2–4 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tegou, T.; Kalamaras, I.; Tsipouras, M.; Giannakeas, N.; Votis, K.; Tzovaras, D. A Low-Cost Indoor Activity Monitoring System for Detecting Frailty in Older Adults. Sensors 2019, 19, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanca, L. The Effects of Attendance on Academic Performance: Panel Data Evidence for Introductory Microeconomics. J. Econ. Educ. 2006, 37, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.P. Absenteeism and performance in a quantitative module A quantile regression analysis. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2016, 8, 376–389. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, S.; Saquib, S.M.T.; ul Hassan, M.; Junejo, F. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Based Attendance & Assessment System with Wireless Database Records. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar]
- Iio, J. Attendance Management System Using a Mobile Device and a Web Application. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Network-Based Information Systems (NBiS), Ostrava, Czech Republic, 7–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ichimura, T.; Kamada, S. Early Discovery of Chronic Non-attenders by Using NFC Attendance Management System. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Applications (IWCIA 2013), Hiroshima, Japan, 13 July 2013; ISBN 978-1-4673-5725-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mohandes, M.A. Class Attendance Management System Using NFC Mobile Devices. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2017, 23, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, V. Bluetooth Based Attendance Management System. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2013, 3, 227–233. [Google Scholar]
- Lodha, R.; Gupta, S.; Jain, H.; Narula, H. Bluetooth Smart based attendance management system. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 45, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apoorv, R.; Mathur, P. Smart attendance management using Bluetooth Low Energy and Android. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Singapore, 22–25 November 2016; pp. 1048–1052. [Google Scholar]
- What Are Estimote Stickers. Available online: https://community.estimote.com/hc/en-us/articles/203323543-What-are-Estimote-Stickers- (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- Saraswat, G.; Garg, V. Beacon controlled campus surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Jaipur, India, 21–24 September 2016; pp. 2582–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Jacksi, K.; Ibrahim, F.; Zebari, S. Student Attendance Management System. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Topak, F.; Pekeriçli, M.K.; Tanyer, A.M. An Assessment of Bluetooth Low Energy Technology for Indoor Localization. In Proceedings of the International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction—33rd International CIB W78 IT in Construction Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 31 October–2 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, C.; Oller, J.; Paradells, J. Overview and Evaluation of Bluetooth Low Energy: An Emerging Low-Power Wireless Technology. Sensors 2012, 12, 11734–11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiouny, Y.; Arafa, M.; Sarhan, A.M. Enhancing Wi-Fi fingerprinting for indoor positioning system using single multiplicative neuron and PCA algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems (ICCES), Cairo, Egypt, 19–20 December 2017; pp. 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Burgess, T.; Neuner, H.; Fercher, S. Neural Network Based Radio Fingerprint Similarity Measure. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Nantes, France, 24–27 September 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Chair | Deviation in Position Calculation of Chairs(m) | Chair | Deviation in Position Calculation of Chairs(m) | Chair | Deviation in Position Calculation of Chairs(m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | avg | min | max | avg | min | max | avg | |||
| 11 | 0.165 | 1.368 | 0.528 | 31 | 0.140 | 1.114 | 0.534 | 31 | 0.140 | 1.114 | 0.534 |
| 12 | 0.279 | 0.856 | 0.600 | 32 | 0.255 | 1.614 | 0.852 | 32 | 0.255 | 1.614 | 0.852 |
| 13 | 0.539 | 1.722 | 1.253 | 33 | 0.515 | 2.038 | 1.396 | 33 | 0.515 | 2.038 | 1.396 |
| 21 | 0.060 | 1.518 | 0.605 | 41 | 0.384 | 0.849 | 0.578 | 41 | 0.384 | 0.849 | 0.578 |
| 22 | 0.100 | 1.441 | 0.711 | 42 | 0.183 | 2.168 | 0.982 | 42 | 0.183 | 2.168 | 0.982 |
| 23 | 0.641 | 1.934 | 1.171 | 43 | 0.755 | 2.195 | 1.421 | 43 | 0.755 | 2.195 | 1.421 |
| Chair | Deviation in Position Calculation of Chairs(m) | Chair | Deviation in Position Calculation of Chairs(m) | Chair | Deviation in Position Calculation of Chairs(m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min | max | avg | min | max | avg | min | max | avg | |||
| 00 | 2.137 | 3.245 | 2.694 | 25 | 0.567 | 1.054 | 0.803 | 50 | 0.822 | 4.493 | 2.432 |
| 01 | 0.255 | 3.211 | 1.674 | 26 | 0.232 | 1.548 | 1.061 | 51 | 0.716 | 3.669 | 1.632 |
| 02 | 0.516 | 3.583 | 2.411 | 27 | 0.862 | 3.530 | 2.385 | 52 | 1.053 | 4.968 | 2.540 |
| 03 | 0.286 | 2.392 | 1.268 | 28 | 0.161 | 3.469 | 2.127 | 53 | 0.831 | 5.060 | 1.454 |
| 04 | 0.711 | 3.828 | 1.896 | 29 | 0.296 | 1.805 | 0.959 | 54 | 0.854 | 4.015 | 2.142 |
| 05 | 0.452 | 2.841 | 1.528 | 30 | 0.516 | 4.105 | 1.520 | 55 | 0.769 | 3.387 | 1.828 |
| 06 | 0.213 | 2.366 | 1.035 | 31 | 0.341 | 3.570 | 1.758 | 56 | 0.293 | 1.869 | 0.867 |
| 07 | 0.682 | 3.109 | 1.848 | 32 | 0.095 | 3.316 | 1.683 | 57 | 0.699 | 1.419 | 1.069 |
| 08 | 0.836 | 2.971 | 1.672 | 33 | 0.208 | 2.536 | 1.259 | 58 | 0.525 | 2.201 | 1.438 |
| 09 | 0.737 | 2.553 | 1.407 | 34 | 0.398 | 1.776 | 1.282 | 59 | 0.890 | 5.225 | 2.089 |
| 10 | 1.148 | 3.493 | 2.045 | 35 | 0.124 | 1.426 | 0.751 | 60 | 0.324 | 3.536 | 1.144 |
| 11 | 0.847 | 4.268 | 2.602 | 36 | 1.276 | 3.295 | 2.069 | 61 | 0.833 | 1.880 | 1.243 |
| 12 | 0.467 | 2.661 | 1.550 | 37 | 0.207 | 2.886 | 1.590 | 62 | 0.139 | 3.882 | 1.695 |
| 13 | 0.253 | 4.750 | 1.732 | 38 | 0.328 | 2.826 | 1.311 | 63 | 0.535 | 3.939 | 2.211 |
| 14 | 0.692 | 2.019 | 1.427 | 39 | 1.056 | 5.023 | 2.006 | 64 | 1.234 | 3.034 | 1.628 |
| 15 | 0.294 | 2.711 | 1.233 | 40 | 0.247 | 2.061 | 1.277 | 65 | 0.853 | 3.454 | 1.744 |
| 16 | 0.473 | 4.196 | 2.146 | 41 | 0.349 | 3.138 | 1.528 | 66 | 0.626 | 4.989 | 2.223 |
| 17 | 1.685 | 4.771 | 2.132 | 42 | 0.932 | 2.087 | 1.558 | 67 | 0.685 | 3.136 | 1.865 |
| 18 | 0.809 | 3.623 | 1.997 | 43 | 1.423 | 2.697 | 2.108 | 68 | 0.408 | 4.023 | 1.089 |
| 19 | 1.510 | 3.949 | 3.115 | 44 | 0.818 | 4.183 | 2.703 | 69 | 0.460 | 2.956 | 2.079 |
| 20 | 0.367 | 5.148 | 3.469 | 45 | 0.382 | 2.264 | 1.342 | ||||
| 21 | 0.510 | 3.326 | 1.227 | 46 | 0.218 | 2.258 | 1.321 | ||||
| 22 | 0.090 | 1.994 | 0.849 | 47 | 1.457 | 5.106 | 2.677 | ||||
| 23 | 0.393 | 1.782 | 1.005 | 48 | 0.334 | 4.078 | 2.221 | ||||
| 24 | 0.507 | 5.795 | 1.661 | 49 | 1.024 | 3.335 | 2.225 | ||||
| Experiment Area | RMSE | Position Estimation (Euclidean Distance Error) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 m–0.5 m. | 0.5 m–1 m. | 1 m–1.5 m. | >1.5 m. | ||
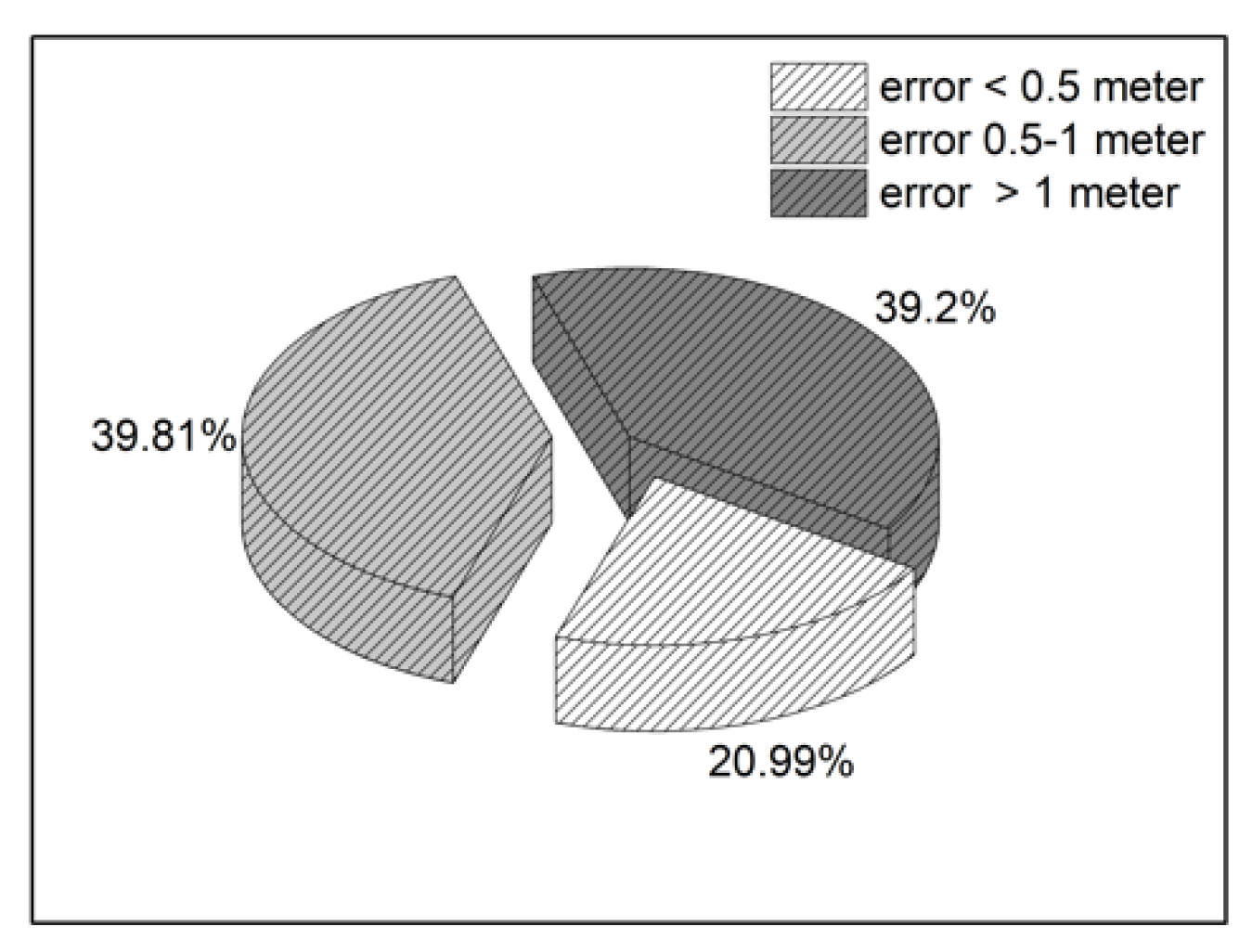
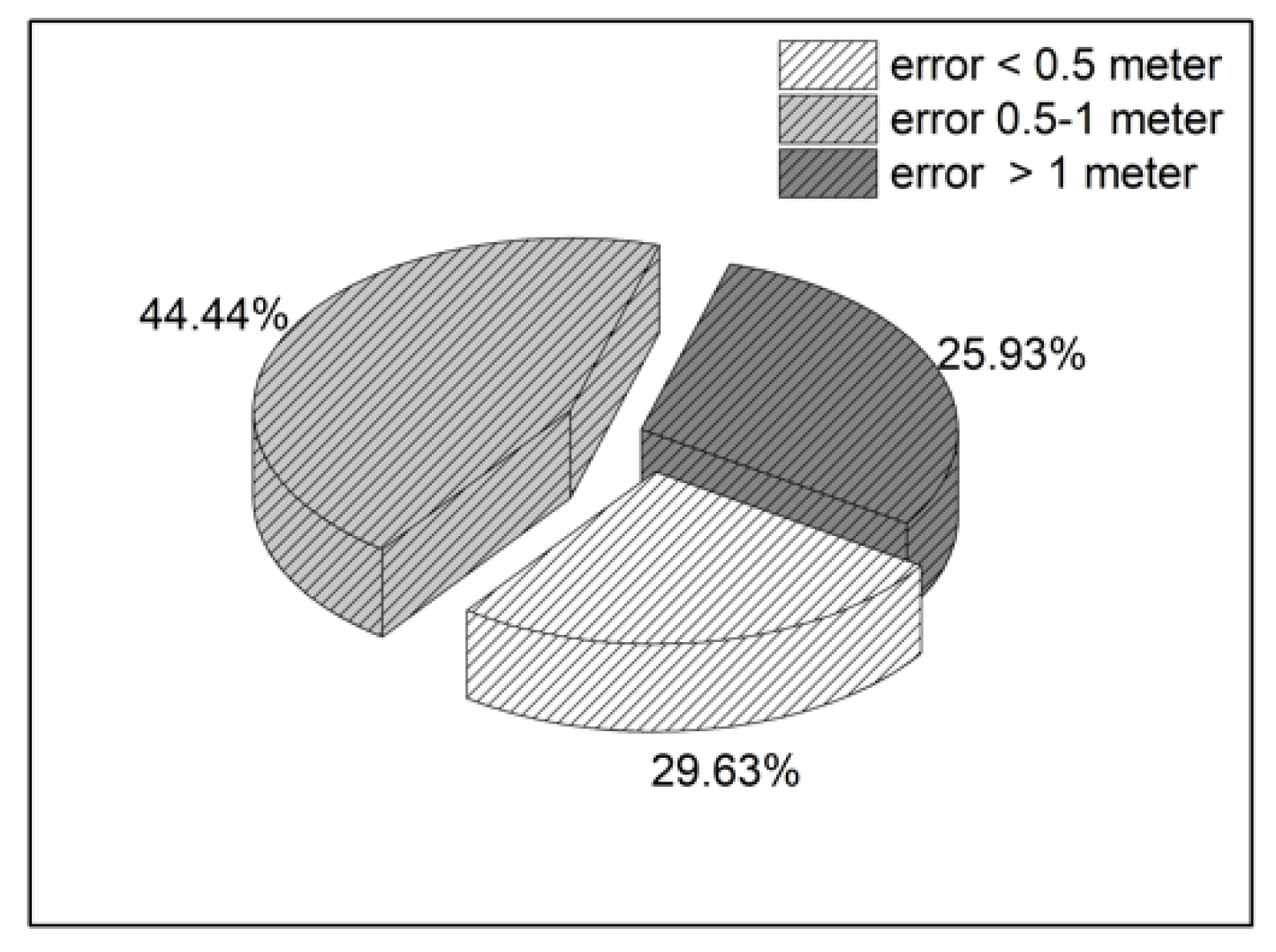
| Classroom type I | 1.2041 | 29.63% | 44.44% | 15.29% | 10.64% |
| Classroom type II | 1.4716 | 30.06% | 42.5% | 12.15% | 15.29% |
| Classroom type III | 2.267 | 21.87% | 26.76% | 21.06% | 29.87% |
| Positioning Technique | Accuracy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| iBeacon [23] | 97 cm highest | Good accuracy and readily available on users’ devices | Not real time, requires extra hardware |
| Indoo.rs [28] | Accuracy from 2 to 5 m. | Fair accuracy and readily available on users’ devices | Accuracy can be improved by adding more beacons and requires fingerprinting |
| FF-MLP and RBF | 72.56% accuracy within tolerances of less than 1 m | Low cost and good accuracy | Not real time, requires fingerprinting |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puckdeevongs, A.; Tripathi, N.K.; Witayangkurn, A.; Saengudomlert, P. Classroom Attendance Systems Based on Bluetooth Low Energy Indoor Positioning Technology for Smart Campus. Information 2020, 11, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11060329
Puckdeevongs A, Tripathi NK, Witayangkurn A, Saengudomlert P. Classroom Attendance Systems Based on Bluetooth Low Energy Indoor Positioning Technology for Smart Campus. Information. 2020; 11(6):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11060329
Chicago/Turabian StylePuckdeevongs, Apiruk, N. K. Tripathi, Apichon Witayangkurn, and Poompat Saengudomlert. 2020. "Classroom Attendance Systems Based on Bluetooth Low Energy Indoor Positioning Technology for Smart Campus" Information 11, no. 6: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11060329
APA StylePuckdeevongs, A., Tripathi, N. K., Witayangkurn, A., & Saengudomlert, P. (2020). Classroom Attendance Systems Based on Bluetooth Low Energy Indoor Positioning Technology for Smart Campus. Information, 11(6), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11060329





