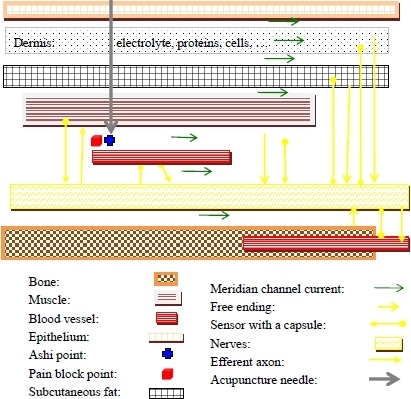
Information Models of Acupuncture Analgesia and Meridian Channels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion


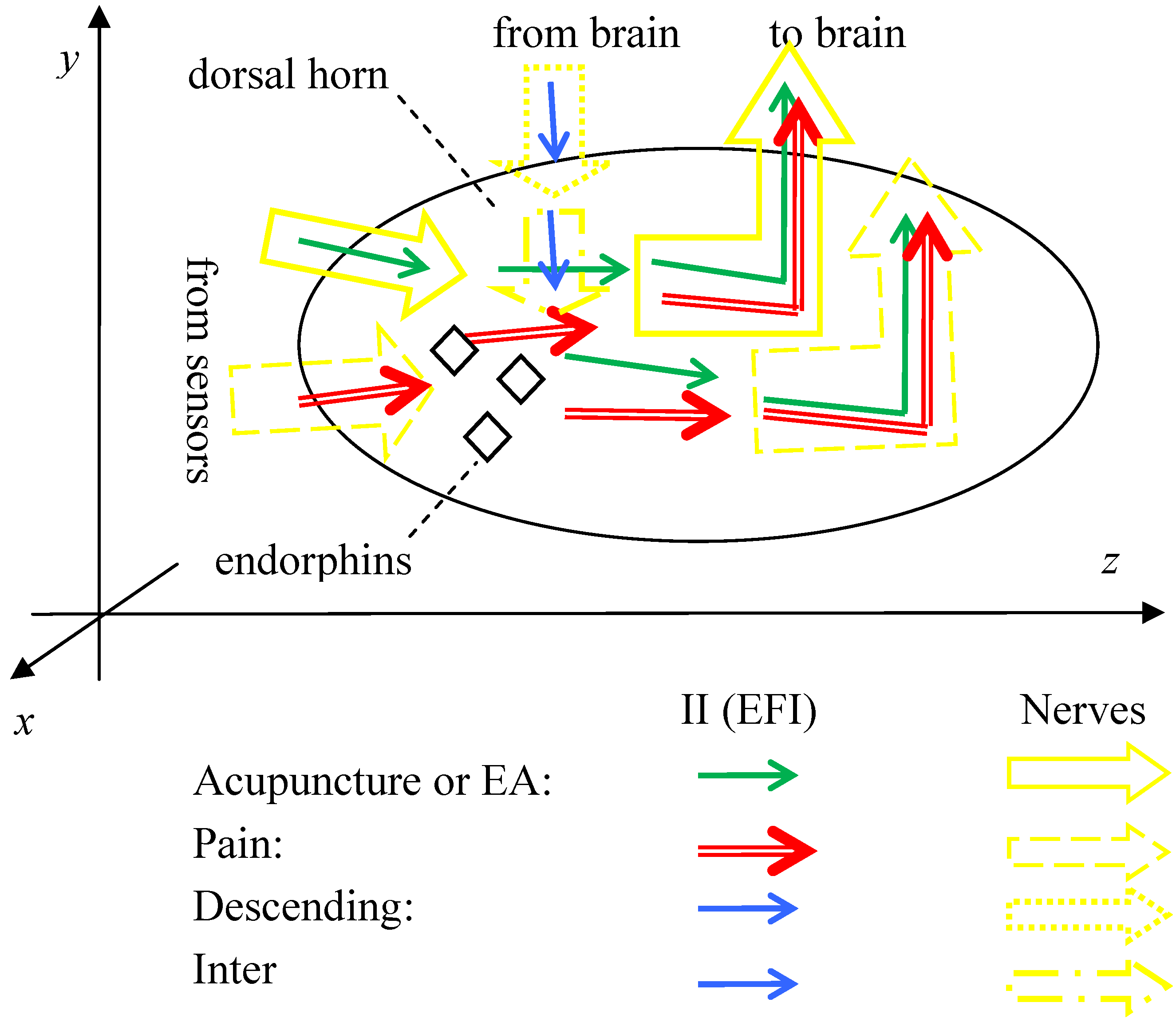

2.1. Information Regulation (Interference) of Frequencies
2.2. Information Regulation of Amplitudes
2.3. Information Regulation of Wave Numbers
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Fung, Y.L. History of Chinese Philosophy; Princeton University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- TaiGu, Z.R. HuangDi’s Internal Classic; Sichuan Science and Technology Publishing House: Chengdu, SiChuan, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, P.C. Probing the mystery of Chinese medicine meridian channels with special emphasis on the connective tissue interstitial fluid system, mechanotransduction, cells durotaxis and mast cell degranulation. Chin. Med. 2009, 4, 10:1-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäcker, M.; Hammes, M.G.; Valet, M.; Deppe, M.; Conrad, B.; Tölle, T.R.; Dobos, G. Different modes of manual acupuncture stimulation differentially modulate cerebral blood flow velocity, arterial blood pressure and heart rate in human subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 333, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Deng, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Effects of electroacupuncture at different frequencies on the nociceptive response and central contents of GABA and Glutamic acid in Arthritic Rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 1993, 18, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Analgesic effects of electroacupuncture stimulation at different intensities and frequencies. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 1993, 18, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Beitz, A.J. The Distribution of brain-stem and spinal cord nuclei associated with different frequencies of electroacupuncture analgesia. Pain 1993, 52, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, M.; Wei, J.; Tan, Z.; Hu, Q.; Tang, J. The influence of electroacupuncture with different frequencies on the discharges of neurons in rostral ventromedial medulla on rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 1996, 21, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Jiang, Y.H.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J.K.; Han, J.S. Endomorphin-1 Meiates 2 Hz but not 100 Hz Electroacupuncture analgesia in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 274, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Kuo, C.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Li, T.C.; Hsieh, C.T.; Lao, C.J.; Lee, C.J.; Li, J.G. Analgesic effect of electric stimulation of peripheral nerves with different electric frequencies using the formalin test. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2000, 28, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attele, A.S.; Mehendale, S.; Guan, X.; Dey, L.; Yuan, C.S. Analgesic effects of different acupoint stimulation frequencies in humans. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2003, 31, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.G.; Liu, F.Y.; Qu, X.X.; Han, J.S.; Wan, Y. Long-term synaptic plasticity in the spinal dorsal horn and its modulation by electroacupuncture in rats with neuropathic pain. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 208, 323–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, T.; Taguchi, R. Effect of varying frequency and duration of electroacupuncture stimulation on Carrageenan-Induced Hyperalgesia. Acupunct. Med. 2007, 25, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.X. Comparison between therapeutic effects of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation with the frequency of 2 Hz and 100 Hz on chronic inflammatory pain in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2001, 21, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bjordal, J.M.; Johnson, M.I.; Ljunggreen, A.E. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) can reduce postoperative analgesic consumption. A meta-analysis with assessment of optimal treatment parameters for postoperative pain. Eur. J. Pain 2003, 7, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.; Yang, H.Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, H. Comparison of analgesic effects of electroacupuncture of multi-factor quantitative parameters on inflammatory pain in rats. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2008, 28, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cherkin, D.C; Sherman, K.J.; Avins, A.L.; Erro, J.H.; Ichikawa, L.; Barlow, W.E.; Delaney, K.; Hawkes, R.; Hamilton, L.; Pressman, A.; Khalsa, P.S.; Deyo, R.A. A randomized trial comparing acupuncture, simulated acupuncture, and usual care for chronic low back pain. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, M.; Müller, H.H.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Basler, H.D.; Schäfer, H.; Maier, C.; Endres, H.G.; Trampisch, H.J.; Molsberger, A. German Acupuncture Trials (GERAC) for chronic low back pain. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuchi, J. Discussion of the relationship between meridians and connective tissues. Nanjing Zhongyi Xueyuan Xuebao 1986, 2, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.J. The relation of connective tissue to meridian. Zhongguo Zhenjiu 1989, 9, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, R.S; Chen, E.Y.; Shen, X.Y.; Zhu, W.J.; Wang, P.J.; Fei, L. Relation of connective tissue to the acupoints of the lung meridian. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi 1997, 16, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, E.Y.; Shen, X.Y.; Dang, R.S.; Cheng, H.S.; Cai, D.H.; He, W.S.; Fei, L. A relationship between connective tissue and accumulation of calcium with points on GB channel below head. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi 1998, 17, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.Y.; Dang, R.S.; Chen, E.Y.; Cheng, H.S.; He, W.Q.; Cai, D.H.; Ding, G.H.; Fei, L. Relation of acupoints of the stomach channel with structure of connective tissue and accumulation of calcium. Zhenci Yanjiu 1998, 10, 595–597. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Cheng, H.S.; Cai, D.H.; Yang, S.X.; Xu, J.R.; Chen, E.Y.; Dang, R.S.; Ding, G.H.; Shen, X.Y.; Tang, Y. Experimental investigation and scientific demonstration of the materialistic foundation of meridians and their functional specialties. Kexue Tongbao 1998, 43, 658–672. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, H.M.; Yandow, J.A. Relationship of acupuncture points and meridians to connective tissue planes. Anat. Rec. 2002, 269, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Yao, D.W.; Tang, L.; Huang, W.H.; Jiao, P.F.; Lu, Y.T.; Dai, J.X.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.Q.; Zhong, S.Z. A study on morphological basis of chinese acupuncture and Moxibustion from digital human body. Jiepou Xuebao 2004, 35, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, K.R. The Best Alternative Medicine; Simon & Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kapit, W.; Macey, R.; Meisami, E. The Physiology Coloring Book, 2nd ed.; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture: Neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004, 361, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.; Berlin, I.; Lee, T.L.; Hee, S.W.; Tan, A.S.W.; Picard, D.; Han, J.S. A standardized transcutaneous electric acupoint stimulation for relieving tobacco urges in dependent smokers. eCAM 2009, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stux, G.; Berman, B.; Pomeranz, B.; Kofen, P.; Sahm, K.A. Basics of Acupuncture, 5th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Zou, C.H. Informatics and physics models of recognitions of DNA replication and their biomedical applications. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 3, 2059–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, K.; Zou, C.H. Biomedicine and informatics model of Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 3, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Zou, C.H. BioInfoPhysics models of neuronal signal processes based on theories of electromagnetic fields. Am. J. Neurosci. 2010, 1, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Zou, C.H. A logarithmic spiral function to plot a Cochleaogram. Trends. Med. Res. 2008, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, K.; Zou, C.H. Four dimensional BioChemInfoPhysics models of cardiac cellular and sub-cellular vibrations (oscillations). Online J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 9, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, H. XML: The Complete Reference; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, M.H.; Pawlina, W. Histology: A Text and Atlas: With Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McCann, S.; Tillotson, J.; Reichert, S.E. Anatomy Coloring Book, 3rd ed.; Kaplan Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, D. Neuroscience, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Tarjan, P.P.; Mertz, P.M. Electrical conductivities of pig skin dermis and subcutaneous fat with rectangular pulsed electrical current. Bioelectromagnetics 1996, 17, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, C.; Peyman, A.; Grant, E.H. Electrical conductivity of tissue at frequencies below 1 MHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 4863–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Tarjan, P.P; Mertz, P.M. In vivo electrical potential and three dimensional electrical fields in pig skin with rectangular pulsed electrical current stimulation. Bioelectromagnetics 1996, 17, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Mertz, P.M.; Tarjan, P.P. Theoretical study of Rectangular Pulse Electrical Stimulation (RPES) on skin cells (in vivo) under conforming electrodes. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 29, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K. A biomechanical model of electroporation of a biological membrane. In Proceedings of 16th Southern Biomedical Engineering Conference, Broadwater Beach Resort, Bilaxi, MS, USA, 4–6 April, 1997; Bumgardner, J.D., Puckett, A.A., Eds.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Tarjan, P.P.; Zou, C.H. Schrodinger equation, Maxwell-Bolzmann distribution and single channel current. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 29, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K. Improved 3-D quantum mechanical models of ion movements in a cylindrical ion-channel. In Proceedings of 16th Southern Biomedical Engineering Conference, Broadwater Beach Resort, Bilaxi, Mississippi, USA, 4–6 April, 1997; Bumgardner, J.D., Puckett, A.A., Eds.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1997; pp. 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, F.S. Interaction of DC electric fields with living matter. In CRC Handbook of Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields; Polk, C., Postow, E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen, K.; Ainsworth, M.; Steenholdt, C.; Thomsen, O.Ø.; Brynskov, J. Individual medicine in inflammatory bowel disease: Monitoring Bioavailability, Pharmacokinetics and Immunogenicity of Anti-tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha Antibodies. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture research is part of my life. Am. Acad. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, A.G.; Trodella, L.; Valentini, V.; Barbi, S.; Macchia, G.; Mantini, G.; Turriziani, A.; Cellini, N. Pain relief with short-term irradiation in locally advanced Carcinoma of the Pancreas. J. Palliat. Care 2003, 19, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kenny, D.T.; Faunce, G. The impact of group singing on mood, coping, and perceived pain in chronic pain patients attending a multidisciplinary pain clinic. J. Music Ther. 2004, 41, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Weelden, K.; Cevasco, A.M. Recognition of geriatric popular song repertoire: a comparison of geriatric clients and music therapy students. J. Music Ther. 2010, 47, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, M.J. The effect of pitch, rhythm, and familiarity on working memory and anxiety as measured by digit recall performance. J. Music Ther. 2010, 47, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulehan, J. Poetry therapy. Patient Educ. Couns. 2010, 81, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, K.; Zou, C.H. Information Models of Acupuncture Analgesia and Meridian Channels. Information 2010, 1, 153-168. https://doi.org/10.3390/info1020153
Cheng K, Zou CH. Information Models of Acupuncture Analgesia and Meridian Channels. Information. 2010; 1(2):153-168. https://doi.org/10.3390/info1020153
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Kang, and Chang Hua Zou. 2010. "Information Models of Acupuncture Analgesia and Meridian Channels" Information 1, no. 2: 153-168. https://doi.org/10.3390/info1020153
APA StyleCheng, K., & Zou, C. H. (2010). Information Models of Acupuncture Analgesia and Meridian Channels. Information, 1(2), 153-168. https://doi.org/10.3390/info1020153