An Acoustic Treatment to Mitigate the Effects of the Apple Snail on Agriculture and Natural Ecosystems
Abstract
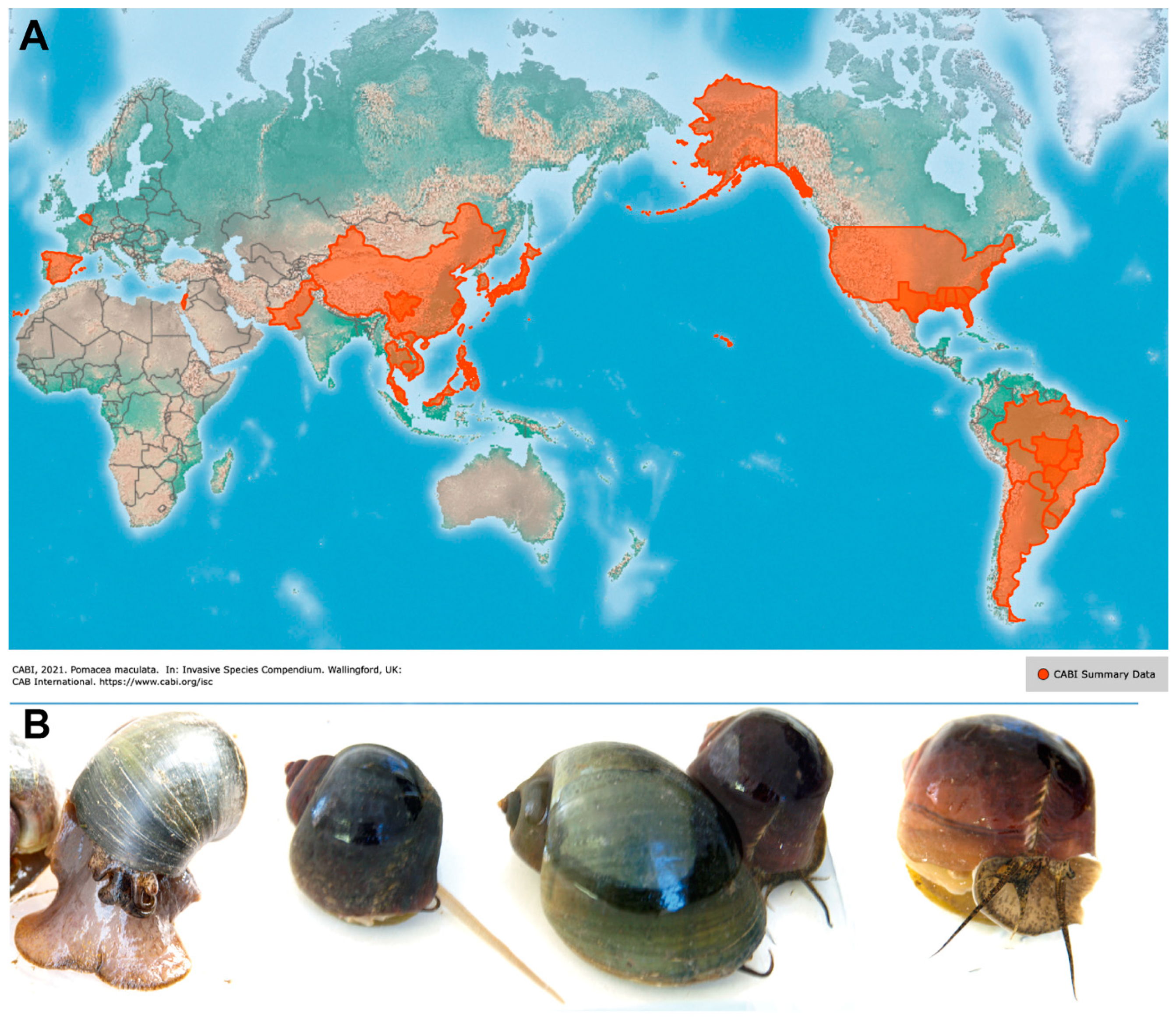
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
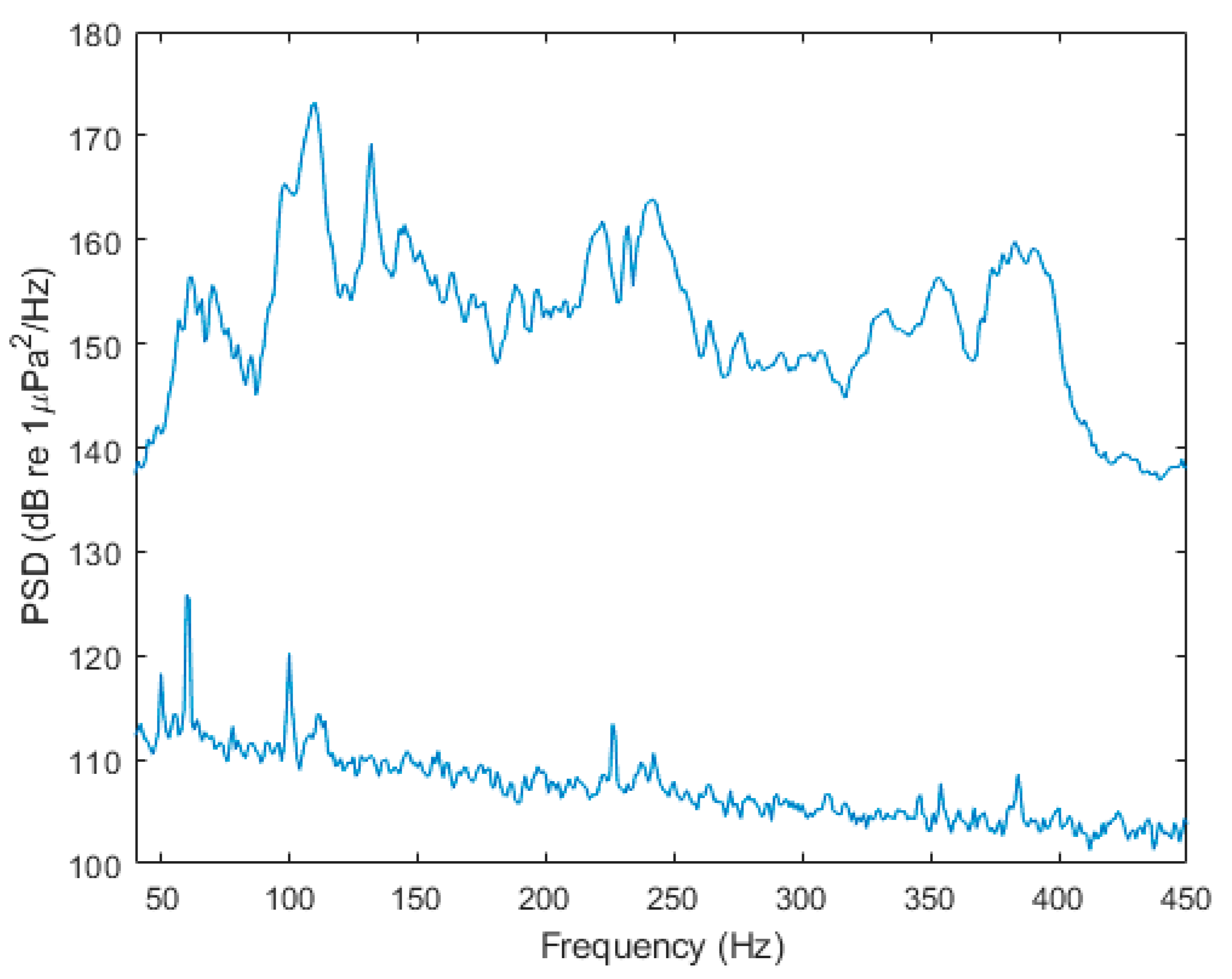
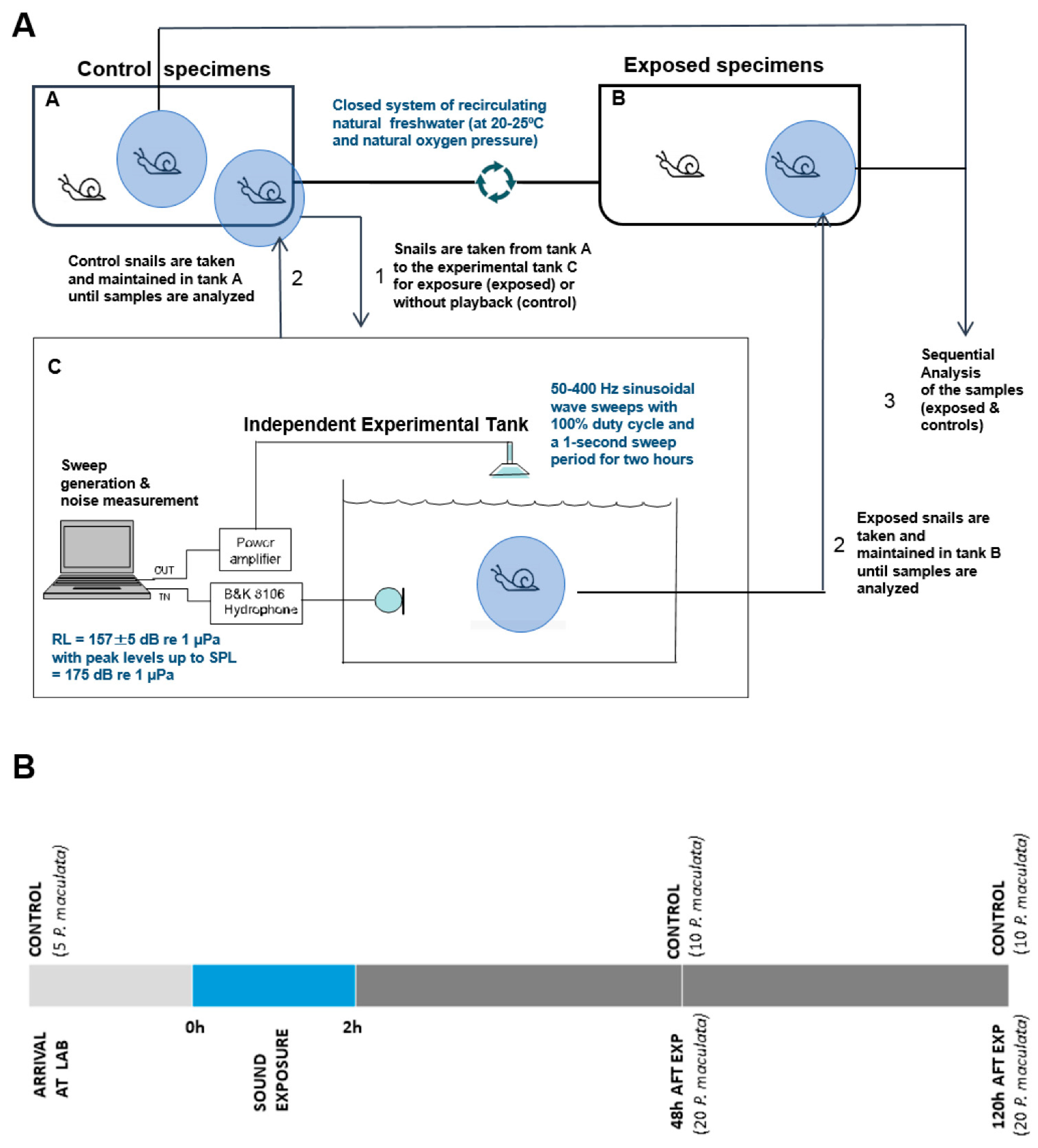
2.1. Sound Exposure Protocol
2.2. Removal of Statocysts
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
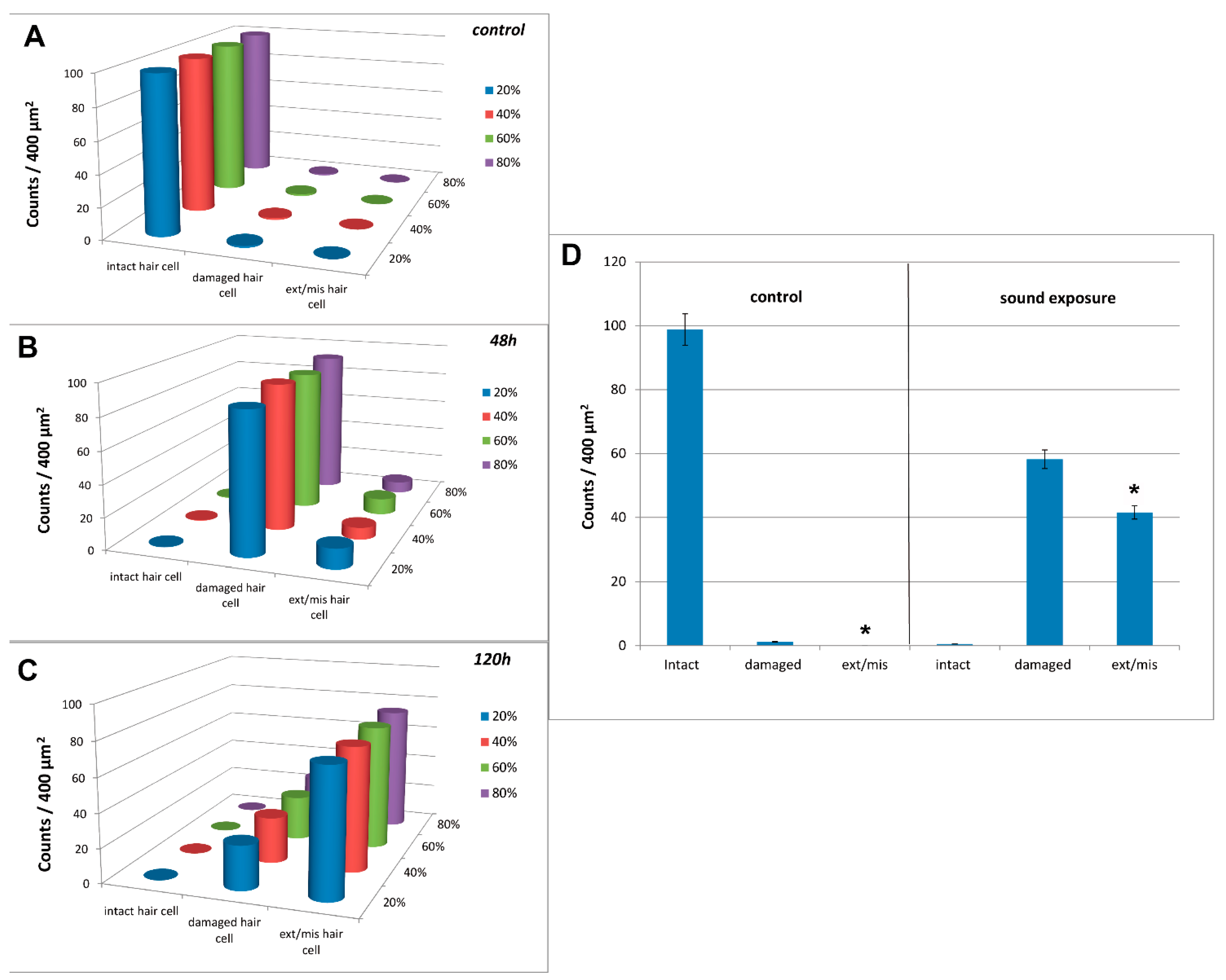
2.4. Quantification and Data Analysis
3. Results
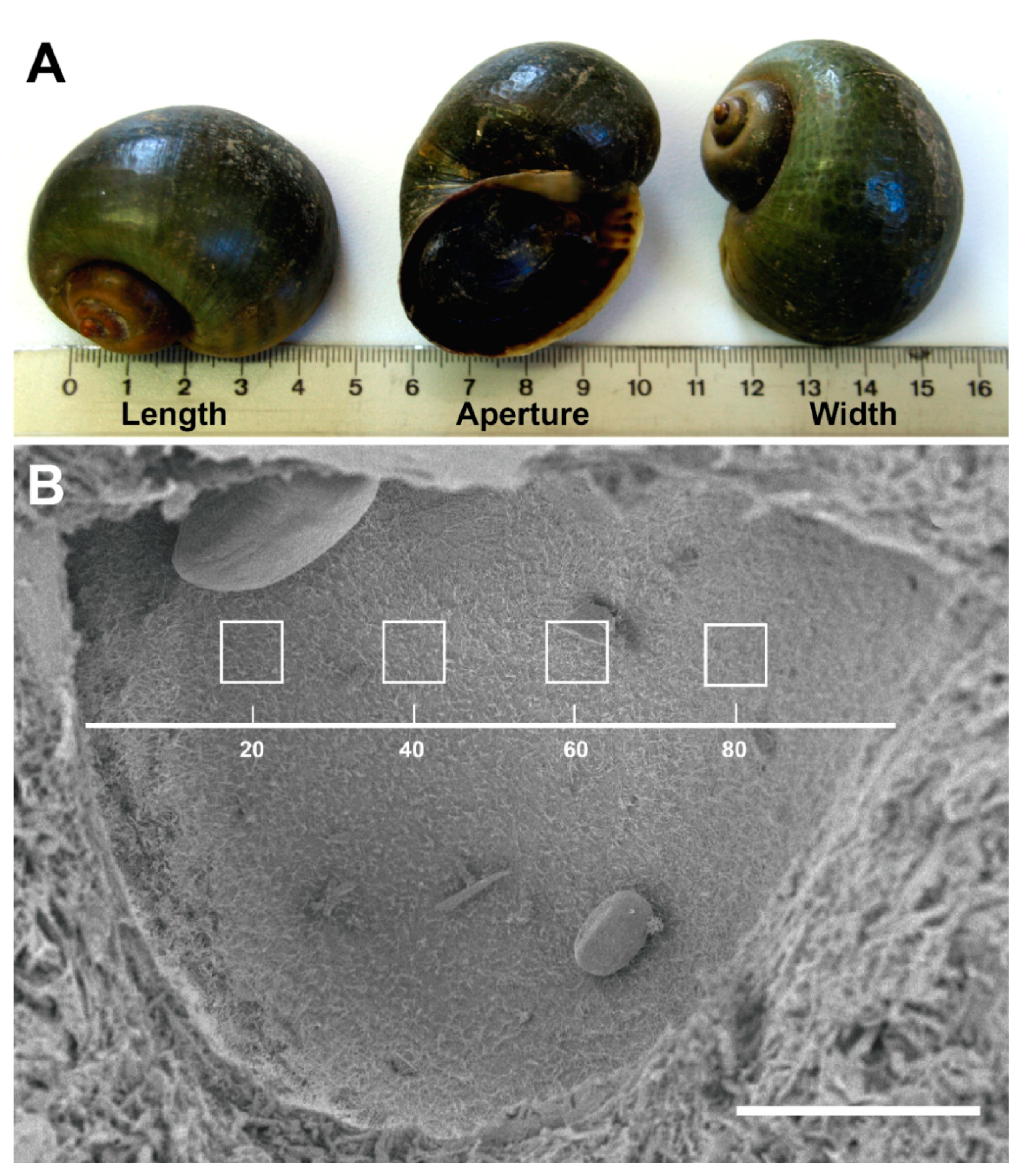
3.1. P. maculata Statocyst Morphology
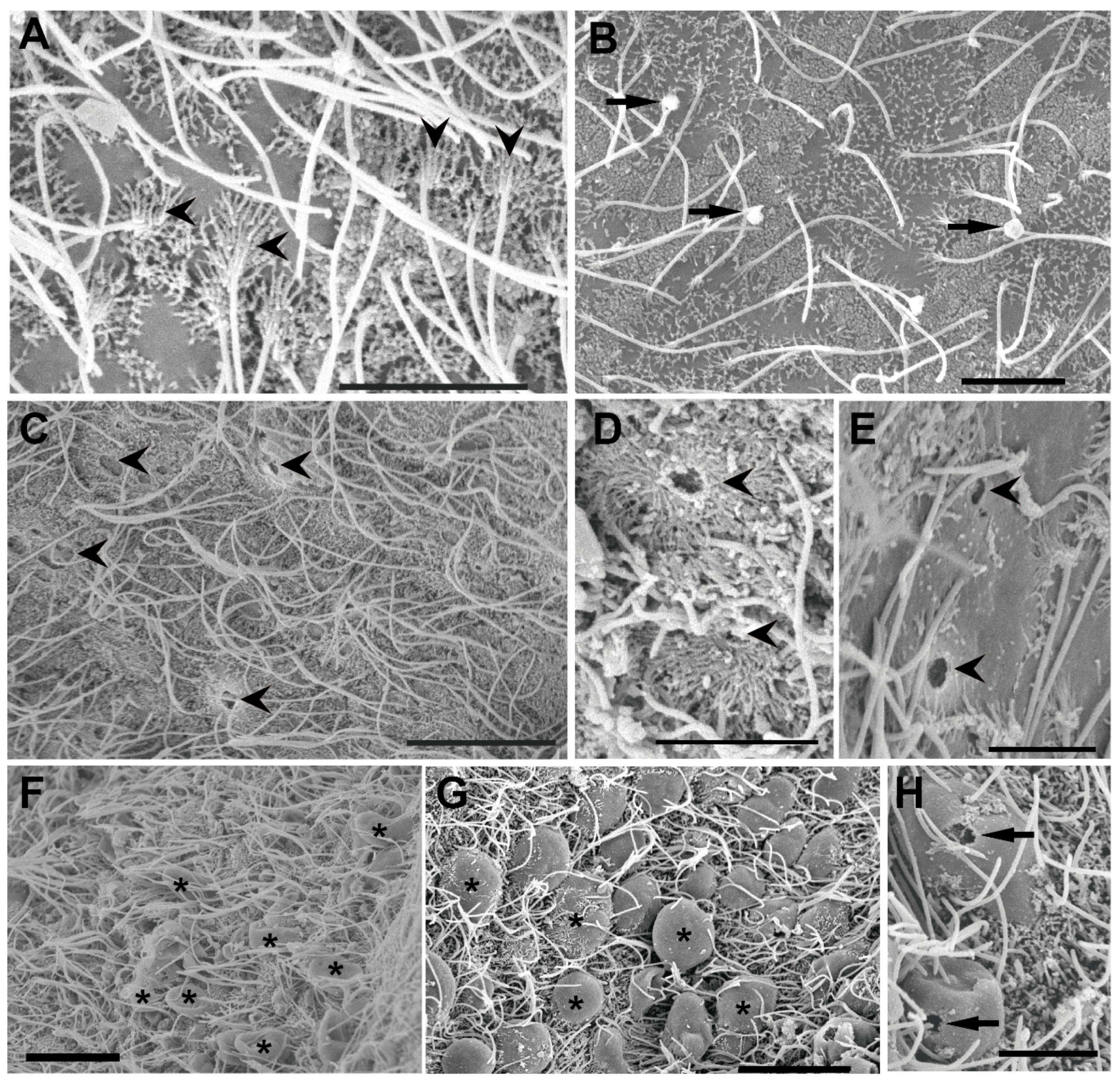
3.2. Ultrastructural Analysis of the Statocyst Sensory Epithelium
3.3. Image and Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Patent
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarke, B.; Murray, J.; Johnson, M.S. The extinction of endemic species by a program of biological control. Pac. Sci. 1984, 38, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Savidge, J.A. Extinction of an Island Forest Avifauna by an Introduced Snake. Ecology 1987, 68, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.; Thébault, E.; Anneville, O.; Duyck, P.-F.; Chapuis, E.; Loeuille, N. Impacts of Invasive Species on Food Webs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiana, N.; Lurgi, M.; Montoya, J.M.; López, B.C. Invasions cause biodiversity loss and community simplification in vertebrate food webs. Oikos 2014, 123, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahel, F.J.; Olden, J. Assessing the Effects of Climate Change on Aquatic Invasive Species. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Fordham, R.K.; Burks, R.L.; Hand, J.J. Fecundity of the exotic applesnail, Pomacea insularum. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, T.A.; Hayes, K.A.; Cowie, R.H.; Collins, T.M. The identity, distribution, and impacts of non-native apple snails in the continental United States. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CABI. Pomacea maculata. In Invasive Species Compendium; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/116486#toDistributionMaps (accessed on 24 August 2021).
- Naylor, R. Invasions in agriculture: Assessing the cost of the golden apple snail in Asia. Ambio 1996, 25, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.-B.; Wu, Z.-D.; Lun, Z.-R. The Apple Snail Pomacea canaliculata, A Novel Vector of the Rat Lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis: Its Introduction, Spread, and Control in China. Hawai'i. J. Med. Public Health J. Asia Pac. Med. Public Health 2013, 72, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.W.; Bayha, K.M.; Valentine, J.F. Establishment of the Invasive Island Apple Snail Pomacea insularum (Gastropoda: Ampullaridae) and Eradication Efforts in Mobile, Alabama, USA. Gulf Mexico Sci. 2012, 1–2, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel, E.; Plh, H.; Baker, R.; Candresse, T.; Simon, E.D.; Gilioli, G.; Grégoire, J.; Puglia, P.; Rafoss, T.; Rossi, V.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the evaluation of the pest risk analysis on Pomacea insularum, the island apple snail, prepared by the Spanish Ministry of Environment and Rural and Marine Affairs. EFSA J. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.A.; Joshi, R.C.; Thiengo, S.; Cowie, R.H. Out of South America: Multiple origins of non-native apple snails in Asia. Divers. Distrib. 2008, 14, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, U.; Dayan, T.; Simberloff, D.; Mienis, H.K. Non-indigenous land and freshwater gastropods in Israel. Biol. Invasions 2008, 11, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, P.; Cowie, R.; Taylor, J.; Hayes, K.; Burnett, K.; CA, F. Apple snail invasions and the slow road to control: Ecological, economic, agricultural, and cultural perspectives in Hawaii. In Global Advances in Ecology and Management of Golden Apple Snails; Joshi, R.C., Sebastian, L.S., Eds.; Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice): Los Baños, Philippines, 2006; pp. 325–335. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, W.E.; Hay, M.E. Herbivore Preference for Native vs. Exotic Plants: Generalist Herbivores from Multiple Continents Prefer Exotic Plants That Are Evolutionarily Naïve. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowie, R. Apple snails (Ampullariidae) as agricultural pests: Their biology, impacts and management. In Molluscs as Crop Pests; Barker, G.M., Ed.; CABI: Los Baños, Philippines, 2002; pp. 145–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, V. Salinity, pH, Temperature, Desiccation and Hypoxia Tolerance in the Invasive Freshwater Apple Snail Pomacea insularum. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, N.; Kestrup, Å.; Mårtensson, M.; Nyström, P. Lethal and non-lethal effects of multiple indigenous predators on the invasive golden apple snail (Pomacea canaliculata). Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren GL Nonindigenous freshwater invertebrates. In Strangers in Paradise; Simberloff, D.; Schmitz, D.C.; Brown, T.C. (Eds.) Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, T.S.; Anurakpongsatorn, P.; Chaichana, R.; Mahujchariyawong, J.; Satapanajaru, T. Heavy Predation on Freshwater Bryozoans by the Golden Apple Snail, Pomacea canaliculata Lamarck, 1822 (Ampullariidae). Nat. Hist. J. Chulalongkorn Univ. 2006, 6, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, N.O.L.; Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L.-A. Invading herbivory: The golden apple snail alters ecosystem functioning in asian wetlands. Ecology 2004, 85, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cattau, C.E.; Martin, J.; Kitchens, W.M. Effects of an exotic prey species on a native specialist: Example of the snail kite. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, M.; Islam, Z.; Heong, K.; Joshi, R. Ants in tropical irrigated rice: Distribution and abundance, especially of Solenopsis geminata (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bull. Èntomol. Res. 1998, 88, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Departament D’agricultura Alimentació i Acció Rural. Generalitat de Catalunya Ordre AAR/404/2010, de 27 de Juliol, per la Qual es Declara Oficialment l’existència d’un Focus del Cargol Poma (Pomacea sp.) A L’hemidelta Esquerra del Delta de l’Ebre; DOGC: Catalonia, Spain, 2010; Available online: https://portaljuridic.gencat.cat/eli/es-ct/o/2010/07/27/aar404 (accessed on 24 August 2021).
- Budelmann, B.U. Hearing in N onarthropod Invertebrates. In The Evolutionary Biology of Hearing; Webster, D.B., Fay, R.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wiederhold, M.L.; Sharma, J.S.; Driscoll, B.P.; Harrison, J.L. Development of the statocyst in Aplysia californica I. Observations on statoconial development. Hear. Res. 1990, 49, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, P.M.; Malyshev, A.Y.; Ierusalimsky, V.; Aseyev, N.; Korshunova, T.A.; Bravarenko, N.I.; Lemak, M.S.; Roshchin, M.; Zakharov, I.S.; Popova, Y.; et al. Functional Changes in the Snail Statocyst System Elicited by Microgravity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, R.D.; McCauley, R.D.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Hartmann, K.; Semmens, J.M. Assessing the Impact of Marine Seismic Surveys on Southeast Australian Scallop and Lobster Fisheries; University of Tasmania: Hobart, Tasmania, 2016; ISBN 9780646959108. [Google Scholar]
- Solé, M.; Sigray, P.; Lenoir, M.; Van Der Schaar, M.; Lalander, E.; André, M. Offshore exposure experiments on cuttlefish indicate received sound pressure and particle motion levels associated with acoustic trauma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solé, M.; Monge, M.; André, M.; Quero, C. A proteomic analysis of the statocyst endolymph in common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis): An assessment of acoustic trauma after exposure to sound. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, M.; Lenoir, M.; Fontuño, J.M.; Durfort, M.; Van Der Schaar, M.; André, M. Evidence of Cnidarians sensitivity to sound after exposure to low frequency noise underwater sources. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solé, M.; Lenoir, M.; Durfort, M.; Fortuño, J.-M.; van der Schaar, M.; De Vreese, S.; André, M. Seagrass Posidonia is impaired by human-generated noise. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Bella, G.; Cannata, S.; Froglia, C.; Ratti, S.; Rivas, G. First assessment of effects of air-gun seismic shooting on marine resources in the Central Adriatic Sea. Int. Conf. Heal. Saf. Environ. Oil Gas Explor. Prod. 1996, 1, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocks, J.R. Response of Marine Invertebrate Larvae to Natural and Anthropogenic Sound: A Pilot Study. Open Mar. Biol. J. 2012, 6, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelec, S.L.; Radford, A.N.; Simpson, S.D.; Nedelec, B.; Lecchini, D.; Mills, S.C. Anthropogenic noise playback impairs embryonic development and increases mortality in a marine invertebrate. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep05891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Soto, N.A.; Delorme, N.; Atkins, J.; Howard, S.; Williams, J.M.; Johnson, M.J.A. Anthropogenic noise causes body malformations and delays development in marine larvae. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solé, M.; Lenoir, M.; Durfort, M.; López-Bejar, M.; Lombarte, A.; van der Schaar, M.; André, M. Does exposure to noise from human activities compromise sensory information from cephalopod statocysts? Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2013, 95, 160–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlschmidt, V.; Wolff, H.G. The fine structure of the statocyst of the prosobranch mollusc Pomacea paludosa. Z. Mikroskop. Anat. 1972, 133, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitseva, O. Structural organization of the sensory systems of the snail. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 1994, 24, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononenko, N.L.; Kiss, T.; Elekes, K. The neuroanatomical and ultrastructural organization of statocyst hair cells in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. Acta Biol. Hung. 2012, 63, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgiladze, G.I.; Bukia, R.D.; Davitashvili, M.T.; Taktakishvili, A.D.; Gelashvili, N.S.; Kalandarishvili, E.L.; Satdykova, G.P. Morphological peculiarities statoconia in statocysts of terrestrial pulmonary snail Helix lucorum. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 149, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.L.; Shin, J.-B. Mechanisms of Hair Cell Damage and Repair. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonova, E.V.; Raphael, Y. Organization of cell junctions and cytoskeleton in the reticular lamina in normal and ototoxically damaged organ of Corti. Hear. Res. 1997, 113, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atieh, Y.; Wyatt, T.; Zaske, A.M.; Eisenhoffer, G.T. Pulsatile contractions promote apoptotic cell extrusion in epithelial tissues. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, M.; Lenoir, M.; Fortuño, J.-M.; van der Schaar, M.; André, M. A critical period of susceptibility to sound in the sensory cells of cephalopod hatchlings? Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio033860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Day, R.D.; McCauley, R.D.; Fitzgibbon, Q.; Hartmann, K.; Semmens, J.M. Exposure to seismic air gun signals causes physiological harm and alters behavior in the scallop Pecten fumatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8537–E8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spoendlin, H. Primary Structural Changes in the Organ of Corti After Acoustic Overstimulation. Acta Oto Laryngolog. 1971, 71, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, J.; Cotanche, D. Regeneration of sensory hair cells after acoustic trauma. Science 1988, 240, 1772–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé, M.; Lenoir, M.; Fortuño, J.-M.; De Vreese, S.; van der Schaar, M.; André, M. Sea Lice Are Sensitive to Low Frequency Sounds. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehring, S. Invasion History and Success of the American Blue Crab Callinectes sapidus in European and Adjacent Waters. In the Wrong Place Alien Marine Crustaceans: Distribution, Biology and Impacts; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 607–624. [Google Scholar]
- Castejón, D.; Guerao, G. A new record of the American blue crab, Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896 (Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunidae), from the Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula. BioInvasions Rec. 2013, 2, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generalitat de Catalunya. Memòria D’actuacions de Control del Cargol Poma. Periode 2015–2018. 2018. Available online: http://mediambient.gencat.cat/web/.content/home/ambits_dactuacio/patrimoni_natural/especies_exotiques_medinatural/llista_sp_catalogades/invertebrat/cargol/Memoria-cargol-poma.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2021).



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solé, M.; Fortuño, J.-M.; van der Schaar, M.; André, M. An Acoustic Treatment to Mitigate the Effects of the Apple Snail on Agriculture and Natural Ecosystems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090969
Solé M, Fortuño J-M, van der Schaar M, André M. An Acoustic Treatment to Mitigate the Effects of the Apple Snail on Agriculture and Natural Ecosystems. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(9):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090969
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolé, Marta, José-Manuel Fortuño, Mike van der Schaar, and Michel André. 2021. "An Acoustic Treatment to Mitigate the Effects of the Apple Snail on Agriculture and Natural Ecosystems" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 9: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090969
APA StyleSolé, M., Fortuño, J.-M., van der Schaar, M., & André, M. (2021). An Acoustic Treatment to Mitigate the Effects of the Apple Snail on Agriculture and Natural Ecosystems. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(9), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090969






