Flow Field Measurement of Laboratory-Scaled Cross-Flow Hydrokinetic Turbines: Part I—The Near-Wake of a Single Turbine
Abstract
1. Introduction
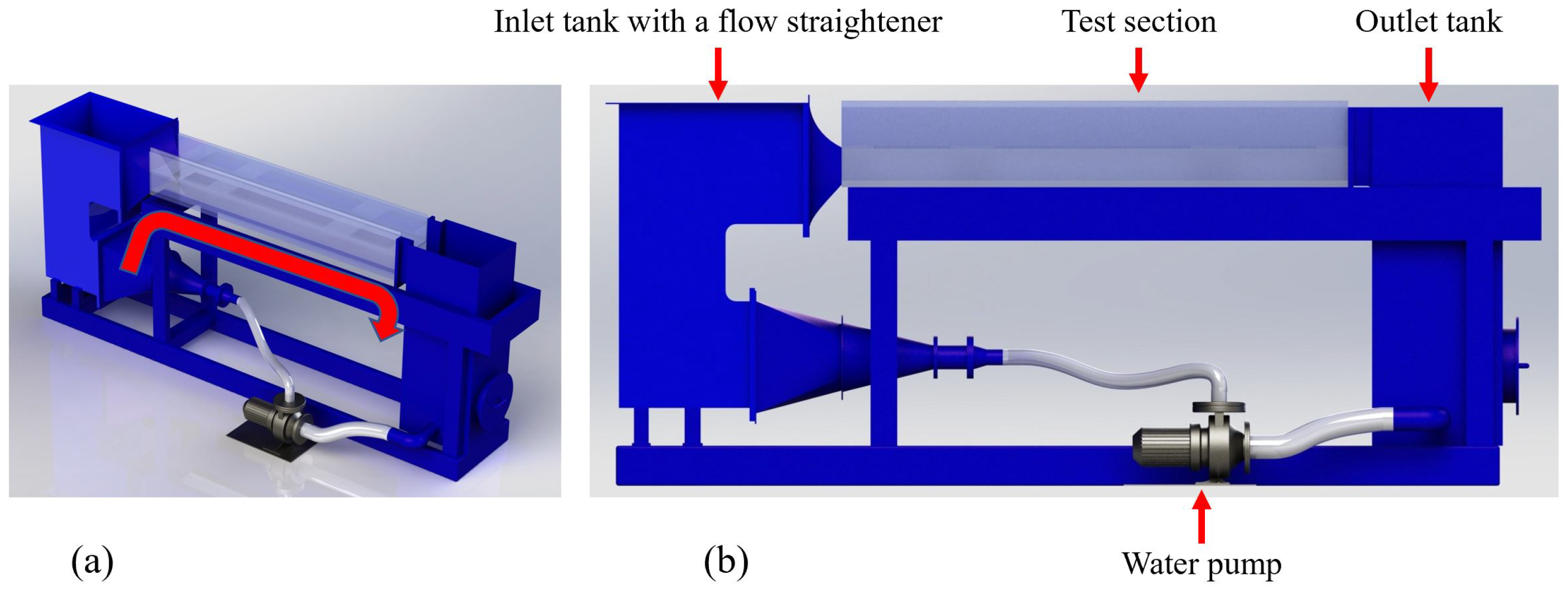
2. Apparatus and Methodology
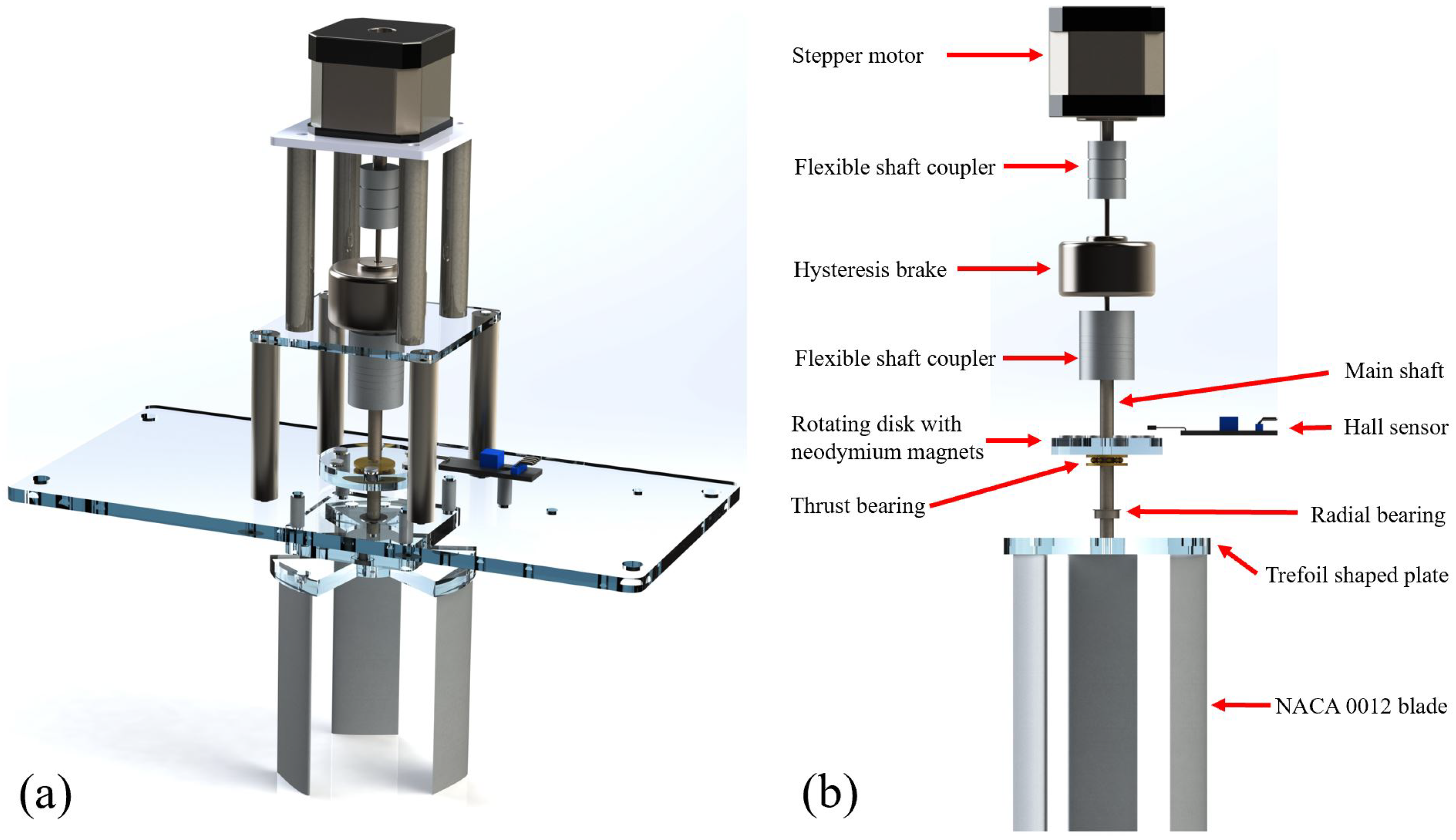
2.1. Turbine Towers and Mechanical Design
2.2. Electronics
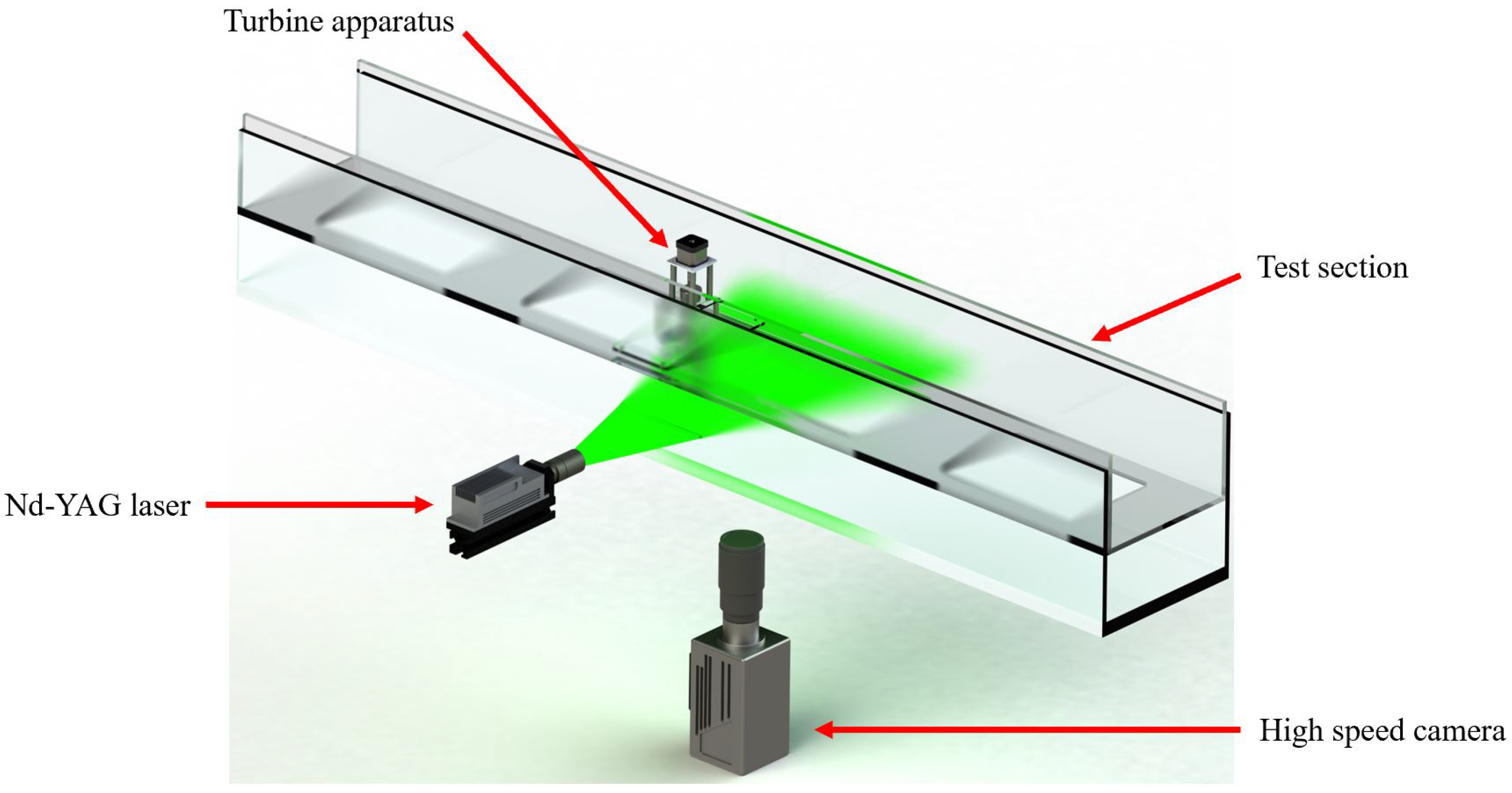
2.3. Particle Image Velocimetry
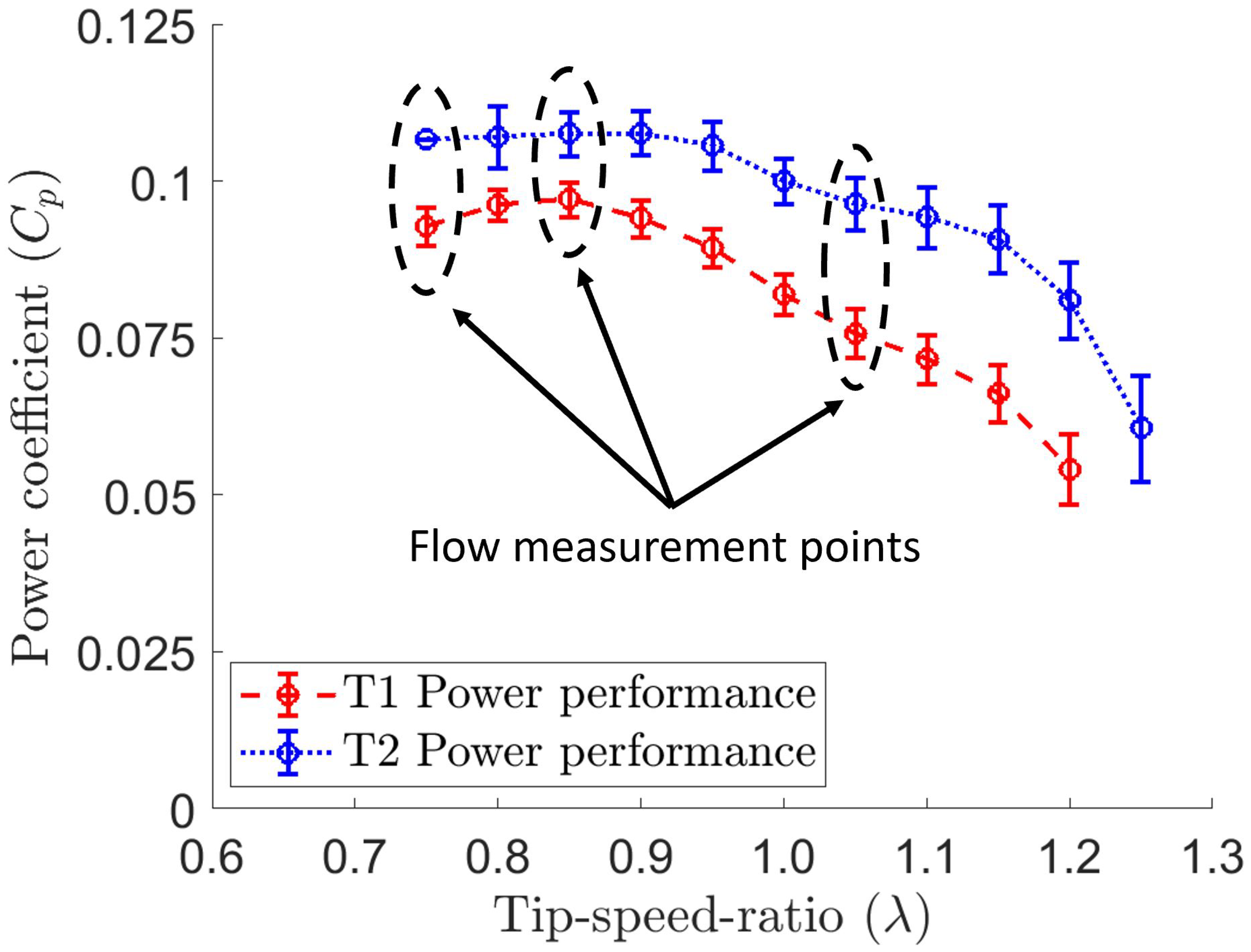
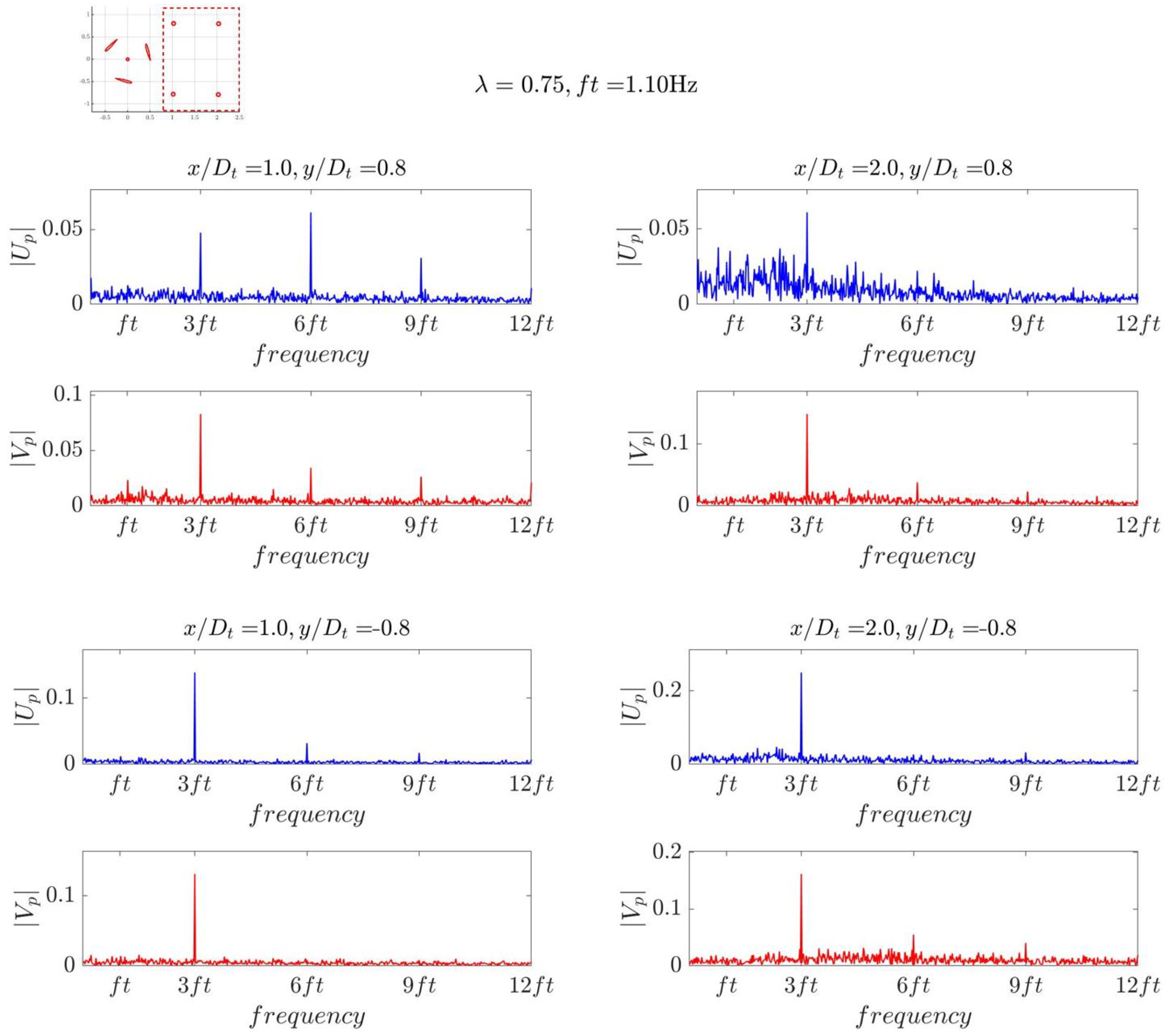
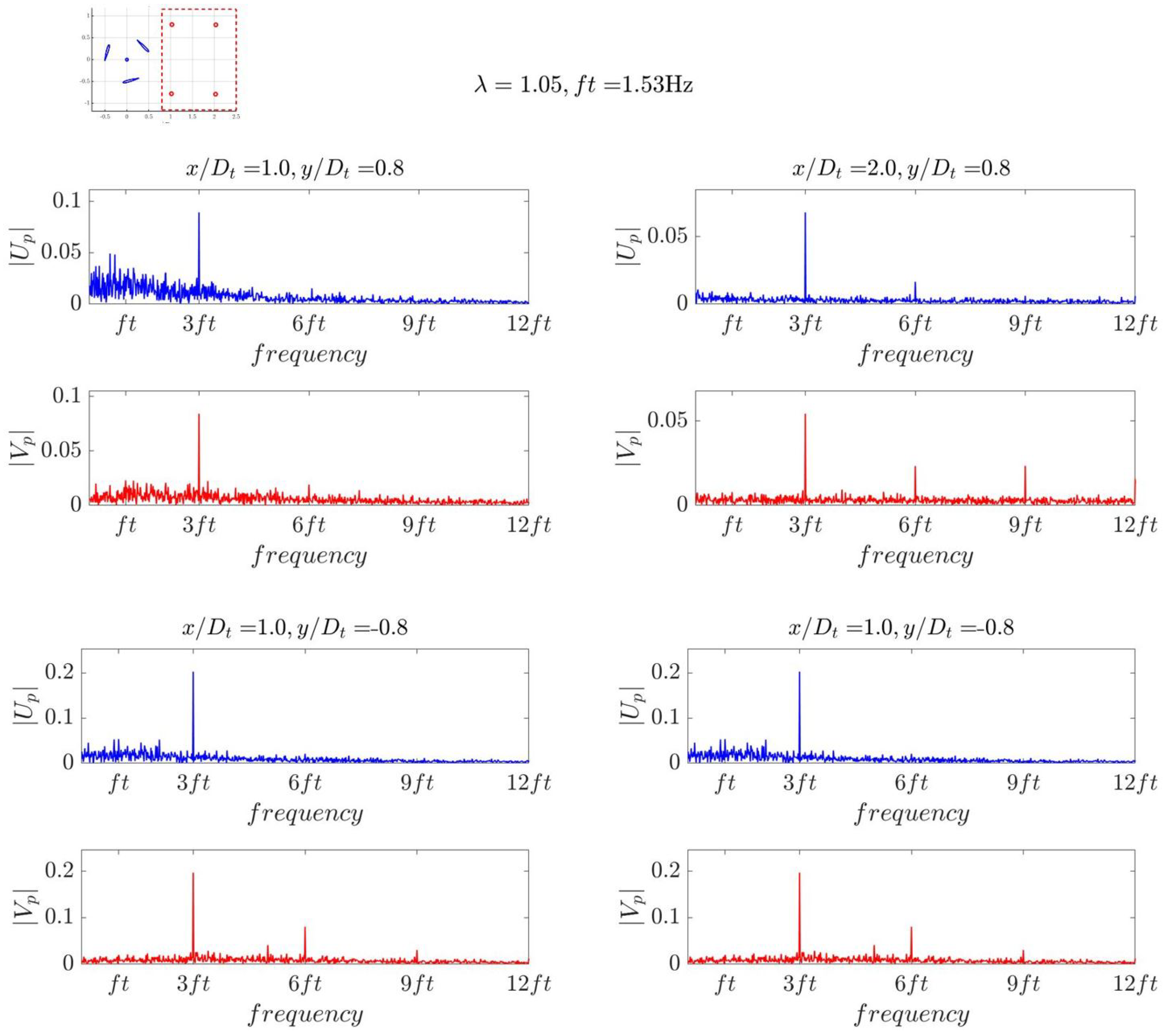
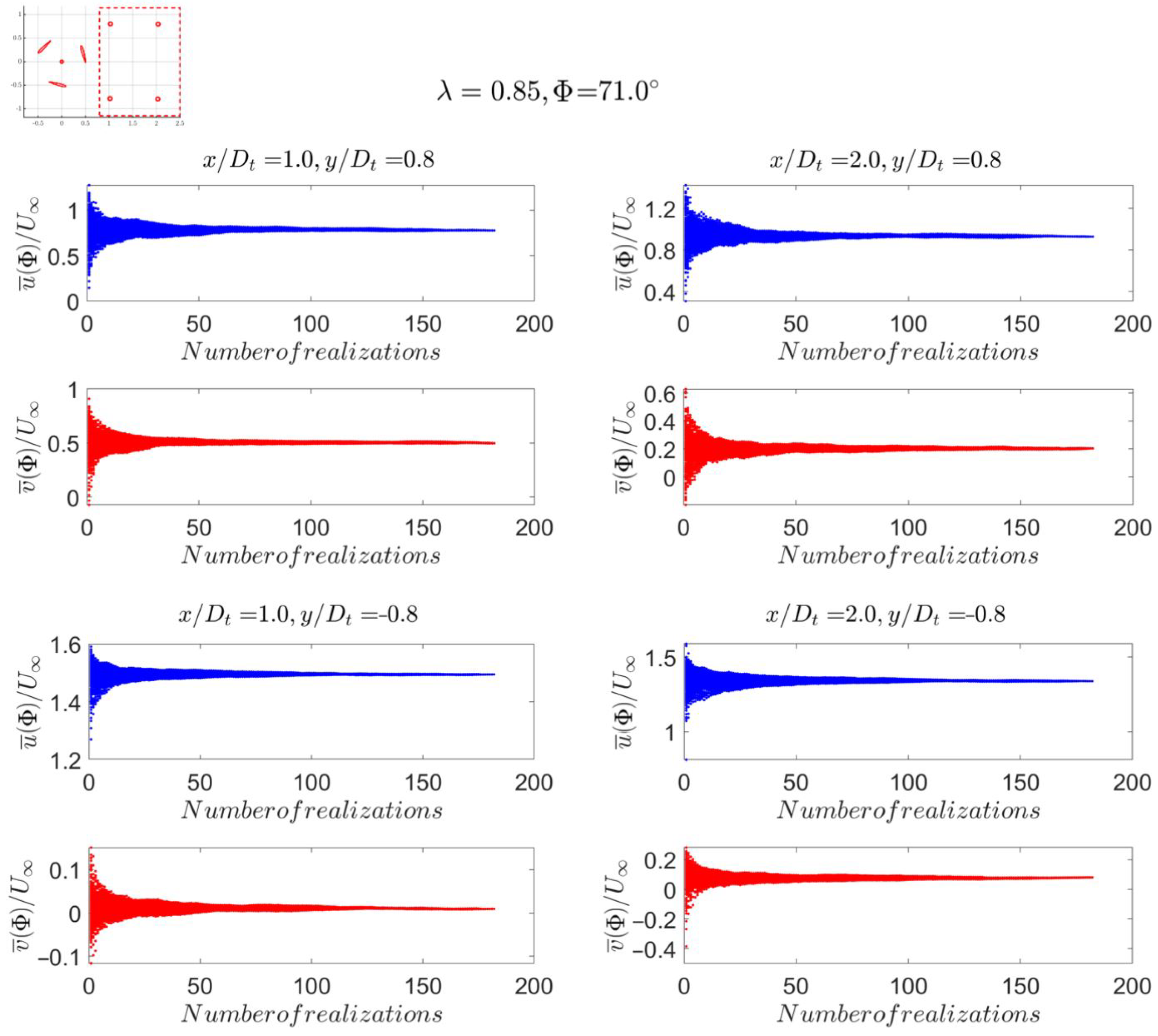
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fast Fourier Analysis
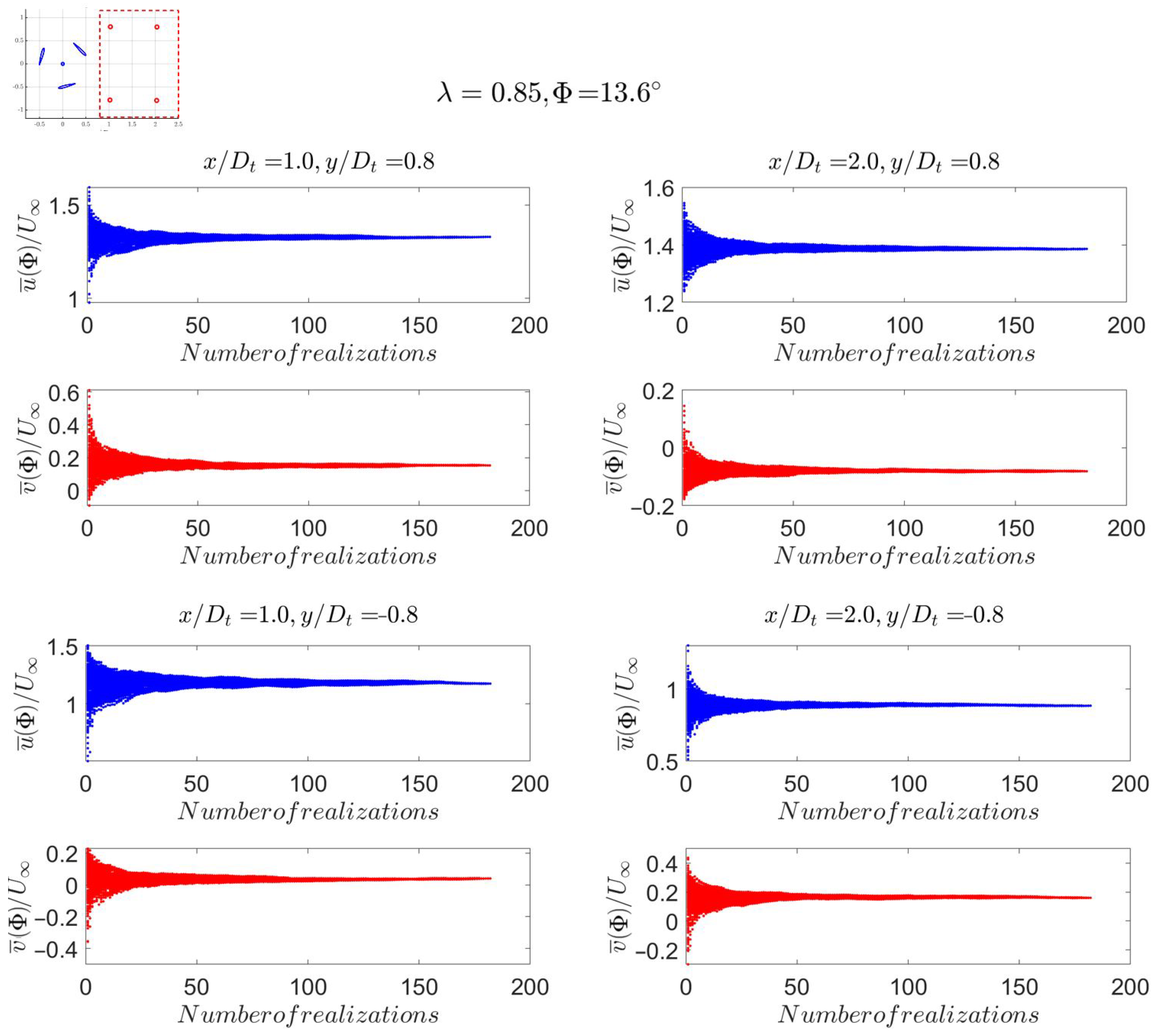
3.2. Data Convergence
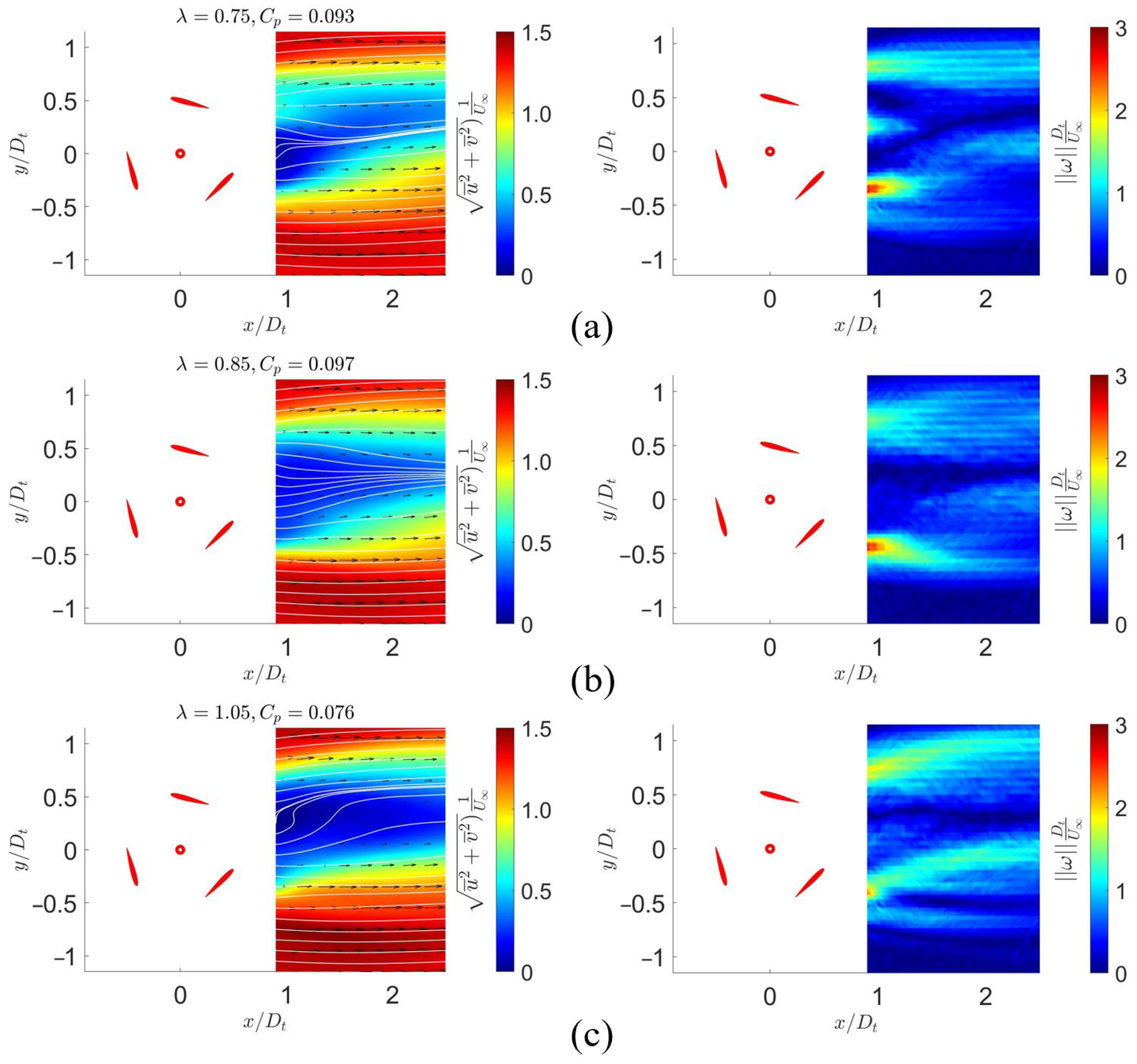
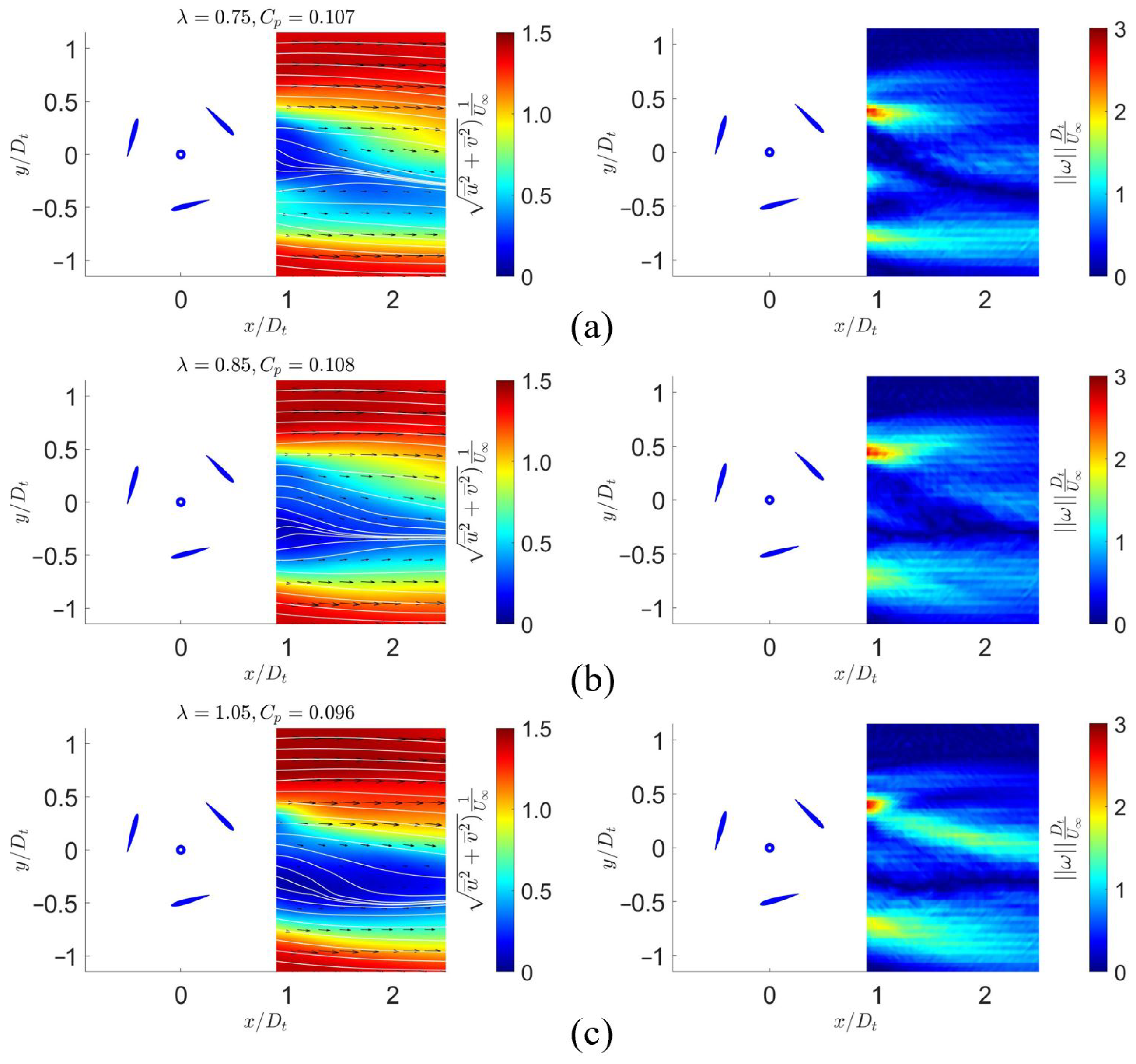
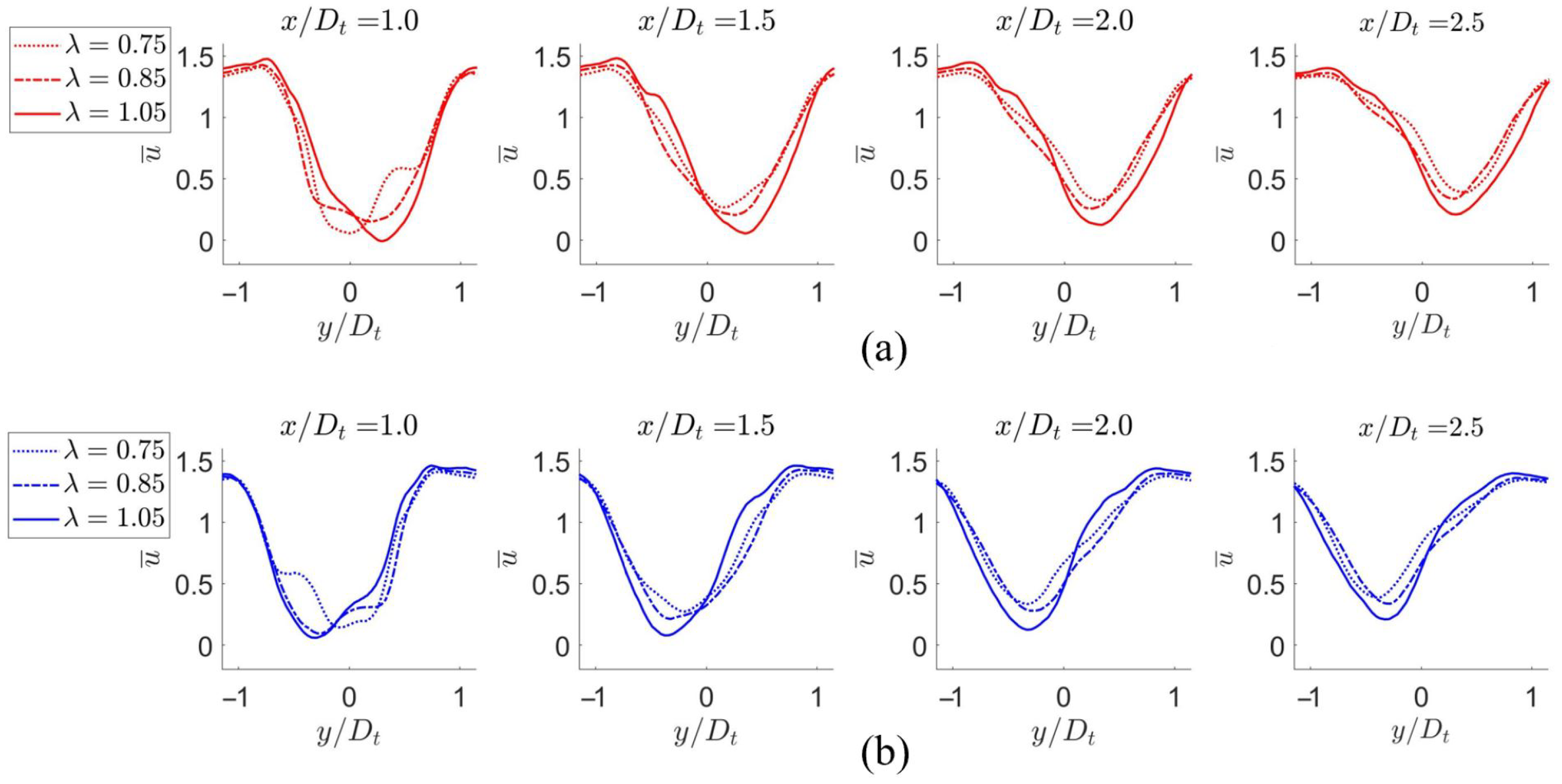
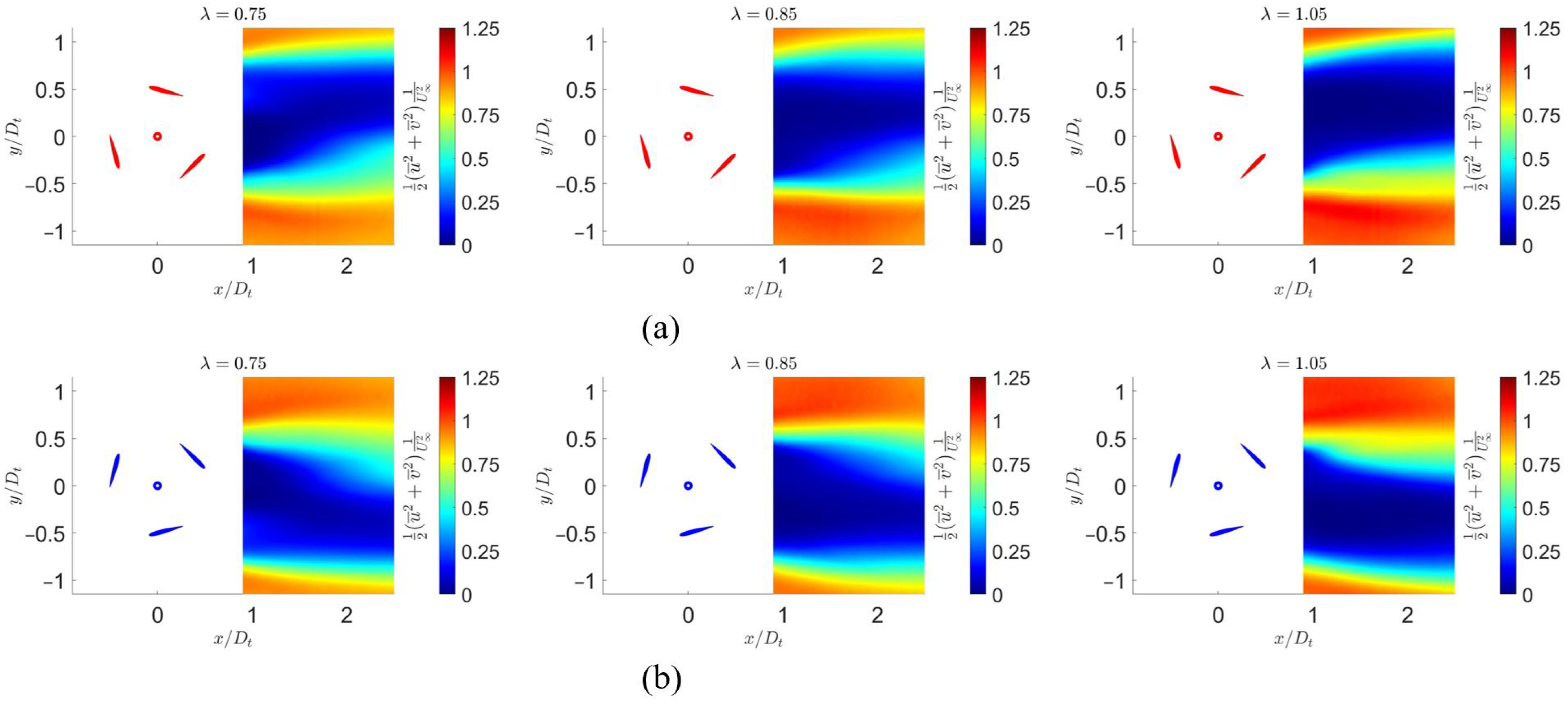
3.3. Mean Flow
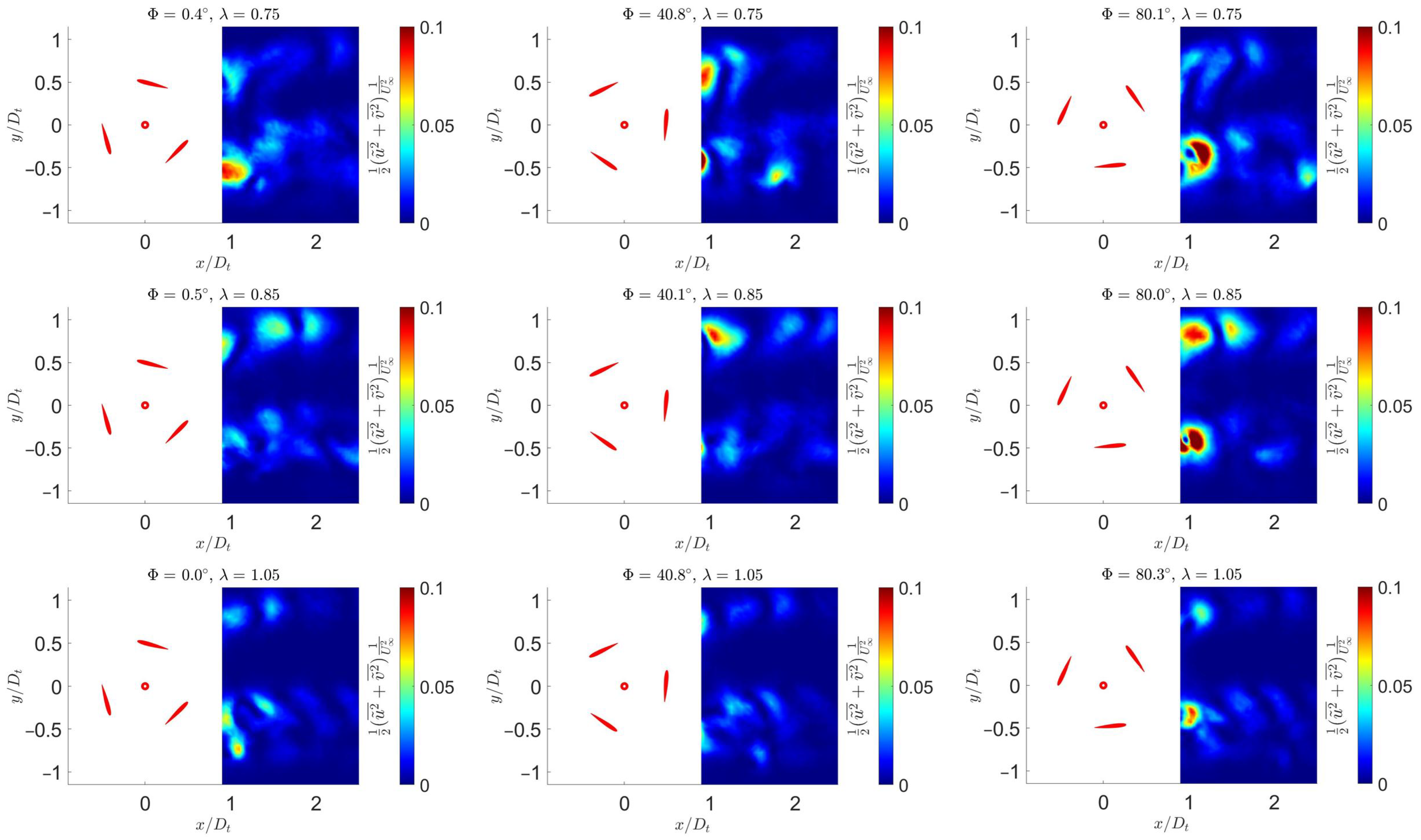
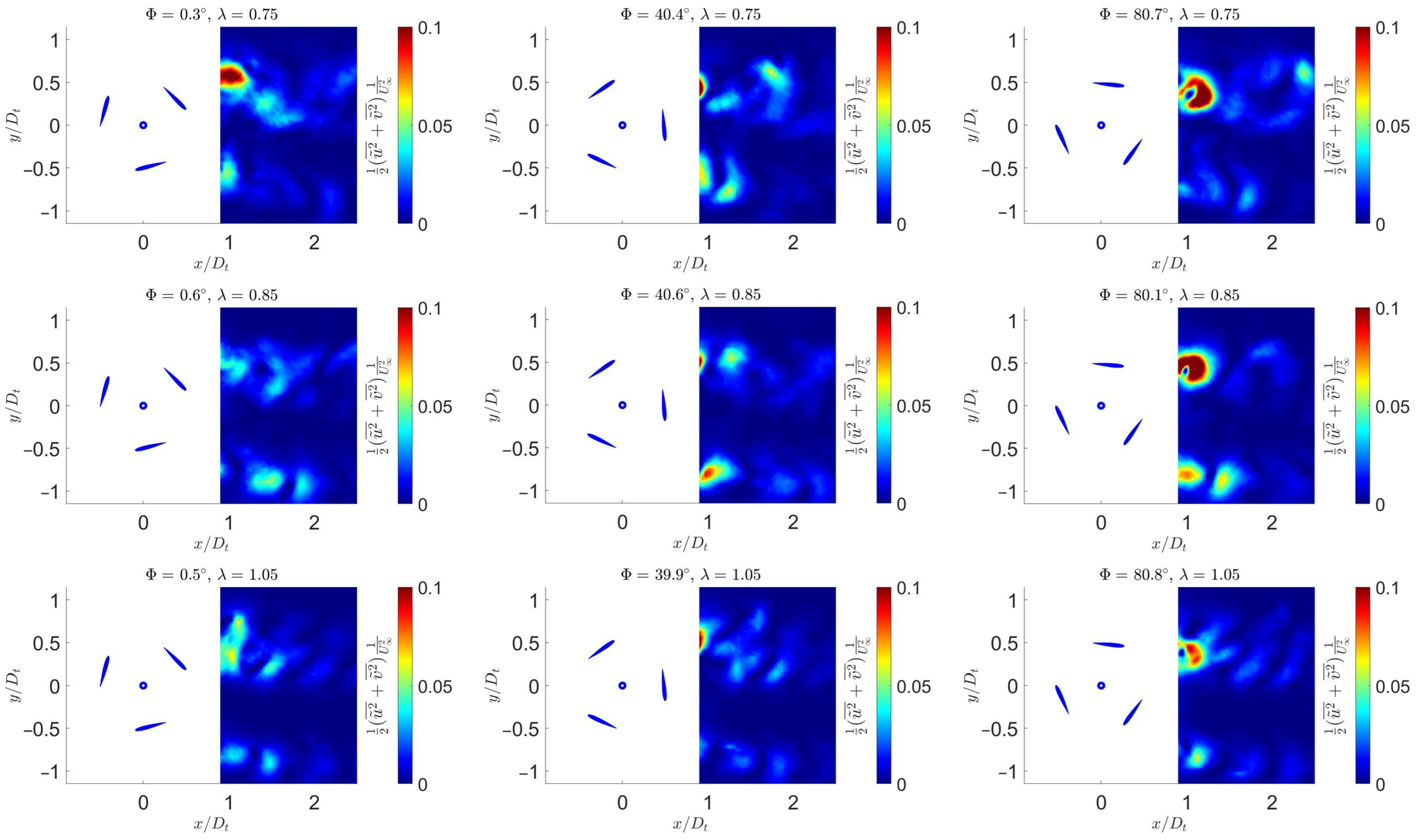
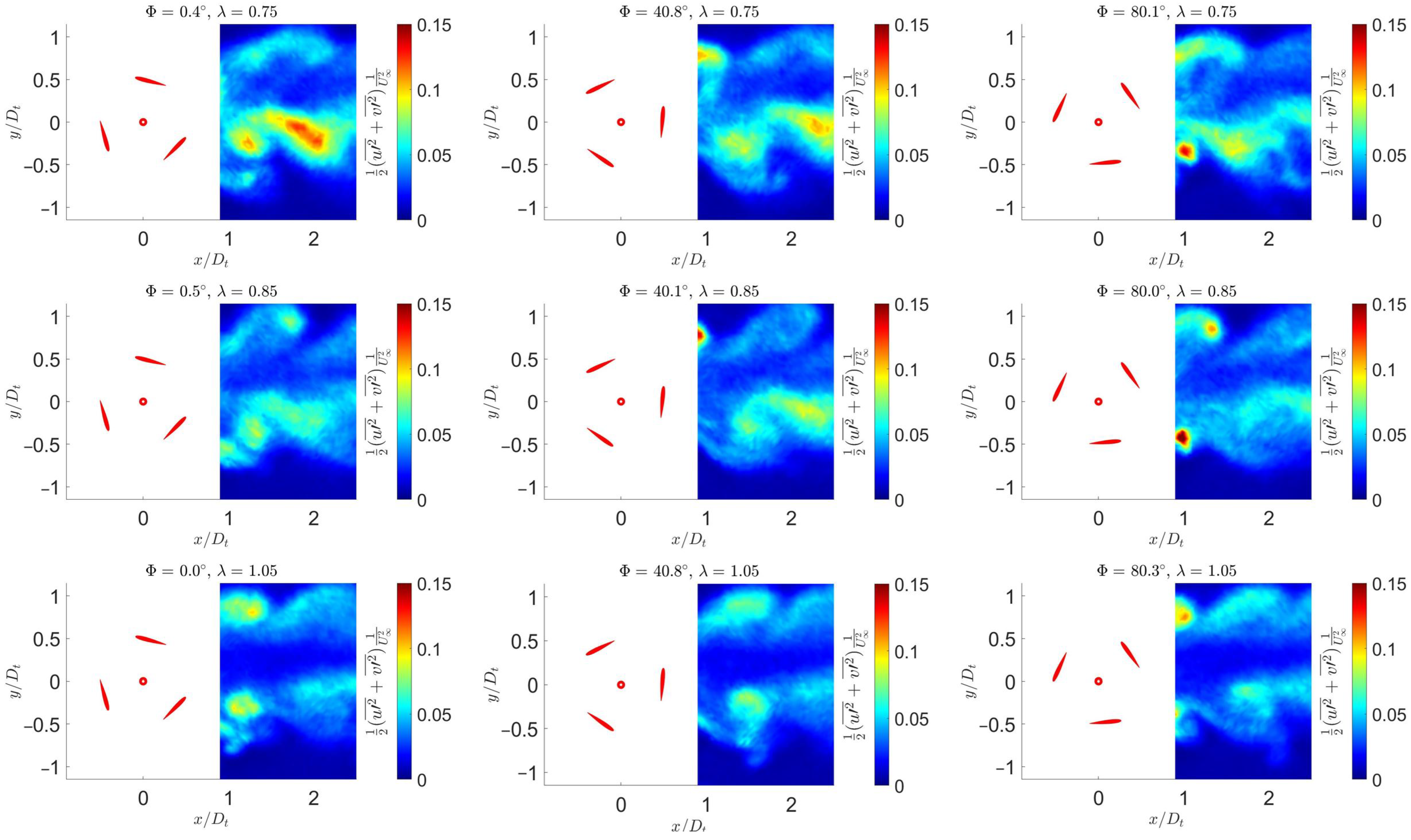
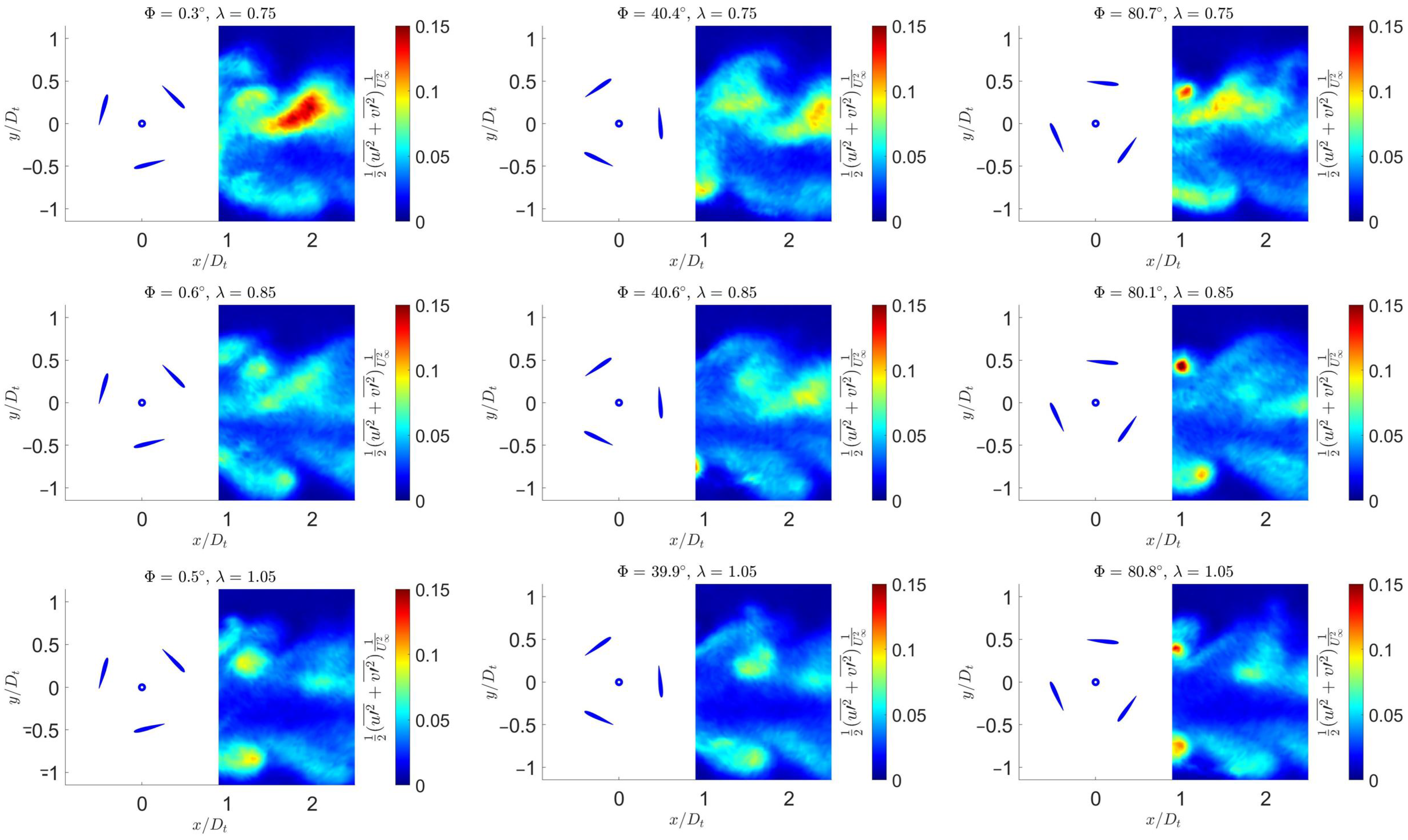
3.4. Kinetic Energy
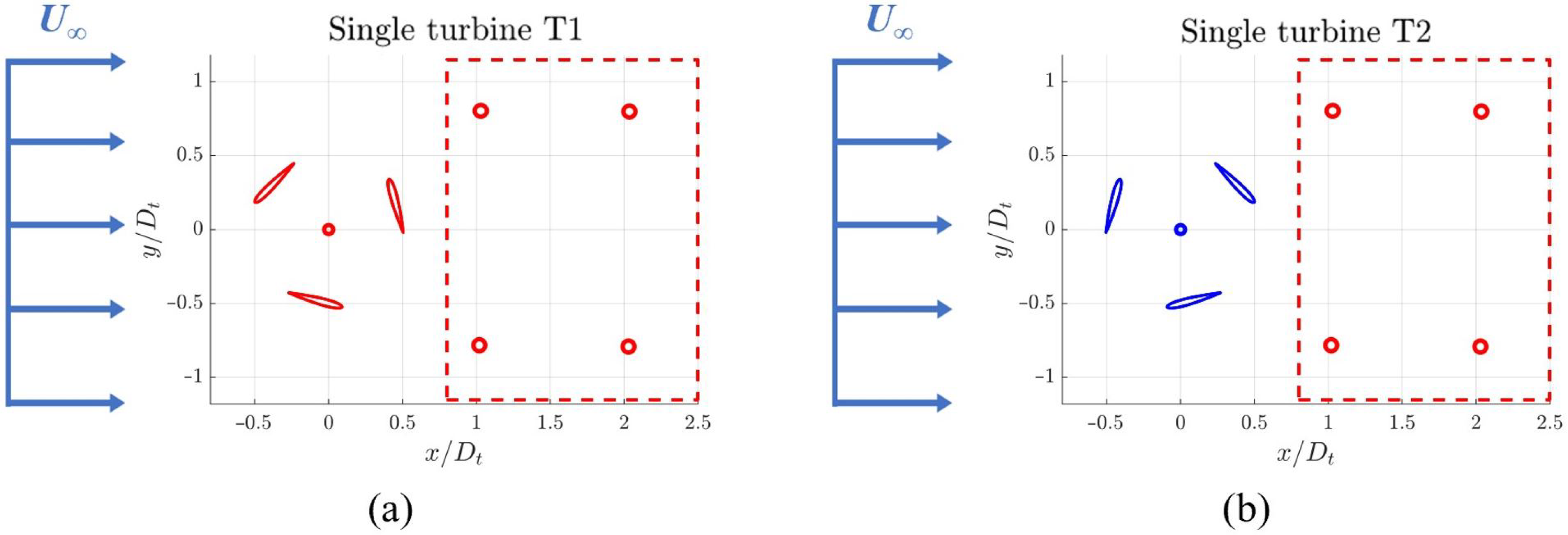
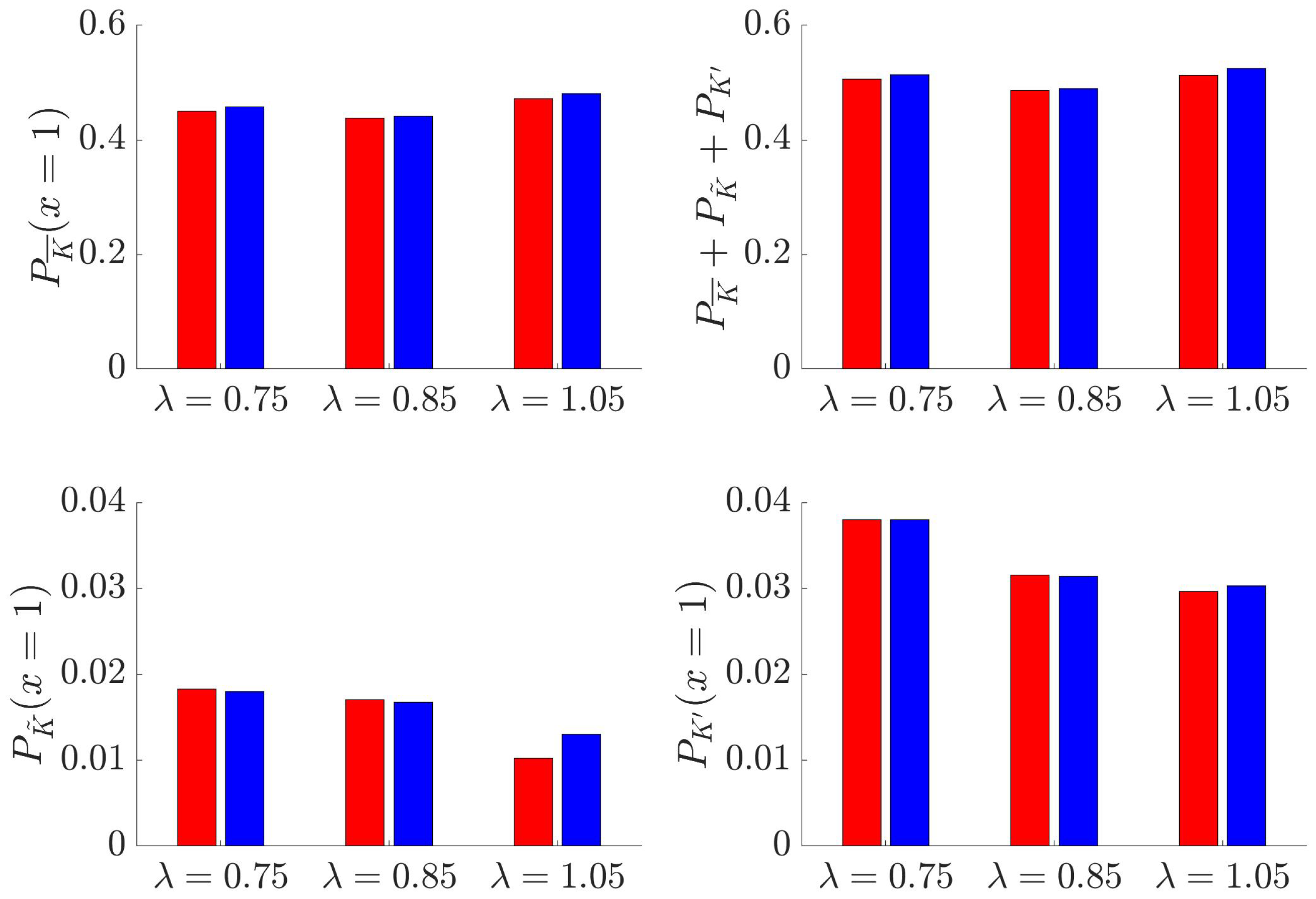
3.5. Quantitative Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MHK | Marine hydrokinetic turbine |
| EDM | Electrical discharge machining |
| VAWT | Vertical axis wind turbine |
| LDV | Laser Doppler velocimetry |
References
- Bahar, H. Renewables 2020—Analysis and Forecast to 2025; Report; International Energy Angency: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2020 (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Narune, A.; Prasad, E. Renewable Energy Market by Type (Hydroelectric Power, Wind Power, Bioenergy, Solar Energy, and Geothermal Energy), and End Use (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, and Others): Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2018–2025; Report EN 17140; Allied Market Research: Portland, OR, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Han, X.; Xie, Z.; Gao, X. Ecology: Three-Gorges dam experiment in habitat fragmentation? Science 2003, 300, 1239–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Sleigh, A. Resettlement for China’s Three Gorges Dam: Socio-economic impact and institutional tensions. Communist Post Commun. Stud. 2000, 33, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilt, B.; Braun, Y.; He, D. Social impacts of large dam projects: A comparison of international case studies and implications for best practice. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, S249–S257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, J. Potential order-of-magnitude enhancement of wind farm power density via counter-rotating vertical-axis wind turbine arrays. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2011, 3, 043104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstein, I.D.; Wei, N.J.; Dabiri, J.O. Aerodynamically Interacting Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines: Performance Enhancement and Three-Dimensional Flow. Energies 2019, 12, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Stoesser, T.; Wang, K.; Zhou, L. Experimental and numerical investigation of twin vertical axis wind turbines with a deflector. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 209, 112588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Calisal, S. Modeling of twin-turbine systems with vertical axis tidal current turbines: Part 1—Power Output. Ocean. Eng. 2010, 37, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Calisal, S. Modeling of twin-turbine systems with vertical axis tidal current turbine: Part 2—Torque Fluctuation. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 38, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachant, P.; Wosnik, M. Performance measurements of cylindrical- and spherical-helical cross-flow marine hydrokinetic turbines, with estimates of exergy efficiency. Renew. Energy 2014, 74, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachant, P.; Wosnik, M.; Gunawan, B.; Neary, V. Experimental study of a reference model vertical-axis cross-flow turbine. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachant, P.; Wosnik, M. Effects of Reynolds number on the energy conversion and near-wake dynamics of a high solidity vertical-axis cross-flow turbine. Energies 2016, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.; Brunton, S.; Polagye, B. Intracycle angular velocity control of cross-flow turbines. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachant, P.; Wosnik, M. Modeling the near-wake of a vertical-axis cross-flow turbine with 2-D and 3-D RANS. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 053311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, B.; Leen, S.; Nash, S. A two and three-dimensional CFD investigation into performance prediction and wake characterisation of a vertical axis turbine. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 034503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, B.; McCormack, V.; Leen, S.; Nash, S. A CFD investigation of a variable-pitch vertical axis hydrokinetic turbine with incorporated flow acceleration. J. Ocean. Eng. Mar. Energy 2019, 5, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, B.; McCormack, V.; Kennedy, C.; Leen, S.; Nash, S. An experimental study of a flow-accelerating hydrokinetic device. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Power Energy 2018, 1, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, H.; Polagye, B. An experimental assessment of analytical blockage corrections for turbines. Renew. Energy 2020, 152, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, D.; Colonius, T.; Dabiri, J. Transition to Bluff-Body Dynamics in the Wake of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 813, 346–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, M.N.; Alayeto, I.H.; Padricelli, C.; Obi, S.; Totsuka, Y. Experimental and computational fluid dynamic analysis of laboratory-scaled counter-rotating cross-flow turbines in marine environment. In Proceedings of the ASME 2018 5th Joint US-European Fluids Engineering Division Summer, Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–20 July 2018; American Society of Mechanical Engineer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 2, p. V002T14A003. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, M.N.; Alayeto, I.H.; Kumazawa, K.; Obi, S. Computational fluid dynamic analysis of a marine hydrokinetic crossflow turbine in low Reynolds number flow. In Proceedings of the ASME-JSME-KSME 2019 8th Joint Fluids Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 July–1 August 2019; American Society of Mechanical Engineer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2, p. V002T02A067. [Google Scholar]
- Alayeto, I.H.; Doan, M.N.; Kumazawa, K.; Obi, S. Wake characteristics comparison between isolated and pair configurations of marine hydrokinetic crossflow turbines at low Reynolds numbers. In Proceedings of the ASME-JSME-KSME 2019 8th Joint Fluids Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 July–1 August 2019; American Society of Mechanical Engineer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1, p. V001T01A037. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, U.V. Characterizing the Wake and the Performance of a Marine Hydrokinetic Turbine in a Tandem Array Configuration. Master’s Thesis, Bucknell University, Lewisburg, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, M.; Kai, Y.; Obi, S. Twin Marine Hydrokinetic Cross-Flow Turbines in Counter Rotating Configurations: A Laboratory-Scaled Apparatus for Power Measurement. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lust, E.; Flack, K.; Luznik, L. Survey of the near wake of an axial-flow hydrokinetic turbine in quiescent conditions. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, D.; Dabiri, O. A comparison of wake measurements in motor-driven and flow-driven turbine experiments. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadi, A.; Ishii, T.; Obi, S. Stereo PIV measurement of a finite, flapping rigid plate in hovering condition. Exp. Fluids 2010, 49, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadi, A. The Phase-Avreaged Velocity Measurement and the Estimation of Pressure Force of a Periodically Moving Body. Ph.D. Thesis, Keio University, Yokohama, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- MathWroks. Fast Fourier Transform. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/fft.html (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Antonia, R.; Bisset, D.; Browne, L. Effect of Reynolds number on the topology of the organized motion in a turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 213, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kline, S.; Reynolds, W. The production of turbulence near a smooth wall in a turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 1971, 15, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| T1 | T2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.75 | 0.285 | 0.312 |
| 0.85 | 0.232 | 0.247 |
| 1.05 | 0.318 | 0.328 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doan, M.N.; Kai, Y.; Kawata, T.; Obi, S. Flow Field Measurement of Laboratory-Scaled Cross-Flow Hydrokinetic Turbines: Part I—The Near-Wake of a Single Turbine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050489
Doan MN, Kai Y, Kawata T, Obi S. Flow Field Measurement of Laboratory-Scaled Cross-Flow Hydrokinetic Turbines: Part I—The Near-Wake of a Single Turbine. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(5):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050489
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoan, Minh N., Yuriko Kai, Takuya Kawata, and Shinnosuke Obi. 2021. "Flow Field Measurement of Laboratory-Scaled Cross-Flow Hydrokinetic Turbines: Part I—The Near-Wake of a Single Turbine" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 5: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050489
APA StyleDoan, M. N., Kai, Y., Kawata, T., & Obi, S. (2021). Flow Field Measurement of Laboratory-Scaled Cross-Flow Hydrokinetic Turbines: Part I—The Near-Wake of a Single Turbine. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(5), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050489






