Assessment of the Performance of an Artificial Reef Made of Modular Elements through Small Scale Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
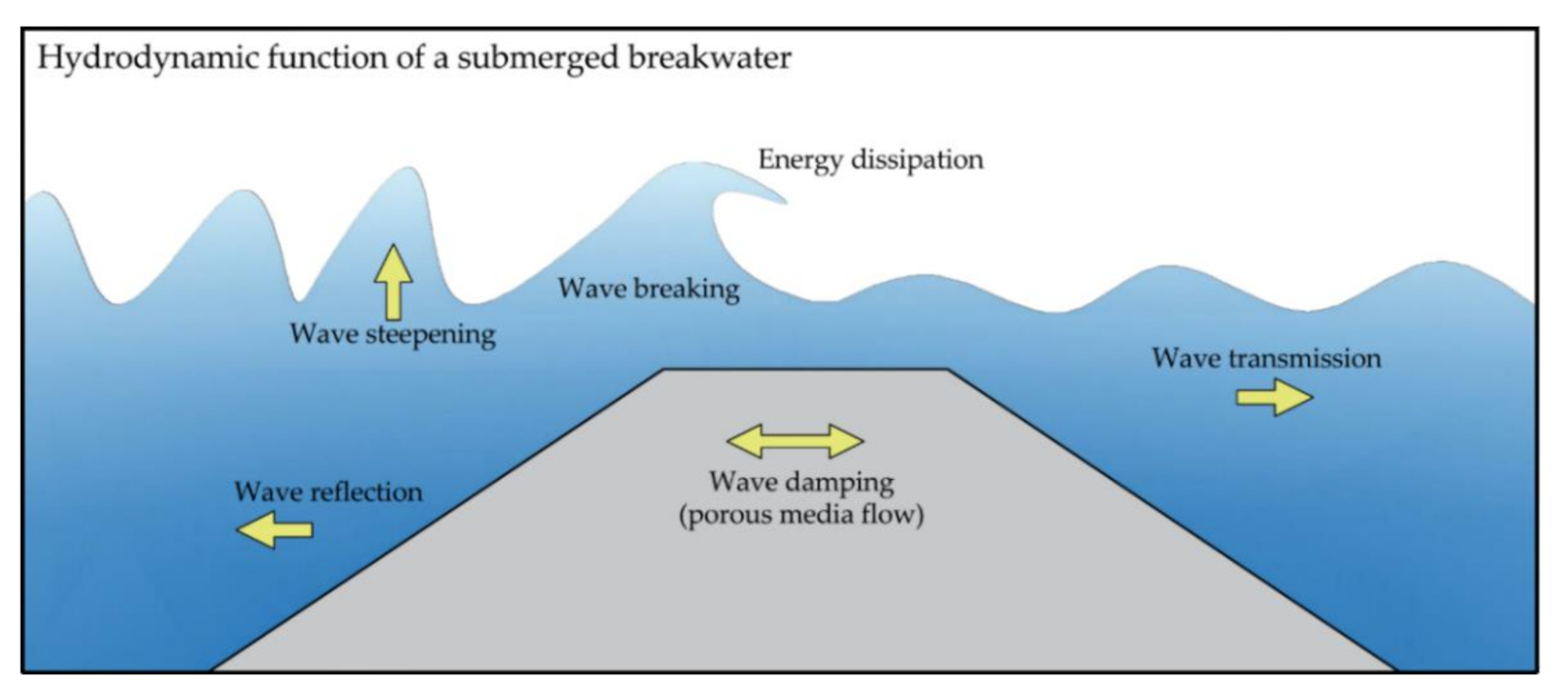
1.1. Hydrodynamic Function
1.2. Morphological Function
1.3. Ecological Function
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Modular Element Description
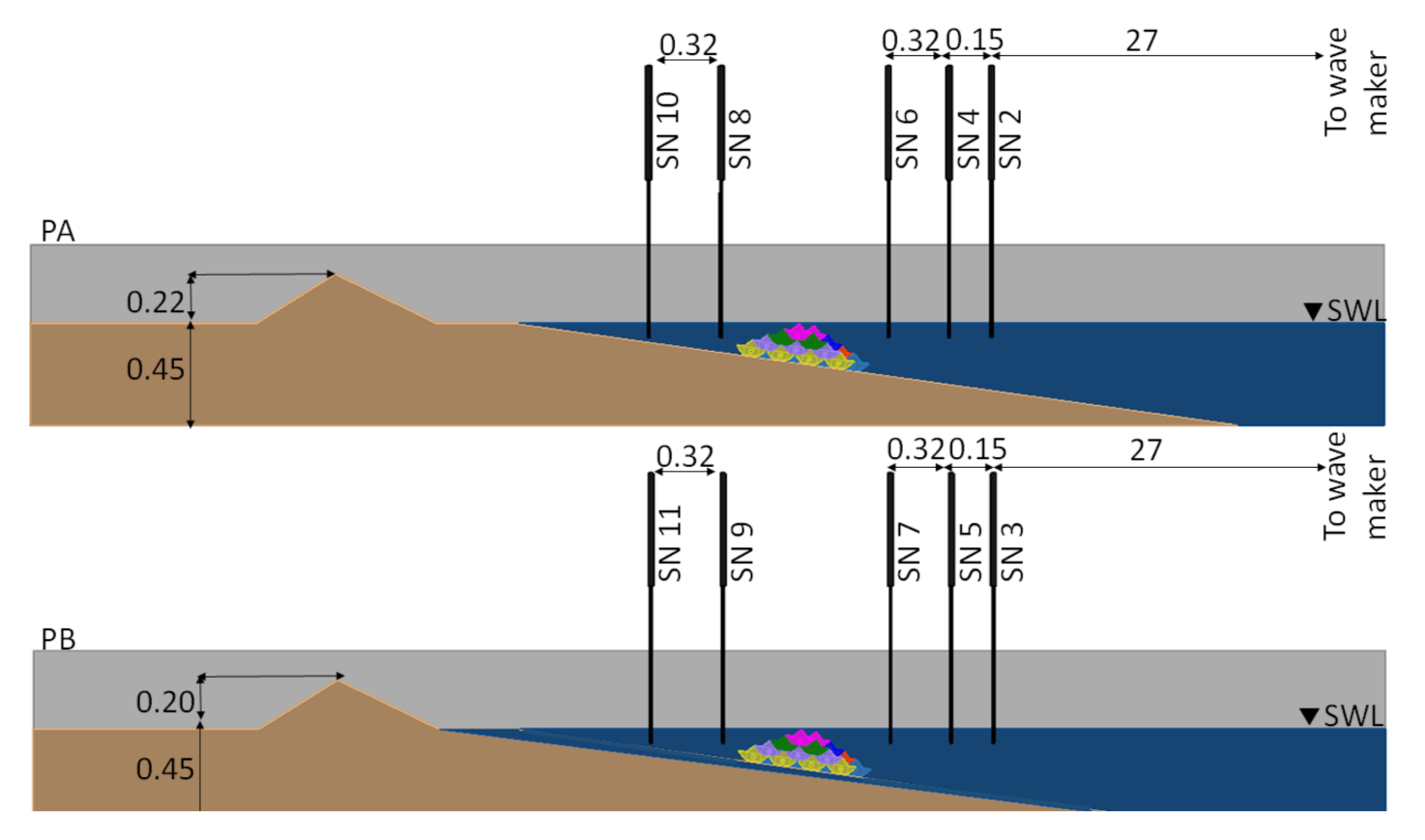
2.2. Experimental Set-Up and Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Hydraulic Performance
3.2. Morphodynamic Performance
3.3. Ecological Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sánchez, A.; Jiménez, J.A. Ingeniería de Playas (I): Conceptos de Morfología Costera. Ingen. Agua. 1994, 1, 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkey, O.H.; Thieler, E.R. Erosion of the United States shoreline. In Quaternary Coasts of the United States. Marine and Lacustrine Systems; Fletcher, C.H., III, Wehmiller, J.F., Eds.; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1992; Volume 48, pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Cleary, P.; Newby, P.; Ettinger, R. Coupling instrumental and geological records of sea-level change: Evidence from southern New England of an increase in the rate of sea-level rise in the late 19th century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán, J.M.; de Andrés, M. Analysis and trends of the world’s coastal cities and agglomerations. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 114, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.; Collins, K.; Lockwood, P. Current issues relating to artificial reefs in European Seas. In Artificial Reefs in European Seas; Jensen, A.C., Collins, K.J., Lockwood, A.P.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 489–499. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Tweedley, J.R.; Loneragan, N.R.; Zhang, X. Artificial reefs can mimic natural habitats for fish and macroinvertebrates in temperate coastal waters of the Yellow Sea. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 139, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, M.; Patterson, J.K.; Malleshappa, H.; Gladwin, N.; Mathews, G.; Diraviya, K.; Deepak, S.B.; Ashok, T.K.; Sannasiraj, S.A. Perforated trapezoidal artificial reefs can augment the benefits of restoration of island and its marine ecosystem. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 28, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kim, J.; Nam, J.; Song, D.; Lee, H. Changes in the behavioral characteristics of the Gangmun and Anmok beaches following the construction of artificial reefs. J. Coast. Res. 2019, SI 91, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Shim, K.T.; Shin, B.S. Morphological Change near the Artificial Reefs as a Beach Erosion Countermeasure. J. Coast. Res. 2016, SI 75, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, M. Artificial reefs: A review of their design, application, management and performance. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2001, 44, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Rosental, I.; Milton, Z. Overview and trends of ecological and socioeconomic research on artificial reefs. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 145, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Seabrook, S.R.; Hall, K.R. Wave transmission at submerged rubblemound breakwaters. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, ASCE, Copenhagen, Denmark, 22–26 June 1998; pp. 2000–2013. [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer, J.W.; Pilarczyk, K.W. Stability of low-crested and reef breakwaters. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Coastal Engineering, ASCE, Delft, The Netherlands, 2–6 June 1990; pp. 1375–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Kuang, C.; Han, X.; Niu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, C. Experimental Study on the Influence of an Artificial Reef on Cross-Shore Morphodynamic Processes of a Wave-Dominated Beach. Water 2020, 12, 2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.; Mao, X.; Gu, J.; Niu, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qui, R.; Zhang, J. Morphological processes of two artificial submerged shore-parallel sandbars for beach nourishment in a nearshore zone. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 179, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Allgeier, J.E. An ecosystem ecology perspective on artificial reef production. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 2139–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, K.W. Design of low-crested (submerged) structures: An overview. In Proceedings of the 6th COPEDEC (Int. Conf. on Coastal and Port Engng. in Develop. Countries), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 15–19 September 2003; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- ‘Izzat Na’im, I.; Razak Mohd Shahrizal, A.R.; Safari, M.D. A Short Review of Submerged Breakwaters. MATEC Web Conf. 2008, 203, 01005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Turner, I.L. Shoreline response to submerged structures: A review. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnsack, J.A.; Sutherland, D.L. Artificial reef research: A review with recommendations for future priorities. Bullet. Marine Sci. 1985, 37, 11–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Hakimzadeh, H.; Ketabdari, M.J.; Cartwright, N.; Vaghefi, M. Experimental Study on Wave Transmission and Reflection at Impermeable Submerged Breakwaters. Int. J. Coast. Offshore Eng. 2017, 1, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lokesha; Sannasiraj, S.A.; Sundar, V. Hydrodynamic characteristics of a submerged trapezoidal artificial reef unit. Proc. Inst. Mecha. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2019, 233, 1226–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.V.; Hamilton, D.; Murray, T.; Strauss, D.; Shaeri, S.; Faivre, G.; Silva, A.P.; Tomlinson, R. Impacts of a Multi-Purpose Artificial Reef on Hydrodynamics, Waves and Long-Term Beach Morphology. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 95, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.; Bond, T.; Prince, J.; Hovey, R.K.; McLean, D.L. An assessment of change to fish and benthic communities following installation of an artificial reef. Region. Stud. Marine Sci. 2020, 39, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, H.R.; Paxton, A.B.; Anisfeld, S.C.; Rosemond, R.C.; Peterson, C.H. Selecting the optimal artificial reefs to achieve fish habitat enhancement goals. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 238, 108200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Mendoza, E.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Martínez, M.L.; Escalante, E. An artificial reef improves coastal protection and provides a base for coral recovery. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, S.J.; Burcharth, H.F.; Zanuttigh, B.; Lamberti, A. Environmental Design Guidelines for Low Crested Coastal Structures; Elsevier: Cham, Switzerland, 2007; 448p. [Google Scholar]
- Strain, E.M.A.; Olabarria, C.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Cumbo, C.; Morris, R.L.; Bugnot, A.B.; Dafforn, K.A.; Heery, E.; Firth, L.B.; Brooks, P.R.; et al. Eco-engineering urban infrastructure for marine and coastal biodiversity: Which interventions have the greatest ecological benefit? J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Buck, M.; Payo, A.; Johnson, B.D. Berm and dune erosion during a storm. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2009, 135, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Martínez, M.L.; Odériz, I.; Mendoza, E.; Feagin, R.A. Response of vegetated dune–beach systems to storm conditions. Coast. Eng. 2016, 109, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquerizo, A. Reflexión del Oleaje en Playas. Métodos de Evaluación y de Predicción. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Cantabria, Santander, Spain, 1995; 180p. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, Y. Random Seas and Design of Maritime Structures, 3rd ed.; World Scientific: New York, NY, USA, 2010; 732p. [Google Scholar]
- Pecher, A.; Kofoed, J.P. Handbook of Ocean Wave Energy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; 287p. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, B.M.; Allen, R. Wave transmission through artificial reef breakwaters. In Proceedings of the Coastal Structures and Solutions to Coastal Disasters, Boston, MA, USA, 9–11 September 2015; pp. 432–441. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Bae, I.; Lee, J.I. Three-dimensional Variation of Wave Transmission around the Artificial Reefs: An Experimental Study. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 85, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srineash, V.K.; Murali, K. Effects of Seaward Slope on Wave Transmission of Porous and Non-Porous Reef Breakwaters with Smooth and Stepped Slopes. In Proceedings of the Coastal Structures 2019, Hannover, Germany, 30 September–2 October 2019; pp. 275–285. [Google Scholar]
- Frau, L.; Marzeddu, A.; Dini, E.; Gracia, V.; Gironella, X.; Erioli, A.; Zomparelli, A.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A. Effects of ultra-porous 3D printed reefs on wave kinematics. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 75, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Razak, M.S.; Yusof, B.; Desa, S.M. The performance of narrow and broad-crested submerged breakwaters in dissipating wave heights. J. Teknologi. 2020, 82, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M.; Medina, R.; Losada, M.A. Equilibrium beach profile model for perched beaches. Coast. Eng. 1999, 36, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Villatoro, M.; Ramos, F.; Pedroza, D.; Ortiz, M.; Mendoza, E.; Cid, A. Caracterización de la Zona Costera y Planteamiento de Elementos Técnicos para la Elaboración de Criterios de Regulación y Manejo Sustentable; UNAM/SEMARNAT: Mexico City, Mexico, 2014; 125p. [Google Scholar]
- Komar, P.D. Handbook of Coastal Processes and Erosion; CRC Press: Galveston, TX, USA, 1997; Volume 53, pp. 1689–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Kubowicz-Grajewska, A. Morpholithodynamical changes of the beach and the nearshore zone under the impact of submerged breakwaters-A case study (Orłowo Cliff, the Southern Baltic). Oceanologia 2015, 57, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alegria-Arzaburu, A.R.; Mariño-Tapia, I.; Enriquez, C.; Silva, R.; González-Leija, M. The role of fringing coral reefs on beach morphodynamics. Geomorphology 2013, 198, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, A.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Oakley, J.A.; Williams, A.T. Use of ecosystems in coastal erosion management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 156, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, S.; Porter, J.S.; Wilding, T.A. Artificial reef design affects benthic secondary productivity and provision of functional habitat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLachlan, A. Physical factors in benthic ecology: Effects of changing particle size on beach fauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 131, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeds, K.A.; Smith, J.A.; Suthers, I.M.; Johnston, E.L. An ecological halo surrounding a large offshore artificial reef: Sediments, infauna, and fish foraging. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 141, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komyakova, V.; Chamberlain, D.; Jones, G.P.; Swearer, S.E. Assessing the performance of artificial reefs as substitute habitat for temperate reef fishes: Implications for reef design and placement. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Smith, J.A.; Lowry, M.B.; Taylor, M.D.; Suthers, I.M. Multispecies presence and connectivity around a designed artificial reef. Marine Freshwater Res. 2017, 68, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Taylor, M.D.; Lowry, M.B. Monitoring of reef associated and pelagic fish communities on Australia’s first purpose built offshore artificial reef. ICES J. Marine Sci. 2017, 74, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vita, I. Hydraulic Response of Submerged Breakwaters. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Black, K.; Mead, S. Design of the Gold Coast reef for surfing, public amenity and coastal protection: Surfing aspects. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 29, 115–130. [Google Scholar]
- Matlock, M.; Morgan, R.A. Ecological Engineering Design, Restoring and Conserving Ecological Services; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; 353p. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Lima, J.S.; Atalah, J.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Zalmon, I.R. Evaluating the performance and management of artificial reefs using artificial reef multimetric index (ARMI). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 198, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Test | Hs (m) | Tp (s) | h (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Profiles PA and PB | PWS | RM T1 T2 T3 | 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.05 | 0.894 0.894 1.118 1.118 | 0.45 0.45 0.48 0.45 |
| PEN | RM T1 T2 T3 | 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.05 | 0.894 0.894 1.118 1.118 | 0.45 0.45 0.48 0.45 | |
| PES | RM T1 T2 T3 | 0.05 0.10 0.10 0.05 | 0.894 0.894 1.118 1.118 | 0.45 0.45 0.48 0.45 |
| Total Profile | Above SWL | Below SWL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | PB | PA | PB | PA | PB | |
| PEN-T1 | 0.999 | 0.962 | 0.620 | 0.918 | 1.051 | 0.971 |
| PEN-T2 | 1.039 | 0.933 | 0.783 | 0.749 | 1.075 | 0.979 |
| PEN-T3 | 0.878 | 0.933 | 1.279 | 0.749 | 0.821 | 0.979 |
| PES-T1 | 0.992 | 0.948 | 0.748 | 0.827 | 1.022 | 0.967 |
| PES-T2 | 0.947 | 1.005 | 1.009 | 1.194 | 0.940 | 0.972 |
| PES-T3 | 0.990 | 1.093 | 1.035 | 0.619 | 0.983 | 1.172 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardenas-Rojas, D.; Mendoza, E.; Escudero, M.; Verduzco-Zapata, M. Assessment of the Performance of an Artificial Reef Made of Modular Elements through Small Scale Experiments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020130
Cardenas-Rojas D, Mendoza E, Escudero M, Verduzco-Zapata M. Assessment of the Performance of an Artificial Reef Made of Modular Elements through Small Scale Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardenas-Rojas, Dea, Edgar Mendoza, Mireille Escudero, and Manuel Verduzco-Zapata. 2021. "Assessment of the Performance of an Artificial Reef Made of Modular Elements through Small Scale Experiments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 2: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020130
APA StyleCardenas-Rojas, D., Mendoza, E., Escudero, M., & Verduzco-Zapata, M. (2021). Assessment of the Performance of an Artificial Reef Made of Modular Elements through Small Scale Experiments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(2), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9020130








