Boat Noise and Black Drum Vocalizations in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon (Argentina)
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The level of boat noise in the mouth of the lagoon;
- (2)
- The temporal overlapping of black drum sounds and boat noises in the mouth of the lagoon;
- (3)
- The potential effect on black drum acoustic activity;
- (4)
- The effectiveness of the fishing ban on boat noise in the mouth of the lagoon.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Sound Analysis
- 1.
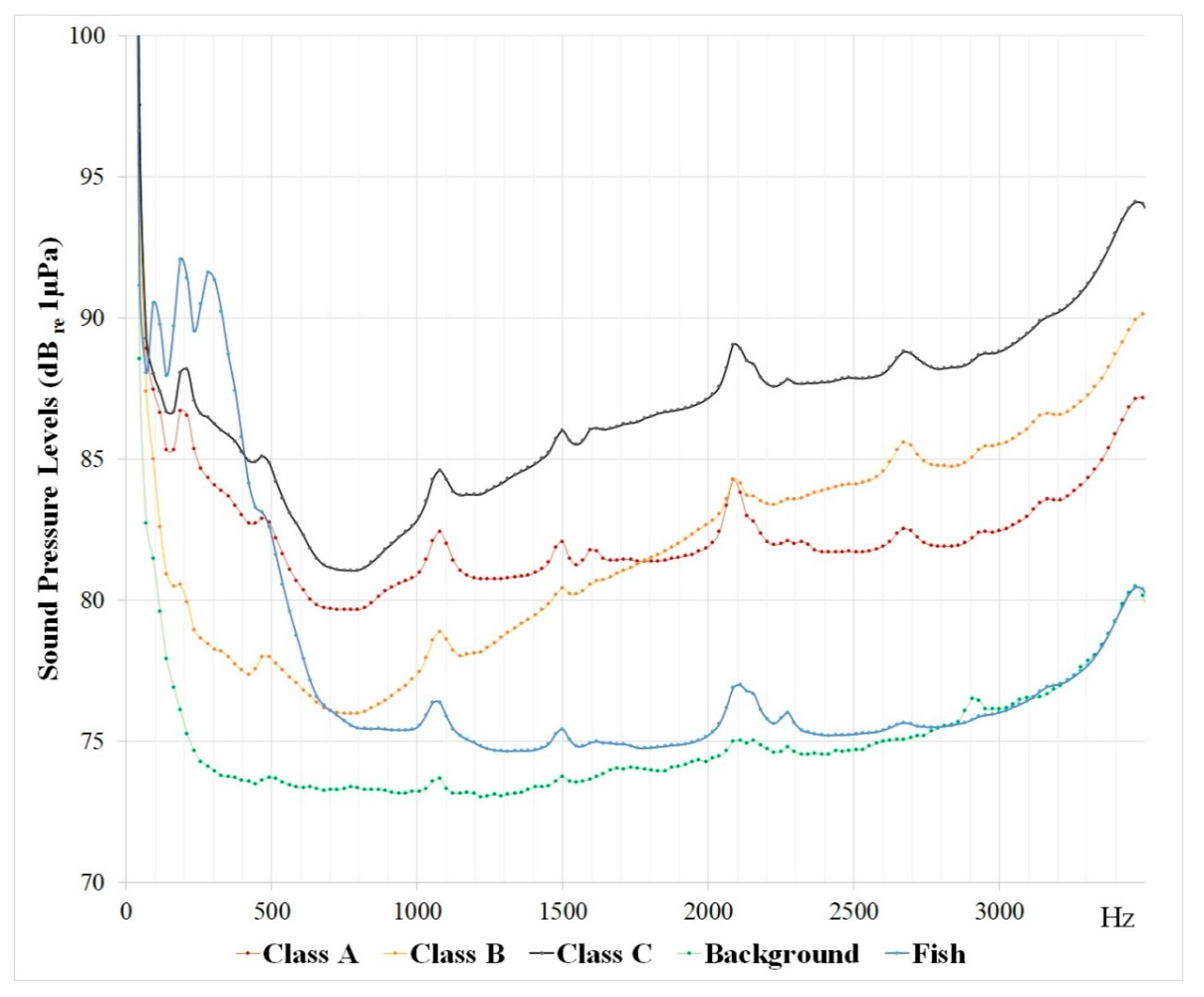
- Class A: narrow band noise, with low frequency noise in a range below 700 Hz;
- 2.
- Class B: mid-frequency noise, with mid-to-high frequency noise in a range over 700 Hz;
- 3.
- Class C: burst broadband noise, with the entire band noise covering the entire spectrum (below and above 700 Hz).
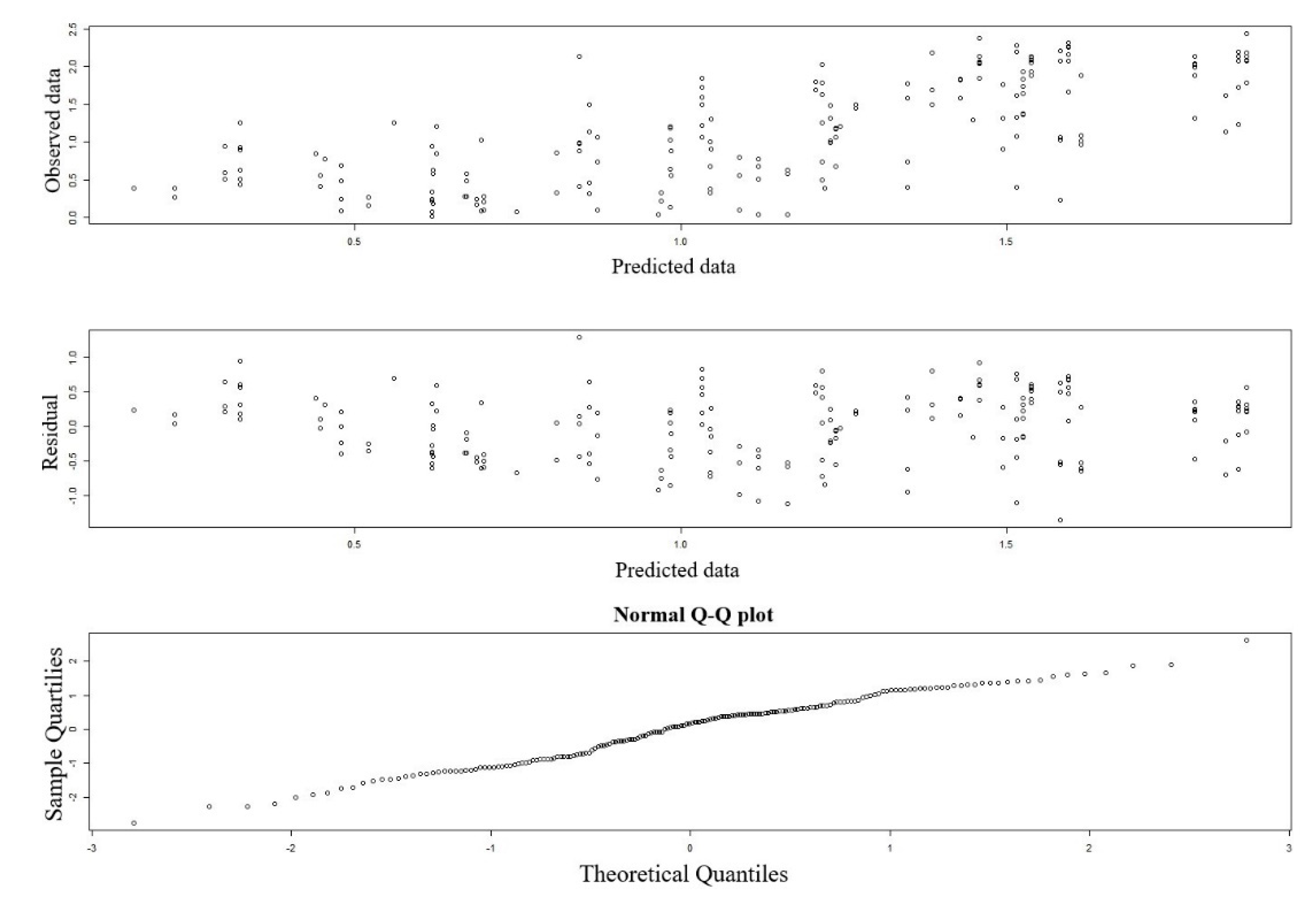
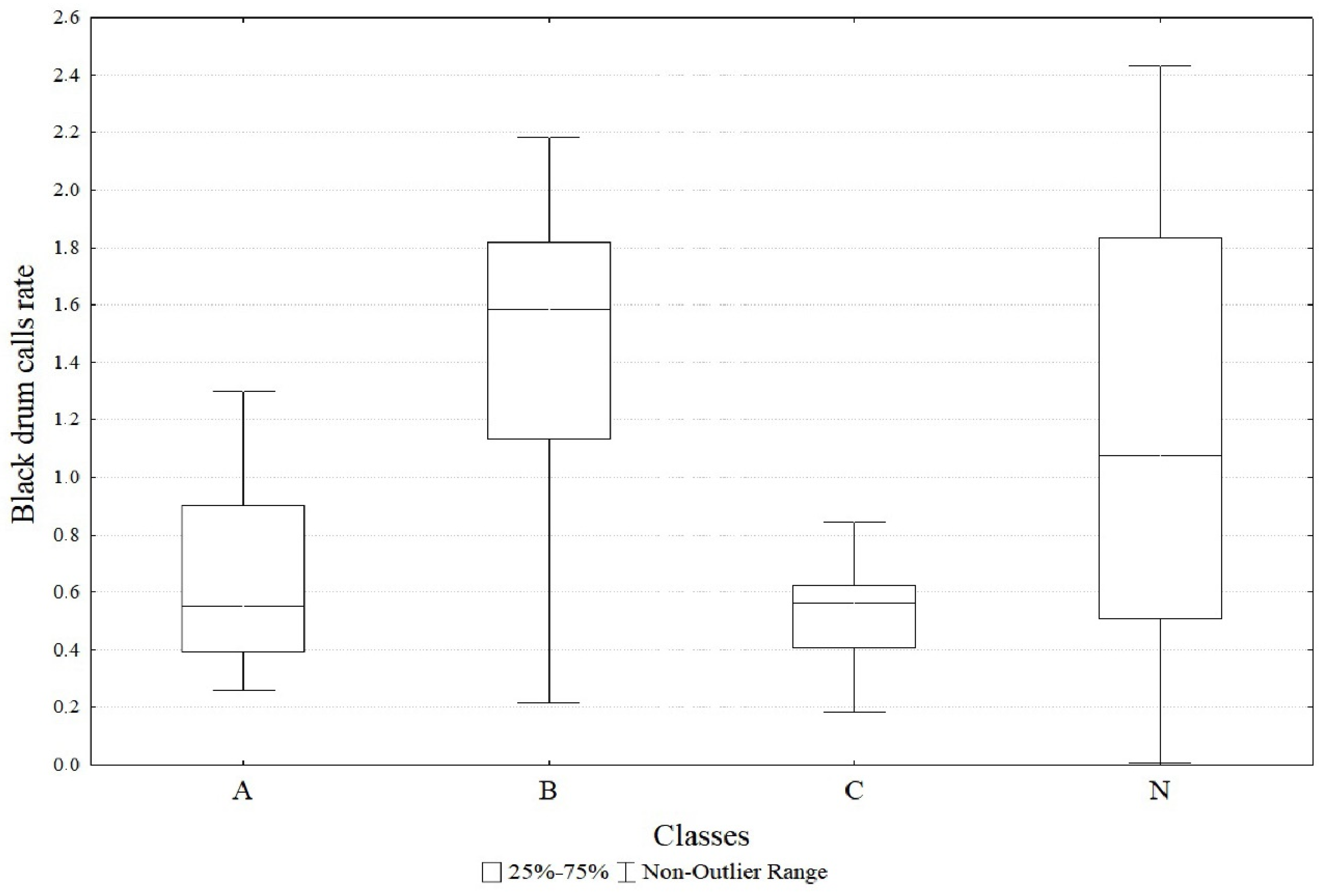
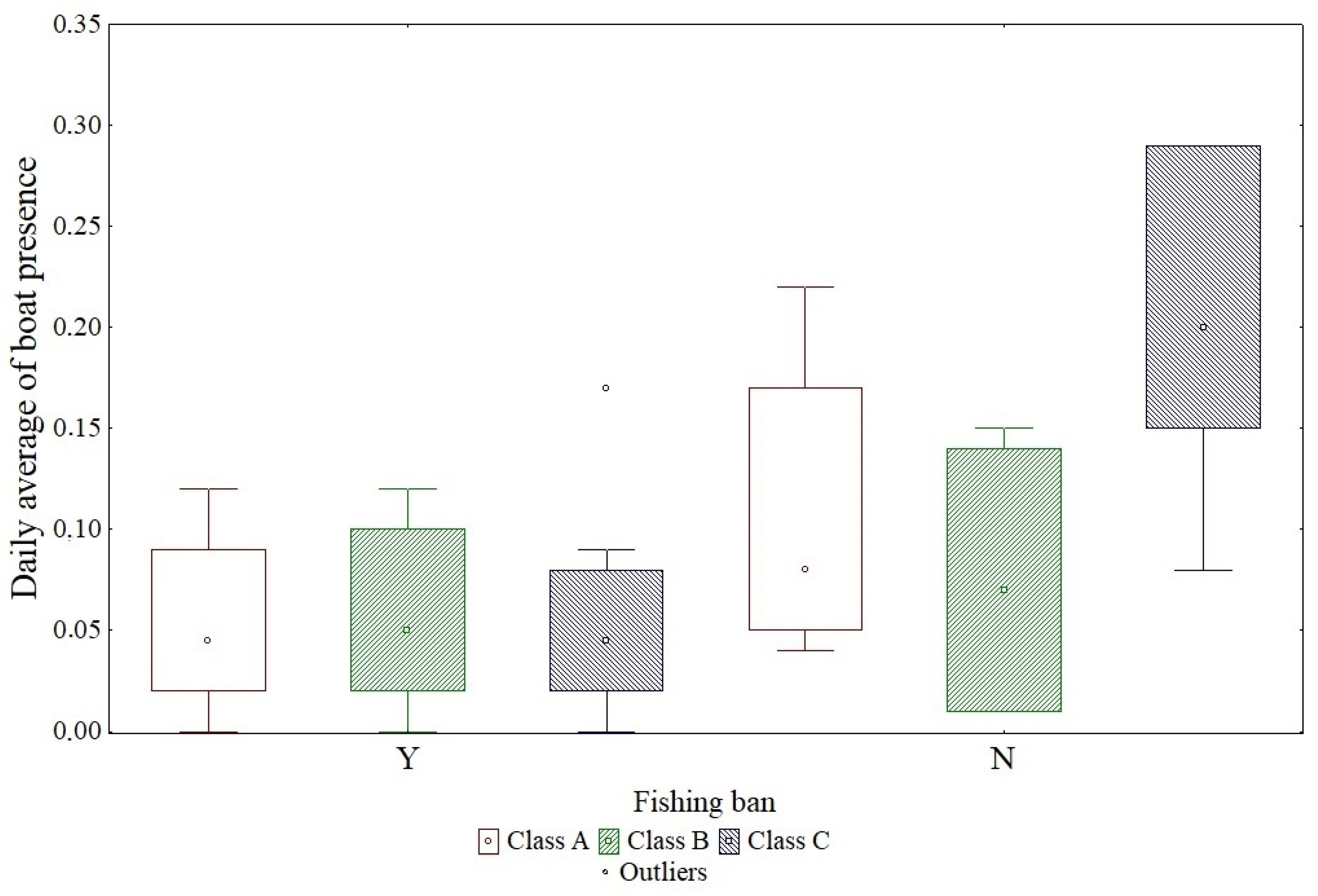
3. Results
4. Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Buscaino, G.; Ceraulo, M.; Pieretti, N.; Corrias, V.; Farina, A.; Filiciotto, F.; Maccarrone, V.; Grammauta, R.; Caruso, F.; Alonge, G.; et al. Temporal patterns in the soundscape of the shallow waters of a Mediterranean marine protected area. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceraulo, M.; Papale, E.; Caruso, F.; Filiciotto, F.; Grammauta, R.; Parisi, I.; Mazzola, S.; Farina, A.; Buscaino, G. Acoustic comparison of a patchy Mediterranean shallow water seascape: Posidonia oceanica meadow and sandy bottom habitats. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; Verma, A.; McCauley, R.; Gavrilov, A.; Parnum, I. The marine soundscape of the Perth Canyon. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 137, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermannsen, L.; Mikkelsen, L.; Tougaard, J.; Beedholm, K.; Johnson, M.; Madsen, P.T. Recreational vessels without Automatic Identification System (AIS) dominate anthropogenic noise contributions to a shallow water soundscape. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunc, H.P.; McLaughlin, K.E.; Schmidt, R. Aquatic noise pollution: Implications for individuals, populations, and ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Wright, A.J.; Ashe, E.; Blight, L.K.; Bruintjes, R.; Canessa, R.; Clark, C.W.; Cullis-Suzuki, S.; Dakin, D.T.; Erbe, C. Impacts of anthropogenic noise on marine life: Publication patterns, new discoveries, and future directions in research and management. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2015, 115, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C. Effects of underwater noise on marine mammals. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Rolland, R.M.; Parks, S.E.; Hunt, K.E.; Castellote, M.; Corkeron, P.J.; Nowacek, D.P.; Wasser, S.K.; Kraus, S.D. Evidence that ship noise increases stress in right whales. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 2363–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.J.; Soto, N.A.; Baldwin, A.L.; Bateson, M.; Beale, C.M.; Clark, C.; Deak, T.; Edwards, E.F.; Fernández, A.; Godinho, A.; et al. Do Marine Mammals Experience Stress Related to Anthropogenic Noise? Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 274–316. [Google Scholar]
- Buscaino, G.; Filiciotto, F.; Buffa, G.; Bellante, A.; Stefano, V.D.; Assenza, A.; Fazio, F.; Caola, G.; Mazzola, S. Impact of an acoustic stimulus on the motility and blood parameters of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiciotto, F.; Vazzana, M.; Celi, M.; Maccarrone, V.; Ceraulo, M.; Buffa, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G. Behavioural and biochemical stress responses of Palinurus elephas after exposure to boat noise pollution in tank. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiciotto, F.; Vazzana, M.; Celi, M.; Maccarrone, V.; Ceraulo, M.; Buffa, G.; Arizza, V.; de Vincenzi, G.; Grammauta, R.; Mazzola, S.; et al. Underwater noise from boats: Measurement of its influence on the behaviour and biochemistry of the common prawn (Palaemon serratus, Pennant 1777). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 478, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, R.A.; Noad, M.J.; McCauley, R.D.; Scott-Hayward, L.; Kniest, E.; Slade, R.; Paton, D.; Cato, D.H. Determining the behavioural dose–response relationship of marine mammals to air gun noise and source proximity. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 2878–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, M.M.; Noren, D.P.; Veirs, V.; Emmons, C.K.; Veirs, S. Speaking up: Killer whales (Orcinus orca) increase their call amplitude in response to vessel noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 125, EL27–EL32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.; Sigray, P.; Backström, T.; Magnhagen, C. Stress Response and Habituation to Motorboat Noise in Two Coastal Fish Species in the Bothnian Sea. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Popper, A.N., Hawkins, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 513–521. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, S.E.; Clark, C.W.; Tyack, P.L. Short-and long-term changes in right whale calling behavior: The potential effects of noise on acoustic communication. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 3725–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picciulin, M.; Sebastianutto, L.; Codarin, A.; Farina, A.; Ferrero, E.A. In situ behavioural responses to boat noise exposure of Gobius cruentatus (Gmelin, 1789; fam. Gobiidae) and Chromis chromis (Linnaeus, 1758; fam. Pomacentridae) living in a Marine Protected Area. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 386, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.N. Sciaenidae. Fishes North-East. Atl. Mediterr. 1986, 2, 865–874. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S. Fishes of the World, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ramcharitar, J.; Gannon, D.P.; Popper, A.N. Bioacoustics of fishes of the family Sciaenidae (croakers and drums). Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2006, 135, 1409–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connaughton, M.A.; Taylor, M.H. Seasonal and daily cycles in sound production associated with spawning in the weakfish, Cynoscion regalis. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1995, 42, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, H.-K.; Gilmore, R.G. Analysis of sound production in estuarine aggregations of Pogonias cromis, Bairdiella chrysoura, and Cynoscion nebulosus (Sciaenidae). Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1983, 22, 157–186. [Google Scholar]
- Azpelicueta, M.L.M.; Delpiani, S.M.; Cione, A.L.; Oliveira, C.; Marceniuk, A.P.; de Astarloa Díaz, J.M. Morphology and molecular evidence support the validity of Pogonias courbina (Lacepède, 1803) (Teleostei: Sciaenidae), with a redescription and neotype designation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, G.J.; Acha, E.M.; Lasta, C.A. Reproduction of black drum (Pogonias cromis) in the Rıo de la Plata estuary, Argentina. Fish. Res. 2002, 59, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousseau, M.B.; Perrotta, R.G. Peces Marinos de Argentina. Biologıa, Distribucion, Pesca; INIDEP: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2004; ISBN 987-20245-4-5. [Google Scholar]
- Norbis, W.; Paesch, L.; Galli, O. Los recursos pesqueros de la costa de Uruguay: Ambiente, biología y gestión. In Bases Para La Conservación y el Manejo de la Costa Uruguaya; Menafra, R., Rodriguez-Gallego, L., Scarabino, F., Eds.; Vida Silvestre Uruguay: Montevideo, Uruguay, 2006; pp. 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Locascio, J.V.; Burghart, S.; Mann, D.A. Quantitative and temporal relationships of egg production and sound production by black drum Pogonias cromis. J. Fish. Biol. 2012, 81, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locascio, J.V.; Mann, D.A. Localization and source level estimates of black drum (Pogonias cromis) calls. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 1868–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellechea, J.S.; Norbis, W.; Olsson, D.; Fine, M.L. Calls of the black drum (Pogonias cromis: Sciaenidae): Geographical differences in sound production between northern and southern hemisphere populations. J. Exp. Zool. Part Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2011, 315A, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcharitar, J.; Popper, A.N. Masked auditory thresholds in sciaenid fishes: A comparative study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locascio, J.V.; Mann, D.A. Diel and seasonal timing of sound production by black drum (Pogonias cromis). Fish. Bull. 2011, 109, 327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Nieland, D.L.; Wilson, C.A. Reproductive biology and annual variation of reproductive variables of black drum in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1993, 122, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, E.-L.; Kvarnemo, C.; Dekhla, I.; Schöld, S.; Andersson, M.H.; Svensson, O.; Amorim, M.C.P. Continuous but not intermittent noise has a negative impact on mating success in a marine fish with paternal care. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.D.; Popper, A.N. A sound approach to assessing the impact of underwater noise on marine fishes and invertebrates. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, E.; Gamba, M.; Perez-Gil, M.; Martin, V.M.; Giacoma, C. Dolphins Adjust Species-Specific Frequency Parameters to Compensate for Increasing Background Noise. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiga, I.; Aldred, N.; Caldwell, G.S. Anthropogenic noise compromises the anti-predator behaviour of the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smott, S.; Monczak, A.; Miller, M.E.; Montie, E.W. Boat noise in an estuarine soundscape—A potential risk on the acoustic communication and reproduction of soniferous fish in the May River, South Carolina. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.O.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Ladich, F. Effects of ship noise on the detectability of communication signals in the Lusitanian toadfish. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, K.; Forland, T.N.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Rieucau, G.; Slabbekoorn, H.; Sivle, L.D. Predicting the effects of anthropogenic noise on fish reproduction. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2020, 30, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciulin, M.; Sebastianutto, L.; Codarin, A.; Calcagno, G.; Ferrero, E.A. Brown meagre vocalization rate increases during repetitive boat noise exposures: A possible case of vocal compensation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D.E.; Johnston, C.E. Evidence of the Lombard effect in fishes. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 25, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, K.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Fonseca, P.J.; Fox, C.J.; Heubel, K.U. Noise can affect acoustic communication and subsequent spawning success in fish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isla, F.I. Seasonal behaviour of Mar Chiquita tidal inlet in relation to adjacent beaches, Argentina. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 13, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Iribarne, O. Reserva de Biosfera Mar Chiquita: Características Físicas, Biológicas y Ecológicas; Editorial Martín: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Isacch, J.P. Implementing the biosphere reserve concept: The case of Parque Atlántico Mar Chiquito biosphere reserve from Argentina. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousseau, M.B.; Díaz de Astarloa, J.M.; Figueroa, D.E. La ictiofauna de la laguna Mar Chiquita. In Reserva de Biosfera Mar Chiquita Características Físicas Biológicas Ecológicas; Iribarne, O., Ed.; Editorial Martín: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2001; pp. 187–203. [Google Scholar]
- Lucifora, L.O. Tiburones y Pesca de Tiburones en Mar Chiquita; Editorial Martín: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, D.O.; Barbini, S.A.; Díaz de Astarloa, J.M.; Martos, P. Fish abundance and distribution patterns related to environmental factors in a choked temperate coastal lagoon (Argentina). Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 61, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Castro, M.; Díaz de Astarloa, J.M.; Cousseau, M.B.; Figueroa, D.E.; Delpiani, S.M.; Bruno, D.O.; Guzzoni, J.M.; Blasina, G.E.; Deli Antoni, M.Y. Fish composition in a south-western Atlantic temperate coastal lagoon: Spatial–temporal variation and relationships with environmental variables. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2009, 89, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiciotto, F.; Sal Moyano, M.P.; Hidalgo, F.; de Vincenzi, G.; Bazterrica, M.C.; Ceraulo, M.; Corrias, V.; Quinci, E.M.; Lorusso, M.; Mazzola, S.; et al. Underwater acoustic communication during the mating behaviour of the semi-terrestrial crab Neohelice Granulata. Sci. Nat. 2019, 106, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sal Moyano, M.P.; Ceraulo, M.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G.; Gavio, M.A. Sound production mechanism in the semiterrestrial crab Neohelice granulata (Brachyura, Varunidae). J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3466–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceraulo, M.; Sal Moyano, M.P.; Bazterrica, M.C.; Hidalgo, F.J.; Papale, E.; Grammauta, R.; Gavio, M.A.; Mazzola, S.; Buscaino, G. Spatial and temporal variability of the soundscape in a Southwestern Atlantic coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 2255–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcovecchio, J.; Freije, H.; De Marco, S.; Gavio, A.; Ferrer, L.; Andrade, S.; Beltrame, O.; Asteasuain, R. Seasonality of hydrographic variables in a coastal lagoon: Mar Chiquita, Argentina. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2006, 16, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazterrica, M.C.; Bruschetti, C.M.; Alvarez, M.F.; Iribarne, O.; Botto, F. Effects of Macroalgae on the Recruitment, Growth, and Body Condition of an Invasive Reef Forming Polychaete in a South-Western Atlantic Coastal Lagoon. J. Sea Res. 2014, 88, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reta, R.; Martos, P.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Piccolo, M.C.; Ferrante, A. Características hidrográficas del estuario de la laguna Mar Chiquita. In Reserva de Biosfera Mar Chiquita: Características Físicas Biológicas Ecológicas; Editorial Martín: Mar del Plata, Argentina, 2001; pp. 31–52. [Google Scholar]
- Fasano, J.L.; Hernandez, M.; Isla, F.I.; Schnack, E.J. Aspectos evolutivos y ambientales de la laguna Mar Chiquita (provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Oceanol. Acta 1982, 185–292. Available online: https://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=12189619 (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Li, S.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Peng, C.; Fang, L.; Lin, M.; Xing, L.; Zhang, P. Mid- to high-frequency noise from high-speed boats and its potential impacts on humpback dolphins. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.A. Anthropogenic and natural sources of ambient noise in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B. lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using S4 Classes 2012. R package version 0.999999-0. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lme4/index.html (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Forrest, T.; Miller, G.; Zagar, J. Sound propagation in shallow water: Implications for acoustic communication by aquatic animals. Bioacoustics 1993, 4, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabbekoorn, H.; Bouton, N.; van Opzeeland, I.; Coers, A.; ten Cate, C.; Popper, A.N. A noisy spring: The impact of globally rising underwater sound levels on fish. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.W.; Ellison, W.T.; Southall, B.L.; Hatch, L.; Van Parijs, S.M.; Frankel, A.; Ponirakis, D. Acoustic masking in marine ecosystems: Intuitions, analysis, and implication. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voellmy, I.K.; Purser, J.; Flynn, D.; Kennedy, P.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N. Acoustic noise reduces foraging success in two sympatric fish species via different mechanisms. Anim. Behav. 2014, 89, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.C.; McCormick, M.I.; Meekan, M.G.; Simpson, S.D.; Nedelec, S.L.; Chivers, D.P. School is out on noisy reefs: The effect of boat noise on predator learning and survival of juvenile coral reef fishes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codarin, A.; Wysocki, L.E.; Ladich, F.; Picciulin, M. Effects of ambient and boat noise on hearing and communication in three fish species living in a marine protected area (Miramare, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladich, F. Effects of noise on sound detection and acoustic communication in fishes. In Animal Communication and Noise; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 65–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bruintjes, R.; Radford, A.N. Chronic playback of boat noise does not impact hatching success or post-hatching larval growth and survival in a cichlid fish. PeerJ 2014, 2, e594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelec, S.L.; Mills, S.C.; Lecchini, D.; Nedelec, B.; Simpson, S.D.; Radford, A.N. Repeated exposure to noise increases tolerance in a coral reef fish. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, M.; Pérez-Arjona, I.; Perez, E.J.B.; Ceraulo, M.; Bou-Cabo, M.; Benson, T.; Espinosa, V.; Beltrame, F.; Mazzola, S.; Vazzana, M. The effect of low frequency noise on the behaviour of juvenile Sparus Aurata. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, 3795–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Recording Sessions | Start Time | End Time | Recordings without Fishing Ban | Recording with Fishing Ban | Total Recording |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Days (minutes) | Number of Days (minutes) | Minutes | |||
| 1 | 01/11/2017 14:00 | 06/11/2017 11:20 | 2 (240) | 4 (420) | 660 |
| 2 | 11/11/2017 01:00 | 15/11/2017 17:50 | 2 (268) | 3 (348) | 616 |
| 3 | 18/11/2017 12:00 | 23/11/2017 07:10 | 3 (364) | 3 (336) | 700 |
| Total Days of Recordings | 7 | 10 |
| Estimate | Standard Error | Z Value | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black drum call rate | (Intercept) | 0.89 | 0.16 | 5.49 | <0.0001 |
| Class A | −0.46 | 0.23 | −1.99 | <0.05 | |
| Class B | 0.22 | 0.19 | 1.17 | 0.24 | |
| Class C | −0.83 | 0.24 | −3.39 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceraulo, M.; Sal Moyano, M.P.; Hidalgo, F.J.; Bazterrica, M.C.; Mazzola, S.; Gavio, M.A.; Buscaino, G. Boat Noise and Black Drum Vocalizations in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon (Argentina). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010044
Ceraulo M, Sal Moyano MP, Hidalgo FJ, Bazterrica MC, Mazzola S, Gavio MA, Buscaino G. Boat Noise and Black Drum Vocalizations in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon (Argentina). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeraulo, Maria, María Paz Sal Moyano, Fernando Jose Hidalgo, María Cielo Bazterrica, Salvatore Mazzola, María Andrea Gavio, and Giuseppa Buscaino. 2021. "Boat Noise and Black Drum Vocalizations in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon (Argentina)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010044
APA StyleCeraulo, M., Sal Moyano, M. P., Hidalgo, F. J., Bazterrica, M. C., Mazzola, S., Gavio, M. A., & Buscaino, G. (2021). Boat Noise and Black Drum Vocalizations in Mar Chiquita Coastal Lagoon (Argentina). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010044







