Performance Assessment of ERA5 Wave Data in a Swell Dominated Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
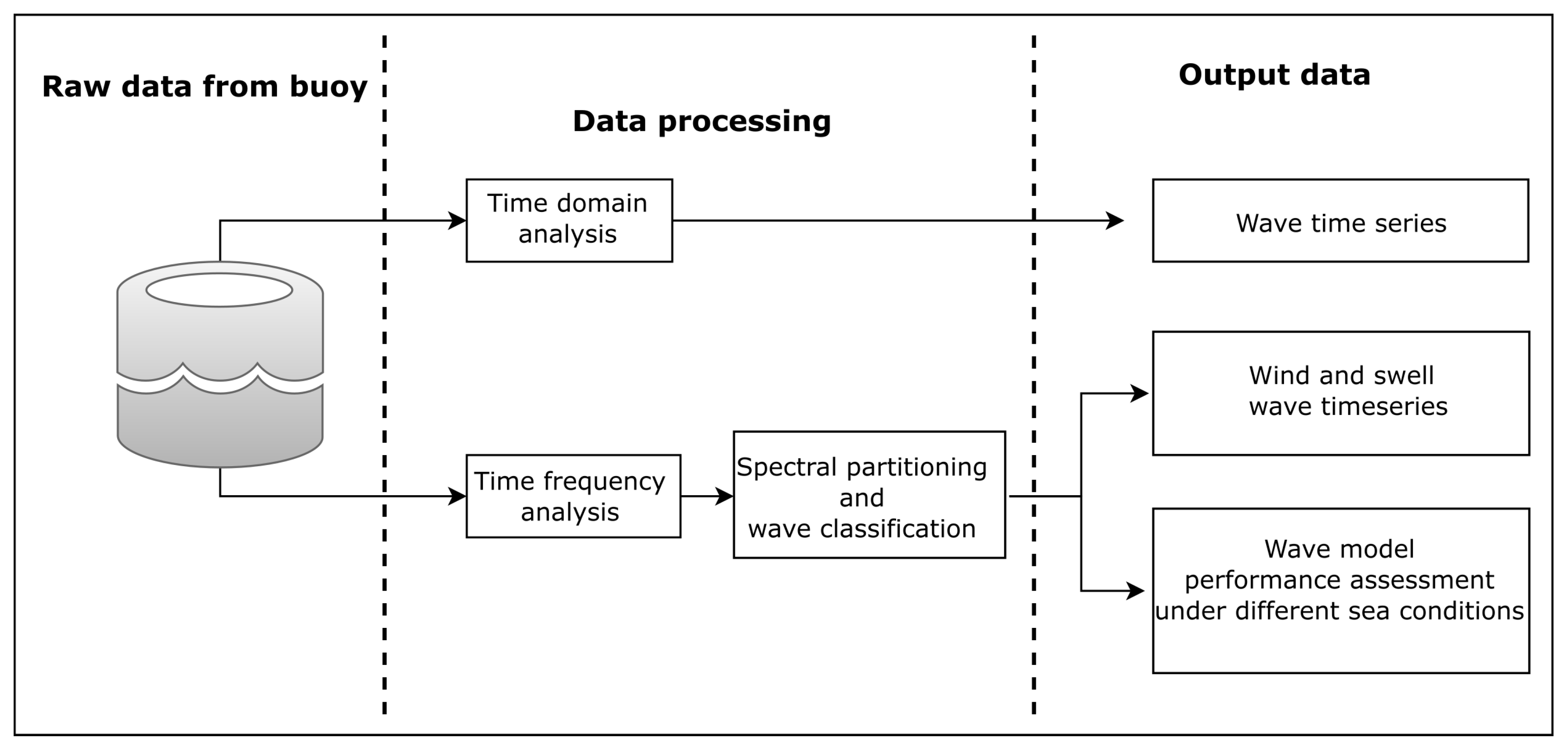
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study and Data Sources
2.2. Spectral Analysis and Partition Schemes
2.3. Performance Evaluation of ERA-I and ERA5 Wave Datasets
3. Observed Data Analysis
3.1. Wave Characteristics
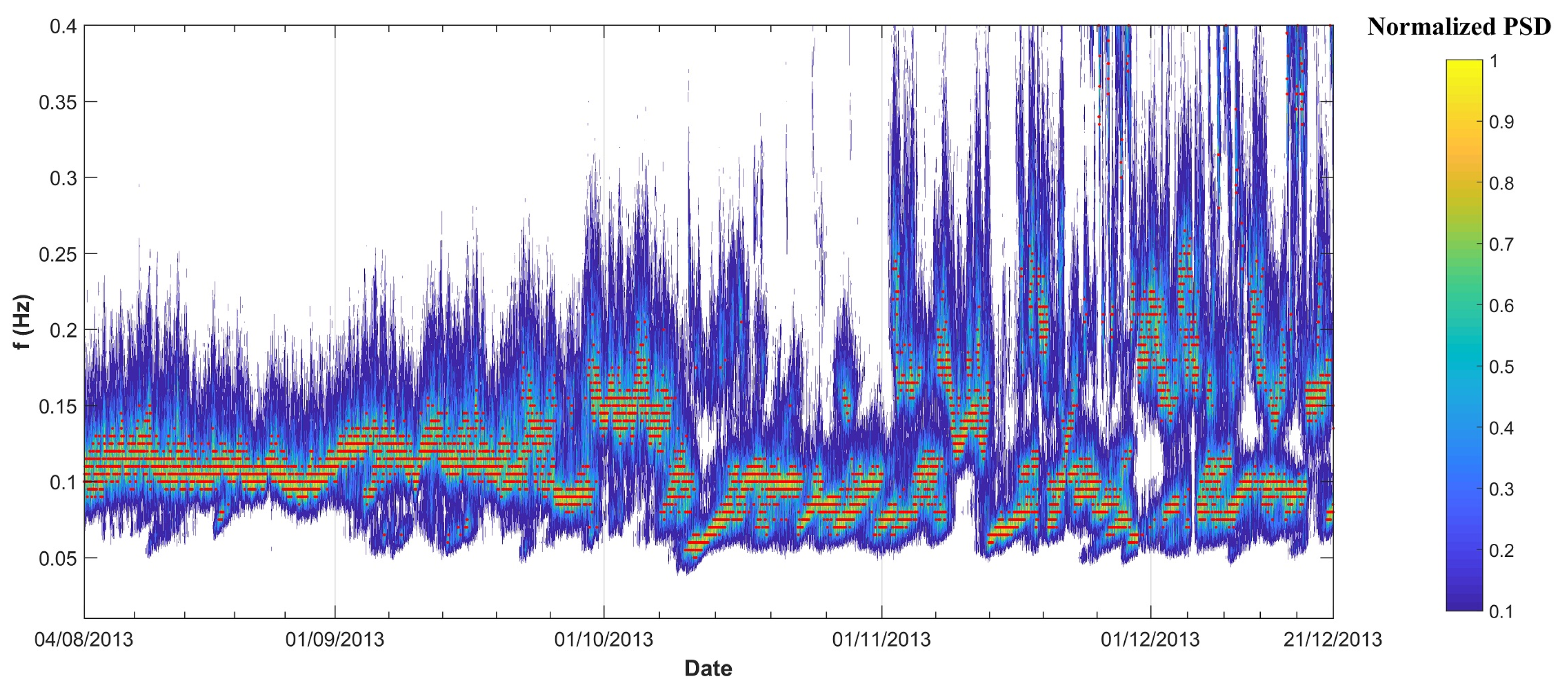
3.2. Wave Spectra
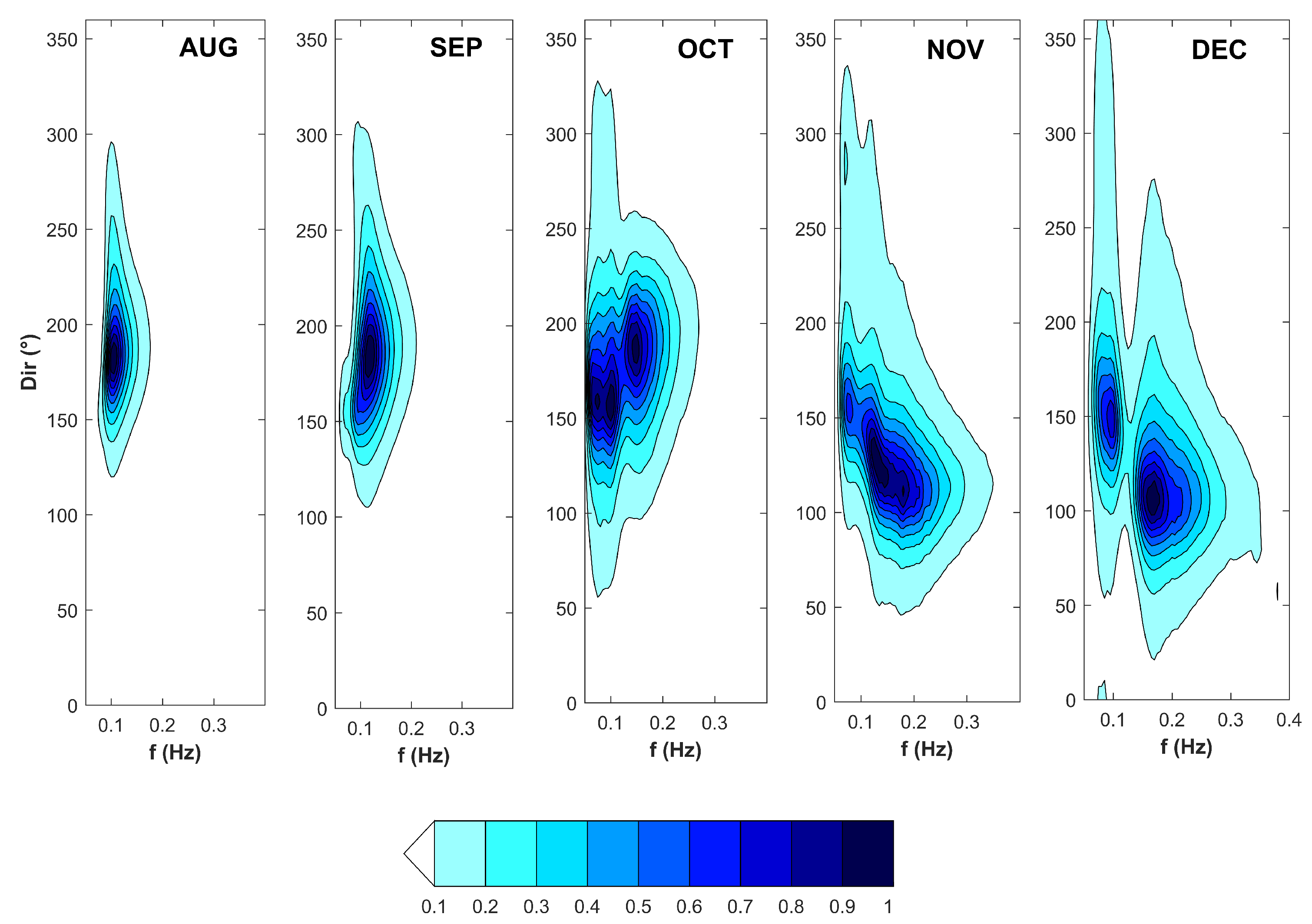
3.3. Spectral Partitioning
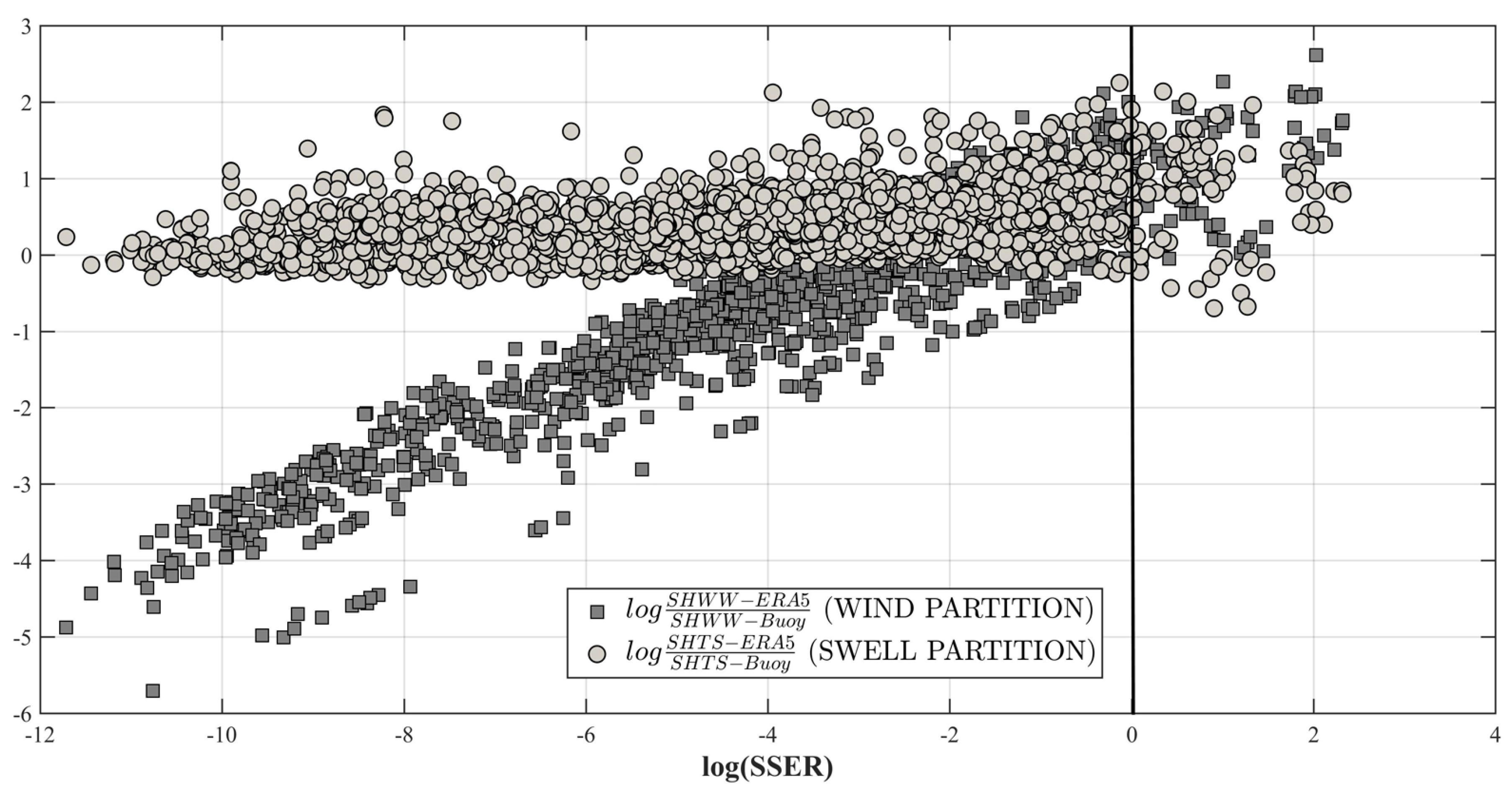
3.4. Comparison between Observed Data and ERA Wave Datasets
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. List of Wave and “Goodness-of-Fit” Parameters
- moment of energy spectrum
- Significant wave height
- Mean wave period
- Mean zero-crossing period
- Energy period
- Mean wave direction
- Directional Spread of
- Significant wave steepness
- Peakedness parameter
- Spectral width parameter
- Narrowness parameter
- Root mean squared error
- Relative bias
- Coefficient of determination
- Coefficient of efficiency
- Circular correlation coefficient
References
- Stopa, J.E.; Cheung, K.F. Intercomparison of wind and wave data from the ECMWF Reanalysis Interim and the NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Ocean Model. 2014, 75, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnes, O.J.; Abdalla, S.; Bidlot, J.R.; Breivik, Ø. Marine wind and wave height trends at different ERA-Interim forecast ranges. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasquali, D.; Bruno, M.; Celli, D.; Damiani, L.; Di Risio, M. A simplified hindcast method for the estimation of extreme storm surge events in semi-enclosed basins. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 85, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, D.O.; Nutricato, R.; Lorusso, R.; Lombardi, N.; Bovenga, F.; Bruno, M.F.; Chiaradia, M.T.; Milillo, G. On the geolocation accuracy of COSMO-SkyMed products. In SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XV; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Volume 9642, pp. 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, M.F.; Molfetta, M.G.; Pratola, L.; Mossa, M.; Nutricato, R.; Morea, A.; Nitti, D.O.; Chiaradia, M.T. A combined approach of field data and earth observation for coastal risk assessment. Sensors 2019, 19, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Risio, M.; Bruschi, A.; Lisi, I.; Pesarino, V.; Pasquali, D. Comparative Analysis of Coastal Flooding Vulnerability and Hazard Assessment at National Scale. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sterl, A.; Caires, S. Climatology, variability and extrema of ocean waves: The Web-based KNMI/ERA-40 wave atlas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semedo, A.; Sušelj, K.; Rutgersson, A.; Sterl, A. A global view on the wind sea and swell climate and variability from ERA-40. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Guan, C. Analysis of the global swell distributions using ECMWF Re-analyses wind wave data. J. Ocean Univ. China (Engl. Ed.) 2011, 10, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhuin, F.; Bertotti, L.; Bidlot, J.R.; Cavaleri, L.; Filipetto, V.; Lefevre, J.M.; Wittmann, P. Comparison of wind and wave measurements and models in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Eng. 2007, 34, 526–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, L. The wind and wave atlas of the Mediterranean Sea-the calibration phase. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 2, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaleri, L.; Sclavo, M. The calibration of wind and wave model data in the Mediterranean Sea. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.S.; Naseef, M. Performance of ERA-Interim wave data in the nearshore waters around India. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2015, 32, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, M.C.; Jha, A.; Chaphekar, A.S.; Ravikant, K. Neural networks for wave forecasting. Ocean Eng. 2001, 28, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Solomatine, D.; Azimian, A.; Heemink, A. Learning from data for wind–wave forecasting. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, P.; Di Risio, M.; Beltrami, G.; Bellotti, G.; Pasquali, D. The use of wave forecasts for maritime activities safety assessment. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 62, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chapron, B.; Ezraty, R.; Vandemark, D. A global view of swell and wind sea climate in the ocean by satellite altimeter and scatterometer. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2002, 19, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulev, S.K.; Grigorieva, V.; Sterl, A.; Woolf, D. Assessment of the reliability of wave observations from voluntary observing ships: Insights from the validation of a global wind wave climatology based on voluntary observing ship data. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Serio, F.; Mossa, M. Environmental monitoring in the Mar Grande basin (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12662–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Serio, F.; Mossa, M. Meteo and Hydrodynamic Measurements to Detect Physical Processes in Confined Shallow Seas. Sensors 2018, 18, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armenio, E.; De Serio, F.; Mossa, M. Analysis of data characterizing tide and current fluxes in coastal basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3441–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentini, N.; Damiani, L.; Molfetta, M.G.; Saponieri, A. New coastal video-monitoring system achievement and development. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2017, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. News from C3S: ERA5. Presented at the Using ECMWF Forecast, Reading, UK, 12–16 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjha, R.; Tjernström, M.; Semedo, A.; Svensson, G.; Cardoso, R.M. Structure and variability of the Oman coastal low-level jet. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2015, 67, 25285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboobacker, V.; Vethamony, P.; Rashmi, R. “Shamal” swells in the Arabian Sea and their influence along the west coast of India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, C.M.; Yavary, M.; Yavary, M. Wave agitation studies for port expansion-Salalah, Oman. In Proceedings of the Ports 2004: Port Development in the Changing World, Houston, TX, USA, 23–26 May 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Goring, D. Ship surging induced by long waves in Port of Salalah, Oman. In Proceedings of the Coasts & Ports 2005 Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 20–23 September 2005; Volume 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Anoop, T.R.; Kumar, V.S.; Shanas, P.R.; Johnson, G. Surface Wave Climatology and Its Variability in the North Indian Ocean Based on ERA-Interim Reanalysis. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2015, 32, 1372–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.S.; Shanas, P.; Dubhashi, K. Shallow water wave spectral characteristics along the eastern Arabian Sea. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.S.; Nair, M.A. Inter-annual variations in wave spectral characteristics at a location off the central west coast of India. Ann. Geophys. 2015, 33, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, R.; Aboobacker, V.; Vethamony, P.; John, M. Co-existence of wind seas and swells along the west coast of India during non-monsoon season. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vethamony, P.; Aboobacker, V.; Menon, H.; Kumar, K.A.; Cavaleri, L. Superimposition of wind seas on pre-existing swells off Goa coast. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 87, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komen, G.J.; Cavaleri, L.; Donelan, M. Dynamics and Modelling of Ocean Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; de Rosnay, P.; Bell, B.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C.; Abdalla, S.; Alonso-Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bechtold, P.; et al. Operational Global Reanalysis: Progress, Future Directions and Synergies with NWP, ERA Report Series; ECMWF Shinfield Park: Reading, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogstad, H.E. Maximum likelihood estimation of ocean wave spectra from general arrays of wave gauges. Model. Identif. Control 1988, 9, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuik, A.; Van Vledder, G.P.; Holthuijsen, L. A method for the routine analysis of pitch-and-roll buoy wave data. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1020–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, M. On the joint distribution of the periods and amplitudes of sea waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. The statistical analysis of a random, moving surface. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1957, 249, 321–387. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, D.; Longuet-Higgins, M.S. The statistical distribution of the maxima of a random function. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences; The Royal Society: London, UK, 1956; Volume 237, pp. 212–232. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, Y. Numerical experiments on wave statistics with spectral simulation. Rept. Port Harb. Res. Inst. 1970, 9, 3–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rye, H. Wave group formation among storm waves. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Coastal Engineering, Copenhagen, Denmark, 24–28 June 1974; pp. 164–183. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, W.C.; Nelson, A.R.; Sedivy, D.G. Wave group anatomy of ocean wave spectra. In Proceedings of the 19th Conference on Coastal Engineering, Houston, TX, USA, 3–7 September 1984; pp. 661–677. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, D. Comparison of spectral partitioning techniques for wind wave and swell. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2012, 14, 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Portilla, J.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J.; Monbaliu, J. Spectral partitioning and identification of wind sea and swell. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2009, 26, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Zhong, J. A Practical Method of Extracting Wind Sea and Swell from Directional Wave Spectrum. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2015, 32, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, W.J., Jr.; Moskowitz, L. A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of SA Kitaigorodskii. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 5181–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.H.G.; Banner, M.L.; Young, I.R. Revisiting the Pierson–Moskowitz asymptotic limits for fully developed wind waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2003, 33, 1301–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Phillips, O.M. Automated analysis of ocean surface directional wave spectra. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2001, 18, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Ocampo-Torres, F.J.; García-Nava, H. Wind sea and swell separation of 1D wave spectrum by a spectrum integration method. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2012, 29, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.W.; Hwang, P.A. An operational method for separating wind sea and swell from ocean wave spectra. J. Atmos. Oceans Technol. 2001, 18, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Performance evaluation of hydrological models: Statistical significance for reducing subjectivity in goodness-of-fit assessments. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; McCabe, G.J. Evaluating the use of “goodness-of-fit” measures in hydrologic and hydroclimatic model validation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, D.; Freni, G.; Iacobellis, V.; Mascaro, G.; Montanari, A. Validation of hydrological models: Conceptual basis, methodological approaches and a proposal for a code of practice. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2012, 42, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammalamadaka, S.R.; Sengupta, A. Topics in Circular Statistics; World Scientific: Singapore, 2001; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, D.; Bhan, S. Monsoon 2013—A Report; India Meteorological Department: Pune, India, 2014; pp. 1–222.
- Glejin, J.; Sanil Kumar, V.; Nair, B.; Singh, J. Influence of winds on temporally varying short and long period gravity waves in the near shore regions of the eastern Arabian Sea. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glejin, J.; Kumar, V.S.; Amrutha, M.; Singh, J. Characteristics of long-period swells measured in the near shore regions of eastern Arabian Sea. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2016, 8, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, G.; Soares, C.G. The bivariate distribution of wave heights and periods in mixed sea states. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 1999, 121, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameter | AUG-SEP | OCT-NOV-DEC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Range | Average | Range | |
| (m) | 2.85 | 1.02–5.94 | 1.13 | 0.30–4.01 |
| (m) | 1.08 | 0.42–2.04 | 0.42 | 0.10–1.50 |
| (m) | 1.21 | 0.46–2.28 | 0.47 | 0.21–1.67 |
| (m) | 1.70 | 0.64–3.22 | 0.66 | 0.29–2.32 |
| (m) | 2.11 | 0.80–3.99 | 0.82 | 0.25–2.96 |
| (s) | 6.81 | 4.97–8.42 | 5.34 | 2.90–9.69 |
| (s) | 8.32 | 5.98–9.87 | 7.14 | 3.23–12.11 |
| (s) | 8.39 | 6.05–10.3 | 7.75 | 3.24–13.74 |
| AUG-SEP | OCT-NOV-DEC | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (m) | 0.32 | 0.19 | |
| Relative Bias (%) | 0.08 | 0.185 | |
| 0.60 | 0.81 | ||
| NSE | 0.515 | 0.679 | |
| RMSE (m) | 0.431 | 0.770 | |
| Relative Bias (%) | −0.02 | −0.05 | |
| 0.36 | 0.72 | ||
| NSE | 0.178 | 0.667 | |
| MWD | RMSE (deg) | 10.29 | 27.29 |
| Bias (deg) | −7.675 | −20.25 | |
| −0.02 | 0.909 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruno, M.F.; Molfetta, M.G.; Totaro, V.; Mossa, M. Performance Assessment of ERA5 Wave Data in a Swell Dominated Region. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030214
Bruno MF, Molfetta MG, Totaro V, Mossa M. Performance Assessment of ERA5 Wave Data in a Swell Dominated Region. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(3):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030214
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruno, Maria Francesca, Matteo Gianluca Molfetta, Vincenzo Totaro, and Michele Mossa. 2020. "Performance Assessment of ERA5 Wave Data in a Swell Dominated Region" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 3: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030214
APA StyleBruno, M. F., Molfetta, M. G., Totaro, V., & Mossa, M. (2020). Performance Assessment of ERA5 Wave Data in a Swell Dominated Region. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(3), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030214







