The Interpretation of Biogeochemical Growths on Gold Coins from the SS Central America Shipwreck: Applications for Biogeochemistry and Geoarchaeology
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Significance of the California Gold Rush
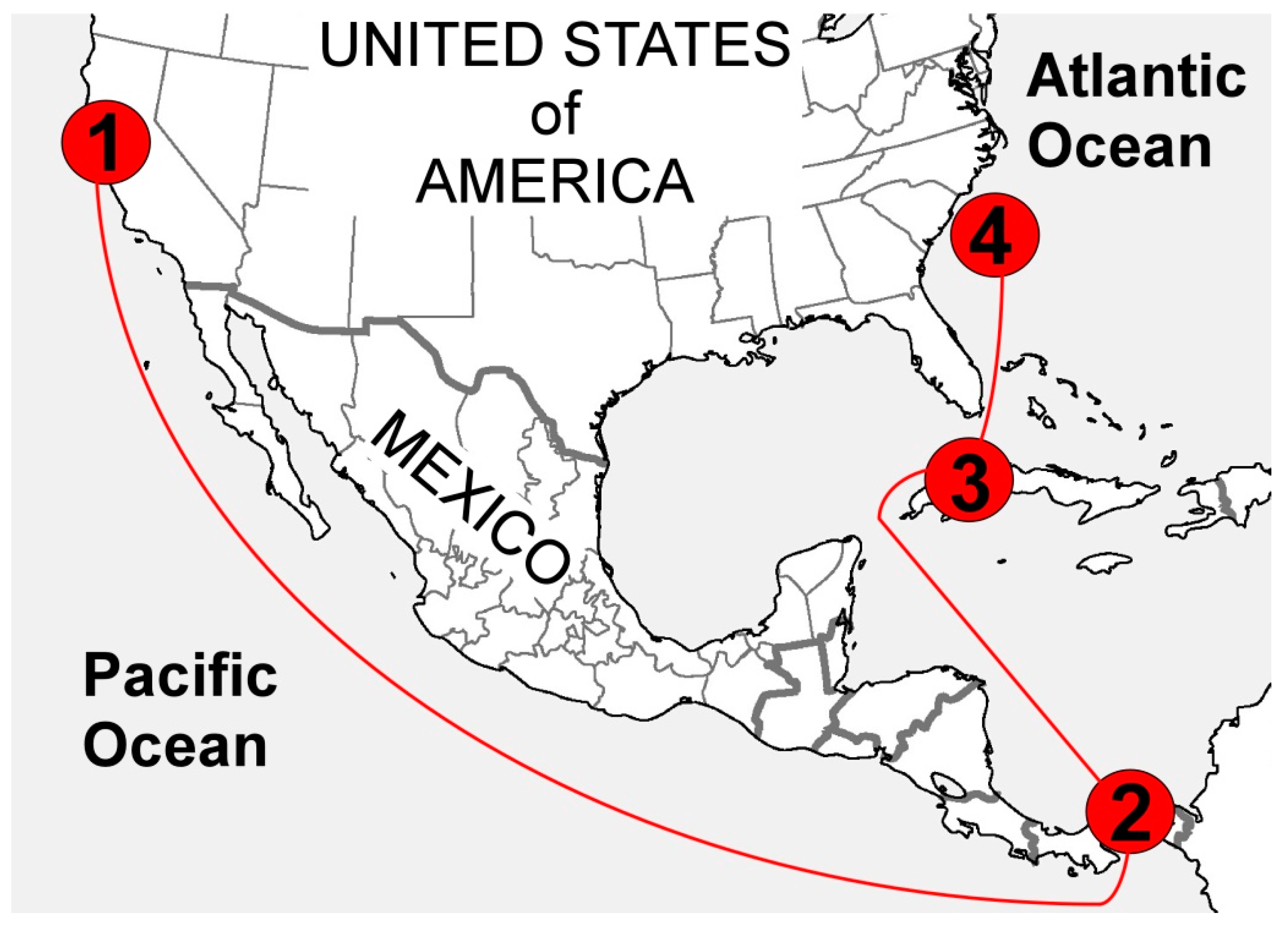
1.2. The Loss of the SS Central America
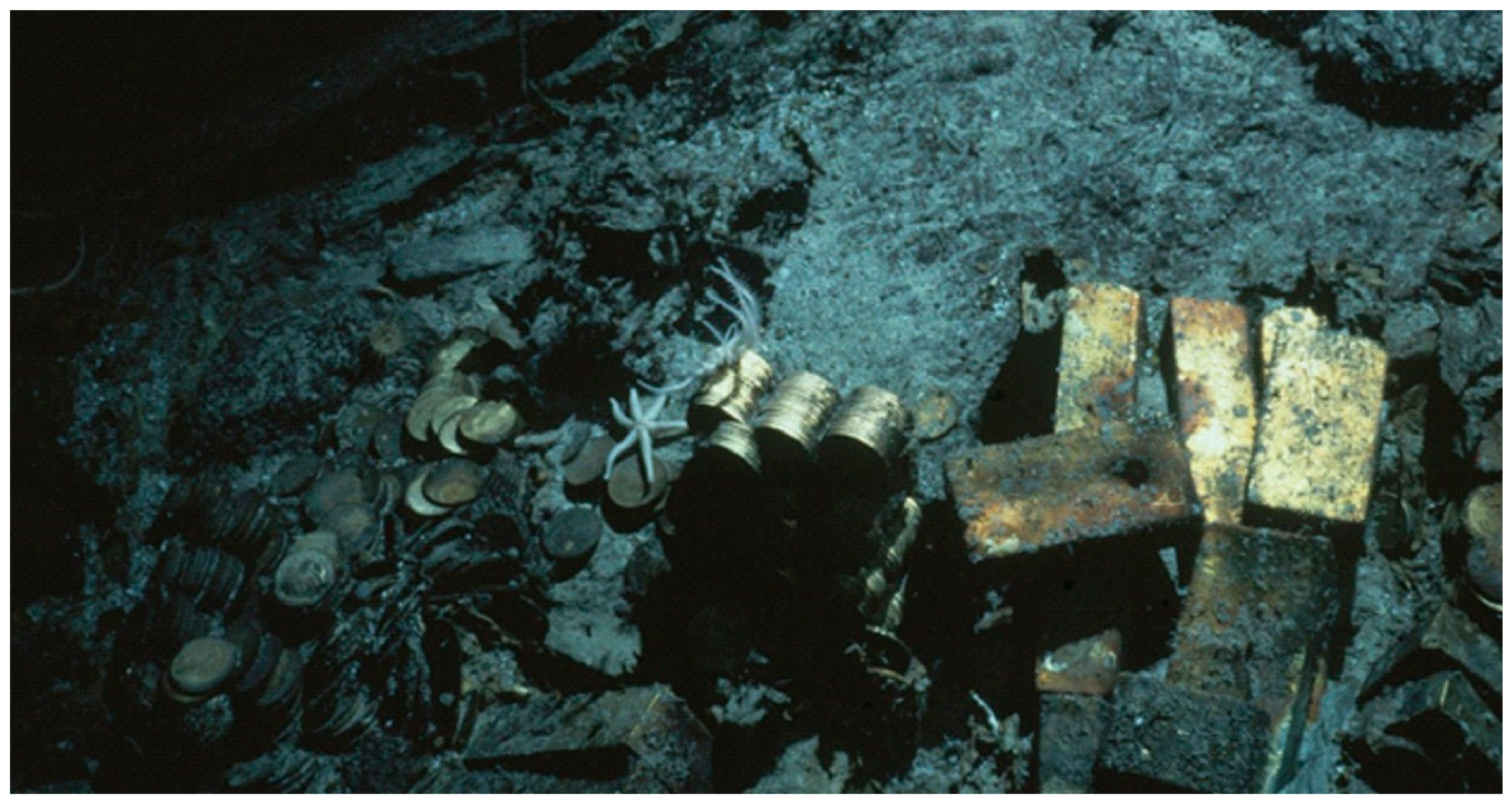
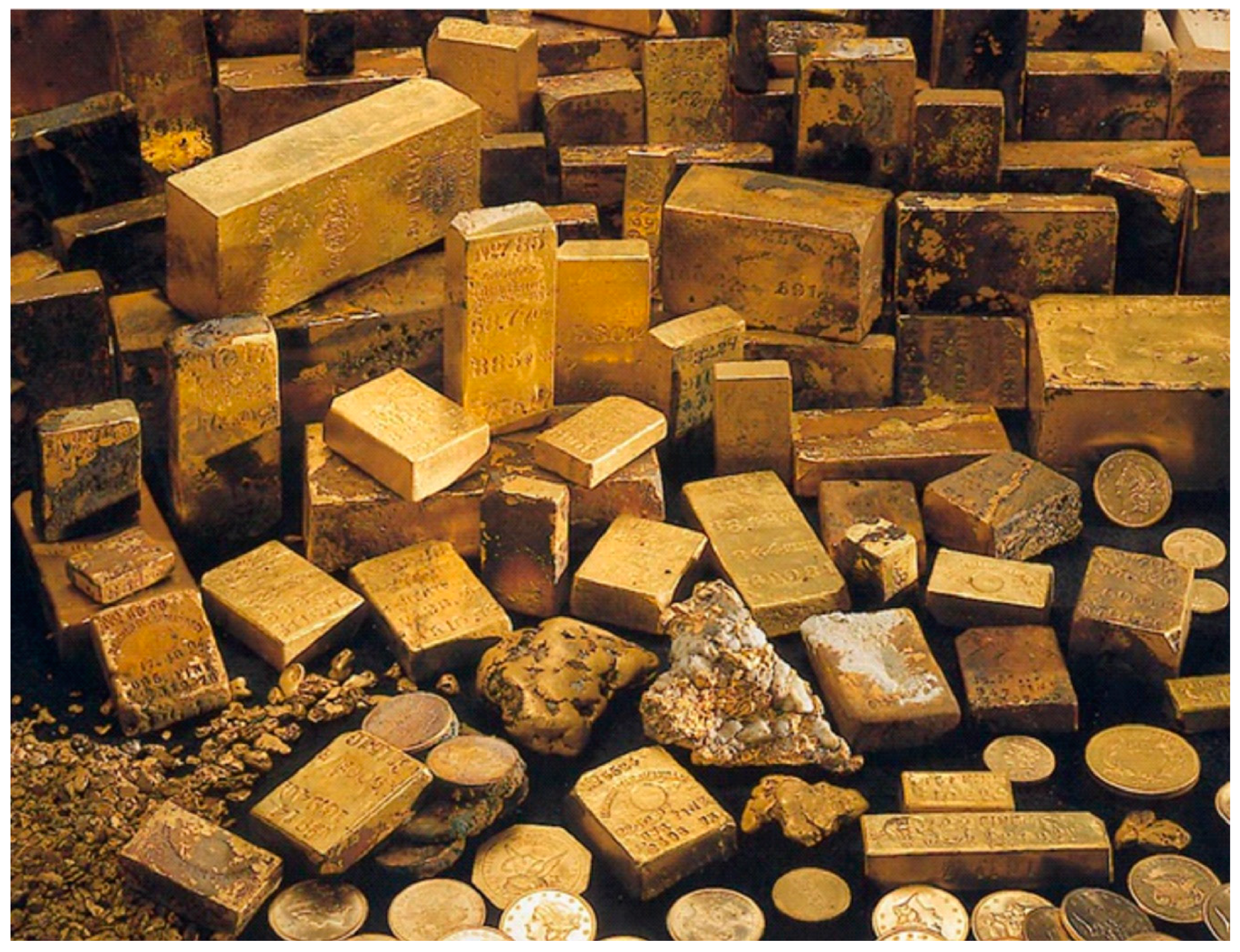
1.3. Discovery of the Shipwreck, and Recovery Efforts
1.4. Previous Work
2. Materials and Methods
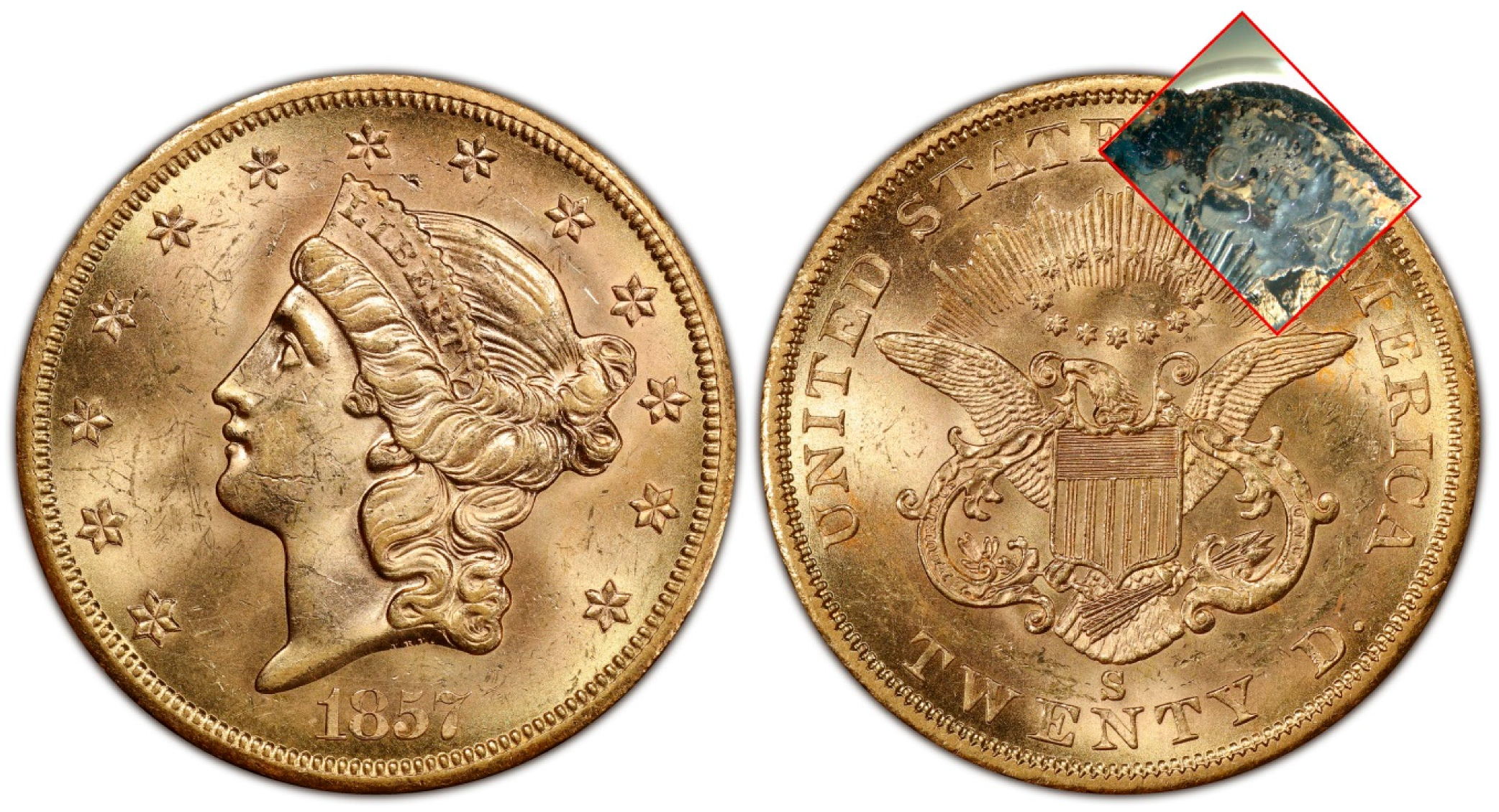
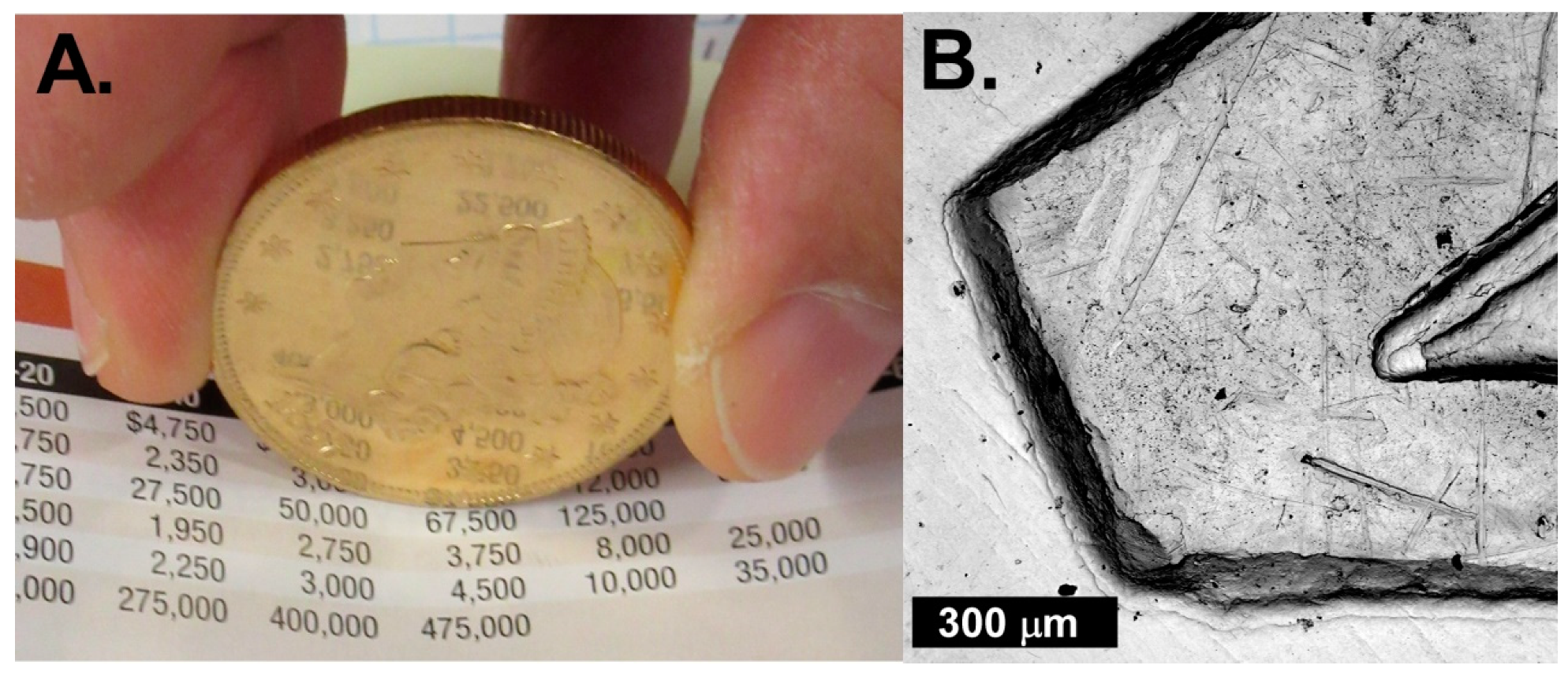
3. Results
4. Discussion
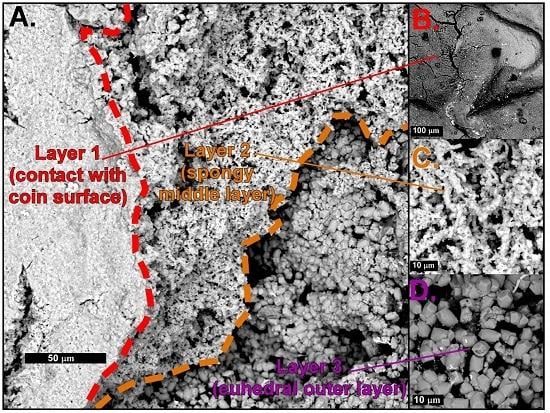
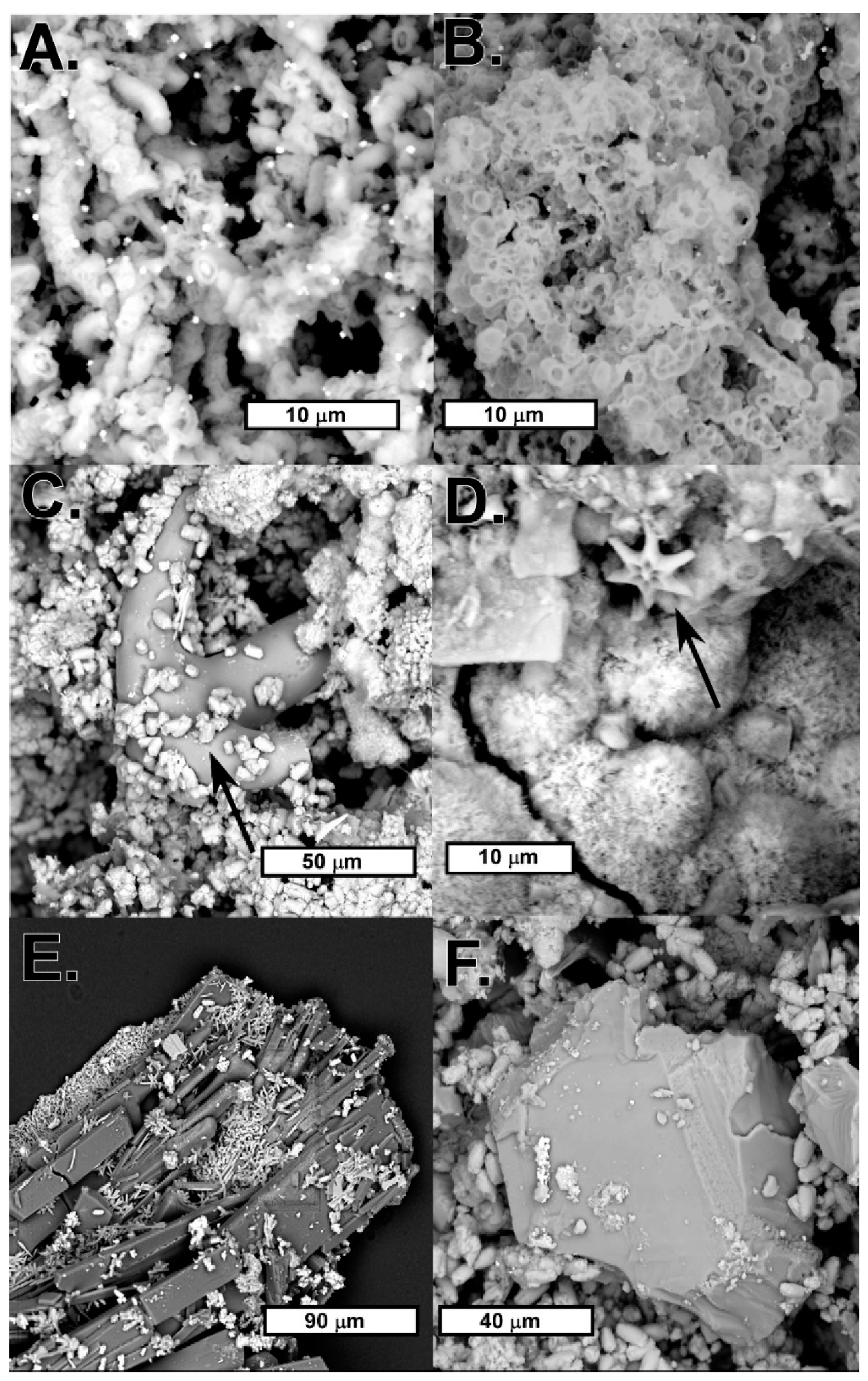
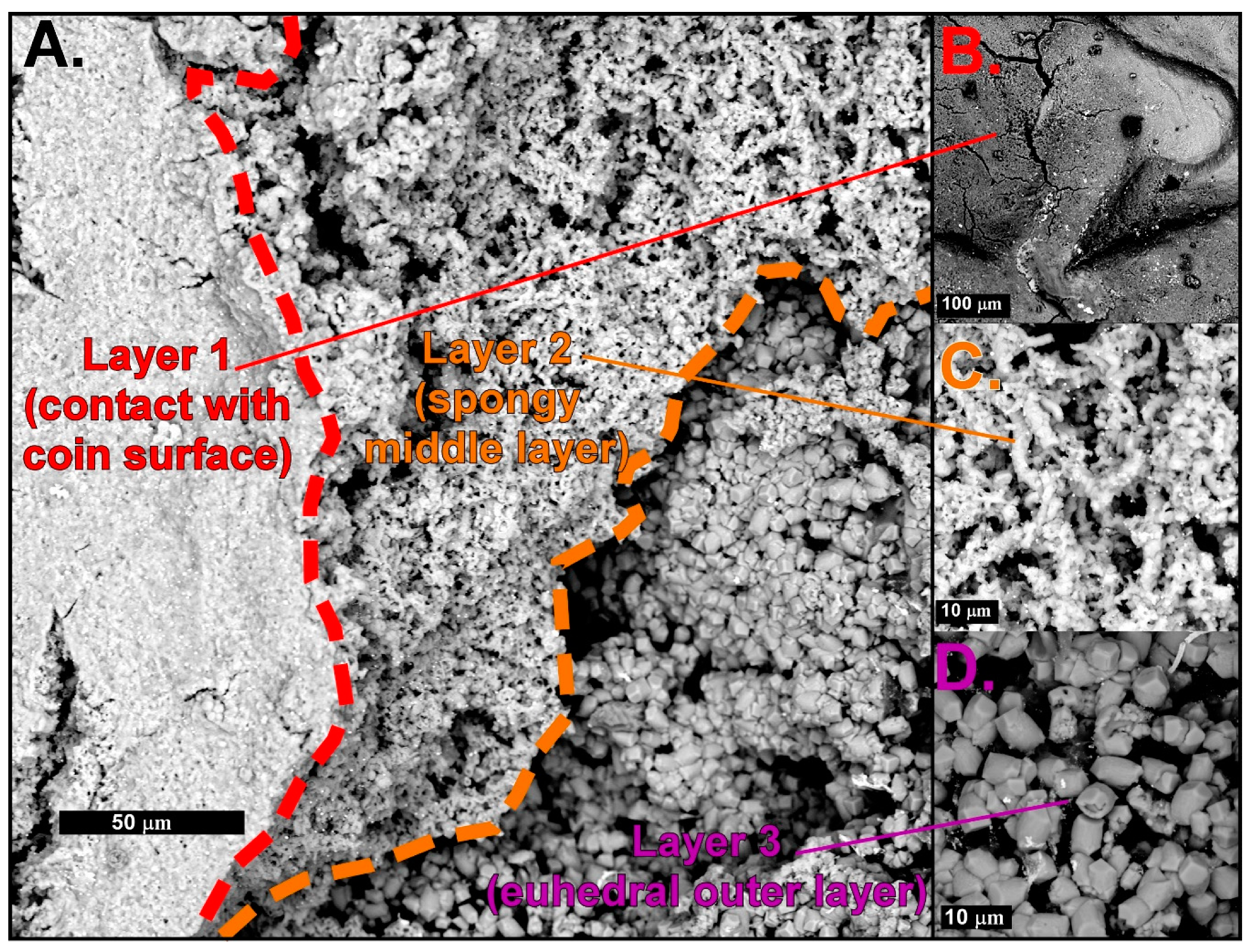
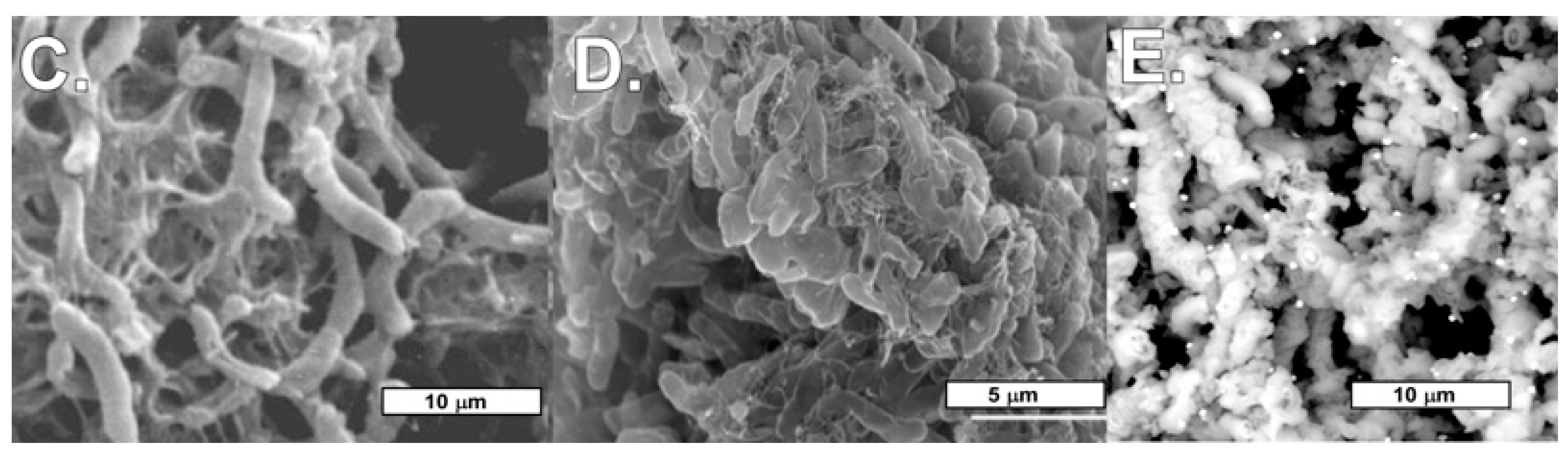
4.1. Mineral Crust Formation
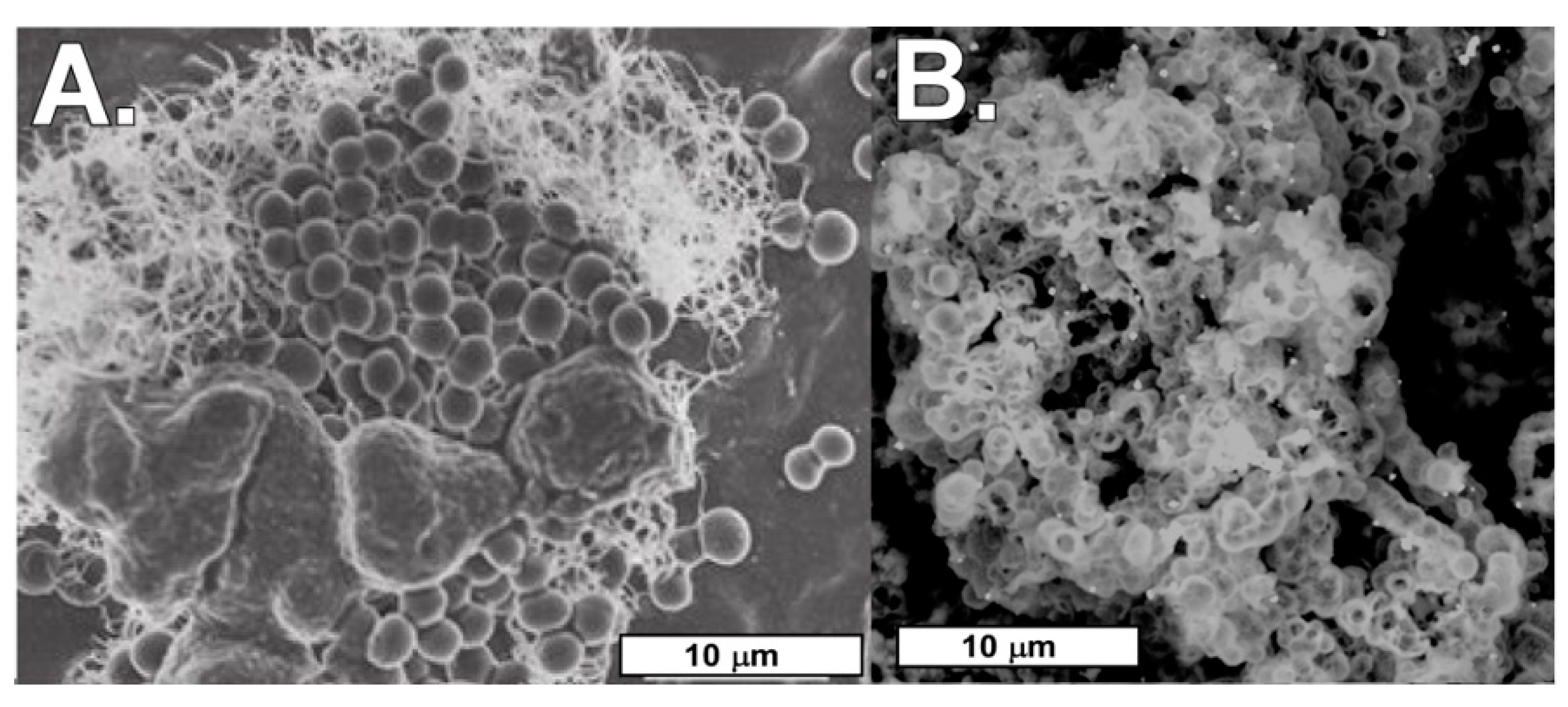
4.2. Biomats and Nanoparticulate Gold
4.2.1. Biomats
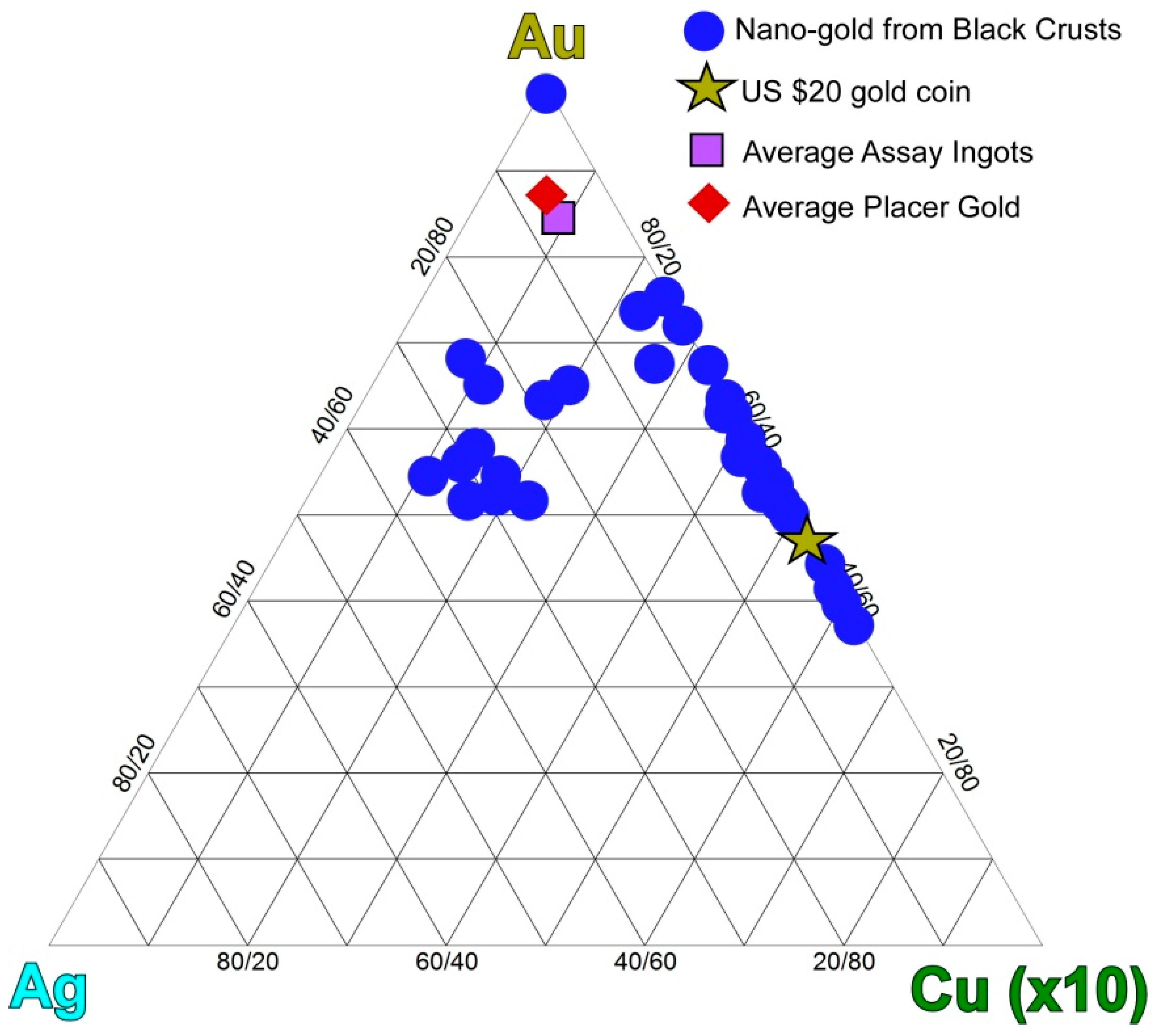
4.2.2. Nanoparticulate Gold and Probable Gold Sources
4.3. Chronology and Significance of Crust Development
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bancroft, H.H. The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft Volume XXII the History of California; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1886; Volume 1846–1848, p. 824. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, B.C. Murder State: California’s Native American Genocide, 1846–1873; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2012; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Madley, B. An American Genocide: The United States and the California Indian Catastrophe, 1846–1873; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2016; p. 712. [Google Scholar]
- Kinder, G. Ship of Gold in the Deep Blue Sea; Atlantic Monthly Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.W. Mines of the San Gabriels; La Siesta Press: Glendale, CA, USA, 1973; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Hamann, W.E. Geology and geochemistry of the Big Horn Gold Mine, San Gabriel Mountains, Southern California. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Herdendorf, C.E.; Thompson, T.G.; Evans, R.D. Science on a deep-ocean shipwreck. Ohio J. Sci. 1995, 95, 4–212. [Google Scholar]
- Landsea, C.W. The Atlantic Hurricane Database Re-Analysis Project: Documentation for the 1851–1910 Alterations and Additions to the HURDAT Database of Hurricanes and Typhoons: Past, Present and Future; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 177–221. [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame, L. The World’s Most Valuable Shipwreck Discoveries; The Weather Channel. Available online: https://weather.com/news/news/12-amazing-sunken-treasure-discoveries-20130816 (accessed on 10 April 2018).
- Shuster, J.; Johnston, W.C.; Magarvey, A.N.; Gordon, A.R.; Barron, K.; Banerjee, R.N.; Southam, G. Structural and chemical characterization of placer gold grains: Implications for bacterial contributions to grain formation . Geomicrobiol. J. 2015, 32, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, J.; Reith, F.; Cornelis, G.; Parsons, J.E.; Parsons, J.M.; Southam, G. Secondary gold structures: Relics of past biogeochemical transformations and implications for colloidal gold dispersion in subtropical environments. Chem. Geol. 2017, 450, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenov, G.D.; Melchiorre, E.B.; Ricker, F.N.; DeWitt, E. Insights from Pb Isotopes for Native Gold Formation During Hypogene and Supergene Processes at Rich Hill, Arizona. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, E.B.; Kamenov, G.D.; Sheets-Harris, C.; Andronikov, A.; Leatham, W.B.; Yahn, J.; Lauretta, D.S. Climate-induced geochemical and morphological evolution of placer gold deposits at Rich Hill, Arizona, USA. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2017, 129, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, E.B.; Orwin, P.M.; Reith, F.; Rea, M.A.D.; Yahn, J.; Allison, R. Biological and Geochemical Development of Placer Gold Deposits at Rich Hill, Arizona, USA. Minerals 2018, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, P.; Canepa, E. A review of studies on corrosion of metals and alloys in deep-sea environment. Ocean Eng. 2014, 87, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.T. Quantitative analysis of silicates and oxide minerals: Comparison of Monte-Carlo, ZAF and Phi-Rho-Z procedures. In Microbeam Analysis Society; Newbury, D.E., Ed.; San Francisco Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Donovan, J.J.; Snyder, D.A.; Rivers, M.L. An improved interference correction for trace element analysis. Microbeam Annu. 1993, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yeoman, R.S. A Guide Book of United States Coins (The Official Red Book), 68th ed.; Whitman Publishing: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014; p. 464. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiorse, W.C. Biology of iron-and manganese-depositing bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1984, 38, 515–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiho, K. Benthic foraminiferal dissolved-oxygen index and dissolved-oxygen levels in the modern ocean. Geology 1994, 22, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech Iwona, B.; Gaylarde Christine, C. Recent advances in the study of biocorrosion: An overview. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 30, 117–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.J.; Henry-Stanley, M.J.; Barnes, A.M.; Dunny, G.M.; Wells, C.L. Ultrastructure of a novel bacterial form located in Staphylococcus aureus In Vitro and In Vivo catheter-associated biofilms. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 60, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reith, F.; Brugger, J.; Zammit, C.M.; Nies, D.H.; Southam, G. Geobiological cycling of gold: From fundamental process understanding to exploration solutions. Minerals 2013, 3, 367–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelissa, S.O.; Abdallah, M.; Jama, C.; Faille, C.; Chihib, N.E. Bacterial contamination and biofilm formation on abiotic surfaces and strategies to overcome their persistence. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 3326–3346. [Google Scholar]
- Westall, F. The nature of fossil bacteria: A guide to the search for extraterrestrial life. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1999, 104, 16437–16451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forty, A.J. Corrosion micromorphology of noble metal alloys and depletion gilding. Nature 1979, 282, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, F.; Etschmann, B.; Grosse, C.; Moors, H.; Benotmane, M.A.; Monsieurs, P.; Grass, G.; Doonan, C.; Vogt, S.; Lai, B.; et al. Mechanisms of gold biomineralization in the bacterium Cupriavidus metallidurans. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17757–17762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, L.; Etschmann, B.; Brugger, J.; Shapter, J.; Southam, G.; Reith, F. Biomineralization of gold in biofilms of Cupriavidus metallidurans. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2013, 47, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, F.; Lengke, M.F.; Falconer, D.; Craw, D.; Southam, G. Winogradski Review: The geomicrobiology of gold. Int. Soc. Microb. Ecol. J. 2007, 1, 567–584. [Google Scholar]
- Reith, F.; Fairbrother, L.; Nolze, G.; Wilhelmi, O.; Clode, P.L.; Gregg, A.; Parsons, J.E.; Wakelin, S.A.; Pring, A.; Hough, R.; et al. Nanoparticle factories: Biofilms hold key to gold dispersion and nugget formation. Geology 2010, 38, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesemann, N.; Mohr, J.; Grosse, C.; Herzberg, M.; Hause, G.; Reith, F.; Nies, D.H. Influence of copper resistance determinants on gold transformation by Cupriavidus metallidurans strain CH34. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, M.G.; Stactile, W. Corrosion Science and Technology; Plenum Press: London, UK, 1970; p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- Cullimore, D.R.; Johnston, L. The impact of bioconcretious structures (rusticles) on the RMS Titanic: Implications to maritime steel structures. In Proceedings of the 2000 Annual Meeting of the Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6 May 2000; Volume 9, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cullimore, D.R.; Johnston, L. Rusticles on the RMS Titanic. JMBA Glob. Mar. Environ. 2007, 4, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Church, R.A.; Warren, D.J.; Irion, J.B. Analysis of deepwater shipwrecks in the Gulf of Mexico: Artificial reef effect of six World War II shipwrecks. Oceanography 2009, 22, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høibråten, S.; Thoresen, P.E.; Haugan, A. The sunken nuclear submarine Komsomolets and its effects on the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 202, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Espada, L.; De la Fuente, D.; Chico, B. Metallic corrosion of the tanker “Prestige” in deep seawater. Rev. Metal 2004, 40, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paul, S. Estimation of corrosion rate of mild steel in sea water and application of genetic algorithms to find minimum corrosion rate. Can. Metall. Q. 2010, 49, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, R.D. The Discovery of the Titanic; Warner Books: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Porro, C.; Kaur, B.; Mann, H.; Ventosa, A. Halomonas titanicae sp. nov. a halophilic bacterium isolated from the RMS Titanic. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, M.D. The Parker Gold Piece. Gold Bull. 1986, 19, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melchiorre, E.B.; Seymour, B.H.; Evans, R.D. The Interpretation of Biogeochemical Growths on Gold Coins from the SS Central America Shipwreck: Applications for Biogeochemistry and Geoarchaeology. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7070209
Melchiorre EB, Seymour BH, Evans RD. The Interpretation of Biogeochemical Growths on Gold Coins from the SS Central America Shipwreck: Applications for Biogeochemistry and Geoarchaeology. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2019; 7(7):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7070209
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelchiorre, Erik B., Bryan H. Seymour, and Robert D. Evans. 2019. "The Interpretation of Biogeochemical Growths on Gold Coins from the SS Central America Shipwreck: Applications for Biogeochemistry and Geoarchaeology" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 7, no. 7: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7070209
APA StyleMelchiorre, E. B., Seymour, B. H., & Evans, R. D. (2019). The Interpretation of Biogeochemical Growths on Gold Coins from the SS Central America Shipwreck: Applications for Biogeochemistry and Geoarchaeology. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 7(7), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7070209