A Reasoned Comparison between Two Hydrodynamic Models: Delft3D-Flow and ROMS (Regional Oceanic Modelling System)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Model Description
2.1.1. Primitive Equations
2.1.2. Boundary Conditions
2.1.3. Turbulence Closures in ROMS
2.1.4. Turbulence Closures in Delft3D
2.2. Description of the Test Cases
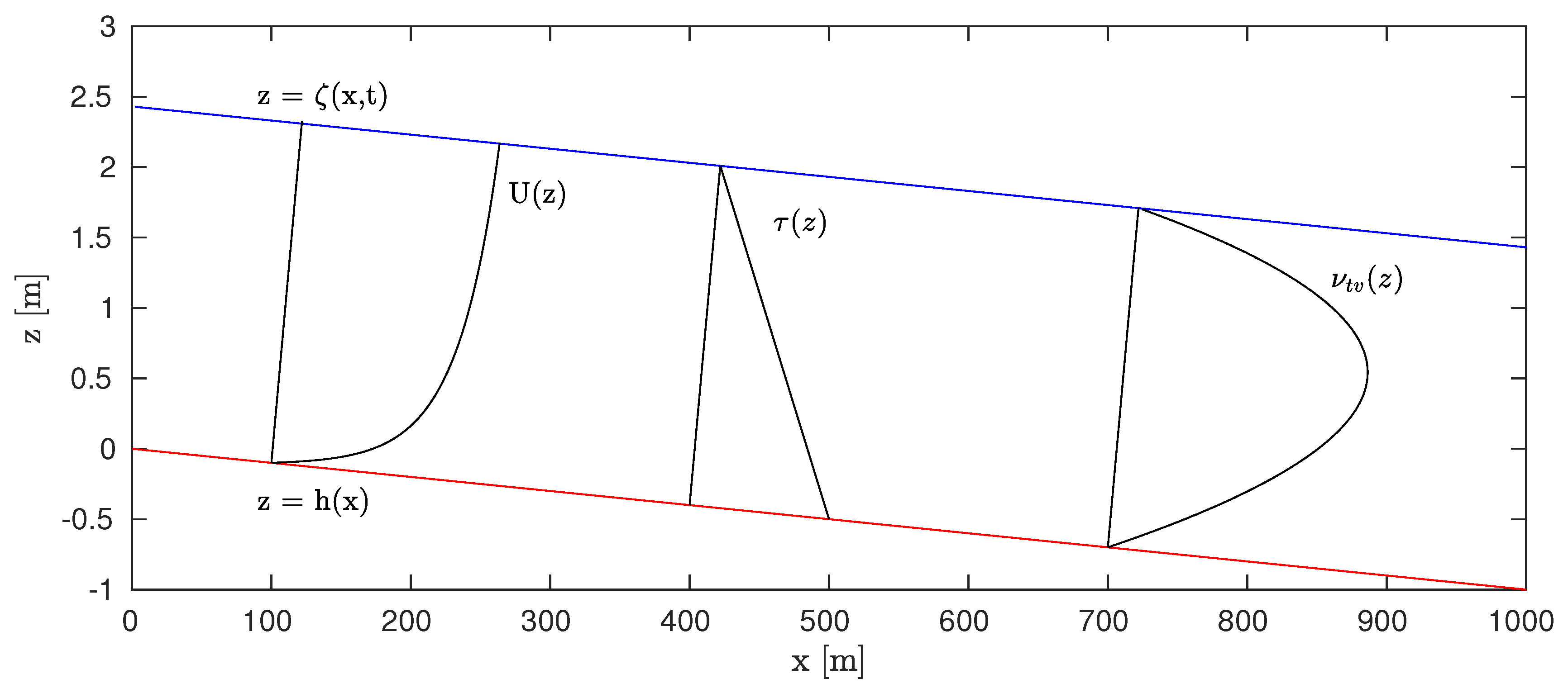
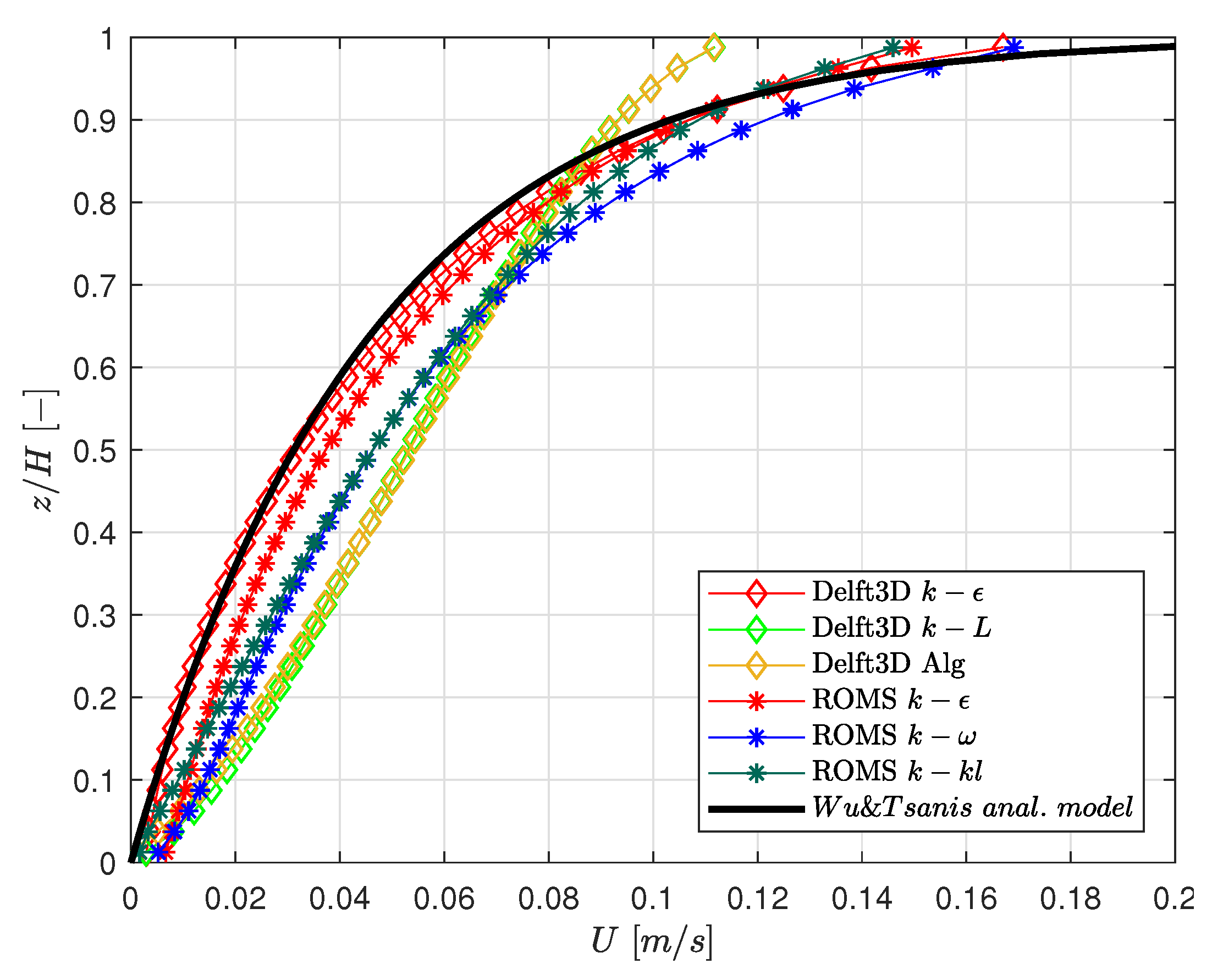
2.2.1. Open Channel Flow
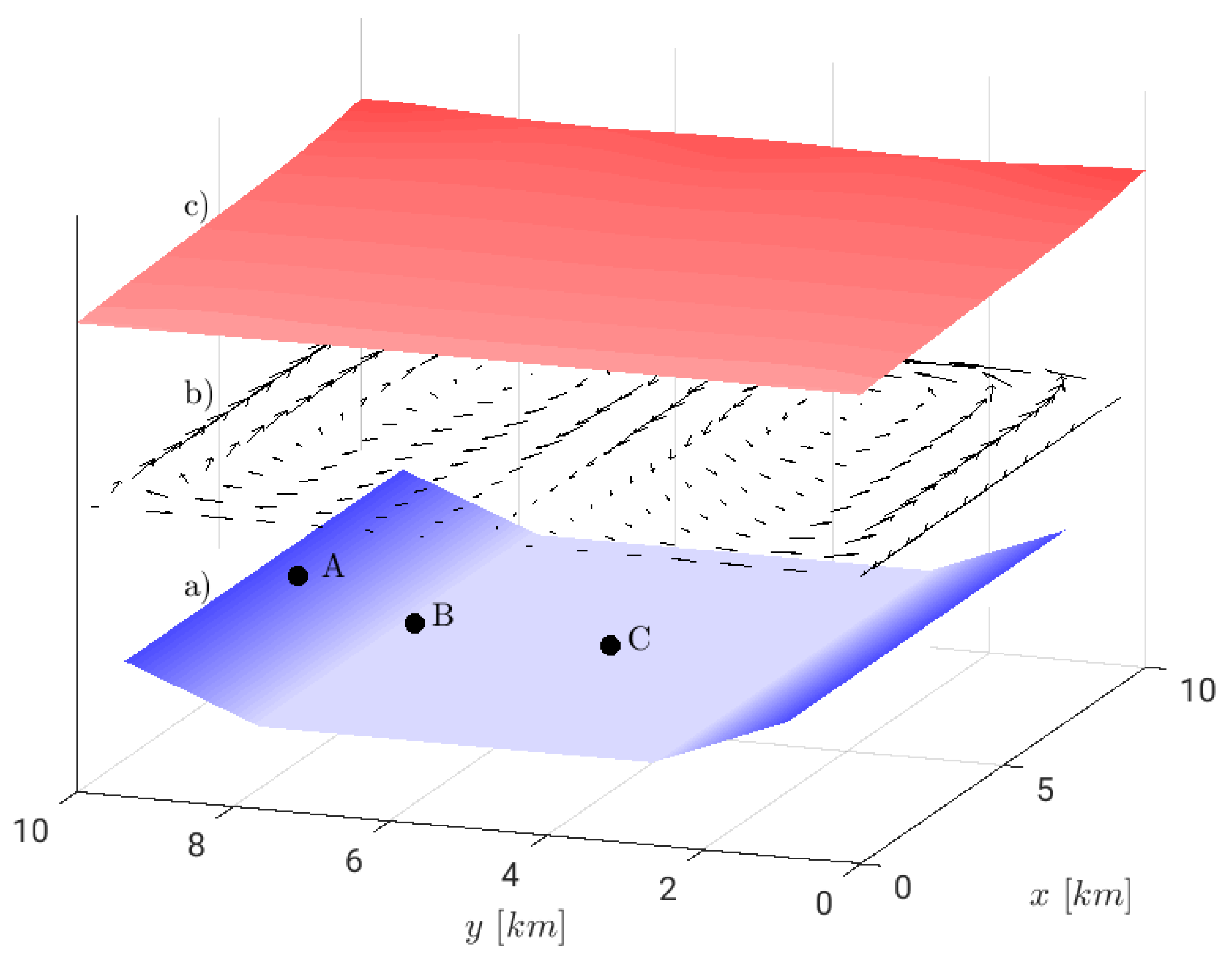
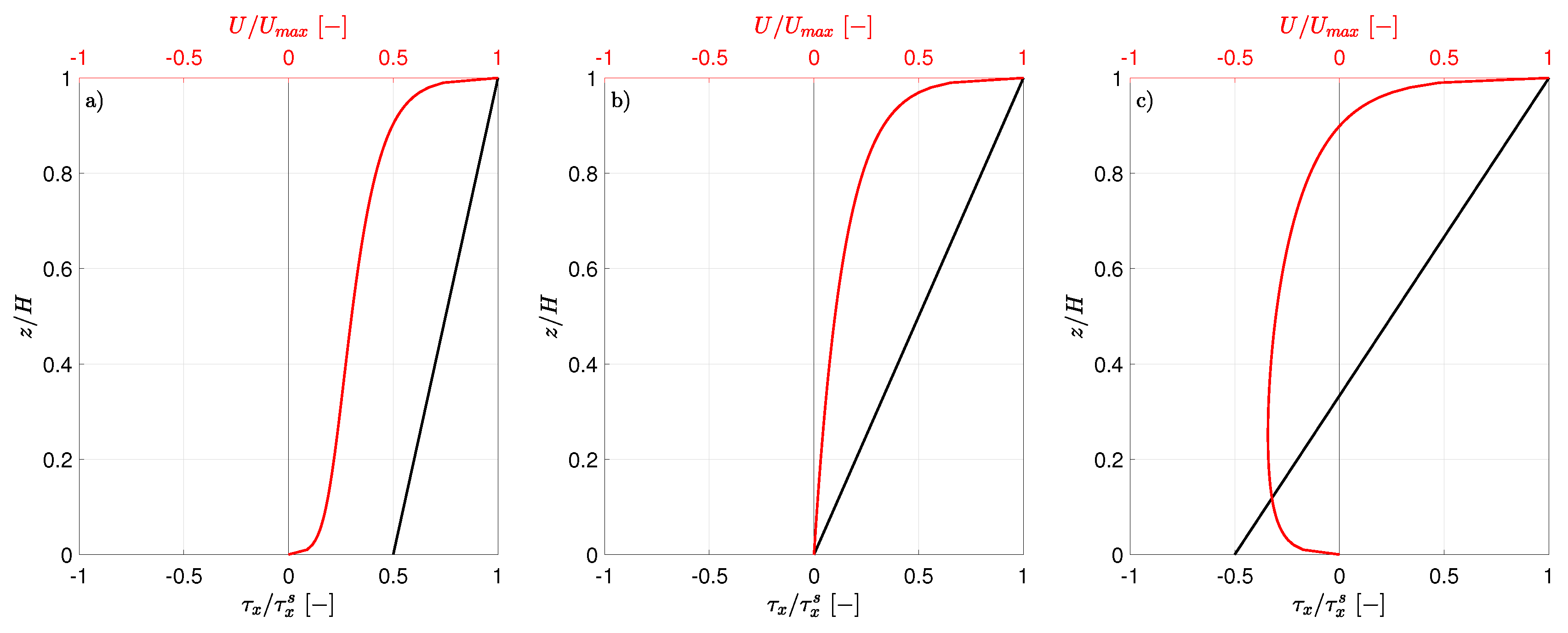
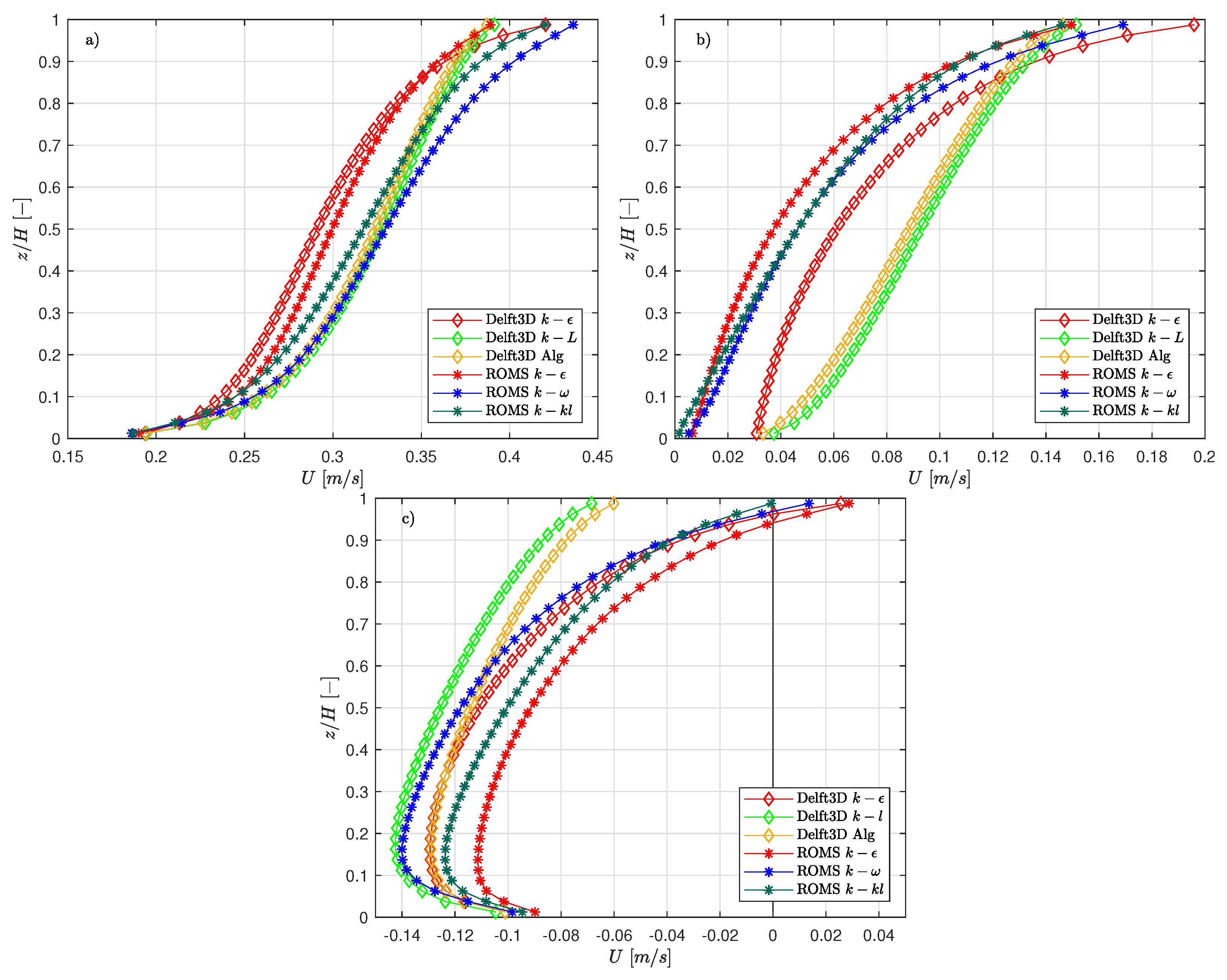
2.2.2. Wind Driven Trapezoidal Closed Basin
3. Results and Discussion
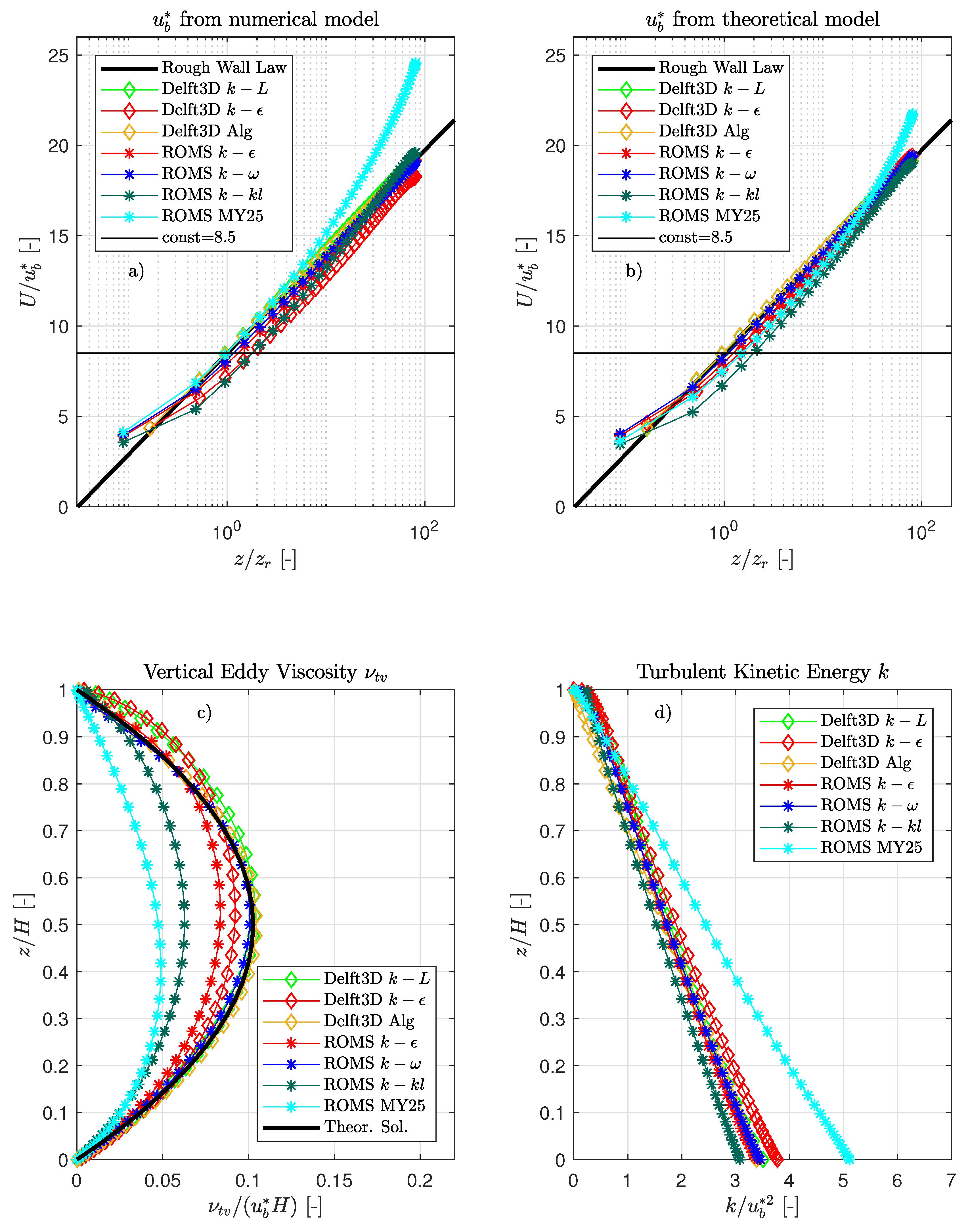
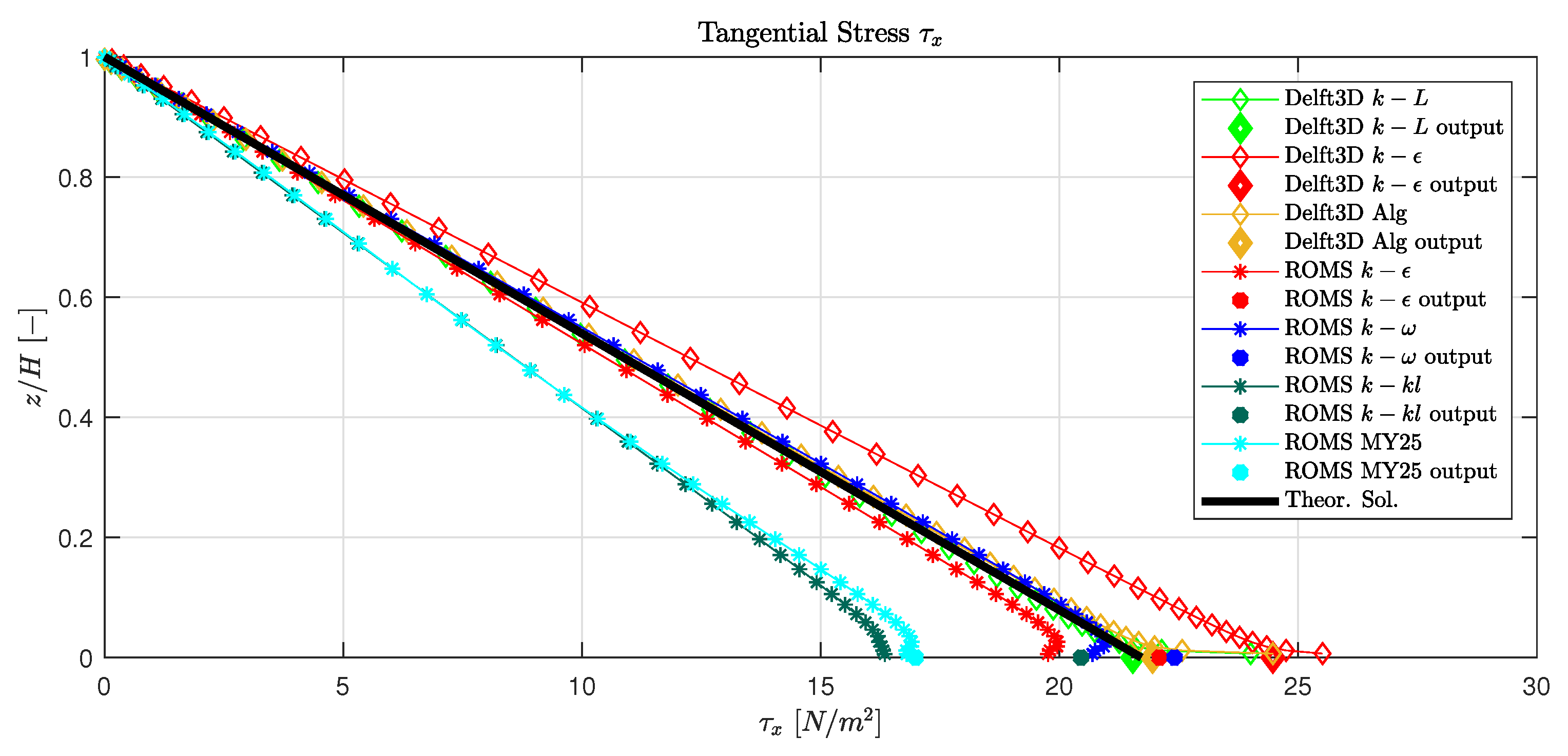
3.1. Open Channel Flow
3.2. Wind Driven Circulation in a Closed Basin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| ROMS | Regional Ocean Modeling System |
| GLS | Generic Length Scale |
| MY25 | Mellor & Yamada 2.5 level |
| WRF | Weather Research and Forecasting model |
References
- Jirka, G.H.; Uijttewaal, W.S. Shallow flows: A definition. In Shallow Flows; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.W.; Busari, A.O. Hybrid modeling of flows over submerged prismatic vegetation with different areal densities. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2019, 13, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.W.; Jiang, Y. A three-dimensional pollutant transport model in orthogonal curvilinear and sigma coordinate system for Pearl River estuary. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 21, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, M.; Tamburrino, A.; Niño, Y. Numerical simulation of scour around circular piles due to unsteady currents and oscillatory flows. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2018, 12, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chau, K. Mathematical model of water quality rehabilitation with rainwater utilization: A case study at Haigang. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 28, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, A.; Mayrhofer, A.; Tritthart, M.; Glas, M.; Habersack, H. Accuracy and comparison of standard k-ϵ with two variants of k-ω turbulence models in fluvial applications. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2018, 12, 216–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.; Jiang, Y. Three-dimensional pollutant transport model for the Pearl River Estuary. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delft3D-Flow User Manual; Deltares: Delft, The Netherlands, 2019.
- Doglioli, A.M.; Griffa, A.; Magaldi, M.G. Numerical study of a coastal current on a steep slope in presence of a cape: The case of the Promontorio di Portofino. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Canu, D.M.; Cucco, A.; Solidoro, C. A finite element model for the Venice Lagoon. Development, set up, calibration and validation. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 51, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madec, G. Nemo-Team. In NEMO Ocean Engine; Institut Pierre-Simon Laplace (IPSL): Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Burchard, H.; Petersen, O. Models of turbulence in the marine environment—A comparative study of two-equation turbulence models. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 21, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, A.; Lamb, V.R. Computational Design of the Basic Dynamical Processes of the UCLA General Circulation Model. In General Circulation Models of the Atmosphere; Chang, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; Volume 17, pp. 173–265. [Google Scholar]
- Roelvink, J.; Van Banning, G. Design and development of DELFT3D and application to coastal morphodynamics. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1995, 11, 925. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, E.P.L.; Walstra, D.J.R.; Roelvink, J.A.; Stive, M.J.F.; Klein, M.D. Hydrodynamic Validation of Delft3D with Field Measurements at Egmond. In Coastal Engineering 2000; ASCE Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2000; pp. 2714–2727. [Google Scholar]
- Horstman, E.; Dohmen-Janssen, M.; Hulscher, S. Modeling tidal dynamics in a mangrove creek catchment in Delft3D. Coast. Dyn. 2013, 2013, 833–844. [Google Scholar]
- Bárcena, J.F.; García, A.; Gómez, A.G.; Álvarez, C.; Juanes, J.A.; Revilla, J.A. Spatial and temporal flushing time approach in estuaries influenced by river and tide. An application in Suances Estuary (Northern Spain). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 112, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost, T.; Blaas, M.; Los, F. The role of atmospheric deposition in the eutrophication of the North Sea: A model analysis. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 125, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidegain, G.; Bárcena, J.F.; García, A.; Juanes, J.A. LARVAHS: Predicting clam larval dispersal and recruitment using habitat suitability-based particle tracking model. Ecol. Model. 2013, 268, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezer, T.; Arango, H.; Shchepetkin, A.F. Developments in terrain-following ocean models: Intercomparisons of numerical aspects. Ocean Model. 2002, 4, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.C.; Sherwood, C.R.; Arango, H.G.; Signell, R.P. Performance of four turbulence closure models implemented using a generic length scale method. Ocean Model. 2005, 8, 81–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, R.; Magaldi, M.G.; Vetrano, A. Current reversal and associated variability within the Corsica Channel: The 2004 case study. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2019, 144, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.C.; Geyer, W.R.; Lerczak, J.A. Numerical modeling of an estuary: A comprehensive skill assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penven, P.; Debreu, L.; Marchesiello, P.; McWilliams, J.C. Evaluation and application of the ROMS 1-way embedding procedure to the central california upwelling system. Ocean Model. 2005, 12, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H. Hydrodynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Umlauf, L.; Burchard, H. A generic length-scale equation for geophysical turbulence models. J. Mar. Res. 2003, 61, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. A Hierarchy of Turbulence Closure Models for Planetary Boundary Layers. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 1791–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandtl, L. Uber die Ausgebildete Turbulenz; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Launder, B.; Sharma, B. Application of the energy-dissipation model of turbulence to the calculation of flow near a spinning disc. Lett. Heat Mass Transf. 1974, 1, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W. Turbulence models and their applications in hydraulics-a state-of-the-art review. IAHR Monogr. 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombini, M.; Stocchino, A. Wind effect in turbulence parametrization. Adv. Water Resour. 2005, 28, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tsanis, I.K. Numerical study of wind-induced water currents. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1995, 121, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberman, E.; Carter, R.; Einstein, H.; Hinds, J.; Powell, R. Friction factors in open channels. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 1963, 89, 97–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, P.K.; Cohen, I.M.; Dowling, D.R. (Eds.) Chapter 13—Geophysical Fluid Dynamics, 5th ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 621–690. [Google Scholar]
- Tsanis, I.K. Simulation of wind-induced water currents. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1989, 115, 1113–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, W.D.; Knapp, D.J. Wind driven water currents. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 1965, 91, 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, W.; Castro, I. The critical Reynolds number for rough-wall boundary layers. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2002, 90, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, B.M.; Le, P.M.; Papavassiliou, D.V. On the Prandtl or Schmidt number dependence of the turbulent heat or mass transfer coefficient. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, A.A. The development of turbulent boundary layers with negligible wall stress. J. Fluid Mech. 1960, 8, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sušelj, K.; Sood, A. Improving the Mellor–Yamada–Janjić Parameterization for wind conditions in the marine planetary boundary layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 136, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD; DCW Industries: La Canada, CA, USA, 1998; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]


| Closure | p | m | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | |||
| 3.0 | 1.5 |
| Model Parameter | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Length, Width | L, W | 1000, 50 m |
| Bed Slope | 0.001 | |
| Number of grid spacing | , , | 200, 10, 40 |
| Bottom roughness | 0.03 m | |
| Time step | 1 s | |
| Total simulation time | 86,400 s | |
| Uniform water depth | H | 2.428 m |
| Hydraulic Radius | 2.213 m | |
| Flow, Velocity | Q, U | 300 m3/s, 2.47 m/s |
| Model Parameter | Variable | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Length, Width | L, W | 10,000, 10,000 m |
| Depth | H | from m to m |
| Number of grid spacing | , , | 100, 100, 40 |
| Bottom roughness | 0.03 m | |
| Time step | 1 s | |
| Total simulation time | 86,400 s | |
| Wind Driven Surface Stress | 0.325 N/m2 |
| ROMS | Relative Error (%) | Delft3D | Relative Error (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22.095 | 1.759 | 24.471 | 12.702 | ||
| 22.411 | 3.215 | 21.537 | 0.811 | ||
| 20.450 | 5.817 | 21.951 | 1.096 | ||
| 16.988 | 21.761 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Putzu, S.; Enrile, F.; Besio, G.; Cucco, A.; Cutroneo, L.; Capello, M.; Stocchino, A. A Reasoned Comparison between Two Hydrodynamic Models: Delft3D-Flow and ROMS (Regional Oceanic Modelling System). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120464
Putzu S, Enrile F, Besio G, Cucco A, Cutroneo L, Capello M, Stocchino A. A Reasoned Comparison between Two Hydrodynamic Models: Delft3D-Flow and ROMS (Regional Oceanic Modelling System). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2019; 7(12):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120464
Chicago/Turabian StylePutzu, Stefano, Francesco Enrile, Giovanni Besio, Andrea Cucco, Laura Cutroneo, Marco Capello, and Alessandro Stocchino. 2019. "A Reasoned Comparison between Two Hydrodynamic Models: Delft3D-Flow and ROMS (Regional Oceanic Modelling System)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 7, no. 12: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120464
APA StylePutzu, S., Enrile, F., Besio, G., Cucco, A., Cutroneo, L., Capello, M., & Stocchino, A. (2019). A Reasoned Comparison between Two Hydrodynamic Models: Delft3D-Flow and ROMS (Regional Oceanic Modelling System). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 7(12), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120464








