Abstract
Fish farm facilities become colonized by biofouling, and in situ cleaning activities may increase the accumulation of biofouling, mostly shell-hash, on the sediment. However, there is a lack of knowledge about the effect of fish farming on this process. We evaluated the effect of fish farming on shell-hash accumulation on sediments in three fish farms in the Western Mediterranean in Spain. On the one hand, coverage of non-degraded shell on the seabed was estimated using an underwater camera attached to a frame of 1 × 1 m. On the other hand, superficial sediment samples were taken by a Van-Veen grab, and from a subsample, shell-hash was sorted at the laboratory, dried, and weighted. A significant increase of shells on sediment was detected under fish farms compared with the other treatments, with average values of 53 g kg-1, and 1.12% of cover. Shell-hash at zones close to the fish farm cages (Zone of Influence located between 40 to 60 m from the closest cage) did not show statistical differences compared to the reference zones, 300–500 m away from the concession limits, but the shell cover showed statistical differences. Fish farming activities produce a local increase in the sedimentation rate of shells under the cages. The derived ecological consequences of this accumulation need to be further studied.
1. Introduction
Surfaces immersed in the marine environment become colonized by marine organisms from macromolecules to larger algae and sessile invertebrates such as mussels, ascidians, and hydroids, through a successional process known as biofouling [1]. The physical structures associated with marine aquaculture such as fish farming, include lines, anchors, nets, floating rings, etc., which introduce a new habitat in the pelagic environment that is colonized by biofouling. This process is a complex and recurring problem in all sectors of the marine aquaculture industry [2].
Fish farming, using floating net pens, is a growing activity across the oceans, especially in the Mediterranean Sea [3]. The development of this activity has been accompanied by the assessment of the interactions with the environment, in particular the impact of sedimentation of organic matter on surrounding benthic habitats [4]. Although marine sediments should be influenced by sediment grain size [5], physical changes due to debris accumulation from biofouling have not been sufficiently studied in the Mediterranean Sea. Marine sediments, especially coastal ones where most human activities are located, support key ecosystem functions such as the mineralization of organic matter and recycling of nutrients [6]. The metabolic capacity of marine sediments depends on the availability of electron acceptors (e.g., oxygen, sulfate, etc.) to oxidize organic matter [7]. Thus, parameters such as sediment grain size, that modify the diffusion rates and the supply of these electron acceptors from the water column to the sediment, significantly influence the metabolic capacity of the sediment. Consequently, changes of sediment grain size may affect several biogeochemical processes, such as the oxygen permeability, modifying benthic metabolism [5]. The shells of mollusks growing as biofouling in fish farms, in various states of decomposition (referred to as the ‘shell-hash’; [8]), could be a relevant element of the sediment structure under the cages promoting the increase of its complexity and modifying the grain size [9]. Thus, shell-hash could ameliorate the negative consequences produced by organic matter accumulation due to human activities, such as fish farming [10].
There is a lack of knowledge about the effect of fish farming on the accumulation of the rest of mollusk shell-hash from the biofouling. To quantify the magnitude of this process, we evaluated the effect of fish farming on the shell-hash accumulation in sediments by comparing the sediment of three fish farms in the Western Mediterranean of Spain with sites that are less or not-at-all influenced by farming activities. We hypothesized that fish farming might increase the quantity of shell-hash on sediments, having reduced impact in near locations (50 m far away from the cages) due to the rapid sedimentation of the biofouling fragment.
2. Materials and Methods
We sampled at three fish farms culturing gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) and European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) at the Western Mediterranean coastline of Spain that aimed to embrace the diversity of fish farms in the Mediterranean (Figure 1). The first fish farm (FF1) was the oldest farm of the investigation (21 years); it was located 3 km away from the coast with a depth of 31 m and a production of 300 t of fish per year. The second fish farm (FF2) has been active for 16 years; it was 2.8 km away from the coast with a depth of 34 m and a production of 1200 t per year. The third fish farm (FF3) has been 13 years in operation; it was located 6 km away from the coast and had many other fish farming facilities in their proximity separated by a distance of at least 1 km. The farm had a depth of 37.5 m and a production of 800 t per year.
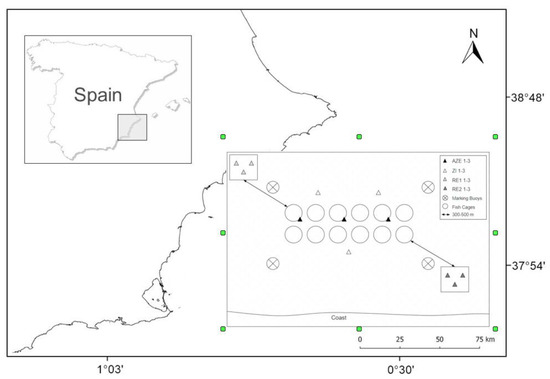
Figure 1.
Geographical localization of the sampling area and experimental design. The exact location of the fish farms cannot be disclosed respecting the fish farm privacy. The scheme of sampling sites. Triangles of the same color represent sites of the same zone (AZE = Allowable Zone of Effects, ZI = Zone of Influence, RE1 and RE2 = reference zones); in each site, three replicates were taken. Empty circles depict the fish cages, crossed circles the marking buoys of the lease and the arrows represent a distance of approximately 300–500 m.
At each location (FF1, FF2, and FF3) four zones were sampled: the “Allowable Zone of Effects” (AZE), which represents an area in immediate proximity of the fish farm cages. At AZE, some exceedance of environmental standards is accepted, but not beyond a certain threshold, so the marine ecosystem is not irreversibly compromised [11]. Secondly, a nearby zone inside the lease, located between 40 to 60 m from the closest cage, and called Zone of Influence (ZI), and finally two different reference zones (RE1 and RE2) approximately 300–500 m away from concession limits (Figure 1).
To calculate the coverage of the nonfragmented shells on the seabed, a GoPro Camera (San Mateo, USA) attached to a metal structure with a frame of 1 × 1 m was lowered to the seabed for one minute and pulled up to avoid agitations of the sediment. This procedure was repeated three times on each site of each zone in each location. The visible cover of shell hash was calculated from the pictures of the camera over a 1 m2 quadrat, using the image editing program ImageJ [12]. The visibility at FF3 was extremely reduced; therefore, it was not possible to estimate the coverage at this location.
To determine shell-hash density, a superficial sediment sample (0–10 cm depth) of approximately 20 × 20 cm was taken by a Van–Veen grab. Samples between 50 and 80 g of sediment were collected. Three random replicates per site were sampled, obtaining nine replicates per zone, and in total 36 replicates per location. 300 ml from each zone (AZE, ZI, RE1, and RE2) of each fish farm were processed to determine the grain size. One subsample gram of sediment was used to estimate the water content by drying it during 24 h at 80 °C. This was used to calculate the actual dry weight of each sample of sediment. Each sample was examined under a stereo macroscope (×20 magnification) checking for shell-hash. Subsequently, the debris of each sample was separated by tweezers, dried, and weighed.
An asymmetrical analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed. We tested whether the shell-hash density and shell cover differed among farms and zones. The experimental design integrated three factors: fish farm (FF1, FF2, and FF3), zone (AZE, ZI, RE1, RE2), and site (three different sites per zone). In the case of shell cover, the factor fish farm included only two treatments. The factor zone was considered fixed, while fish farm and site were considered random. The zone was orthogonal with fish farm, and site nested within the interaction fish farm × zone. The following a priori comparisons were made: RE’s vs. AZE, RE’s vs. ZI, and RE1 vs. RE2. The normality of the residuals with the Shapiro–Wilk test and homogeneity of variances with the C-test could not be confirmed, which is why we used p < 0.01 to determine significant differences. All statistical tests were conducted with the software R (v. 2.15.0) using the statistical package GAD [13].
3. Results
See Figure A1 for detailed description of grain size.
Regarding the shell-hash, the three fish farms showed significant statistical differences among them (p = 0.004; Table 1). Directly below the fish farm cages (AZE), the accumulation of shell-hash was outstanding and significantly different, compared to the reference zones, with an average value of 53 g∙kg−1 and reaching a maximum value of 80 g∙kg−1 at FF3 (Figure 2). The zone of influence (ZI) showed a very slight increase of shell-hash, with an average value of 1.4 g∙kg−1, without statistical differences to reference zones (p = 0.759; Table 1). Only the FF1 exhibit higher values compared with the others (3.4 g∙kg−1). Regarding the shell cover (Figure 3), the three fish farms also showed marginal significant statistical differences (p = 0.058; Table 1). The average value for AZE was 1.12 %, showing statistical differences to RE’s (p < 0.0001; Table 1), and the ZI (0.09% cover) was also statistically different to RE’s (0% and 0.02% cover; p < 0.002; Table 1).

Table 1.
Results of the asymmetrical analysis of variance with three factors: Fish Farms (FF), zone (Allowable Zone of Effects, AZE; Zone of Influence, ZI; Reference zones, RE1 and RE2), and Site (random sites) for the density of shell-hash (g∙kg−1) and shell cover (%).
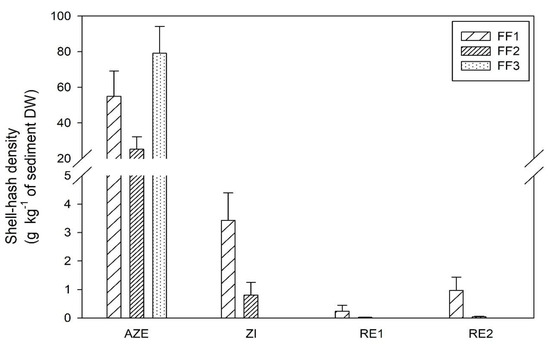
Figure 2.
Density of shell-hash (g∙kg−1 on sediment dry weight) within the four zones (Allowable Zone of Effects, AZE; Zone of Influence, ZI; Reference zones, RE1 and RE2) for all fish farms. Values indicate the mean + SE, each mean was calculated by pooling three sites of which each had three replicates (n = 9).
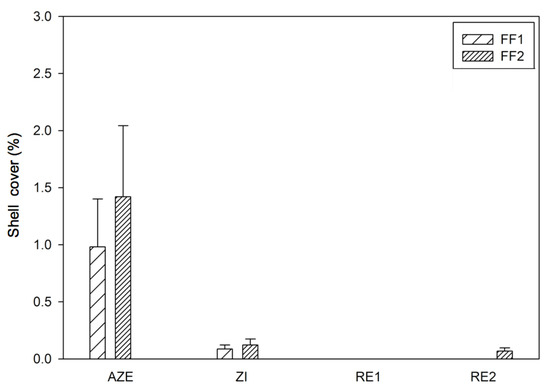
Figure 3.
Shell cover (%) within the four zones (Allowable Zone of Effects, AZE; Zone of Influence, ZI; Reference zones, RE1 and RE2). FF3 was not considered due to the lack of visibility. The values indicate the mean + SE, each mean was calculated by pooling three sites of which each had three replicates (n = 9).
4. Discussion
This study shows that the biofouling falling off from marine fish farms is changing the sediment features by accumulating shell (mainly mussels) and shell-hash. The negative and significant impacts of biofouling on aquaculture have led to a long and persistent effort in biofouling control [14]. For example, the net can be cleaned in situ by divers, cleaning disc, or remote operating vehicles. These activities, which combined with the natural sedimentation of biofouling, produce an increase of the sedimentation rate of shells as we demonstrated in the present study. The principal particulate wastes from net-pens are uneaten feed, fish excretion wastes and, to a lesser extent, debris from dead cultured fish and fouling communities. These organic wastes produce a benthic enrichment and have potentially deleterious consequences for the seabed communities next to the fish farm facilities (see for a review Sanz-Lazaro and Marin 2008 [4]).
As we demonstrate, the fouling deposition could be a relevant waste from fish farming and the degree of fish farm fouling must be an important factor for explaining differences among fish farms [15]. The disposal of fouling organisms during cage cleaning results in a significant organic and nutrient input which may cause environmental drawbacks [16]. However, to date, pen net cleaning has not been thoroughly considered, even though the quantity of deposited biofouling may not be insignificant in comparison to annual feed and fecal emissions [17]. The accretion of fouling, normally during decades of production, may change the ecological conditions of the sediment, with potential effects on the biochemical process and benthic fauna. Nevertheless, the environmental effects of fouling accumulation on the benthic system have not been properly evaluated. For example, before the shell fragmentation, we estimated accumulation of mussel shell at least of 24.7 times higher in the surface of sediment under fish cages compared to reference areas. This accumulation of shells could have an effect of the benthic fauna, increasing the habitat complexity and heterogeneity. Furthermore, we estimated that the mass of shell-hash is 60 times higher in sediments directly below the fish farm cages compared to the reference zones, mostly due to mussel shells (personal observation), which may be relevant to the sediment structure. Therefore, the changes in sediment structure due to shell-hash could be an important aspect for the sediment metabolism under a high organic enrichment, such as fish farming. Martinez–Garcia et al. (2015) demonstrated that organically enriched sediments, with a larger grain size, are more suitable to harbor aquaculture facilities than muddy sediments since their metabolic capacity is higher [5]. Therefore, the increase of sediment size due to the existence of fragment of shells from biofouling, especially for facilities located in muddy sediments, could be considered as a mitigative process. Under these conditions of organic pollution, shell-hash can reduce the accumulation of by-products from anaerobic metabolic pathways, such as sulfides, improving the ecological status of the sediment [10]. Additionally, shell-hash can decrease the release rate of ammonium to the water column, thus preventing the negative ecological consequences derived from eutrophication [10].
5. Conclusions
Fish farming activities produce a local increase on the sedimentation rate of shells under the cages, which may undergo both positive and negatives ecological consequences. Regulations regarding in-water cleaning management could reduce sedimentation of biofouling and reduce potential negative effects on benthic communities. It is necessary to conduct additional research in order to understand the ecological effects of the interaction between organic matter and shell-hash accumulation, and monitoring of benthic organic loading around farms must involve assessments of the environmental effect of organic depositions, including any biofouling material. This is important, as the accretion of shell and shell-hash may have negative ecological effects but also a positive effect by increasing the sediment porosity, the habitat complexity, and heterogeneity, mitigating the input of organic matter from feces and uneaten feed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—P.S.-J.; writing—P.S.-J.; writing—review & editing—P.S.-J., L.K., N.C.-C., C.S.L.; investigation—P.S.-J., L.K., C.V., N.C.-C., C.S.-L.; formal analysis—L.K.; project administration—P.S.-J., C.S.-L.; funding acquisition—P.S.-J., C.S.-L.
Funding
This research was funded by the project CGL2015-70136-R from the Spanish National Agency for Research (MINECO/FEDER), GRE14-19 from the University of Alicante, the project GV/2015/001 from the “Conselleria de Educación, Cultura y Deporte” of the government of the Valencia region. LK was funded by the German Agency DAAD RISE Worldwide (Ref. num.: ES-BI-2977). CSL was funded by the University of Alicante (Ref. UATALENTO 17-11).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to CULMAREX, Piscifactorías Albaladejo and CUDOMAR which kindly allowed us to sample in their fish farm leases. We are also grateful to Francisco José Barrero Vázquez and José Francisco Huesca Pérez for their assistance with the image analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
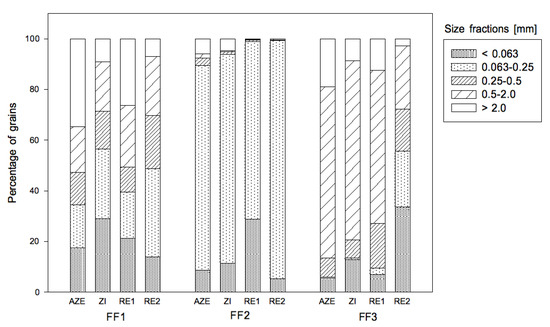
Figure A1.
Grain size structure. In the sediment of fish farm 1 (FF1) all grain size fractions were present and rather evenly distributed within the zones. In FF2, finer sand was present with grain sizes < 0.25 mm (>90%). The sediment of FF3 showed mainly coarser sandy sediments with grain sizes between 0.5 and >2.0 mm (>70%). An exception was RE2 with less than 30% of coarser fractions and a predominant size fraction of <0.063 mm.
References
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, V.; Sanchez-Jerez, P. Fouling assemblages associated with off-coast aquaculture facilities: An overall assessment of the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2017, 18, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collective Research on Aquaculture Biofouling (COLL-CT-2003-500536-CRABCRAB Project). Available online: https://www.crabproject.com (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Trujillo, P.; Piroddi, C.; Jacquet, J. Fish Farms at Sea: The Ground Truth from Google Earth. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Lazaro, C.; Marin, A. Assessment of finfish aquaculture impact on the benthic communities in the Mediterranean sea. In Aquaculture I. Dynamic Biochemistry, Process Biotechnology and Molecular Biology; 2 (special issue 1); Russo, R., Ed.; Global Science Books: Ikenobe, Japan, 2008; pp. 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Garcia, E.; Sundstein Carlsson, M.; Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Sanz-Lazaro, C.; Holmer, M. Effect of sediment grain size and bioturbation on descomposition of organic matter from aquaculture. Biogeochemistry 2015, 125, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetaert, K.; Herman, P.M.J.; Heip, C.H.R.; Middelburg, J.J. Denitrification in marine sediments: A model study. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1996, 10, 661–673. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Lázaro, C.; Marín, A. Diversity Patterns of Benthic Macrofauna Caused by Marine Fish Farming. Diversity 2011, 3, 176–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, T.A. Changes in Sedimentary Redox Associated with Mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) Farms on the West-Coast of Scotland. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.L.; Jones, C.G.; Strayer, D.L.; Iribarne, O.O. Mollusks as ecosystem engineers: The role of shell production in aquatic habitats. Oikos 2003, 101, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Coy, N.; Martínez-García, E.; Sánchez-Jerez, P.; Sanz-Lázaro, C. Mollusc-shell debris can mitigate the deleterious effects of organic pollution on marine sediments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Jerez, P.; Karakassis, I. Allowable Zone of Effect for Mediterranean Marine Aquaculture (AZE) (WGSC-SHoCMed). 2011 (GFCM:CAQ/2012/CMWG-5/Inf.11). Available online: http://bit.ly/GFCM-CAQ-AZE-2011 (accessed on 30 June 2019).
- Image, J. An open platform for scientific image analysis. Available online: https://imagej.net/ (accessed on 2 April 2019).
- GAD: Analysis of Variance from General Principles. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/GAD/index.html (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Fitridge, I.; Dempster, T.; Guenther, J.; De Nys, R. The impact and control of biofouling in marine aquaculture: A review. Biofouling 2012, 28, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromey, C.; Thetmeyer, H.; Lampadariou, N.; Black, K.; Kögeler, J.; Karakassis, I. Meramod: Predicting the deposition and benthic impact of aquaculture in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2012, 2, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R. The environmental impact of marine fish culture: Towards a sustainable future. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floerl, O.; Sunde, L.; Bloecher, N. Potential environmental risks associated with biofouling management in salmon aquaculture. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2016, 8, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).