Development of the Hydrodynamic Model for Long-Term Simulation of Water Quality Processes of the Tidal James River, Virginia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
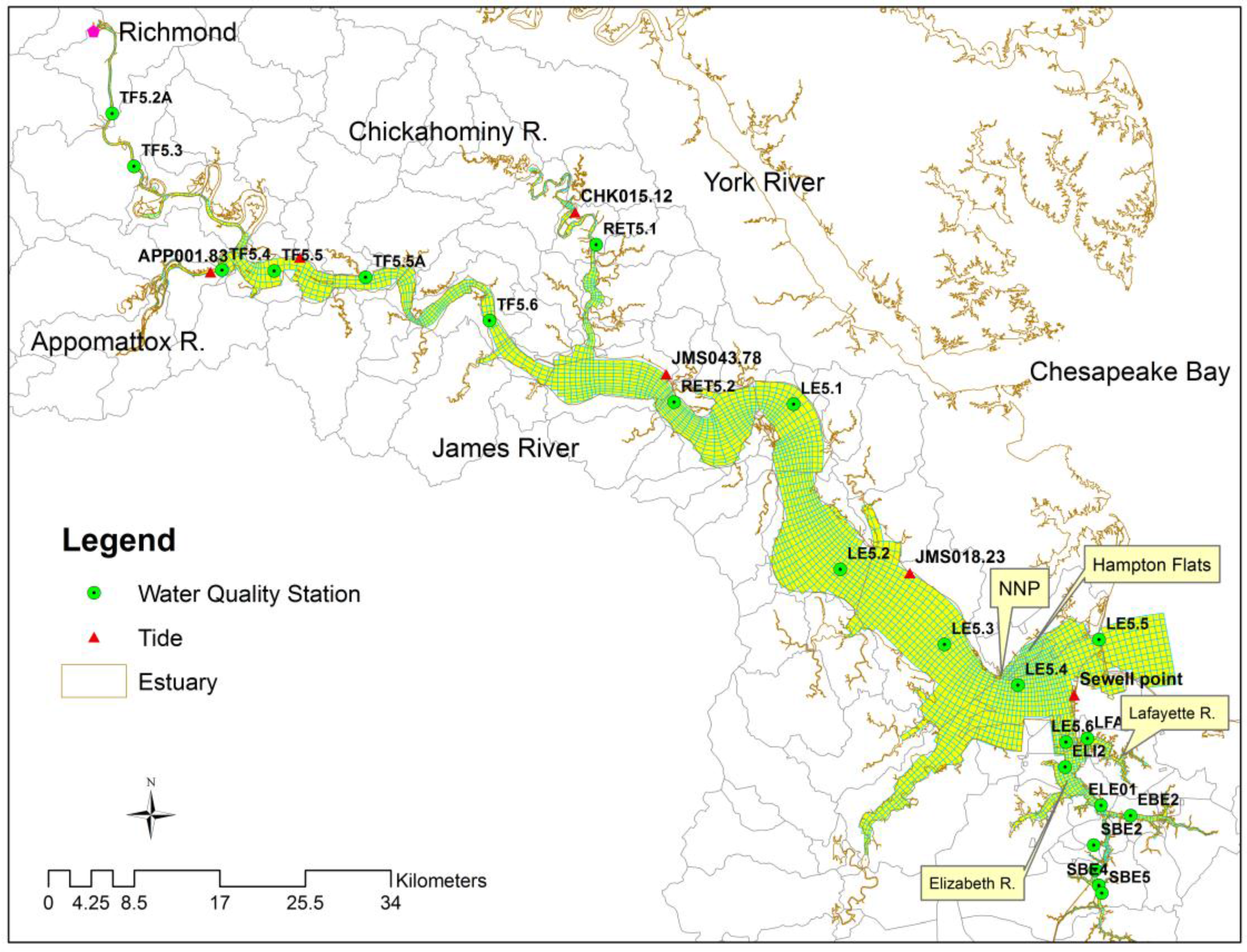
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Model Configuration
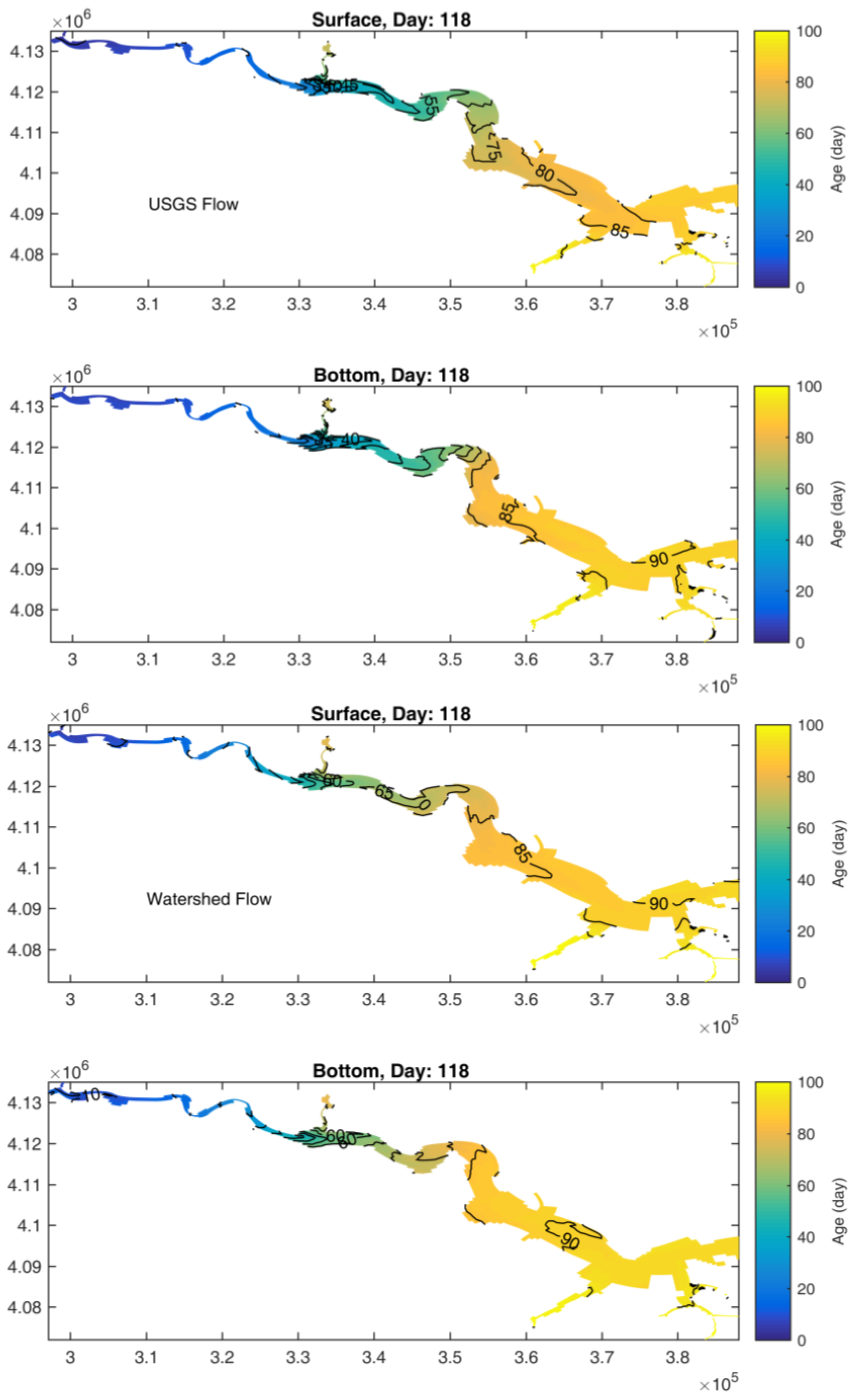
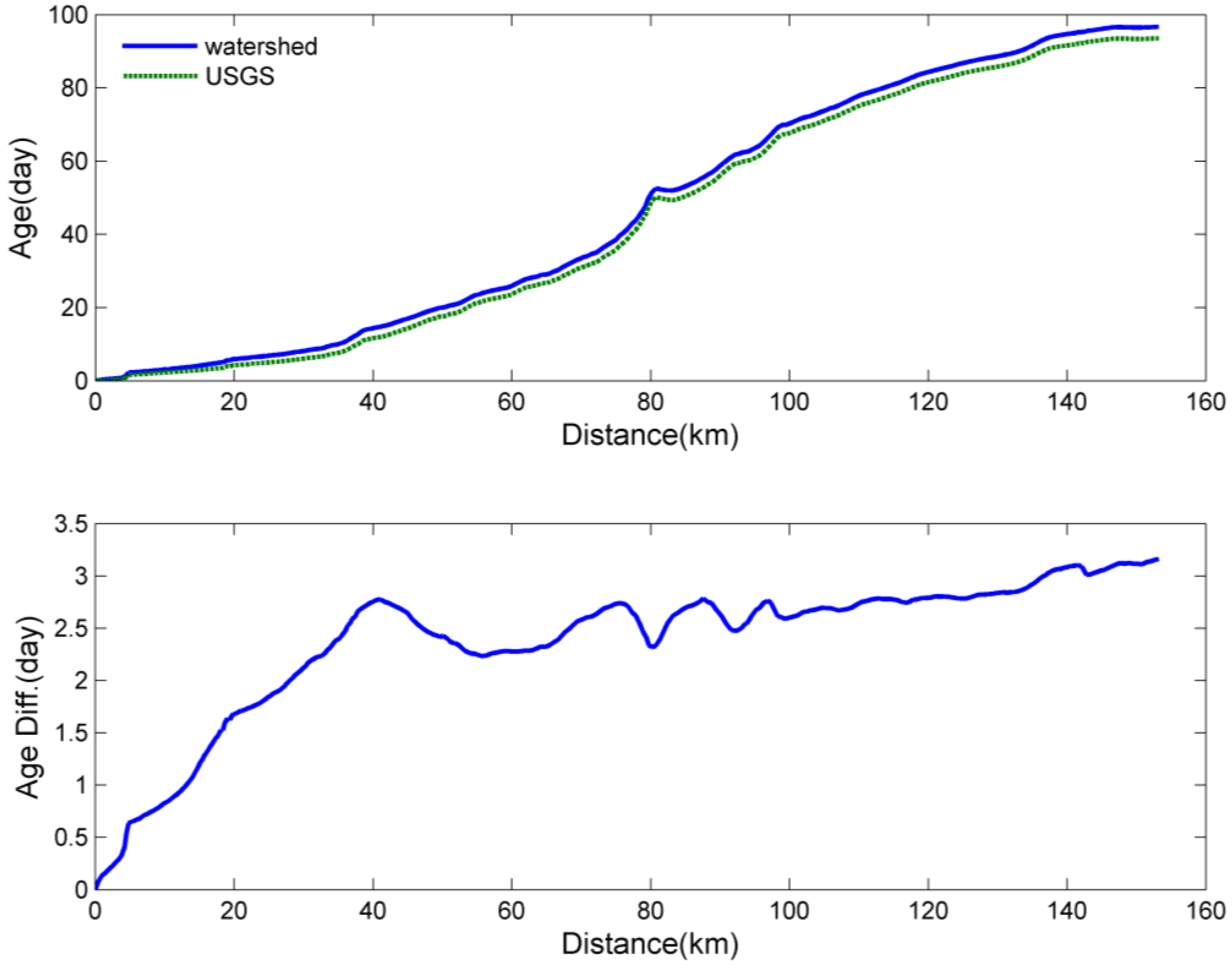
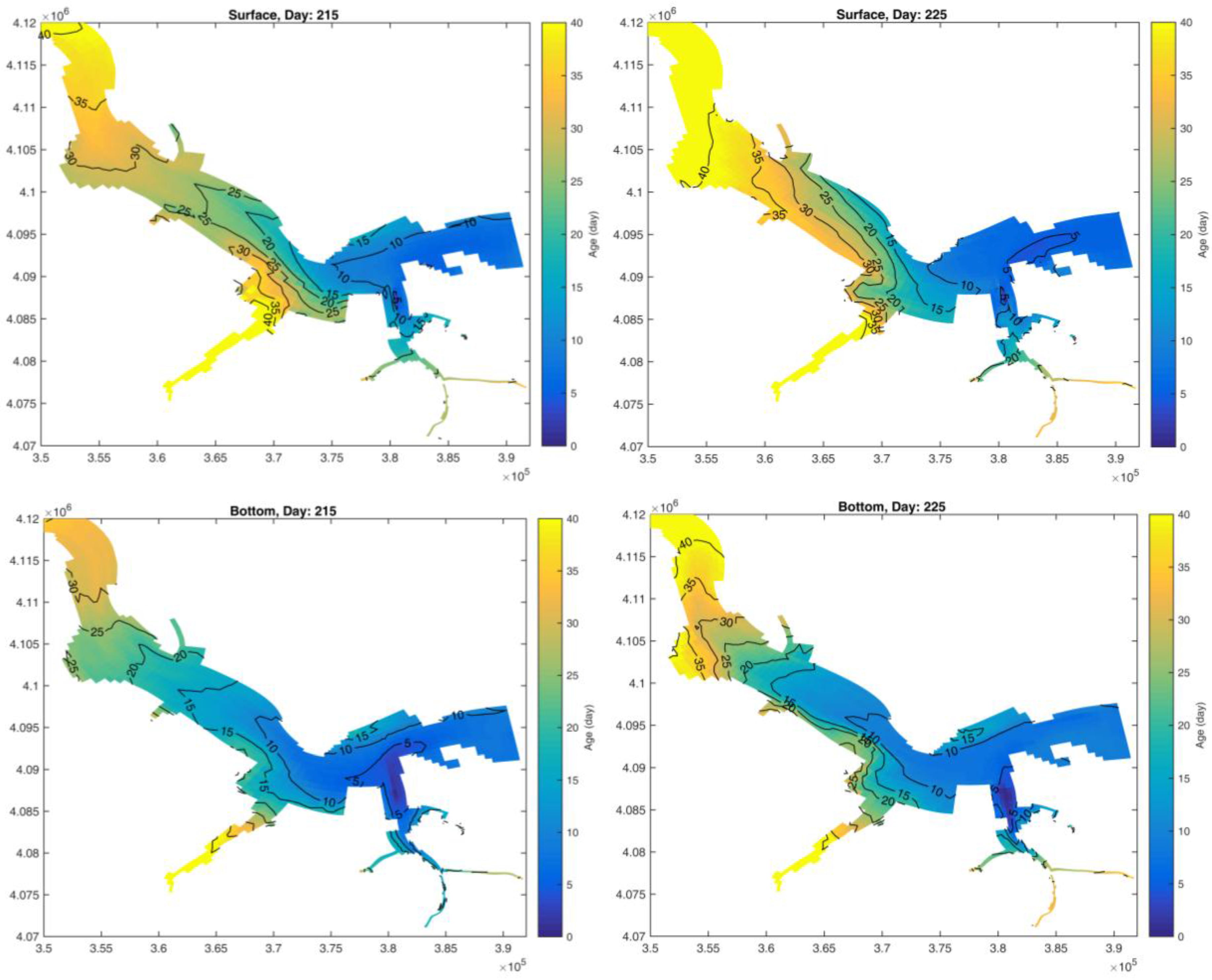
2.3. Age Calculation
3. Results
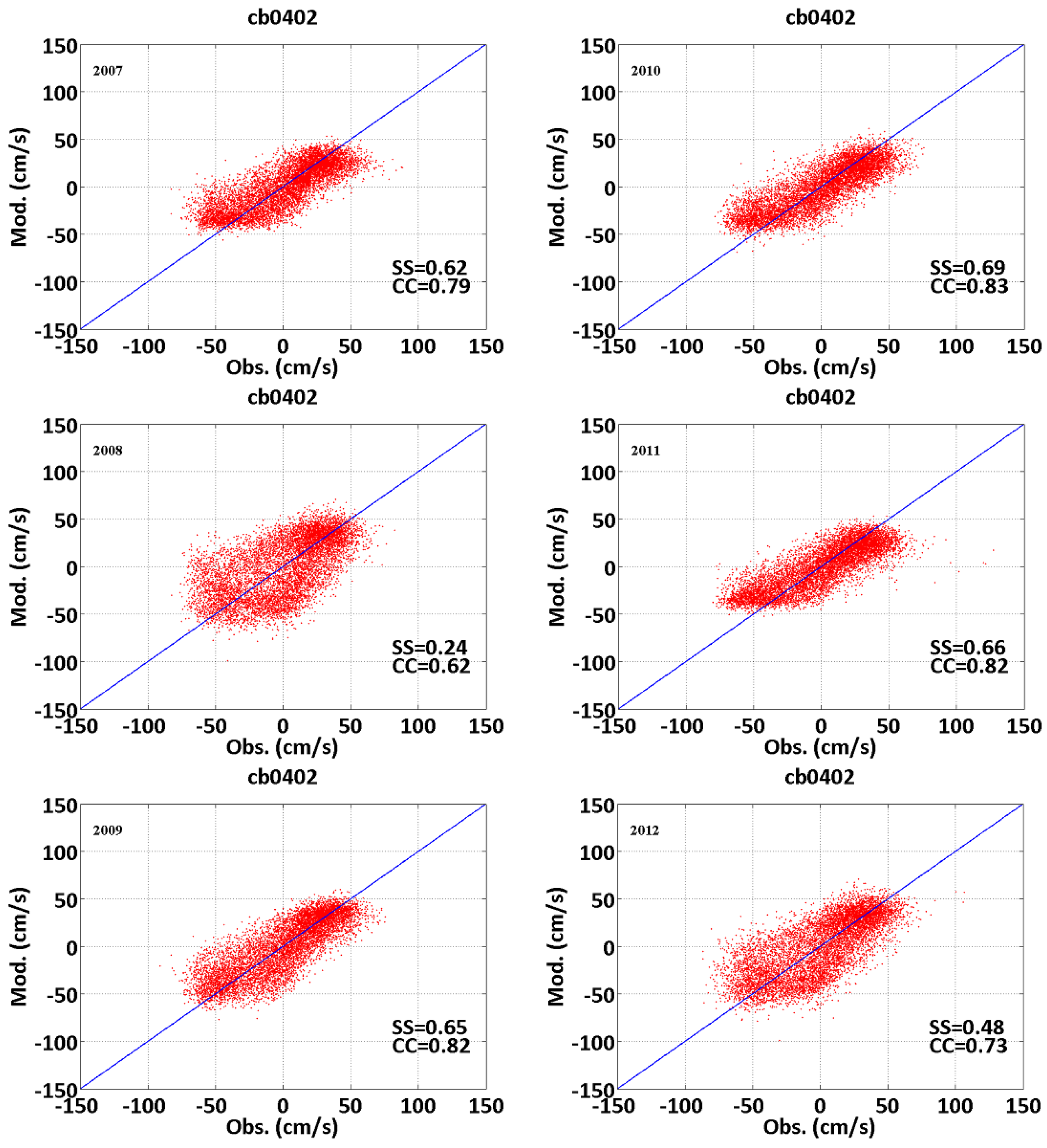
3.1. Tidal Elevation and Current
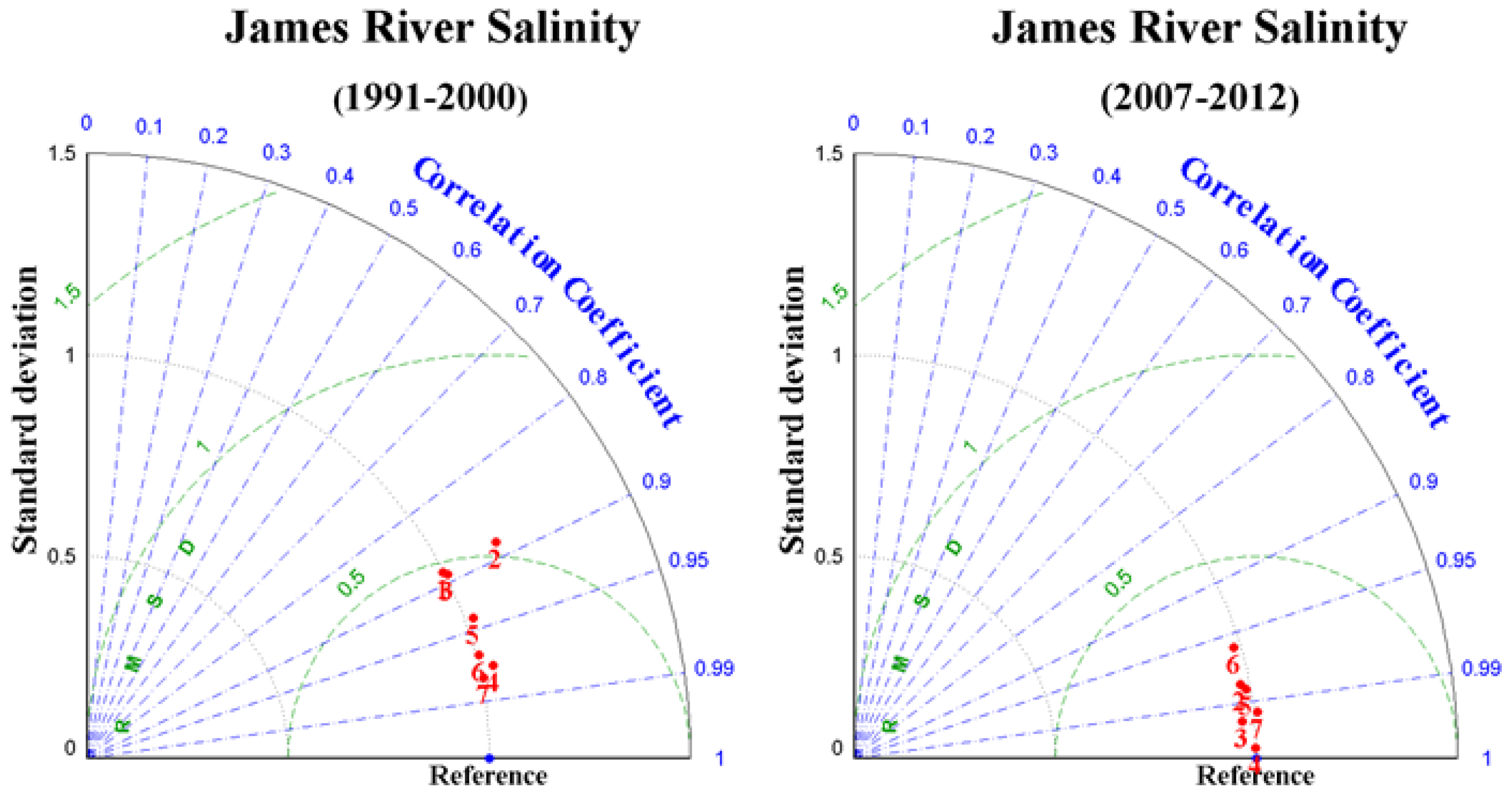
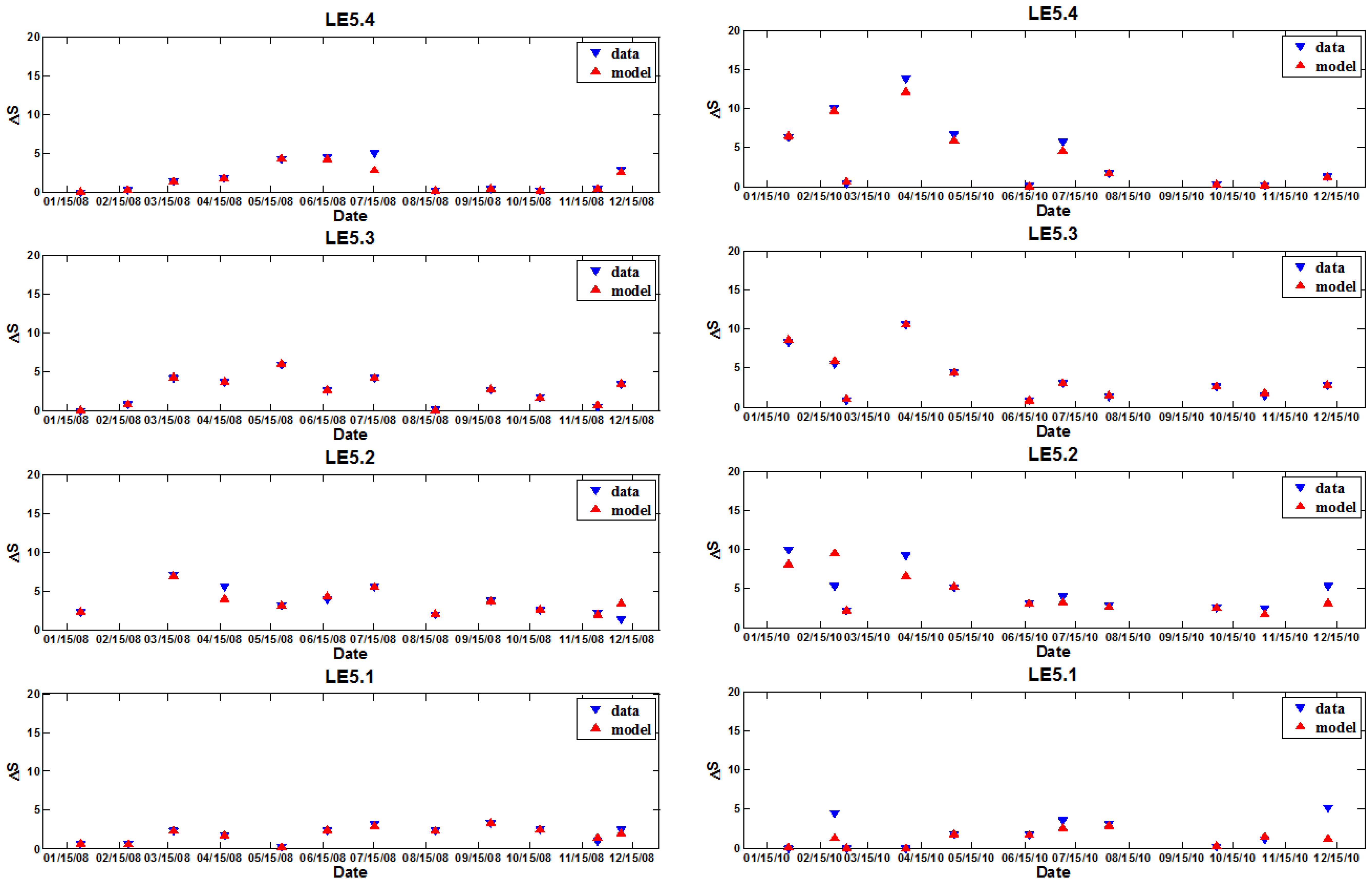
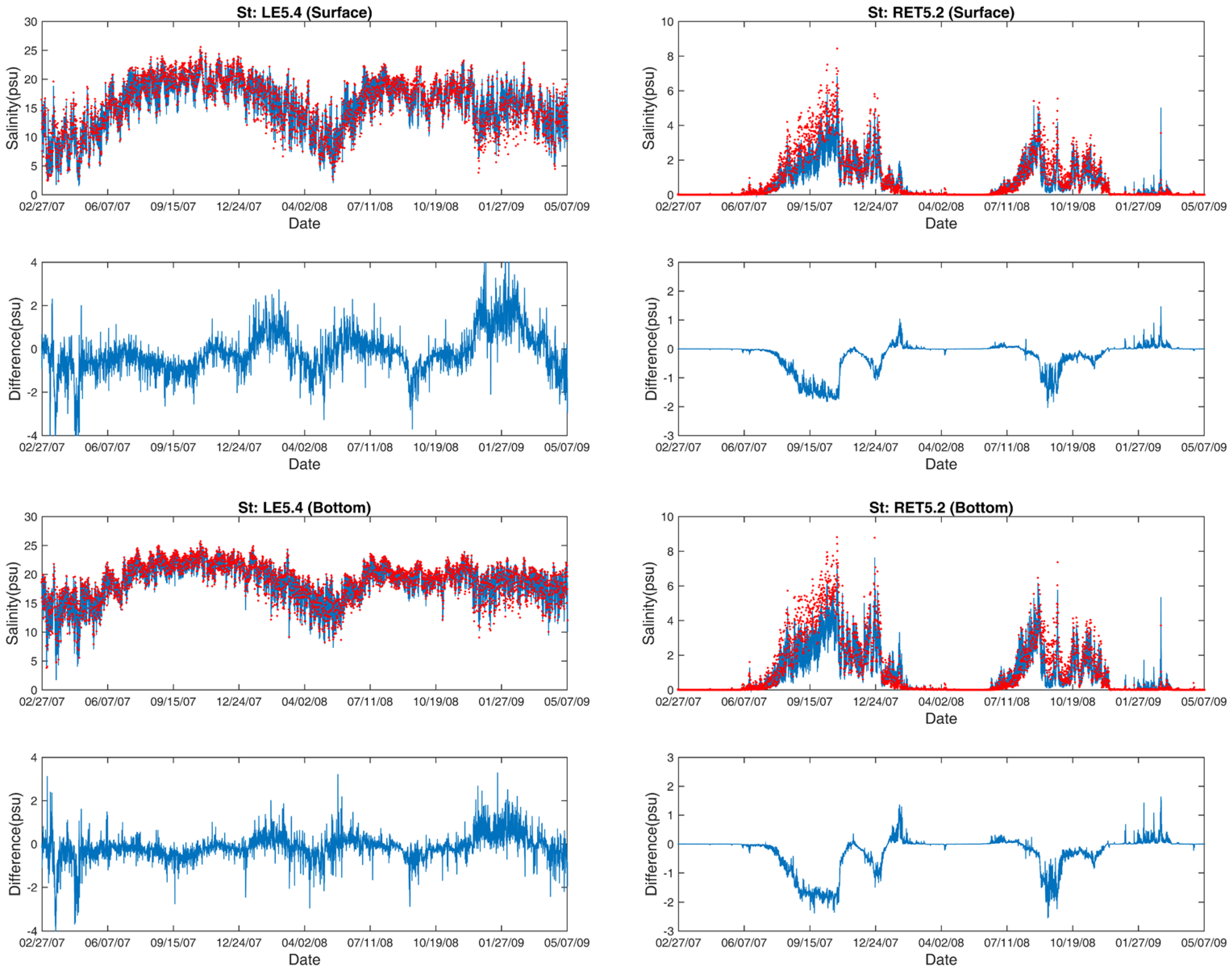
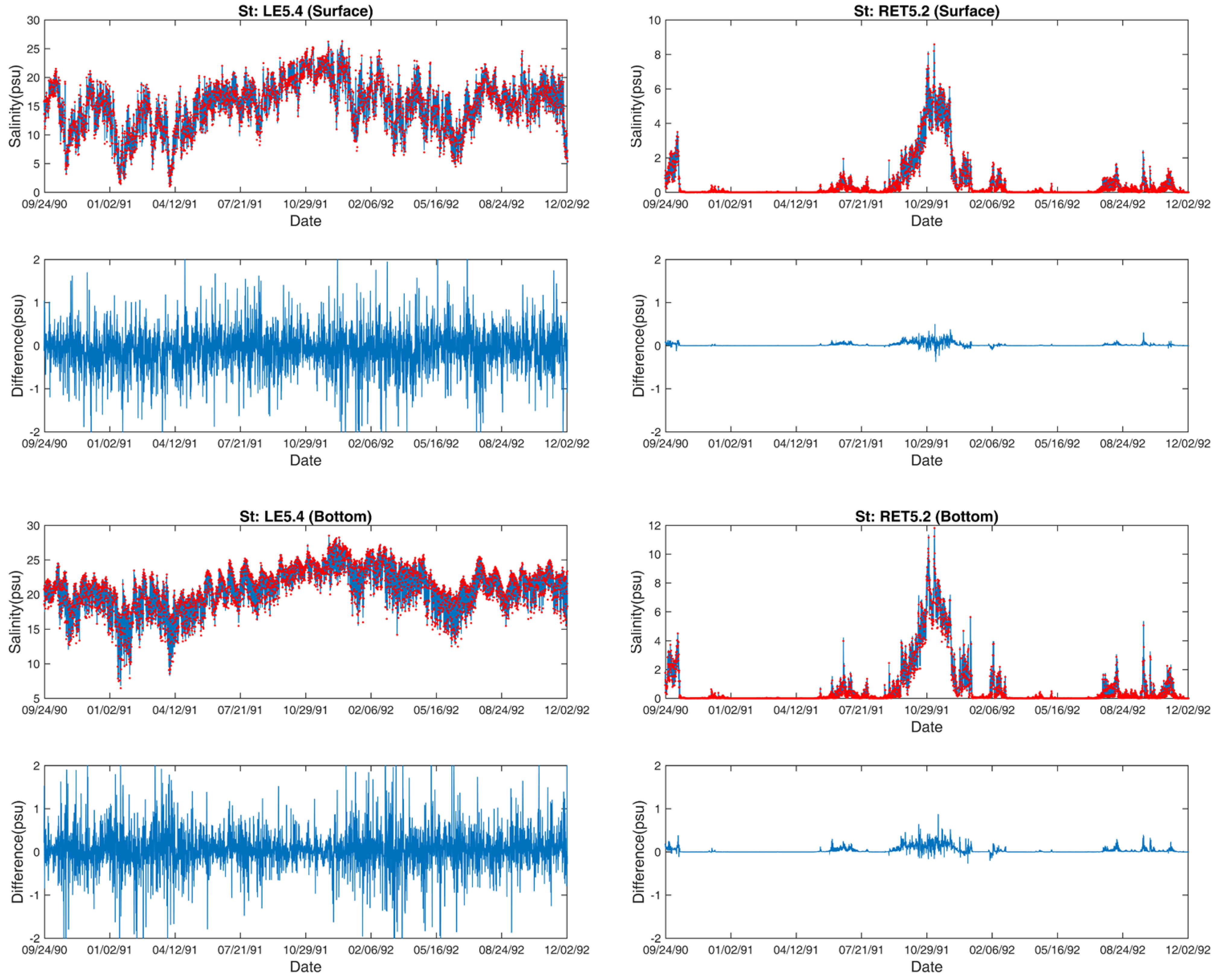
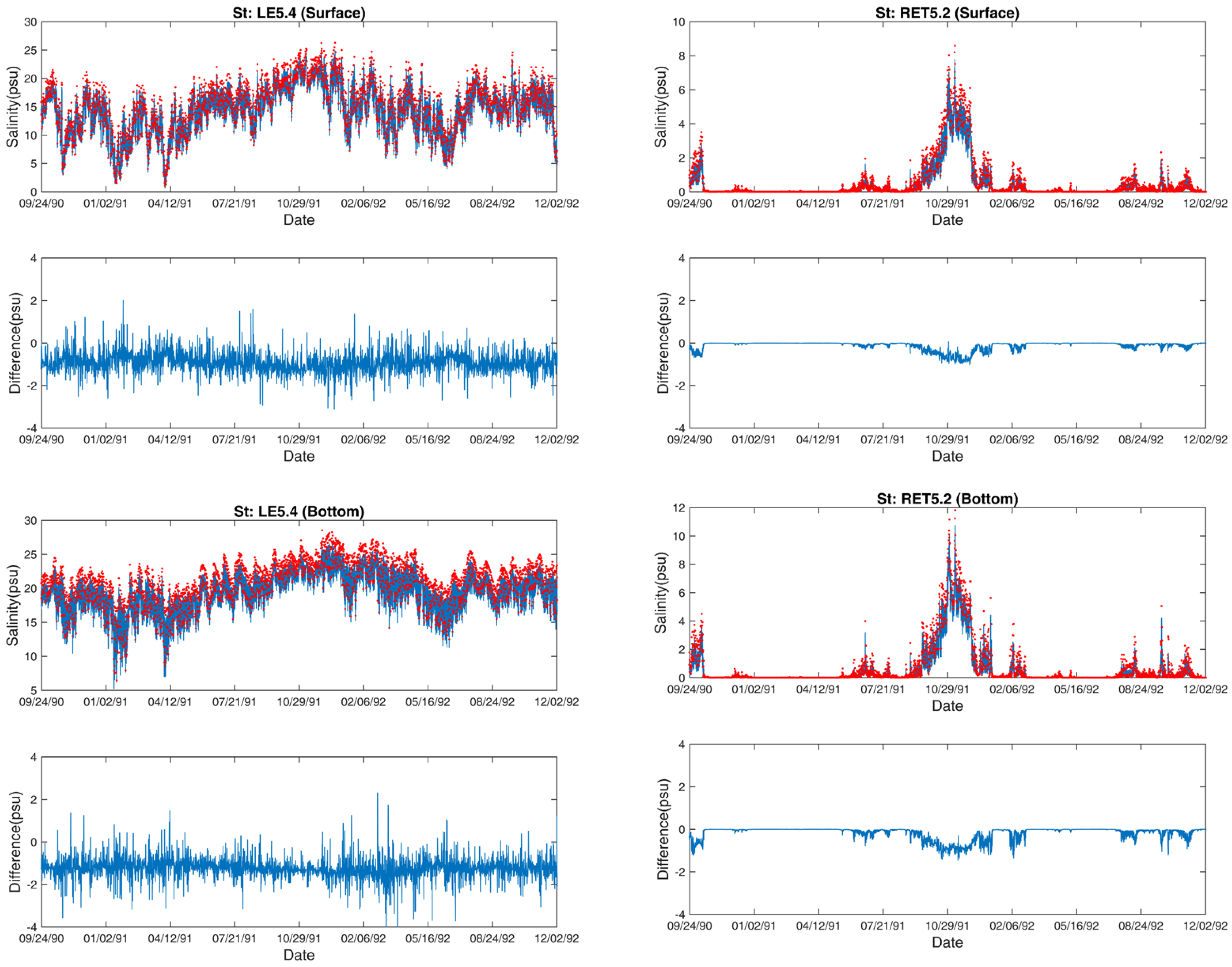
3.2. Salinity
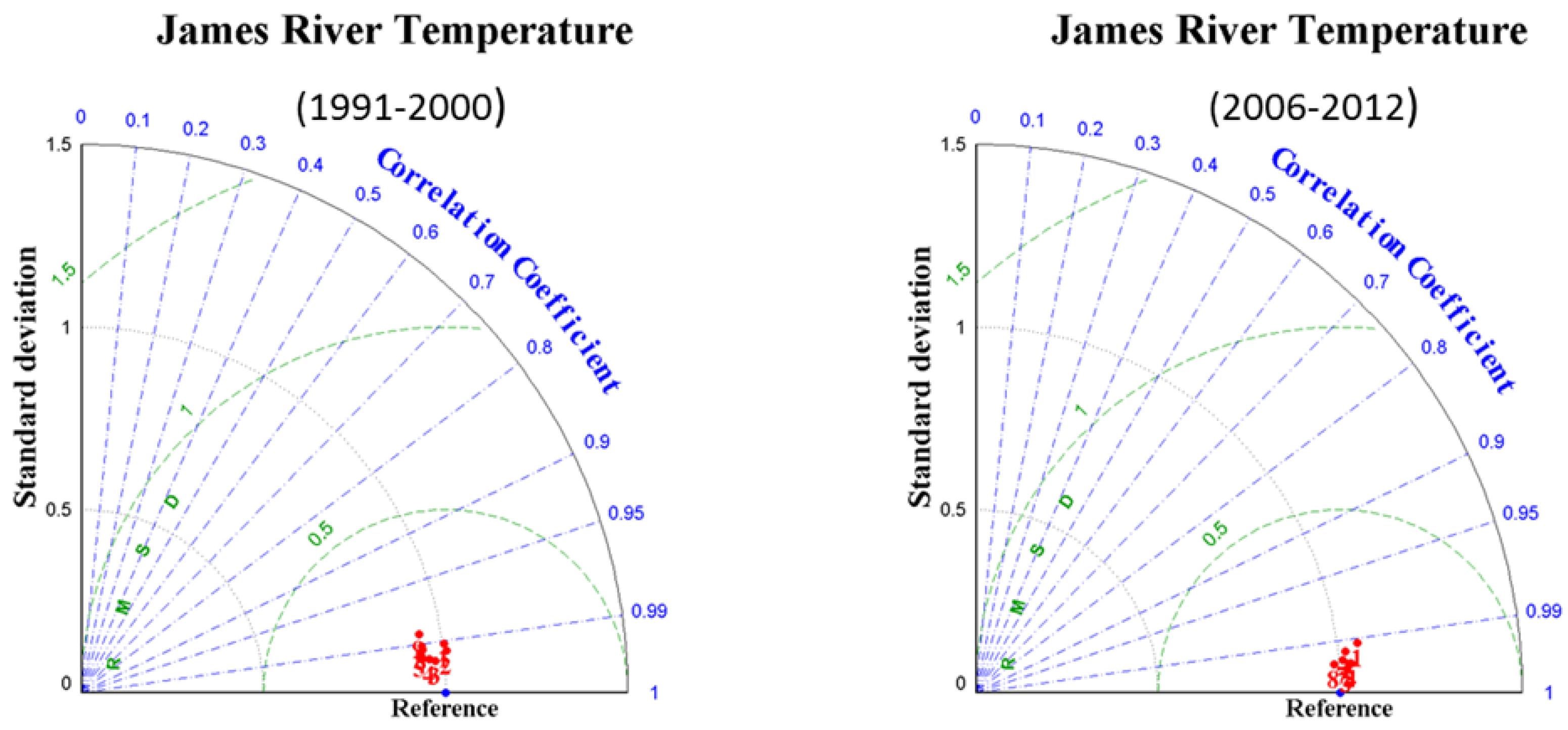
3.3. Temperature
3.4. Sensitivity Tests
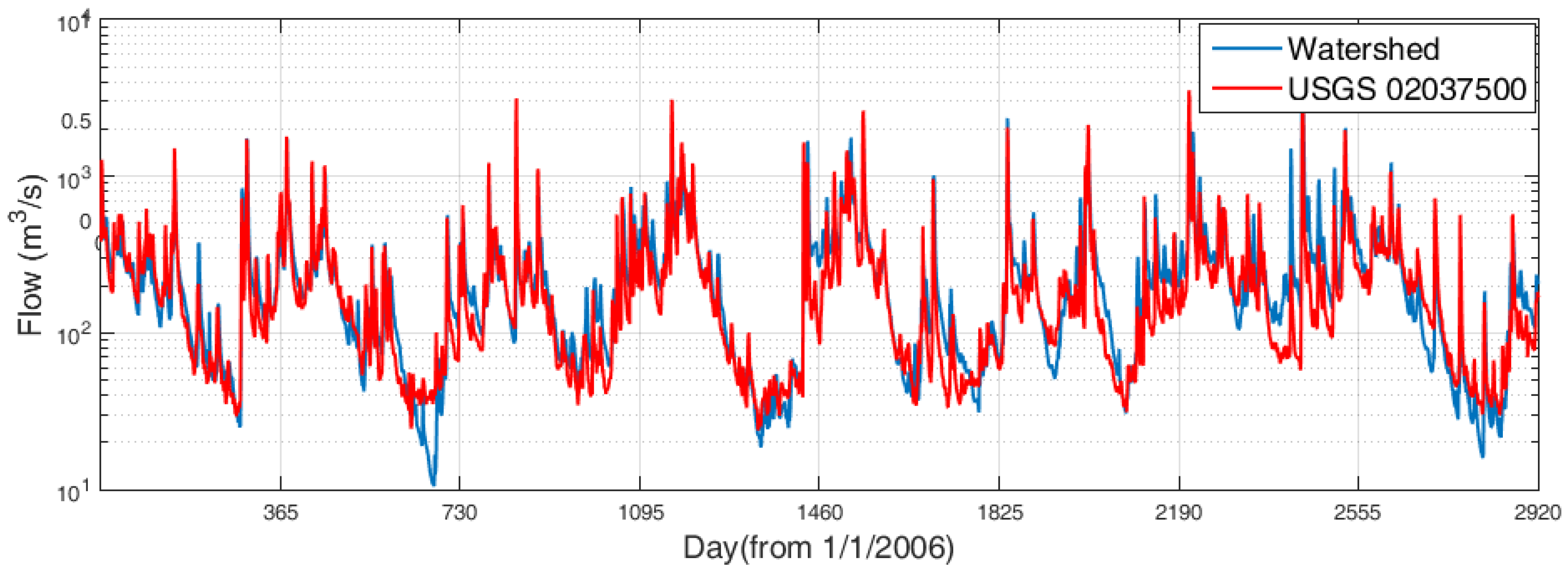
3.4.1. Freshwater Discharge
3.4.2. Wind
3.4.3. Open Boundary Condition
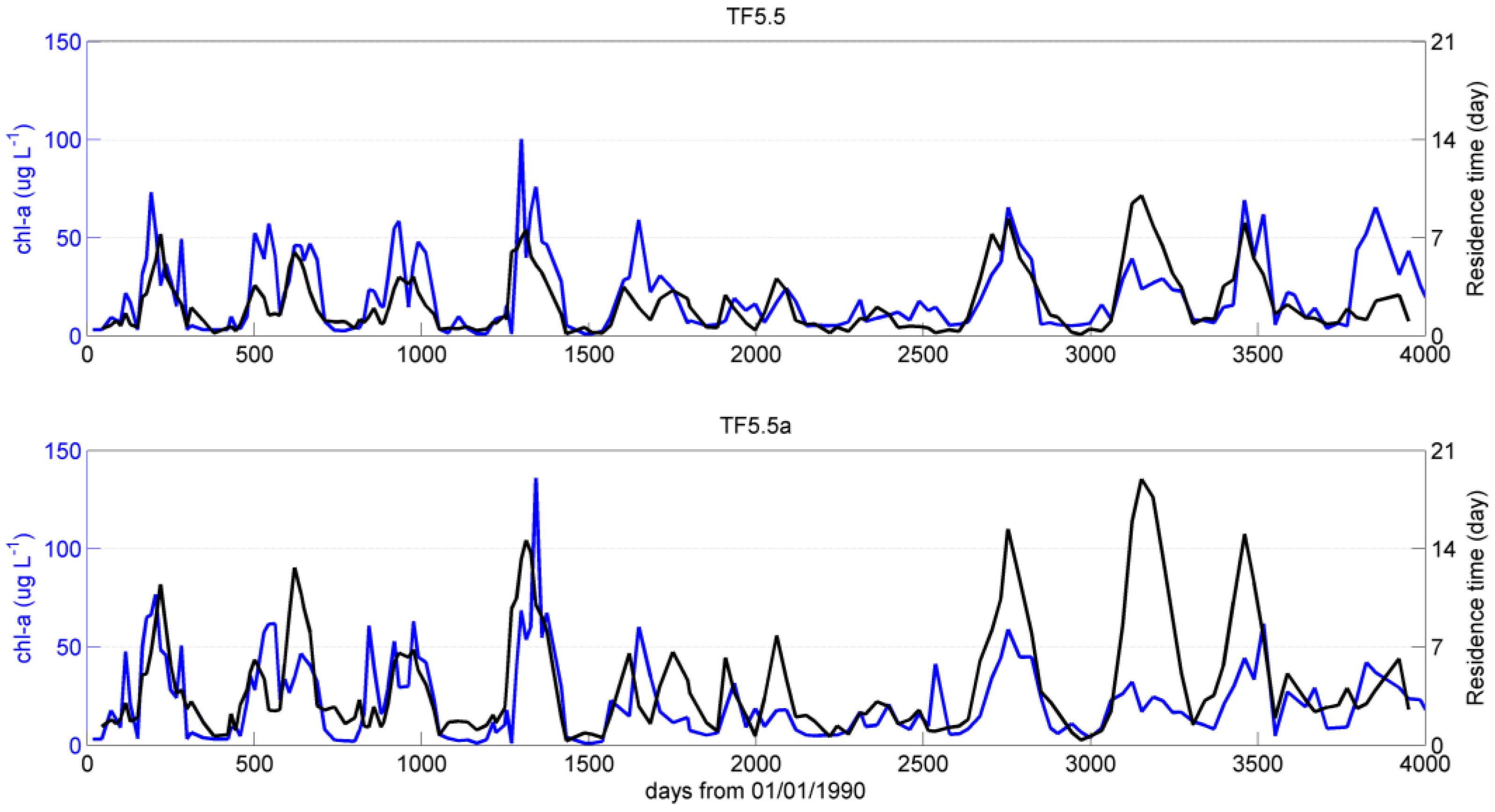
4. Discussion and Summary
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bukaveckas, P.; Barry, L.E.; Beckwith, M.J.; David, V.; Lederer, B. Factors determining the location of the chlorophyll maximum and the fate of algal production within the tidal freshwater James River. Estuar. Coasts 2011, 34, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Boon, J.; Kuo, A.Y. A numerical study of a tidal intrusion front and its impact on larval dispersion in the James River estuary, Virginia. Estuaries 1999, 22, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, R.E.; Shen, J.; Blanco-Garcia, J.L.; Hunley, W.S.; Fentress, S.; Wiggins, M.; Mulholland, M.R. Environmental and physical controls on the formation and transport of blooms of the dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides Margalef in the lower Chesapeake bay and its tributaries. Estuar. Coasts 2011, 34, 1006–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.P. A Three-Dimensional Mathematical Model of Coastal, Estuarine and Lake Currents Using Boundary-Fitted Grid; Technical Report No. 585; Aeronautical Research Associates of Princeton: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.T.; Casulli, V.; Gartner, J.W. Tidal residual intertidal mudflat (TRIM) model and its applications to San Francisco Bay, California. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1993, 36, 235–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerco, C.F.; Cole, T. Three-Dimensional Eutrophication Model of Chesapeake Bay, Volume I: Main Report; EL-94.4; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Waterway Experiment Station: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wool, T.A.; Ambrose, R.B.; Martin, J.L.; Comer, E.A. Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP); version 6.0; Draft User’s Manual; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2001.
- Wan, Y.; Ji, Z.; Shen, J.; Hu, G.; Sun, D. Three dimensional modeling of a shallow subtropical estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 82, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, J.M.; Kemp, W.M.; Boynton, W.R.; Hagy, J.D. Longterm changes in water quality and productivity in the Patuxent River estuary: 1985 to 2003. Estuar. Coasts 2008, 31, 1021–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Beardsley, R.C. An unstructured, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equation ocean model: Application to coastal ocean and estuaries. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerco, C.F.; Kim, S.; Nole, M.R. The 2010 Chesapeake Bay Eutrophication Model; A Report to the US Environmental Protection Agency Chesapeake Bay Program and to the US Army Engineer Baltimore District; US Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, D.W. The dynamic structure of a coastal plain estuary. J. Mar. Res. 1956, 15, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, A.Y.; Neilson, B.J. Hypoxia and salinity in Virginia estuaries. Estuaries 1987, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.M. A Three-Dimensional Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code: Theoretical and Computational Aspects; VIMS SRAMSOE #317; College of William and Mary, Virginia Institute of Marine Science: Gloucester Point, VA, USA, 1992; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Kuo, A.Y.; Shen, J.; Hamrick, J.M. A Three-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Eutrophication Model (HEM-3D): Description of Water Quality and Sediment Process Submodels; Special Report in Applied Marine Science and Ocean Engineering No. 327; Virginia Institute of Marine Science: Gloucester Point, VA, USA, 1995; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, G.L.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, B.; Kantha, L.H.; Hassis, S.; Rosati, A. A quasi-equilibrium turbulent energy model for geophysical flows. J. Atmos. Sci. 1988, 45, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J; Lin, J. Modeling study of the influences of tide and stratification on age of water in the tidal James River. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 68, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesapeake Environmental Communications (CEC). Modeling Support for the James River Chlorophyll Study: Modeling Report, prepared by CRC, HDR, Tetra Tech, and Virginia Institute of Marine Science for Virginia Department of Environmental Quality: Richmond, VA, USA, February 29, 2015.
- Cerco, C.; Noel, M. The 2002 Chesapeake Bay Eutrophication Model; EPA 903-R-04-004; US Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Shen, J. Decoupling the influence of biological and physical processes on the dissolved oxygen in the Chesapeake Bay. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Shen, J. Linking dynamics of transport timescale and variation of hypoxia in the Chesapeake Bay. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 6017–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhez, E.J.M.; Campin, J.M.; Hirst, A.C.; Deleersnijder, E. Toward a general theory of the age in ocean modeling. Ocean Model. 1999, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, E.; Campin, J.M.; Delhez, E.J.M. The concept of age in marine modeling: I. Theory and preliminary model results. J. Mar. Syst. 2001, 28, 229–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.W.; Ammerman, J.W.; Atkinson, L.P.; Berounsky, V.M.; Billen, G.; Boicourt, W.C.; Boynton, W.R.; Church, T.M.; Ditoro, D.M.; Elmgren, R.; et al. The fate of nitrogen and phosphorus at the land-sea margin of the North Atlantic Ocean. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 141–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V.; Thompson, J.K.; Brown, L.R. Why are diverse relationships observed between phytoplankton biomass and transport time. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peierls, B.L.; Hall, N.S.; Paerl, H.W. Non-monotonic responses of phytoplankton biomass accumulation to hydrologic variability: A comparison of two coastal plain North Carolina estuaries. Estuar. Coasts 2012, 35, 1376–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.E. Wind modulation of dissolved oxygen in Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coasts 2010, 33, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hong, B.; Kuo, A.Y. Using timescales to interpret dissolved oxygen distributions in the bottom waters of Chesapeake Bay. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 28, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sisson, M. Development of the Hydrodynamic Model for Long-Term Simulation of Water Quality Processes of the Tidal James River, Virginia. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4040082
Shen J, Wang Y, Sisson M. Development of the Hydrodynamic Model for Long-Term Simulation of Water Quality Processes of the Tidal James River, Virginia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2016; 4(4):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4040082
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Jian, Ya Wang, and Mac Sisson. 2016. "Development of the Hydrodynamic Model for Long-Term Simulation of Water Quality Processes of the Tidal James River, Virginia" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 4, no. 4: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4040082
APA StyleShen, J., Wang, Y., & Sisson, M. (2016). Development of the Hydrodynamic Model for Long-Term Simulation of Water Quality Processes of the Tidal James River, Virginia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 4(4), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse4040082






